Bioactivity of Ionic Liquids Based on Valproate in SH-SY5Y Human Neuroblastoma Cell Line
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis of ILs-API
2.2. Cell Culture Studies at Therapeutic Dosage
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Viability and Cellular Proliferation: ILs-API Bioactivity in Neoplastic Human Tumor Cell Line SH-SY5Y and Non-Neoplastic Gingival Fibroblasts (GF)
3.2. Structural Activity Relationship of Human Tumor Cell Line SH-SY5Y
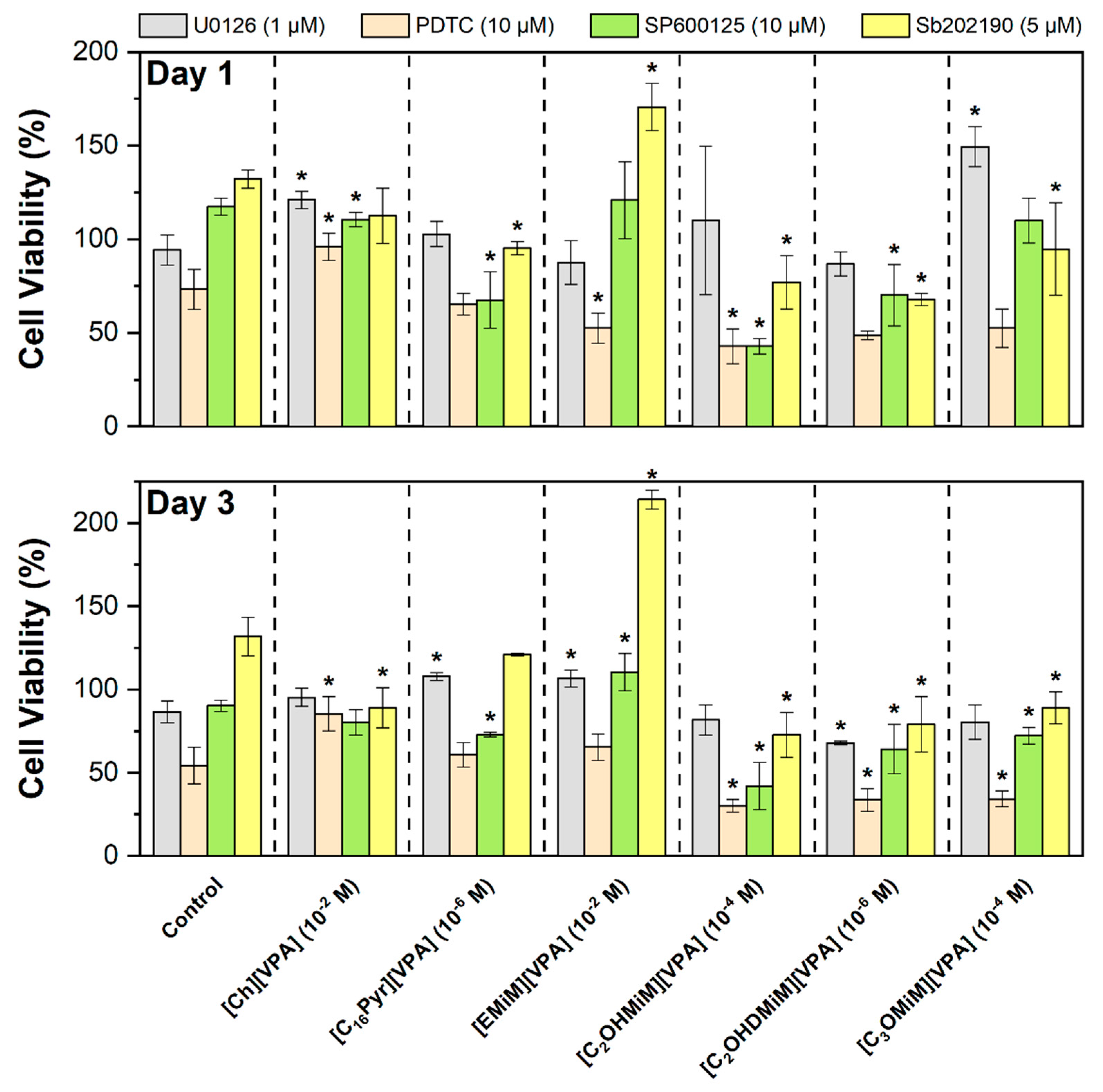
3.3. Cell-Signaling Pathways in Cellular Behavior of Human Tumor Cell Line SH-SY5Y
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Egorova, K.S.; Ananikov, V.P. Fundamental importance of ionic interactions in the liquid phase: A review of recent studies of ionic liquids in biomedical and pharmaceutical applications. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 272, 271–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egorova, K.S.; Gordeev, E.G.; Ananikov, V.P. Biological Activity of Ionic Liquids and Their Application in Pharmaceutics and Medicine. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 7132–7189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacFarlane, D.R.; Seddon, K.R. Ionic liquids—Progress on the fundamental issues. Aust. J. Chem. 2007, 60, 3–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, F.A.E.; Pereira, J.F.B.; Kurnia, K.A.; Ventura, S.P.M.; Silva, A.M.S.; Rogers, R.D.; Coutinho, J.A.P.; Freire, M.G. Temperature dependency of aqueous biphasic systems: An alternative approach for exploring the differences between Coulombic-dominated salts and ionic liquids. Chem. Commun. 2017, 53, 7298–7301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pernak, J.; Niemczak, M.; Zakrocka, K.; Praczyk, T. Herbicidal ionic liquid with dual-function. Tetrahedron 2013, 69, 8132–8136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pernak, J.; Niemczak, M.; Materna, K.; Marcinkowska, K.; Praczyk, T. Ionic liquids as herbicides and plant growth regulators. Tetrahedron 2013, 69, 4665–4669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, Y.C.; Zhang, Y.X.; Ma, J.; Fan, M.H.; Zhang, S.J.; Wang, J.J. Ionic liquids for advanced materials. Mater. Today Nano 2022, 17, 100159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobler, D.; Schmidts, T.; Klingenhöfer, I.; Runkel, F. Ionic liquids as ingredients in topical drug delivery systems. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 441, 620–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florindo, C.; Costa, A.; Matos, C.; Nunes, S.L.; Matias, A.N.; Duarte, C.M.M.; Rebelo, L.P.N.; Branco, L.C.; Marrucho, I.M. Novel organic salts based on fluoroquinolone drugs: Synthesis, bioavailability and toxicological profiles. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 469, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galonde, N.; Nott, K.; Debuigne, A.; Deleu, M.; Jerome, C.; Paquot, M.; Wathelet, J.P. Use of ionic liquids for biocatalytic synthesis of sugar derivatives. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2012, 87, 451–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bica, K.; Rijksen, C.; Nieuwenhuyzen, M.; Rogers, R.D. In search of pure liquid salt forms of aspirin: Ionic liquid approaches with acetylsalicylic acid and salicylic acid. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2010, 12, 2011–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hough, W.L.; Smiglak, M.; Rodriguez, H.; Swatloski, R.P.; Spear, S.K.; Daly, D.T.; Pernak, J.; Grisel, J.E.; Carliss, R.D.; Soutullo, M.D.; et al. The third evolution of ionic liquids: Active pharmaceutical ingredients. New J. Chem. 2007, 31, 1429–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraz, R.; Teixeira, C.; Gomes, P.; Prudencio, C. Chapter 16—Bioactivity of Ionic Liquids. In Ionic Liquid Devices; The Royal Society of Chemistry: London, UK, 2018; pp. 404–422. [Google Scholar]
- Dias, A.R.; Costa-Rodrigues, J.; Fernandes, M.H.; Ferraz, R.; Prudêncio, C. The Anticancer Potential of Ionic Liquids. ChemMedChem 2017, 12, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Vargas, M.R.W.; Raffin, F.N. Strategies used for to improve aqueous solubility of simvastatin: A systematic review. Rev. Ciênc. Farm. Básica E Apl. 2012, 33. [Google Scholar]
- Ferraz, R.; Branco, L.C.; Marrucho, I.M.; Araujo, J.M.M.; Rebelo, L.P.N.; da Ponte, M.N.; Prudencio, C.; Noronha, J.P.; Petrovski, Z. Development of novel ionic liquids based on ampicillin. MedChemComm 2012, 3, 494–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hough-Troutman, W.L.; Smiglak, M.; Griffin, S.; Reichert, W.M.; Mirska, I.; Jodynis-Liebert, J.; Adamska, T.; Nawrot, J.; Stasiewicz, M.; Rogers, R.D.; et al. Ionic liquids with dual biological function: Sweet and anti-microbial, hydrophobic quaternary ammonium-based salts. New J. Chem. 2009, 33, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seter, M.; Thomson, M.J.; Stoimenovski, J.; MacFarlane, D.R.; Forsyth, M. Dual active ionic liquids and organic salts for inhibition of microbially influenced corrosion. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 5983–5985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCrary, P.D.; Beasley, P.A.; Gurau, G.; Narita, A.; Barber, P.S.; Cojocaru, O.A.; Rogers, R.D. Drug specific, tuning of an ionic liquid’s hydrophilic-lipophilic balance to improve water solubility of poorly soluble active pharmaceutical ingredients. New J. Chem. 2013, 37, 2196–2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraz, R.; Teixeira, V.; Rodrigues, D.; Fernandes, R.; Prudencio, C.; Noronha, J.P.; Petrovski, Z.; Branco, L.C. Antibacterial activity of Ionic Liquids based on ampicillin against resistant bacteria. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 4301–4307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florindo, C.; Araujo, J.M.M.; Alves, F.; Matos, C.; Ferraz, R.; Prudencio, C.; Noronha, J.P.; Petrovski, Z.; Branco, L.; Rebelo, L.P.N.; et al. Evaluation of solubility and partition properties of ampicillin-based ionic liquids. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 456, 553–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, A.; Perez, B.; Albuquerque, I.; Machado, M.; Prudencio, M.; Nogueira, F.; Teixeira, C.; Gomes, P. N-Cinnamoylation of Antimalarial Classics: Quinacrine Analogues with Decreased Toxicity and Dual-Stage Activity. ChemMedChem 2014, 9, 305–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, T.; Magalhaes, B.; Maia, S.; Gomes, P.; Nazmi, K.; Bolscher, J.G.M.; Rodrigues, P.N.; Bastos, M.; Gomes, M.S. Killing of Mycobacterium avium by Lactoferricin Peptides: Improved Activity of Arginine- and D-Amino-Acid-Containing Molecules. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 3461–3467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez, B.C.; Teixeira, C.; Albuquerque, I.S.; Gut, J.; Rosenthal, P.J.; Gomes, J.R.B.; Prudencio, M.; Gomes, P. N-Cinnamoylated Chloroquine Analogues as Dual-Stage Antimalarial Leads. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 556–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hough, W.L.; Rogers, R.D. Ionic liquids then and now: From solvents to materials to active pharmaceutical ingredients. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 2007, 80, 2262–2269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.T.; Teixeira, C.; Marques, E.F.; Prudencio, C.; Gomes, P.; Ferraz, R. Surfing the Third Wave of Ionic Liquids: A Brief Review on the Role of Surface-Active Ionic Liquids in Drug Development and Delivery. ChemMedChem 2021, 16, 2604–2611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoimenovski, J.; MacFarlane, D.R.; Bica, K.; Rogers, R.D. Crystalline vs. Ionic Liquid Salt Forms of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients: A Position Paper. Pharm. Res. 2010, 27, 521–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suresh, C.; Zhao, H.; Gumbs, A.; Chetty, C.S.; Bose, H.S. New ionic derivatives of betulinic acid as highly potent anti-cancer agents. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2012, 22, 1734–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chateauvieux, S.; Morceau, F.; Dicato, M.; Diederich, M. Molecular and Therapeutic Potential and Toxicity of Valproic Acid. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2010, 2010, 479364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaheta, R.A.; Cinatl, J., Jr. Anti-tumor mechanisms of valproate: A novel role for an old drug. Med. Res. Rev. 2002, 22, 492–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loscher, W. Valproate: A reappraisal of its pharmacodynamic properties and mechanisms of action. Prog. Neurobiol. 1999, 58, 31–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ximenes, J.C.; de Oliveira Goncalves, D.; Fau-Siqueira, R.M.P.; Siqueira Rm Fau-Neves, K.R.T.; Neves Kr Fau-Santos Cerqueira, G.; Santos Cerqueira, G.; Fau-Correia, A.O.; Correia Ao Fau-Felix, F.H.C.; Felix Fh Fau-Leal, L.K.A.M.; Leal Lk Fau-de Castro Brito, G.A.; et al. Valproic acid: An anticonvulsant drug with potent antinociceptive and anti-inflammatory properties. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 2013, 386, 575–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jentink, J.; Loane, M.A.; Dolk, H.; Barisic, I.; Garne, E.; Morris, J.K.; de Jong-van den Berg, L.T. Valproic acid monotherapy in pregnancy and major congenital malformations. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 362, 2185–2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kostrouchova, M.; Kostrouch, Z. Valproic acid, a molecular lead to multiple regulatory pathways. Folia Biol. 2007, 53, 37–49. [Google Scholar]
- Duenas-Gonzalez, A.; Candelaria, M.; Perez-Plascencia, C.; Perez-Cardenas, E.; de la Cruz-Hernandez, E.; Herrera, L.A. Valproic acid as epigenetic cancer drug: Preclinical, clinical and transcriptional effects on solid tumors. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2008, 34, 206–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, S.; Tian, Y.; Chlenski, A.; Salwen, H.R.; Lu, Z.; Raj, J.U.; Yang, Q. Valproic acid shows potent antitumor effect with alteration of DNA methylation in neuroblastoma. Anticancer Drugs 2012, 23, 1054–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodurga, Y.; Gundogdu, G.; Tekin, V.; Koc, T.; Satiroglu-Tufan, N.L.; Bagci, G.; Kucukatay, V. Valproic acid inhibits the proliferation of SHSY5Y neuroblastoma cancer cells by downregulating URG4/URGCP and CCND1 gene expression. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2014, 41, 4595–4599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, R.; Banipal, P.K.; Banipal, T.S. Binding ability of sodium valproate with cationic surfactants and effect on micellization: Calorimetric, surface tension, light scattering and spectroscopic approach. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2020, 140, 2833–2847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanwar, L.K.S.; Sharma, S.; Ghosh, K.K. Interaction of an imidazolium based ionic liquid with antidepressant drugs: A physicochemical study. Colloids Surf. A—Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2022, 636, 128159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casal-Dujat, L.; Griffiths, P.C.; Rodriguez-Abreu, C.; Solans, C.; Rogers, S.; Perez-Garcia, L. Nanocarriers from dicationic bis-imidazolium amphiphiles and their interaction with anionic drugs. J. Mater. Chem. B 2013, 1, 4963–4971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malik, N.A.; Farooq, U.; Rather, M.A.; Shalla, A.H. Interactions of tricyclic antidepressant drug chlomipramine hydrochloride with imidazolium based surface active ionic liquid in aqueous solution. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 342, 117427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banjare, M.K.; Behera, K.; Banjare, R.K.; Pandey, S.; Ghosh, K.K.; Karpichev, Y. Molecular interactions between novel synthesized biodegradable ionic liquids with antidepressant drug. Chem. Thermodyn. Therm. Anal. 2021, 3–4, 100012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Megison, M.L.; Gillory, L.A.; Beierle, E.A. Cell survival signaling in neuroblastoma. Anticancer Agents Med. Chem. 2013, 13, 563–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louis, C.U.; Shohet, J.M. Neuroblastoma: Molecular pathogenesis and therapy. Annu. Rev. Med. 2015, 66, 49–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stafman, L.; Beierle, E. Cell Proliferation in Neuroblastoma. Cancers 2016, 8, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, S.; Santos, M.M.; Branco, L.C.; Costa-Rodrigues, J. Etidronate-based organic salts and ionic liquids: In vitro effects on bone metabolism. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 610, 121262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Sodies, S.; Rezki, N.; Albelwi, F.F.; Messali, M.; Aouad, M.R.; Bardaweel, S.K.; Hagar, M. Novel Dipyridinium Lipophile-Based Ionic Liquids Tethering Hydrazone Linkage: Design, Synthesis and Antitumorigenic Study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, S.; Santos, M.M.; Fernandes, M.H.; Costa-Rodrigues, J.; Branco, L.C. Alendronic Acid as Ionic Liquid: New Perspective on Osteosarcoma. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, M.M.; Raposo, L.R.; Carrera, G.; Costa, A.; Dionisio, M.; Baptista, P.V.; Fernandes, A.R.; Branco, L.C. Ionic Liquids and Salts from Ibuprofen as Promising Innovative Formulations of an Old Drug. ChemMedChem 2019, 14, 907–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraz, R.; Costa-Rodrigues, J.; Fernandes, M.H.; Santos, M.M.; Marrucho, I.M.; Rebelo, L.P.N.; Prudencio, C.; Noronha, J.P.; Petrovski, Z.; Branco, L.C. Antitumor Activity of Ionic Liquids Based on Ampicillin. ChemMedChem 2015, 10, 1480–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapio, L.; Naviglio, S. Innovation through Tradition: The Current Challenges in Cancer Treatment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokhtari, R.B.; Homayouni, T.S.; Baluch, N.; Morgatskaya, E.; Kumar, S.; Das, B.; Yeger, H. Combination therapy in combating cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 38022–38043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferraz, R.; Silva, D.; Dias, A.R.; Dias, V.; Santos, M.M.; Pinheiro, L.; Prudencio, C.; Noronha, J.P.; Petrovski, Z.; Branco, L.C. Synthesis and Antibacterial Activity of Ionic Liquids and Organic Salts Based on Penicillin G and Amoxicillin hydrolysate Derivatives against Resistant Bacteria. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferraz, R.; Noronha, J.; Murtinheira, F.; Nogueira, F.; Machado, M.; Prudencio, M.; Parapini, S.; D’Alessandro, S.; Teixeira, C.; Gomes, A.; et al. Primaquine-based ionic liquids as a novel class of antimalarial hits. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 56134–56138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loh, G.W.; Mabasa, V.H.; Ensom, M.H.H. Therapeutic drug monitoring in the neurocritical care unit. Curr. Opin. Crit. Care 2010, 16, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Amde, M.; Liu, J.F.; Pang, L. Environmental Application, Fate, Effects, and Concerns of Ionic Liquids: A Review. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 12611–12627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frade, R.F.M.; Rosatella, A.A.; Marques, C.S.; Branco, L.C.; Kulkarni, P.S.; Mateus, N.M.M.; Afonso, C.A.M.; Duarte, C.M.M. Toxicological evaluation on human colon carcinoma cell line (CaCo-2) of ionic liquids based on imidazolium, guanidinium, ammonium, phosphonium, pyridinium and pyrrolidinium cations. Green Chem. 2009, 11, 1660–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, T.P.T.; Cho, C.-W.; Yun, Y.