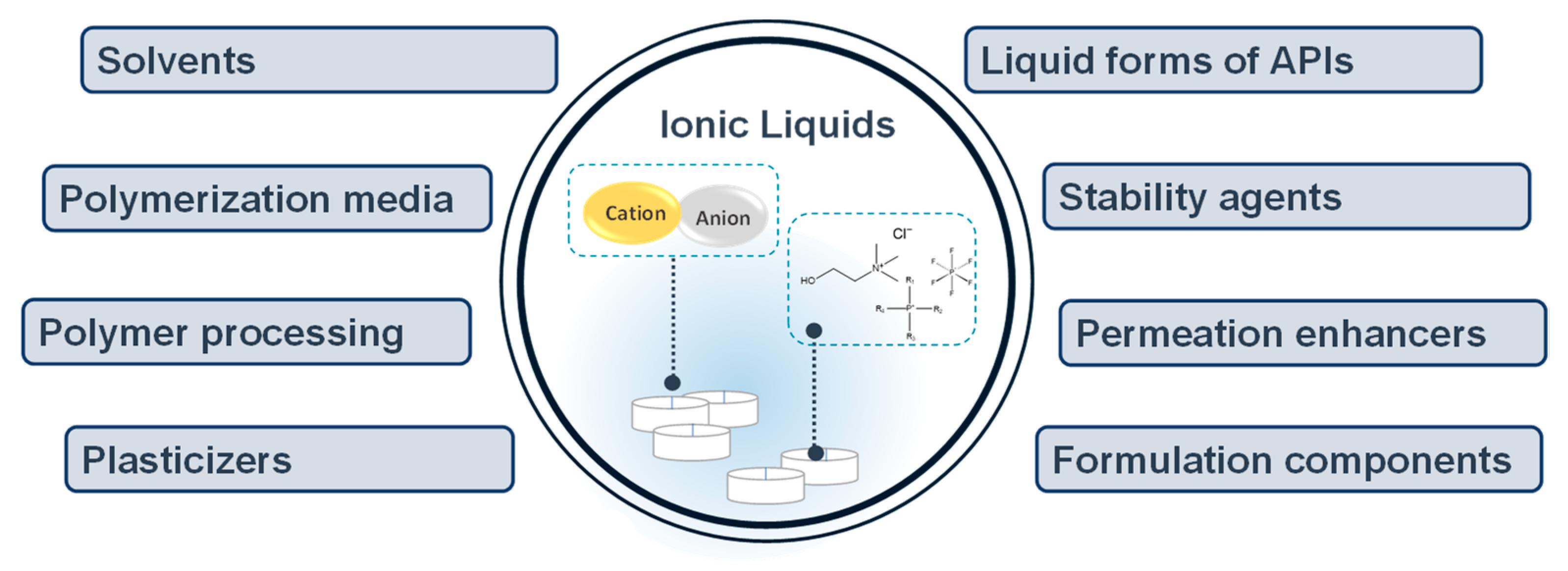
Ionic Liquids in Drug Delivery
Definition
1. Introduction
2. Applications of Ionic Liquids in Drug Delivery
2.1. ILs as Novel Solvents of APIs
2.2. Liquid Forms of APIs
2.3. ILs as Permeation Enhancers and Microemulsion Components for Drug Delivery
2.4. ILs as Novel Solvents of (Bio)Polymers
3. ILs in the Development of (Bio)Polymer-Based Drug Delivery Systems
4. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Entry Link on the Encyclopedia Platform:
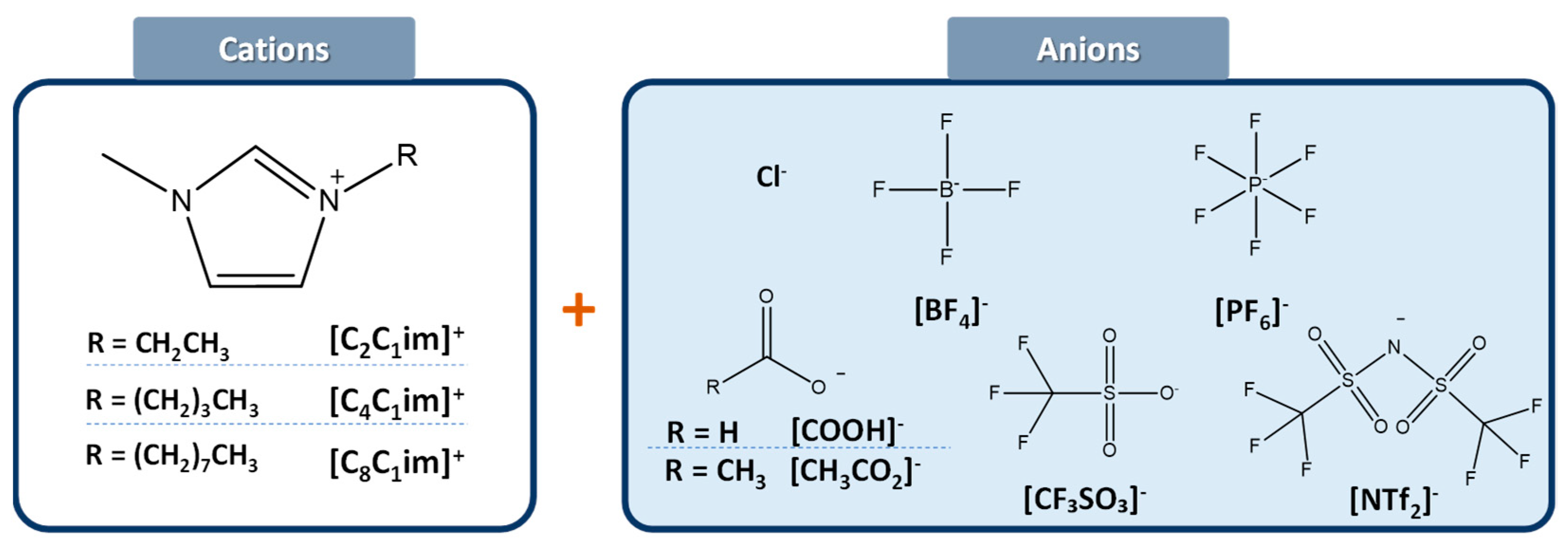
ILs Abbreviations
| [C2C1im][CH3CO2] | 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium acetate |
| [C4NH3][CH3CO2] | N-butylammonium acetate |
| [C6NH3][CH3CO2] | N-hexylammonium acetate |
| [C8NH3][CH3CO2] | N-octylammonium acetate |
| [C4NH3][oleate] | N-butylammonium oleate |
| [C6NH3][oleate] | N-hexylammonium oleate |
| [C8NH3][oleate] | N-octylammonium oleate |
| [C4C1im][BF4] | 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate |
| [C6C1im][BF4] | 1-hexyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate |
| [C8C1im][BF4] | 1-octyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate |
| [C4C1im][PF6] | 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate |
| [C8C1im][PF6] | 1-octyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate |
| [C6C6OCOpy][N(CN)2] | 1-hexyl-3-hexyloxycarbonylpyridinium dicyanamide |
| [C6C6OCOpy][NTf2] | 1-hexyl-3-hexyloxycarbonylpyridinium bis(trifluoromethylsulfonyl)imide |
| [C6C1im][PF6] | 1-hexyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate |
| [C4C1im]Br | 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium bromide |
| [Ch][Gly] | Cholinium glycinate |
| [Ch][Ala] | Cholinium alaninate |
| [Ch][Pro] | Cholinium prolinate |
| [Ch][Phe] | Cholinium phenylalanine |
| [Ch][Ile] | Cholinium isoleucine |
| [Ch][Ser] | Cholinium serinate |
| [Ch][Leu] | Cholinium leucinate |
| [Ran][Doc] | Ranitidinium docusate |
| [C4C1im]Cl | 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride |
| [C4C1im][CH3CO2] | 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium acetate |
| [C2C1im]Cl | 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride |
| [(CH2CH=C2)C1im]Br | 1-allyl-3-methylimidazolium bromide |
| [(CH2CH=C2)C1im]Cl | 1-allyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride |
| [PSC1im][CH3CO2] | 1-methy-3-(3-sulfopropyl) imidazolium acetate |
| [PSC4im][CH3CO2] | 1-butyl-3-(3- sulfopropyl) imidazolium acetate |
| [C4py][BF4] | 1-butyl-3-pyridinium tetrafluoroborate |
| [C2C1im][NTf2] | 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide |
| [C4C1im][NTf2] | 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium bis(trifluoromethylsulfonyl)imide |
| [C2C1im][CF₃SO₃] | 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium trifluoromethanesulfonate |
| [C4C1im][CF₃SO₃] | 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium trifluoromethanesulfonate |
| [C2C1im][BF4] | 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate |
| [C8C1im][NTf2] | 1-octyl-3-methylimidazolium bis[trifluoromethylsulfonyl]amide |
| [C4C1im][HCOO] | 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium formate |
References
- Tiwari, G.; Tiwari, R.; Bannerjee, S.; Bhati, L.; Pandey, S.; Pandey, P.; Sriwastawa, B. Drug delivery systems: An updated review. Int. J. Pharm. Investig. 2012, 2, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shamshina, J.L.; Rogers, R.D. Overcoming the problems of solid-state drug formulations with ionic liquids. Ther. Deliv. 2014, 5, 489–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byrn, S.; Pfeiffer, R.; Ganey, M.; Hoiber, C.; Poochikian, G. Pharmaceutical Solids: A Strategic Approach to Regulatory Considerations. Pharm. Res. 1995, 12, 945–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, K.K. Current Status and Future Prospects of Drug Delivery Systems. Methods Mol. Biol. 2014, 1141, 1–56. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Gao, H.; Wei, G.; Huang, Y.; Yu, H.; Gan, Y. Recent progress in drug delivery. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2019, 9, 1145–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barenholz, Y.C. Doxil®—The first FDA-approved nano-drug: Lessons learned. J. Control Release 2012, 160, 117–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, N.R.H.; Bicanic, T.; Salim, R.; Hope, W. Liposomal Amphotericin B (AmBisome®): A review of the pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, clinical experience and future directions. Eur. PMC Funders Group 2017, 76, 485–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cue, B.W.; Zhang, J. Green process chemistry in the pharmaceutical industry. Green Chem. Lett. Rev. 2009, 2, 193–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riebesehl, B.U. Drug Delivery with Organic Solvents or Colloidal Dispersed Systems. In The Practice of Medicinal Chemistry, 4th ed.; Elsevier Ltd.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 699–722. [Google Scholar]
