Archard’s Law: Foundations, Extensions, and Critiques
Definition
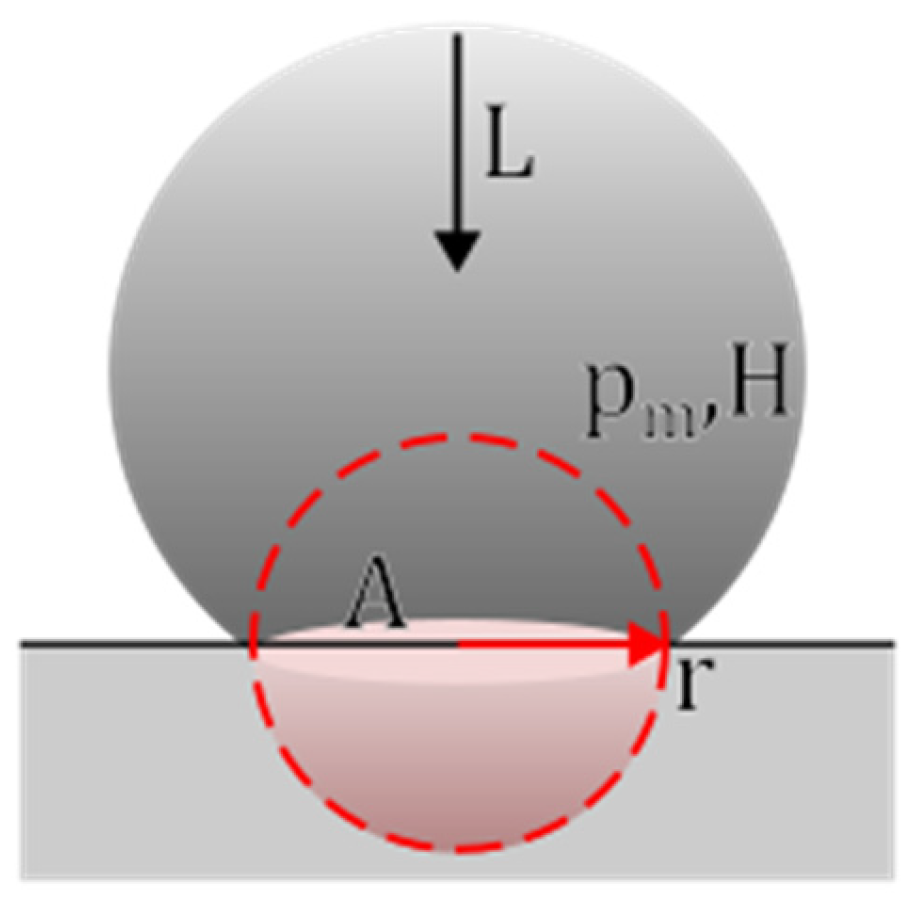
1. Introduction on Archard’s Wear Law
- The geometric transformation from original surface asperities to the plastically deformed contact area that generates wear;
- The relationship between yield strength and hardness;
- The fraction of plastic deformation that contributes to material loss;
- The likelihood that material can be removed from the contact interface;
- The contributions of other factors (e.g., temperature, surface tribochemical activities, lubrication, etc.) not explicitly included by Equation (1) but empirically linked to wear.
2. Model Variance
2.1. Extension and Organization of Archard’s Wear Law
2.2. Evolution and Criticism of Archard-Type Models
2.3. Modern Approaches and Modeling Limitations in Contemporary Wear Research
- Surface evolution during wear resulting from complex, interconnected impacts of phenomena arising from a sliding interface: frictional heating leading to high flash temperatures, thermally induced deformations, and changes in material properties; wear fragment behavior and asperity fatigue; and tribochemical degradation;
- The transition and entwinement of wear mechanisms as a function of operating conditions and material properties;
- The lack of progressive wear characterization and measurement;
- The lack of consistency in wear data measurement, structure, and representation;
- The role of friction.
