Inteins at Eleven Distinct Insertion Sites in Archaeal Helicase Subunit MCM Exhibit Varied Architectures and Activity Levels Across Archaeal Groups
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Retrieving and Curating Amino Acid Sequence Collection of Archaeal MCM Homologs
2.2. Combined Sequence and Structure-Based Approach for Characterizing the Architectures of All Inteins at Each Insertion Site
2.3. Unrooted Amino Acid Sequence Phylogenies
3. Results
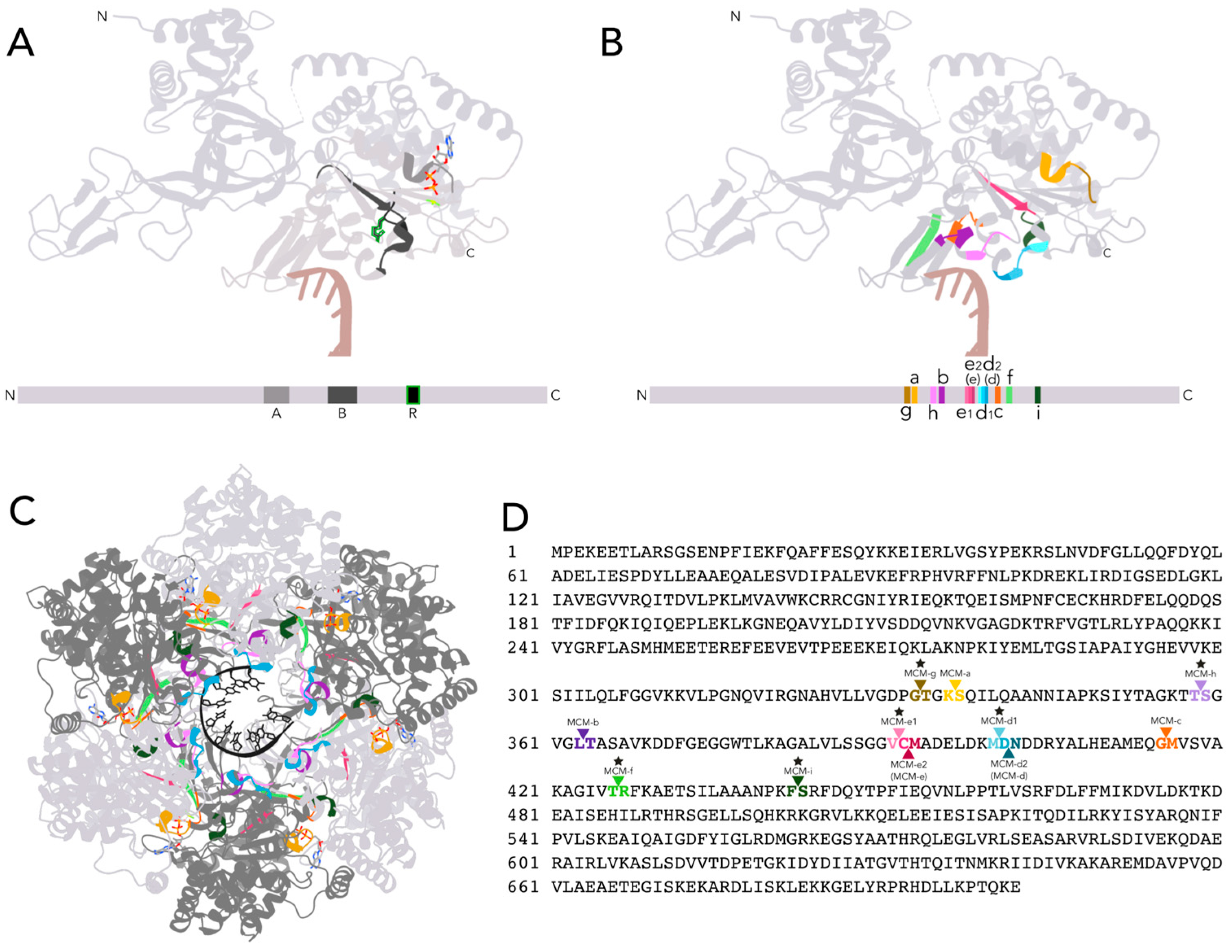
3.1. Analysis of MCM Homologs Across Archaea Reveals Six New Active MCM Intein Insertion Sites
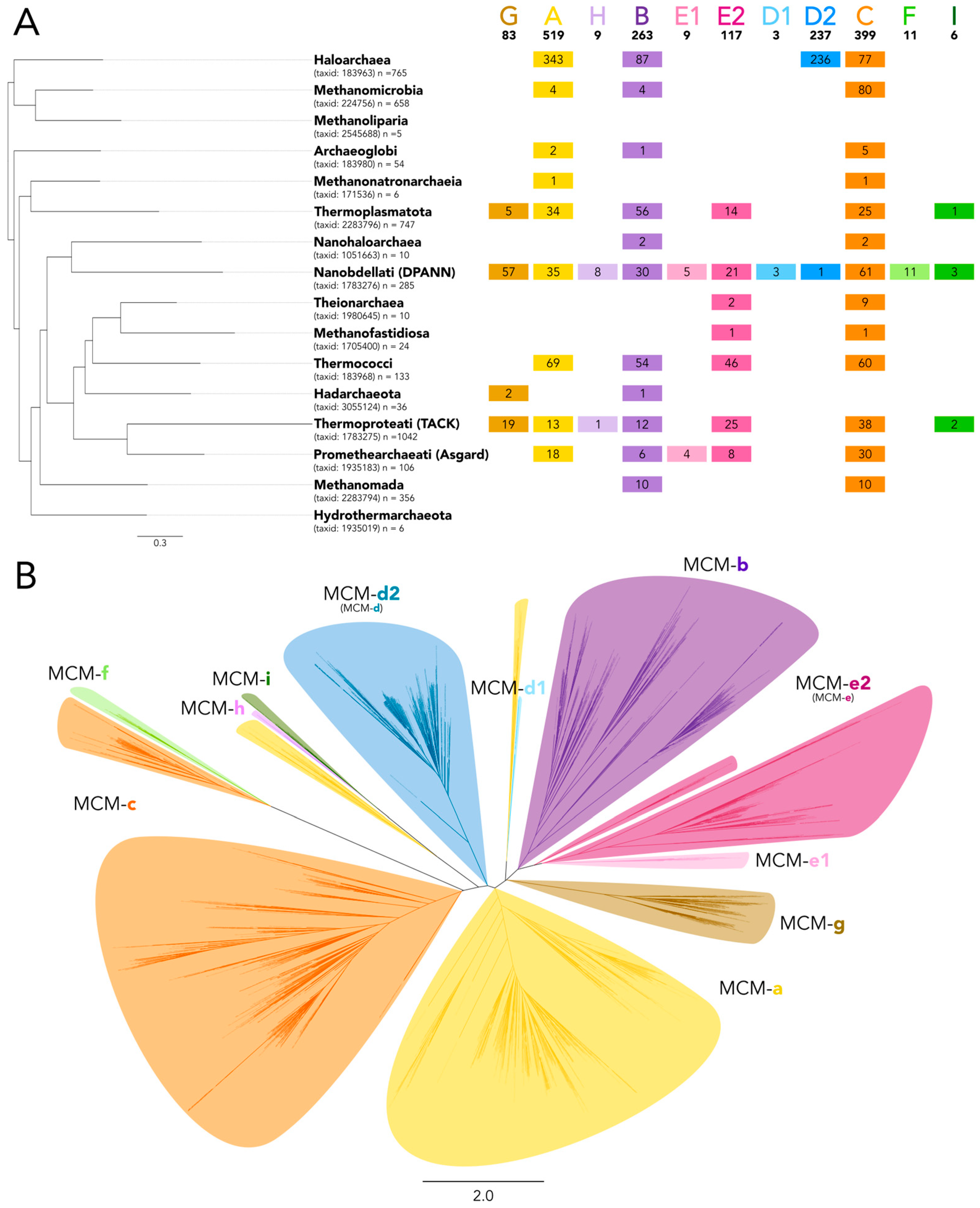
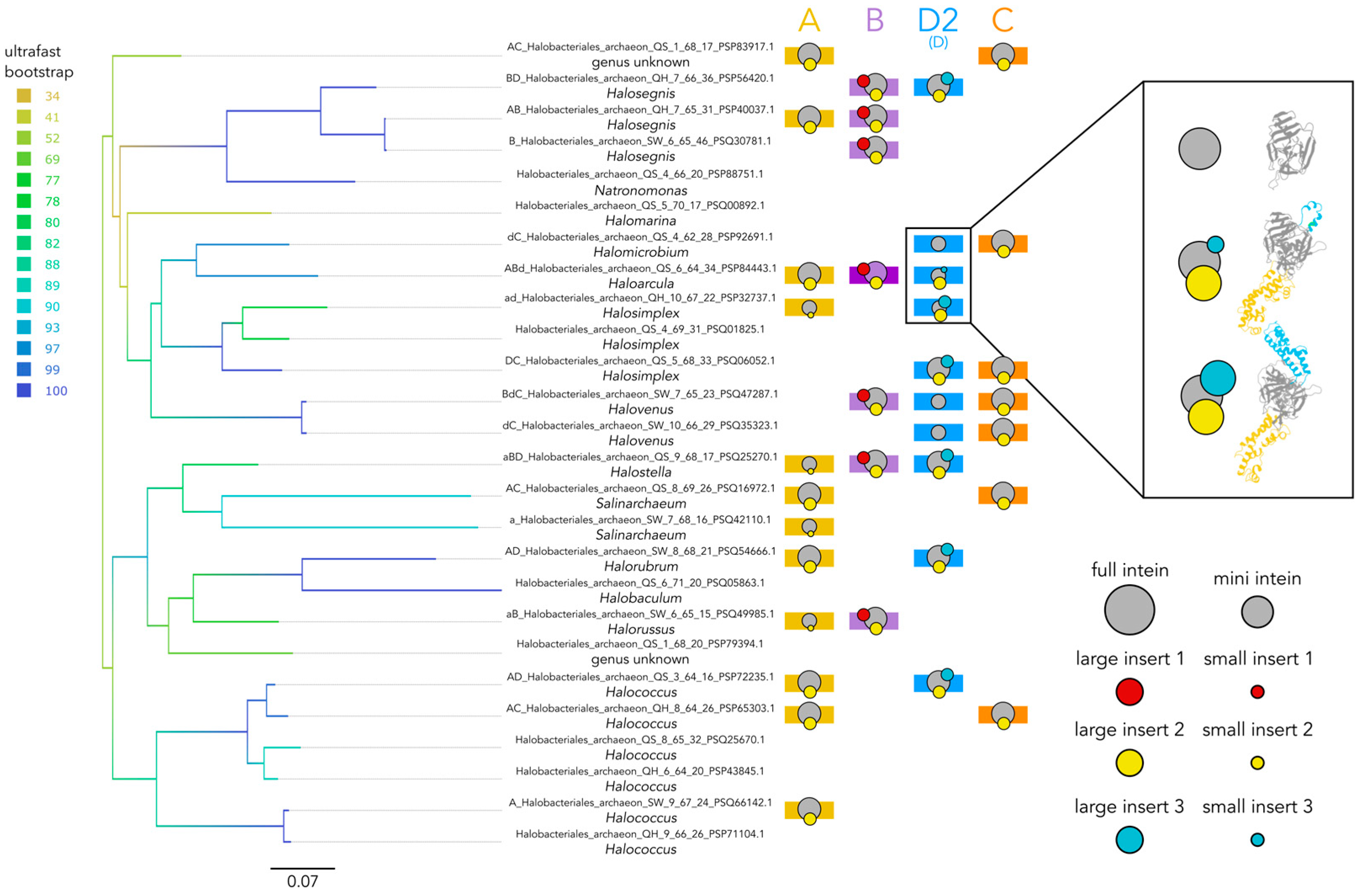
3.2. Varied Invasion Levels and Distinct Evolutionary Histories at Each MCM Intein Insertion Site
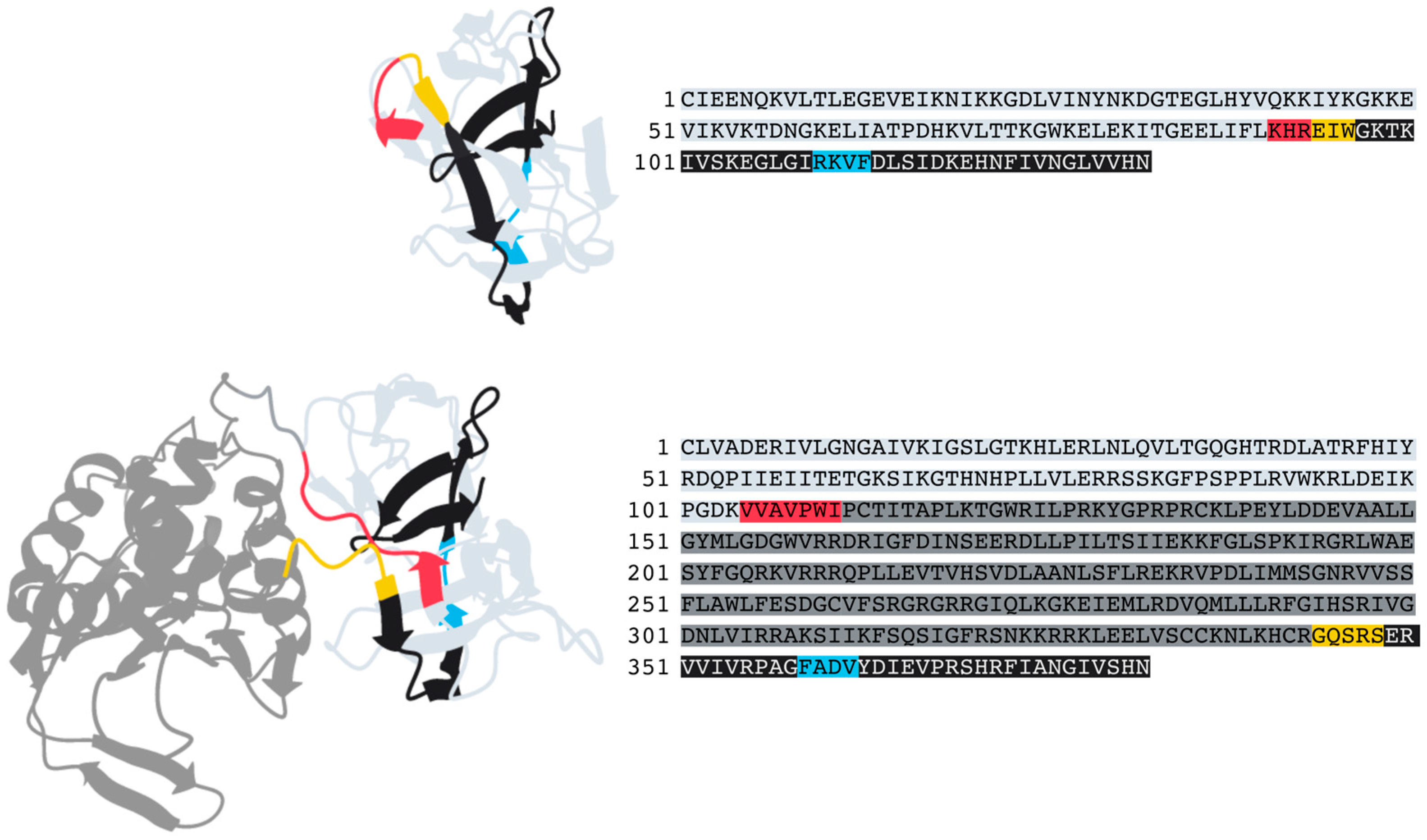
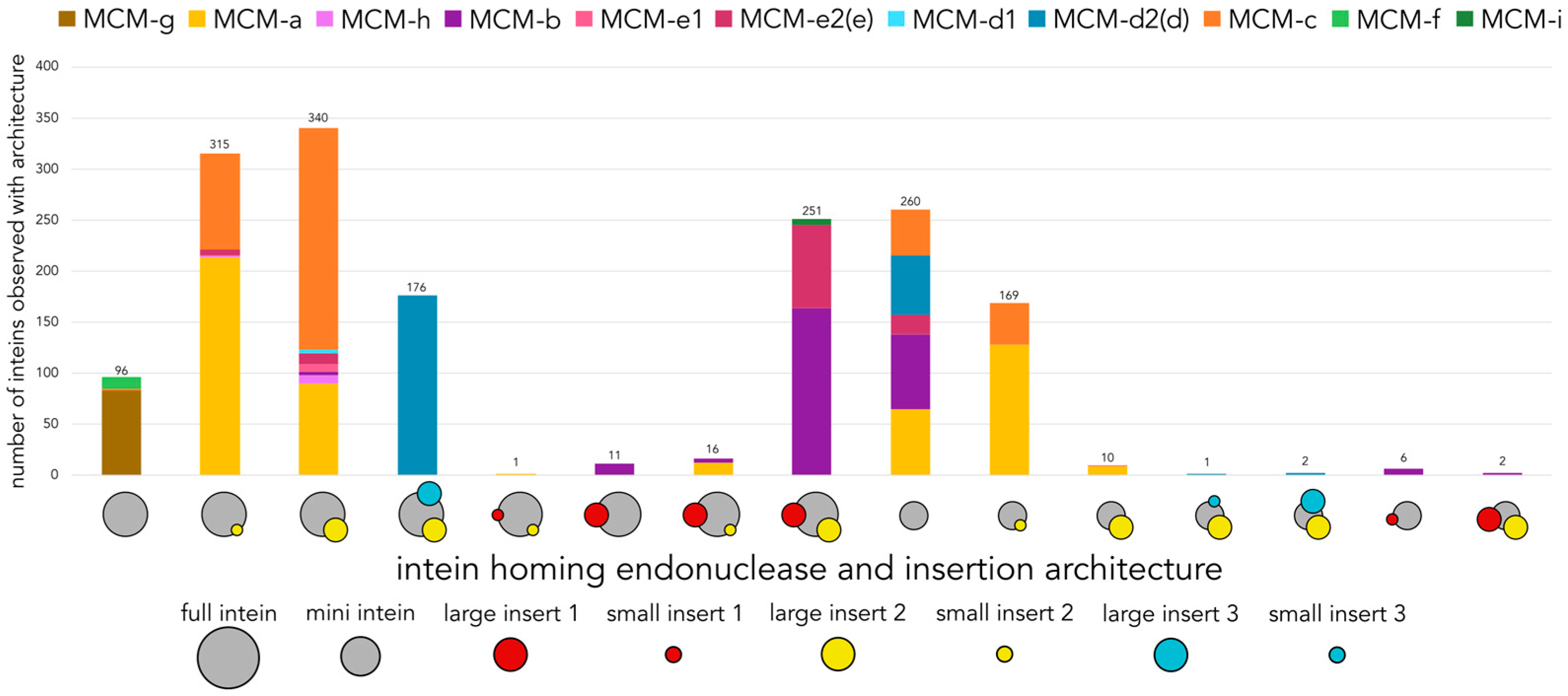
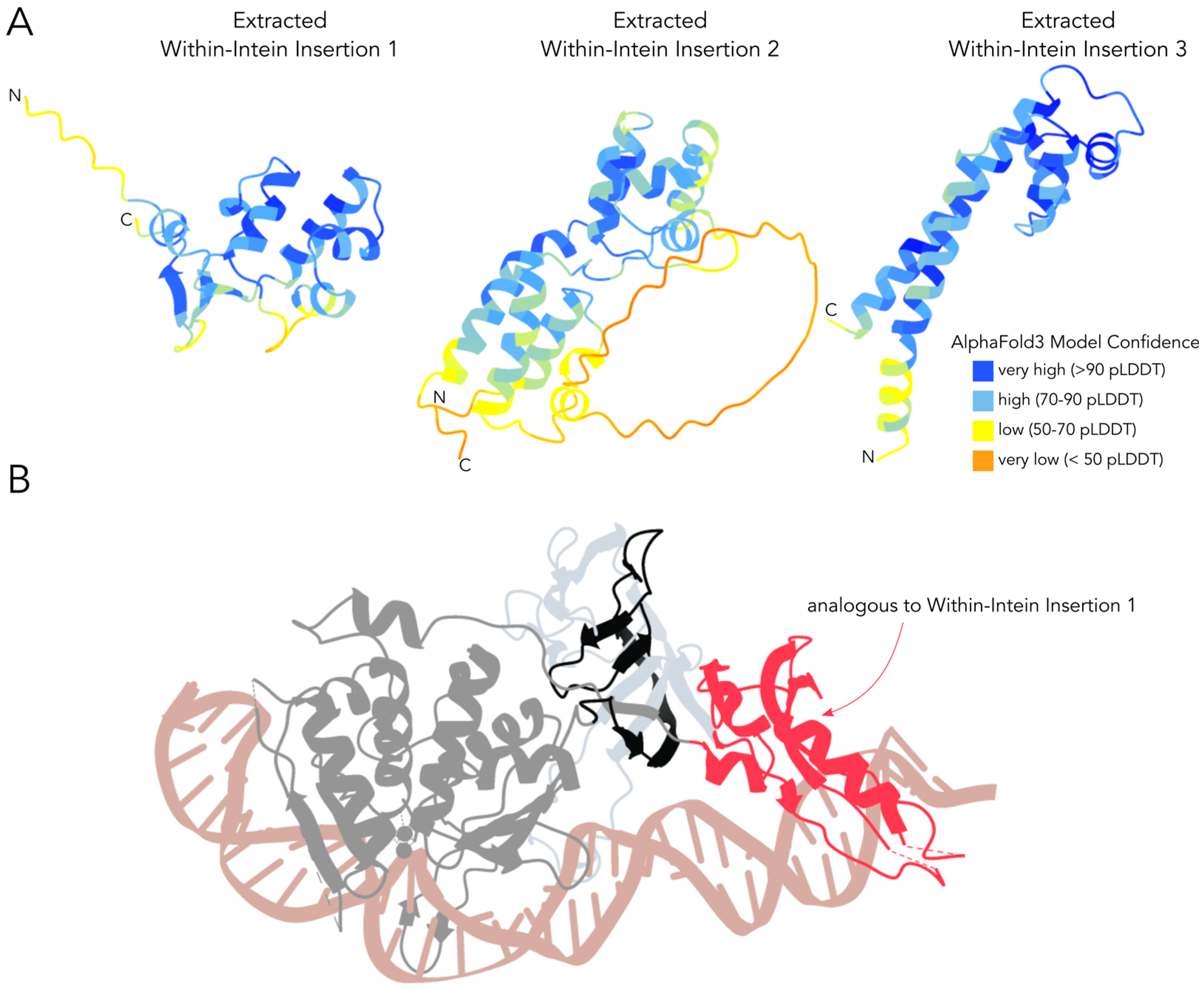
3.3. Decaying Versus Full Homing Endonucleases and Within-Intein Insertions at Three Distinct Sites Generate Architectural Diversity
3.4. Geographically Overlapping Populations in the Atacama Desert Have a Wide Range of MCM Intein Architectures and Invasion Statuses Including Co-Existing Empty, Mini Intein, and Full Intein Alleles
4. Discussion
4.1. Archaeal MCM Is a Powerful System for the Continued Exploration of Multi-Intein Gene Dynamics
4.2. Potential Origin and Role of the Within-Intein Insertions
4.3. Atacama Desert Archaea Provide Support for Co-Existence Model of Intein Persistence
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| aa | amino acid |
| LAGLIDADG | one letter abbreviations of amino acids in a particular homing endonuclease motif |
| MCM | minichromosome maintenance protein, also previously known as cdc21 |
| PDB | Protein Databank |
| pLDDT | predicted local distance difference test |
| PSI-BLAST | position-specific iterated basic local alignment search tool |
| RIR | ribonucleotide reductase |
| taxid | Taxonomy ID |
