Design Guideline for a Cantilever-Type MEMS Switch with High Contact Force
Abstract
:1. Introduction
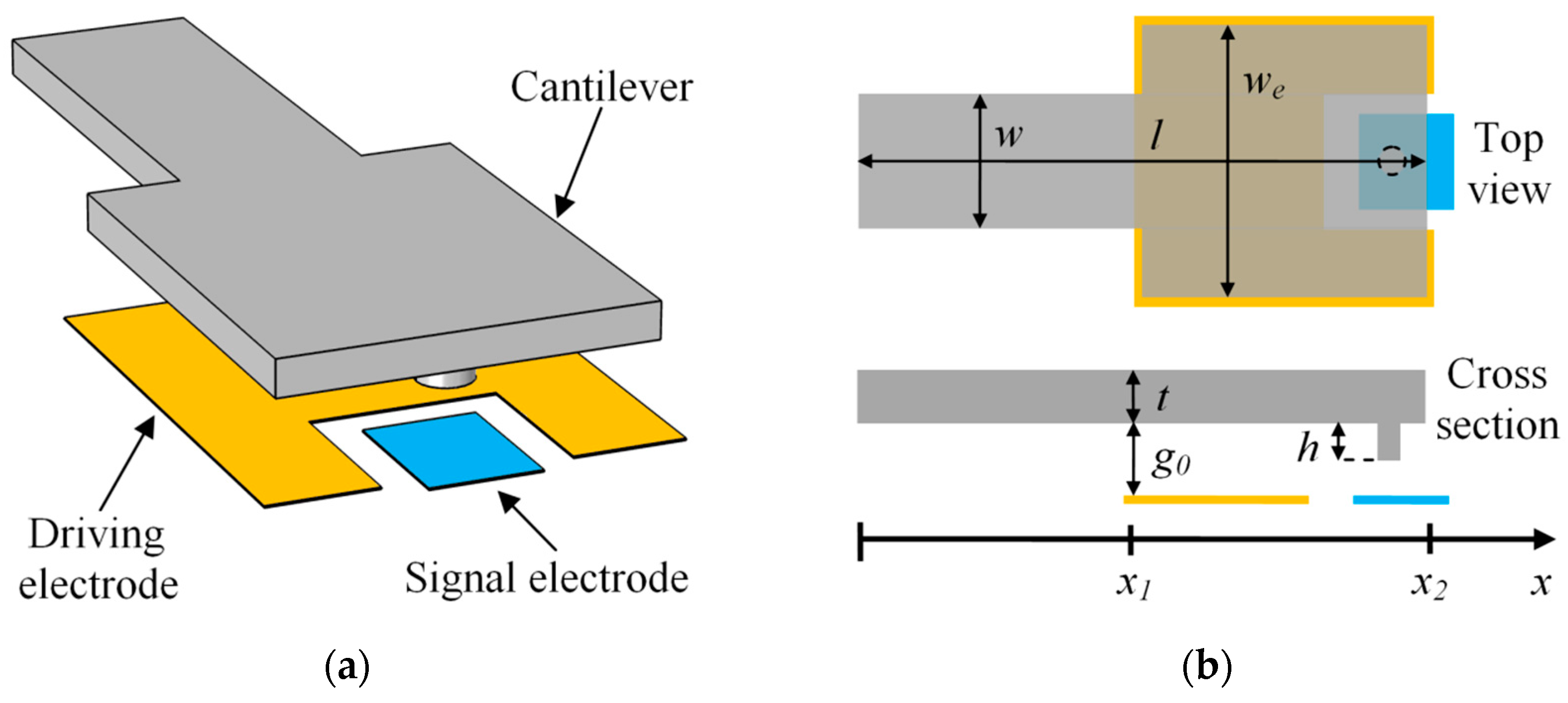
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Choosing the Vertical Dimensions
3.2. Double Cantilever Design
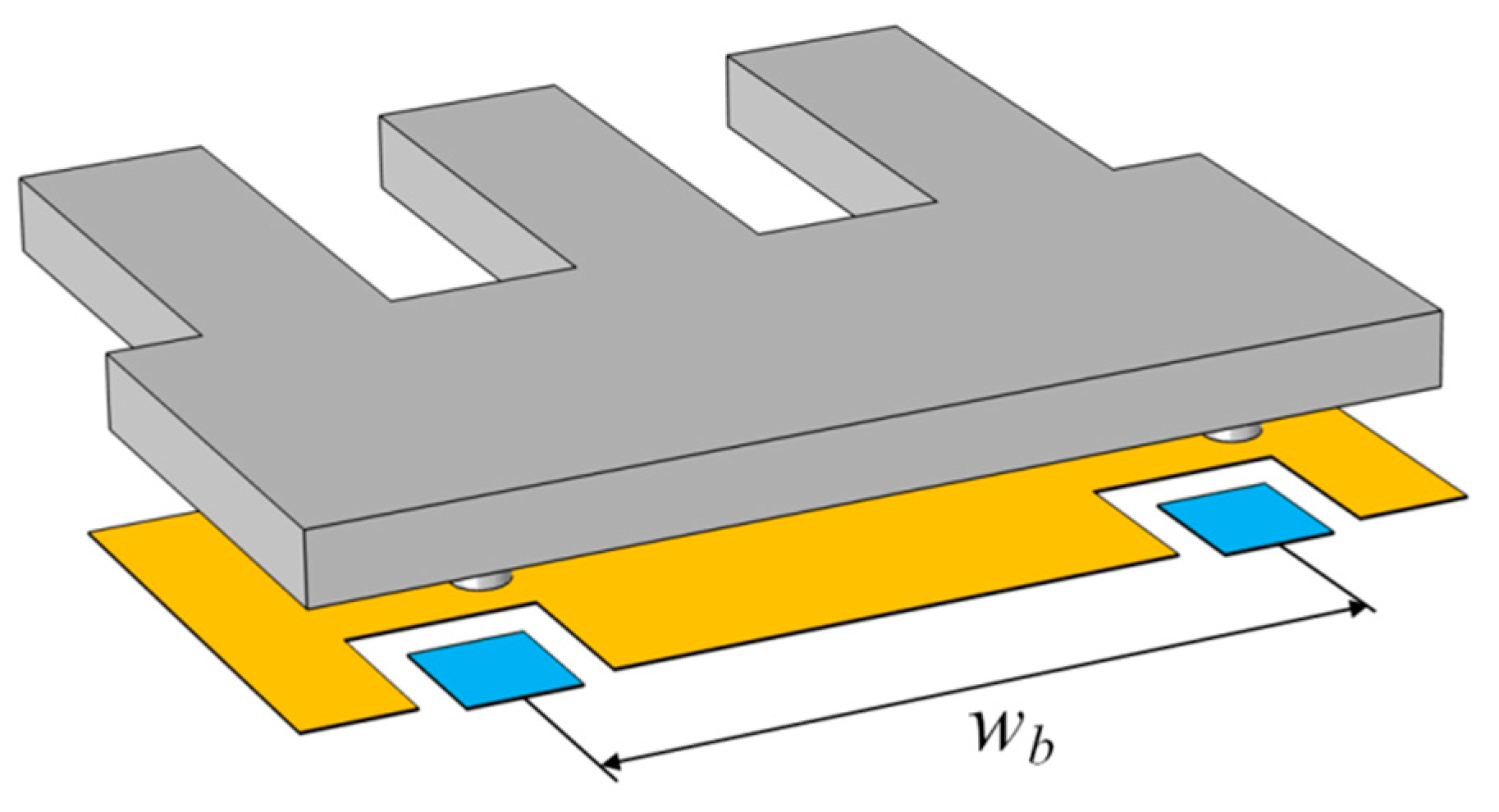
3.3. Multiple Cantilever Design
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rebeiz, G.M.; Patel, C.D.; Han, S.K.; Ko, C.-H.; Ho, K.M.J. The search for a reliable MEMS switch. IEEE Microw. Mag. 2013, 14, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iannacci, J. RF-MEMS for high-performance and widely reconfigurable passive components—A review with focus on future telecommunications, Internet of Things (IoT) and 5G applications. J. King Saud Univ. 2017, 29, 436–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shekhar, S.; Vinoy, K.J.; Ananthasuresh, G.K. Low-voltage high-reliability MEMS switch for millimeter wave 5G applications. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2018, 28, 075012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.-Y.; Soin, N.; Daut, M.H.M.; Hatta, S.F.W.M. Comprehensive study on RF-MEMS switches used for 5G scenario. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 107506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, K.R.; Kumar, P.A.; Guha, K.; Sailaja, B.V.S.; Vineetha, K.V.; Baishnab, K.L.; Sravani, K.G. Design and simulation of fixed-fixed flexure type RF MEMS switch for reconfigurable antenna. Microsyst. Technol. 2021, 27, 455–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, B.; Duan, J.; Yan, L. A novel RF MEMS switch on frequency reconfigurable antenna application. Microsyst. Technol. 2018, 24, 3833–3841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haupt, R.L.; Lanagan, M. Reconfigurable antennas. IEEE Antennas Propag. Mag. 2013, 55, 49–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haider, N.; Caratelli, D.; Yarovoy, A.G. Recent developments in reconfigurable and multiband antenna technology. Int. J. Antennas Propag. 2013, 2013, 869170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Sheng, W.; Cui, J.; Han, Y.; Ma, X.; Zhang, R. SR-Crossbar topology for large-scale RF MEMS switch matrices. IET Microw. Antennas Propag. 2019, 13, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daneshmand, M.; Mansour, R.R. RF MEMS satellite switch matrices. IEEE Microw. Mag. 2011, 12, 92–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, T.; Hu, T.; Zhao, Y. Research status and development trend of MEMS switches: A review. Micromachines 2020, 11, 694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurmendra; Kumar, R. A review on RF micro-electro-mechanical-systems (MEMS) switch for radio frequency applications. Microsyst. Technol. 2021, 27, 2525–2542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaddi, R.; Van Kampen, R.; Unamuno, A.; Joshi, V.; Lacey, D.; Renault, M.; Smith, C.; Knipe, R.; Yost, D. MEMS technology integrated in the CMOS back end. Microelectron. Reliab. 