-S. Environmental fate and toxicity of ionic liquids: A review. Water Res. 2010, 44, 352–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bystrzanowska, M.; Pena-Pereira, F.; Marcinkowski, L.; Tobiszewski, M. How green are ionic liquids? A multicriteria decision analysis approach. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 174, 455–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frade, R.F.M.; Afonso, C.A.M. Impact of ionic liquids in environment and humans: An overview. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2010, 29, 1038–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moniruzzaman, M.; Goto, M. Ionic Liquids: Future Solvents and Reagents for Pharmaceuticals. J. Chem. Eng. Jpn. 2011, 44, 370–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, S.; Santos, M.M.; Ferraz, R.; Prudencio, C.; Fernandes, M.H.; Costa-Rodrigues, J.; Branco, L.C. A Novel Approach for Bisphosphonates: Ionic Liquids and Organic Salts from Zoledronic Acid. ChemMedChem 2019, 14, 1767–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dias, A.R.; Costa-Rodrigues, J.; Teixeira, C.; Prudencio, C.; Gomes, P.; Ferraz, R. Ionic Liquids for Topical Delivery in Cancer. Curr. Med. Chem. 2019, 26, 7520–7532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bubalo, M.C.; Radosevic, K.; Redovnikovic, I.R.; Halambek, J.; Srcek, V.G. A brief overview of the potential environmental hazards of ionic liquids. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2014, 99, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ventura, S.P.M.; de Barros, R.L.F.; Sintra, T.; Soares, C.M.F.; Lima, A.S.; Coutinho, J.A.P. Simple screening method to identify toxic/non-toxic ionic liquids: Agar diffusion test adaptation. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2012, 83, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egorova, K.S.; Ananikov, V.P. Toxicity of Ionic Liquids: Eco(cyto)activity as Complicated, but Unavoidable Parameter for Task-Specific Optimization. ChemSusChem 2014, 7, 336–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanatta, M.; dos Santos, F.P.; Biehl, C.; Marin, G.; Ebeling, G.; Netz, P.A.; Dupont, J. Organocatalytic Imidazolium Ionic Liquids H/D Exchange Catalysts. J. Org. Chem. 2017, 82, 2622–2629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, P.S.; Santos, J.D.; Fernandes, M.H. Cell-induced response by tetracyclines on human bone marrow colonized hydroxyapatite and Bonelike®. Acta Biomater. 2008, 4, 630–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barros, A.V.; Araujo, L.M.; de Oliveira, F.F.; da Conceicao, A.O.; Simoni, I.C.; Fernandes, M.J.B.; Arns, C.W. In Vitro Evaluation of the Antiviral Potential of Guettarda angelica Against Animal Herpesviruses. Acta Sci. Vet. 2012, 40, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Sebaugh, J.L. Guidelines for accurate EC50/IC50 estimation. Pharm. Stat. 2011, 10, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