References
- Hirata, R.; Ohsumk, Y.; Nakano, A.; Kawasaki, H.; Suzuki, K.; Anraku, Y. Molecular structure of a gene, VMA1, encoding the catalytic subunit of H+-translocating adenosine triphosphatase from vacuolar membranes of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J. Biol. Chem. 1990, 265, 6726–6733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kane, P.M.; Yamashiro, C.T.; Wolczyk, D.F.; Neff, N.; Goebl, M.; Stevens, T.H. Protein Splicing Converts the Yeast TFP1 Gene Product to the 69-kdDSubunit of the Vacuolar H+-Adenosine Triphosphatase. Science 1990, 250, 651–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, L.; Zhong, B.; Dai, Z. Protein Splicing of Inteins: A Powerful Tool in Synthetic Biology. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 810180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gosselin, S.P.; Arsenault, D.; Gogarten, J.P. Actinobacteriophage Inteins: Host Diversity, Local Dissemination, and Non-Canonical Architecture. bioRxiv 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goddard, M.R.; Burt, A. Recurrent invasion and extinction of a selfish gene. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 13880–13885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naor, A.; Altman-Price, N.; Soucy, S.M.; Green, A.G.; Mitiagin, Y.; Turgeman-Grott, I.; Davidovich, N.; Gogarten, J.P.; Gophna, U. Impact of a homing intein on recombination frequency and organismal fitness. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E4654–E4661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barzel, A.; Obolski, U.; Gogarten, J.P.; Kupiec, M.; Hadany, L. Home and away-the evolutionary dynamics of homing endonucleases. BMC Evol. Biol. 2011, 11, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yahara, K.; Fukuyo, M.; Sasaki, A.; Kobayashi, I. Evolutionary maintenance of selfish homing endonuclease genes in the absence of horizontal transfer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 