3. Conclusions and Prospects
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Meng, H.C.; Ludema, K.C. Wear Models and Predictive Equations: Their Form and Content. Wear 1995, 181, 443–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archard, J.F. Contact and Rubbing of Flat Surfaces. J. Appl. Phys. 1953, 24, 981–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holm, R. Electric Contacts; Almquist and Wiksells: Stockholm, Sweden, 1946. [Google Scholar]
- Halling, J. Principles of Tribology; The Macmillan Press LTD: London, UK, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Timsit, R.S. Course on Performance and Reliability of Power Electrical Connections. In Electrical Contacts: Principles and Applications; Slade, P.G., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.J.; Chung, Y.-W. Encyclopedia of Tribology; Springer US: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liskiewicz, T.W.; Beake, B.D. Dynamic Changes of Mechanical Properties Induced by Friction in the Archard Wear Model. Wear 2019, 428, 366–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molinari, J.; Aghababaei, R.; Brink, T.; Frérot, L.; Milanese, E. Adhesive Wear Mechanisms Uncovered by Atomistic Simulations. Friction 2018, 6, 245–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delaney, B.C.; Wang, Q.J.; Aggarwal, V.; Chen, W.; Evans, R.D. A Contemporary Review and Data-Driven Evaluation of Archard-Type Wear Laws. Appl. Mech. Rev. 2025, 77, 022101 . [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goryacheva, I.G. Contact Mechanics in Tribology; Solid Mechanics and Its Applications; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1998; Volume 61. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, D.; Martini, A.; Wang, W.; Hu, Y.; Lisowsky, B.; Wang, Q.J. Simulation of Sliding Wear in Mixed Lubrication. J. Tribol. 2007, 129, 544–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhu, D. Interfacial Mechanics: Theories and Methods for Contact and Lubrication; CRC Press/Taylor & Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Kragelsky, I.V. Friction and Wear; Buttersworth: London, UK, 1965. [Google Scholar]
- Rabinowicz, E. Friction and Wear of Materials; John Wiley and Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1965. [Google Scholar]
- Lewis, W.D. Fluorocarbon Resin in Piston Rings—New Performance Data for Reciprocating Nonlubrication Air Compressor. Lubr. Eng. 1968, 24, 112–127. [Google Scholar]
- Khrushchev, M.M.; Babichev, M.A. Abrasive Wear; Nauka: Moscow, Russia, 1970. [Google Scholar]
- Rhee, S.K. Wear Equation for Polymers Sliding against Metal Surfaces. Wear 1970, 16, 431–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lancaster, J.K. Dry Rubbing Bearings. In A Tribology Handbook; Neale, M.J., Ed.; Butterworth Heinemann: Warrendale, PA, USA, 1973. [Google Scholar]
