Abstract
Because soybean is sensitive to salt stress, it is necessary to improve their stress tolerance. Titanium-oxide nanoparticles (TiO2 NPs) enhanced the growth of soybean under salt stress. To elucidate the promotive effects of TiO2 NPs on soybean growth under salt stress, a gel-free/label-free proteomic analysis was carried out. The principal component analysis of proteins showed that TiO2 NPs affected proteins in roots grown under salt stress. The differentially changed proteins were associated with protein metabolism and transport in the biological process, the nucleus in the cellular component, and nucleic acid binding activity in the molecular function. Proteins identified with proteomics were verified using immunoblot analysis. The abundance of V-ATPase decreased in soybean under salt stress and increased with additional TiO2 NPs under stress, whereas xyloglucan endotransglucosylase/hydrolase did not change with any treatment. The abundance of peroxiredoxin increased under salt stress but decreased with additional TiO2 NPs under stress. These results suggest that TiO2 NPs confer salt tolerance in soybean plants at the early growth stage by regulating vacuole transport and reactive oxygen scavenging systems.
1. Introduction
Around 1125 million hectares of global agricultural land are facing the issue of salinity, consequently reducing crop yields [1]. Increased salinity has significant adverse effects on the morphological, physiological, and biochemical characteristics of plants and interferes with the desired metabolic processes of plants, resulting in reduced germination rates, plant growth, and yield [2]. Among crops, soybean is highly sensitive to salinity, which reduces yields by up to 40% [3]. In soybean, salt stress negatively regulated gibberellic acid biogenesis and positively mediated abscisic acid biogenesis, causing delayed seed germination [4]. In soybean roots, salt stress encouraged the accumulation of proteins with binding/catalytic activity [5]. In soybean leaves, salt stress induced dynamic lipid alterations in the recycling of both phospholipids and galactolipids [6]. These findings indicate that increasing salt-tolerant soybean is important to enhance food production.
Nanoparticles (NPs) are ultrafine particles with a size of less than 100 nm in at least one dimension [7]. NPs have been applied in agriculture for plant growth, fertilizers, and pesticides, ensuring sustainable crop production [8]. For example, silver, zinc-oxide, and aluminum-oxide NPs have a positive effect on crop growth [9]. Among NPs, titanium-dioxide (TiO2) NPs have various profound effects on morphological, physiological, and biochemical characteristics of crops [10]. TiO2 NPs’ exposure increased root elongation and plant biomass in wheat and rapeseed [11]. Contrastingly, the phytotoxicity of TiO2 NPs increased with a longer exposure period and a higher dosage, which was stronger in wheat shoots than in roots [12]. The highest concentration of TiO2 NPs had adverse effects on the germination, physiochemical, and yield characteristics of wheat [13]. The elevated concentration of TiO2 NPs had inhibitory effects on wheat germination [14]. In soybean, the increased concentration of TiO2 NPs also inhibited seed germination [15]. These results indicate that TiO2 NPs have two contrasting effects depending on the concentration.
In addition, TiO2 NP-treated plants showed stress tolerance through enhanced content of carotenoides and chlorophyll; the activity of antioxidant enzymes resulted in reduced levels of hydrogen peroxide and malondialdehyde in broad bean under salt stress [16]. The foliar application of TiO2 NPs can help to improve tolerance against salt stress in wheat [13]. TiO2 NPs mediated positive effects on germination parameters, reducing hydrogen peroxide and malondialdehyde contents by enhancing antioxidants on soybean under salt stress [15]. TiO2 NPs alleviated salt stress in soybean through restoring the antioxidants and the cell ultrastructure [17]. However, the biochemical and molecular mechanisms of TiO2 NPs on soybeans under salt stress have not been determined.
To characterize salt-tolerant mechanisms in soybean, TiO2 NPs were used in this study. Three-day-old soybeans grown in sand were treated with TiO2 NPs (15–25 nm) and NaCl solution for 2 days, after which their morphological parameters were analyzed. Based on the morphological results, proteomic analysis was performed using nano-liquid chromatography (LC) and mass spectrometry (MS)/MS. The proteomic results were subsequently confirmed by immunoblot analysis.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials and Treatment
Seeds of soybean (Glycine max L. cultivar Enrei) were used in this study. Seeds were sown in quartz sand in a nursery case. After 3 days of sowing, soybean seedlings were treated with or without 4, 40, and 400 μg/mL TiO2 NPs (Tecnan, Los Arcos, Spain) solution and with or without 150 mM NaCl solution for 2 days. Seedlings were grown at 25 °C in a chamber illuminated with white fluorescent light (200 μmol m−2 s−1, 12 h light period/day). For morphological analysis, roots and hypocotyls were collected. For proteomic analysis, roots were collected. Roots and hypocotyls were collected for immunoblot analysis. Three independent experiments were performed as biological triplicates for all experiments. As independent biological replicates, seeds were sown on different days.
2.2. Protein Extraction
All experiments were performed at 4 °C. A portion (500 mg) of samples was ground with a mortar and pestle in 500 µL of extraction buffer, which contained 50 mM Tris-HCl, 150 mM NaCl, 0.1% sodium deoxycholate, 1% Nonidet-P40, 0.1% sodium dodecyl sulfate, and protease inhibitor. The suspension was centrifuged twice with 16,000× g for 10 min. Protein concentration was determined using Bradford methods [18], and bovine serum albumin was used as the standard.
2.3. Protein Enrichment, Reduction, Alkylation, and Digestion
Quantified proteins (100 µg) were adjusted to a final volume of 100 µL and added to 400 µL of methanol/100 µL of chloroform/300 µL of water. After centrifugation at 16,000× g for 10 min, the upper phase was discarded, and 300 µL of methanol was added. After centrifugation at 16,000× g for 10 min, the supernatant was discarded and the pellet was resuspended in 50 mM ammonium bicarbonate. Proteins were reduced with 50 mM dithiothreitol for 30 min at 56 °C, alkylated with 50 mM iodoacetamide for 30 min at 37 °C, and digested with trypsin (Wako, Osaka, Japan) for 18 h at 37 °C. Peptides were desalted with MonoSpin C18 Column (GL Sciences, Tokyo, Japan) and acidified with 1% trifluoroacetic acid [19].
2.4. Protein Identification Using Nano-LC-MS/MS
The conditions of the nanoLC (EASY-nLC 1000; Thermo Fisher Scientific, San Jose, CA, USA) and MS acquisition (Orbitrap Fusion ETD MS; Thermo Fisher Scientific) were described in the previous study [20].
2.5. MS Data Analysis
The MS/MS searches were carried out using MASCOT (version 2.6.2, Matrix Science, London, UK) and SEQUEST HT search algorithms against the UniProtKB Glycine max (Soybean) protein database (version 20231026) using Proteome Discoverer (version 2.4.1.15; Thermo Fisher Scientific). The workflow was described in the previous study [20].
2.6. Differential Analysis of Proteins Using MS Data
Label-free quantification was performed with Proteome Discoverer using precursor ions quantifier nodes. For differential analysis of the relative abundance of peptides and proteins between samples, the freely available software Perseus (version 1.6.15.0) [21] was used. The workflow was described in the previous study [20].
2.7. Immunoblot Analysis
An SDS sample buffer consisting of 62.5 mM Tris-HCl (pH 6.8), 2% SDS, 50 mM dithiothreitol, 10% glycerol, and 0.01% bromophenol blue was added to the protein samples. Quantified proteins (10 µg) were separated by electrophoresis on a 10% polyacrylamide gel and transferred onto a polyvinylidene difluoride membrane using a semidry transfer blotter. The membrane was blocked for 5 min in Bullet Blocking One regent (Nacalai Tesque, Kyoto, Japan) and cross-reacted with the primary antibodies for 30 min. As the primary antibodies, the following were used: anti-V-ATPase (Agrisera, Vännäs, Sweden), xyloglucan endotransglucosylase/hydrolase (Agrisera), superoxide dismutase (Proteintech, Tokyo, Japan), ascorbate peroxidase [22], peroxiredoxin [23], and glutathione reductase (Agrisera) antibodies. Anti-rabbit IgG conjugated with horseradish peroxidase (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA) was used as the secondary antibody. After 30 min incubation, signals were detected using the TMB Membrane Peroxidase Substrate kit (Nacalai Tesque).
The integrated densities of bands were calculated using ImageJ software (version 1.8, National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD, USA). Coomassie brilliant blue staining was used as a loading control. The intensity of the bandless area on the polyvinylidene difluoride membrane was measured and used as background. The background was subtracted from the intensity of each protein band to obtain the relative abundance of the protein. The ratio means the relative protein abundance of each treatment/relative protein abundance of the control.