2010, 50, 1593–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, C.-L.; Chen, J.-H. Low voltage actuated RF micromechanical switches fabricated using CMOS-MEMS technique. Microsyst. Technol. 2006, 12, 1143–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, S.; Koul, S.K. Design and development of a CPW-based 5-bit switched-line phase shifter using inline metal contact MEMS series switches for 17.25 GHz transmit/receive module application. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2014, 24, 015005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.K.; Gautam, A.K.; Farinelli, P.; Dutta, A.; Singh, S.G. A Ku band 5 bit MEMS phase shifter for active electronically steerable phased array applications. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2015, 25, 035014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, S.; Shen, H.; Barker, N.S. A 60-GHz 2-bit switched-line phase shifter using SP4T RF-MEMS switches. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2011, 59, 894–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-H.; Lee, S.; Kim, J.-M.; Kim, H.-T.; Kwon, Y.; Kim, Y.-K. Reconfigurable millimeter-wave filters using CPW-based periodic structures with novel multiple-contact MEMS switches. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2005, 14, 456–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peroulis, D.; Pacheco, S.; Sarabandi, K.; Katehi, L.P.B. Tunable lumped components with applications to reconfigurable MEMS filters. In Proceedings of the 2001 IEEE MTT-S International Microwave Sympsoium, Phoenix, AZ, USA, 20–24 May 2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Xue, P.; Wu, Q. Design and fabrication of a 4-bit RF MEMS attenuator with a high attenuation accuracy. Analog Integr. Circ. Sig. Process. 2020, 102, 617–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iannacci, J.; Tschoban, C. RF-MEMS for future mobile applications: Experimental verification of a reconfigurable 8-bit power attenuator up to 110 GHz. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2017, 27, 044003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Gong, Z.; Zhong, Q.; Liang, X.; Liu, Z. A miniaturized reconfigurable broadband attenuator based on RF MEMS switches. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2016, 26, 074002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heredia, J.; Ribó, M.; Pradell, L.; Wipf, S.T.; Göritz, A.; Wietstruck, M.; Wipf, C.; Kaynak, M. A 125–143-GHz frequency-reconfigurable BiCMOS compact LNA using a single RF-MEMS switch. IEEE Microw. Compon. Lett. 2019, 29, 339–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Spengen, W.M.; Roobol, S.B.; Klaassen, W.P.; Oosterkamp, T.H. The MEMSamp: Using (RF-)MEMS switches for the micromechanical amplification of electronic signals. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2010, 20, 125011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleem, M.M.; Nawaz, H. A systematic review of reliability issues in RF-MEMS switches. Micro Nanosyst. 