- Jain, N.; Kumar, A.; Chauhan, S.; Chauhan, S.M.S. Chemical and biochemical transformations in ionic liquids. Tetrahedron 2005, 61, 1015–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivier-bourbigou, H.; Magna, L. Ionic liquids: Perspectives for organic and catalytic reactions. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2002, 183, 419–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cave, G.W.V.; Raston, L.; Scott, J.L. Recent advances in solventless organic reactions: Towards benign synthesis with remarkable versatility. Chem. Commun. 2001, 2159–2169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freire, M.G.; Cláudio, A.F.M.; Araújo, J.M.M.; Coutinho, J.A.P.; Marrucho, I.M.; Canongia Lopes, J.N.; Rebelo, L.P.N. Aqueous biphasic systems: A boost brought about by using ionic liquids. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 4966–4995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Earle, M.J.; Esperança, J.M.S.S.; Gile, M.; Lopes, J.N.C.; Rebelo, L.P.N.; Magee, J.W.; Seddon, K.R.; Widegren, J.A. The distillation and volatility of ionic liquids. Nature 2005, 439, 831–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cláudio, A.F.M.; Neves, M.C.; Shimizu, K.; Canongia Lopes, J.N.; Freire, M.G.; Coutinho, J.A.P. The magic of aqueous solutions of ionic liquids: Ionic liquids as a powerful class of catanionic hydrotropes. Green Chem. 2015, 17, 3948–3963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hough, W.L.; Rogers, R.D. Ionic Liquids Then and Now: From Solvents to Materials to Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 2007, 80, 2262–2269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, M.R.; Moshikur, R.M.; Wakabayashi, R.; Tahara, Y.; Kamiya, N.; Moniruzzaman, M.; Goto, M. Ionic-Liquid-Based Paclitaxel Preparation: A New Potential Formulation for Cancer Treatment. Mol. Pharm. 2018, 15, 2484–2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czerniak, K.; Walkiewicz, F. Synthesis and antioxidant properties of dicationic ionic liquids. New J. Chem. 2017, 41, 530–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, A.M.; Morais, E.M.; Leite, A.C.; Mohamadou, A.; Holmbom, B.; Holmbom, T.; Neves, B.M.; Coutinho, J.A.P.; Freire, M.G.; Silvestre, A.J. Enhanced Extraction and Biological Activity of 7- hydroxymatairesinol obtained from Norway Spruce knots using Aqueous Solutions of Ionic Liquids. Green Chem. 2017, 19, 2626–2635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Malhotra, S.V. Study on the potential anti-cancer activity of phosphonium and ammonium-based ionic liquids. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2009, 19, 4643–4646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malhotra, S.V.; Kumar, V. A profile of the in vitro anti-tumor activity of imidazolium-based ionic liquids. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2010, 20, 581–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Huang, W.; Song, Z.; Tang, Z.; Sun, W. Insight into Structure-Antibacterial Activity of Amino Cation- based and Acetate Anion-based Ionic Liquids from the Computational Interaction with POPC Phospholipid Bilayer. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2020, 19, 15573–15581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carson, L.; Chau, P.K.W.; Earle, M.J.; Gilea, M.A.; Gilmore, B.F.; Gorman, S.P.; Mccann, T.; Seddon, K.R. Antibiofilm activities of 1-alkyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride ionic liquids. Green Chem. 2009, 44, 492–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anvari, S.; Hajfarajollah, H.; Mokhtarani, B.; Enayati, M. Antibacterial and anti-adhesive properties of ionic liquids with various cationic and anionic heads toward pathogenic bacteria. J. Mol. Liq. 2016, 221, 685–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, P.; Nancharaiah, Y.V.; Reddy, G.K.K.; Lalithamanasa, P.; Venugopalan, V.P. The ionic liquid 1-alkyl-3-methylimidazolium demonstrates comparable antimicrobial and antibiofilm behavior to a cationic surfactant. Biofouling J. Bioadhesion Biofilm 2012, 28, 1141–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Docherty, K.M.; Kulpa, C.F. Toxicity and antimicrobial activity of imidazolium and pyridinium ionic liquids. Green Chem. 2005, 7, 185–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamshina, J.L.; Barber, P.S.; Rogers, R.D. Ionic liquids in drug delivery. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2013, 10, 1367–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cojocaru, O.A.; Bica, K.; Gurau, G.; Narita, A.; Mccrary, P.D.; Shamshina, J.L.; Barber, S.; Rogers, R.D. Prodrug ionic liquids: Functionalizing neutral active ionic liquid form. Med. Chem. Commun. 