2.8. Hydrogen Peroxide Content Measurement
The hydrogen peroxide contents were measured using the Amplite Colorimetric Hydrogen Peroxide Assay Kit (AAT Bioquest, Pleasanton, CA, USA). A portion (200 mg) of fresh roots was ground with a mortar and pestle in 200 μL of phosphate buffer on ice. The homogenates were collected and centrifuged at 16,000× g for 20 min. The supernatant was immediately used for the hydrogen peroxide assay. A working solution (25 µL) containing horseradish peroxidase and hydrogen peroxidase substrate was added to the sample (25 µL) and reacted for 10 and 60 min. The samples were protected from light. The absorbance was measured at 650 nm. The hydrogen peroxide content was determined using hydrogen peroxide as the standard and calculated from a standard curve.
2.9. Statistical Analysis
The statistical significance of the 2 groups was evaluated by Student’s t-test. A p-value of less than 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
3. Results
3.1. Morphological Analysis of Soybean Treated with TiO2 NPs Under Salt Stress
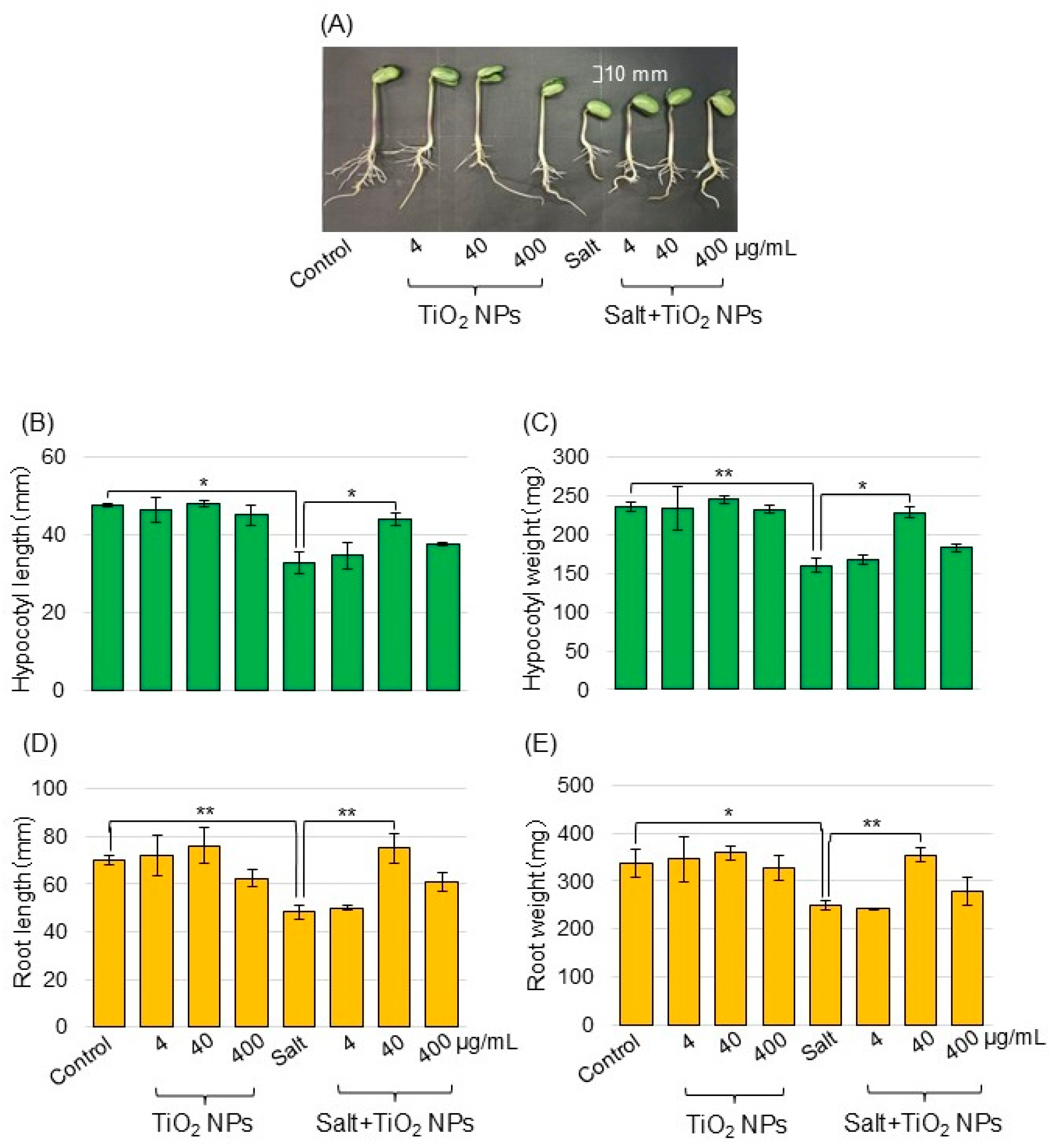
To investigate the effects of TiO2 NPs on soybeans under salt stress, morphological analysis was performed. Soybean seeds were sown, and 3-day-old seedlings were treated with or without TiO2 NPs with or without 150 mM NaCl for 2 days. Four treatments were performed: nontreatment, TiO2 NPs, salt, and salt + TiO2 NP treatment. As morphological parameters, the hypocotyl length (Figure 1B), hypocotyl fresh weight (Figure 1C), main root length (Figure 1D), and total root fresh weight (Figure 1E) were measured. Soybean growth was suppressed by salt stress and recovered with TiO2 NPs, especially 40 μg/mL TiO2 NPs compared with the control. The main root length, and total root fresh weight increased with the application of TiO2 NPs, even under salt stress. Based on these results, soybean was treated with 40 μg/mL TiO2, and roots were used for the proteomic analysis.
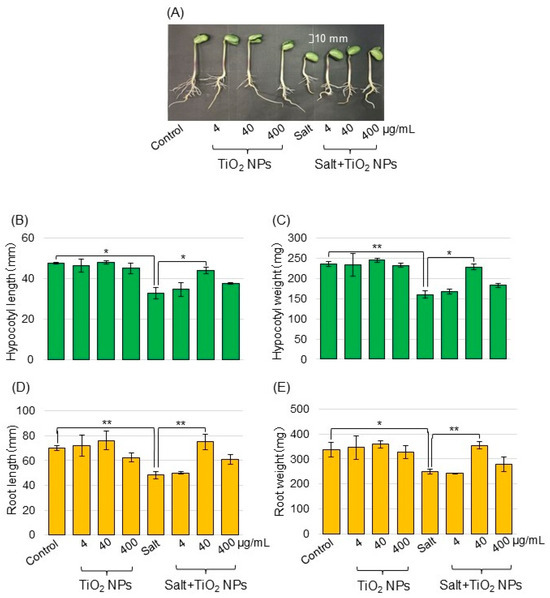
Figure 1.
Morphological analysis of soybean treated with TiO2 NPs under salt stress. Soybean seeds were sown and grown for 3 days. Seedlings were treated with or without 4, 40, and 400 μg/mL TiO2 NPs with or without 150 mM NaCl for 2 days. Before morphological analysis, a photograph was taken. The bar in the picture indicates 10 mm (A). As morphological parameters, hypocotyl length (B), hypocotyl fresh weight (C), main root length (D), and total root fresh weight (E) were analyzed at 5 days after sowing. Data are presented as the mean ± SD from 3 independent biological replicates. The statistical significance of the 2 groups was evaluated by Student’s t-test. A p-value of less than 0.05 was considered statistically significant (**, p < 0.01; *, p < 0.05).
