First-Stage Dynamics of the Immune System and Cancer
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Linear Model
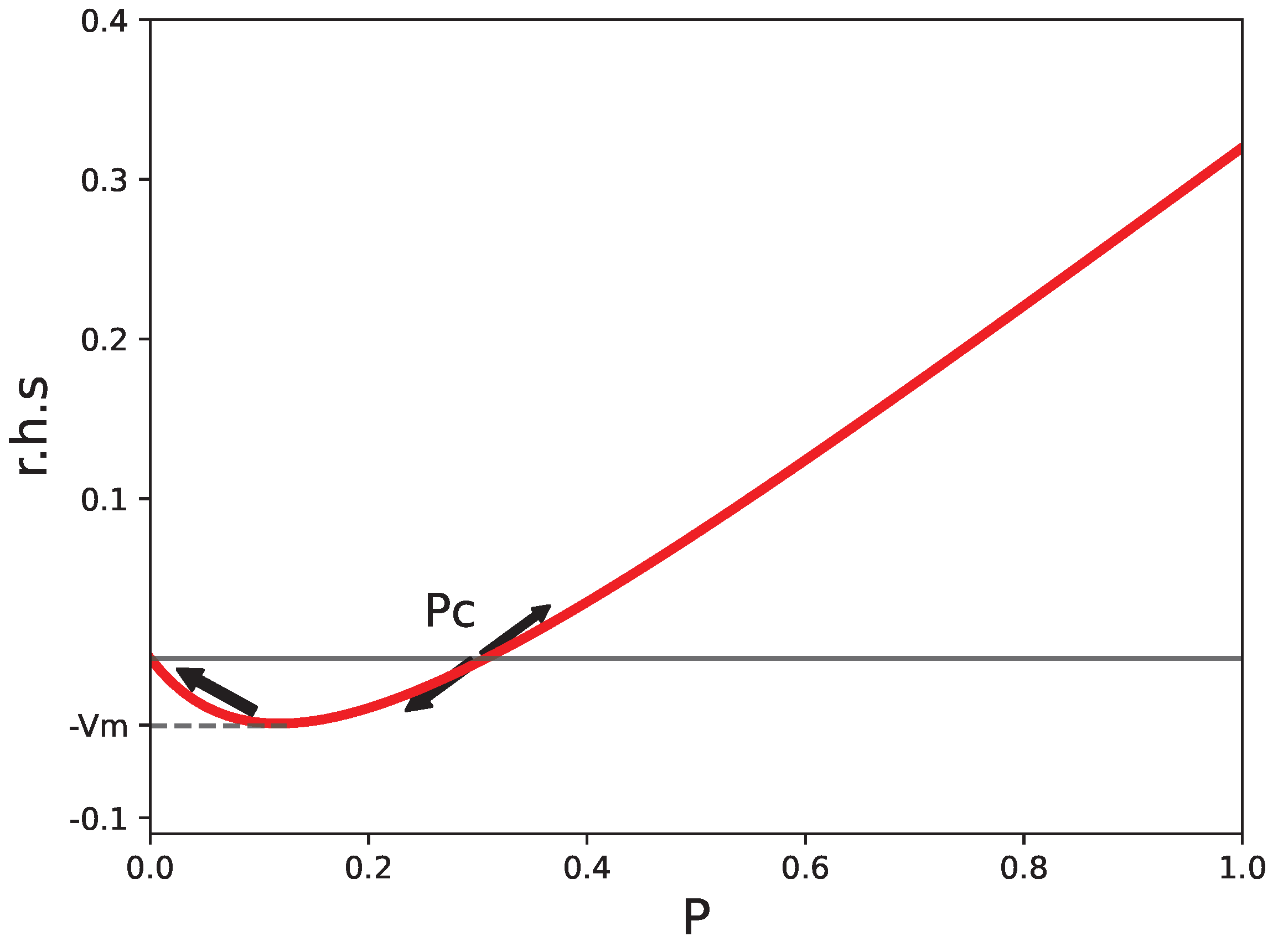
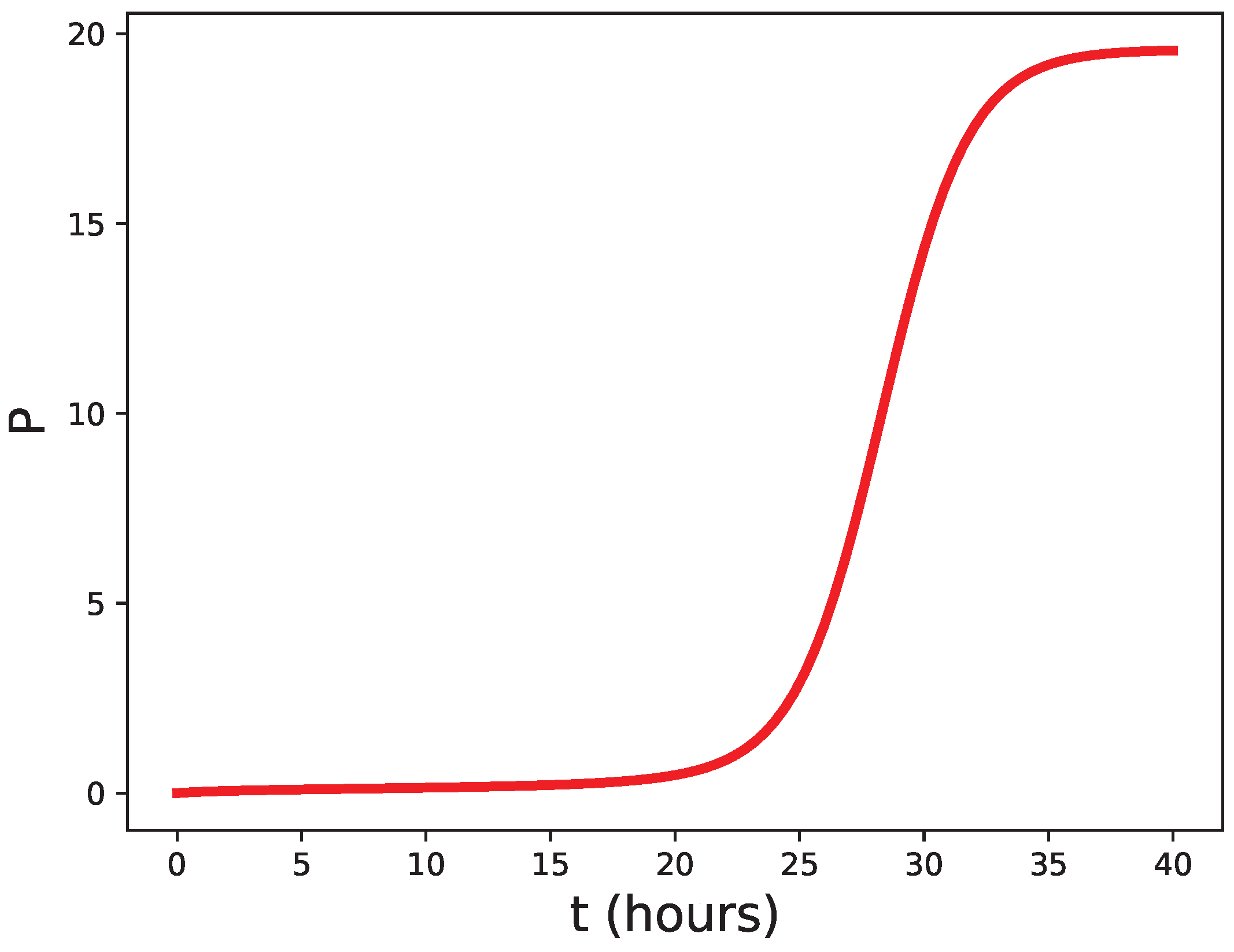
2.2. Nonlinear Model
2.3. Reference Value for the Number of Pathogens
2.4. Stability Condition in Tissues
2.5. A Second Consequence of the Unstable Fixed Point
2.6. A Qualitative Comparison
2.7. Other Tissues
2.8. Immunity to Cancer
3. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Murphy, K.; Weaver, C. Janeway’s Immunobiology; Garland Science: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Akira, S.; Uematsu, S.; Takeuchi, O. Pathogen recognition and innate immunity. Cell 2006, 124, 783–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demaria, O.; Cornen, S.; Daëron, M.; Morel, Y.; Medzhitov, R.; Vivier, E. Harnessing innate immunity in cancer therapy. Nature 2019, 574, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eftimie, R.; Gillard, J.J.; Cantrell, D.A. Mathematical models for immunology: Current state of the art and future research directions. Bull. Math. Biol. 2016, 78, 2091–2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, M.M.; Tato, C.M.; Furman, D. Systems immunology: Just getting started. Nat. Immunol. 2017, 18, 725–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlazaki, M.; Huber, J.; Restif, O. Integrating mathematical models with experimental data to investigate the within-host dynamics of bacterial infections. Pathog. Dis. 2019, 77, ftaa001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xavier, J.B.; Monk, J.M.; Poudel, S.; Norsigian, C.J.; Sastry, A.V.; Liao, C.; Bento, J.; Suchard, M.A.; Arrieta-Ortiz, M.L.; Peterson, E.J.R.; et al. Mathematical models to study the biology of pathogens and the infectious diseases they cause. iScience 2022, 25, 104079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Dyke, T.; Jacks, T. Cancer modeling in the modern era: Progress and challenges. Cell 2002, 108, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quaranta, V.; Weaver, A.M.; Cummings, P.T.; Anderson, A.R. Mathematical modeling of cancer: The future of prognosis and treatment. Clin. Chim. Acta 2005, 357, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altrock, P.M.; Liu, L.L.; Michor, F. The mathematics of cancer: Integrating quantitative models. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2015, 15, 730–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabassum, S.; Rosli, N.B.; Binti Mazalan, M.S.A. Mathematical modeling of cancer growth process: A review. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2019, 1366, 012018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohler, R.R.; Lee, K.S.; Asachenkov, A.L.; Marchuk, G.I. A systems approach to immunology and cancer. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 1994, 24, 632–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchuk, G.I. Mathematical Modelling of Immune Response in Infectious Diseases; Springer Science & Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 1997; Volume 395. [Google Scholar]
- Foryś, U. Marchuk’s model of immune system dynamics with application to tumour growth. J. Theor. Med. 2002, 4, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, B.; Zhou, W.; Dorman, K.; Jones, D. Mathematical modelling of immune response in tissues. Comput. Math. Methods Med. 2009, 10, 9–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomasetti, C.; Vogelstein, B. Variation in cancer risk among tissues can be explained by the number of stem cell divisions. Science 2015, 347, 78–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrero, R.; Leon, D.A.; Gonzalez, A. A one-dimensional parameter-free model for carcinogenesis in gene expression space. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 4748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, L.C.; Jenkins, S.J.; Allen, J.E.; Taylor, P.R. Tissue-resident macrophages. Nat. Immunol. 2013, 14, 986–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckers, H.; Van der Hoeven, J. Growth rates of Actinomyces viscosus and Streptococcus mutans during early colonization of tooth surfaces in gnotobiotic rats. Infect. Immun. 1982, 35, 583–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mai, M.; Wang, K.; Huber, G.; Kirby, M.; Shattuck, M.D.; O’Hern, C.S. Outcome prediction in mathematical models of immune response to infection. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0135861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nemytskii, V.V. Qualitative Theory of Differential Equations; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2015; Volume 2083. [Google Scholar]