18861–18866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gogarten, J.P.; Hilario, E. Inteins, introns, and homing endonucleases: Recent revelations about the life cycle of parasitic genetic elements. BMC Evol. Biol. 2006, 6, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson-Sathi, S.; Sousa, F.L.; Roettger, M.; Lozada-Chávez, N.; Thiergart, T.; Janssen, A.; Bryant, D.; Landan, G.; Schönheit, P.; Siebers, B.; et al. Origins of major archaeal clades correspond to gene acquisitions from bacteria. Nature 2015, 517, 77–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson-Sathi, S.; Dagan, T.; Landan, G.; Janssen, A.; Steel, M.; McInerney, J.O.; Deppenmeier, U.; Martin, W.F. Acquisition of 1000 eubacterial genes physiologically transformed a methanogen at the origin of Haloarchaea. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 20537–20542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gophna, U.; Altman-Price, N. Horizontal Gene Transfer in Archaea—From Mechanisms to Genome Evolution. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2022, 76, 481–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novikova, O.; Jayachandran, P.; Kelley, D.S.; Morton, Z.; Merwin, S.; Topilina, N.I.; Belfort, M. Intein Clustering Suggests Functional Importance in Different Domains of Life. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 783–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naor, A.; Lazary, R.; Barzel, A.; Papke, R.T.; Gophna, U. In Vivo Characterization of the Homing Endonuclease within the polB Gene in the Halophilic Archaeon Haloferax volcanii. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e15833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Turgeman-Grott, I.; Arsenault, D.; Yahav, D.; Feng, Y.; Miezner, G.; Naki, D.; Peri, O.; Papke, R.T.; Gogarten, J.P.; Gophna, U.; et al. Neighboring inteins interfere with one another’s homing capacity. PNAS Nexus 2023, 2, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brewster, A.S.; Chen, X.S. Insights into the MCM functional mechanism: Lessons learned from the archaeal MCM complex. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2010, 45, 243–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maine, G.T.; Sinha, P.; Tye, B.-K. Mutants of S. cerevisiae defective in the maintenance of minichromosomes. Genetics 1984, 106, 365–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yalala, V.R.; Lynch, A.K.; Mills, K.V. Conditional Alternative Protein Splicing Promoted by Inteins from Haloquadratum walsbyi. Biochemistry 2022, 61, 294–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- In Base2.0. Available online: https://inbase.ligsciss.com/index.php?r=site/index (accessed on 23 May 2025).[Green Version]
- Perler, F.B. In Base: The Intein Database. Nucleic Acids. Res. 2002, 30, 383–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finstad, K.M.; Probst, A.J.; Thomas, B.C.; Andersen, G.L.; Demergasso, C.; Echeverría, A.; Amundson, R.G.; Banfield, J.F. Microbial Community Structure and the Persistence of Cyanobacterial Populations in Salt Crusts of the Hyperarid Atacama Desert from Genome-Resolved Metagenomics. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altschul, S.F.; Madden, T.L.; Schäffer, A.A.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Miller, W.; Lipman, D.J. Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: A new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic. Acids. Res. 1997, 25, 3389–3402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C. MUSCLE: A multiple sequence alignment method with reduced time and space complexity. BMC Bioinform. 