Cost-Effective and Simple Prototyping PMMA Microfluidic Chip and Open-Source Peristaltic Pump for Small Volume Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
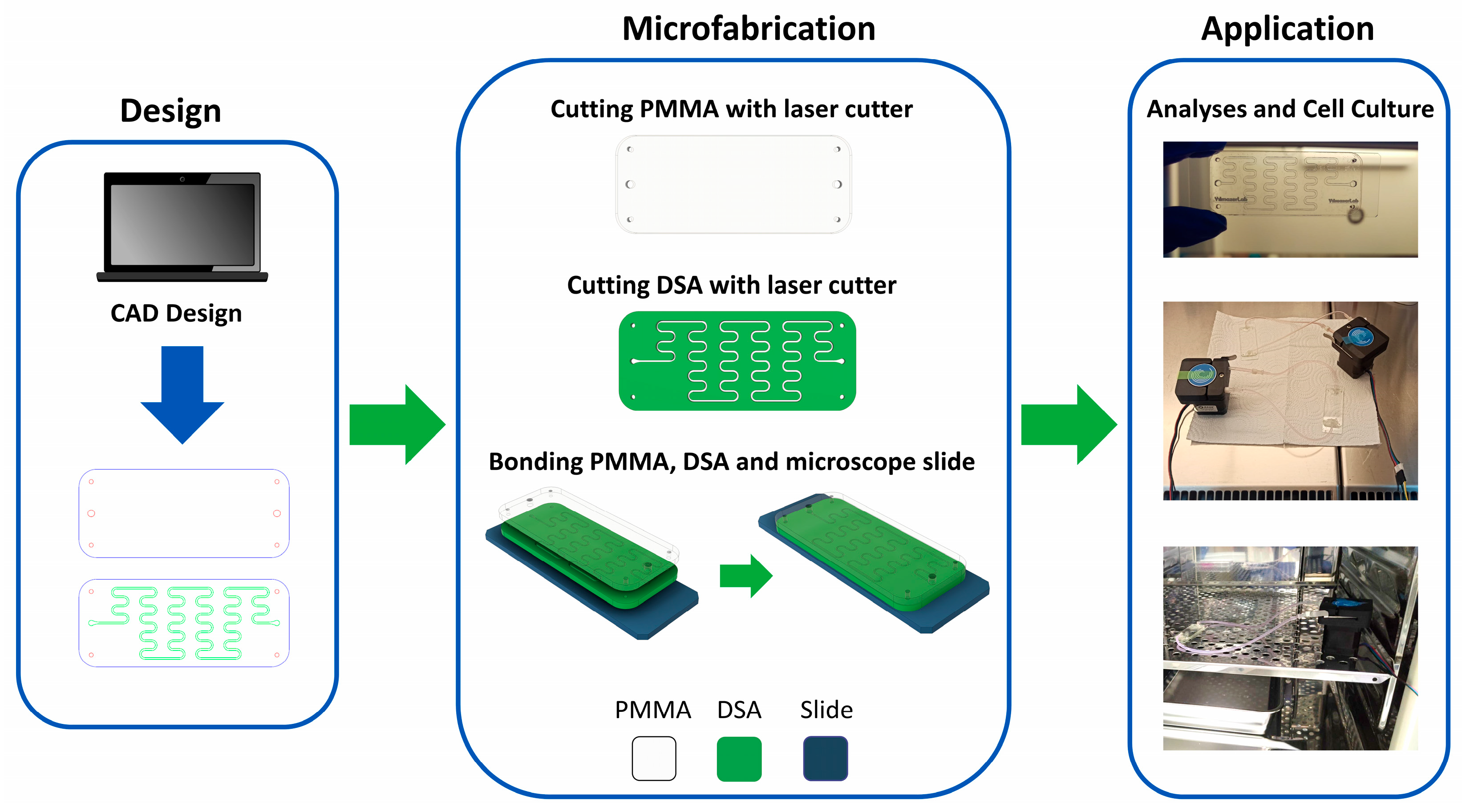
2.2.1. Fabrication of Microfluidic Chips by Laser Cutting Method
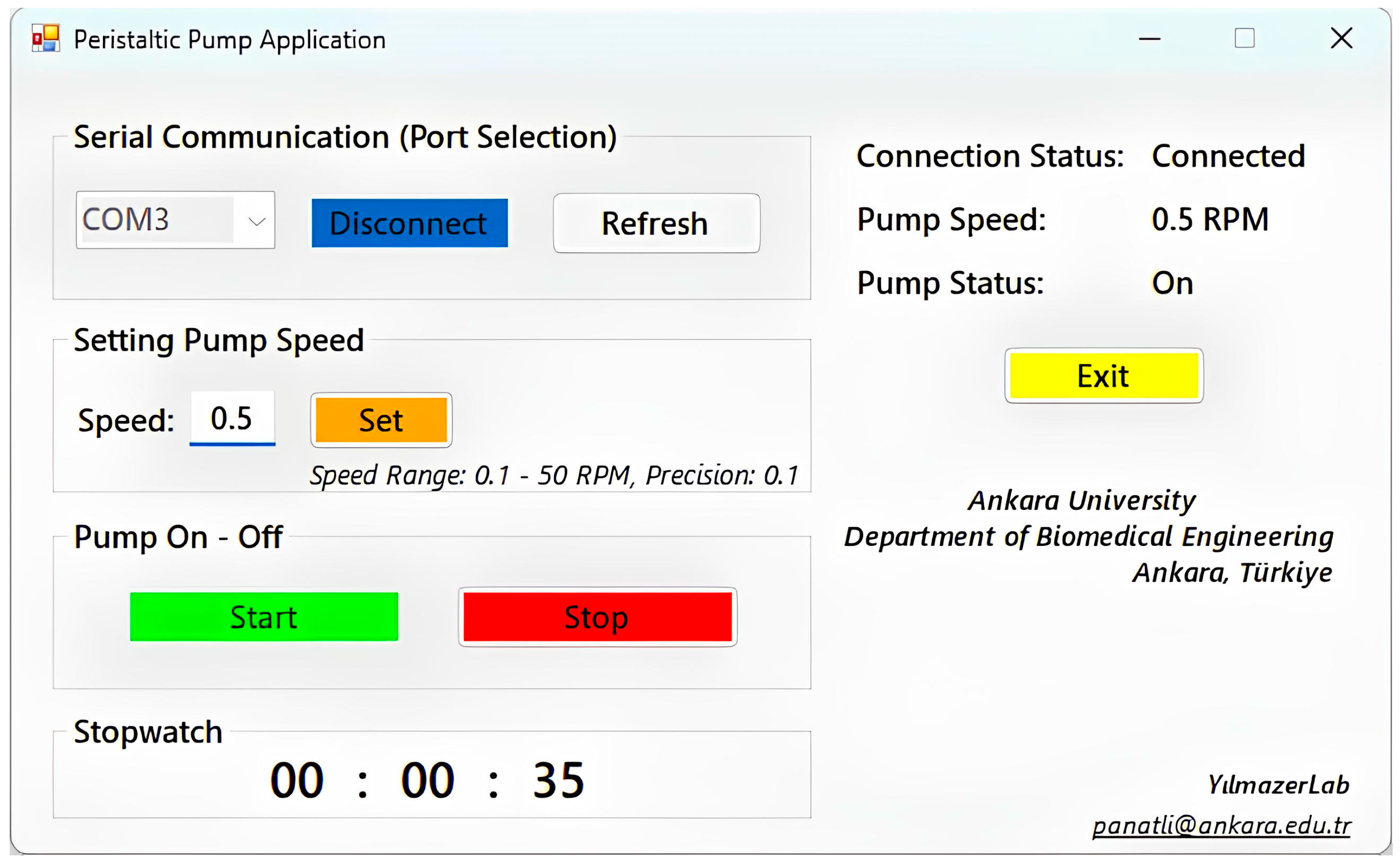
2.2.2. Construction and Control of Peristaltic Pump System
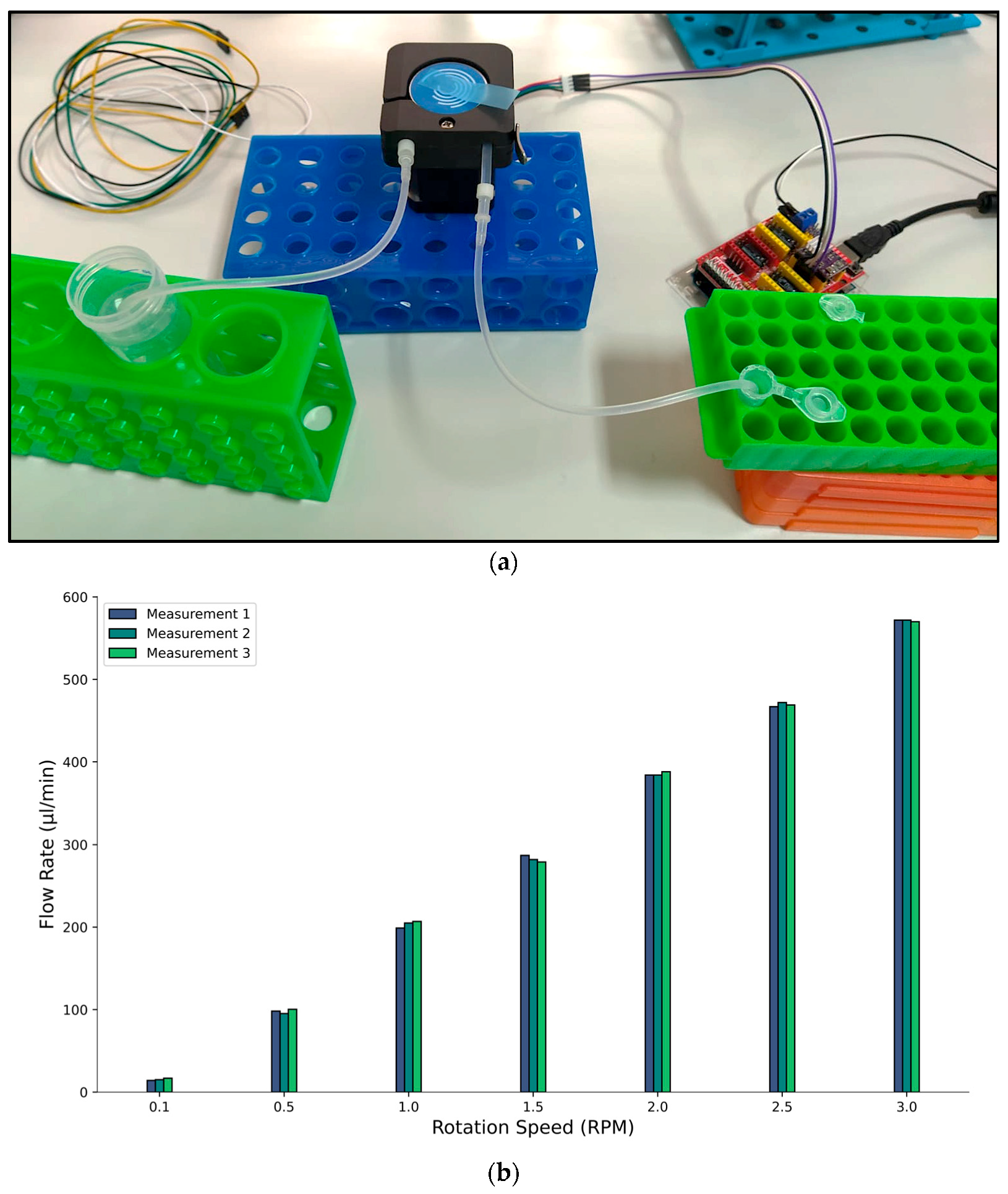
2.2.3. Fluid Flow Rate Determination
2.2.4. Leakage Test
2.2.5. Occlusion Test
2.2.6. Conventional and Microfluidic Cell Cultures
2.2.7. LDH Assay
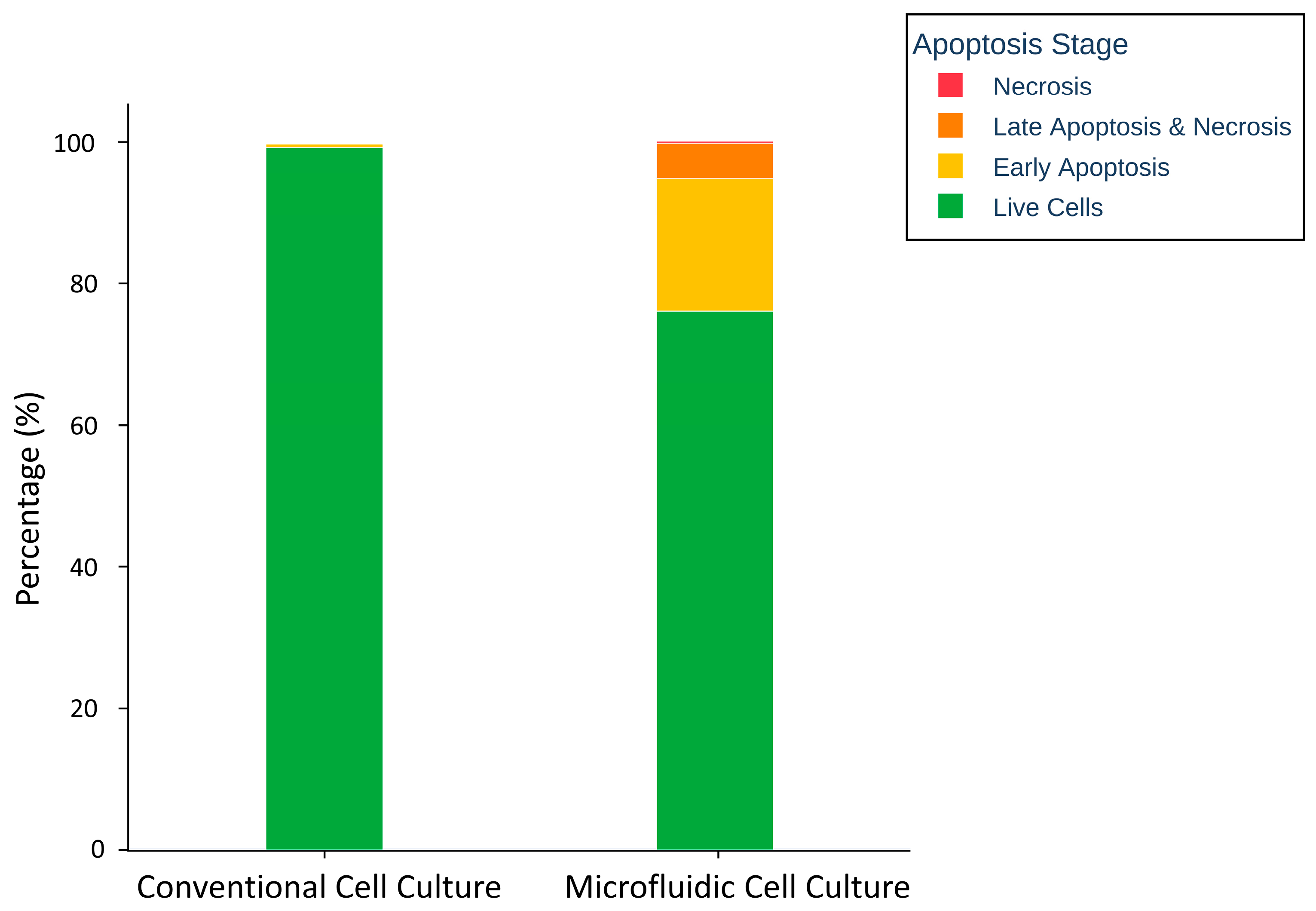
2.2.8. Apoptosis Assay
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Fluid Flow Rate Analysis
3.2. Leakage Analysis
3.3. Occlusion Analysis
3.4. LDH Assay
3.5. Apoptosis Assay
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Weiskirchen, S.; Schröder, S.K.; Buhl, E.M.; Weiskirchen, R. A beginner’s guide to cell culture: Practical advice for preventing needless problems. Cells 2023, 12, 682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halldorsson, S.; Lucumi, E.; Gómez-Sjöberg, R.; Fleming, R.M. Advantages and challenges of microfluidic cell culture in polydimethylsiloxane devices. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 63, 218–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, E.W.; Beebe, D.J. Fundamentals of microfluidic cell culture in controlled microenvironments. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 39, 1036–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varan, G.; Unal, S. Three-dimensional cell culture methods in infectious diseases and vaccine research. Future Pharmacol. 