2019, 11, 11–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Vasan, A.S.S.; Doraiswami, R.; Osterman, M.; Pecht, M. MEMS reliability review. IEEE Trans. Device Mater. Reliab. 2012, 12, 482–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toler, B.F.; Coutu, R.A.; McBride, J.W. A review of micro-contact physics for microelectromechanical systems (MEMS) metal contact switches. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2013, 23, 103001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, A.; Adams, G.G.; McGruer, N.E. A review of micro-contact physics, materials, and failure mechanisms in direct-contact RF MEMS switches. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2016, 26, 104004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Tran, Q.; Chou, T.-K.A.; Heck, J.; Bar, H.; Kant, R.; Rao, V. RF Metal contact reliability of RF MEMS switches. Proc. SPIE 2007, 6463, 646305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broue, A.; Fourcade, T.; Dhennin, J.; Courtade, F.; Charvet, P.-L.; Pons, P.; Lafontan, X.; Plana, R. Validation of bending tests by nanoindentation for micro-contact analysis of MEMS switches. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2010, 20, 085025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broue, A.; Dhennin, J.; Charvet, P.-L.; Pons, P.; Ben Jemaa, N.; Heeb, P.; Coccetti, F.; Plana, R. Comparative study of RF MEMS micro-contact materials. Int. J. Microw. Wirel. Technol. 2012, 4, 413–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, T.; Itoh, T.; Suga, T. Investigation of anti-stiction coating for ohmic contact MEMS switches with thiophenol and 2-naphthalenethiol self-assembled monolayer. Sens. Actuators A 2011, 172, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Guo, Z.J.; Joshi, N.; Eid, H.; Adams, G.G.; McGruer, N.E. An improved SPM-based contact tester for the study of microcontacts. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2012, 22, 045017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schimkat, J. Contact measurements providing basic design data for microrelay actuators. Sens. Actuators A 1999, 73, 138–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, H.; Park, J.-H.; Lee, H.-C.; Choi, D.-J.; Park, Y.-H.; Nam, H.-J.; Joo, Y.-C. Investigation of similar and dissimilar metal contacts for reliable radio frequency micorelectromechanical switches. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2008, 47, 6558–6562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coutu, R.A.; Tomer, D. Micro-contacts testing using a micro-force sensor compatible with biological systems. Int. J. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 3, 00052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bull, T.G.; McBride, J.W. In-situ contact surface characterization in a MEMS ohmic switch under low current switching. Technologies 2018, 6, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahanta, P.; Anwar, F.; Coutu, R.A. Novel test fixture for characterizing MEMS switch microcontact reliability and performance. Sensors 2019, 19, 579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-B.; Yoon, Y.