1. Introduction
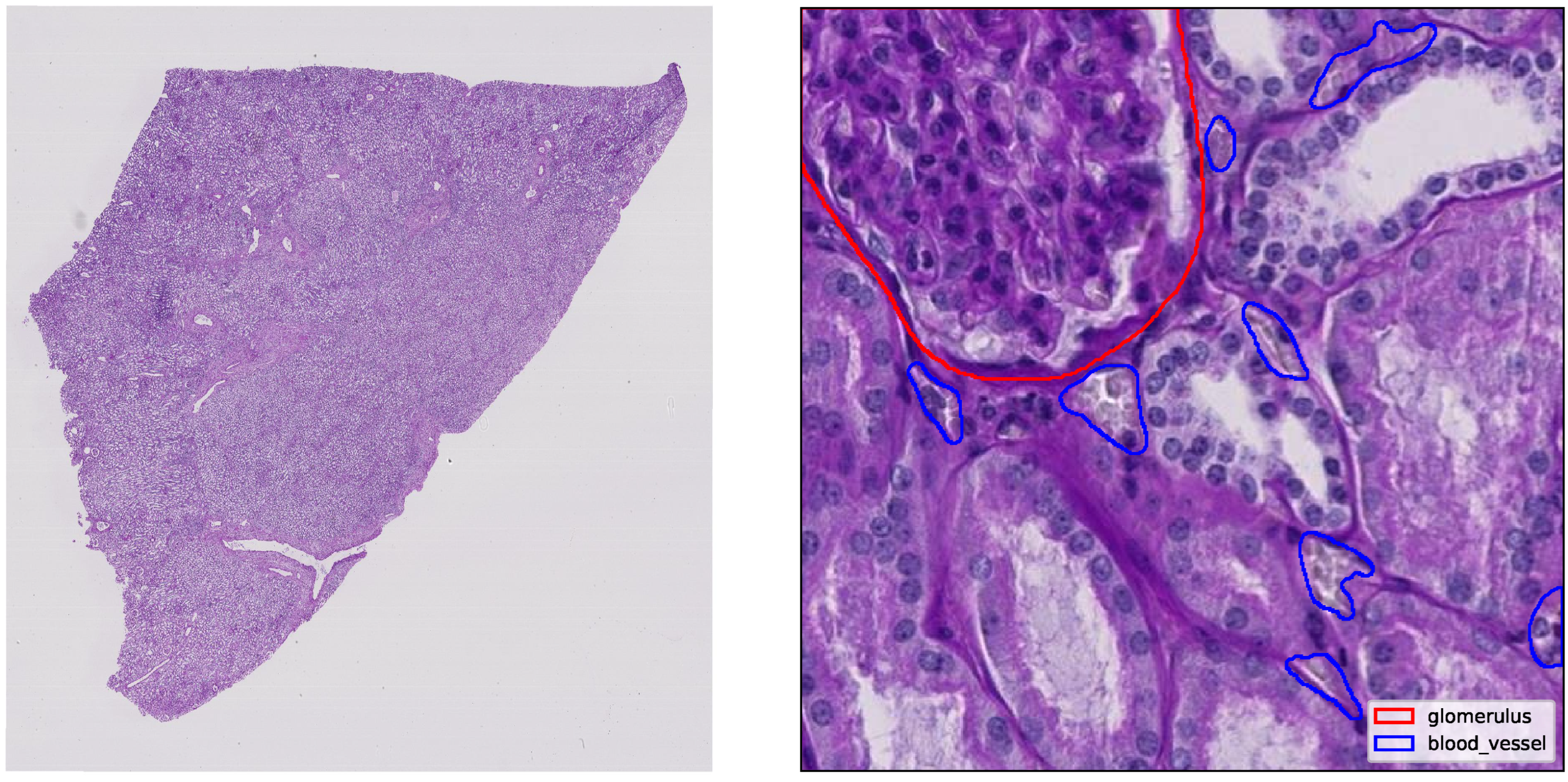
The kidney is a vital organ responsible for maintaining systemic homeostasis by regulating blood filtration, fluid balance, electrolyte composition and acid-base status. Each kidney contains around one million nephrons, with each beginning at the glomerulus, a specialized capillary network that serves as the primary blood filtration site. Approximately one-fifth of cardiac output is delivered through the renal vasculature to maintain an adequate glomerular filtration rate [
1]. The capillaries, arterioles and venules within the kidney ensure this filtration process and support metabolic demands. Damage to these microvascular structures or to the glomerular filtration barrier can lead to conditions, such as proteinuria, chronic kidney disease, or end-stage renal disease [
2]. Additionally, vascular dysfunction and microvascular rarefaction contribute to progressive loss of kidney function [
1].