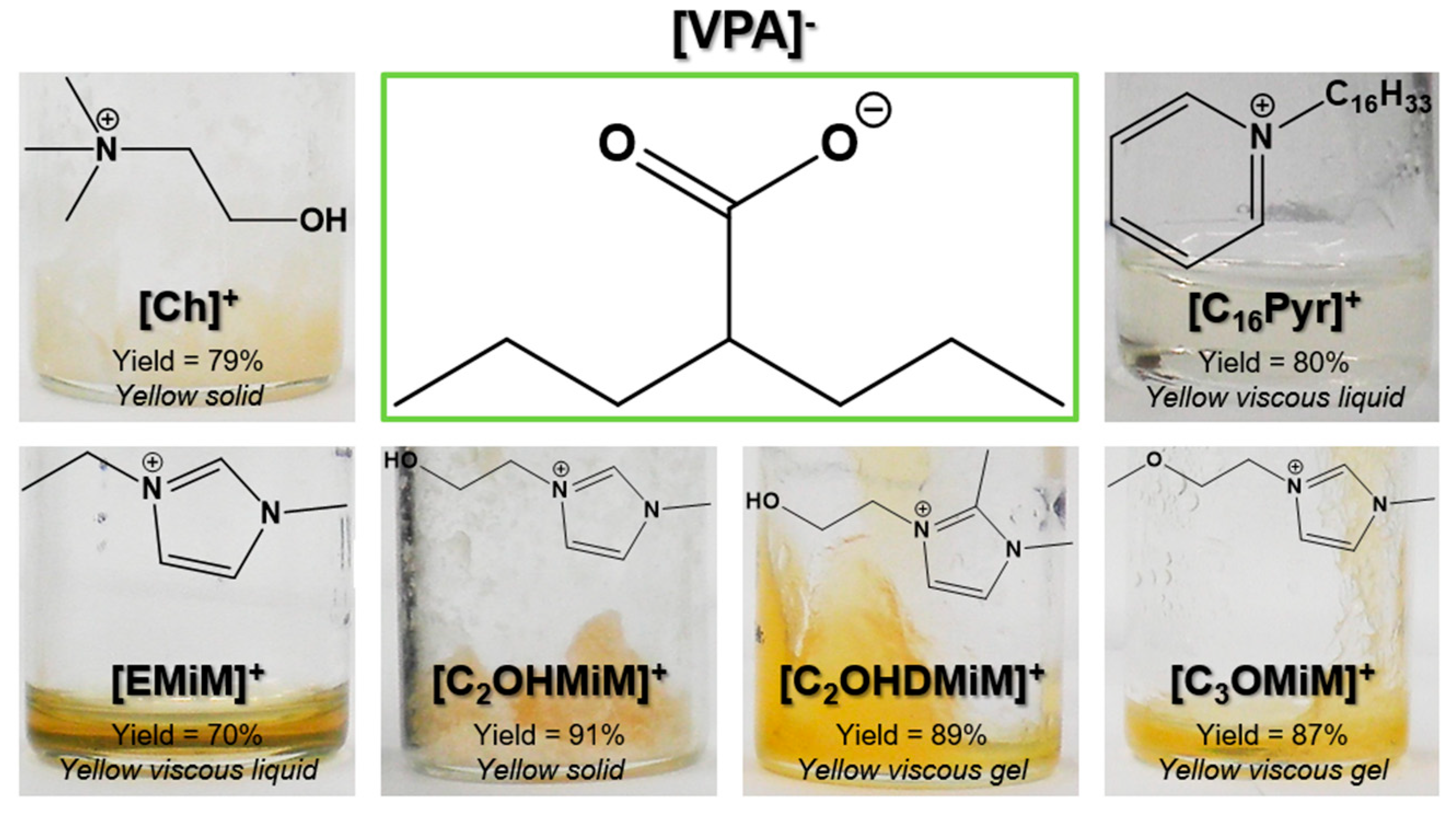
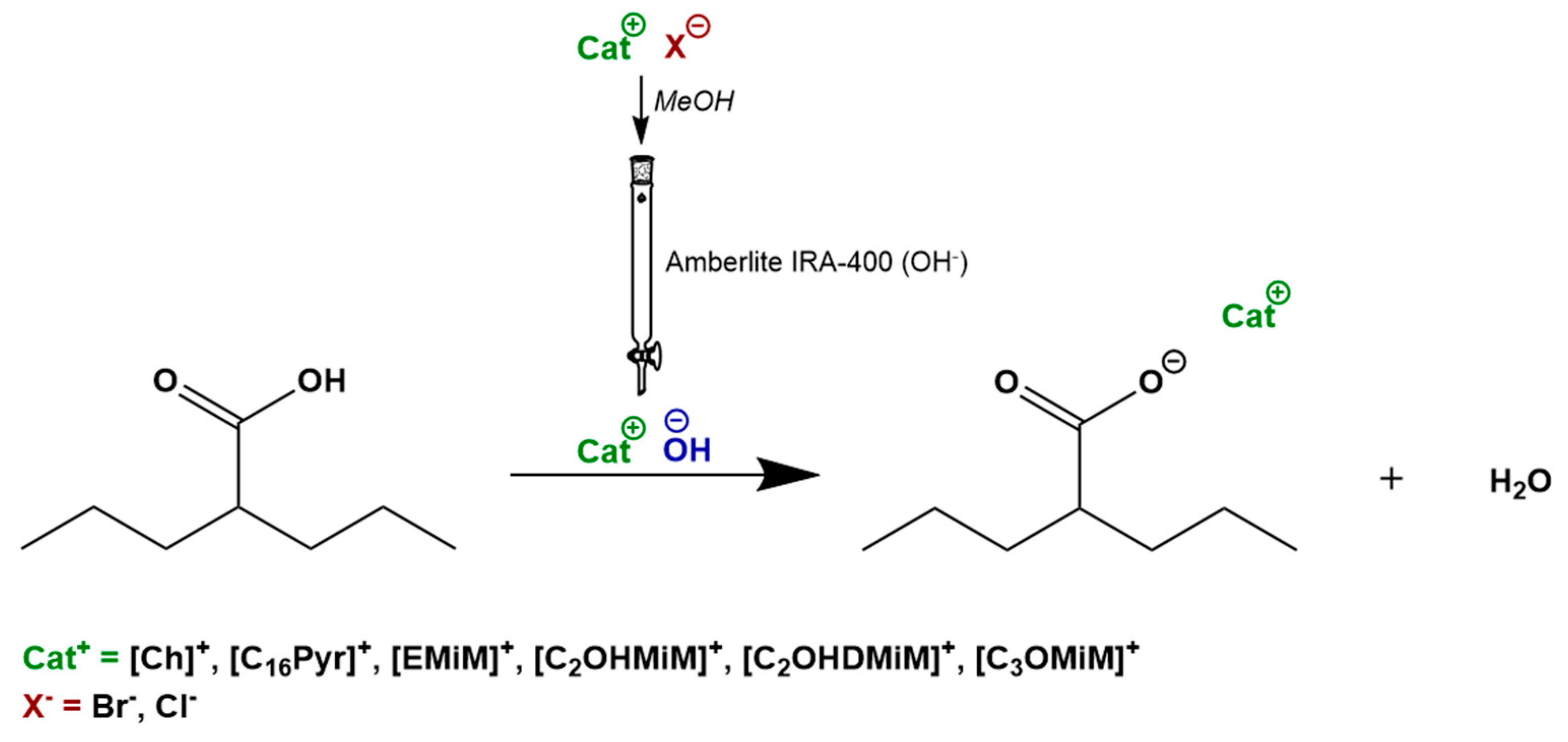
| Cell Line | Tested Concentrations (mol dm−3) | Tested Concentrations (mg L−1) | Therapeutic Dosage (mg L−1) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SH-SY5Y | 10−7–10−2 | 0.01442–1442 | 50–100 | [55] |
| GF | 10−5–10−1 | 1.442–14,421 |
| Compound | IC50 (µM) | EC50 (µM) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GF | SH-SY5Y | GF | SH-SY5Y | |||
| Day 1 | Day 1 | Day 3 | Day 1 | Day 1 | Day 3 | |
| VPA 1 | 294.2 | 0.633 | n.d. | 299.3 | 60.72 | n.d. |
| [Ch][VPA] | n.d. | 0.049 | n.d. | n.d. | 0.158 | 3528 |
| [C16Pyr][VPA] | 75.54 | 1.408 | 1.411 | 76.07 | 4.358 | 1.681 |
| [EMiM][VPA] | 1058 | 1.038 | n.d. | >1058 | 0.086 | 126.0 |
| [C2OHMiM][VPA] | 23.66 | 31.09 | 3560 | 27.42 | 21.03 | 2.824 |
| [C2OHDMiM][VPA] | n.d. | 0.263 | 227.8 | n.d. | 6.000 | 44.58 |
| [C3OMiM][VPA] | 1374 | 0.646 | n.d. | >1374 | 27.30 | 14.71 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dias, A.R.; Ferraz, R.; Costa-Rodrigues, J.; Santos, A.F.M.; Jacinto, M.L.; Prudêncio, C.; Noronha, J.P.; Branco, L.C.; Petrovski, Ž. Bioactivity of Ionic Liquids Based on Valproate in SH-SY5Y Human Neuroblastoma Cell Line. Future Pharmacol. 2022, 2, 320-329. https://doi.org/10.3390/futurepharmacol2030022
Dias AR, Ferraz R, Costa-Rodrigues J, Santos AFM, Jacinto ML, Prudêncio C, Noronha JP, Branco LC, Petrovski Ž. Bioactivity of Ionic Liquids Based on Valproate in SH-SY5Y Human Neuroblastoma Cell Line. Future Pharmacology. 2022; 2(3):320-329. https://doi.org/10.3390/futurepharmacol2030022
Chicago/Turabian StyleDias, Ana Rita, Ricardo Ferraz, João Costa-Rodrigues, Andreia F. M. Santos, Manuel L. Jacinto, Cristina Prudêncio, João Paulo Noronha, Luis C. Branco, and Željko Petrovski. 2022. "Bioactivity of Ionic Liquids Based on Valproate in SH-SY5Y Human Neuroblastoma Cell Line" Future Pharmacology 2, no. 3: 320-329. https://doi.org/10.3390/futurepharmacol2030022
APA StyleDias, A. R., Ferraz, R., Costa-Rodrigues, J., Santos, A. F. M., Jacinto, M. L., Prudêncio, C., Noronha, J. P., Branco, L. C., & Petrovski, Ž. (2022). Bioactivity of Ionic Liquids Based on Valproate in SH-SY5Y Human Neuroblastoma Cell Line. Future Pharmacology, 2(3), 320-329. https://doi.org/10.3390/futurepharmacol2030022