-H.; Lee, Y.-B.; Choi, K.-W.; Jo, M.-S.; Min, H.-W.; Yoon, J.-B. 4 W power MEMS relay with extremely low contact resistance: Theoretical analysis, design and demonstration. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2020, 29, 1304–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-B.; Min, H.-W.; Lee, Y.-B.; Kim, S.-H.; Choi, P.-K.; Yoon, J.-B. Utilizing mechanical adhesion force as a high contact force in a MEMS relay. Sens. Actuators A 2021, 331, 112894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blondy, P.; Pothier, A.; Stefanini, R.; Gauvin, J.; Passerieux, D.; Vendier, O.; Courtade, F. Development of an all-metal large contact force reliable RF-MEMS relay for space applications. In Proceedings of the 42nd European Microwave Conference, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 29 October–1 November 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, C.D.; Rebeiz, G.M. A high-reliability high-linearity high-power RF MEMS metal-contact switch for DC-40-GHz applications. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2012, 60, 3096–3112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, C.D.; Rebeiz, G.M. RF MEMS metal-contact switches with mN-contact and restoring forces and low process sensitivity. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2011, 59, 1230–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seki, T.; Uno, Y.; Narise, K.; Masuda, T.; Inoue, K.; Sato, S.; Sato, F.; Imanaka, K.; Sugiyama, S. Development of a large-force low-loss metal-contact RF MEMS switch. Sens. Actuators A 2006, 132, 683–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedaghat-Pisheh, H.; Rebeiz, G.M. Variable spring constant, high contact force RF MEMS switch. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE MTT-S International Microwave Symposium, Anaheim, CA, USA, 23–28 May 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanini, R.; Chatras, M.; Blondy, P.; Rebeiz, G.M. Miniature MEMS switches for RF applications. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2011, 20, 1324–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spasos, M.; Nilavalan, R. Resistive damping implementation as a method to improve controllability in stiff ohmic RF-MEMS switches. Microsyst. Technol. 2013, 19, 1935–1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Lv, Z.; He, X.; Liu, M.; Hao, Y.; Li, Z. Improving performance of the metal-to-metal contact RF MEMS switch with a Pt-Au microspring contact design. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2011, 21, 065038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishijima, N.; Hung, J.-J.; Rebeiz, G.M. Parallel-contact metal-contact RF-MEMS switches for high power applications. In Proceedings of the 17th IEEE International Conference on Micro Electro Mechanical Systems, Maastricht, The Netherlands, 25–29 January 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.-H.; Kim, M.-W.; Seo, M.-H.; Yoon, J.-B. A complementary dual-contact MEMS switch using a “zipping” technique. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2014, 23, 710–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belozerov, I.A.; Uvarov, I.V. Performance optimization of the cantilever-based MEMS switch. St. Petersburg Polytechn. Univ. J. Phys. Math. 2022, 15, 140–144. [Google Scholar]