Given the central role of microvascular health in renal pathology, accurate assessment of glomerular and vascular structures is essential for diagnosis and monitoring. High-resolution kidney biopsies remain the clinical gold standard and modern whole slide imaging allows the digitization of entire biopsy slides at subcellular resolution, often producing gigapixel scale images. However, manual analysis methods are labor-intensive, subjective and often inconsistent across imaging conditions [
3]. Deep learning methods, particularly convolutional neural networks (CNN), have shown promise in automating such analyses but face computational limitations when processing entire WSIs directly.
One of the key challenges in this context is small object detection. In renal histopathology, microvascular structures occupy small pixel regions and exhibit high morphological variability [
4,
5]. These factors, along with class imbalance and anatomical complexity [
6,
7], limit the effectiveness of conventional detection models, as small objects often lack sufficient semantic and contextual features for reliable extraction. To address this, tiling-based inference has become a common approach, where WSIs are divided into smaller patches to allow localized, high-resolution predictions.
A widely adopted tiling strategy is slicing aided hyper inference [
8], which enables large-scale inference by slicing images into overlapping or non-overlapping tiles. However, SAHI introduces postprocessing challenges. Since objects may be fragmented across tiles, a consolidation step is needed to merge redundant or partial detections. Traditional Non-Maximum Suppression (NMS) [
9] is commonly used for this purpose but is suboptimal for instance segmentation due to its box-centric logic and inability to preserve full object extent, especially for irregular or boundary-crossing structures [
10]. Syncretic NMS [
11] improves upon this by merging correlated neighboring detections, yet it still suffers in low-overlap or sparsely tiled settings, which are common in WSI processing.
Recent advances have explored various strategies to improve object detection and segmentation in high-resolution images. The importance of pre- and post-processing in whole slide image analysis pipelines has been highlighted, with tiling and reconstruction steps introducing unique challenges that impact the reliability of clinical predictions [
12]. Combining the SAHI algorithm with modern neural networks has been shown to enhance the detection of small objects in high-resolution images, supporting the use of tiling-based inference [
13]. However, the fragmentation of objects across tiles remains problematic, particularly for boundary-spanning structures. A hybrid two-stage cascade has been proposed to mitigate segmentation errors in overlapping objects, yet mask inaccuracies persist in complex spatial arrangements, similar to the microvascular structures observed in kidney histology [
14]. Optimization-based methods, such as the particle swarm optimization approach for enhancing segmentation accuracy, have also been explored but not systematically applied to the postprocessing of tiled WSI segmentations [
15]. Overall, current merging strategies largely rely on heuristic, box-centric approaches that struggle to reconstruct irregularly shaped or elongated objects and lack principled mechanisms for adapting parameters across datasets or imaging conditions. These limitations frequently result in fragmented or incomplete masks, leading to precision losses for fine microvascular structures that cross tile boundaries in renal WSIs.
There is currently no postprocessing framework explicitly designed to address spatial fragmentation and boundary-crossing inconsistencies in tiled WSI instance segmentation. Existing solutions rely on heuristic, non-adaptive methods that fail to accurately reconstruct irregular microvascular objects and cannot dynamically balance segmentation precision with computational efficiency in gigapixel-scale images. This raises the research question: How can mask merging strategies in tiled whole slide image inference be optimized to accurately reconstruct boundary-spanning microvascular structures, maximizing segmentation precision while maintaining computational efficiency beyond what existing postprocessing methods offer?
To address this gap, this work introduces an enhanced syncretic mask merging algorithm specifically designed to handle irregularly shaped, low-density and partially detected microvascular structures in renal WSIs. The approach is integrated into a complete segmentation pipeline that
Provides a comparative evaluation of YOLOv11 and YOLOv12 instance segmentation models, validated using SAHI tiling on high-resolution kidney WSIs.
Investigates the impact of tile overlap on segmentation accuracy and identifies optimal overlap configurations.
Introduces a novel syncretic mask merging algorithm capable of reconstructing fragmented objects more effectively across tile boundaries.
