Unpacking Transdisciplinary Research Scenarios in Architecture and Urbanism
Definition
1. Introduction
Rationale: Transdisciplinarity and the Need for Robust Research Scenarios
2. An Approach to Transdisciplinary Research in Architecture and Urbanism
- Hybrid scenario development forms a cornerstone of this approach. It leverages the integration of phenomenological analysis with advanced spatial data analytical tools, such as GIS and visual attention software (VAS), to develop intricate research scenarios. It combines qualitative insights from user experiences with quantitative spatial data. This component is applied across various research areas, including practice-based research, city dynamics, and housing dynamics. Primary techniques, like attitude surveys and user perspectives, gather experiential feedback and enrich the analysis and examination of phenomena. Scenario planning and content analysis aid in interpreting qualitative data. Walking tour assessments are applied to evaluate the practical implications and real-world pertinence.
- Integrated socio-spatial analysis is another pivotal component which fuses sociological theories with spatial data. Employing GIS tools, it examines areas like urban governance and public space use and utilization to offer a nuanced perspective of the relationship between social dynamics and physical manifestations. Sociocultural surveys and ethnographic studies gather in-depth insights into community behaviors and social interactions. User participation and community design are fundamental in understanding and integrating the social and behavioral dynamics into decision making.
- A revised experiential approach represents a modern reinterpretation of phenomenological methods in architecture. This component integrates technological advancements, particularly VAS and GIS, to deepen our understanding of the human experience. It espouses philosophical and aesthetic considerations with functional elements. This component is crucial in building anatomy research and post-occupancy evaluations as it enables a more profound and data-informed understanding of user experiences and behaviors.
- The integration of environmental psychology into urban studies is gaining momentum in recent years as an approach that embeds psychological considerations directly into urban studies. Utilizing GIS for spatial representation of psychological and behavioral factors, it paves new pathways for examining spaces that focus on psychological well-being of individuals and communities. This is essential in housing dynamics research and user perception studies as it offers insights into how urban environments affect human behavior and well-being.
Imperative Constituents of Selected Research Scenarios
- Interdisciplinary Integration: This imperative recognizes that complex research topics frequently necessitate a pluri-epistemological approach to gain a thorough understanding of the phenomena or the challenges being studied. Hybrid scenario development and integrated socio-spatial analysis exemplify interdisciplinary integration by merging experiential analysis with advanced spatial tools such as GIS and AI and by applying sociological theories within the context of spatial analysis. This imperative enables a comprehensive understanding of complex architectural and urban phenomena and allows for richer insights into both the qualitative and quantitative aspects of the phenomena being examined.
- Empirical Validation: The emphasis of this imperative is on ensuring that research scenarios go beyond theoretical constructs and become practical tools for real-world applications. The revised phenomenological approach in architecture and the integration of environmental psychology into urban studies ensure that research scenarios are grounded in the practicalities of the real world. This involves the collection and analysis of empirical data to assess the applicability of the scenarios, ensuring they effectively bridge the gap between theoretical conceptualizations and practical realities. The objective, in this sense, is to evaluate how successfully these scenarios convert theoretical knowledge into implementable strategies and insights that have a tangible impact.