3.2. Identification and Functional Investigation of Proteins in Soybean Treated with TiO2 NPs Under Salt Stress
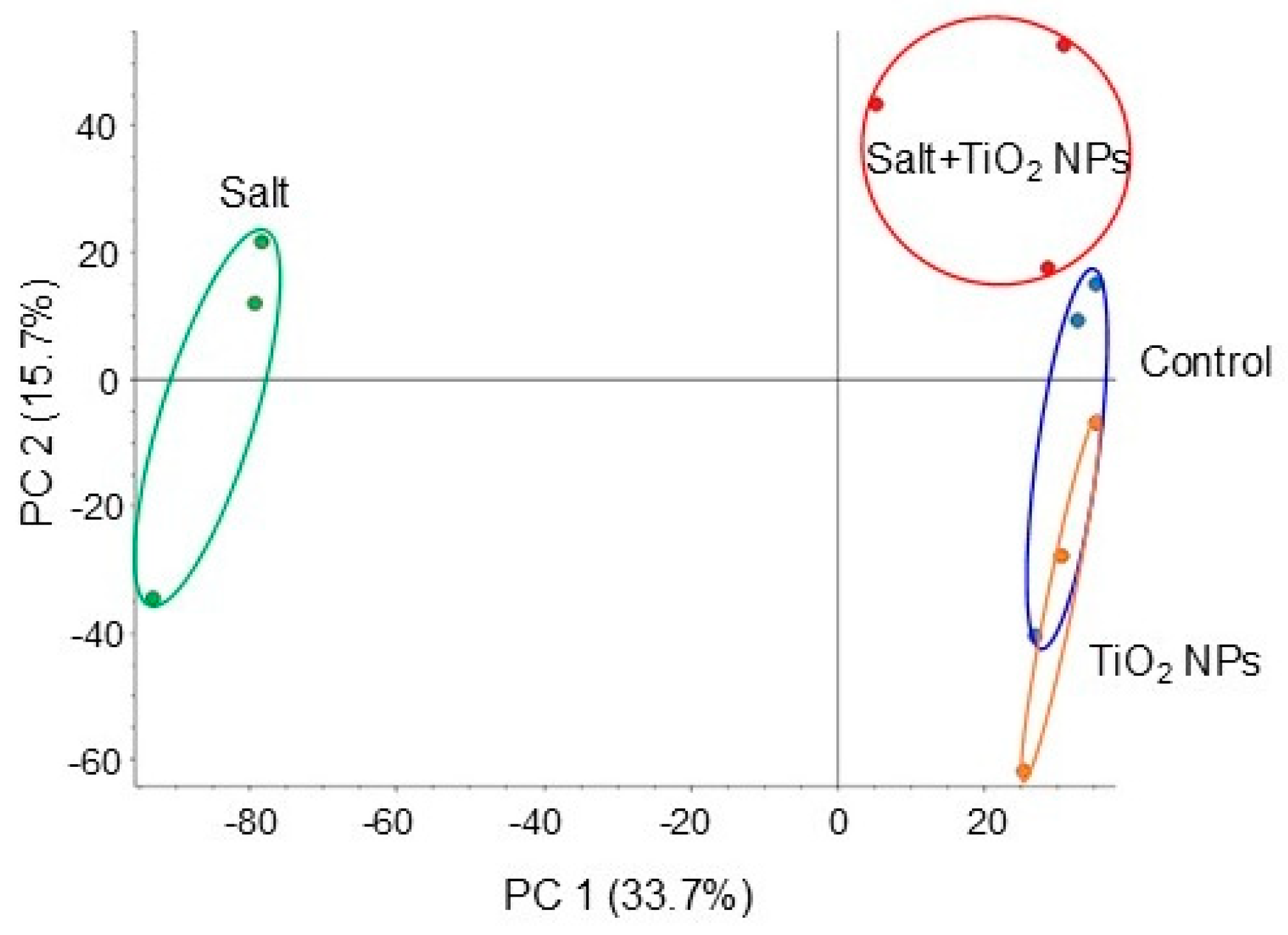
To investigate the cellular mechanisms in soybean growth by application of TiO2 NPs under salt stress, proteomics was performed. Four types of treatments were performed: nontreatment, TiO2 NPs, salt, and salt + TiO2 NPs. The proteins extracted from soybean root were concentrated, reduced, alkylated, and digested. Gel-free/label-free proteomics was performed and investigated the biological process, cellular components, and molecular functions. A total of 8316 proteins were detected by LC-MS/MS analysis. The proteomic results of all samples from different groups were compared by principal component analysis, which showed different accumulation patterns of proteins from different treatments. The principal component analysis of proteins showed that TiO2 NPs affected proteins in root grown under salt stress (Figure 2).
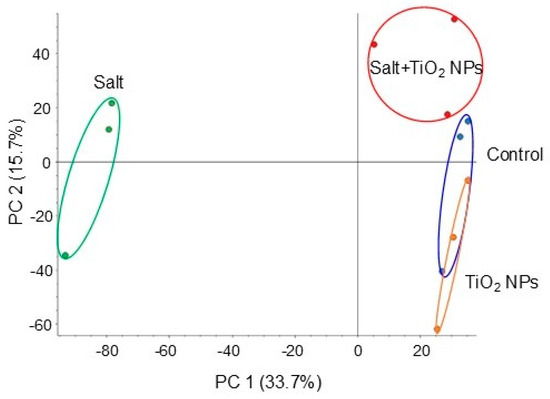
Figure 2.
Summary of whole proteomic data from 12 samples based on principal component analysis. Soybean seeds were sown and grown for 3 days. Seedlings were treated with or without 40 μg/mL TiO2 NPs with or without 150 mM NaCl for 2 days. Proteins were extracted from roots and analyzed using nanoLC-MS/MS. Proteomic analysis was performed using 3 independent biological replicates for each treatment. Principal component analysis was performed using Proteome Discoverer.
A total of 2155 proteins were identified by a t-test after LC-MS/MS analysis (Tables S1 and S2). Among 1188 proteins, 245 proteins increased, and 943 proteins decreased in soybean under salt stress. On the other hand, among 967 proteins, 794 proteins increased, and 173 proteins decreased in soybean treated with TiO2 NPs under salt stress. Because the principal component analysis of proteins displayed an overlap between the control and TiO2 NP-treated clusters (Figure 2), proteins identified by TiO2 NP treatment under salt stress were compared with those of the control (Table S3). Among 132 proteins, 70 proteins increased, and 64 proteins decreased in soybean treated by TiO2 NP treatment under salt stress compared with those of the control.
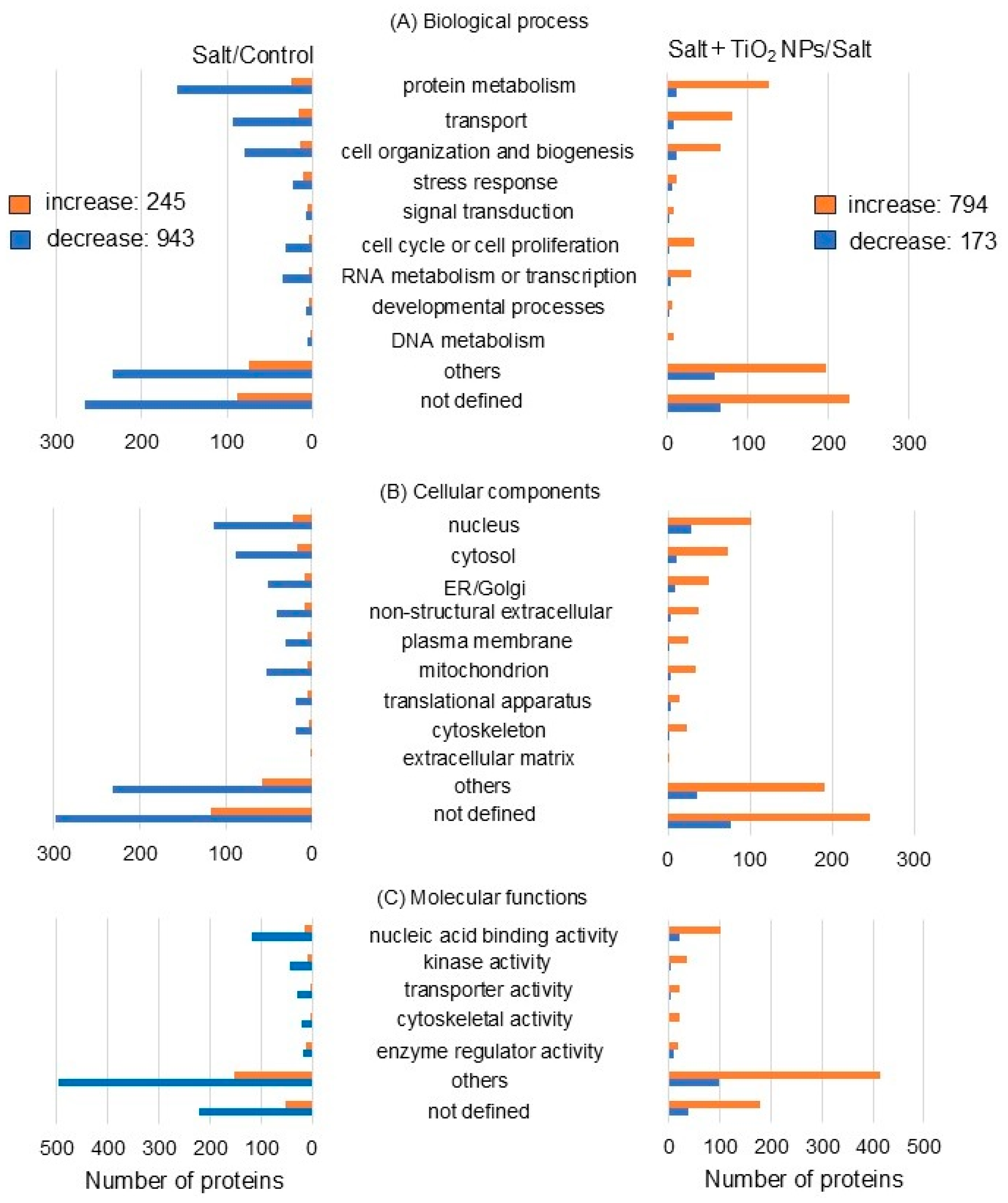
Functional classification by gene ontology analysis after proteomic analysis showed opposite trends in the increase and decrease in proteins between salt treatment/control and salt + TiO2 NP/salt treatment. The number of proteins increased or decreased by more than six times with the addition of TiO2 NPs to soybeans under salt stress compared to nontreatment. Differentially abundant proteins were associated with protein metabolism and transport in the biological processes (Figure 3A), nucleus and cytosol in the cellular component (Figure 3B), and nucleic acid binding activity in the molecular functions (Figure 3C) between salt treatment/nontreatment and salt + TiO2 NP treatment/salt treatment (Figure 3).