2023, 3, 48–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapałczyńska, M.; Kolenda, T.; Przybyła, W.; Zajączkowska, M.; Teresiak, A.; Filas, V.; Ibbs, M.; Bliźniak, R.; Łuczewski, Ł.; Lamperska, K. 2D and 3D cell cultures—A comparison of different types of cancer cell cultures. Arch. Med. Sci. 2018, 14, 910–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saydé, T.; El Hamoui, O.; Alies, B.; Gaudin, K.; Lespes, G.; Battu, S. Biomaterials for three-dimensional cell culture: From applications in oncology to nanotechnology. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmazer, A. Cancer cell lines involving cancer stem cell populations respond to oxidative stress. Biotechnol. Rep. 2018, 17, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, M.-H.; Huang, S.-B.; Lee, G.-B. Microfluidic cell culture systems for drug research. Lab A Chip 2010, 10, 939–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sattari, A.; Hanafizadeh, P.; Hoorfar, M. Multiphase flow in microfluidics: From droplets and bubbles to the encapsulated structures. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 282, 102208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- İnce, G.T.; Yüksekkaya, M.; Haberal, O.E. Micro-polymerase chain reaction for point-of-care detection and beyond: A review microfluidics and nanofluidics. Microfluid. Nanofluidics 2023, 27, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- İçöz, K.; Akar, Ü.; Ünal, E. Microfluidic Chip based direct triple antibody immunoassay for monitoring patient comparative response to leukemia treatment. Biomed. Microdevices 2020, 22, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Battat, S.; Weitz, D.A.; Whitesides, G.M. An outlook on microfluidics: The promise and the challenge. Lab A Chip 2022, 22, 530–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehling, M.; Tay, S. Microfluidic cell culture. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2014, 25, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sözmen, A.B.; Arslan Yildiz, A. Cost-effective and rapid prototyping of PMMA microfluidic device via polymer-assisted bonding. Microfluid. Nanofluidics 2021, 25, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niculescu, A.-G.; Chircov, C.; Bîrcă, A.C.; Grumezescu, A.M. Fabrication and applications of microfluidic devices: A review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, K.; Zhou, J.; Wu, H. Materials for microfluidic chip fabrication. Acc. Chem. Res. 2013, 46, 2396–2406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mou, L.; Jiang, X. Materials for microfluidic immunoassays: A review. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2017, 6, 1601403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agha, A.; Dawaymeh, F.; Alamoodi, N.; Abu-Nada, E.; Alazzam, A. Microfluidic fabrication using cyclic olefin copolymer and hydrocarbon solvents. Eur. Polym. J. 2023, 196, 112329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agha, A.; Dawaymeh, F.; Alamoodi, N.; Alazzam, A. Enhancing fabrication of hybrid microfluidic devices through silane-based bonding: A focus on polydimethylsiloxane-cyclic olefin copolymer and PDMS-lithium niobate. Appl. Res. 2024, 3, e202300116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agha, A.; Abu-Nada, E.; Alazzam, A. Integration of acoustic micromixing with cyclic olefin copolymer microfluidics for enhanced lab-on-a-chip applications in nanoscale liposome synthesis. Biofabrication 2024, 16, 045004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Y.; Zhang, H.; Yan, Z.; Wei, X.