- Triadic Structuring: Triads are made up of three interconnected elements and are an important imperative addressed in the five scenarios. This imperative organizes the scenarios in a systematic manner and engages in a process of identifying key interconnected elements within a research scenario and the way in which they contribute to a structured understanding of the components with a research domain or topic.
- Multidimensional Exploration: Multidimensional exploration is emphasized as an imperative that entails identifying and examining the various dimensions or facets of the research topic. It considers diverse viewpoints and the understanding of how they interact to provide a well-rounded perspective that speaks to various aspects of the research challenge being addressed.
- Adaptation and Refinement: Given the dynamic nature of research in architecture and urbanism, this imperative is crucial for upholding scenarios to remain flexible and adaptable as new challenges emerge, as new knowledge develops, and as the overall research landscape evolves. Because of this adaptability, the scenarios can be updated and refined to remain relevant and effective in addressing emerging challenges in various contexts.
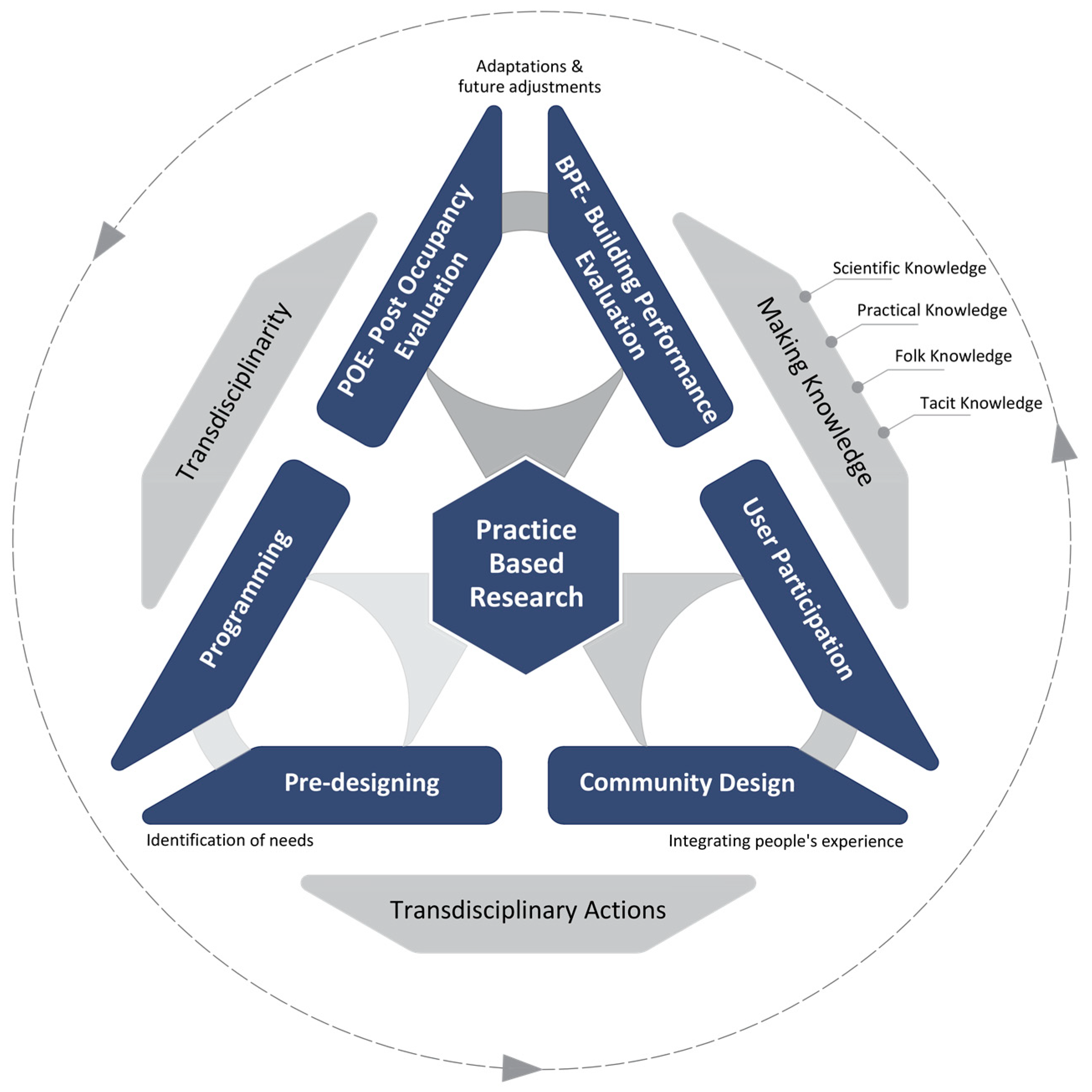
3. Scenario 1: Practice-Based Research
3.1. Theoretical Tenets of Practice-Based Research
3.2. Components of Practice-Based Research
3.2.1. Programming: Articulating Architectural Values and Goals
3.2.2. Post-Occupancy Evaluation and Building Performance Evaluation: Learning from Experience and Precedents
3.2.3. Community Design and User Participation: Fostering Democratic Architecture
3.3. Operationalization of Practice-Based Research Scenario
- The Changing Role of Architects: The conventional role of architects is undergoing a paradigm shift, driven by technological advancements and rapid societal value changes. Integrated design and construction teams are replacing pure design practices, making architects key team players in a spectrum of responsibilities. From programming and feasibility analysis to construction management and building operation, architects are adapting to a more interactive agenda that redefines their societal and professional impact.
- Challenges in Architectural Education: Architectural education faces challenges in aligning with the evolving professional landscape. The traditional architectural studio often perpetuates an egoist role model, limiting students to a singular view of design. To address this, contemporary teaching practices must expose students to diverse architect role models which emanate from the three components of practice-based research, which adopt and employ critical thinking and evidence-based decision making as core skills.
- Transdisciplinary Pedagogy: A responsive pedagogy in architecture demands a departure from conventional models. Concepts such as programming, post-occupancy evaluation, and user participation are becoming integral to design teaching. The community/university-learning lab concept, embodied in ‘design-build’ or ‘live projects’, immerses students in real-world design problems through an action research approach that fosters a transdisciplinary knowledge production and evidence-based design decision making.
- Integration of Ethical Considerations: Ethical considerations play a pivotal role in the future of architectural education and practice. Integrating social and ethical approaches to design requires exposing students to alternative social roles and user needs. In this respect, programming and post-occupancy evaluation become important vehicles for making ethical design decisions while emphasizing their impact on the well-being of users and rigorous learning from precedents.
- Knowledge Types and Transdisciplinarity: Knowledge making within the architectural profession involves four distinct types: scientific expert knowledge, folk knowledge, practical knowledge, and tacit knowledge. Transdisciplinarity emerges as a guiding principle that places emphasis on the holistic integration of these knowledge types, ethical considerations, and responsive decision making. Notably, this underscores the unique knowledge-building mode in architectural design.
