Abstract
The discovery of novel probiotic bacteria from free-ranging animals for the treatment of inflammatory bowel disease in domestic pets is a unique approach. The chloroform extraction of gastrointestinal (GI) tract material was used to inactivate vegetative cells and select for spore-forming bacteria. A bacterium identified as a novel Paenibacillus sp. strain via small ribosomal RNA (16S) gene sequencing was isolated from the GI tract of a gray wolf (Canis lupus). The bacterium was typed as Gram-variable, both catalase/oxidase-positive and positive via starch hydrolysis and lipase assays. The bacterium inhibited the growth of Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli and Micrococcus luteus. The draft whole genome sequence (WGS) assembly was 7,034,206 bp in length, encoding 6543 genes, and is similar in size and coding capacity to other closely related Paenibacillus spp. The isolate’s genome encodes several germination and sporulation gene products along with antimicrobials such as a bacteriocin system and chitinase. Enzyme genes such as alpha amylase, cellulase, lipases and pectin lyase are also present in the genome. An incomplete lysogenic bacteriophage genome was also present in the isolate’s genome. Phenotypic characteristics combined with a WGS genotype analysis indicate that this bacterium, designated Paenibacillus sp. ClWae2A, could be a potential candidate probiotic for domestic dogs.
1. Introduction
Canine inflammatory bowel disease (cIBD) is described as the chronic dysbiosis of a dog’s gastrointestinal (GI) tract with no known cure and limited treatment options. A variety of treatments are utilized, such as corticosteroids, fiber-enriched diets, and prebiotics, with no success in curing cIBD [1,2,3]. Underlying factors that contribute to GI disease include an animal’s genetics, environmental factors, the immunological state of the GI tract and, importantly, an altered GI tract microbiome [4]. Microbial metabolism in the GI tract is important for the fermentation of various carbohydrates and the generation of short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) that impact host health [5], such as by reducing intestinal inflammation [6].
The canine fecal microbiota was characterized to consist primarily of members of the phyla Firmicutes, Bacteroidetes and Fusobacterium [7], with various genera present in the gut [8]. The effect of a multi-species synbiotic on the canine GI tract resulted in changes such as increases in Enterococcus spp. and Streptococcus spp., accompanied by no changes in the major bacterial phyla or immune markers [9]. Also, certain microbial taxa such as Clostridiaceae, Erysipelotrichaceae and Bacteroidaceae are important for protein and fat digestion in canines [10].
Lifestyle changes that occurred during human evolution, such as diet, have resulted in a deviation from the ancestral state that includes a depletion of the gut microflora that has potentially included impacts on increased instances of cIBD [11]. Mammalian adaptation and diversification during evolution altered the gut microbiota, especially during domestication [12]. Dogs were the first domesticated animal and shared a common ancestry with the gray wolf [13,14], which accompanied relationships with humans [15]. Consequently, the diet of the modern dog does not reflect the diet of its ancestor, the wolf [16]. For instance, the starch in the diets of domestic dogs [17] is resistant to digestion, which can potentially have a negative impact on gastric physiology [18].
Probiotics are defined by the FAO/WHO as “live microorganisms that, when administered in adequate amounts, confer a health benefit on the host”, as put forth in a consensus statement by the International Scientific Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics (ISAPP). This includes a set of “core” benefits such as improved host immunomodulation, an improved production of short-chain fatty acids in the GI tract, the competitive exclusion of certain pathogens and the normalization of host microbiota [19]. As humans increase their ownership of companion animals, the importance of maintaining canine health, specifically the use of probiotics to treat cIBD, will become more important [20,21]. Since there have been changes in the diet and environment of the domestic dog relative to its evolutionary counterpart the gray wolf, it is conceivable that there are differences in their respective microbiota. The results reported herein indicate we have isolated a potentially unique probiotic bacterium from a wolf for use in dogs; this bacterium was characterized as a Paenibacillus sp. from a gray wolf.
2. Materials and Methods
Gastrointestinal (GI) tract material was collected from the ileum of a one-day-dead gray wolf, Canis lupus (which was killed in an automobile accident), following its necropsy at the Oregon Veterinary Diagnostic Laboratory, College of Veterinary Medicine, Oregon State University, Corvallis, OR, USA (https://vetmed.oregonstate.edu/ovdl, accessed on 19 September 2023). The GI tract samples were suspended in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) and treated with 3% chloroform for 30 min to eliminate vegetative bacterial cells ([22] Honda K, personal communication). Briefly, GI tract material mixed with chloroform was then incubated in a 15 mL conical polypropylene tube while it was shaken at room temperature for 60 min. The chloroform was separated via centrifugation at 500× g for 20 min, and the treated samples were drawn off with a pipette for bacterial culture. The chloroform-treated GI tract sample aliquots were cultured on different types of media, brucella agar with blood and vitamin K/hemin (BBHK) and tryptose–sulfite–cycloserine (TSC), via aerobic techniques at 37 °C. These media types are routinely used to propagate fastidious bacteria [23,24], and a total of twenty-five axenic bacterial cultures were obtained for analyses. Subsequently, a single aerobic isolate, designated ClWae2A, was cultured for growth on a brain heart infusion (BHI) and nutrient agar (NA), using standard methods [23,24].