2013, 4, 559–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Liu, J.; Tian, T.; Gao, Y.; Ji, X.; Li, Z. Pharmaceutically Active Ionic Liquid Self-Assembled Vesicles for the Application as an Efficient Drug Delivery System. ChemPhysChem 2013, 14, 3454–3457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trivedi, T.J.; Srivastava, D.N.; Rogers, R.D.; Kumar, A. Agarose processing in protic and mixed protic-aprotic ionic liquids: Dissolution, regeneration and high conductivity, high strength ionogels. Green Chem. 2012, 14, 2831–2839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viau, L.; Tourné-Péteilh, C.; Devoisselle, J.M.; Vioux, A. Ionogels as drug delivery system: One-step sol-gel synthesis using imidazolium ibuprofenate ionic liquid. Chem. Commun. 2010, 46, 228–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Liu, B.; Wang, S.; Liu, T.; Fu, C.; Ren, X.; Tan, L.; Duan, W.; Meng, X. Doxorubicin-loaded Ionic Liquid-Polydopamine nanoparticles for combined chemotherapy and microwave thermal therapy of cancer. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 32434–32440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, J.W.; Hwang, J.Y.; Shin, U.S. Ionic liquid-doped and p-NIPAAm-based copolymer (p-NIBIm): Extraordinary drug-entrapping and -releasing behaviors at 38–42 °C. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 26738–26747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adawiyah, N.; Moniruzzaman, M.; Hawatulaila, S.; Goto, M. Ionic liquids as a potential tool for drug delivery systems. Med. Chem. Commun. 2016, 7, 1881–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizuuchi, H.; Jaitely, V.; Murdan, S.; Florence, A.T. Room temperature ionic liquids and their mixtures: Potential pharmaceutical solvents. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2008, 33, 326–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaitely, V.; Mizuuchi, H.; Florence, A.T. Current-stimulated release of solutes solubilized in water-immiscible room temperature ionic liquids (RTILs). J. Drug Target. 2010, 18, 787–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, H.D.; Sahbaz, Y.; Ford, L.; Nguyen, T.H.; Scammells, P.J.; Porter, C.J.H. Ionic liquids provide unique opportunities for oral drug delivery: Structure optimization and in vivo evidence of utility. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 1688–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCrary, P.D.; Beasley, P.A.; Gurau, G.; Narita, A.; Barber, P.S.; Cojocaru, O.A.; Rogers, R.D. Drug specific, tuning of an ionic liquid’s hydrophilic-lipophilic balance to improve water solubility of poorly soluble active pharmaceutical ingredients. New J. Chem. 2013, 37, 2196–2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goindi, S.; Kaur, R.; Kaur, R. An ionic liquid-in-water microemulsion as a potential carrier for topical delivery of poorly water soluble drug: Development, ex-vivo and in-vivo evaluation. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 495, 913–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, K.B.; Bridson, R.H.; Leeke, G.A. Solubilities of pharmaceutical compounds in ionic liquids. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2011, 56, 2039–2043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goindi, S.; Arora, P.; Kumar, N.; Puri, A. Development of novel ionic liquid-based microemulsion formulation for dermal delivery of 5-fluorouracil. AAPS PharmSciTech 2014, 15, 810–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalepu, S.; Nekkanti, V. Insoluble drug delivery strategies: Review of recent advances and business prospects. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2015, 5, 442–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savjani, K.T.; Gajjar, A.K.; Savjani, J.K. Drug Solubility: Importance and Enhancement Techniques. ISRN Pharm. 2012, 2012, 195727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brittain, H.G.; Grant, D.J.R. Effects of Polymorphism and Solid-State Solvation on Solubility and Dissolution Rate. In Polymorphism in Pharmaceutical Solids, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2009; pp. 436–480. [Google Scholar]
- Censi, R.; Martino, P. Di Polymorph Impact on the Bioavailability and Stability of Poorly Soluble Drugs. Molecules 2015, 20, 18759–18776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubio-Bonilla, M.V.; Londono, R.; Rubio, A. Liquid Dosage Forms. In Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Handbook: Production and Processes; John Wiley Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008; pp. 313–344. [Google Scholar]