Proposes and explores the viability of metaheuristics PSO for adaptive tuning of mask merging parameters, aiming to improve segmentation precision while maintaining computational efficiency.
The objective of this study is to develop and evaluate a scalable, accuracy-focused segmentation pipeline tailored for complex microvascular structures in renal WSIs, providing a solution that overcomes the limitations of existing postprocessing techniques.
2. Materials and Methods
This section presents the components of the proposed instance segmentation pipeline, including the base segmentation models, the tiling and inference strategy, the enhanced merging algorithm and the optimization of its hyperparameters.
Among the core components of our pipeline, the segmentation backbone is based on the YOLO architecture, which performs object detection and segmentation using a unified forward pass. The loss function guiding YOLO training combines four terms: localization, object confidence, objectness penalty for background regions and classification. For improved stability, particularly for small, fragmented anatomical features, advanced variants such as Complete Intersection-over-Union (CIoU) loss are used to better align predicted and ground truth boxes [
16]. A detailed mathematical description of the YOLO loss function and its role in this study is provided in
Appendix A.
SAHI [
8] is employed to enable object detection on whole slide images by dividing them into overlapping patches. Each tile is processed independently and predictions are later merged to produce whole-image instance segmentation. Key slicing parameters such as tile size and overlap ratios are explored and tuned to balance efficiency and object continuity. However, due to the challenges of merging fragmented detections near tile borders, especially for irregular objects, we propose a postprocessing algorithm designed to enhance merging accuracy. Further details of the SAHI algorithm and its formal implementation are provided in
Appendix B.
To improve postprocessing in tiled inference scenarios, we build upon Syncretic NMS [
11], an extension of standard NMS that merges spatially correlated detections to recover more complete object instances. While originally developed for general instance segmentation, its applicability to whole slide images is limited due to challenges such as sparse tile overlap and low IoU across tile boundaries. In this work, we adapt and extend the Syncretic framework to address those issues, enabling robust merging of fragmented microvascular detections across tiles. A detailed description of the original Syncretic NMS algorithm and its merging criteria is provided in
Appendix C.
To further improve the accuracy and coherence of reconstructed instances, we introduce a refinement operator
applied to each cluster
A of correlated detections. This operator merges the binary masks of all objects in
A using a logical union, followed by a set of morphological operations. These include mask smoothing via morphological closing, hole filling and selective dilation of small or fragmented regions. The purpose is to enhance shape continuity, close gaps introduced by tile boundaries and correct under-segmentation in low-contrast or irregularly shaped structures. The refined object retains its semantic class and has its bounding box and geometry recomputed from the updated mask. The full morphological refinement procedure, along with implementation details and parameters, is provided in
Appendix D.
2.4. Proposed Enhanced Syncretic Mask Merging
To overcome the limitations of traditional bounding box-based merging in large-scale image inference, the Syncretic NMS framework is extended with modified merging criteria and a morphological postprocessing procedure. The proposed method is specifically tailored for tiled instance segmentation and introduces object-level reasoning that preserves the continuity of biological structures across tile borders.
The enhanced Syncretic strategy generalizes prior approaches by applying merging to binary object masks rather than bounding boxes, using a flexible mergeability predicate and additional morphological operations to resolve overlapping or fragmented instances across tiles. Specifically, border objects are detected and clustered using a spatial proximity radius, with merging decisions guided by contour similarity
, feature similarity
, bounding box IoU
and semantic label agreement
. The resulting clusters are fused into unified masks via logical union, followed by contour simplification and polygon extraction. A final morphological refinement stage applies gap closing, hole filling and one pass dilation to improve continuity and recover thin or clipped regions.
