Effects of Increased Growth Rates Prior to the First Breeding as Ewe Lambs and Pregnancy Rank on Mammary Glands of Two-Year-Old Ewes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
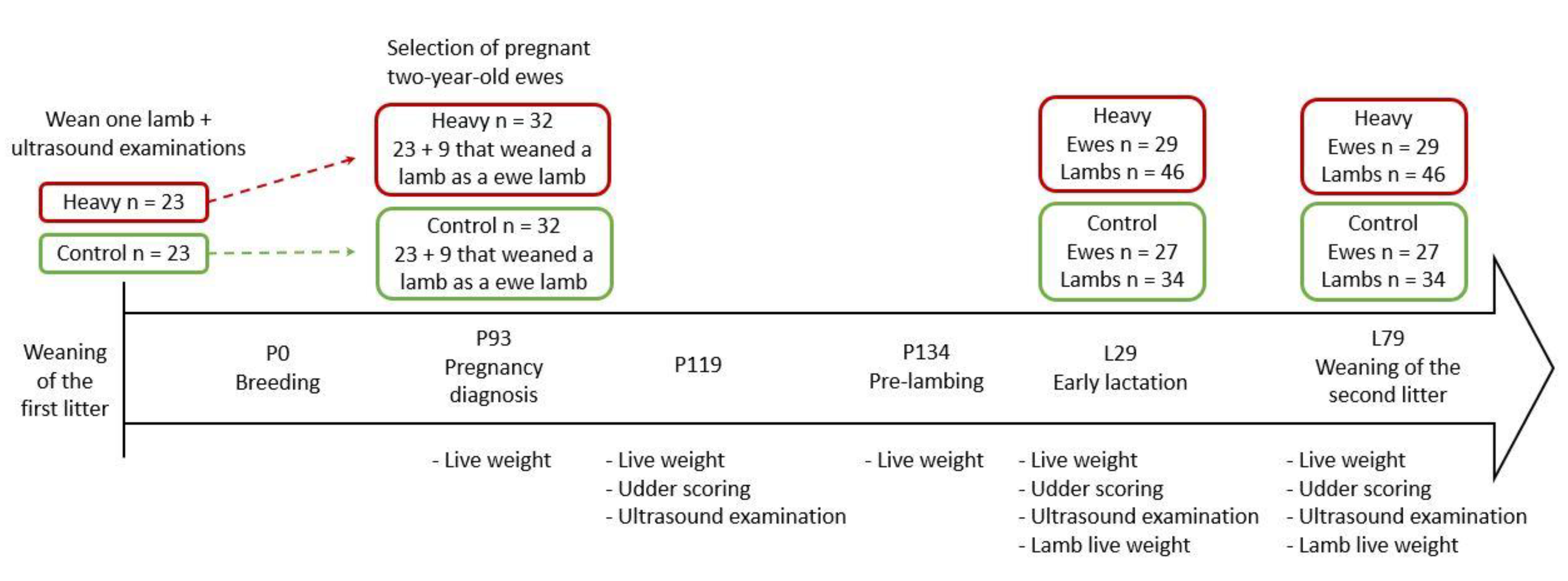
2.1. Experimental Design
2.2. Animal Measurements
2.2.1. Udder Score and Morphology
2.2.2. Ultrasound Examination
2.3. Statistical Analysis
2.3.1. Selection of the Predictive Variables
2.3.2. Backward Manual Predictive Variable Elimination
3. Results
3.1. Ewe Live Weight and Lamb Growth
3.2. Udder Score and Morphology
3.3. Ultrasound Measures
3.4. Correlations between Growth of the Lambs and Udder Measures
3.5. Prediction of the Growth of Lambs Using Udder Measures
4. Discussion
4.1. Difference between Treatments and Pregnancy Rank
4.2. Udder Growth between Pregnancy and Weaning
4.3. Predictions of Growth of Lambs Using Udder Morphological and Ultrasound Measures
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Johnsson, I.D.; Hart, I.C. Pre-pubertal mammogenesis in the sheep 1. The effects of level of nutrition on growth and mammary development in female lambs. Anim. Sci. 1985, 41, 323–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hovey, R.C.; McFadden, T.B.; Akers, R.M. Regulation of mammary gland growth and morphogenesis by the mammary fat pad: A species comparison. J. Mammary Gland. Biol. Neoplasia 1999, 4, 53–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolman, B.; McKusick, B.C. The Effect of Growth Rate on Mammary Gland Development in Ewe Lambs: A Review. In Proceedings of the Dairy Sheep Symposium, Eau Claire, WI, USA, 1 November 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Villeneuve, L.; Cinq-Mars, D.; Lacasse, P. Effects of restricted feeding of prepubertal ewe lambs on growth performance and mammary gland development. Animal 2010, 4, 944–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berryhill, G.E.; Trott, J.E.; Derpinghaus, A.L.; Hovey, R.C. Triennal Lactation Symposium/Bolfa: Dietary regulation of allometric ductal growth in the mammary glands. J. Anim. Sci. 2017, 95, 5664–5674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hue-Beauvais, C.; Faulconnier, Y.; Charlier, M.; Leroux, C. Nutritional Regulation of Mammary Gland Development and Milk Synthesis in Animal Models and Dairy Species. Genes 2021, 12, 523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, R.R. Mammary gland growth in sheep. J. Anim. Sci. 1975, 41, 118–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, M.J.; Capuco, A.V.; Ross, D.A.; Lintault, L.M.; Van Amburgh, M.E. Developmental and nutritional regulation of the prepubertal heifer mammary gland: I. Parenchyma and fat pad mass and composition. J. Dairy Sci. 2006, 89, 4289–4297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Amburgh, M.E.; Soberon, F.; Meyer, M.J.; Molano, R.A. Symposium review: Integration of postweaning nutrient requirements and supply with composition of growth and mammary development in modern dairy heifers. J. Dairy Sci. 2019, 102, 3692–3705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villeneuve, L.; Cinq-Mars, D.; Lacasse, P. Effects of restricted feeding of prepubertal ewe lambs on reproduction and lactation performances over two breeding seasons. Animal 2010, 4, 1997–2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nudda, A.; Pulina, G.; Vallebella, R.; Bencini, R.; Enne, G. Ultrasound