- Hough, W.L.; Smiglak, M.; Rodríguez, H.; Swatloski, R.P.; Spear, S.K.; Daly, D.T.; Pernak, J.; Grisel, J.E.; Carliss, R.D.; Soutullo, M.D.; et al. The third evolution of ionic liquids: Active pharmaceutical ingredients. New J. Chem. 2007, 31, 1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Holmes, S.S.; Baker, G.A.; Challa, S.; Bose, H.S.; Song, Z. Ionic derivatives of betulinic acid as novel HIV-1 protease inhibitors. J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 2012, 27, 715–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bica, K.; Rogers, R.D. Confused ionic liquid ions—A “liquification” and dosage strategy for pharmaceutically active salts. Chem. Commun. 2010, 46, 1215–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bica, K.; Rijksen, C.; Nieuwenhuyzena, M.; Rogers, R.D. In search of pure liquid salt forms of aspirin: Ionic liquid approaches with acetylsalicylic acid and salicylic acid. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2010, 12, 2011–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frizzo, C.P.; Wust, K.; Tier, A.Z.; Vaucher, R.A.; Bolzan, L.P.; Terra, S.; Martins, M.A.P. Novel ibuprofenate- and docusate-based ionic liquids: Emergence of antimicrobial activity. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 100476–100486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, R.D.; Daly, D.T.; Swatloski, R.P.; Hough-Troutman, W.L.; Hough-Troutman, J.J.H.L.; Marcin, S.; Juliusz, P.; Spear, S.K. Multifunctional Ionic Liquid Compositions for Overcoming Polymorphism and Imparting Improved Properties for Active Pharmaceutical, Biological, Nutritional and Energetic Ingredients. U.S. Patent No. 8,232,265, 18 October 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez-Stefanuto, V.; Tojo, E. New Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient-Ionic Liquids (API-ILs) Derived from Indomethacin and Mebendazole. Proceedings 2019, 9, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sastry, N.V.; Singh, D.K. Surfactant and Gelation Properties of Acetylsalicylate Based Room Temperature Ionic Liquid in Aqueous Media. Langmuir 2016, 32, 10000–10016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miwa, Y.; Hamamoto, H.; Ishida, T. Lidocaine self-sacrificially improves the skin permeation of the acidic and poorly water-soluble drug etodolac via its transformation into an ionic liquid. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2016, 102, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bica, K.; Rodríguez, H.; Gurau, G.; Cojocaru, O.A.; Riisager, A.; Fehrmann, R.; Rogers, R.D. Pharmaceutically active ionic liquids with solids handling, enhanced thermal stability, and fast release. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 5422–5424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoimenovski, J.; Dean, P.M.; Izgorodina, E.I.; Macfarlane, D.R. Protic pharmaceutical ionic liquids and solids: Aspects of protonics. Faraday Discuss. 2012, 154, 335–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, P.C.A.G.; Ribeiro, D.M.G.P.; Azevedo, A.M.O.; Justina, V.D.; Cunha, E.; Bica, K.; Vasiloiu, M.; Reis, S.; Saraiva, M.L.M.F.S. Active pharmaceutical ingredients based on salicylate ionic liquids: Insights into the evaluation of pharmaceutical profiles. New J. Chem. 2013, 37, 4095–4102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, F.; Oliveira, F.S.; Oder, B.S.; Matos, C.; Marrucho, I.M. Synthesis, Characterization, and Liposome Partition of a Novel Tetracycline Derivative Using the Ionic Liquids Framework. J. Pharma Scienc. 2013, 102, 1504–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miwa, Y.; Hamamoto, H.; Hikake, S.; Kuwabara, Y. A Phase I, Randomized, Open-Label, Cross-Over Study of the Pharmacokinetics, Dermal Tolerability, and Safety of MRX-7EAT Etodolac-Lidocaine Topical Patch in Healthy Volunteers. J. Pain 2013, 14, S72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Megwa, S.A.; Cross, S.E.; Benson, H.A.E.; Roberts, M.S. Ion-pair Formation as a Strategy to Enhance Topical Delivery of Salicylic Acid. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2000, 919–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoimenovski, J.; Macfarlane, D.R. Enhanced membrane transport of pharmaceutically active protic ionic liquids. Chem. Commun. 2011, 11429–11431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zavgorodnya, O.; Shamshina, J.L.; Mittenthal, M.; McCrary, P.D.; Rachiero, G.P.; Titi, H.M.; Rogers, R.D. Polyethylene Glycol Derivatization of the Non-active Ion in Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient Ionic Liquids Enhances Transdermal Delivery. New J. Chem. 2017, 41, 1499–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furukawa, S.; Hattori, G.; Sakai, S.; Kamiya, N. Highly Efficient and Low Toxic Skin Penetrants Composed of Amino Acid Ionic Liquids. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 87753–87755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahajan, S.; Sharma, R.; Mahajan, R.K. An Investigation of Drug Binding Ability of a Surface Active Ionic Liquid: Micellization, Electrochemical, and Spectroscopic Studies. Langmuir 2012, 18, 17238–17246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, B.; Lan, N.; Qiu, J.; Zhu, Y. Interaction of Ionic Liquids with Lipid Bilayer: A Biophysical Study of Ionic Liquid Cytotoxicity. J. Phys. Chem. B 2016, 120, 2781–2789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benedetto, A.; Bingham, R.J.; Ballone, P. Structure and dynamics of POPC bilayers in water solutions of room temperature ionic liquids. J. Chem. Phys. 2015, 142, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benedetto, A.; Heinrich, F.; Gonzalez, M.A.; Fragneto, G.; Watkins, E.; Ballone, P. Structure and Stability of Phospholipid Bilayers Hydrated by a Room-Temperature Ionic Liquid/Water Solution: A Neutron Reflectometry Study. J. Phys. Chem. B. 2014, 118, 12192–12206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakrewsky, M.; Lovejoy, K.S.; Kern, T.L.; Miller, T.E.; Le, V.; Nagy, A. Ionic liquids as a class of materials for transdermal delivery and pathogen neutralization. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 13313–13318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubota, K.; Shibata, A.; Yamaguchi, T. The molecular assembly of the ionic liquid/aliphatic carboxylic acid/aliphatic amine as effective and safety transdermal permeation enhancers. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 86, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zech, O.; Thomaier, S.; Kolodziejski, A.; Touraud, D.; Grillo, I.; Kunz, W. Ionic Liquids in Microemulsions—A Concept To Extend the Conventional Thermal Stability Range of Microemulsions. Chem. Eur. J. 2010, 16, 783–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharmoria, P.; Singh, T.; Kumar, A. Complexation of chitosan with surfactant like ionic liquids: Molecular interactions and preparation of chitosan nanoparticles. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2013, 407, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solans, C.; García-Celma, M.J. Garcıa-Celma Microemulsions and Nano-emulsions for Cosmetic Applications. In Cosmetic Science and Technology; Elsevier Ltd.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 507–518. [Google Scholar]
- Dobler, D.; Schmidts, T.; Klingenhöfer, I.; Runkel, F. Ionic liquids as ingredients in topical drug delivery systems. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 441, 620–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, R.; Chowdhury, R.; Wakabayashi, R.; Kamiya, N. Ionic Liquid-In-Oil Microemulsions Prepared with Biocompatible Choline Carboxylic Acids for Improving the Transdermal Delivery of a Sparingly Soluble Drug. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, S.S.; Oliveira, N.M.; Oliveira, M.B.; Soares, D.P.; Naskar, D.; Mano, J.F.; Kundu, S.C.; Reis, R.L. Fabrication and characterization of Eri silk fibers-based sponges for biomedical application. Acta Biomater. 2016, 32, 178–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, D.M.; Drummy, L.F.; Conrady, D.G.; Fox, D.M.; Naik, R.R.; Stone, M.O.; Trulove, P.C.; De Long, H.C.; Mantz, R.A. Dissolution and Regeneration of Bombyx mori Silk Fibroin Using Ionic Liquids. JACS 2004, 126, 14350–14351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, X.; Li, X.; Chen, L.; Xie, F. Solubility of starch and microcrystalline cellulose in 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium acetate ionic liquid and solution rheological properties. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2016, 18, 27584–27593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, B.; Li, Q.; Zhuang, L.; Wang, Q.; Li, C.; Wang, G.; Xie, F.; Halley, P.J. Dissolution and Regeneration Behavior of Chitosan in 3-methyl-1-(ethylacetyl)imidazolium Chloride. Fibers Polym. 2016, 17, 1741–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Qing, M.; Chen, L.; Liu, J.; Zhong, F.; Jiang, P.; Wang, G.; Zhuang, L. Chitosan dissolution with sulfopropyl imidazolium Brönsted acidic ionic liquids. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 293, 111533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takada, A.; Kadokawa, J. Fabrication and Characterization of Polysaccharide Ion Gels with Ionic Liquids and Their Further Conversion into Value-Added Sustainable Materials. Biomolecules 2015, 5, 244–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.; Mondal, D.; Mukesh, C.; Prasad, K. Solvent responsive healing of guar gum and guar gum-multiwalled carbon nanotube nanocomposite gels prepared in an ionic liquid. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 16509–16515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remsing, R.C.; Swatloski, R.P.; Rogers, D.; Moyna, G. Mechanism of cellulose dissolution in the ionic liquid 1-n-butyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride: A 13C and 35/37Cl NMR relaxation study on model systems. Chem. Commun. 2006, 1271–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zhu, J.; Wang, X.; Huang, Y.; Wang, Z. Dissolution Behavior of Chitin in Ionic Liquids Dissolution Behavior of Chitin in Ionic Liquids. J. Macromol. Sci. Part B Phys. 2010, 49, 528–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Lu, X.; Sun, N.; Rogers, R.D. Dissolution or extraction of crustacean shells using ionic liquids to obtain high molecular weight purified chitin and direct production of chitin films and fibers. Green Chem. 2010, 12, 968–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamshina, J.L.; Barber, P.S.; Gurau, G.; Griggs, C.S.; Rogers, R.D. Pulping of crustacean waste using ionic liquids: To extract or not to extract. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 6072–6081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamshina, J.L.; Rogers, R.D. Are Ionic Liquids Enabling Technology? Startup to Scale-Up to Find Out. In Commercial Applications of Ionic Liquids, 1st ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Q.; Xu, A.; Li, Z.; Zhang, S. Influence of anionic structure on the dissolution of chitosan in 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium-based ionic liquids. Green Chem. 2011, 13, 3446–3452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero-Sanchez, C.; Erdmenger, T.; Petr, S.; Schubert, U.S. Water-Soluble Ionic Liquids as Novel Stabilizers in Suspension Polymerization Reactions: Engineering Polymer Beads. Chemistry 2006, 9036–9045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patil, C.M.; Meshram, J.S.; Borse, A.U. Ionic liquid: Green solvent for the synthesis of cellulose/guar gum/PVA biocomposite. Green Mater. 2018, 6, 23–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, S.S.; Santos, T.C.; Cerqueira, M.T.; Marques, A.P.; Reys, L.L. The use of ionic liquids in the processing of chitosan / silk hydrogels for biomedical applications. Green Chem. 2012, 14, 1463–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, F.; Wang, C.; Zhu, P. Characterization of chitosan microparticles reinforced cellulose biocomposite sponges regenerated from ionic liquid. Cellulose 2014, 21, 4405–4418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, J.F.B.; Kurnia, K.A.; Freire, M.G.; Coutinho, J.A.P.; Rogers, R.D. Controlling the Formation of Ionic-Liquid-based Aqueous Biphasic Systems by Changing the Hydrogen-Bonding Ability of Polyethylene Glycol End Groups. ChemPhysChem 2015, 16, 2219–2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, H.; Francisco, M.; Rahman, M.; Sun, N.; Rogers, R.D. Biphasic liquid mixtures of ionic liquids and polyethylene glycols. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2009, 11, 10916–10922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noda, A.; Watanabe, M. Highly conductive polymer electrolytes prepared by in situ polymerization of vinyl monomers in room temperature molten salts. Electrochim. Acta 2000, 45, 1265–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triolo, A.; Russina, O.; Keiderling, U.; Kohlbrecher, J. Morphology of poly(ethylene oxide) dissolved in a room temperature ionic liquid: A small angle neutron scattering study. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 1513–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodama, K.; Tsuda, R.; Niitsuma, K.; Tamura, T.; Ueki, T.; Kokubo, H.; Watanabe, M. Structural effects of polyethers and ionic liquids in their binary mixtures on lower critical solution temperature liquid-liquid phase separation. Polym. J. 2011, 43, 242–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benton, M.G.; Brazel, C.S. Effect of Room-Temperature Ionic Liquids as Replacements for Volatile Organic Solvents in Free-Radical Polymerization. ACS Symp. Ser. 2002, 818, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Ke, F.; Zhou, J.; Wang, H.; Liang, D. Solubility of neutral and charged polymers in ionic liquids studied by laser light scattering. Polymer 2011, 52, 481–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueno, K.; Fukai, T.; Nagatsuka, T.; Yasuda, T.; Watanabe, M. Solubility of poly(methyl methacrylate) in ionic liquids in relation to solvent parameters. Langmuir 2014, 30, 3228–3235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, B.; Xu, A.; Wang, J. Cation does matter: How cationic structure affects the dissolution of cellulose in ionic liquids. Green Chem. 2014, 16, 1326–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winterton, N. Solubilization of polymers by ionic liquids. J. Mater. Chem. 2006, 16, 4281–4293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chem, P.; Lacroix, C.; Sultan, E. Functional galactomannan platform from convenient esterification in imidazolium-based ionic liquids. Polym. Chem. 2012, 3, 538–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Huang, Y.; Boamah, P.O.; Cao, L.; Zhang, Q.; Lu, Z.; Li, H. Homogeneous synthesis of linoleic acid-grafted chitosan oligosaccharide in ionic liquid and its self-assembly performance in aqueous solution. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2015, 132, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanan, R.; Kaur, R.; Mahajan, R.K. Micellar Transitions in Catanionic Ionic liquid—Ibuprofen Aqueous Mixtures, Effects of Composition and Dilution. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 64877–64889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morais, E.S.; Silva, N.H.C.S.; Sintra, T.E.; Santos, S.A.O.; Neves, B.M.; Almeida, I.F.; Costa, P.C.; Correia-Sá, I.; Ventura, S.P.M.; Silvestre, A.J.D.; et al. Anti-inflammatory and antioxidant nanostructured cellulose membranes loaded with phenolic-based ionic liquids for cutaneous application. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 206, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chantereau, G.; Sharma, M.; Abednejad, A.; Neves, B.M.; Se, G.; Freire, M.G.; Freire, C.S.R.; Silvestre, A.J.D. Design of Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drug-Based Ionic Liquids with Improved Water Solubility and Drug Delivery. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 14126–14134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.H.; Phuong, T.; Pham, T.; Yun, Y.S. Ionic liquid—assisted cellulose coating of chitosan hydrogel beads and their application as drug carriers. Sci. Rep. 2020, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, H.; Xu, Q.; Li, Y.; Mo, S.; Cai, S.; Liu, L. The synthesis of biodegradable graft copolymer cellulose-graft-poly(l-lactide) and the study of its controlled drug release. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2008, 66, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pyne, A.; Kuchlyan, J.; Maiti, C.; Dhara, D.; Sarkar, N. A Cholesterol Based Surface Active Ionic Liquid That Can Form Microemulsions and Spontaneous Vesicles. Langmuir 2017, 33, 5891–5899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, L.; Zhang, X.; Mikael, P.E.; Lin, L.; Dong, W.; Zheng, Y.; Simmons, T.J.; Zhang, F.; Linhardt, R.J. Biodegradable and Bioactive PCL—PGS Core—Shell Fibers for Tissue Engineering. ACS Omega 2017, 2, 6321–6328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dias, A.M.A.; Cortez, A.R.; Barsan, M.M.; Santos, J.B.; Brett, C.M.A.; De Sousa, H.C. Development of greener multi-responsive chitosan biomaterials doped with biocompatible ammonium ionic liquids. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2013, 1, 1480–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chantereau, G.; Sharma, M.; Abednejad, A.; Vilela, C.; Costa, E.M.; Veiga, M.; Antunes, F.; Pintado, M.M.; Sèbe, G.; Coma, V.; et al. Bacterial nanocellulose membranes loaded with vitamin B-based ionic liquids for dermal care applications. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 302, 112547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuddushi, M.; Nehal, P. Temperature—Responsive Low Molecular Weight Ionic Liquid Based Gelator: Temperature-Responsive Low Molecular Weight Ionic Liquid Based Gelator: An Approach to Fabricate an Anti-Cancer Drug-Loaded Hybrid Ionogel. Chem Syst. Chem 2020, 2, e1900053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Jiang, X.; Wen, X.; Xu, Q.; Zeng, H.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, M.; Wang, Z. Bio-responsive smart polymers and biomedical applications. J. Phys. Mater. 2019, 2, 032004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, O.; Grubjesic, S.; Lee, S.; Firestone, M.A. The design of polymeric ionic liquids for the preparation of functional materials. Polym. Rev. 2009, 49, 339–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, W.; Lu, X.; Cui, K.; Niu, L.; Wei, Y.; Lu, Q. Dual-responsive controlled drug delivery based on ionically assembled nanoparticles. Langmuir 2012, 28, 9413–9420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| API | Water Solubility | IL | Solubility | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amphotericin B | 2.0 × 10−4 a | [C2C1im][CH3CO2] | 85 a | [38] |
| [C4NH3][CH3CO2] | 30 a | |||
| [C6NH3][CH3CO2] | 30 a | |||
| [C8NH3][CH3CO2] | 20 a | |||
| [C4NH3][Oleate] | <5 a | |||
| [C6NH3][Oleate] | <5 a | |||
| [C8NH3][Oleate] | <5 a | |||
| Albendazole | 0.0020 b | [C4C1im][BF4] | 1.49 b | [35] |
| [C6C1im][BF4] | 2.97 b | |||