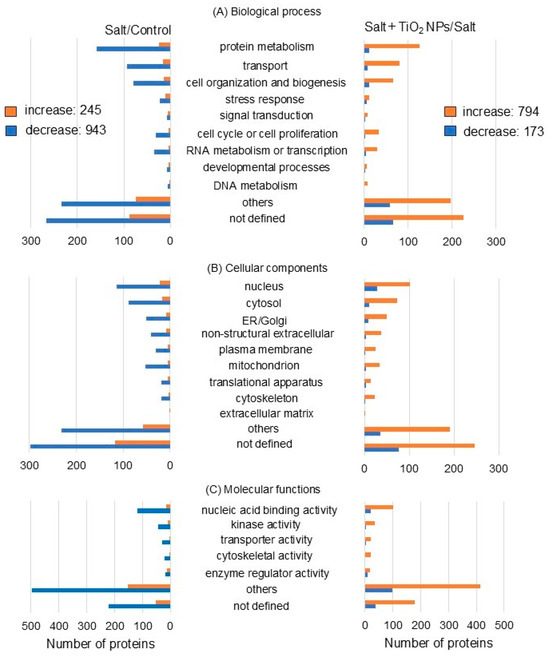
Figure 3.
Functional categories of proteins present in different abundance in soybean root with TiO2 NPs under salt stress. Four kinds of treatments, including nontreatment, TiO2 NPs, salt, and salt + TiO2 NPs, were conducted. Proteins extracted from soybean root after treatment were enriched, reduced, alkylated, digested, and analyzed by nanoLC-MS/MS. The relative abundance of proteins from treatments with or without TiO2 NPs under salt stress was compared to that of the nontreatment. Functional categories of changed proteins were determined using gene ontology analysis. (A) biological process, (B) cellular component, and (C) Molecular function. The orange and blue columns indicate the increased and decreased proteins, respectively, which are matched peptides ≧ 2 and p-value < 0.05.
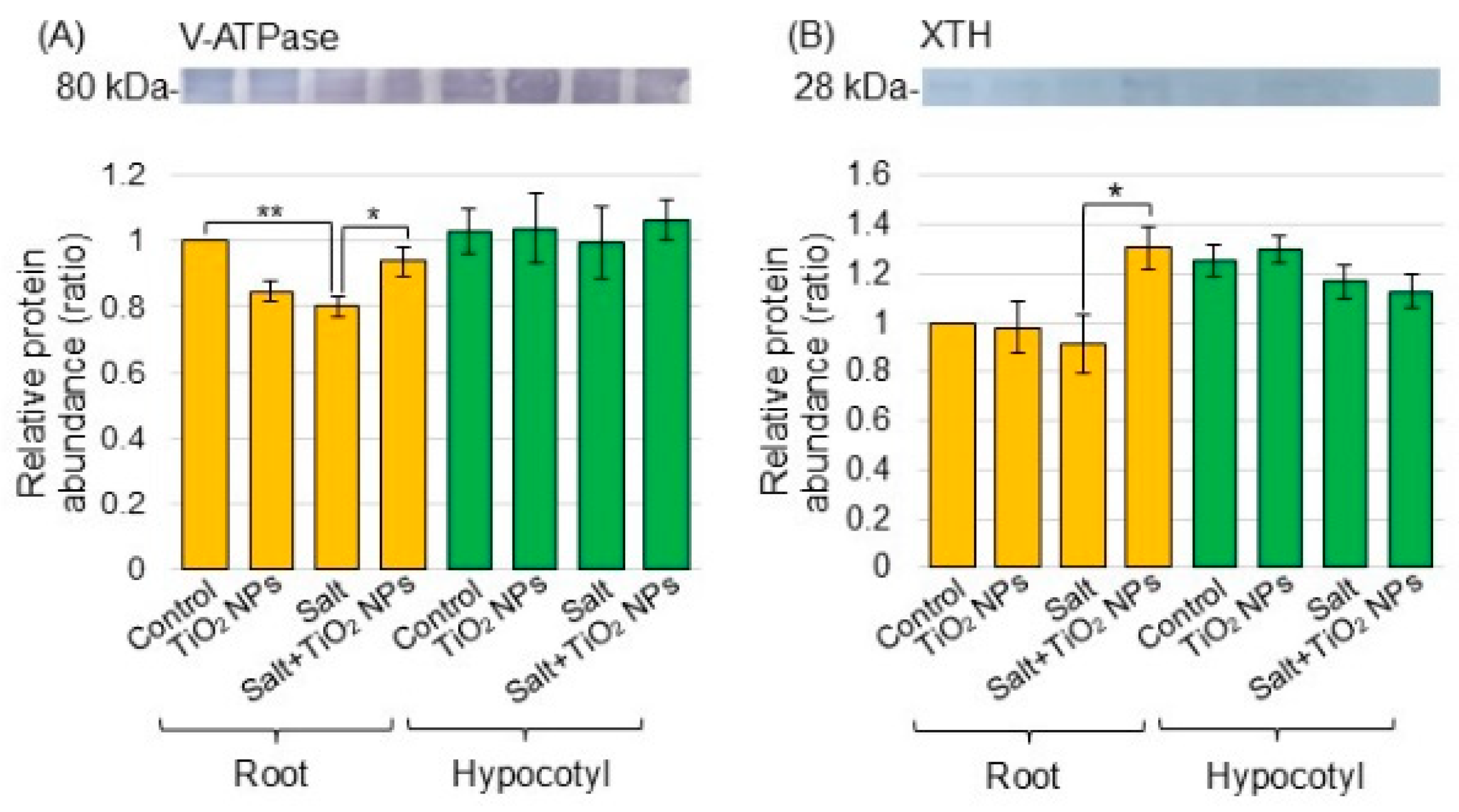
Proteomic analysis revealed that the most significantly altered proteins were in the biological process category compared to the cellular component and molecular function categories. V-ATPase (C6TBY6) related to transport and xyloglucan endotransglucosylase/hydrolase (A0A0R0JVY2) related to the cell wall significantly changed in the biological process category (Tables S1 and S2). In more detail, V-ATPase decreased by −1.86 times under salt stress compared to the control and increased by 1.48 times with additional TiO2 NPs under salt stress. Xyloglucan endotransglucosylase/hydrolase decreased by −2.20 times under salt stress compared to the control and increased by 2.22 times with additional TiO2 NPs under salt stress. For this reason, V-ATPase and xyloglucan endotransglucosylase/hydrolase were selected for immunoblot analysis.
Furthermore, proteomic analysis detected 22 types of peroxidases (Tables S2 and S3); however, because their classification was unclear, the main enzymes and hydrogen peroxide content involved in the ROS scavenging system were confirmed using immunoblot and metabolite analyses.