2004, 5, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gouy, M.; Tannier, E.; Comte, N.; Parsons, D.P. Seaview Version 5: A Multiplatform Software for Multiple Sequence Alignment, Molecular Phylogenetic Analyses, and Tree Reconciliation. Methods Mol. Biol. 2021, 2231, 241–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sievers, F.; Higgins, D.G. Clustal Omega for making accurate alignments of many protein sequences. Protein. Sci. 2018, 27, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katoh, K.; Misawa, K.; Kuma, K.; Miyata, T. MAFFT: A novel method for rapid multiple sequence alignment based on fast Fourier transform. Nucleic. Acids. Res. 2002, 30, 3059–3066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jumper, J.; Evans, R.; Pritzel, A.; Green, T.; Figurnov, M.; Ronneberger, O.; Tunyasuvunakool, K.; Bates, R.; Žídek, A.; Potapenko, A.; et al. Highly accurate protein structure prediction with AlphaFold. Nature 2021, 596, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellegrini-Calace, M. Detecting DNA-binding helix-turn-helix structural motifs using sequence and structure information. Nucleic. Acids. Res. 2005, 33, 2129–2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minh, B.Q.; Schmidt, H.A.; Chernomor, O.; Schrempf, D.; Woodhams, M.D.; von Haeseler, A.; Lanfear, R. IQ-TREE 2: New Models and Efficient Methods for Phylogenetic Inference in the Genomic Era. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2020, 37, 1530–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalyaanamoorthy, S.; Minh, B.Q.; Wong, T.K.F.; von Haeseler, A.; Jermiin, L.S. ModelFinder: Fast model selection for accurate phylogenetic estimates. Nat. Methods 2017, 14, 587–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, D.T.; Chernomor, O.; von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q.; Vinh, L.S. UFBoot2: Improving the Ultrafast Bootstrap Approximation. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 518–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woese, C.R.; Kandler, O.; Wheelis, M.L. Towards a natural system of organisms: Proposal for the domains Archaea, Bacteria, and Eucarya. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1990, 87, 4576–4579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Göker, M.; Oren, A. Valid publication of names of two domains and seven kingdoms of prokaryotes. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2024, 74, 006242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoch, C.L.; Ciufo, S.; Domrachev, M.; Hotton, C.L.; Kannan, S.; Khovanskaya, R.; Leipe, D.; Mcveigh, R.; O’nEill, K.; Robbertse, B.; et al. NCBI Taxonomy: A comprehensive update on curation, resources and tools. Database 2020, 2020, baaa062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swithers, K.S.; Senejani, A.G.; Fournier, G.P.; Gogarten, J.P. Conservation of intron and intein insertion sites: Implications for life histories of parasitic genetic elements. BMC Evol. Biol. 2009, 9, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brewster, A.S.; Wang, G.; Yu, X.; Greenleaf, W.B.; Carazo, J.M.; Tjajadi, M.; Klein, M.G.; Chen, X.S. Crystal structure of a near-full-length archaeal MCM: Functional insights for an AAA+ hexameric helicase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 20191–20196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meagher, M.; Epling, L.B.; Enemark, E.J. DNA translocation mechanism of the MCM complex and implications for replication initiation. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mills, K.V.; Johnson, M.A.; Perler, F.B. Protein Splicing: How Inteins Escape from Precursor Proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 14498–14505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tori, K.; Dassa, B.; Johnson, M.A.; Southworth, M.W.; Brace, L.E.; Ishino, Y.; Pietrokovski, S.; Perler, F.B. Splicing of the Mycobacteriophage Bethlehem DnaB Intein. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 2515–2526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Zhang, B.; Gao, Z.; Xu, R.; Liu, X.; Ishino, S.; Feng, M.; Shen, Y.; Ishino, Y.; She, Q.; et al. A Well-Conserved Archaeal B-Family Polymerase Functions as an Extender in Translesion Synthesis. mBio 2022, 13, e02659-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makarova, K.S.; Krupovic, M.; Koonin, E.V. Evolution of replicative DNA polymerases in archaea and their contributions to the eukaryotic replication machinery. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albert, J.; Eduard, T.; Irma, S.; Ulf, H.; Isidre, G.; Peter, R. Ribonucleotide Reduction in Pseudomonas Species: Simultaneous Presence of Active Enzymes from Different Classes. J. Bacteriol. 1999, 181, 3974–3980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirdis, E.; Jonsson, I.-M.; Kubica, M.; Potempa, J.; Josefsson, E.; Masalha, M.; Foster, S.J.; Tarkowski, A. Ribonucleotide reductase class III, an essential enzyme for the anaerobic growth of Staphylococcus aureus, is a virulence determinant in septic arthritis. Microb. Pathog. 2007, 43, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.-Q.; Yang, J.; Meng, Q. Four Inteins and Three Group II Introns Encoded in a Bacterial Ribonucleotide Reductase Gene. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 46826–46831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aravind, L.; Koonin, E.V. DNA-binding proteins and evolution of transcription regulation in the archaea. Nucleic. Acids. Res. 1999, 27, 4658–4670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohlendorf, D.H.; Anderson, W.F.; Fisher, R.G.; Takeda, Y.; Matthews, B.W. The molecular basis of DNA–protein recognition inferred from the structure of cro repressor. Nature 1982, 298, 718–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sauer, R.T.; Yocum, R.R.; Doolittle, R.F.; Lewis, M.; Pabo, C.O. Homology among DNA-binding proteins suggests use of a conserved super-secondary structure. Nature 1982, 298, 447–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moure, C.M.; Gimble, F.S.; Quiocho, F.A. Crystal structure of the