- O’Hara, A.M.; Shanahan, F. The gut flora as a forgotten organ. EMBO Rep. 2006, 7, 688–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clevers, H.C.; Bevins, C.L. Paneth cells: Maestros of the small intestinal crypts. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2013, 75, 289–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, C.; Hugot, J.P.; Barreau, F. Peyer’s patches: The immune sensors of the intestine. Int. J. Inflamm. 2010, 2010, 823710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Sorge, N.M.; Doran, K.S. Defense at the border: The blood–brain barrier versus bacterial foreigners. Future Microbiol. 2012, 7, 383–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- França, L.R.; Auharek, S.A.; Hess, R.A.; Dufour, J.M.; Hinton, B.T. Blood-tissue barriers: Morphofunctional and immunological aspects of the blood-testis and blood-epididymal barriers. In Biology and Regulation of Blood-Tissue Barriers; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 237–259. [Google Scholar]
- Merritt, M.E.; Donaldson, J.R. Effect of bile salts on the DNA and membrane integrity of enteric bacteria. J. Med. Microbiol. 2009, 58, 1533–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, S.A. Dynamics of Cancer: Incidence, Inheritance, and Evolution; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Reya, T.; Morrison, S.J.; Clarke, M.F.; Weissman, I.L. Stem cells, cancer, and cancer stem cells. Nature 2001, 414, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Powers, S.; Zhu, W.; Hannun, Y.A. Substantial contribution of extrinsic risk factors to cancer development. Nature 2016, 529, 43–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hooper, D.C.; Phares, T.W.; Kean, R.B.; Mikheeva, T. Regional Differences in Blood-Brain Barrier. J. Immunol. 2006, 176, 7666–7675. [Google Scholar]
- Varoga, D.; Wruck, C.; Tohidnezhad, M.; Brandenburg, L.; Paulsen, F.; Mentlein, R.; Seekamp, A.; Besch, L.; Pufe, T. Osteoblasts participate in the innate immunity of the bone by producing human beta defensin-3. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2009, 131, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perrotta, C.; De Palma, C.; Clementi, E.; Cervia, D. Hormones and immunity in cancer: Are thyroid hormones endocrine players in the microglia/glioma cross-talk? Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Gonzalez, A. Estimating the number of tissue resident macrophages. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1603.08397. [Google Scholar]