3.3. Immunoblot Analysis of Proteins in Soybean Treated with TiO2 NPs Under Salt Stress
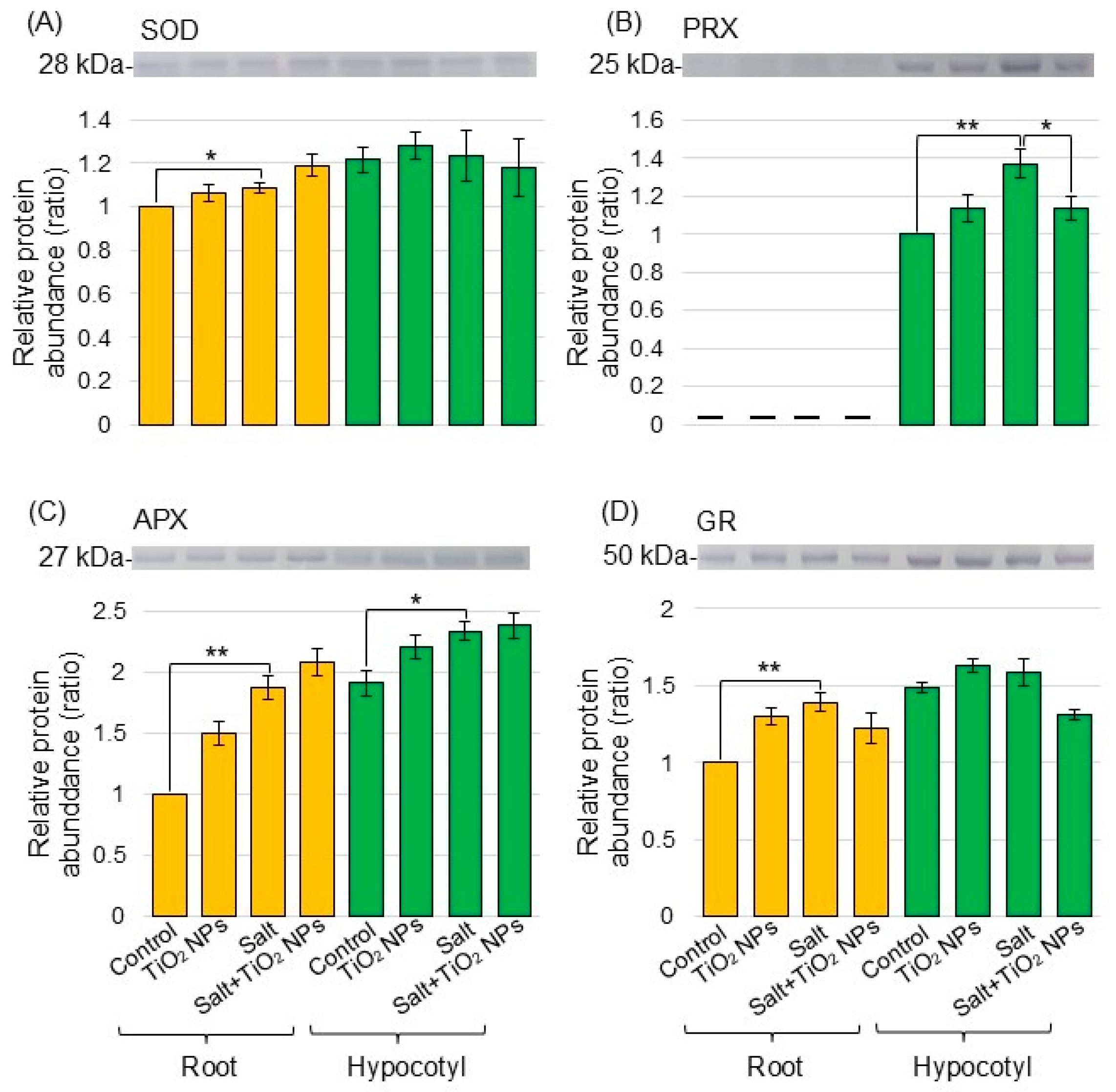
To better reveal the differential abundance of proteins between the salt/nontreatment group and salt + TiO2 NPs/salt group identified using proteomic analysis, immunoblot analysis was conducted. V-ATPase (Figure 4A) and xyloglucan endotransglucosylase/hydrolase (Figure 4B) were analyzed as transport proteins and cell-wall related protein, respectively, in the biological process category from the proteomic data. Superoxide dismutase (Figure 5A), peroxiredoxin (Figure 5B), ascorbate peroxidase (Figure 5C), and glutathione reductase (Figure 5D) were selected as proteins related to the reactive oxygen scavenging system. Proteins extracted from the root and hypocotyl of soybean were separated by electrophoresis on SDS-polyacrylamide gel and transferred to polyvinylidene-difluoride membranes. The membranes were cross-reacted with the antibodies of selected proteins. A Coomassie brilliant blue staining pattern was used as a loading control (Figure S2). The integrated density of bands was calculated from the results of triplicated immunoblots using ImageJ software (Figures S3–S8). The abundance of V-ATPase decreased with salt stress and recovered to the control level with additional TiO2 NPs on soybean roots under salt stress (Figure 4A). The abundance of xyloglucan endotransglucosylase/hydrolase decreased under salt stress; however, it did not change with additional TiO2 NPs (Figure 4B). The abundance of peroxiredoxin increased with salt stress and decreased with additional TiO2 NPs in hypocotyl under salt stress (Figure 5B). On the other hand, the abundance of superoxide dismutase, ascorbate peroxidase, and glutathione reductase increased in root under salt stress; however, it did not change with additional TiO2 NPs (Figure 5A,C,D).
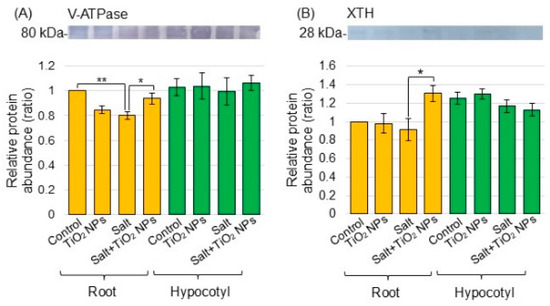
Figure 4.
Immunoblot analysis of proteins involved in soybeans treated with TiO2 NPs under salt stress. Four treatments were performed: nontreatment, TiO2 NPs, salt, and salt + TiO2 NPs. Proteins extracted from root and hypocotyl of soybean were separated on SDS-polyacrylamide gel by electrophoresis. Proteins were transferred onto membranes. The membranes cross-reacted with anti-V-ATPase (A) and xyloglucan endotransglucosylase/hydrolase (XTH) (B) antibodies. The integrated densities of the bands were calculated using ImageJ software. The statistical significance of the 2 groups was evaluated by Student’s t-test. A p-value of less than 0.05 was considered statistically significant (**, p < 0.01; *, p < 0.05).
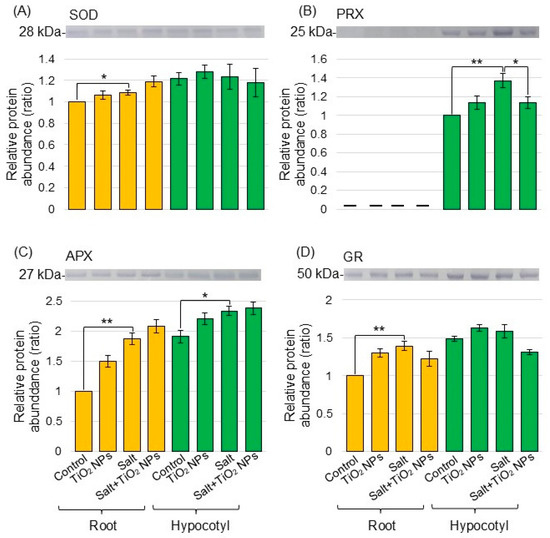
Figure 5.
Immunoblot analysis of proteins involved in soybeans treated with TiO2 NPs under salt stress. Proteins blotted on the membrane were cross-reacted with anti-superoxide dismutase (SOD) (A), peroxiredoxin (PRX) (B), ascorbate peroxidase (APX) (C), and glutathione reductase (GR) (D) antibodies. The data are presented as mean ± SD from 3 independent biological replicates. The data analysis is the same as in Figure 5. The statistical significance of the 2 groups was evaluated by Student’s t-test. A p-value of less than 0.05 was considered statistically significant (**, p < 0.01; *, p < 0.05).