- Larsen-Basse, J. Wear of Hard-Metals in Rock Drilling: A Survey of the Literature. Powder Metall. 1973, 16, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurricks, P.L. The Mechanism of Fretting and the Influence of Temperature. Ind. Lubr. Tribol. 1976, 28, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, N.B.; Walker, B.H.; Appl, F.C. A Model of Performance and Life of Diamond Drill Bits. J. Press. Vessel Technol. 1978, 100, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Cheng, K.; Holt, R.; Liu, X. Modeling Flank Wear of Carbide Tool Insert in Metal Cutting. Wear 2005, 259, 1235–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cayer-Barrioz, J.; Mazuyer, D.; Kapsa, P.; Chateauminois, A.; Robert, G.; Bouquerel, F. On the Correlation Abrasive Wear Resistance—Molecular Weight: A Quantitative Wear Law for Polymeric Fibres. Wear 2006, 261, 460–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Lei, T.C.; Gao, C.Q. Influence of Isothermal Hardening on the Sliding Wear Behaviour of 52100 Bearing Steel. Tribol. Int. 1990, 23, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siniawski, M.T.; Harris, S.J.; Wang, Q.; Liu, S. Wear Initiation of 52100 Steel Sliding against a Thin Boron Carbide Coating. Tribol. Lett. 2003, 15, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartha, B.B.; Zawadzki, J.; Chandrasekar, S.; Farris, T.N. Wear of Hard-Turned AISI 52100 Steel. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2005, 36, 1417–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegadekatte, V.; Huber, N.; Kraft, O. Finite Element Based Simulation of Dry Sliding Wear. Model. Simul. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2005, 13, 57–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Wang, Y.; Yan, M.F. Wear Rate, Frictional Temperature, and Energy Consumption of Steel 52100 with Different Microstructures during Sliding. J. Mater. Sci. 2005, 40, 5635–5640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bressan, J.D.; Battiston, G.A.; Gerbasi, R.; Daros, D.P.; Gilapa, L.M. Wear on Tool Steel AISI M2, D6 and 52100 Coated with Al2O3 by the MOCVD Process. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2006, 179, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, S.; Sen, U. Sliding Wear Behavior of Niobium Carbide Coated AISI 1040 Steel. Wear 2008, 264, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, S.; Sen, U. The Effect of Boronizing and Boro-Chromizing on Tribological Performance of AISI 52100 Bearing Steels. Ind. Lubr. Tribol. 2009, 61, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Wu, L.; Li, M.; Zhou, Y. Tribological Properties of γ-Y2Si2O7 Ceramic against AISI 52100 Steel and Si3N4 Ceramic Counterparts. Wear 2009, 266, 960–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, J.; Almqvist, A.; Larsson, R. Numerical Simulation of a Wear Experiment. Wear 2011, 271, 2947–2952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barunovic, R.; Haas, V.; Langlade, C.; Krill, C.E. Sliding Wear of 100Cr6 in a Diesel-Lubricated Flat–Flat Contact under Realistic Loads. Tribol. Int. 2012, 53, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taltavull, C.; Torres, B.; López, A.J.; Rams, J. Dry Sliding Wear Behavior of AM60B Magnesium Alloy. Wear 2013, 301, 615–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunes, I.; Cicek, A.; Aslantas, K.; Kara, F. Effect of Deep Cryogenic Treatment on Wear Resistance of AISI 52100 Bearing Steel. Trans. Indian. Inst. Met. 2014, 67, 909–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Castro, V.V.; Fontoura, L.A.M.; Benfica, J.D.; Seferin, M.; Pacheco, J.L.; dos Santos, C.A. Lubricated Sliding Wear of SAE 1045 and SAE 52100 Steel against Alumina in the Presence of Biodiesel, Diesel and