Abstract
Two Streptomyces strains, named N11-26 and DC10-5, were isolated from deep-sea and non-photosynthetic stony coral, respectively. Strain N11-26 produces lobophorin C and divergolides, which are antimicrobial substances. This study aimed to classify these strains and reveal their cryptic potential to synthesize other secondary metabolites, such as polyketides and nonribosomal peptides. Strains N11-26 and DC10-5 showed 16S rRNA gene sequence similarities of 100% and 99.9% to Streptomyces olivaceus NRRL B-3009T, respectively. By digital DNA–DNA hybridization using whole-genome sequences, these strains were classified as Streptomyces olivaceus. Strain N11-26 was closer to the type strain of S. olivaceus than strain DC10-5 and possessed 17 clusters of polyketide synthase (PKS) and/or nonribosomal peptide synthetases (NRPS) genes, whereas strain DC10-5 harbored 19 clusters. Putative products by these gene clusters were predicted by bioinformatic analyses. Although 15 clusters were conserved between the two strains, two and four clusters were specific in strains N11-26 and DC10-5, respectively. This represents a diversity of potential polyketide and nonribosomal peptide compounds between strains of S. olivaceus. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first report annotating all the PKS and NRPS gene clusters in S. olivaceus strains with their putative products to provide useful information for genome mining.
1. Introduction
Microbial secondary metabolites, such as antibiotics, are a promising pharmaceutical source of antimicrobial materials, many of which have been developed as therapeutic agents [1]. Terrestrial environments are recognized as the main habitat of members of the genus Streptomyces, which is the representative genus in actinomycetes and well-known as a rich source of useful secondary metabolites. Recently, marine-derived Streptomyces strains have been attracting attention as an untapped and promising source for new compounds. Many bioactive substances have indeed been discovered from them [2]. In recent years, whole-genome sequencing of Streptomyces strains revealed their greater potential to synthesize diverse secondary metabolites, than expected through bioactivity-based screening. Genome mining is a currently developed and often employed approach for the search for novel secondary metabolites [3]. Accessible whole-genome sequences of many strains are essential for the progress of genome mining in this research field. To progress the approach, whole-genome sequences of publicly available strains, such as culture collections, should be sequenced and published with useful information to enrich the materials.
During our search for new bioactive secondary metabolites, a Streptomyces strain designated as N11-26 was isolated from deep-sea water in the Sea of Japan and found to produce lobophorin C, divergolides C and D, and germicidins (1 to 4 in Figure 1) by the chemical screening using HPLC coupled with a photodiode array detector [4]. Lobophorins, divergolides and germicidins are spirotetronate-, ansamycin- and alpha-pyrone-compounds and their backbones are biosynthesized by polyketide synthases (PKSs) [5,6,7]. Lobophorins and divergolides show antimicrobial activities [8,9,10], whereas germicidins inhibit spore germination and hyphae growth [11]. Another Streptomyces strain named DC10-5 was isolated from a non-photosynthetic stony coral in the Pacific Ocean. This strain is phylogenetically close to N11-26. In this study, whole-genome sequences of these two strains, which are available from the NBRC Culture Collection, were sequenced to provide information useful for genome mining. Subsequently, we classified these strains at the species level and investigated their potential to synthesize other polyketide and nonribosomal peptide compounds by analyzing polyketide synthase (PKS) and nonribosomal peptide synthetase (NRPS) gene clusters since nonribosomal peptides as well as polyketides are major secondary metabolites in actinomycetes [12]. Type-I PKSs are large multifunctional enzymes composed of multiple domains, such as ketoacylsynthase (KS), acyltransferase (AT), acyl carrier protein (ACP), dehydratase (DH), enoylreductase (ER), ketoreductase (KR) and thioesterase (TE) domains, whereas NRPS are those such as condensation (C), adenylation (A), a peptidyl carrier protein (PCP), epimerization (E) and TE domains. Backbones synthesized by type-I PKS and NRPS gene clusters can be bioinformatically predicted according to the domain organizations of these enzymes in each cluster with substrates of each AT and A domain [13]. Consequently, this study revealed the diversity of strains in Streptomyces olivaceus.
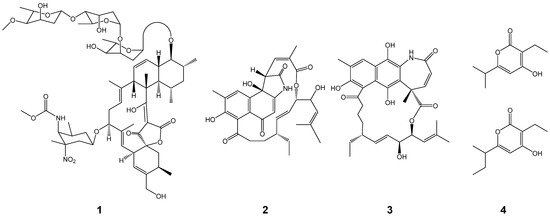
Figure 1.
Chemical structures of lobophorin C (1), divergolides C (2) and D (3) and germicidins (4).