3.4. Analysis of Hydrogen Peroxide Content in Soybean Root Treated with TiO2 NPs Under Salt Stress
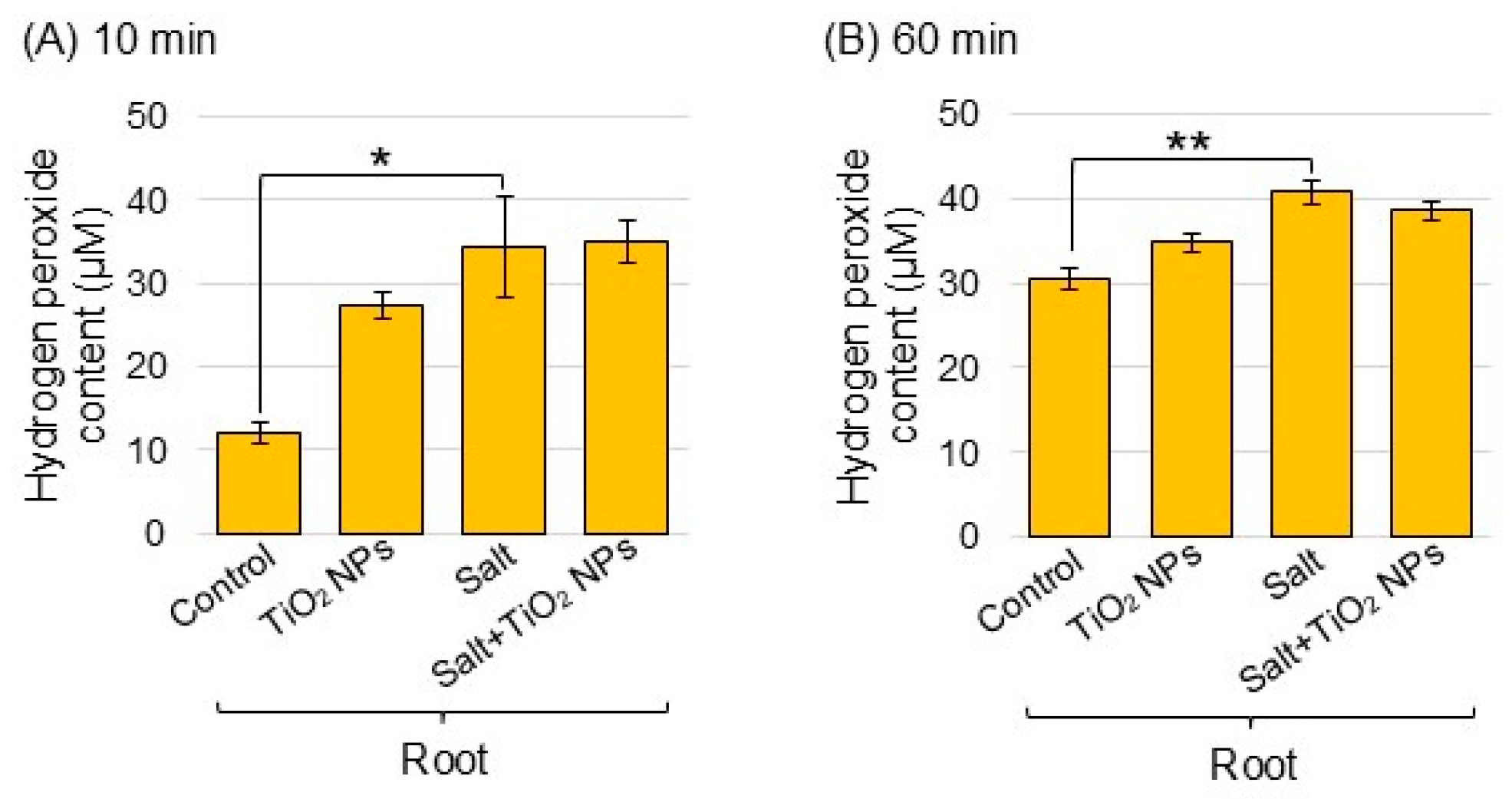
To understand the ROS accumulation of TiO2 NPs in soybean plants under salt stress, the amount of hydrogen peroxide was measured. The amount of hydrogen peroxide after reactions for 10 and 60 min increased in the root with salt stress compared to the control, but did not change with addition of TiO2 NPs under salt stress (Figure 6A,B).
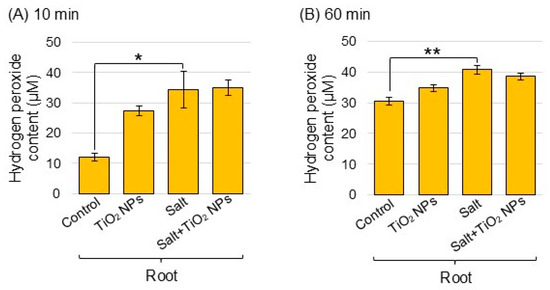
Figure 6.
Analysis of hydrogen peroxide content in soybean roots treated with TiO2 NPs under salt stress. Four treatments were performed: control, TiO2 NPs, salt, and salt + TiO2 NPs. After the addition of working solution, samples were reacted for 10 min (A) and 60 min (B). The data are presented as mean ± SD from 3 independent biological replicates. The statistical significance of the 2 groups was evaluated by Student’s t-test. A p-value of less than 0.05 was considered statistically significant (**, p < 0.01; *, p < 0.05).
4. Discussion
4.1. TiO2 NPs Enhance Soybean Seedling and Salt Stress Tolerance
NPs enter the plant root system through the lateral root junctions and reach the xylem through the cortex and pericycle [24]. The entry of NPs into cells is prevented by the cell wall, which allows the transport of NPs due to the size of the pores in the cell [25]. NPs, which are within the size range of the cell wall pores, can effectively pass through the cell wall and reach the cell membrane [26]. Smaller silver NPs (20 nm) could enter cells and induce cellular stress, such as ROS generation and protein carbonylation, whereas, larger NPs (100 nm) only indirectly induced oxidative stress [27]. In this study, small-sized NPs, which are TiO2 NPs of 15–25 nm, were used to investigate what changes occur within cells due to NP-induced morphological changes. When 2-day-old soybeans were treated by aluminum oxide NPs for 0, 2, 3, and 4 days, significant protein changes were observed from day 2 of treatment [28] and this tendency on soybean was the same for silver NPs [29] and zinc oxide NPs [30]. Therefore, in this study, 2 days of treatment with NPs was used for soybeans.
In this study, soybean growth was suppressed by salt stress and recovered with TiO2 NP treatment compared with the control (Figure 1). It is also reported that TiO2 NPs enhanced seedling emergence, vigor, and tolerance in soybean under salinity stress [15]. To elucidate the promotive effects of TiO2 NPs on soybean growth under salt stress, a gel-free/label-free proteomic analysis was carried out. Proteomic analysis revealed that many proteins increased under salt stress compared with the control, and these were reduced or restored when TiO2 NPs were applied under salt stress (Figure 3). These findings suggest that they may be related to the inhibition of soybean growth caused by salt stress and its recovery by the addition of TiO2 NPs. Further confirmatory experiments are needed to prove this.
4.2. Membrane Transport Is Related to a Salt-Tolerant Mechanism in Soybean with TiO2 NPs
Although the process of metal storage in vacuoles is well characterized, the transformation of cellular metal ions into NPs remains unclear. In roots, the uptake metals are bound to some complex molecules of the cell wall components, thus reducing their translocation to other parts of the plant, or directed into the storage vacuoles [31]. For example, iron NPs protected plant cells from arsenic phytotoxicity by promoting the accumulation of chelators and the sequestration and immobilization of arsenic in the vacuole and cell wall [32]. Proteomic analysis indicated that V-ATPase and xyloglucan endotransglucosylase/hydrolase, which are membrane and cell-wall related proteins, decreased with salt stress and increased with additional TiO2 NPs, even under stress (Tables S1 and S2). Using immunoblot analysis as a confirmation experiment, the abundance of V-ATPase decreased under salt stress and increased with additional TiO2 NPs under stress, whereas xyloglucan endotransglucosylase/hydrolase did not change with any treatment (Figure 4). Compared with xyloglucan endotransglucosylase/hydrolase, V-ATPase is considered to be more involved in the effect of TiO2 NPs.
There are three types of ATPases on the plant cell membrane, which are P-ATPase, V-ATPase, and F-ATPase [33]. V-ATPase catalyzes the decomposition of ATP into ADP and free phosphate ions. As a kind of dominant enzyme, V-ATPase not only maintains the dynamic balance of cytoplasmic ions and cellular metabolism, but also responds to environmental factors [34]. In the vacuole, the V-ATPase energizes transport processes, contributes to nitrate storage and zinc deposition, as well as ensures the resting calcium concentration in the cytoplasm [35]. V-ATPase plays a key role in establishing an electrochemical H+ gradient across the tonoplast and activating Na+ sequestration into the central vacuole, resulting in enhanced salt stress tolerance in plants [36]. In an additional example, V-ATPase decreased in soybean under salt stress and increased with additional plant-derived smoke solution, which shows stress tolerance [37]. These findings and the present results suggest that TiO2 NPs confer tolerance to salt stress through V-ATPase accumulation in the vacuolar transport system of soybean roots.