technique for measuring mammary cistern size of dairy ewes. J. Dairy Res. 2000, 67, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rovai, M.; Caja, G.; Such, X. Evaluation of udder cisterns and effects on milk yield of dairy ewes. J. Dairy Sci. 2008, 91, 4622–4629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caja, G.; Such, X.; Ruberte, J.; Carretero, A.; Navarro, M. The use of ultrasonography in the study of mammary gland cisterns during lactation in sheep. Proc. Eur. Soc. Anim. Prod. 1999, 95, 91–93. [Google Scholar]
- Haslin, E.; Corner-Thomas, R.A.; Kenyon, P.R.; Peterson, S.W.; Morris, S.T.; Blair, H.T. Associations among Mammary Ultrasound Measurements, Milk Yield of Non-Dairy Ewe Lambs and the Growth of Their Single Lambs. Animals 2021, 11, 2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haslin, E.; Corner-Thomas, R.A.; Kenyon, P.R.; Molenaar, A.J.; Morris, S.T.; Blair, H.T. Mammary Gland Structures Are Not Affected by an Increased Growth Rate of Yearling Ewes Post-Weaning but Are Associated with Growth Rates of Singletons. Animals 2021, 11, 884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haslin, E.; Corner-Thomas, R.A.; Kenyon, P.R.; Pettigrew, E.J.; Hickson, R.E.; Morris, S.T.; Blair, H.T. Effects of heavier live weight of ewe lambs at mating on fertility, lambing percentage, subsequent live weight and the performance of their progeny. N. Z. J. Agric. Res. 2020, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, K.J.; Ridler, A.L.; Compton, C.W.R.; Corner-Thomas, R.A.; Kenyon, P.R. Investigating associations between lamb survival to weaning and dam udder and teat scores. N. Z. Vet. J. 2019, 67, 167–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayadi, M.; Such, X.; Ezzehizi, N.; Zouari, M.; Najar, T.; M’Rad, M.B.; Casals, R. Relationship between mammary morphology traits and milk yield of Sicilo-Sarde dairy sheep in Tunisia. Small Rumin. Res. 2011, 96, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruberte, J.; Carretero, A.; Fernandez, M.; Navarro, M.; Caja, G.; Kirchner, F.; Such, X. Ultrasound mammography in the lactating ewe and its correspondence to anatomical section. Small Rumin. Res. 1994, 13, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albino, R.L.; Marcondes, M.I.; Akers, R.M.; Detmann, E.; Carvalho, B.C.; Silva, T.E. Mammary gland development of dairy heifers fed diets containing increasing levels of metabolisable protein: Metabolisable energy. J. Dairy Res. 2015, 82, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Albino, R.L.; Guimarães, S.E.F.; Daniels, K.M.; Fontes, M.M.S.; Machado, A.F.; Dos Santos, G.B.; Marcondes, M.I. Mammary gland ultrasonography to evaluate mammary parenchymal composition in prepubertal heifers. J. Dairy Sci. 2017, 100, 1588–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molenaar, A.J.; Maclean, P.H.; Gilmour, M.L.; Draganova, I.G.; Symes, C.W.; Margerison, J.K.; McMahon, C.D. Effect of whole-milk allowance on liveweight gain and growth of parenchyma and fat pads in the mammary glands of dairy heifers at weaning. J. Dairy Sci. 2020, 103, 5061–5069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, T.; Rasband, W.S. ImageJ User Guide—IJ 1.46. Available online: imagej.nih.gov/ij/docs/guide/ (accessed on 20 June 2019).