a 50:50 Blend of Those Fuels. Wear 2016, 368, 267–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furustig, J.; Dobryden, I.; Almqvist, A.; Almqvist, N.; Larsson, R. The Measurement of Wear Using AFM and Wear Interpretation Using a Contact Mechanics Coupled Wear Model. Wear 2016, 350, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, J.; Shen, X.; Chen, X. Wear Experiment and Model of Rolling Balls in Sliding-Rolling Conditions. Mech. Ind. 2017, 18, 511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.; Grejtak, T.; Krick, B.; Vermaak, N. Experimentally Calibrated Abrasive Sliding Wear Model: Demonstrations for Rotary and Linear Wear Systems. J. Appl. Mech. 2018, 85, 121011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; Chen, J.; Guo, S.; Meng, Q.; Luo, J. Finite Element Simulation and Experimental Test of the Wear Behavior for Self-Lubricating Spherical Plain Bearings. Friction 2018, 6, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Xia, W.; Song, Z.; Wu, R.; Wang, S.; Yao, Y. Wear-Life Analysis of Deep Groove Ball Bearings Based on Archard Wear Theory. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2018, 32, 3329–3336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cross, P.S.G.; Limbert, G.; Stewart, D.; Wood, R.J.K. A Multiscale Finite Element Model of Sliding Wear for Cobalt-Chromium Undergoing Ratcheting Wear. Wear 2020, 462, 203482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshua, S.P.; Babu, P.D. Effect of Laser Textured Surface with Different Patterns on Tribological Characteristics of Bearing Material AISI 52100. J. Cent. South. Univ. 2020, 27, 2210–2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghaddam, P.V.; Hardell, J.; Vuorinen, E.; Prakash, B. Dry Sliding Wear of Nanostructured Carbide-Free Bainitic Steels—Effect of Oxidation-Dominated Wear. Wear 2020, 454, 203317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özkan, D.; Yılmaz, M.A.; Ataş Bakdemir, S.; Sulukan, E. Wear and Friction Behavior of TiB2 Thin Film-Coated AISI 52100 Steels under the Lubricated Condition. Tribol. Trans. 2020, 63, 1008–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bildik, O.; Yaşar, M. Manufacturing of Wear Resistant Iron-Steel: A Theoretical and Experimental Research on Wear Behavior. Eng. Technol. Appl. Sci. Res. 2021, 11, 7251–7256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaelani, Y.; Syaifudin, A. Mathematical Model of Wear Volumes Due to Sliding Speed Using Buckingham Pi Model. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 1034, 012165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Ma, L.; Zhi, C.; Ma, Z.; Zhou, C.; Zhao, G.; Fan, Q.; Jia, W. Effect of Annealing on Heavy-Load Wear Performance of Wear Resisting Steel-Carbon Steel-Cladded Plate. Tribol. Trans. 2021, 64, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichelt, M.; Cappella, B. Large Scale Multi-Parameter Analysis of Wear of Self-Mated 100Cr6 Steel—A Study of the Validity of Archard’s Law. Tribol. Int. 2021, 159, 106945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabrizi, A.T.; Aghajani, H.; Saghafian, H.; Farhang Laleh, F. Correction of Archard Equation for Wear Behavior of Modified Pure Titanium. Tribol. Int. 2021, 155, 106772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Ren, Z.; Huang, J.; Zhong, S. Fretting