The following phenotypic characterizations were completed via standard microbial assays: Gram stains, starch hydrolysis and catalase, lipase and oxidase assays [23,24]. Additional phenotypic characterizations included assaying for motility using a motility indole ornithine medium (MIO), in addition to determining growth in maltose, lactose, dextrose, nitrate broth and urea. The isolate was assayed for antibiotic sensitivities to streptomycin, erythromycin, chloramphenicol, penicillin and tetracycline via disc diffusion to assay for antibiotic resistances [23,24]. Furthermore, growth inhibition assays were completed to determine its antibacterial activity against Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli and Micrococcus luteus [25], and positive results were used to select bacterial isolates for obtaining a genome sequence. Target bacteria and the putative spore-forming bacterial isolate were streaked from stocks on BHI agar (Becton Dickinson). Overnight cultures of both the target bacteria and the wolf GI tract isolate (2.5 mL) were propagated in liquid BHI media. In total, 25 -five µL of the target bacteria (∼106 cells) were inoculated into 15 mL of sterile BHI agar that had been cooled to 55 °C. The inoculated agar was poured into a sterile petri dish and allowed to solidify under sterile conditions. The wolf test bacterium was pelleted and suspended in 200 µL of BHI media, into which sterile filter discs were saturated with the test bacterium and then placed on the target bacterial agar plates. The inoculated plates with discs were incubated at 37 °C, and the formation of a zone of clearance (ZOC) was visually assessed after 24–36 h, as described in [25].
The isolated wolf bacterial colony was assayed for bacterial typing via 16S sequencing [26,27,28], using IDGenomics INC. DNA was extracted from bacterial colonies via the Illustra Nucleic Acid PurificationTM system for the completion of 16S rRNA gene sequencing, and this was repeated for whole genome sequencing (WGS). The phylogenetically nearest neighbor was determined via 16S rRNA sequence analyses, following BLAST searches [29], and sequences were obtained for related isolates via the BLAST searches (https://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi, accessed on 19 September 2023). The 16S rRNA sequences were used to infer initial phylogenetic relationships using MEGA [30].
As stated, the bacterial genomic DNA was purified using the Illustra Nucleic Acid PurificationTM system. Nucleotide sequencing was completed using 400 Mbp Illumina Reads, with assembly (CD Genomics; https://www.cd-genomics.com/microbial-whole-genome-sequencing.html, accessed on 19 September 2023, [31]) and annotation via the JGI IMG/MER Pipeline [32], followed by conserved domain analyses [33]. We functionally characterized the genes present in the ClWae2A assembly by assigning genes to COG categories [32]. Additionally, we performed a more specific functional characterization by searching for keywords associated with certain functions of interest. The assembled scaffolds for the genome sequences were submitted to NCBI for BLAST and BLAST+ analyses using microbial genome Blast analysis tools [29]. The PHAge Search Tool Enhanced Release program was utilized to identify and annotate potential prophage sequences within the bacterial genome [34].
A BLAST analysis was used to find the six closest relatives and an outgroup for the ClWae2A genome [29]. The subsequent output was created via TreeViewer [35] to generate phylogenetic relationships. Subsequently, a conda environment was developed to install the Mugsy alignment tool [36] with RAxML with bootstrap replications for a phylogenetic analysis of the six closely related genomes with an outgroup [37]. Figtree was used to visualize the phylogenetic relationships relative to ClWae2A [38].
3. Results
3.1. The Isolation of Bacteria from a Gray Wolf’s Gastointestinal Tract and Its Phenotypic Characterisitcs