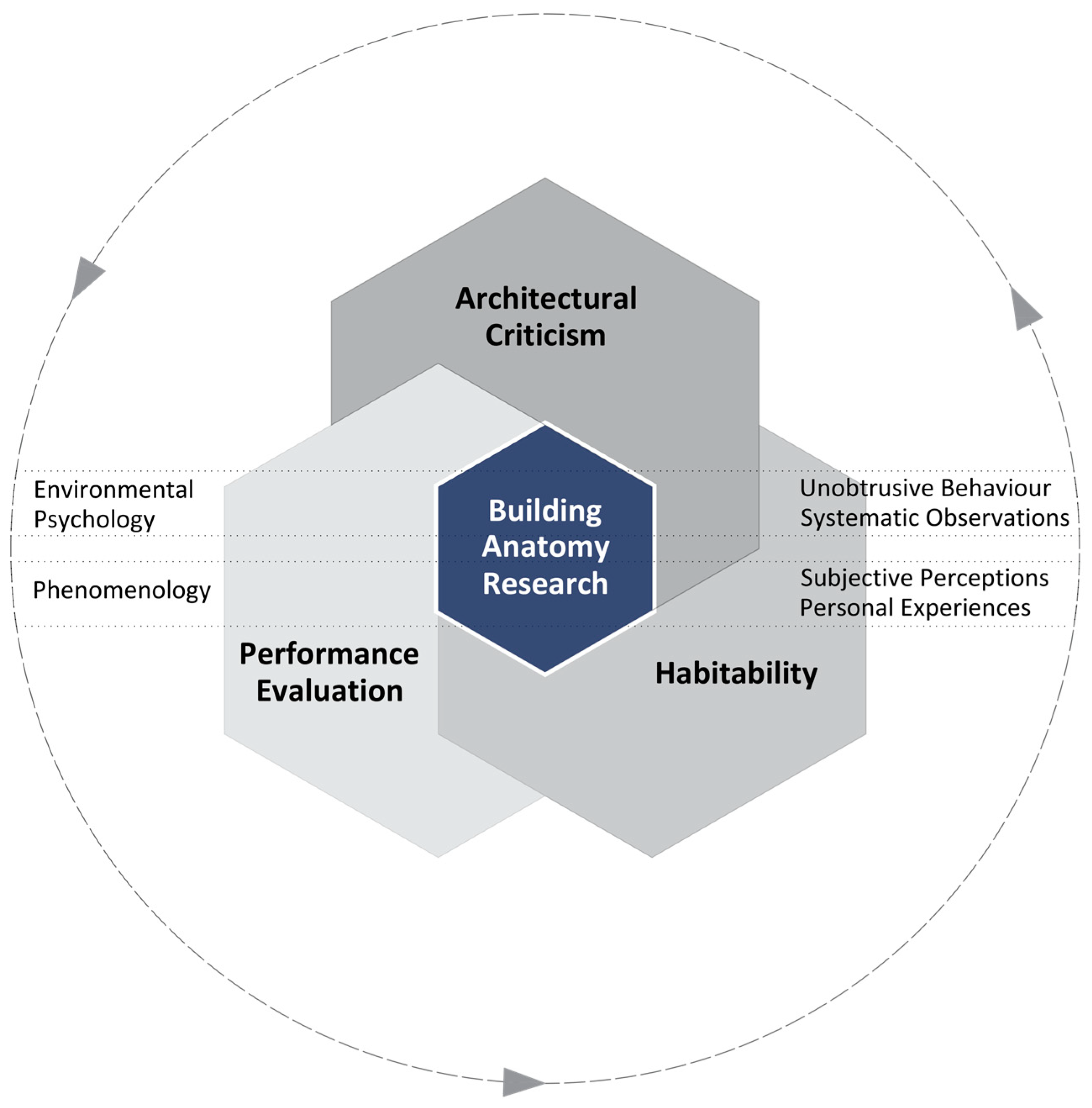
4. Scenario 2: Building Anatomy Research
4.1. Theoretical Tenets of Building Anatomy Research
4.2. Components of Building Anatomy Research
4.2.1. Architectural Criticism
4.2.2. Building Performance Evaluation (BPE)
4.2.3. Habitability
4.3. Operationalization of Building Anatomy Research
- Content Analysis for Architectural Criticism: Content analysis served as an invaluable approach involving a selection of 33 articles and clippings representing diverse perspectives, including those of the architect/design team, the client/Glasgow City Council, professional organizations, architects, and critics. Through systematic examination, content analysis effectively confirmed the framework’s ability to critique various dimensions including the museum’s role in the city, its position within the architectural community, design metaphors, building form, and the overall design quality.
- Walking Tour Assessment (PLANDES) for Performance Evaluation: The utilization of PLANDES (Planning, Landscaping, Designing) for structured walking tour assessments involving a six-point Likert Scale validated the framework’s effectiveness in evaluating performance aspects such as planning and zoning, landscaping, and designing. The engagement of 25 postgraduate students in the assessment demonstrated the capability to provide a structured assessment of the spatial environment.
- Examining Emotional Reactions: Soliciting responses from 22 participants who had visited the museum and analyzing their emotional reactions at 12 identified locations confirmed the framework’s ability to assess habitability and user perspectives. The tool efficiently assessed user satisfaction and emotional reactions.
- Direct Observation, and Behavioral and Navigational Mapping: Mapping users’ behavior and activities, coupled with direct observation, efficiently documented the spatial experience, providing valuable insights into attitudes and behaviors. Structured observations of activities, settings, and timings, essential to avoid redundancy [49], have been implemented. Employing contemplating settings (place-centered) and navigational mapping (user-centered) [50,51,52] reinforced effectiveness in establishing a clear relationship between architectural criticism (what is writing about the building), performance evaluation and habitability (how it performs).
5. Scenario 3: City Dynamics Research
5.1. Theoretical Tenets of City Dynamics Research
5.2. Components of City Dynamics Research
5.2.1. Urban Governance Triad
5.2.2. Spatial Practice Triad
5.2.3. Identification Process Triad
5.3. Operationalization of City Dynamics Research
- Understanding the Historical Evolution of Urban Governance: Conducting a historical analysis was critical in tracing the impacts of urban governance on urban transformation processes in Doha. This involved the examination of archival records, policy documents, and historical data to map the introduction of investment strategies, new development visions and master planning processes. This approach assisted in identifying and anticipating the new challenges that lead to the establishment of a diversified economy to address them.
- Analysis of Company Networks in a Knowledge Economy Context: This objective investigated the networks of multi-branch companies that established offices in Doha. Employing comprehensive network analyses, this entry investigated the structures and role of these companies at local, regional, and global levels. This analysis served as a key indicator of the current state of economic transformation in Qatar’s capital city revealing connections and complexities in the new knowledge economies.
- Understanding the Role of the “Expatriate Professionals” in Urbanism: This objective examined the burgeoning “creative class” in Doha, which comprised migrant professionals and was a consequence of the emergence of new economic sectors. The approach included sociocultural surveys and interviews to explore how individuals from diverse backgrounds perceive and experience their urban surroundings. It validated the importance of various socio-cultural groups in redefining urbanism in emerging cities, shedding light on the social dynamics that result from its development and evolution.