Wear Evolution Model of the Metal Filaments inside Metal Rubber. Wear 2022, 506, 204438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morón, R.C.; Melo-Máximo, L.; Campos-Silva, I.; Melo-Máximo, D.V.; Arzate-Vázquez, I.; López-Perrusquia, N.; Solis-Romero, J. Dry and Grease-Lubricated Reciprocating Wear Resistance of Borided AISI 52100 Steel. Mater. Lett. 2022, 320, 132404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosbacher, M.; Hilzenthaler, M.; Galetz, M.; Glatzel, U. Oxygen Diffusion Hardened Zirconium Alloy ZrNb7—Tribological Properties Derived from Calo Wear and Wheel on Flat Experiments. Tribol. Int. 2022, 165, 107304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudnytskyj, A.; Larsson, R.; Gachot, C. A Closer Look at the Contact Conditions of a Block-on-Flat Wear Experiment. Lubricants 2022, 10, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torkamani, H.; Vrček, A.; Larsson, R.; Antti, M.-L. Micro-Pitting and Wear Damage Characterization of through Hardened 100Cr6 and Surface Induction Hardened C56E2 Bearing Steels. Wear 2022, 492, 204218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birleanu, C.; Cioaza, M.; Serdean, F.; Pustan, M.; Bere, P.; Contiu, G. Tribological Investigation of Glass Fiber Reinforced Polymer Composites against 52100 Chrome Alloy Steel Based on Electre Decision-Making Method. Polymers 2023, 16, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Y.; Helmons, R.; Carr, M.; Wheeler, C.; Schott, D. Modelling of Material Removal Due to Sliding Wear Caused by Bulk Material. Powder Technol. 2023, 415, 118109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhry, J.; Almqvist, A.; Larsson, R. Improving Archard’s Wear Model: An Energy-Based Approach. Tribol. Lett. 2024, 72, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Li, L.; Wang, P.; Li, D.; Xue, W.; Duan, D. Wear Behavior and Damage Characterization for AISI 52100 Bearing Steels: Effect of Hardness and Spherical Carbides. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 30, 8359–8370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Deng, J.; Bao, Y.; Zhang, Z. Synergistic Effects of Heat-Assisted Ultrasonic Rolling Textures and Self-Lubricating Coatings on the Friction and Wear Properties of AISI 52100 Steel. Mater. Today Commun. 2024, 38, 108256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, K.L. Contact Mechanics; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Hardy, C.; Baronet, C.N.; Tordion, G.V. The Elasto-Plastic Indentation of a Half-Space by a Rigid Sphere. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 1971, 3, 451–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Zhu, J.; Yu, L.; Wang, Q.J. Elasto-Plastic Contact of Rough Surfaces. Tribol. Trans. 2001, 44, 437–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.W.; Wang, Q.J.; Liu, Y.; Chen, W.; Cao, J.; Xia, C.; Talwar, R.; Lederich, R. Analysis and Convenient Formulas for Elasto-Plastic Contacts of Nominally Flat Surfaces: Average Gap, Contact Area Ratio, and Plastically Deformed Volume. Tribol. Lett. 2007, 28, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, N.; Zhu, D.; Wang, Q.J. Three-Dimensional Plasto-Elastohydrodynamic Lubrication (Pehl) for Surfaces with Irregularities. J. Tribol. 