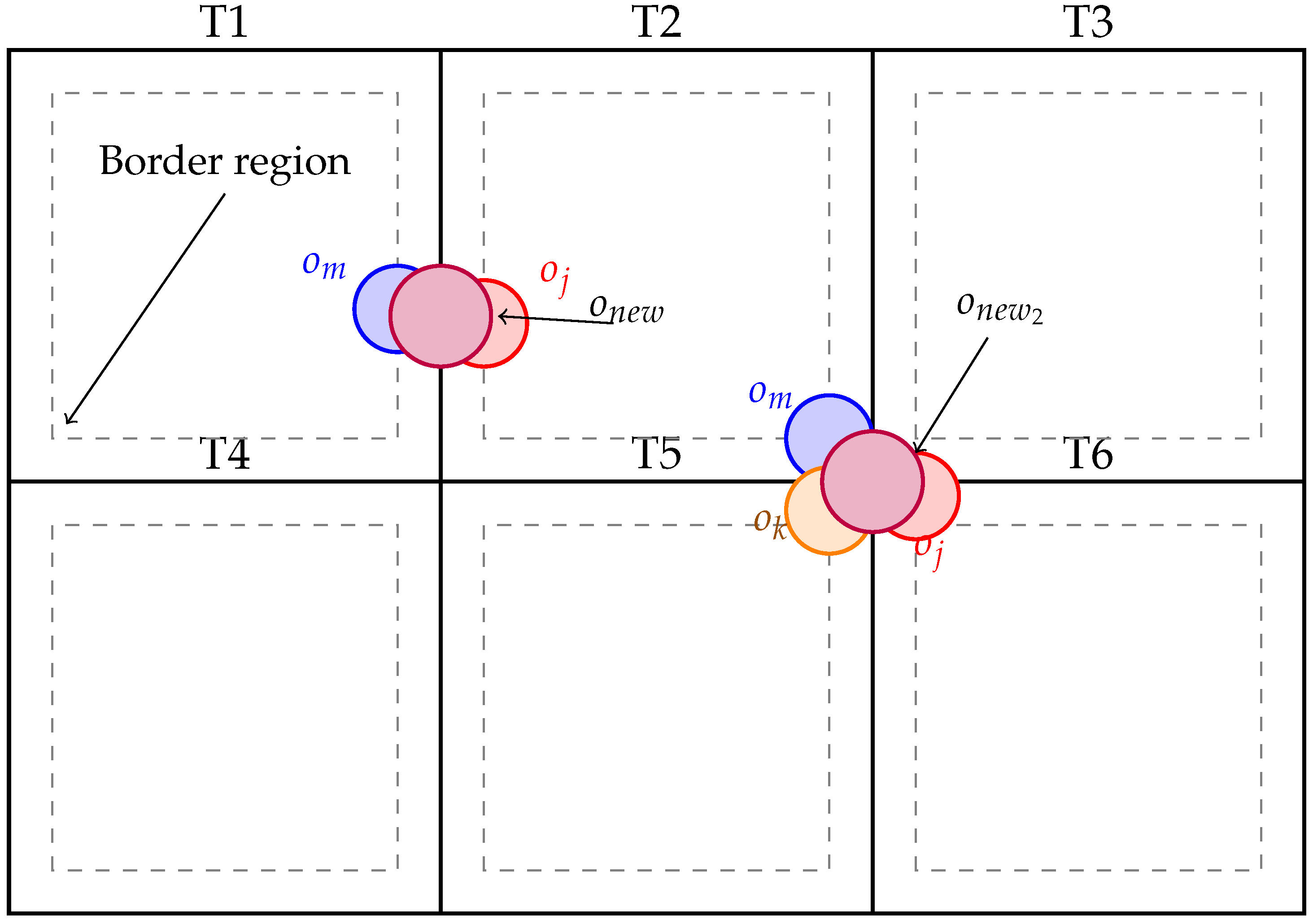
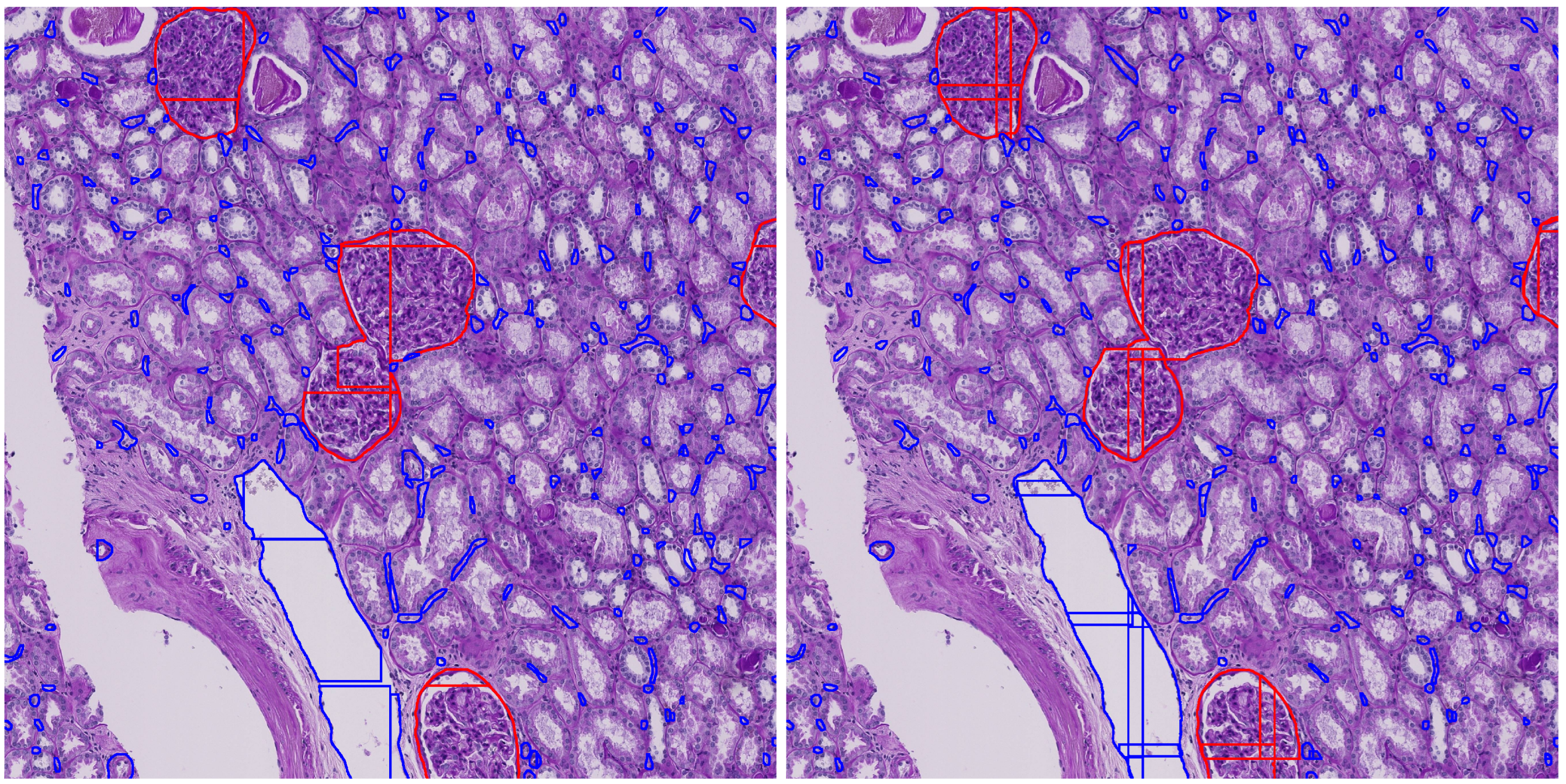
Figure 2 illustrates the mask merging process, showing how fragmented instances are accurately grouped and reconstructed across adjacent tiles.
Algorithm 1 operates in two major stages: (1) object-level clustering based on spatial, semantic, and feature similarity, and (2) morphological refinement. First, all detected instances are converted from local tile coordinates into a unified global space. Objects near tile boundaries are designated as merge candidates and grouped into a global candidate set. Merging proceeds iteratively: at each step, the highest confidence object is selected as a seed, and neighboring candidates are evaluated for compatibility using a mergeability predicate
. This predicate considers semantic class consistency, contour proximity, feature vector similarity, and geometric overlap. Compatible objects are grouped into a cluster and merged via the operator
, producing a unified mask instance.
| Algorithm 1 Enhanced Syncretic Merging Algorithm (adapted from [11]) |
Require: Tiles with local masks, confidence scores and class labels; tile offsets
Ensure: Merged global object set G- 1:
Convert all objects to global coordinates: - 2:
Identify candidate objects near tile edges: - 3:
Combine border objects into global pool: - 4:
Initialize empty set G - 5:
Build candidate list B from unmatched objects in - 6:
while do - 7:
Select object with maximum confidence - 8:
Initialize set - 9:
for each in B near do - 10:
if holds then - 11:
Add to A - 12:
Remove from B - 13:
end if - 14:
end for - 15:
- 16:
- 17:
Remove from B - 18:
end while - 19:
return G
|
Where:
: The i-th tile in the WSI, with local detections, masks, scores and class labels.