2. Results
2.1. Classification of Streptomyces Strains N11-26 and DC10-5
Strain N11-26 showed 16S rRNA gene sequence similarities of 100, 99.3 and 99.1% to the type strains of Streptomyces olivaceus, Streptomyces parvulus and Streptomyces malachitospinus, respectively, as the closest species whereas strain DC10-5 were 99.9, 99.4 and 99.2% to them. The difference in 16S rRNA gene sequences was only 1 bp between strains N11-26 and DC10-5. In a phylogenetic tree based on 16S rRNA gene sequences (Figure 2), Streptomyces sp. N11-26 and Streptomyces sp. DC10-5 formed an independent clade with S. olivaceus. The other species showing >99.0% similarities to these strains were separated from the clade.
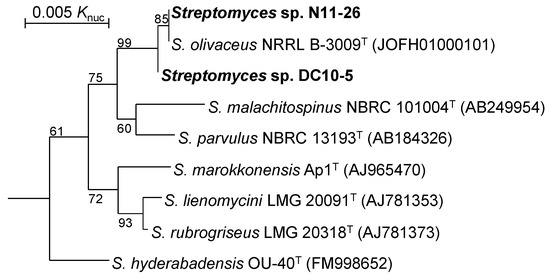
Figure 2.
Phylogenetic tree based on 16S rRNA gene sequences. Type strains of species showing sequence similarities of >99.0% to strains N11-26 and DC10-5 are included in this tree. Numbers on the branches are the confidence limits estimated by bootstrap analysis with 1000 replicates, and values above 50% are indicated at branching points. Streptomyces albus NBRC 13014T (AB490769) was used as an outgroup (not shown) to show the root.
Subsequently, we sequenced the whole genomes of the two strains. As shown in Table 1, the draft genome sequences were composed of six contig sequences. Their genome sizes and G+C contents were close to those of S. olivaceus NRRL B-3009T.

Table 1.
Whole-genome sequences of Streptomyces sp. N11-26, Streptomyces sp. DC10-5 and a type strain of their closest species.
DNA–DNA relatedness of the two strains to S. olivaceus NRRL B-3009T were 88.0 and 80.5% (Table 2). As these values exceeded 70%, the threshold for species delineation in procaryotes, these two strains were identified as S. olivaceus. Streptomyces sp. N11-26 is closer to S. olivaceus NRRL B-3009T (88.0%) than to Streptomyces sp. DC10-5 (80.5%). These distances are also supported by the 16S rRNA gene sequence similarities.

Table 2.
DNA–DNA relatedness and 16S rRNA gene similarities among Streptomyces sp. N11-26 (1), Streptomyces sp. DC10-5 (2) and S. olivaceus NRRL B-3009T (3).
2.2. Secondary Metabolite-Biosynthetic Gene Clusters Encoding PKSs and/or NRPSs
S. olivaceus N11-26 harbored four type-I PKS, one type-II PKS, two type-III PKS, six NRPS and four hybrid PKS/NRPS gene clusters in its genome, whereas S. olivaceus DC10-5 harbored four type-I PKS, two type-II PKS, two type-III PKS, eight NRPS and three hybrid PKS/NRPS gene clusters. Except for the duplication, 21 PKS and NRPS gene clusters were found in these two strains, as listed in Table 3.

Table 3.
PKS and NRPS gene clusters in the genomes of S. olivaceus N11-26, DC10-5 and NRRL B-3009T.
In an analysis by antiSMASH, nrps-1, t3pks-1, and t3pks-2 showed 100% similarities to BGCs of coelichelin, flaviolin and 1,3,6,8-tetrahydroxynaphthalene, and germicidin, respectively, as their ‘Most similar known cluster’ (Tables S1 and S2). Even if similarities are not high like the others, we should not annotate the clusters to be novel because the antiSMASH database does not include information on all reported BGCs. Additionally, since similarities of domain organizations are not mainly considered in antiSMASH under the algorism of ClusterBlast, similar gene clusters, which synthesize similar polyketide- and/or peptide-chains, could not be searched in many cases, as exemplified in Tables S1 and S2. Thus, we searched known biosynthetic enzymes, whose product is already identified, corresponding to the PKSs and/or NRPSs of the gene clusters in strains N11-26 and DC10-5 by Protein BLAST (protein-protein BLAST, blastp) on the NCBI website (Tables S3 and S4). If the sequence similarities are high and domain organizations match well, then we annotated the clusters to be responsible for the compounds shown in the column of ‘Product’ in Tables S3 and S4. The products and their chemical