2011, 133, 031502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pintaude, G. Hardness as an Indicator of Material Strength: A Critical Review. Crit. Rev. Solid. State Mater. Sci. 2023, 48, 623–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.-T.; Cheng, C.-M. Scaling Approach to Conical Indentation in Elastic-Plastic Solids with Work Hardening. J. Appl. Phys. 1998, 84, 1284–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preston, F.W. The Theory and Design of Plate Glass Polishing Machines. J. Soc. Glass Technol. 1927, 11, 214–256. [Google Scholar]
- Kragelsky, I.V.; Dobychin, M.N.; Kombalov, V.S. Friction and Wear: Calculations Methods; Pergamon Press: Oxford, UK, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Argatov, I.I.; Chai, Y.S. An Artificial Neural Network Supported Regression Model for Wear Rate. Tribol. Int. 2019, 138, 211–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasha, M.B.; Rao, R.N.; Ismail, S.; Gupta, M.; Prasad, P.S. Tribo-Informatics Approach to Predict Wear and Friction Coefficient of Mg/Si3N4 Composites Using Machine Learning Techniques. Tribol. Int. 2024, 196, 109696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouvry, S.; Liskiewicz, T.; Kapsa, P.; Hannel, S.; Sauger, E. An Energy Description of Wear Mechanisms and its Applications to Oscillating Sliding Contacts. Wear 2003, 255, 287–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, F.; Ke, L.-L. Numerical Study of Coupled Electrical-Thermal-Mechanical-Wear Behavior in Electrical Contacts. Metals 2021, 11, 955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhang, W.; Li, G.; Wang, J.; Li, L.; Xie, M. Simulation Study of Thermal–Mechanical Coupling Fretting Wear of Ti-6Al-4V Alloy. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 7400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, J.; Mohammadpour, M.; Theodossiades, S.; Bewsher, R.; Offner, G.; Bansal, H.; Leighton, M.; Braunstingl, M.; Flesch, H.-G. A Multi-Physics Transient Wear Model for Helical Gear Pairs. Tribol. Int. 2022, 169, 107463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Dong, N.; Min, J. Study on the Coupling Relationship between Wear and Dynamics in Planetary Gear Systems. Machines 2023, 11, 986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Zhao, B.; Xin, Q.; Niu, X.; Xie, Z.; Lu, X.; Zou, D. Analysis of Transient Lubrication and Wear Coupling Behaviors Considering Thermal Effect and Journal Misalignment for Main Bearings under Dynamic Load. Wear 2024, 554–555, 205478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayasinghe, R.; Ramos, M.; Nand, A.; Ramezani, M. An Adaptive Artificial Neural Network Model for Predicting Friction and Wear in Polymer Matrix Composites: Integrating Kragelsky and Archard Laws. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2025, e70004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Goltsberg, R.; Etsion, I. Modeling Adhesive Wear in Asperity and Rough Surface Contacts: A Review. Materials 2022, 15, 6855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghababaei, R.; Warner, D.H.; Molinari, J.-F. Critical Length Scale Controls Adhesive Wear Mechanisms. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhaskaran, H.; Gotsmann, B.; Sebastian, A.; Drechsler, U.; Lantz, M.A.; Despont, M.; Jaroenapibal, P.; Carpick, R.W.; Chen, Y.; Sridharan, K. Ultralow Nanoscale Wear through Atom-by-Atom Attrition in Silicon-Containing Diamond-Like Carbon. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2010, 5, 181–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xu, J.; Ootani, Y.; Ozawa, N.; Adachi, K.; Kubo, M. Non-Empirical Law for Nanoscale Atom-by-Atom Wear. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, 2002827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, P.; Li, R.; Gong, H. Molecular Dynamics Simulation of Nanoscale Abrasive Wear of Polycrystalline Silicon. Crystals 2018, 8, 463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.-W.; Qiu, R.-Z.; Fang, T.-H. Atomistic Simulation of Atomic Force Microscopy-Based Nanoscratching on Monocrystalline Copper. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2017, 8, 2283–2295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
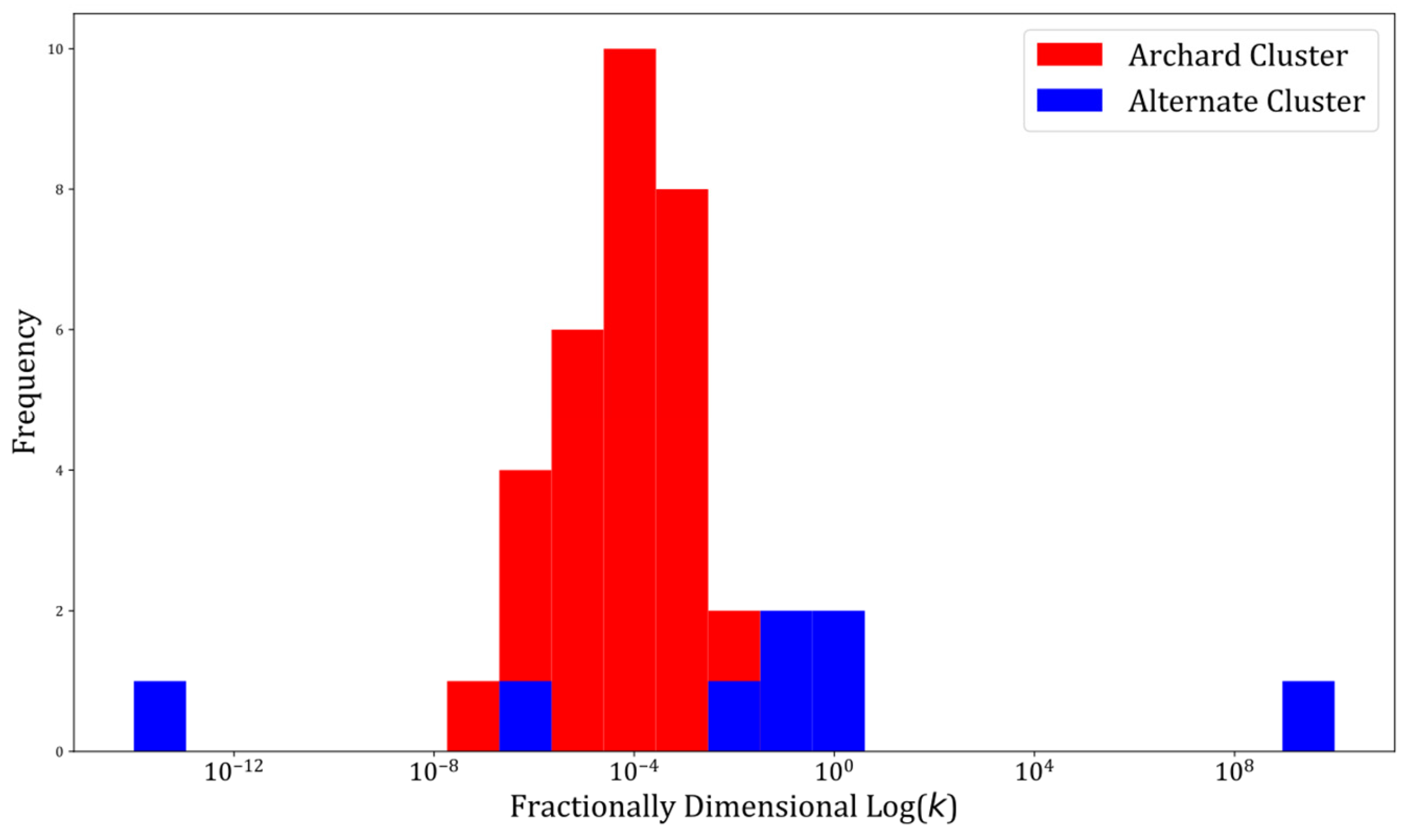
| Author (Year) | Additional Terms Used | Wear Mechanisms | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Holm [3] (1946) | 1 | 1 | 1 | Adhesion | |
| Archard [2] (1953) | 1 | 1 | 1 | Adhesion | |
| Kragelsky [13] (1965) | >1 | 1 | 0 | Fatigue | |
| Rabinowicz [14] (1965) | 1 | 1 | 1 | Abrasion/fretting | |
| Lewis [15] (1968) | 1 | 1 | 0 | Adhesion of filled PTFE and piston rings | |
| Khrushchev and Babichev [16] (1970) | 1 | 1 | 1 | Microcutting of metals | |
| Rhee 1 [17] (1970) | 0 | Exponential function of | Adhesion with thermal effects | ||
| Lancaster [18] (1973) | 1 | 1 | 0 | Includes wear rate correction factors | Filled thermoplastics and filled PTFE |
| Larsen-Basse [19] (1973) | 1 | 1 | 0 | Defined in terms of impact frequency | Thermal fatigue and carbine polishing |
| Hurricks [20] (1976) | 1 | 1 | 0 | Fretting | |
| Moore et al. [21] (1978) | 1 | 1.8 | 0 | (rock volume removed/distance) | Wear of diamond inserts and rotary drag bits |
| Luo et al. [22] (2005) | 0 | 1 | 1 | Normal stress between tool flank face and work piece | Adhesion/abrasion of cutting tool flank |
| Cayer-Barrioz et al. [23] (2006) | 2 | 1 | 0 | Molecular weight | Abrasion of polymeric fibers |
| Author (Year) | Additional Terms Used | Wear Mechanisms | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wang et al. [24] (1990) | 1 | 1 | 0 | Effect of Material Hardening on Wear Rate | |
| Siniawski et al. [25] (2003) | 1 | 1 | 1 | Wear Development of Boron Carbide Coatings | |
| Bartha et al. [26] (2005) | 0 | 1 | 1 | Proportional to mass loss W | High-Precision Machining |
| Hegadekatte et al. [27] (2005) | 1 | 1 | 0 | Archard’s Law as a Foundation of Wear Simulation | |
| Li et al. [28] (2005) | 1 | 1 | 0 | Wear Effects of Microstructure | |
| Bressan et al. [29] (2006) | 1 | 1 | 1 | Wear-Resistant Steel Coating | |
| Sen and Sen [30] (2008) | 1 | 1 | 0 | Wear of Niobium Carbide Coating | |
| Sen and Sen [31] (2009) | 1 | 1 | 0 | Wear of Boronizing and Chromizing Steel | |
| Sun et al. [32] (2009) | 1 | 1 | 0 | Wear of Steel on Ceramics | |
| Andersson et al. [33] (2011) | 1 | 1 | 1 | Wear Simulation Validation | |
| Barunovic et al. [34] (2012) | 1 | 1 | 0 | High-Load, Diesel-Lubricated Sliding | |
| Taltavull et al. [35] (2013) | 1 | 1 | 0 | Wear Resistance of Magnesium alloys | |
| Gunes et al. [36] (2014) | 1 | 1 | 0 | Cryogenic Treatment to Improve Wear Resistance | |