- Dohoo, I.R.; Martin, W.; Stryhn, H.E. (Eds.) Model-Building Strategies. In Veterinary Epidemiologic Research; AVC Inc.: Charlottetown, PEI, Canada, 2003; pp. 317–334. [Google Scholar]
- Nakagawa, S.; Schielzeth, H. A general and simple method for obtaining R2 from generalized linear mixed-effects models. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2013, 4, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haslin, E.; Corner-Thomas, R.A.; Kenyon, P.R.; Morris, S.T.; Blair, H.T. Impacts of a heavier live weight at breeding on the morphology of mammary glands of non-dairy ewe lambs. Anim. Prod. Sci. 2021, 61, 165. [Google Scholar]
- Umberger, S.H.; Goode, L.; Caruolo, E.V.; Harvey, R.W.; Britt, J.H.; Linnerud, A.C. Effects of accelerated growth during rearing on reproduction and lactation in ewes lambing at 13 to 15 months of age. Theriogenology 1985, 23, 555–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbagianni, M.S.; Gouletsou, P.G.; Valasi, I.; Petridis, I.G.; Giannenas, I.; Fthenakis, G.C. Ultrasonographic findings in the ovine udder during lactogenesis in healthy ewes or ewes with pregnancy toxaemia. J. Dairy Res. 2015, 82, 293–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murawski, M.; Schwarz, T.; Jamieson, M.; Ahmadi, B.; Bartlewski, P.M. Echotextural characteristics of the mammary gland during early lactation in two breeds of sheep varying in milk yields. Anim. Reprod. 2019, 16, 853–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, S.R.; Hughson, G.; Farquhar, P.A.; Rattray, P.V. The relationship between the degree of udder development and milk production in Coopworth ewes. Proc. N. Z. Soc. Anim. Prod. 1980, 40, 163–165. [Google Scholar]
- Kenyon, P.R.; van der Linden, D.S.; Blair, H.T.; Morris, S.T.; Jenkinson, C.M.C.; Peterson, S.W.; Mackenzie, D.D.S.; Firth, E.C. Effects of dam size and nutritional plane during pregnancy on lamb performance to weaning. Small Rumin. Res. 2011, 97, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, S.R. Triennial Lactation Symposium/Bolfa: Mammary growth during pregnancy and lactation and its relationship with milk yield. J. Anim. Sci. 2017, 95, 5675–5688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akers, R.M. Overview of Mammary Development. In Lactation and the Mammary Gland; Akers, R.M., Ed.; Blackwell Publishing Company: Ames, IA, USA, 2002; Chapter 1; pp. 3–44. [Google Scholar]
- Pourlis, A. Ovine mammary morphology and associations with milk production, milkability and animal selection. Small Rumin. Res. 2020, 184, 106009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, R.; Porter, R.-H.; Blache, D.; Dwyer, C.M. Behaviour and the Welfare of the Sheep. In The Welfare of Sheep; Dwyer, C.M., Philips, C., Eds.; Animal Welfare; Springer: Edinburgh, UK, 2008; Chapter 3; Volume 6, pp. 81–134. [Google Scholar]