- Analysis of the Spatial Transformations to Accommodate Economic Growth: The spatial analysis of the urban fabric provided insights into how urban structures in Doha transformed to accommodate the needs of companies, inhabitants, and acclimatize to the visions of rapid urban growth. This approach examined the formation of new urban centers, spatial accessibility, and transformation in urban areas and residential neighborhoods to align with new economies and emerging spatial practices.
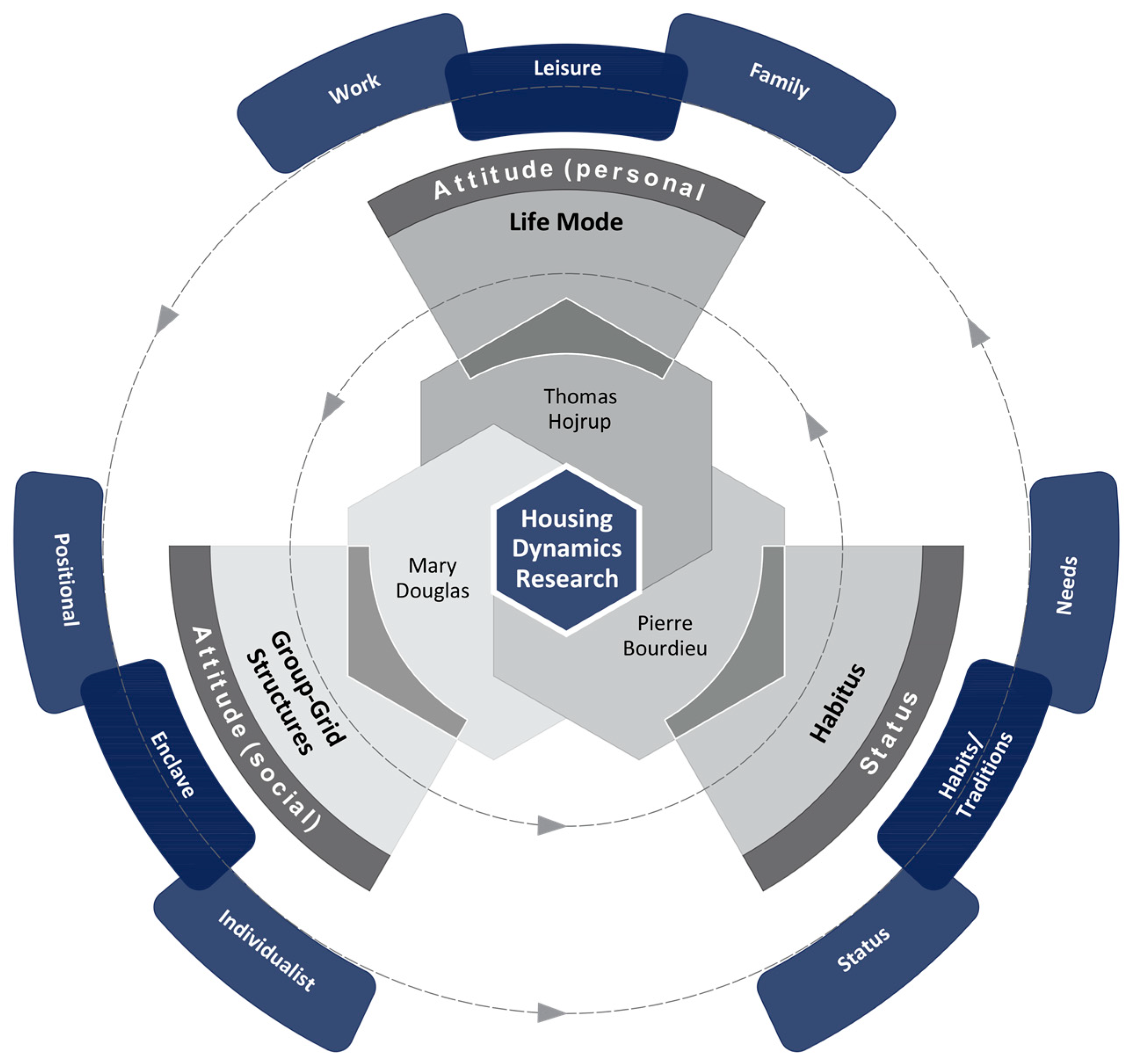
6. Scenario 4: Housing Dynamics Research
6.1. Theoretical Tenets of Housing Dynamics Research
6.2. Components of the Housing Dynamics Research
6.2.1. The Habitus Triad
6.2.2. The Group–Grid Structure Triad
6.2.3. Life Mode Triad
6.3. Operationalization of Housing Dynamics Research
- Understanding Housing Typological Transformations: A thorough literature review was conducted to identify contextual factors affecting housing typological transformations in Gulf Cities. The review examined global housing development trends and scientific theories related to lifestyles.
- Analysis of New Lifestyles in Housing: Employing attitude surveys and ethnographic studies, this phase measured neighborhood satisfaction and perceptions of societal changes relevant to housing choices. It identified emerging lifestyle dynamics within local housing market and urban development while mapping them to various sociocultural and socio-economic groups. This offered a validation of the concept of evolving lifestyles and emphasized the need for adaptable housing types.
- Scenario Planning: The introduction of housing guidelines, considered in diverse Gulf contexts, facilitated the development of approaches for future housing development. This validated the framework’s effectiveness in anticipating changes in socio-cultural, economic, and environmental factors which further emphasized the framework’s capacity to address multiple factors amenable to improving housing projects.