intein homing endonuclease PI-SceI bound to its recognition sequence. Nat. Struct. Biol. 2002, 9, 764–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christ, F.; Steuer, S.; Thole, H.; Wende, W.; Pingoud, A.; Pingoud, V. A Model for the PI-SceI×DNA Complex Based on Multiple Base and Phosphate Backbone-specific Photocross-links. J. Mol. Biol. 2000, 300, 841–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, D.; Crist, M.; Duan, X.; Quiocho, F.A.; Gimble, F.S. Probing the Structure of the PI-SceI-DNA Complex by Affinity Cleavage and Affinity Photocross-linking. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 2705–2712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| MCM Intein Invasion Status | Total Homologs with Invasion Status |
|---|---|
| Empty | 3125 |
| Single | 709 |
| Double | 305 |
| Triple | 79 |
| Quadruple | 25 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Arsenault, D.; Stack, G.F.; Gogarten, J.P. Inteins at Eleven Distinct Insertion Sites in Archaeal Helicase Subunit MCM Exhibit Varied Architectures and Activity Levels Across Archaeal Groups. DNA 2025, 5, 39. https://doi.org/10.3390/dna5030039
Arsenault D, Stack GF, Gogarten JP. Inteins at Eleven Distinct Insertion Sites in Archaeal Helicase Subunit MCM Exhibit Varied Architectures and Activity Levels Across Archaeal Groups. DNA. 2025; 5(3):39. https://doi.org/10.3390/dna5030039
Chicago/Turabian StyleArsenault, Danielle, Gabrielle F. Stack, and Johann Peter Gogarten. 2025. "Inteins at Eleven Distinct Insertion Sites in Archaeal Helicase Subunit MCM Exhibit Varied Architectures and Activity Levels Across Archaeal Groups" DNA 5, no. 3: 39. https://doi.org/10.3390/dna5030039
APA StyleArsenault, D., Stack, G. F., & Gogarten, J. P. (2025). Inteins at Eleven Distinct Insertion Sites in Archaeal Helicase Subunit MCM Exhibit Varied Architectures and Activity Levels Across Archaeal Groups. DNA, 5(3), 39. https://doi.org/10.3390/dna5030039