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, X. Surface Modification of Cyclic-Olefin-Copolymer (COC)-Based Microchannels for the Large-Scale Industrial Production of Droplet Microfluidic Devices. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yavuz, C.; Oliaei, S.N.B.; Cetin, B.; Yesil-Celiktas, O. Sterilization of PMMA microfluidic chips by various techniques and investigation of material characteristics. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2016, 107, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Moon, B.-U.; Hidrovo, C.H. Enhancement of the thermo-mechanical properties of PDMS molds for the hot embossing of PMMA microfluidic devices. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2013, 23, 095024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trinh, K.T.L.; Thai, D.A.; Chae, W.R.; Lee, N.Y. Rapid fabrication of poly (methyl methacrylate) devices for lab-on-a-chip applications using acetic acid and UV treatment. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 17396–17404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, L.; Chen, G. Fabrication, modification, and application of poly (methyl methacrylate) microfluidic chips. Electrophoresis 2008, 29, 1801–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liga, A.; Morton, J.A.; Kersaudy-Kerhoas, M. Safe and cost-effective rapid-prototyping of multilayer PMMA microfluidic devices. Microfluid. Nanofluidics 2016, 20, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thurgood, P.; Suarez, S.A.; Chen, S.; Gilliam, C.; Pirogova, E.; Jex, A.R.; Baratchi, S.; Khoshmanesh, K. Self-sufficient, low-cost microfluidic pumps utilising reinforced balloons. Lab A Chip 2019, 19, 2885–2896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warkiani, M.E.; Khoo, B.L.; Wu, L.; Tay, A.K.P.; Bhagat, A.A.S.; Han, J.; Lim, C.T. Ultra-fast, label-free isolation of circulating tumor cells from blood using spiral microfluidics. Nat. Protoc. 