| de Castro et al. [37] (2016) | 1 | 1 | 1 | Wear Performance of Automobile Lubricants | |
| Furustig et al. [38] (2016) | 1 | 1 | 0 | Wear Simulation Validation | |
| Xi et al. [39] (2017) | 1 | 1 | 1 | Substitution of Hardness with Yield Stress | Wear Simulation Validation |
| Jia et al. [40] (2018) | 1 | 1 | 0 | Negative sign introduced to indicate direction of wear | Rotary and Linear Wear Modeling |
| Xue et al. [41] (2018) | m | n | 0 | Simulation of Wear Failure | |
| Yu et al. [42] (2018) | 1 | 1 | 1 | Wear Life of Deep-Groove Ball Bearings | |
| Liu et al. [7] (2019) | 1 | 1 | 1 | (Peak Load, Stiffness, Wear Depth) | Improved Modeling of Fretting Wear |
| Cross et al. [43] (2020) | 1 | 1 | 0 | Ratcheting Wear of Cobalt-Chromium | |
| Joshua and Babu [44] (2020) | 0 | 1 | 0 | Sliding distance expressed as product of angular velocity, disk radius, and time | Bearings used in Automobile and Railway Industries |
| Moghaddam et al. [45] (2020) | 1 | 1 | 0 | Effect of Carbide-free Bainitic Microstructure on Oxidation-dominated Wear | |
| Özkan et al. [46] (2020) | 1 | 1 | 0 | Friction Reduction for thin-film coatings | |
| Bildik and Yaşar [47] (2021) | m = 1 | n = 0 | 1 | Manufacturing Process Impact on Wear Resistance | |
| Kaelani and Syaifudin [48] (2021) | 1 | 1 | 1 | Mathematical Modeling of Wear | |
| Liu, et al. [49] (2021) | 1 | 1 | 0 | Mining and Agriculture | |
| Reichelt and Cappella [50] (2021) | 1 | 1 | 1 | Validity of Archard’s Law | |
| Tabrizi et al. [51] (2021) | 1 | 1 | 1 | Proportional to height of asperity peaks, surface roughness, squared tangent of asperity slope, and inversely to difference in interfacing surface hardnesses | Extension of the Archard Model |
| Li et al. [52] (2022) | 1 | 1 | 0 | Wear Life of Metal Rubbers | |
| Morón et al. [53] (2022) | 1 | 1 | 0 | Dry and Lubricated Borided Bearing Steel Wear | |
| Mosbacher et al. [54] (2022) | 1 | 1 | 0 | Effect of Heat Treatment on Tribological Performance | |
| Rudnytskyj et al. [55] (2022) | 1 | 1 | 0 | Wear Simulation Validation | |
| Torkamani et al. [56] (2022) | 1 | 1 | 0 | Damage Mechanisms in Modern Machinery | |
| Birleanu et al. [57] (2023) | 1 | 1 | 0 | Improved Tribological Properties of Composites | |
| Yan et al. [58] (2023) | 1 | 1 | 1 | Surface Texture to Reduce Sliding Wear | |
| Choudhry et al. [59] (2024) | 1 | 1 | 1 | Improved model of Adhesive Wear | |
| Li et al. [60] (2024) | 1 | 1 | 0 | Wear Influence of Hardness and Spherical Carbides | |
| Wu et al. [61] (2024) | 1 | 1 | 0 | Wear Life of Bearing Steel |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Delaney, B.; Wang, Q.J. Archard’s Law: Foundations, Extensions, and Critiques. Encyclopedia 2025, 5, 124. https://doi.org/10.3390/encyclopedia5030124
Delaney B, Wang QJ. Archard’s Law: Foundations, Extensions, and Critiques. Encyclopedia. 2025; 5(3):124. https://doi.org/10.3390/encyclopedia5030124
Chicago/Turabian StyleDelaney, Brian, and Q. Jane Wang. 2025. "Archard’s Law: Foundations, Extensions, and Critiques" Encyclopedia 5, no. 3: 124. https://doi.org/10.3390/encyclopedia5030124
APA StyleDelaney, B., & Wang, Q. J. (2025). Archard’s Law: Foundations, Extensions, and Critiques. Encyclopedia, 5(3), 124. https://doi.org/10.3390/encyclopedia5030124