structures are shown in Table 3 and Figure 3, respectively, which include predicted structures. Gene clusters named t1pks-2, t3pks-2 and t1pks-5 were biosynthetic gene clusters (BGCs) for divergolides [6,15], germicidins [16] and lobophorins [17], respectively. They were present in the genome of strain N11-26, which is a producer of these compounds, as expected, and also in the other strains, including the type strain NRRL B-3009T. Gene clusters named nrps-1, nrps-3, nrps-4, nrps-6, t1pks-3, pks/nrps-1, t2pks-1, t3pks-1 and pks/nrps-4 were BGCs for known compounds, such as coelichelin [18], mirubactin [19], coelibactin [18], SF2768 [20], arsono-polyketides [21,22], pactamide [23], rishirilides etc. [24,25], flaviolin and 1,3,6,8-tetrahydroxynaphthalene [26] and totopotensamides [27], respectively. The NRPS in nrps-3 showed a high sequence similarity to SpnA, which is responsible for streptopeptolin synthesis [28], but it lacked the first module present in SpnA (Table S4). Hence, the product was predicted to be a streptopeptolin congener derived from the partial structure of streptopeptolin (7, Figure 3). The other gene clusters were orphans. The domain organization of t1pks-1 (KSQ-ATm-ACP-KS-ATm-DH-KR-ACP-KS-ATmm-KR-ACP, KS-ATm-ACP-KS-ATmm-DH-KR-ACP-KS-ATm-DH-KR-ACP-KS-ATmm-KR-ACP, KS-ATm-DH-ER-ACP-KS-ATmm-DH-KR-ACP and KS-ATm-(DH)-ACP-TE) suggested that the product is derived from a decaketide with the structure shown as 5 in Figure 3. As the domain organization not completely but partly resembles those of BGCs for E-837 and E-492/E-975 [29], the putative product of t1pks may be alkenyl-furanone as described in Table 3. Recently a non-natural furan anticancer compound was discovered from a marine Streptomyces strain [30]. Although this may be the product of t1pks-1, lengths of the carbon chains appear different between the furan compound and 5. Domain organization of t1pks-4 is KSQ-ATmm-ACP-KS-ATmm-DH-ER-KR-ACP, KS-ATmm-DH-KR-ACP, KS-ATmm-DH-ER-KR-ACP-KS-KR-ACP, KS-ATm-KR-ACP-KS-ATm-KR-ACP, and KS-DH-KR-ACP. This partly resembles to that of the butyrolactol-BGC (AT-ACP-KS-ATm-DH-ER-KR-ACP-KS-ATm-KR-ACP-KS-ATm-DH-KR-ACP, KS-ATm-DH-ER-KR-ACP, KS-ATm-DH-KR-ACP-KS-ATm-DH-KR-ACP, KS-ATmm-DH-ER-KR-ACP-KS-KR-ACP, KS-AT-KR-ACP-KS-AT-KR-ACP, and KS-KR-ACP) [31] as underlined, except for KSQ in the first module, the DH in the last module and substrates of some AT domains. The presence of two AT-less modules composed of KS-KR-ACP is one of the characters in butyrolactol-BGC, which was also observed in t1pks-4. Thus, the product may be a butyrolactol congener derived from 14, which is shorter than butyrolactol due to less modules. Pks/nrps-3 partially resembled rimosamide-BGC [32]. However, pks/nrps-3 encoded one NRPS (C-Aval-PCP-TE) and one hybrid PKS/NRPS (Aile-T-C-Apro-PCP-KS-KR-ACP-TE) whereas rimosamide-BGC encoded two NRPSs (RmoG: C-Agly-PCP, RmoH: C-Aval-PCP-TE) and one hybrid PKS/NRPS (RmoI: A-T-C-Apro-PCP-KS-KR-ACP-TE). Considering the biosynthetic pathway of rimosamide and difference between these module organizations, we predicted the putative product to be 15 in Figure 3. Very recently, diketopiperazines cyclo-L-proline-L-tyrosine was reported from a marine-derived Streptomyces sp. VN1 [30]. This might be the final product of pks/nrps-3, but the relationship between the compound and 15 is still unclear. The remaining orphan clusters, nrps-5, nrps-7, pks/nrps-2 and nrps-8, did not show high similarities to BGCs of identified products (Tables S3 and S4). Their domain numbers were one, three, three and four. The product of nrps-7 was predicted to be a tripeptide composed of three ornithine residues. However, as amino acid substrates were unclear for many A domains of NRPSs in the other three clusters, we could not show their chemical structures in Figure 3.
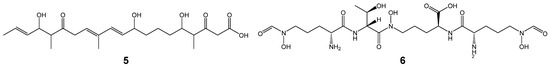
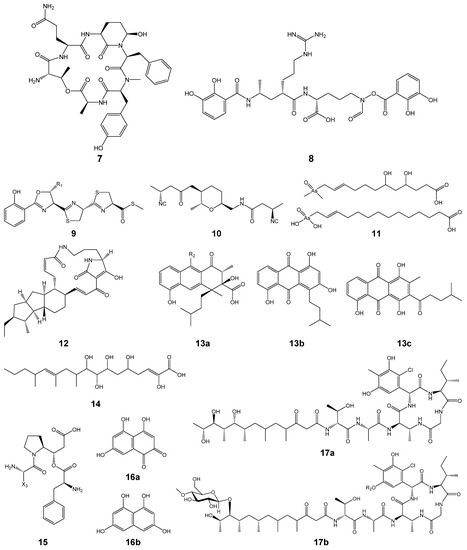
Figure 3.