Gastrointestinal tract (GI) material collected from a North American gray wolf (Canis lupus) was treated with chloroform. Subsequently, the chloroform-treated GI tract material was plated on BBHK agar media to isolate potential spore-forming bacteria. From this plate, several isolates were chosen for further characterization. A unique bacterial colony that had grayish-white, smooth colonies with irregular forms was visually identified for further analyses. Specifically, one was chosen that stained Gram-variable with visible spores (Supplementary Figure S1) which also propagated on a brain heart infusion (BHI) medium and nutrient agar (NA). Subsequently, the BHI medium was used for the propagation of the bacterium.
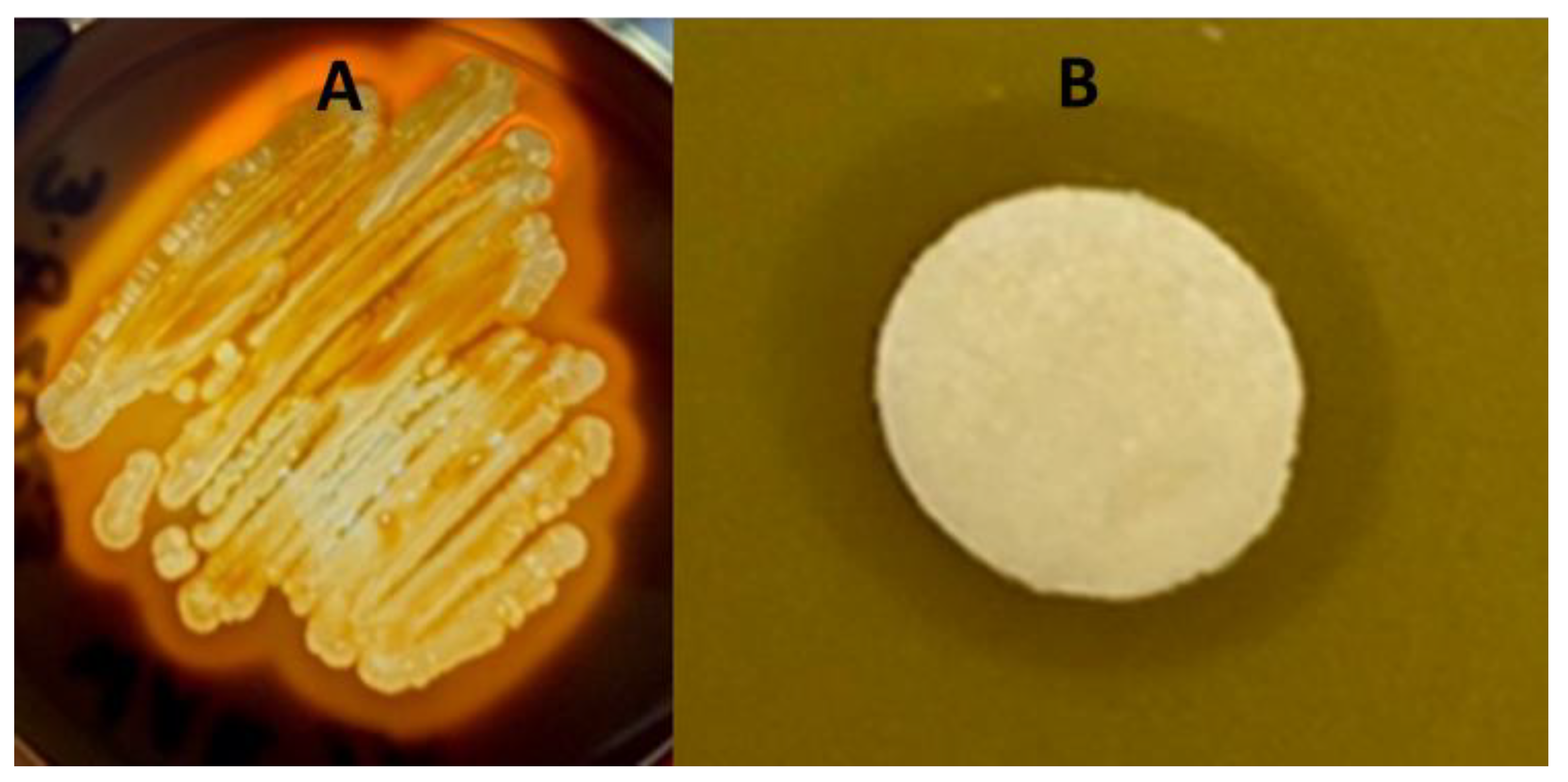
The bacterial isolate was both catalase- and oxidase-positive. Catalase protects the organism against the bactericidal effects of hydrogen peroxide and indicates that the isolate could be a or closely related to a Bacillus spp. The bacterial isolate, designated ClWae2A, also digested starch (Figure 1A) and lipase via the clearing of a spirit blue agar plate (Supplementary Figure S1). Furthermore, the isolate was phenotypically characterized as MIO-media-positive with slight motility but would not propagate in Simmons citrate media, which is used for differentiating Gram-negative bacteria. Isolate ClWae2A did metabolize maltose, lactose and dextrose but was growth-negative for nitrate broth and urea. The isolate was sensitive to several antibiotics, including tetracycline, erythromycin, penicillin, ampicillin, kanamycin, neomycin and novobiocin, but not streptomycin (Supplementary Figure S1).
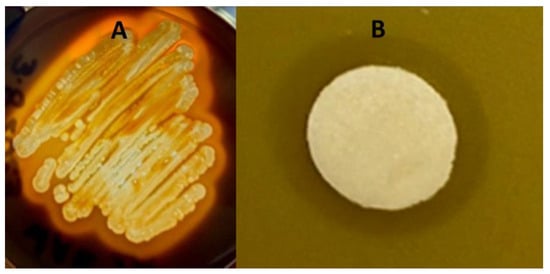
Figure 1.
Representative starch gel digestion assay and growth inhibition spot assay with a Staphylococcus aureus target on BHI media. Data for ClWae2A, a potential Paenibacillus sp., are presented for starch digestion (A) and the growth inhibition of the target bacteria (B).
3.2. Growth Inhibition of the Target Bacteria
The bacterial isolate inhibited the growth of three target bacteria, including S. aureus (Figure 1B), E. coli (Supplementary Figure S1) and M. luteus (data not shown). Clear zones of inhibition were reproducible following three replications, while no zones of inhibition were produced when using BHI-media-soaked discs as a control. Interestingly, zones of inhibition were produced against two Gram-positive organisms and were also obtained against the Gram-negative bacterium E. coli. The ClWae2A isolate routinely produced a visibly transparent ZOC of at least 2 mm in length with a defined edge of target bacterial growth, demonstrating that it inhibited the growth of the target bacterium.
3.3. Genomic Analyses of the Gray Wolf Bacterium
The whole genome sequence (WGS) of the Paenibacillus sp. ClWae2A is 7,034,206 bp encoding 6543 genes, including 133 genes involved with spore formation and germination (Table 1). Other genes identified included those encoding bacteriocins, lantibiotics, lysins and chitinases, along with cytochrome c oxidase. The metabolic genes identified following WGS included those encoding exoenzymes involved in starch and lipase digestion such as alpha amylase, cellulase and pectin lyase (Table 1 and Supplementary Table S1). Genome searches also revealed an incomplete viral lysogenic DNA with potential for antimicrobial activity, with 48 phage-derived genes found, including a terminase, amidase, holin and tail fiber protein genes. The phage genome sequences are most closely related (93–98%) to those found in the Paenibacillus sp. strain, designated OVF10 (GenBank: CP094668.1). Importantly, no toxin genes were identified in the Paenibacillus sp. ClWae2A genome, but an antitoxin gene was also encoded in the genome (Supplementary Table S1).

Table 1.
Paenibacillus sp. ClWae2A genome sequence and a summary of the identified genes.