2016, 11, 134–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behrens, M.R.; Fuller, H.C.; Swist, E.R.; Wu, J.; Islam, M.M.; Long, Z.; Ruder, W.C.; Steward, R., Jr. Open-source, 3D-printed peristaltic pumps for small volume point-of-care liquid handling. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, M.; Thurgood, P.; Gilliam, C.; Nguyen, N.; Pirogova, E.; Peter, K.; Khoshmanesh, K.; Baratchi, S. Studying the response of aortic endothelial cells under pulsatile flow using a compact microfluidic system. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 12077–12084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazzi, A.; Fusco, L.; Orecchioni, M.; Ferrari, S.; Franzoni, G.; Yan, J.S.; Rieckher, M.; Peng, G.; Lucherelli, M.A.; Vacchi, I.A. Graphene, other carbon nanomaterials and the immune system: Toward nanoimmunity-by-design. J. Phys. Mater. 2020, 3, 034009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurcan, C.; Taheri, H.; Bianco, A.; Delogu, L.G.; Yilmazer, A. A closer look at the genotoxicity of graphene based materials. J. Phys. Mater. 2019, 3, 014007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karatay, A.; Erdener, D.; Gürcan, C.; Yildiz, E.A.; Yilmazer, A.; Boyacıoğlu, B.; Unver, H.; Yıldız, M.; Elmali, A. Amino-functionalized nitrogen-doped graphene quantum dots and silver-graphene based nanocomposites: Ultrafast charge transfer and a proof-of-concept study for bioimaging applications. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2022, 426, 113741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orecchioni, M.; Bordoni, V.; Fuoco, C.; Reina, G.; Lin, H.; Zoccheddu, M.; Yilmazer, A.; Zavan, B.; Cesareni, G.; Bedognetti, D. Toward High-Dimensional Single-Cell Analysis of Graphene Oxide Biological Impact: Tracking on Immune Cells by Single-Cell Mass Cytometry. Small 2020, 16, 2000123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fusco, L.; Gazzi, A.; Shuck, C.E.; Orecchioni, M.; Ahmed, E.I.; Giro, L.; Zavan, B.; Yilmazer, A.; Ley, K.; Bedognetti, D. V4C3 MXene immune profiling and modulation of T cell-dendritic cell function and interaction. Small Methods 2023, 7, 2300197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fusco, L.; Gazzi, A.; Giro, L.; Schefer, R.B.; D’Almeida, S.M.; Cagliani, R.; Zoccheddu, M.; Uyar, R.; Besbinar, Ö.; Çelik, D. Nanoplastics: Immune Impact, Detection, and Internalization after Human Blood Exposure by Single-Cell Mass Cytometry. Adv. Mater. 2024, 37, e2413413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asghar, W.; Yuksekkaya, M.; Shafiee, H.; Zhang, M.; Ozen, M.O.; Inci, F.; Kocakulak, M.; Demirci, U. Engineering long shelf life multi-layer biologically active surfaces on microfluidic devices for point of care applications. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 21163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gale, B.K.; Jafek, A.R.; Lambert, C.J.; Goenner, B.L.; Moghimifam, H.; Nze, U.C.; Kamarapu, S.K. A review of current methods in microfluidic device fabrication and future commercialization prospects. Inventions 2018, 3, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epilog Laser. Owner’s Manuals. 5 June 2023. Available online: https://www.epiloglaser.com/support/laser-manuals/ (accessed on 15 March 2025).