- West, G.B.; Brown, J.H.; Enquist, B.J. A general model for the origin of allometric scaling laws in biology. Science 1997, 276, 122–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savage, V.M.; Gillooly, J.F.; Woodruff, W.H.; West, G.B.; Allen, A.P.; Enquist, B.J.; Brown, J.H. The predominance of quarter-power scaling in biology. Funct. Ecol. 2004, 18, 257–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Starkey, P.M.; Gordon, S. Quantitative analysis of total macrophage content in adult mouse tissues. Immunochemical studies with monoclonal antibody F4/80. J. Exp. Med. 1985, 161, 475–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, K.; Wu, Z.X.; Chen, X.Y.; Wang, J.Q.; Zhang, D.; Xiao, C.; Zhu, D.; Koya, J.B.; Wei, L.; Li, J.; et al. Microbiota in health and diseases. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Tissue | Pathogen Flow () | Barrier Height () | Annihilation Rate () | Cancer Risk |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Small bowel | Very High | High | High | Low |
| Colon | Very High | Very High | Normal | Normal |
| Lung | Very High | Very High | Normal | Normal |
| Skin | Very High | Very High | Normal | Normal |
| Duodenum | High | High | Normal | Normal |
| Blood | Normal | Normal | Normal | Normal |
| Pancreas | Normal | Normal | Normal | Normal |
| Liver | High | High | Normal | Normal |
| Cerebellum | Normal | High | Normal | Normal |
| Esophagus | High | High | Normal | Normal |
| Head and Neck | Normal | Normal | Normal | Normal |
| Germ cells | Normal | High | Low | High |
| Brain | Normal | High | Low | High |
| Gallbladder | Normal | High | Low | High |
| Bone | Normal | High | Low | High |
| Thyroid | Normal | High | Low | High |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Herrero, R.; Nieves, J.; Gonzalez, A. First-Stage Dynamics of the Immune System and Cancer. AppliedMath 2023, 3, 1034-1044. https://doi.org/10.3390/appliedmath3040052
Herrero R, Nieves J, Gonzalez A. First-Stage Dynamics of the Immune System and Cancer. AppliedMath. 2023; 3(4):1034-1044. https://doi.org/10.3390/appliedmath3040052
Chicago/Turabian StyleHerrero, Roberto, Joan Nieves, and Augusto Gonzalez. 2023. "First-Stage Dynamics of the Immune System and Cancer" AppliedMath 3, no. 4: 1034-1044. https://doi.org/10.3390/appliedmath3040052
APA StyleHerrero, R., Nieves, J., & Gonzalez, A. (2023). First-Stage Dynamics of the Immune System and Cancer. AppliedMath, 3(4), 1034-1044. https://doi.org/10.3390/appliedmath3040052