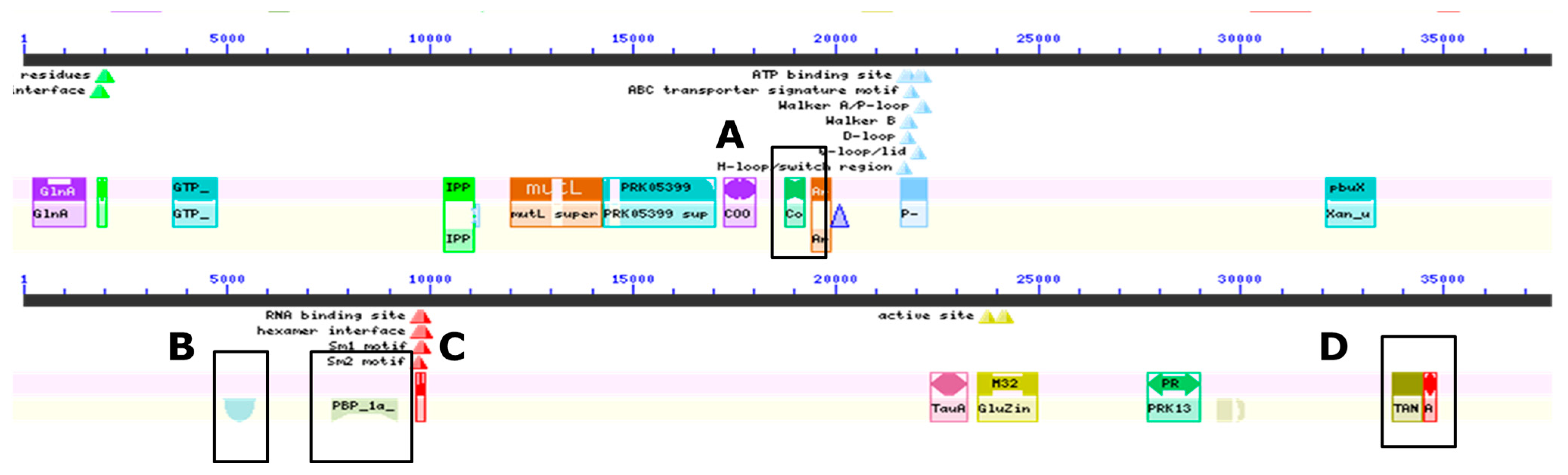
Domain searches within the genome confirmed the genome annotation results (Figure 2 and Supplementary Table S2). Specifically, outer-spore-coat-protein- and sporulation-protein-K-encoding genes were identified in the genome. Other genes identified included those encoding penicillin-binding proteins, transport and Golgi organization and antibiotic synthesis proteins. Although genes involved in unique metabolic properties such as the degradation of lignin and pectin were in greater numbers, there were genes identified that synthesize antimicrobials such as a chitinase, lantibiotic-and-bacteriocin-secretion systems and genes involved in polyketide biosynthesis. Genes encoding lysins and amidase were also identified in the genome (Table 1 and Supplementary Table S2).
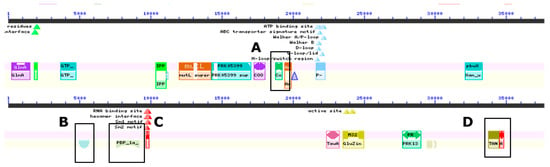
Figure 2.
Representative identification of genes from whole genome conserved domain sequence analyses of the wolf GI tract isolate ClWae2A. The genes identified encode (A) outer spore coat proteins, and (B) sporulation protein K, (C) as well as penicillin binding, (D) transport and Golgi organization and antibiotic synthesis proteins.
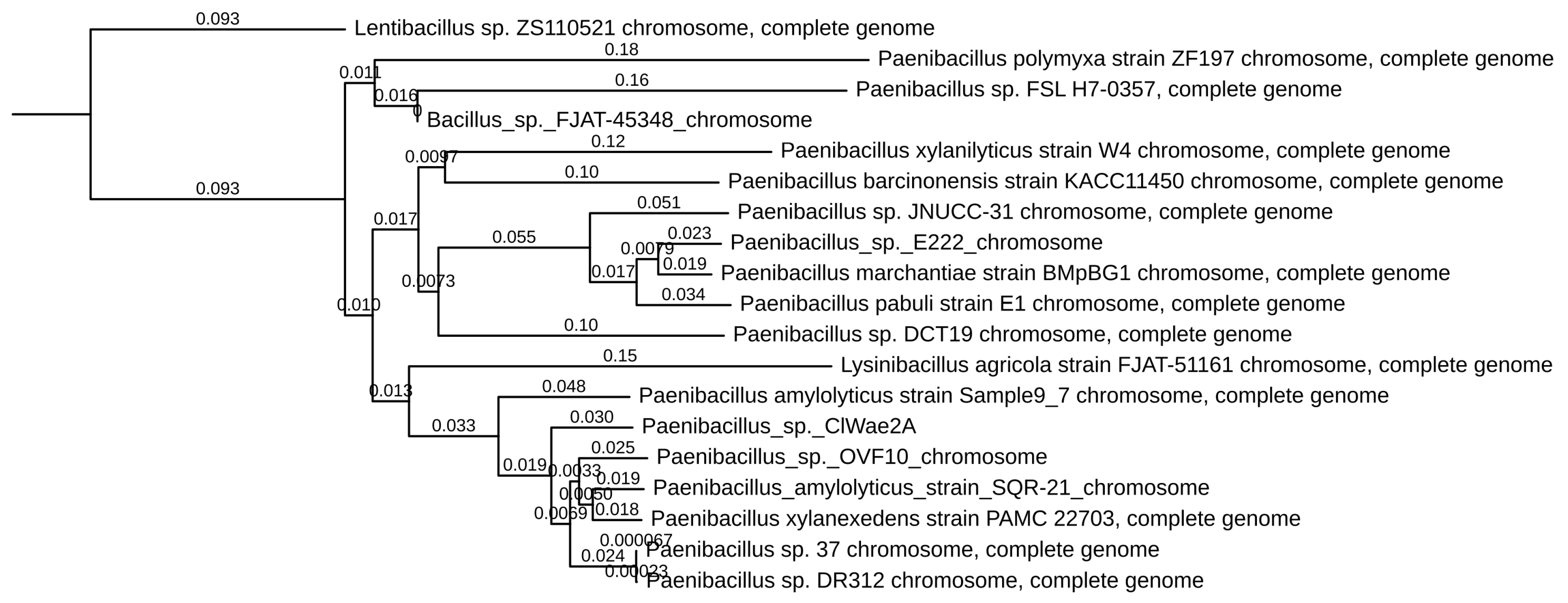
The DNA from the bacterium ClWae2A was initially typed via 16S rRNA gene sequencing as most closely related to the Paenibacillus xylanexedens strain PAMC 22703 (GenBank accession NZ_CP018620.1), with a sequence identity of 99%. Further phylogenetic analyses of Paenibacillus sp. ClWae2A using whole genome sequences revealed that the isolate was most closely related to a Paenibacillus amylolyticus strain, Sample 9–7 (GenBank accession CP121451.1) and the Paenibacillus sp. strain designated OVF10 (Genbank accession CP094668.1), as depicted in Figure 3. Interestingly, many Paenibacillus sp. such as P. amylolyticus and P. xylanilyticus do not group as individual clades, while several members of the genus do not yet have a species designation, resulting in a paraphyletic genus. Also, a Lysinibacillus agricola strain, FJAT-51161, groups within the Paenibacillus spp., while Lentibacillus sp. ZS110521 (GenBank accession ZS110521) separates as an outgroup.