- Rebeiz, G.M. RF MEMS: Theory, Design, and Technology; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2003; 512p. [Google Scholar]
- Kimiaeifar, A.; Tolou, N.; Barari, C.; Herder, J.L. Large deflection analysis of cantilever beam under end point and distributed loads. J. Chin. Inst. Eng. 2014, 37, 438–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uvarov, I.V.; Kupriyanov, A.N. Stiction-protected MEMS switch with low actuation voltage. Microsyst. Technol. 2019, 25, 3243–3251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uvarov, I.V.; Kupriyanov, A.N. Investigation of characteristics of electrostatically actuated MEMS switch with an active contact breaking mechanism. Russ. Microelectron. 2018, 47, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.-H.; Kim, M.-W.; Lee, J.O.; Ko, S.-D.; Yoon, J.-B. Complementary dual-contact switch using soft and hard contact materials for achieving low contact resistance and high reliability simultaneously. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2013, 22, 846–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, P.; Wang, N.; Cai, F.; Chen, L. A high-force and high isolation metal-contact RF MEMS switch. Microsyst. Technol. 2017, 23, 4699–4708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uvarov, I.V.; Marukhin, N.V.; Naumov, V.V. Contact resistance and lifecycle of a single- and multiple-contact MEMS switch. Microsyst. Technol. 2019, 25, 4135–4141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majumder, S.; McGruer, N.E.; Adams, G.G.; Zavracky, P.M.; Morrison, R.H.; Krim, J. Study of contacts in an electrostatically actuated microswitch. Sens. Actuators A 2001, 93, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majumder, S.; Lampen, J.; Morrison, R.; Maciel, J. MEMS switches. IEEE Instrum. Meas. Mag. 2003, 6, 12–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Uvarov, I.V.; Belozerov, I.A. Design Guideline for a Cantilever-Type MEMS Switch with High Contact Force. Micro 2024, 4, 1-13. https://doi.org/10.3390/micro4010001
Uvarov IV, Belozerov IA. Design Guideline for a Cantilever-Type MEMS Switch with High Contact Force. Micro. 2024; 4(1):1-13. https://doi.org/10.3390/micro4010001
Chicago/Turabian StyleUvarov, Ilia V., and Igor A. Belozerov. 2024. "Design Guideline for a Cantilever-Type MEMS Switch with High Contact Force" Micro 4, no. 1: 1-13. https://doi.org/10.3390/micro4010001
APA StyleUvarov, I. V., & Belozerov, I. A. (2024). Design Guideline for a Cantilever-Type MEMS Switch with High Contact Force. Micro, 4(1), 1-13. https://doi.org/10.3390/micro4010001