4.3. ROS Scavenging System Is Related to Salt-Tolerant Mechanism in Soybean with TiO2 NPs
ROS production is a common occurrence in plants under normal growth conditions and further increased under stress conditions, which led to cellular toxicity [38]. When plants are exposed to environmental stresses, the levels of ROS can excessively increase and cause significant oxidative damage to DNA, RNA, proteins, lipids, and other redox-sensitive molecules [39]. Salinity-tolerant wheat effectively scavenged ROS through regulating the transcriptional level of ROS enzyme [40]. In an additional example, the activity of ascorbate peroxidase increased in ethanol-supplemented soybean under salt stress [41]. In the present study, the abundance of superoxide dismutase, ascorbate peroxidase, and glutathione reductase increased under salt stress; however, this did not change with additional TiO2 NPs (Figure 5). Furthermore, the amount of hydrogen peroxide increased with salt stress, but did not change with the addition of TiO2 NPs (Figure 6). These findings and the present results suggest that the unchanged levels of hydrogen peroxide in TiO2 NP-treated seedlings may be the result of an increased activation of ROS scavenging systems that efficiently degrade hydrogen peroxide and thereby prevent its accumulation in soybean roots under salt stress.
On the other hand, peroxiredoxin increased in soybean leaf under salt stress and decreased with additional TiO2 NPs under stress (Figure 5). Peroxiredoxins act as second messengers in intracellular signaling and protect cells from oxidative stress through hydrogen peroxide [42]. Peroxiredoxin was specifically distributed in organelles, such as chloroplasts and mitochondria [43]. It decreased in wheat leaf and root with the treatment of silver oxide NPs mixed with nicotinate and potassium nitrate [44]. It increased in soybean with chemically synthesized NPs compared to bio-synthesized zinc oxide NPs [45]. These findings, along with these results, suggest that TiO2 NPs might improve soybean growth under salt stress through the accumulation of peroxiredoxin, which reduces oxidative stress. However, because other ROS scavenging enzymes did not change with TiO2 NP application, the importance of peroxiredoxins requires further research.
5. Conclusions
In this study, TiO2 NPs enhanced soybean growth, even under salt stress. The proteomic technique indicated that the differentially changed proteins were related to transport in biological process categories. Using immunoblot analysis, the key findings were confirmed as follows: V-ATPase decreased in salt stress conditions and increased with additional TiO2 NPs, whereas xyloglucan endotransglucosylase/hydrolase did not change with any treatment. Additionally, the ROS scavenging system was confirmed using immunoblot analysis. Peroxiredoxin increased under salt stress and decreased with additional TiO2 NPs. On the other hand, ascorbate peroxidase, superoxide dismutase, and glutathione reductase increased under salt stress, but they were not improved with additional TiO2 NPs. The present results suggest that TiO2 NPs enhance soybean growth by stress reduction even under salinity through regulating vacuole transport and the ROS scavenging system.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/oxygen5020004/s1, Table S1. List of changed proteins in soybean roots under salt stress compared with the control. Table S2. List of changed proteins in soybean roots treated with TiO2 NPs under salt stress compared with salt stress only. Table S3. List of changed proteins in soybean roots treated with TiO2 NPs under salt stress compared with the control. Figure S1. Experimental design to investigate the effects of TiO2 NPs on soybeans under salt stress. Figure S2. Coomassie brilliant blue staining pattern of proteins used for immunoblot analysis. Figure S3. Blots of the entire membrane with anti-V-ATPase antibody, which were used in Figure 4A. Figure S4. Blots of the entire membrane with anti-xyloglucan endotransglucosylase/hydrolase antibody, which were used in Figure 4B. Figure S5. Blots of the entire membrane with anti-superoxide dismutase antibody, which were used in Figure 5A. Figure S6. Blots of the entire membrane with anti-peroxiredoxin antibody, which were used in Figure 5B. Figure S7. Blots of the entire membrane with anti-ascorbate peroxidase antibody, which were used in Figure 5C. Figure S8. Blots of the entire membrane with anti-glutathione reductase antibody, which were used in Figure 5D.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.K.; methodology, P.P.W., H.Y. and K.H.; software, P.P.W., S.K., H.Y. and K.H.; validation, P.P.W. and S.K.; data curation, S.K., H.Y., K.H. and K.T.; writing—original draft preparation, P.P.W.; writing—review and editing, S.K., H.Y., K.H. and K.T.; planting and identification of experimental materials, S.K.; project administration, S.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the University-Special Research Grants (F/S, 2024) of Fukui University of Technology for S.K.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The MS data, RAW data, peak lists and result files have been deposited in the ProteomeXchange Consortium [46] via the jPOST [47] partner repository under dataset identifiers PXD046599.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Kumar, S.; Li, G.; Yang, J.; Huang, X.; Ji, Q.; Liu, Z.; Ke, W.; Hou, H. Effect of salt stress on growth, physiological parameters, and ionic concentration of water dropwort (Oenanthe javanica) cultivars. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 660409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munns, R.; Day, D.A.; Fricke, W.; Watt, M.; Arsova, B.; Barkla, B.J.; Bose, J.; Byrt, C.S.; Chen, Z.H.; Foster, K.J.; et al. Energy costs of salt tolerance in crop plants. New Phytol. 2020, 225, 1072–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Zhang, H.; Hu, X.; Xu, L.; An, X.; Jin, T.; Ma, R.; Li, Z.; Chen, S.; Du, S.; et al. Comparing the potential of silicon nanoparticles and conventional silicon for salinity stress alleviation in soybean (Glycine max L.): Growth and physiological traits and rhizosphere/endophytic bacterial communities. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2024, 72, 10781–10793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, K.; Qi, Y.; Chen, F.; Meng, Y.; Luo, X.; Shuai, H.; Zhou, W.; Ding, J.; Du, J.; Liu, J.; et al. Salt stress represses soybean seed germination by negatively regulating GA biosynthesis while positively mediating ABA biosynthesis. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, R.; Li, M.; Zhang, H.; Duan, L.; Sun, X.; Jiang, Q.; Zhang, H.; Hu, Z. Continuous salt stress-induced long non-coding RNAs and DNA methylation patterns in soybean roots. BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, A.; Xiao, Z.; Wang, Z.; Lam, H.M.; Chye, M.L. Galactolipid and phospholipid profile and proteome alterations in soybean leaves at the onset of salt stress. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 644408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajpai, V.K.; Kamle, M.; Shukla, S.; Mahato, D.K.; Chandra, P.; Hwang, S.K.; Kumar, P.; Huh, Y.S.; Han, Y.K. Prospects of using nanotechnology for food preservation, safety, and security. J. Food Drug Anal. 2018, 26, 1201–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Y.; Hasan, M.K.; Ahammed, G.J. Applications of nanotechnology in plant growth and crop protection: A review. Molecules 2019, 24, 2558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hossain, Z.; Yasmeen, F.; Komatsu, S. Nanoparticles: Synthesis, morphophysiological effects, and proteomic responses of crop plants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, V.; Mishra, R.K.; Dikshit, A.; Pandey, A.C. Interactions of nanoparticles with plants. In Emerging Technologies and Management of Crop Stress Tolerance; Academic Press Elsevier: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2014; pp. 159–180. [Google Scholar]
- Larue, C.; Veronesi, G.; Flank, A.M.; Surble, S.; Herlin-Boime, N.; Carrière, M. Comparative uptake and impact of TiO2 nanoparticles in wheat and rapeseed. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health Part A 2012, 75, 722–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, S.; Craveiro, S.C.; Oliveira, H.; Calado, A.J.; Pinto, R.J.B.; Silva, A.M.S.; Santos, C. Wheat chronic exposure to TiO2-nanoparticles: Cyto- and genotoxic approach. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 121, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mustafa, N.; Raja, N.I.; Ilyas, N.; Abasi, F.; Ahmad, M.S.; Ehsan, M.; Mehak, A.; Badshah, I.; Proćków, J. Exogenous application of green titanium dioxide nanoparticles (TiO2 NPs) to improve the germination, physiochemical, and yield parameters of wheat plants under salinity stress. Molecules 2022, 27, 4884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmoodzadeh, H.; Aghili, R. Effect on germination and early growth characteristics in wheat plants (Triticum aestivum L.) seeds exposed to TiO2 nanoparticles. J. Chem. Health Risks 2014, 4, 467–472. [Google Scholar]