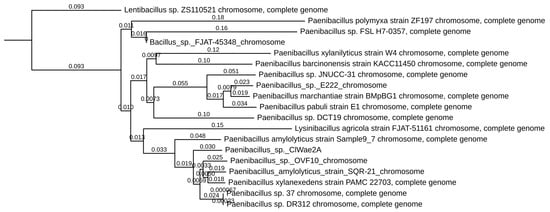
Figure 3.
Phylogenetic analysis of wolf bacteria isolate ClWae2A. Topology indicates that ClWae2A is most closely related to other strains in the Paenibacillus genus. Phylogenetic analyses were completed using BLAST+, using the Fast Minimum Evolution phylogeny inference algorithm followed by visualization and labeling in TreeViewer. Branch labels represent genetic distance.
Further analyses via blocked alignments followed by the creation of phylogenies for each block confirmed the close relationships among the Paenibacillus spp. (Supplementary Figure S2). Only isolates which represented scaffolds that consistently aligned to the ClWae2A genome were utilized for the analyses. Specifically, ClWae2A aligned to closely related isolates such as the P. amylolyticus strain SQR-21 (GenBank accession CP107037.1), which is reportedly associated with helping wheat resist drought. The P. xylanexedens strain PAMC 22703, is a xylan-degrading bacterium (GenBank accession CP018620.1), and the Paenibacillus sp. OVF10 (GenBank accession CP094668.1) reported in the GenBank file was isolated from a medicinal plant. The phylogeny bootstrap confidence intervals were 83% or greater (Supplementary Figure S2), and all the reported closely related isolates in GenBank have genome lengths that are similar to ClWae2A. However, none of the isolates were reported to have been isolated from animals, as reported in the GenBank files.
4. Discussion
The domestication of dogs includes their adaptation to processed feed high in carbohydrates that include cereal grains. This has resulted in the GI tracts of domestic dogs having microbiota which now more support polysaccharide metabolism [39]. Moreover, even when switched to a raw meat diet, a dog’s fecal microbiota only partially resembles that of a wolf [40]. Since the gut microbiomes of captive wolves may adapt to become more similar to domestic dogs [41,42], it makes sense to obtain new probiotics from free-ranging species to replace microbiota lost due to domestication. Consequently, free-ranging species, in this case, the gray wolf, could be utilized as a source of new bacterial species that might be used as probiotics in domestic animals such as the dog.
Paenibacillus-expressed antimicrobials include antibacterials and antifungals that have applications in both human and veterinary medicine. Importantly these bacteria also express exo-polysaccharides (EPS) and enzymes such as amylases, cellulases, hemicellulases, lipases, pectinases and lignin-modifying enzymes that can be used as feed additives [43]. The most commonly known Paenibacillus sp. that produces known antimicrobials such as the lipopeptide polymyxin, fusaricidins, paenilipoheptin, paenilan and tridecaptin is P. polymyxa [44]. For monogastric animals, a P. xylanexedens strain reportedly improved broiler performance by impacting intestinal morphology, enhanced the overall immune response and reduced E. coli in the cecum [45]. Also, a P. konkukensis sp., nov. SK3146, has been proposed as a probiotic for swine [46]. For example, other Paenibacillus spp. that produce antimicrobials [47,48,49] or degrade complex carbohydrates [50,51] have been isolated from environmental or plant sources.
Herein, we report a Paenibacillus sp. we designated ClWae2A, wolf aerobe 2A, due to its isolation from a gray wolf (Canis lupus), hence the Cl moniker. Its genome size is similar to other closely related Paenibacillus spp. and encodes genes such as those synthesizing antimicrobials, including bacteriocins, lantibiotics, amidases and chitinase. Other genes encode enzymes that would be of value in digesting carbohydrates and could contribute to energy metabolism for a monogastric animal. These are important functional attributes of a probiotic for potential use in companion animals such as dogs [52], especially since dogs have adapted to a starch-rich diet [53].
Prebiotics, probiotics, synbiotics and postbiotic compounds have all been proposed as treatments for IBD in humans [54], and the same can be stated for dogs [1,2,3]. Consequently, it is important to move toward a more precise delineation of bacterial probiotics to address the heterogeneity inherent to many probiotic strains [55]. The importance of whole genome sequencing (WGS), which enables the determination of virulence, toxin and antibiotic-resistance genes, as well as the clear assignment of species and strain identity [54,55], is important to help find new probiotic treatments for cIBD.