| Danazol | 0.00030 b | [C4C1im][BF4] | 18.9 b | [35] |
| [C8C1im][BF4] | >59 b | [37] | ||
| [C4C1im][PF6] | 11.9 b | |||
| [C8C1im][PF6] | 35 b | |||
| [C6C6OCOpy][N(CN)2] | >90 c | |||
| [C6C6OCOpy][NTf2] | 25 c | |||
| Itraconazole | 1.0 × 10−6 a | [C2C1im][CH3CO2] | <5 a | [38] |
| [C4NH3][CH3CO2] | <5 a | [37] | ||
| [C6NH3][CH3CO2] | <5 a | |||
| [C8NH3][CH3CO2] | <5 a | |||
| [C4NH3][Oleate] | <5 a | |||
| [C6NH3][Oleate] | <5 a | |||
| [C8NH3][Oleate] | <5 a | |||
| [C6C6OCOpy][N(CN)2] | 40 c | |||
| [C6C6OCOpy][NTf2] | 8 c | |||
| Etodolac | Insoluble | [C4C1im][PF6] | 374.33 a* | [39] |
| Acetaminophen | 98.8 b | [C4C1im][BF4] | >132 b | [35] |
| [C8C1im][BF4] | 126 b | |||
| [C4C1im][PF6] | 52 b | |||
| [C8C1im][PF6] | 10 b | |||
| Ibuprofen | 0.124 a | [C4C1im][PF6] | 6.95 a | [40] |
| [C6C1im][PF6] | 26.38 a | |||
| 5-Fluorouracil | 12.21 a * | [C4C1im]Br | 31.19 a * | [41] |
| Paclitaxel | <4.0 × 10−6 a | [Ch][Gly] | 22.34 a | [17] |
| [Ch][Ala] | 18.52 a | |||
| [Ch][Pro] | 16.16 a | |||
| [Ch][Phe] | 14.15 a | |||
| [Ch][Ile] | 9.39 a | |||
| [Ch][Ser] | 7.32 a | |||
| [Ch][Leu] | 6.61 a |
| API-IL | Cation Activity | Anion Activity | Application | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ranitidinium docusate | Decreases acid stomach production | Laxative | Prevents drug polymorphism Increases API absorption | [47] |
| Procainium salicylate | Local anesthetic | Antimicrobial | Enhanced solubility | [50] |
| Tramadolium salicylate | Analgesic | Antimicrobial | Enhanced solubility | [50] |
| Lidocainium etodolac | Anesthetic | Anti-inflammatory | Enhanced skin Permeation (In vivo testing) | [55] |
| Lidocainium ibuprofenate | Anesthetic | Anti-inflammatory | Supported ILs Fast release profile in GI environment | [56] |
| Bromohexinium ibuprofenate | Mucolytic | Anti-inflammatory | Enhanced membrane permeation | [57] |
| Benzalkonium salicylate | Antimicrobial | Antimicrobial | Enhanced solubility Binding affinity to HSA | [58] |
| Tetracycline docusate | Antimicrobial | Laxative | Higher partition coefficient | [59] |
| Biopolymers | IL | Solubility (wt%) | Dissolution Conditions | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Silk fibroin | [C4C1im][CH3CO2] | 10 | 95 °C, 6 h | [76] |
| [C4C1im]Cl | 13 | 100 °C | ||
| [C2C1im]Cl | 23 | 100 °C | [77] | |
| Cellulose | [C2C1im][CH3CO2] | 23 | 90 °C, 2 h | [78] |
| Chitin | [(CH2CH=C2)C1im]Br | 4.8 | 100 °C, 48 h | [81] |
| Chitosan | [(CH2CH=C2)C1im]Cl | 3 | 100 °C, 30 min | [92] |
| [C4C1im]Cl | 0.2–0.8 | 70–110 °C, 2 h | [79] | |
| [PSC1im][CH3CO2] | 1 | 30 °C, 35 min using 5% w/w of IL aqueous solution | [80] | |
| [PSC4im][CH3CO2] | 1 | 30 °C, 37 min using 5% w/w of IL aqueous solution | ||
| Guar gum | [C4C1im]Cl | 10 | 80–100 °C, 1 h | [82] |
| Polymer | IL | Solubility (w/w%) | T (°C) | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Poly(ethylene glycol)(PEG) | [C4C1im][BF4] | 3.55 | 25.0 | [96] |
| [C2C1im][NTf2] | 10 | 25–200 | [97] | |
| [C4C1im][NTf2] | ||||
| [C4C1im][PF6] | ||||
| Polypropylene glycol (PPG) | [C4C1im][NTf2] | 10 | 48.0 | [97] |
| Poly(ethyl glycidyl ether) (PEGE) | [C2C1im][NTf2] | 10 | 84.4 | [97] |
| [C4C1im][NTf2] | 167 | |||
| [C4C1im][PF6] | Insoluble | 25–200 | ||
| [C2C1im][CF₃SO₃] | Insoluble | |||
| [C4C1im][CF₃SO₃] | ||||
| [C4C1im][BF4] | ||||
| [C8C1im][PF6] | 10 | 67.0 | ||
| Poly(hydroxyethyl methacrylate) (PHEMA) | [C4py][BF4] | Soluble | 80.0 | [95] |
| [C2C1im][BF4] | ||||
| [C4C1im]Cl | Soluble | 55.0 | [98] | |
| Poly(methyl methacrylate) (PMMA) | [C4py][BF4] | Insoluble | [95] | |
| [C4C1im][PF6] | 55.0 | [98] | ||
| [C4C1im]Cl | ||||
| [C2C1im][NTf2] | 0.1 | [100] | ||
| [C4C1im][NTf2] | 25.0 | |||
| [C8C1im][NTf2] | ||||
| Polyacrylonitrile (PAN) | [C4py][BF4] | Insoluble | 80.0 | [95] |
| [C4C1im][BF4] | ||||
| Poly(vinyl alcohol) (PVA) | [C4C1im][HCOO] | 0.03 | 25.0 | [99] |
| [(CH2CH=C2)C1im]Cl | Insoluble | 50.0 | ||
| Poly(styrene sulfonate) (PSS) | [C4C1im][HCOO] | 0.026 | 25.0 | |
| [(CH2CH=C2)C1im]Cl | 0.026 | 50.0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pedro, S.N.; Freire, C.S.R.; Silvestre, A.J.D.; Freire, M.G. Ionic Liquids in Drug Delivery. Encyclopedia 2021, 1, 324-339. https://doi.org/10.3390/encyclopedia1020027
Pedro SN, Freire CSR, Silvestre AJD, Freire MG. Ionic Liquids in Drug Delivery. Encyclopedia. 2021; 1(2):324-339. https://doi.org/10.3390/encyclopedia1020027
Chicago/Turabian StylePedro, Sónia N., Carmen S. R. Freire, Armando J. D. Silvestre, and Mara G. Freire. 2021. "Ionic Liquids in Drug Delivery" Encyclopedia 1, no. 2: 324-339. https://doi.org/10.3390/encyclopedia1020027
APA StylePedro, S. N., Freire, C. S. R., Silvestre, A. J. D., & Freire, M. G. (2021). Ionic Liquids in Drug Delivery. Encyclopedia, 1(2), 324-339. https://doi.org/10.3390/encyclopedia1020027