Chemical structures of 5 to 17 shown in Table 3. X1 to X3, derived from unidentified amino acid residues; 5, predicted decaketide according to the domain organization of t1pks-1; 6, coelichelin [18]; 7, putative streptopeptolin congener inferred from the domain organization of nrps-2; 8, mirubactin [19]; 9, coelibactin (R1 = CH3 or H) [18]; 10, SF2768 [20]; 11, arsono-polyketides [21,22]; 12, pactamide [23]; 13a, rishirilides B and C (B, R2 = H; C, R2 = OH); 13b, lupinacidin A; 13c, galvaquinone B [24,25]; 14, putative polyketide chain deduced from the domain organization of t1pks-4 and considering the butyrolactol-biosynthetic pathway, but where the lactone ring forms is unclear; 15, presumed putative peptide chain from the domain organization of pks/nrps-3 and considering the biosynthesis of rimosamide C; 16a, flaviolon; 16b, 1,3,6,8-tetrahydroxynaphthalene [26]; 17a, totopotensamide B; 17b, totopotensamides A and C (A, R2 = H; C, R2 = SO3H) [27].
Among the 21 gene clusters, fifteen were conserved between the two strains, N11-26 and DC10-5 (not asterisked in Table 3). On the other hand, nrps-2 (a streptopeptolin congener), t1pks-3 (arsono-polyketide), t2pks-1 (rishirilides etc.) and nrps-8 were specific to DC10-5, whereas pks/nrps-2 and t1pks-4 were specific to N11-26. All the discovered 17 clusters from N11-26 were conserved in NRRL B-3009T (type strain of S. olivaceus), although NRRL B-3009T possessed nrps-2, which was found from DC10-5. Except for nrps-2, N11-26 and NRRL B-3009T shared the same set of PKS and NRPS gene clusters. Thus, not in comparison between N11-26 and DC10-5 but among the three strains and expecting 15 conserved clusters among all strains, two clusters (pks/nrps-2 and t1pks-4) are shared between N11-26 and NRRL B-3009T. One cluster (nrps-2) is shared between DC10-5 and NRRL B-3009T, and three (t1pks-3, t2pks-1, nrps-8) are specific in DC10-5.
Although the whole-genome sequences determined in this study are not complete but are a draft, the positions of the PKS and NRPS gene clusters in the putative chromosomal DNAs are shown in Figure 4. S. olivaceus NRRL B-3009T is not included in this figure because its draft genome sequence is composed of 188 contigs, and most sequences are too short to be compared. Gene clusters conserved between strains N11-26 and DC10-5 are located at similar positions, which are in the left or right arms of the putative chromosomes. Specific clusters did not gather in a specific region that can be considered an island.
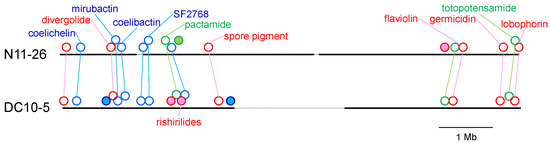
Figure 4.
Positions of PKS and NRPS gene clusters in the putative chromosomal DNAs of S. olivaceus N11-26 and DC10-5. Contig sequences encoding these gene clusters are shown in bold black lines. Red circle, PKS gene cluster; blue circle, NRPS gene cluster; green circle, hybrid PKS/NRPS gene cluster. The same gene clusters are connected by lightly colored lines. Gene clusters specific to one of the strains are filled by pink (PKS gene cluster), light blue (NRPS gene cluster) or light green (hybrid PKS/NRPS gene cluster). Although known compounds that were predicted by our bioinformatic analysis are indicated here, putative products of orphan clusters are not shown since their compound names are unclear, as shown in Table 3. The ‘rishirilides’ in DC10-5 includes rishirilides B and C, lupinacidin A and galvaquinone B [25]. The ‘flaviolin’ includes flaviolin and 1,3,6,8-tetrahydroxynaphthalene.