- Abdalla, H.; Adarosy, M.H.; Hegazy, H.S.; Abdelhameed, R.E. Potential of green synthesized titanium dioxide nanoparticles for enhancing seedling emergence, vigor and tolerance indices and DPPH free radical scavenging in two varieties of soybean under salinity stress. BMC Plant Biol. 2022, 22, 560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel Latef, A.A.H.; Srivastava, H.K.; El-Sadek, M.S.; Kordrostami, M.; Tran, L.S.P. Titanium dioxide nanoparticles improve growth and enhance tolerance of broad bean plants under saline soil conditions. Land. Degrad. Dev. 2018, 29, 1065–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelhameed, R.E.; Hegazy, H.S.; Abdalla, H.; Adarosy, M.H. Efficacy of green synthesized titanium dioxide nanoparticles in attenuation salt stress in Glycine max plants: Modulations in metabolic constituents and cell ultrastructure. BMC Plant Biol. 2025, 25, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komatsu, S.; Nanjo, Y.; Nishimura, M. Proteomic analysis of the flooding tolerance mechanism in mutant soybean. J. Proteom. 2013, 79, 231–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Rehman, S.U.; Yamaguchi, H.; Hitachi, K.; Tsuchida, K.; Yamaguchi, T.; Sunohara, Y.; Matsumoto, H.; Komatsu, S. Proteomic analysis of the effect of plant-derived smoke on soybean during recovery from flooding stress. J. Proteome 2018, 181, 238–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyanova, S.; Temu, T.; Sinitcyn, P.; Carlson, A.; Hein, M.Y.; Geiger, T.; Mann, M.; Cox, J. The peruses computational platform for comprehensive analysis of omics data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 731–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komatsu, S.; Yamamoto, A.; Nakamura, T.; Nouri, M.Z.; Nanjo, Y.; Nishizawa, K.; Furukawa, K. Comprehensive analysis of mitochondria in roots and hypocotyls of soybean under fooding stress using proteomics and metabolomics techniques. J. Proteome Res. 2011, 10, 3993–4004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, X.; Komatsu, S. Nuclear proteomics reveals the role of protein synthesis and chromatin structure in root tip of soybean during the initial stage of fooding stress. J. Proteome Res. 2016, 15, 2283–2298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietz, K.J.; Herth, S. Plant nanotoxicology. Trends Plant Sci. 2011, 16, 582–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleischer, A.; O’Neill, M.A.; Ehwald, R. The pore size of non-graminaceous plant cell walls is rapidly decreased by borate ester cross-linking of the pectic polysaccharide rhamnogalacturonan II. Plant Physiol. 1999, 121, 829–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, E.; Baun, A.; Behra, R.; Hartmann, N.B.; Filser, J.; Miao, A.J.; Quigg, A.; Santschi, P.H.; Sigg, L. Environmental behavior and ecotoxicity of engineered nanoparticles to algae, plants, and fungi. Ecotoxicology 2008, 17, 372–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verano-Braga, T.; Miethling-Graff, R.; Wojdyla, K.; Rogowska-Wrzesinska, A.; Brewer, J.R.; Erdmann, H.; Kjeldsen, F. Insights into the cellular response triggered by silver nanoparticles using quantitative proteomics. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 2161–2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, G.; Sakata, K.; Hossain, Z.; Komatsu, S. Proteomic study on the effects of silver nanoparticles on soybean under flooding stress. J. Proteom. 2015, 122, 100–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, T.; Mustafa, G.; Nishiuchi, T.; Komatsu, S. Comparative analysis of the effect of inorganic and organic chemicals with silver nanoparticles on soybean under flooding stress. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komatsu, S.; Murata, K.; Yakeishi, S.; Shimada, K.; Yamaguchi, H.; Hitachi, K.; Tsuchida, K.; Obi, R.; Akita, S.; Fukuda, R. Morphological and proteomic analyses of soybean seedling interaction mechanism affected by fiber crosslinked with zinc-oxide nanoparticles. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 7415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadi, M.; Mostafavi, E.; Saleh, B.; Davaran, S.; Aliyeva, I.; Khalilov, R.; Nikzamir, M.; Nikzamir, N.; Akbarzadeh, A.; Panahi, Y.; et al. Current developments in green synthesis of metallic nanoparticles using plant extracts: A review. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2018, 46 (Suppl. S3), S336–S343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bidi, H.; Fallah, H.; Niknejad, Y.; Barari Tari, D. Iron oxide nanoparticles alleviate arsenic phytotoxicity in rice by improving iron uptake, oxidative stress tolerance and diminishing arsenic accumulation. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2021, 163, 348–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaxiola, R.A.; Palmgren, M.G.; Schumacher, K. Plant proton pumps. FEBS Lett. 2007, 581, 2204–2214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishi, T.; Forgac, M. The vacuolar (H+)-ATPases-nature’s most versatile proton pumps. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2002, 3, 94–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.L.; Song, H.X.; Liao, Q.; Yu, Y.; Jian, S.F.; Lepo, J.E.; Liu, Q.; Rong, X.M.; Tian, C.; Zeng, J.; et al. Nitrogen use efficiency is mediated by vacuolar nitrate sequestration capacity in roots of brassica napus. Plant Physiol. 2016, 170, 1684–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.H.; Li, B.; Hu, Y.G.; Chen, L.; Min, D.H. The wheat E subunit of V-type H+-ATPase is involved in the plant response to osmotic stress. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 16196–16210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komatsu, S.; Kimura, T.; Rehman, S.U.; Yamaguchi, H.; Hitachi, K.; Tsuchida, K. Proteomic analysis reveals salt-tolerant mechanism in soybean applied with plant-derived smoke solution. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 13734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Ambuj, B.J.; Dubey, R.S.; Pessarakli, M. Reactive oxygen species, oxidative damage, and antioxidative defense mechanism in plants under stressful conditions. J. Bot. 2012, 2012, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittler, R.; Zandalinas, S.I.; Fichman, Y.; Van Breusegem, F. Reactive oxygen species signaling in plant stress responses. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2022, 23, 663–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Xu, B.; Gan, Y. Seed treatment with Trichoderma longibrachiatum T6 promotes wheat seedling growth under NaCl stress through activating the enzymatic and nonenzymatic antioxidant defense systems. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.K.; Anik, T.R.; Rahman, M.M.; Keya, S.S.; Islam, M.R.; Rahman, M.A.; Sultana, S.; Ghosh, P.K.; Khan, S.; Ahamed, T.; et al. Ethanol treatment enhances physiological and biochemical responses to mitigate saline toxicity in soybean. Plants 2022, 11, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Immenschuh, S.; Baumgart-Vogt, E. Peroxiredoxins, oxidative stress, and cell proliferation. Antioxid. Redox Signal 2005, 7, 768–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedrajas, J.R.; Barcena, J.A. Peroxiredoxins: Types, Characteristics and Functions in Higher Plants; Springer International Publisher: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 95–121. [Google Scholar]
- Komatsu, S.; Yamaguchi, H.; Hitachi, K.; Tsuchida, K. Proteomic, biochemical, and morphological analyses of the effect of silver nanoparticles mixed with organic and inorganic chemicals on wheat growth. Cells 2022, 11, 1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mustafa, G.; Miyagawa, S.; Hasan, M.; Yamaguchi, H.; Hitachi, K.; Tsuchida, K.; Komatsu, S. Bio-synthesized nanoflowers and chemically synthesized nanowires zinc-oxide induced changes in the redox and protein folding in soybean seedlings: A proteomic analysis. J. Plant Growth Reg. 2022, 42, 2570–2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vizcaíno, J.A.; Côté, R.G.; Csordas, A.; Dianes, J.A.; Fabregat, A.; Foster, J.M.; Griss, J.; Alpi, E.; Birim, M.; Contell, J.; et al. The PRoteomics IDEntifications (PRIDE) database and associated tools: Status in 2013. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D1063–D1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okuda, S.; Watanabe, Y.; Moriya, Y.; Kawano, S.; Yamamoto, T.; Matsumoto, M.; Takami, T.; Kobayashi, D.; Araki, N.; Yoshizawa, A.C.; et al. jPOSTTrepo: An international standard data repository for proteomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, D1107–D1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).