- Naher, S.; Orpen, D.; Brabazon, D.; Poulsen, C.; Morshed, M. Effect of micro-channel geometry on fluid flow and mixing. Simul. Model. Pract. Theory 2011, 19, 1088–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, R.D.; Shen, H.; Piao, Y.-j. The morphometrical analysis on the ultrastructure of A549 cells. Rom. J. Morphol. Embryol 2010, 51, 663–667. [Google Scholar]
- Im, D.J.; Jeong, S.-N. Transfection of Jurkat T cells by droplet electroporation. Biochem. Eng. J. 2017, 122, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vashishtha, S.; Nazarali, A.; Dimmock, J. Application of fluorescence microscopy to measure apoptosis in Jurkat T cells after treatment with a new investigational anticancer agent (NC 1213). Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 1998, 18, 437–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamorina, S.; Khramtsov, P.; Rayev, M.; Timganova, V.; Bochkova, M.; Nechaev, A.; Shunkin, E.; Khaziakhmatova, O.; Malaschenko, V.; Litvinova, L. Graphene oxide nanoparticels interaction with Jurkat cell line in Cell-IQ system. Dokl. Biochem. Biophys. 2021, 501, 438–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metto, E.C.; Evans, K.; Barney, P.; Culbertson, A.H.; Gunasekara, D.B.; Caruso, G.; Hulvey, M.K.; Fracassi da Silva, J.A.; Lunte, S.M.; Culbertson, C.T. An integrated microfluidic device for monitoring changes in nitric oxide production in single T-lymphocyte (Jurkat) cells. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 10188–10195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.; Kim, S.-E.; Doh, J.; Kim, K.; Chung, W.K. User-friendly image-activated microfluidic cell sorting technique using an optimized, fast deep learning algorithm. Lab A Chip 2021, 21, 1798–1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ching, T.; Vasudevan, J.; Tan, H.Y.; Lim, C.T.; Fernandez, J.; Toh, Y.-C.; Hashimoto, M. Highly-customizable 3D-printed peristaltic pump kit. HardwareX 2021, 10, e00202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fotakis, G.; Timbrell, J.A. In vitro cytotoxicity assays: Comparison of LDH, neutral red, MTT and protein assay in hepatoma cell lines following exposure to cadmium chloride. Toxicol. Lett. 2006, 160, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Nagarajan, A.; Uchil, P.D. Analysis of cell viability by the lactate dehydrogenase assay. Cold Spring Harb. Protoc. 2018, 2018, pdb.prot095497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Gelein, R.; Corson, N.; Wade-Mercer, P.; Jiang, J.; Biswas, P.; Finkelstein, J.N.; Elder, A.; Oberdörster, G. Validation of an LDH assay for assessing nanoparticle toxicity. Toxicology 2011, 287, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koopman, G.; Reutelingsperger, C.; Kuijten, G.; Keehnen, R.; Pals, S.; Van Oers, M. Annexin V for flow cytometric detection of phosphatidylserine expression on B cells undergoing apoptosis. Blood 1994, 84, 1415–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sgonc, R.; Gruber, J. Apoptosis detection: An overview. Exp. Gerontol. 1998, 33, 525–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mustafa, M.; Ahmad, R.; Tantry, I.Q.; Ahmad, W.; Siddiqui, S.; Alam, M.; Abbas, K.; Moinuddin Hassan, M.I.; Habib, S. Apoptosis: A Comprehensive Overview of Signaling Pathways, Morphological Changes, and Physiological Significance and Therapeutic Implications. Cells 2024, 13, 1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Q.; Liu, J.; Wang, X.; Feng, L.; Wu, J.; Zhu, X.; Wen, W.; Gong, X. Organ-on-a-chip: Recent breakthroughs and future prospects. Biomed. Eng. Online 2020, 19, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Panatli, O.; Gurcan, C.; Ari, F.; Unal, M.A.; Yuksekkaya, M.; Yilmazer, A. Cost-Effective and Simple Prototyping PMMA Microfluidic Chip and Open-Source Peristaltic Pump for Small Volume Applications. Micro 2025, 5, 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/micro5020025
Panatli O, Gurcan C, Ari F, Unal MA, Yuksekkaya M, Yilmazer A. Cost-Effective and Simple Prototyping PMMA Microfluidic Chip and Open-Source Peristaltic Pump for Small Volume Applications. Micro. 2025; 5(2):25. https://doi.org/10.3390/micro5020025
Chicago/Turabian StylePanatli, Oguzhan, Cansu Gurcan, Fikret Ari, Mehmet Altay Unal, Mehmet Yuksekkaya, and Açelya Yilmazer. 2025. "Cost-Effective and Simple Prototyping PMMA Microfluidic Chip and Open-Source Peristaltic Pump for Small Volume Applications" Micro 5, no. 2: 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/micro5020025
APA StylePanatli, O., Gurcan, C., Ari, F., Unal, M. A., Yuksekkaya, M., & Yilmazer, A. (2025). Cost-Effective and Simple Prototyping PMMA Microfluidic Chip and Open-Source Peristaltic Pump for Small Volume Applications. Micro, 5(2), 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/micro5020025