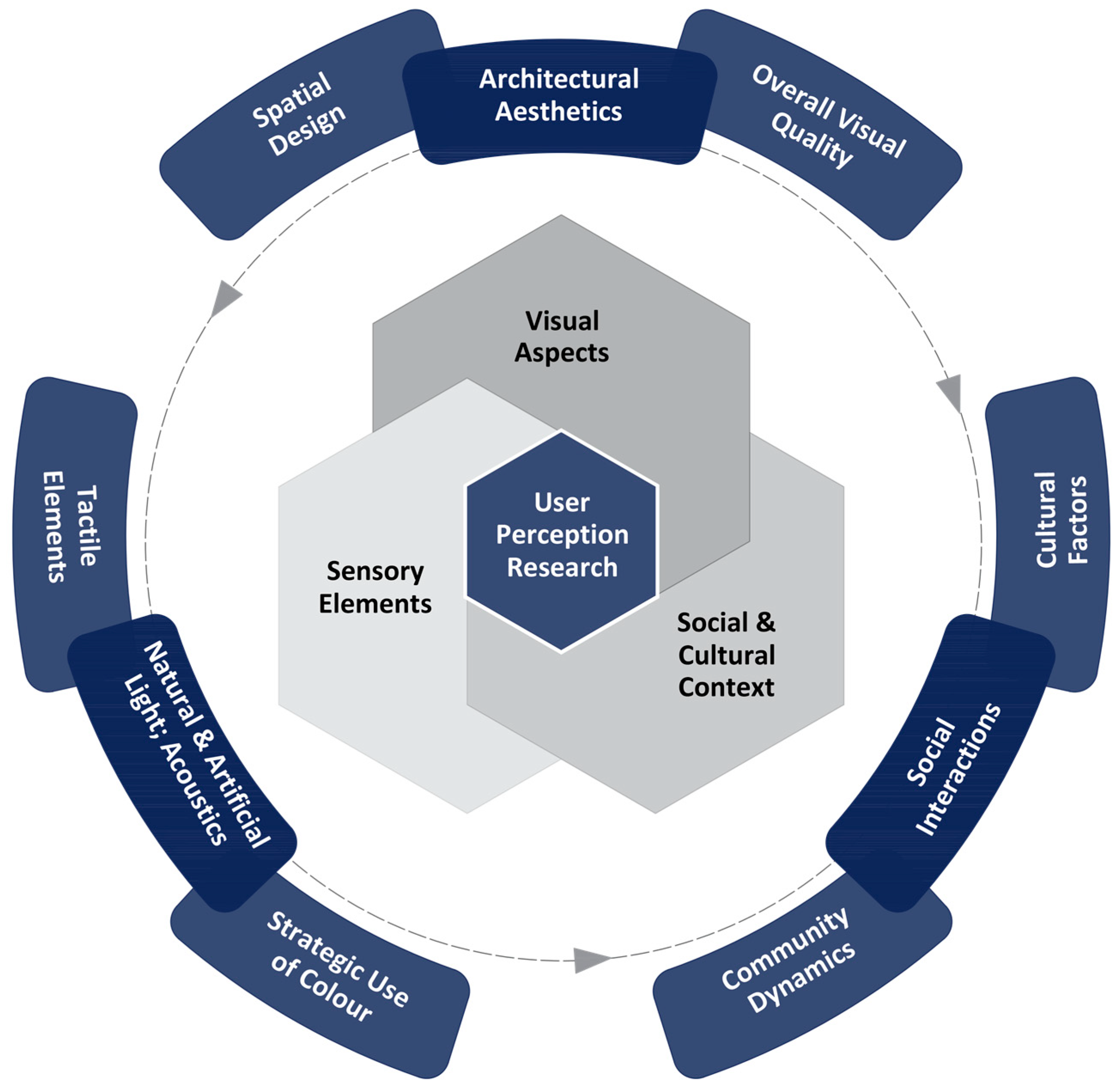
7. Scenario 5: A Multidimensional Examination of User Perceptions
7.1. Theoretical Tenets Guiding the User Perceptions Research
7.2. Components of the User Perceptions Research
- Visual Aspects: This triad engages in a comprehensive examination of how individuals interpret the visual attributes of their built surroundings. It delves into the realms of architectural aesthetics, spatial design, and the overall visual quality of the environment [69,70,74]. Researchers undertaking this exploration can discover the subjective aspects of what individuals find visually appealing in their built environment. This encompasses a nuanced analysis of building design, urban landscapes, streetscapes, and aesthetic preferences to uncover the elements that captivate and enhance the visual experience of users.
- Sensory Elements: Shifting the focus to the sensory realm, the second triad probes into the interplay between individuals and their environment [66,67]. It investigates the profound influence of sensory factors on user experiences. This includes a detailed examination of the interplay of natural and artificial light, the acoustic environment, tactile elements such as textures, and the strategic use of color [74,75,76,77]. In this sense, it aims to disclose how these sensory elements dynamically shape users’ perceptions and evoke specific feelings.
- Social and Cultural Context: This triad expands the exploration to encompass the broader societal and cultural context in which the built environment exists. It explores the complex network of social interactions, community dynamics, and cultural elements that significantly impact the way in which people perceive and engage with their environment [76,77,78]. Researchers can examine the relationship between the social environment, local community norms, and cultural context and how they shape users’ perceptions and behaviors. This holistic understanding acknowledges that user experiences are not isolated but intricately connected to the social and cultural fabric of the community.
7.3. Operationalization of the User Perceptions Research
- Sorting Tasks: These tasks [80,81] were conducted to evaluate the framework’s ability to categorize and prioritize visual and social/cultural aspects of user perception of density. Participants sorted various images representing different degrees of density (low, moderate, high) based on their perceived significance and similarity of the content. The results demonstrated the capacity of this approach to effectively capture the multidimensional nature of user perceptions. This entry identified 63 factors covering built form, site organization, emotional responses, and other aspects, which would have not been identified using traditional methods.