5. Conclusions
To meet the objective of characterizing potential new probiotics for dogs, we completed a draft WGS on a new wolf GI tract bacterial isolate characterized as a Paenibacillus sp. The bacterium inhibits the growth of other bacteria such as Staphylococcus aureus and encodes enzymes capable of digesting complex carbohydrates along with other gene systems expressing antimicrobials, thus indicating that this bacterial isolate could be a potential useful probiotic for domestic dogs.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/applmicrobiol3040077/s1, Figure S1: Phenotypic Characterizations of Paenibacillus sp. ClWae2A; Figure S2: Blocked alignment followed by phylogenies for each block [56]; Table S1: JGI IMG Genome Annotation. Table S2: Functional Genes Categories.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, B.S.S. and P.N.B.; methodology, J.M., J.L.B., C.C.K., M.J., A.N.A., T.W.C., A.D., M.G., K.M., N.A.B., H.M.B., M.R.A., R.B. and P.N.B.; software, J.L.B., J.M., M.J., C.C.K., K.M.S., B.S.S. and E.S.F.; validation, B.S.S. and P.N.B.; formal analysis, J.M., J.L.B., C.C.K., M.J., A.N.A., T.W.C., A.D., M.G., K.M., N.A.B. and B.S.S.; Data curation, J.L.B., J.M., M.J., C.C.K. and B.S.S.; Writing—original draft preparation, B.S.S.; Review and editing, J.M., J.L.B., C.C.K., M.J., P.N.B., E.S.F. and B.S.S.; Supervision and Project Administration, P.N.B., E.S.F. and B.S.S.; Funding acquisition, B.S.S., P.N.B. and E.S.F. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript. NOTE: J.M., J.L.B., C.C.K. and M.J. all contributed equally to the preparation of this manuscript.
Funding
Research funding support was provided to PNB as a start-up grant from the OSU Faculty Innovation Committee and the Gaskins Fund, and the OSU AID grant #M6008M Org: 192520 “Animal Probiotics Discovery” awarded to PNB and BSS. The project was also supported by a National Science Foundation grant (IOS-2114641) awarded to ESF.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The Oregon State University Institutional Biosafety Committee has approved the research reported herein as IBC Proposal #3923.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The draft whole genome sequence GenBank accession is Paenibacillus sp. ClWae2A as JAULSQ000000000, while the SRA submission is SUB13699518 Paenibacillus sp. ClWae2A isolate: ClWae2A genome sequencing and assembly. These investigations are listed as NCBI BioProject submission SUB13575117 and BioProject ID PRJNA987742, with the locus tag prefix QVE09 (SAMN35991278). The bacterial isolate reported herein is deposited in the USDA culture collection NRRL accession and assigned B-65673.
Acknowledgments
Funding was provided to AD as an URSA Scholar; to MG and TC as a Layman/URSA Fellows; and to J.M. and C.K. as Layman Fellows, all at Oregon State University—Cascades. The results reported are part of ongoing undergraduate research at Oregon State University—Cascades and have been presented at the annual Cascades Research and Scholarship Symposium: https://osucascades.edu/research/students/cascades-research-and-scholarship-symposium, accessed on 19 September 2023.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Vázquez-Baeza, Y.; Hyde, E.R.; Suchodolski, J.S.; Knight, R. Dog and human inflammatory bowel disease rely on overlapping yet distinct dysbiosis networks. Nat. Microbiol. 2016, 1, 16177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kopper, J.J.; Iennarella-Servantez, C.; Jergens, A.E.; Sahoo, D.K.; Guillot, E.; Bourgois-Mochel, A.; Martinez, M.N.; Allenspach, K.; Mochel, J.P. Harnessing the biology of canine intestinal organoids to heighten understanding of inflammatory bowel disease pathogenesis and accelerate drug discovery: A one health approach. Front. Toxicol. 2021, 3, 773953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rhimi, S.; Kriaa, A.; Mariaule, V.; Saidi, A.; Drut, A.; Jablaoui, A.; Akermi, N.; Maguin, E.; Hernandez, J.; Rhimi, M. The Nexus of Diet, Gut Microbiota, and Inflammatory Bowel Diseases in Dogs. Metabolites 2022, 12, 1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doulidis, P.G.; Galler, A.I.; Hausmann, B.; Berry, D.; Rodríguez-Rojas, A.; Burgener, I.A. Gut microbiome signatures of Yorkshire Terrier enteropathy during disease and remission. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 4337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minamoto, Y.; Minamoto, T.; Isaiah, A.; Sattasathuchana, P.; Buono, A.; Rangachari, V.R.; McNeely, I.H.; Lidbury, J.; Steiner, J.M.; Suchodolski, J.S. Fecal short-chain fatty acid concentrations and dysbiosis in dogs with chronic enteropathy. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2019, 33, 1608–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bansal, T.; Alaniz, R.C.; Wood, T.K.; Jayaraman, A. The bacterial signal indole increases epithelial-cell tight-junction resistance and attenuates indicators of inflammation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 228–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hand, D.; Wallis, C.; Colyer, A.; Penn, C.W. Pyrosequencing the canine faecal microbiota: Breadth and depth of biodiversity. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e53115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pilla, R.; Suchodolski, J.S. The gut microbiome of dogs and cats, and the influence of diet. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Small Anim. Pract. 2021, 51, 605–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Mazcorro, J.F.; Lanerie, D.J.; Dowd, S.E.; Paddock, C.G.; Grützner, N.; Steiner, J.M.; Ivanek, R.; Suchodolski, J.S. Effect of a multi-species synbiotic formulation on fecal bacterial microbiota of healthy cats and dogs as evaluated by pyrosequencing. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2011, 78, 542–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bermingham, E.N.; Maclean, P.; Thomas, D.G.; Cave, N.J.; Young, W. Key bacterial families (Clostridiaceae, Erysipelotrichaceae and Bacteroidaceae) are related to the digestion of protein and energy in dogs. PeerJ 2017, 2, e3019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halfvarson, J.; Brislawn, C.J.; Lamendella, R.; Vázquez-Baeza, Y.; Walters, W.A.; Bramer, L.M.; D’Amato, M.; Bonfiglio, F.; McDonald, D.; Gonzalez, A.; et al. Dynamics of the human gut microbiome in inflammatory bowel disease. Nat. Microbiol. 2017, 2, 17004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moeller, A.H.; Sanders, J.G. Roles of the gut microbiota in the adaptive evolution of mammalian species. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2020, 375, 20190597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergström, A.; Frantz, L.; Schmidt, R.; Ersmark, E.; Lebrasseur, O.; Girdland-Flink, L.; Lin, A.T.; Storå, J.; Sjögren, K.G.; Anthony, D.; et al. Origins and genetic legacy of prehistoric dogs. Science 2020, 370, 557–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergström, A.; Stanton, D.W.G.; Taron, U.H.; Frantz, L.; Sinding, M.S.; Ersmark, E.; Pfrengle, S.; Cassatt-Johnstone, M.; Lebrasseur, O.; Girdland-Flink, L.; et al. Grey wolf genomic history reveals a dual ancestry of dogs. Nature 2022, 607, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perri, A.R.; Feuerborn, T.R.; Frantz, L.A.F.; Larson, G.; Malhi, R.S.; Meltzer, D.J.; Witt, K.E. Dog domestication and the dual dispersal of people and dogs into the Americas. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2010083118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arendt, M.; Cairns, K.M.; Ballard, J.W.; Savolainen, P.; Axelsson, E. Diet adaptation in dog reflects spread of prehistoric agriculture. Heredity 2016, 117, 301–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corsato Alvarenga, I.; Aldrich, C.G. Starch characterization of commercial extruded dry pet foods. Transl. Anim. Sci. 2020, 4, txaa018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richards, T.L.; Rankovic, A.; Cant, J.P.; Shoveller, A.K.; Adolphe, J.L.; Ramdath, D.; Verbrugghe, A. Effect of total starch and resistant starch in commercial extruded dog foods on gastric emptying in Siberian huskies. Animals 2021, 11, 2928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, C.; Guarner, F.; Reid, G.; Gibson, G.R.; Merenstein, D.J.; Pot, B.; Morelli, L.; Canani, R.B.; Flint, H.J.; Salminen, S.; et al. Expert consensus document. The International Scientific Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics consensus statement on the scope and appropriate use of the term probiotic. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 8, 506–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitz, S.S. Value of probiotics in canine and feline gastroenterology. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Small. Anim. Pract. 2021, 1, 171–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.; Goh, T.W.; Kang, M.G.; Choi, H.J.; Yeo, S.Y.; Yang, J.; Huh, C.S.; Kim, Y.Y.; Kim, Y. Perspectives and advances in probiotics and the gut microbiome in companion animals. J. Anim. Sci. Technol. 2022, 64, 197–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atarashi, K.; Tanoue, T.; Shima, T.; Imaoka, A.; Kuwahara, T.; Momose, Y.; Cheng, G.; Yamasaki, S.; Saito, T.; Ohba, Y.; et al. Induction of colonic regulatory T cells by indigenous Clostridium species. Science 2011, 331, 337–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapin, K.; Murray, P. Manual of Clinical Microbiology, 7th ed.; Murray, P.R., Baron, E.J., Pfaller, M.A., Tenover, F.C., Yolken, R.H., Eds.; American Society for Microbiology: Washington, DC, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Mahon, C.R.; Lehman, D.C.; Manuselis, G. Textbook of Diagnostic Microbiology, 5th ed.; W. B Saunders Co.: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Hardy, B.L.; Bansal, G.; Hewlett, K.H.; Arora, A.; Schaffer, S.D.; Kamau, E.; Bennett, J.W.; Merrell, D.S. Antimicrobial Activity of Clinically Isolated Bacterial Species Against Staphylococcus aureus. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 2977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woese, C.R.; Fox, G.E. Phylogenetic structure of the prokaryotic domain: The primary kingdom. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1977, 74, 5088–5090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weisburg, W.G.; Barns, S.M.; Pelletier, D.A.; Lane, D.J. 16S ribosomal DNA amplification for phylogenetic study. J. Bacteriol. 1991, 173, 697–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stackebrandt, E.; Frederiksen, W.; Garrity, G.M.; Grimont, P.A.D.; Kämpfer, P.; Maiden, M.C.J.; Nesme, X.; Rosselló-Mora, R.; Swings, J.; Trüper, H.G.; et al. Report of the ad hoc committee for the re-evaluation of the species definition in bacteriology. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2002, 52, 1043–1047. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Altschul, S.F.; Madden, T.L.; Schäffer, A.A.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Miller, W.; Lipman, D.J. Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: A new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997, 25, 3389–3402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Kumar, S. MEGA11: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis version 11. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 3022–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bankevich, A.; Nurk, S.; Antipov, D.; Gurevich, A.A.; Dvorkin, M.; Kulikov, A.S.; Lesin, V.M.; Nikolenko, S.I.; Pham, S.; Prjibelski, A.D.; et al. SPAdes: A new genome assembly algorithm and its applications to single-cell sequencing. J. Comput. Biol. 2012, 19, 455–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, I.A.; Chu, K.; Palaniappan, K.; Ratner, A.; Huang, J.; Huntemann, M.; Hajek, P.; Ritter, S.J.; Webb, C.; Wu, D.; et al. The IMG/M data management and analysis system v.7: Content updates and new features. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, D723–D732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchler-Bauer, A.; Derbyshire, M.K.; Gonzales, N.R.; Lu, S.; Chitsaz, F.; Geer, L.Y.; Geer, R.C.; He, J.; Gwadz, M.; Hurwitz, D.I.; et al. CDD: NCBI’s conserved domain database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, D222–D226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arndt, D.; Grant, J.R.; Marcu, A.; Sajed, T.; Pon, A.; Liang, Y.; Wishart, D.S. PHASTER: A better, faster version of the PHAST phage search tool. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, W16–W21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchini, G.; Sánchez-Baracaldo, P. TreeViewer—Cross-Platform Software to Draw Phylogenetic Trees (Version 2.1.0); Zenodo: Geneva, Switzerland, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angiuoli, S.V.; Salzberg, S.L. Mugsy: Fast multiple alignment of closely related whole genomes. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 334–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamatakis, A. RAxML version 8: A tool for phylogenetic analysis and post-analysis of large phylogenies. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 1312–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rambaut, A. Figtree; v1.3.1; Institute of Evolutionary Biology, University of Edinburgh: Edinburgh, UK, 2010; Available online: http://tree.bio.ed.ac.uk/software/figtree/ (accessed on 19 September 2023).