- Castillo, V.; Such, X.; Caja, G.; Salama, A.A.K.; Albanell, E.; Casals, R. Changes in alveolar and cisternal compartments induced by milking interval in the udder of dairy ewes. J. Dairy Sci. 2008, 91, 3403–3411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hinch, G.N. The sucking behaviour of triplet, twin and single lambs at pasture. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 1989, 22, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lérias, J.R.; Hernández-Castellano, L.E.; Suárez-Trujillo, A.; Castro, N.; Pourlis, A.; Almeida, A.M. The mammary gland in small ruminants: Major morphological and functional events underlying milk production—A review. J. Dairy Res. 2014, 81, 304–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutinaud, M.; Hervé, L.; Quesnel, H.; Lollivier, V.; Finot, L.; Dessauge, F.; Chanat, E.; Lacasse, P.; Charton, C.; Guinard-Flament, J. Review: The cellular mechanisms underlying mammary tissue plasticity during lactation in ruminants. Animal 2019, 13, s52–s64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuźnicka, E.; Gburzyński, P. Automatic detection of suckling events in lamb through accelerometer data classification. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2017, 138, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petridis, I.G.; Fthenakis, G.C. Mammary involution and relevant udder health management in sheep. Small Rumin. Res. 2019, 181, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatarczuch, L.; Philip, C.; Lee, C.S. Involution of the sheep mammary gland. J. Anat. 1997, 190, 405–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, J.E.; Fogarty, N.M.; Nielsen, S.; Gilmour, A.R. Milk yield and milk composition from grazing primiparous non-dairy crossbred ewes. Aust. J. Agric. Res. 2006, 57, 377–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danso, A.S.; Morel, P.C.H.; Kenyon, P.R.; Blair, H.T. Brief communication: Effect of early life diet on lamb growth and organ development. Proc. N. Z. Soc. Anim. Prod. 2014, 74, 205–208. [Google Scholar]
- Akers, R.M. Mammary Development, Anatomy, and Physiology. In Lactation and the Mammary Gland; Akers, R.M., Ed.; Blackwell Publishing Company: Ames, IA, USA, 2002; Chapter 2; pp. 45–65. [Google Scholar]
- Torres-Hernandez, G.; Hohenboken, W. Relationships between ewe milk production and composition and preweaning lamb weight gain. J. Anim. Sci. 1980, 50, 597–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Parameters | Pregnancy (P119) | Early Lactation (L29) | Weaning (L79) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Abnormal udder palpation scores (%) | 2.8 (0.8–8.8) a | 3.7 (1.3–10.3) a | 29.3 (18.3–43.5) b |
| Asymmetry (%) | 3.5 (0.9–13) a | 14.1 (7.0–26.5) b | 12.5 (5.9–24.5) b |
| Udder depth score | 4.7 (4.6–4.8) c | 4.1 (3.9–4.2) b | 3.7 (3.6–3.9) a |
| Descriptors | Pregnancy (P119) | Early Lactation (L29) | Weaning (L79) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Single | Twin | Single | Twin | Single | Twin | |
| UH (cm) | 4.7 ± 0.19 **a | 6.2 ± 0.19 **a | 10.5 ± 0.25 **c | 11.7 ± 0.24 **c | 10.1 ± 0.29 b | 10.8 ± 0.28 b |
| UC (cm) | 29.1 ± 0.42 *a | 30.9 ± 0.41 *a | 46.8 ± 0.67 c | 48.5 ± 0.64 c | 39.4 ± 0.62 b | 38.1 ± 0.62 b |
| UV (cm3) | 330.5 ± 23.5 **a | 482.9 ± 23.1 **a | 1854 ± 83 *c | 2198 ± 79 *c | 1262 ± 58 b | 1271 ± 58 b |
| GC (mm) | 8.3 ± 0.54 a | 9.0 ± 0.52 a | 18.1 ± 1.00 b | 16.2 ± 1.01 b | 17.7 ± 1.08 b | 17.8 ± 1.07 b |
| PAR (mm) | 17.3 ± 0.72 **a | 20.7 ± 0.70 **a | 55.4 ± 1.62 c | 61.8 ± 1.63 c | 31.7 ± 1.85 b | 29.4 ± 1.82 b |