- Situation Judgment Tasks: These tasks [82] were designed to assess the framework’s applicability in practical decision-making situations related to urban planning and design. Participants were presented with situations depicting different density situations, and their judgments (positive or negative) were analyzed against the established factors. The outcomes indicated that this technique provides a practical and relevant tool for making informed decisions, aligning with user perceptions in diverse urban contexts.
- Image Segmentation Analysis: Employing image segmentation techniques [82], the effectiveness of the framework in dissecting and interpreting visual components within urban environments was rigorously tested. Image datasets comprising diverse built environments with varying density levels were segmented into eight components: buildings, vegetation, sky, streets, people, vehicles, pavements, and streetscape elements. The framework demonstrated accuracy in identifying and categorizing these visual elements, showcasing its robustness in analyzing the visual aspects of user perception. Additionally, it facilitated the identification of the proportion of each element relative to the respective density level.
- Applications to Real-World Cases: The framework underwent practical application to real-world cases, encompassing high-density situations globally, with a specific focus on the city of Glasgow. The objective was to validate whether the results align with those derived from Glasgow’s urban environment, considering the contextual variations in built environments and user perceptions of density. While the factors influencing user perception of density remained consistent, the proportion of the built environment varied. This variability is attributed to the relative nature of density, often dependent on the visual composition within a specific frame of reference [82]. The findings derived from these applications underscored the framework’s capacity to uncover meaningful insights and offer valuable inputs for informing urban planning and design strategies.
8. Conclusions: Prospects for Research in Architecture and Urbanism
8.1. Deriving Framework Components from Theoretical Foundations
8.2. Contribution to Architectural and Urban Discourse
8.3. Transforming Theories into Research Frameworks
8.4. Operationalizing Theoretical Frameworks in Architectural and Urban Research
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kiyashchenko, L. Philosophy of Transdisciplinarity: Approaches to the Definition. Transdiscipl. J. Eng. Sci. 2017, 8, 20–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Piaget, J. L’Epistémologie des Relations Interdisciplinaires. In Band 1 Wissenschaft als interdisziplinäres Problem, Teil 1; Schwarz, R., Ed.; De Gruyter: Boston, MA, USA; Berlin, Germany, 1974; pp. 154–172. [Google Scholar]
- Morin, E. On Complexity. Advances in Systems Theory, Complexity and the Human Sciences; Hampton Press: Cresskill, NJ, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Nicolescu, B.; Voss, K.C. Manifesto of Transdisciplinarity; State University of New York Press: Albany, NY, USA, 2002; pp. 39–48. [Google Scholar]
- Franz, J.M. A critical framework for methodological research in architecture. Des. Stud. 1994, 15, 433–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groat, L.N.; Wang, D. Architectural Research Methods; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Salama, A. Post-professional Architecture and Academia. In Neo-liberalism and the Architecture of the Post Professional Era; Sadri, H., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 271–277. [Google Scholar]
- Klein, J.T. Reprint of “Discourses of Transdisciplinarity: Looking back to the future”. Futures 2015, 65, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salama, A.M. Integrationist triadic agendas for city research: Cases from recent urban studies. J. Archit. Urban. 2019, 43, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pohl, C. Core Terms in Transdisciplinary Research. In Handbook of Transdisciplinary Research; Hadorn, G.H., Pohl, C., Hoffmann-Riem, H., Biber-Klemm, S., Grossenbacher-Mansuy, W., Wiesmann, U., Zemp, E., Eds.; Spinger: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; pp. 427–432. [Google Scholar]
- Dunin-Woyseth, H.; Nielsen, L.M. Discussing Transdisciplinarity: Making Professions and the New Mode of Knowledge Production: The Nordic Reader 2004; AHO, The Oslo School of Architecture and Design: Oslo, Norway, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Doucet, I.; Janssens, N. Editorial: Transdisciplinarity, the Hybridisation of Knowledge Production and Space-Related Research. In Transdisciplinary Knowledge Production in Architecture and Urbanism: Towards Hybrid Modes of Inquiry; Doucet, I., Janssens, N., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2010; pp. 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence, R.J.; Després, C. Futures of Transdisciplinarity. Futures 2004, 36, 397–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Pickett, S.T.A.; McPhearson, T. Conceptual frameworks facilitate integration for transdisciplinary urban science. npj Urban Sustain. 2021, 1, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanoff, H. Integrating Programming, Evaluation and Participation in Design (Routledge Revivals): A Theory Z Approach, 1st ed.; Routledge: London, UK, 2016; pp. 1–127. [Google Scholar]
- Preiser, W.F.E.; Rabinowitz, H.Z.; White, E.T. Post-Occupancy Evaluation; Van Nostrand Reinhold Company Limited: New York, NY, USA, 1988; pp. 16–97. [Google Scholar]
- Preiser, W.; Nasar, J. Assessing Building Performance: Its Evolution from Post-Occupancy Evaluation. Archnet-IJAR Int. J. Archit. Res. 2008, 2, 84–99. [Google Scholar]