3. Discussion
According to the Dictionary of Natural Products, seven marine-derived Streptomyces strains are recorded as lobophorin producers. Among them, only the strain FXJ7.023 [17] was identified as S. olivaceus; the others, such as strains MS100061 [33], 1053U.I.1a.3b [34], 12A35 [34], SCSIO 01127 [35], 7790-N4 [36] and M-207 [37], have not been classified at the species level. Very recently, S. olivaceus JB1 was isolated as an endophyte of Maesa japonica and produced lobophorins [10]. Although its isolation source is not marine, the strain is tolerant to saline. In the present study, all the strains belonging to S. olivaceus harbored a lobophorin-BGC. Therefore, most lobophorin producers may be S. olivaceus, although the six unclassified lobophorin-producing Streptomyces strains need to be classified at the species level. As divergolide producers, Streptomyces strains KFD18 [38], HKI0576 [8], W112 [6] and S. olivaceus SCSIO T05 [39] are reported. Although the isolation source of strain W112 is unclear, strains KFD18 and HKI0576 are derived from mangroves. S. olivaceus SCSIO T05 was isolated from marine sediment. Although the unidentified Streptomyces strains need to be classified at the species level, divergolide producers may also belong to S. olivaceus because all the genomes that we sequenced in this study also encode the divergolide-BGC and, consequently, it seems that lobophorin- and divergolide-BGCs are ubiquitously distributed in members of S. olivaceus. If antibiotic producers were not classified at the species level, it would be hard to elucidate the relationship between a product and the species of its producer. Thus, antibiotic producers without species names should be appropriately and taxonomically classified more to deepen our knowledge of the relationship, as shown in this study.
Although strains N11-26 and DC10-5 were classified as S. olivaceus, their 16S rRNA gene sequences differed in 1 bp. Strain N11-26 was closer to the type strain than strain DC10-5 by DNA–DNA relatedness as well as 16S rRNA gene sequence similarity. Almost the same set of PKS and NRPS gene clusters were conserved between the S. olivaceus strains N11-26 and NRRL B-3009T. In contrast, the sets were not the same between strain DC10-5 and N11-26: DC10-5 possesses four specific clusters that were not present in N11-26, whereas N11-26 harbors two specific clusters that DC10-5 lacks. The difference seems to be due to strain diversity in secondary metabolite-BGCs within a species. Strain diversification is believed to be driven by geographic and ecological factors. Isolation sources differ between strains N11-26 and DC10-5: N11-26 is derived from deep-sea water, while DC10-5 is isolated from coral. Regions where we collected the isolation sources, the Sea of Japan and the Pacific Ocean, are separated by the Japanese Archipelago. Such factors may have played a role in yielding diversity. Wang et al. reported that isolates belonging to S. olivaceus were phylogenetically divided into two clades, which can represent two distinct species [40]. However, our isolates cannot be classified into different species due to DNA–DNA relatedness of >80%, although strains N11-26 and DC10-5 may be included in each of the lineages. Strain DC10-5 should not be discriminated as an independent subspecies, a lower taxonomic rank than species, since the DNA–DNA relatedness value, 80.5%, is slightly higher than the threshold for subspecies delineation (79–80%) [41] and we have not yet found essential characteristic features to propose a new subspecies.
4. Materials and Methods
Strains N11-26 and DC10-5 were isolated from deep-sea water collected in Toyama [4], Japan and a non-photosynthetic stony coral collected in Mie, Japan, respectively. These strains are preserved as TP-A0909 and TP-A0905 in Toyama Prefectural University and have been deposited to the NBRC Culture Collection, whose strain numbers are NBRC 113676 and NBRC 113677, respectively. Their 16S rRNA genes were amplified using 9F and 1541R primers, and the amplicons were sequenced following the previously described method [42]. The EzBioCloud server was used for searching the closest species [43]. A phylogenetic tree was reconstructed by the NJ method using ClustalX 2.1 [44]. Whole genomes were sequenced by a single-molecule real-time (SMRT) sequencing technology using PacBio, as reported in [45], and the sequences have been deposited under the accession numbers BNEG01000001-BNEG01000006 and BNEF01000001-BNEF01000006. DNA–DNA relatedness was calculated by digital DNA–DNA hybridization using GGDC [46], and DDH estimates by Formula 2 were employed. The PKS and NRPS gene clusters in the whole genome were searched with antiSMASH [47]. Products of these gene clusters were predicted according to similarities of gene sequences and syntenies of genes in BGCs of known compounds and domain organizations of PKSs and NRPSs [48]. The presence of gene clusters identified from strains N11-26 and/or DC10-5 in S. olivaceus NRRL B-3009T was examined by BLAST search of their PKSs and/or NRPSs as the queries.