| FP (mm) 1 | 19.5 ± 0.93 b | 19.2 ± 0.90 b | - | - | 15.9 ± 1.14 a | 18.2 ± 1.13 a |
| MTc (mm) | 46.0 ± 1.83 a | 49.7 ± 1.76 a | 76.1 ± 1.82 c | 82.0 ± 1.84 c | 67.0 ± 2.20 b | 66.4 ± 2.15 b |
| MTg (mm) | 52.3 ± 1.04 a | 56.2 ± 0.99 a | 84.5 ± 1.99 c | 90.2 ± 2.01 c | 75.8 ± 2.53 b | 74.7 ± 2.49 b |
| Descriptor | Time | Birth to L29 | L29 to L79 | Birth to L79 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| UH | P119 RS | −0.138 | −0.209 | −0.247 * |
| P119 LS | −0.131 | −0.236 * | −0.257 * | |
| UC | L79 | 0.155 | 0.260 * | 0.328 ** |
| UV | P119 | −0.119 | −0.237 * | −0.263 * |
| FP | L79 | −0.298 * | 0.275 * | 0.074 |
| MTg | P119 | 0.155 | 0.169 | 0.227 * |
| L79 | 0.200 | 0.402 ** | 0.466 *** |
| Independent Variables | Birth to L29 | Birth to L79 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Estimate | SE | Estimate | SE | ||
| Intercept | 361 | 74 | −846 | 1038 | |
| Br1 | −59.2 | 20 | 47 | 15 | |
| Br2 | 59.2 | 20 | −47 | 15 | |
| FP at P119 1 | - | - | −0.53 | 1.8 | |
| UC at P119 1 | - | - | 2.5 | 3.4 | |
| GC at L29 | 2.0 | 1.8 | −2.3 | 1.7 | |
| PAR at L29 1 | - | - | −0.36 | 0.9 | |
| UH at L29 | −5.7 | 7.4 | −90.1 | 100 | |
| UH at L29 × UC at L79 1,2 | - | - | −2.4 | 2.6 | |
| GC at L79 1 | - | - | 0.59 | 1.9 | |
| MTc at L79 1 | - | - | 1.4 | 0.7 | |
| UH at L79 1 | - | - | −7.8 | 7.5 | |
| UC at L79 1 | - | - | 31 | 27 | |
| Ewe | 1.9 | 44 | 0.97 | 0.3 | |
| Descriptors | Minimum | 10th Percentile | Mean | 90th Percentile | Maximum |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GC (mm) | |||||
| P119 | 4.9 | 5.8 | 8.7 | 11.8 | 19.6 |
| L29 | 8.4 | 11.5 | 17.4 | 23.8 | 30.7 |
| L79 | 11.1 | 11.7 | 18.3 | 24.6 | 33.3 |
| PAR (mm) | |||||
| P119 | 11.1 | 14.0 | 19.3 | 24.2 | 30.0 |
| L29 | 44.4 | 48.5 | 58.5 | 67.1 | 85.7 |
| L79 | 15.3 | 20.2 | 30.5 | 43.3 | 56.0 |
| FP (mm) | |||||
| P119 | 7.3 | 13.3 | 19.4 | 24.3 | 28.2 |
| L79 | 8.2 | 11.0 | 17.5 | 24.2 | 29.4 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Haslin, E.; Corner-Thomas, R.A.; Kenyon, P.R.; Morris, S.T.; Blair, H.T. Effects of Increased Growth Rates Prior to the First Breeding as Ewe Lambs and Pregnancy Rank on Mammary Glands of Two-Year-Old Ewes. Ruminants 2021, 1, 72-86. https://doi.org/10.3390/ruminants1020006
Haslin E, Corner-Thomas RA, Kenyon PR, Morris ST, Blair HT. Effects of Increased Growth Rates Prior to the First Breeding as Ewe Lambs and Pregnancy Rank on Mammary Glands of Two-Year-Old Ewes. Ruminants. 2021; 1(2):72-86. https://doi.org/10.3390/ruminants1020006
Chicago/Turabian StyleHaslin, Emmanuelle, Rene A. Corner-Thomas, Paul R. Kenyon, Stephen T. Morris, and Hugh T. Blair. 2021. "Effects of Increased Growth Rates Prior to the First Breeding as Ewe Lambs and Pregnancy Rank on Mammary Glands of Two-Year-Old Ewes" Ruminants 1, no. 2: 72-86. https://doi.org/10.3390/ruminants1020006
APA StyleHaslin, E., Corner-Thomas, R. A., Kenyon, P. R., Morris, S. T., & Blair, H. T. (2021). Effects of Increased Growth Rates Prior to the First Breeding as Ewe Lambs and Pregnancy Rank on Mammary Glands of Two-Year-Old Ewes. Ruminants, 1(2), 72-86. https://doi.org/10.3390/ruminants1020006