- Norberg-Schulz, C. Genius Loci: Towards a Phenomenology of Architecture; Rizzoli: New York, NY, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Sanoff, H. Three Decades of Design and Community: History of the Community Development Group; NC State University, School of Architecture, College of Design: Raleigh, NC, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Hershberger, R.G. Architectural Programming and Predesign Manager; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Sanoff, H. Methods of Architectural Programming; Dowden, Hutchinson & Ross: Stroudsburg, PA, USA, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Alexander, C.; Ishikawa, S.; Silverstein, M.; Jacobson, M.; Fiksdahl-King, I.; Shlomo, A. A Pattern Language: Towns, Buildings, Construction; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Habraken, N.J. Towards a new professional role. Des. Stud. 1986, 7, 139–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habraken, N.J. To tend a garden: Thoughts on strengths and limits of studio pedagogy. In Design Studio Pedagogy: Horizons for the Future; Salama, A.M., Wilkinson, N., Eds.; Urban International Press: Gateshead, UK, 2007; pp. 11–17. [Google Scholar]
- Sanoff, H. Community Participation Methods in Design and Planning; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Davidoff, P. Advocacy and Pluralism in Planning. J. Am. Inst. Plan. 1965, 31, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, W.R.; Cuff, D. Architects’ People; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Salama, A.M. Media coverage and users’ reactions: Al Azhar Park in Cairo re-examined. In Architecture beyond Criticism: Expert Judgment and Performance Evaluation; Preiser, W.F.E., Davis, A.T., Salama, A.M., Hardy, A., Eds.; Taylor & Francis: London, UK, 2014; pp. 91–103. [Google Scholar]
- Salama, A.M. Design Intentions and Users Responses: Assessing Outdoor Spaces of Qatar University Campus. Open House Int. 2009, 34, 82–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salama, A.; Salingaros, N.; MacLean, L. A Multimodal Appraisal of Zaha Hadid’s Glasgow Riverside Museum—Criticism, Performance Evaluation, and Habitability. Buildings 2023, 13, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidegger, M. The Basic Problems of Phenomenology; Indiana University Press: Bloomington, IN, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Husserl, E. Ideas: General Introduction to Pure Phenomenology; Routledge: Oxfordshire, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Merleau-Ponty, M.; Smith, C. Phenomenology of Perception; Humanities Press: New York, NY, USA, 1962. [Google Scholar]
- Preiser, W.F.E.; Hardy, A. Historical review of building performance evaluation. In Architecture Beyond Criticism: Expert Judgment and Performance Evaluation; Preiser, W.F.E., Davis, A.T., Salama, A.M., Hardy, A., Eds.; Routledge: London, UK, 2014; pp. 181–193. [Google Scholar]
- Mahdavi, A. Steps to a General Theory of Habitability. Hum. Ecol. Rev. 1998, 5, 23–30. [Google Scholar]
- Casals Tres, M.; Arcas Abella, J.; Cuchí Burgos, A.; Altés Arlandis, A. Habitability, the Scale of Sustainability. In Proceedings of the CISBAT 2009 Renewables in changing climate, Lausanne, Switzerland, 2–3 September 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Sharp, D. Criticism in Architecture. In Proceedings of the Regional Seminar of the Aga Khan Award for Architecture, Valetta, Malta, 7–9 December 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Attoe, W. Architecture and Critical Imagination; Wiley: Chichester, UK, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Fisher, T. Making Criticism More Critical. J. Archit. Educ. 2009, 62, 14–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silverstein, M.; Van Der Ryn, S. Dorms at Berkeley; An Environmental Analysis; Center for Planning and Development Research, University of California: Berkeley, CA, USA, 1967. [Google Scholar]
- Hsia, V.W.-T. Residence Hall Environment, A Comparative Study in Architectural Psychology; University of Utah: Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 1968. [Google Scholar]
- Markus, T.A. Building Performance; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Bordass, B.; Leaman, A. Building performance evaluation in the UK: So many false dawns. In Architecture Beyond Criticism: Expert Judgement and Performance Evaluation; Preiser, W., Davis, A., Salama, A., Hardy, A., Eds.; Routledge: London, UK, 2014; pp. 194–204. [Google Scholar]
- Shibley, R. Toward a Military Construction Model for Quality Architectural Design: A Long Range Corps of Engineers Architectural Research Plan. J. Archit. Educ. 1973, 26, 87–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, A.A. Humanizing outer space: Architecture, habitability, and behavioral health. Acta Astronaut. 2010, 66, 890–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lantrip, D.B. ISOKIN: A quantitative model of the kinesthetic aspects of spatial habitability. In Proceedings of the Human Factors Society Annual Meeting, Dayton, OH, USA, 29 September–3 October 1986; pp. 33–37. [Google Scholar]
- Cubillos-González, R.-A. Testing habitability for sustainable building design. Teka Kom. Archit. Urban. Stud. Kraj. 2015, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- APA. Sociofugal. In APA Dictionary of Psychology; American Psychological Association (APA): Worcester, MA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Kelly, G. A brief introduction to personal construct theory. Costruttivismi 2017, 4, 3–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommer, R.; Sommer, B.B. A Practical Guide to Behavioral Research: Tools and Techniques, 5th ed.; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Ng, C.F. Behavioral Mapping and Tracking. In Research Methods for Environmental Psychology; Gifford, R., Ed.; Wiley Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 29–51. [Google Scholar]
- Klein, C.; Kuhnen, A.; Longhinotti Felippe, M.; Barboza da Silveira, B. Place-Centered or Person-Centered? Considerations about the Behavioral Mapping Approach. Temas Em Psicol. 2018, 26, 605–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefebvre, H.; Nicholson-Smith, D. The Production of Space; Blackwell: Oxford, UK, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Salama, A.; Wiedmann, F.; Thierstein, A.; Alghatam, W. Knowledge economy as an initiator of sustainable urbanism in emerging metropolises: The case of Doha, Qatar. Archnet-IJAR Int. J. Archit. Res. 2016, 10, 274–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiedmann, F.; Salama, A.M. Building Migrant Cities in the Gulf: Urban Transformation in the Middle East; I. B. Tauras & Co.: Bloomsbury: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Bourdieu, P. Distinction: A Social Critique of the Judgement of Taste; Harvard University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Benedikter, R. Lifestyles. In Encyclopedia of Global Studies; Anheier, H.K., Juergensmeyer, M., Faessel, V., Eds.; SAGE: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2012; pp. 1076–1080. [Google Scholar]