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/hydrobiology2010010/s1, Table S1: Most similar known cluster searched with antiSMASH for the gene clusters in S. olivaceus N11-26; Table S2: Most similar known cluster searched with antiSMASH for the gene clusters in S. olivaceus DC10-5; Table S3: Closest biosynthetic enzymes to PKSs and/or NRPSs in the gene clusters of S. olivaceus N11-26; Table S4: Closest biosynthetic enzymes to PKSs and/or NRPSs in the gene clusters of S. olivaceus DC10-5.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, H.K. and Y.I.; methodology, T.T.; software, H.K.; validation, H.K.; formal analysis, H.K.; investigation, H.K.; resources, Y.I.; data curation, H.K.; writing—original draft preparation, H.K.; writing—review and editing, Y.I. and T.T.; visualization, H.K.; supervision, T.T. and Y.I.; project administration, T.T. and Y.I.; funding acquisition, T.T. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported in part by a commissioned project from the Japan Patent Office.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The whole-genome shotgun project of Streptomyces sp. N11-26 and DC10-5 have been deposited at GenBank under the accession numbers BNEG00000000.1 and BNEF00000000.1, and at BioProject and BioSample, with the accession numbers of strain N11-26 as PRJDB9817 and SAMD00228007, and those of strain DC10-5 as PRJDB9816 and SAMD00228006.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful for Shinpei Ino and Takahiro Matsuyama’s genomic DNA preparation from the two strains, and we thank Moriyuki Hamada and Aya Uohara for sequencing the 16S rRNA genes and depositing whole-genome sequences in DDBJ, respectively.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Berdy, J. Bioactive microbial metabolites. J. Antibiot. 2005, 58, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carroll, A.R.; Copp, B.R.; Davis, R.A.; Keyzers, R.A.; Prinsep, M.R. Marine natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2019, 36, 122–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, N.; Hwang, S.; Kim, J.; Cho, S.; Palsson, B.; Cho, B. Mini review: Genome mining approaches for the identification of secondary metabolite biosynthetic gene clusters in Streptomyces. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2020, 18, 1548–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harunari, E.; Ogino, K.; Kanaki, S.; Kumagai, T.; Igarashi, Y. Isolation and metabolites analysis of actinomycetes from deep-sea water in Toyama Bay. Deep Ocean Water Res. 2021, 22, 49–57. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Xiao, J.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, G.; Yang, C.; Zhang, H.; Ma, L.; Zhang, C. Dissecting glycosylation steps in lobophorin biosynthesis implies an iterative glycosyltransferase. Org. Lett. 2013, 15, 1374–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhao, G.; Sun, M.; He, H.; Wang, H.; Li, Y.; Lu, C.; Shen, Y. Identification and characterization of the biosynthetic gene cluster of divergolides from Streptomyces sp. W112. Gene 2014, 544, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.; Barona-Gomez, F.; Corre, C.; Xiang, L.; Udwary, D.W.; Austin, M.B.; Noel, J.P.; Moore, B.S.; Challis, G.L. Type III polyketide synthase beta-ketoacyl-ACP starter unit and ethylmalonyl-CoA extender unit selectivity discovered by Streptomyces coelicolor genome mining. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 14754–14755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.; Maier, A.; Fiebig, H.H.; Gorls, H.; Lin, W.; Peschel, G.; Hertweck, C. Divergolides A-D from a mangrove endophyte reveal an unparalleled plasticity in ansa-macrolide biosynthesis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2011, 50, 1630–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M.; Tang, L.; Dong, Y.; Huang, H.; Deng, Z.; Sun, Y. Antibacterial natural products lobophorin L and M from the marine-derived Streptomyces sp. 4506. Nat. Prod. Res. 2021, 35, 5581–5587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Um, S.; Lee, J.; Kim, S. Lobophorin producing endophytic Streptomyces olivaceus JB1 associated with Maesa japonica (Thunb.) Moritzi & Zoll. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 881253. [Google Scholar]
- Aoki, Y.; Matsumoto, D.; Kawaide, H.; Natsume, M. Physiological role of germicidins in spore germination and hyphal elongation in Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). J. Antibiot. 2011, 64, 607–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nett, M.; Ikeda, H.; Moore, B.S. Genomic basis for natural product biosynthetic diversity in the actinomycetes. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2009, 26, 1362–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischbach, M.A.; Walsh, C.T. Assembly-line enzymology for polyketide and nonribosomal peptide antibiotics: Logic, machinery, and mechanisms. Chem. Rev. 2006, 106, 3468–3496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doroghazi, J.R.; Albright, J.C.; Goering, A.W.; Ju, K.S.; Haines, R.R.; Tchalukov, K.A.; Labeda, D.P.; Kelleher, N.L.; Metcalf, W.W. A roadmap for natural product discovery based on large-scale genomics and metabolomics. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2014, 10, 963–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Baunach, M.; Ding, L.; Peng, H.; Franke, J.; Hertweck, C. Biosynthetic code for divergolide assembly in a bacterial mangrove endophyte. ChemBioChem 2014, 15, 1274–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becerril, A.; Alvarez, S.; Brana, A.F.; Rico, S.; Diaz, M.; Santamaria, R.I.; Salas, J.A.; Mendez, C. Uncovering production of specialized metabolites by Streptomyces argillaceus: Activation of cryptic biosynthesis gene clusters using nutritional and genetic approaches. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0198145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, C.; Niu, J.; Liu, N.; Lu, Y.; Liu, M.; Li, Y. Cloning and identification of the lobophorin biosynthetic gene cluster from marine Streptomyces olivaceus strain FXJ7.023. Pak. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 29, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bentley, S.D.; Chater, K.F.; Cerdeno-Tarraga, A.M.; Challis, G.L.; Thomson, N.R.; James, K.D.; Harris, D.E.; Quail, M.A.; Kieser, H.; Harper, D.; et al. Complete genome sequence of the model actinomycete Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). Nature 2002, 417, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giessen, T.W.; Franke, K.B.; Knappe, T.A.; Kraas, F.I.; Bosello, M.; Xie, X.; Linne, U.; Marahiel, M.A. Isolation, structure elucidation, and biosynthesis of an unusual hydroxamic acid ester-containing siderophore from Actinosynnema mirum. J. Nat. Prod. 2012, 75, 905–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhu, M.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, X.; Yang, P.; Liu, Z.; Deng, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Huang, X.; Han, L.; et al. Diisonitrile natural product SF2768 functions as a chalkophore that mediates copper acquisition in Streptomyces thioluteus. ACS Chem. Biol. 2017, 12, 3067–3075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Morales, P.; Kopp, J.F.; Martinez-Guerrero, C.; Yanez-Guerra, L.A.; Selem-Mojica, N.; Ramos-Aboites, H.; Feldmann, J.; Barona-Gomez, F. Phylogenomic analysis of natural products biosynthetic gene clusters allows discovery of arseno-organic metabolites in model streptomycetes. Genome Biol. Evol. 2016, 8, 1906–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Morales, P.; Vijgenboom, E.; Iruegas-Bocardo, F.; Girard, G.; Yanez-Guerra, L.A.; Ramos-Aboites, H.E.; Pernodet, J.L.; Anne, J.; van Wezel, G.P.; Barona-Gomez, F. The genome sequence of Streptomyces lividans 66 reveals a novel tRNA-dependent peptide biosynthetic system within a metal-related genomic island. Genome Biol. Evol. 2013, 5, 1165–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saha, S.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, G.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Liu, W.; Yuan, C.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, L.; et al. Activation and characterization of a cryptic gene cluster reveals a cyclization cascade for polycyclic tetramate macrolactams. Chem. Sci. 2017, 8, 1607–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, X.; Probst, K.; Linnenbrink, A.; Arnold, M.; Paululat, T.; Zeeck, A.; Bechthold, A. Cloning and heterologous expression of three type II PKS gene clusters from Streptomyces bottropensis. ChemBioChem 2012, 13, 224–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Sun, C.; Huang, H.; Gui, C.; Wang, L.; Li, Q.; Ju, J. Biosynthetic Baeyer-Villiger chemistry enables access to two anthracene scaffolds from a single gene cluster in deep-dea-derived Streptomyces olivaceus SCSIO T05. J. Nat. Prod. 2018, 81, 1570–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, J.; Decker, R.; Zhan, J. Biochemical characterization of a type III polyketide biosynthetic gene cluster from Streptomyces toxytricini. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2012, 166, 1020–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Zhang, Q.; Tan, B.; Zheng, L.; Li, H.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, C. Genome mining and activation of a silent PKS/NRPS gene cluster direct the production of totopotensamides. Org. Lett. 2017, 19, 5697–5700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodani, S.; Komaki, H.; Hemmi, H.; Miyake, Y.; Kaweewan, I.; Dohra, H. Streptopeptolin, a cyanopeptolin-type peptide from Streptomyces olivochromogenes. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 8104–8110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banskota, A.H.; McAlpine, J.B.; Sorensen, D.; Aouidate, M.; Piraee, M.; Alarco, A.M.; Omura, S.; Shiomi, K.; Farnet, C.M.; Zazopoulos, E. Isolation and identification of three new 5-alkenyl-3,3(2H)-furanones from two Streptomyces species using a genomic screening approach. J. Antibiot. 2006, 59, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.T.; Pokhrel, A.R.; Nguyen, C.T.; Pham, V.T.T.; Dhakal, D.; Lim, H.N.; Jung, H.J.; Kim, T.; Yamaguchi, T.; Sohng, J.K. Streptomyces sp. VN1, a producer of diverse metabolites including non-natural furan-type anticancer compound. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komaki, H.; Ichikawa, N.; Hosoyama, A.; Fujita, N.; Igarashi, Y. Draft genome sequence of Streptomyces sp. TP-A0882 reveals putative butyrolactol biosynthetic pathway. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2015, 362, fnv155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClure, R.A.; Goering, A.W.; Ju, K.S.; Baccile, J.A.; Schroeder, F.C.; Metcalf, W.W.; Thomson, R.J.; Kelleher, N.L. Elucidating the rimosamide-detoxin natural product families and their biosynthesis using metabolite/gene cluster correlations. ACS Chem. Biol. 2016, 11, 3452–3460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Wang, J.; Guo, H.; Hou, W.; Yang, N.; Ren, B.; Liu, M.; Dai, H.; Liu, X.; Song, F.; et al. Three antimycobacterial metabolites identified from a marine-derived Streptomyces sp. MS100061. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 97, 3885–3892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, H.; Zhang, S.; Wang, N.; Li, Z.; Hua, H.; Hu, J.; Wang, S. New spirotetronate antibiotics, lobophorins H and I, from a South China Sea-derived Streptomyces sp. 12A35. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 3891–3901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, S.; Li, S.; Chen, Y.; Tian, X.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, W.; Yang, X.; Zhang, S.; Ju, J.; et al. Lobophorins E and F, new spirotetronate antibiotics from a South China Sea-derived Streptomyces sp. SCSIO 01127. J. Antibiot. 2011, 64, 711–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruz, P.G.; Fribley, A.M.; Miller, J.R.; Larsen, M.J.; Schultz, P.J.; Jacob, R.T.; Tamayo-Castillo, G.; Kaufman, R.J.; Sherman, D.H. Novel lobophorins inhibit oral cancer cell growth and induce Atf4- and Chop-dependent cell death in murine fibroblasts. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2015, 6, 877–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brana, A.F.; Sarmiento-Vizcaino, A.; Osset, M.; Perez-Victoria, I.; Martin, J.; de Pedro, N.; de la Cruz, M.; Diaz, C.; Vicente, F.; Reyes, F.; et al. Lobophorin K, a new natural product with cytotoxic activity produced by Streptomyces sp. M-207 associated with the deep-sea coral Lophelia pertusa. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Kong, F.; Xie, Q.; Ma, Q.; Hu, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Luo, D. Divergolides T–W with apoptosis-inducing activity from the mangrove-derived actinomycete Streptomyces sp. KFD18. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhang, H.; Ju, J. On-PKS Baeyer-Villiger-type O-atom insertion catalyzed by luciferase-like monooxygenase OvmO during olimycin biosynthesis. Org. Lett. 2020, 22, 1780–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Pinto-Tomas, A.A.; Cheng, K.; Huang, Y. Habitat adaptation drives speciation of a Streptomyces species with distinct habitats and disparate geographic origins. mBio 2022, 13, e0278121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier-Kolthoff, J.P.; Hahnke, R.L.; Petersen, J.; Scheuner, C.; Michael, V.; Fiebig, A.; Rohde, C.; Rohde, M.; Fartmann, B.; Goodwin, L.A.; et al. Complete genome sequence of DSM 30083T, the type strain (U5/41T) of Escherichia coli, and a proposal for delineating subspecies in microbial taxonomy. Stand. Genom. Sci. 2014, 9, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komaki, H.; Ichikawa, N.; Oguchi, A.; Hamada, M.; Harunari, E.; Kodani, S.; Fujita, N.; Igarashi, Y. Draft genome sequence of Streptomyces sp. TP-A0867, an alchivemycin producer. Stand. Genom. Sci. 2016, 11, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, S.; Ha, S.; Kwon, S.; Lim, J.; Kim, Y.; Seo, H.; Chun, J. Introducing EzBioCloud: A taxonomically united database of 16S rRNA gene sequences and whole-genome assemblies. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2017, 67, 1613–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larkin, M.A.; Blackshields, G.; Brown, N.P.; Chenna, R.; McGettigan, P.A.; McWilliam, H.; Valentin, F.; Wallace, I.M.; Wilm, A.; Lopez, R.; et al. Clustal W and Clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 2947–2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komaki, H.; Igarashi, Y.; Tamura, T. Taxonomic positions of a nyuzenamide-producer and its closely related strains. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meier-Kolthoff, J.P.; Carbasse, J.S.; Peinado-Olarte, R.L.; Goker, M. TYGS and LPSN: A database tandem for fast and reliable genome-based classification and nomenclature of prokaryotes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, D801–D807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blin, K.; Shaw, S.; Kloosterman, A.M.; Charlop-Powers, Z.; van Wezel, G.P.; Medema, M.H.; Weber, T. antiSMASH 6.0: Improving cluster detection and comparison capabilities. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, W29–W35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komaki, H.; Ichikawa, N.; Hosoyama, A.; Takahashi-Nakaguchi, A.; Matsuzawa, T.; Suzuki, K.; Fujita, N.; Gonoi, T. Genome based analysis of type-I polyketide synthase and nonribosomal peptide synthetase gene clusters in seven strains of five representative Nocardia species. BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).