- Reese, A.T.; Chadaideh, K.S.; Diggins, C.E.; Schell, L.D.; Beckel, M.; Callahan, P.; Ryan, R.; Emery Thompson, M.; Carmody, R.N. Effects of domestication on the gut microbiota parallel those of human industrialization. eLife 2021, 10, e60197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, T.; Liu, G.; Zhang, H.; Wang, L.; Zhou, S.; Dou, H.; Pang, B.; Sha, W.; Zhang, H. Changes in feeding habits promoted the differentiation of the composition and function of gut microbiotas between domestic dogs (Canis lupus familiaris) and gray wolves (Canis lupus). AMB Express 2018, 8, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Becker, A.A.M.J.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, W.; Ge, B.; Leng, C.; Leng, C.; Wang, G.; Ding, L.; Wang, J.; et al. The Fecal Microbiota of Dogs Switching to a Raw Diet Only Partially Converges to That of Wolves. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 701439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Sun, M.; Xu, D.; Gao, Z.; Shi, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhou, Y. Gut microbiome of captive wolves is more similar to domestic dogs than wild wolves indicated by metagenomics study. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1027188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grady, E.N.; MacDonald, J.; Liu, L.; Richman, A.; Yuan, Z.C. Current knowledge and perspectives of Paenibacillus: A review. Microb. Cell Fact. 2016, 15, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, A.K.; Barbetti, M.J.; Lamichhane, J.R. Paenibacillus polymyxa. Trends Microbiol. 2023, 31, 657–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ekim, B.; Calik, A.; Ceylan, A.; Saçakli, P. Effects of Paenibacillus xylanexedens on growth performance, intestinal histomorphology, intestinal microflora, and immune response in broiler chickens challenged with Escherichia coli K88. Poult. Sci. 2020, 99, 214–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.I.; Park, S.; Niu, K.M.; Lee, S.W.; Kothari, D.; Yi, K.J.; Kim, S.K. Complete genome sequence of Paenibacillus konkukensis sp. nov. SK3146 as a potential probiotic strain. J. Anim. Sci. Technol. 2021, 63, 666–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, E.; Guo, Y.; Yousef, A.E. Draft genome sequence of Paenibacillus sp. strain OSY-SE, a bacterium producing the novel broad-spectrum lipopeptide antibiotic paenibacterin. J. Bacteriol. 2012, 78, 3156–3165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pajor, M.; Sogin, J.; Worobo, R.W.; Szweda, P. Draft genome sequence of antimicrobial producing Paenibacillus alvei strain MP1 reveals putative novel antimicrobials. BMC Res. Notes 2020, 13, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eltokhy, M.A.; Saad, B.T.; Eltayeb, W.N.; Yahia, I.S.; Aboshanab, K.M.; Ashour, M.S.E. Exploring the nature of the antimicrobial metabolites produced by Paenibacillus ehimensis soil isolate MZ921932 using a metagenomic nanopore sequencing coupled with LC-mass analysis. Antibiotics 2021, 1, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keggi, C.; Doran-Peterson, J. Paenibacillus amylolyticus 27C64 has a diverse set of carbohydrate-active enzymes and complete pectin deconstruction system. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 46, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, W.; Liu, P.; Liao, W.; Miao, L. Complete Genome of the Chitin-Degrading Bacterium, Paenibacillus xylanilyticus W4. Genome Biol. Evol. 2019, 10, 2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, H.-J.; Son, S.; Kim, J.-A.; Jung, M.Y.; Choi, Y.-j.; Kim, D.-H.; Lee, H.K.; Shin, D.; Kim, Y. Characterization and functional test of canine probiotics. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 625562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, B.; Liu, C.; Hu, Y.; Liu, C.; Li, X.; Li, X.; Zhang, X.; Irwin, D.M.; Wu, Z.; et al. Differences in the gut microbiomes of dogs and wolves: Roles of antibiotics and starch. BMC Vet. Res. 2021, 17, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veiga, P.; Suez, J.; Derrien, M.; Elinav, E. Moving from probiotics to precision probiotics. Nat. Microbiol. 2020, 5, 878–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collado, M.C.; Morelli, L.; Montoya, G.A.; Szajewska, H.; Tancredi, D.J.; Sanders, M.E. Emerging issues in probiotic safety: 2023 perspectives. Gut Microbes 2023, 15, 2185034. [Google Scholar]
- Altschul, S.F.; Gish, W.; Miller, W.; Myers, E.W.; Lipman, D.J. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 1990, 215, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).