- Douglas, M. Natural Symbols: Explorations in Cosmology; Pelican Books: London, UK, 1970. [Google Scholar]
- Douglas, M. A History of Grid and Group Cultural Theory; University of Toronto: Toronto, ON, Canada, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Højrup, T. State, Culture, and Life-Modes: The Foundations of Life-Mode Analysis; Routledge: London, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Salama, A. Trans-Disciplinary Knowledge for Affordable Housing. Open House Int. 2011, 36, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, E.; Sabater, A. Population Change and Housing Across the Life-Course: Demographic Perspectives, Methodological Challenges and Emerging Issues; CPC Centre for Population Change: Southampton, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Veblen, T. The Theory of the Leisure Class; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Salama, A. A Lifestyle Theories Approach for Affordable Housing Research in Saudi Arabia. Emir. J. Eng. Res. 2006, 11, 67–76. [Google Scholar]
- Lynch, K. The image of the city; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Rapoport, A. The Meaning of the Built Environment: A Nonverbal Communication Approach; University of Arizona Press: Tucson, AZ, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Rapoport, A. Human Aspects of Urban Form: Towards a Man-Environment Approach to Urban Form and Design; Pergamon Press: Oxford, UK, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Moore, G.T. Environmental Aesthetics. In Handbook of Environmental Psychology; Stokols, D., Altman, I., Eds.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1987; Volume 1, pp. 827–872. [Google Scholar]
- Nasar, J.L. Perception, Cognition, and Evaluation of Urban Places. In Public Places and Spaces; Altman, I., Zube, E.H., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1989; pp. 31–56. [Google Scholar]
- Nasar, J.L. The Evaluative Image of the City. J. Am. Plan. Assoc. 1990, 56, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, R.; Kaplan, S. The Experience of Nature: A Psychological Perspective; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Ewing, R.H. Characteristics, Causes, and Effects of Sprawl: A Literature Review. In Urban Ecology: An International Perspective on the Interaction between Humans and Nature; Marzluff, J.M., Shulenberger, E., Endlicher, W., Alberti, M., Bradley, G., Ryan, C., Simon, U., ZumBrunnen, C., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2008; pp. 519–535. [Google Scholar]
- Ewing, R.; Handy, S.; Brownson, R.C.; Clemente, O.; Winston, E. Identifying and Measuring Urban Design Qualities Related to Walkability. J. Phys. Act. Health 2006, 3, S223–S240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gjerde, M. Visual Aesthetic Perception and Judgement of Urban Streetscapes. In Proceedings of the 18th CIB World Building Congress, Salford, UK, 10–13 May 2010; CIB Publication: Geneva, Switzerland, 2010; Volume 338, pp. 12–22. [Google Scholar]
- Erwine, B. Creating Sensory Spaces: The Architecture of the Invisible; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Goodey, B.; Gold, J. Environmental Perception: The Relationship with Urban Design. Prog. Hum. Geogr. 1987, 11, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degen, M.; Rose, G. The Sensory Experiencing of Urban Design: The Role of Walking and Perceptual Memory. Urban Stud. 2012, 49, 3271–3287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapoport, A. The Mutual Interaction of People and their Built Environment: A Cross-Cultural Perspective; De Gruyter Mouton: Berlin, Germany; New York, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Patil, M.P. The Role of Urban Form in the Perception of Density. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Strathclyde, Glasgow, UK, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Barnett, J. The Multiple Sorting Procedure (MSP). In Doing Social Psychology Research; Breakwell, G.M., Ed.; The British Psychological Society and Blackwell Publishing Ltd.: Malden, MA, USA, 2004; pp. 289–304. [Google Scholar]
- Canter, D.; Groat, J. A Multiple Sorting Procedure for Studying Conceptual Systems. In The Research Interview: Uses and Approaches; Brenner, M., Canter, D., Brown, J., Eds.; Academic Press: London, UK, 1985; pp. 79–114. [Google Scholar]
- Whetzel, D.; Sullivan, T.; McCloy, R. Situational Judgment Tests: An Overview of Development Practices and Psychometric Characteristics. Pers. Assess. Decis. 2020, 6, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Approaches and Tools | Transdisciplinary Research Scenarios | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Practice-Based Research | Building Anatomy Research | City Dynamics Research | Housing Dynamics Research | User Perception Research | |
| GIS Analysis | |||||
| Surveys | |||||
| Scenario Planning | |||||
| Content Analysis | |||||
| Walking Tour Assessments | |||||
| User Perspectives | |||||
| User Participation | |||||
| Sorting Tasks | |||||
| Situation Judgement Tasks | |||||
| Image Segmentation Analysis | |||||
| Historical Analysis | |||||
| Network Analysis | |||||
| Sociocultural Surveys | |||||
| Ethnographic Studies | |||||
| Community Design | |||||
| Architectural Criticism | |||||
| Programming | |||||
| Post-Occupancy Evaluation | |||||
| Performance Evaluation | |||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Salama, A.M.; Patil, M.P. Unpacking Transdisciplinary Research Scenarios in Architecture and Urbanism. Encyclopedia 2024, 4, 352-378. https://doi.org/10.3390/encyclopedia4010025
Salama AM, Patil MP. Unpacking Transdisciplinary Research Scenarios in Architecture and Urbanism. Encyclopedia. 2024; 4(1):352-378. https://doi.org/10.3390/encyclopedia4010025
Chicago/Turabian StyleSalama, Ashraf M., and Madhavi P. Patil. 2024. "Unpacking Transdisciplinary Research Scenarios in Architecture and Urbanism" Encyclopedia 4, no. 1: 352-378. https://doi.org/10.3390/encyclopedia4010025
APA StyleSalama, A. M., & Patil, M. P. (2024). Unpacking Transdisciplinary Research Scenarios in Architecture and Urbanism. Encyclopedia, 4(1), 352-378. https://doi.org/10.3390/encyclopedia4010025