: Tile upper left corner.
n: Total number of tiles in the WSI.
: List of border objects in tile , whose bounding boxes or masks lie within border_threshold_px of any tile edge.
: List of all objects near border .
B: Working candidate list built from unmatched objects in at the start of each iteration.
: Object in B with the highest confidence in the current iteration.
A: Merge group initialized with and extended with nearby compatible objects.
: A candidate object in B evaluated for merging with .
: New merged object resulting from applying .
G: Final list of merged global objects to be returned.
border_threshold_px: Pixel threshold defining how close an object must be to a tile edge to be considered a border object.
search_radius: Maximum spatial distance (in pixels) within which object pairs are considered for merging.
The mergeability predicate
is evaluated using the following criteria:
where:
: Euclidean distance between outlines of
and
[
24].
: Cosine similarity between shape features of
and
[
25].
: IoU score between the and boxes.
: Semantic label match indicator, equals 1 if classes match, else 0.
The functions defining the mergeability predicate and their thresholds are as follows:
in Equation (
3) captures contour-based spatial proximity and is constrained by the distance contour_proximity_thresh (
);
in Equation (
2), measures cosine similarity of features that are over the cosine_sim_thresh (
);
, representing the IoU between bounding boxes, which must meet the minimum threshold bbox_iou_thresh (
);
in Equation (
5), a binary indicator ensuring semantic class consistency [
26].
In the Equations (
2)–(
5),
and
denote the sets of foreground pixels (or sampled points) from the masks of objects
and
, respectively.
and
represent their corresponding feature vectors, which may be derived from intermediate neural network embeddings.
and
are the sets of contour or boundary points extracted from the object masks. The
represents the confidence score of object
predicted. The operator
refers to the Euclidean norm and
denotes the cardinality of a set. The dot product
is used in computing cosine similarity and the intersection and union operators in
correspond to standard binary mask operations. The proposed merging framework incorporates this refinement operator
as a final step, ensuring spatial continuity and accurate reconstruction of merged object instances. Implementation details are included in
Appendix D.
In terms of computational complexity, the Enhanced Mask Merge algorithm scales as , where N is the number of border objects, k is the average number of nearby candidates considered for merging and d is the dimensionality of the feature vectors used in similarity evaluation. These feature vectors encode appearance or shape characteristics and are used to compute cosine similarity between objects. In contrast, the Syncretic NMS algorithm does not rely on feature vectors and instead performs pairwise comparisons based solely on geometric overlap and confidence scores. As a result, its worst-case complexity is , since each box may be compared with all others. While Syncretic NMS is simpler and effective for small-scale scenarios, its quadratic growth becomes computationally expensive as N increases. Enhanced Mask Merge, by leveraging spatial locality and feature-based filtering, offers a scalable alternative for large-scale instance merging tasks.
3. Results
To assess the proposed training strategy and model architectures, an evaluation was conducted across multiple training epochs and inference settings. Loss components for both models consistently decreased across epochs, with no signs of overfitting observed. In the inference phase, both models successfully integrated SAHI, enabling dense and overlapping tile aggregation across high-resolution whole slide images. This approach allowed for precise instance segmentation while maintaining computational efficiency on large-scale histology data.
Table 2 presents a comparative evaluation of instance segmentation performance between YOLOv11s-seg and YOLOv12s-seg across key kidney tissue structures.
Both models achieved high segmentation performance for glomerulus, with precision and recall consistently above 88%. Blood vessel segmentation was more variable due to the finer and more diffuse structure of vascular elements. However, YOLOv11s-seg maintained a higher F1 score overall, making it more balanced in performance across both classes.
As shown in
Table 3, YOLOv11s-seg was considerably more efficient, with lower GPU memory usage and faster epoch and inference times. This is particularly important in whole slide image workflows, where inference must be both accurate and fast. The reduced GPU footprint of YOLOv11s-seg also enhances its applicability in clinical or resource-limited deployment environments. Given the strong segmentation performance, compact architecture, and superior computational efficiency, YOLOv11s-seg was selected for downstream tasks, including framework validation and segmentation-based postprocessing.
Figure 3 shows the Mask F1 score curve and the mask Precision Recall (PR) curve for YOLOv11s-seg. The F1 curve tracks the harmonic mean of mask precision and recall throughout training. Glomerular segmentation demonstrates particularly strong separation, while blood vessel performance is slightly more variable.
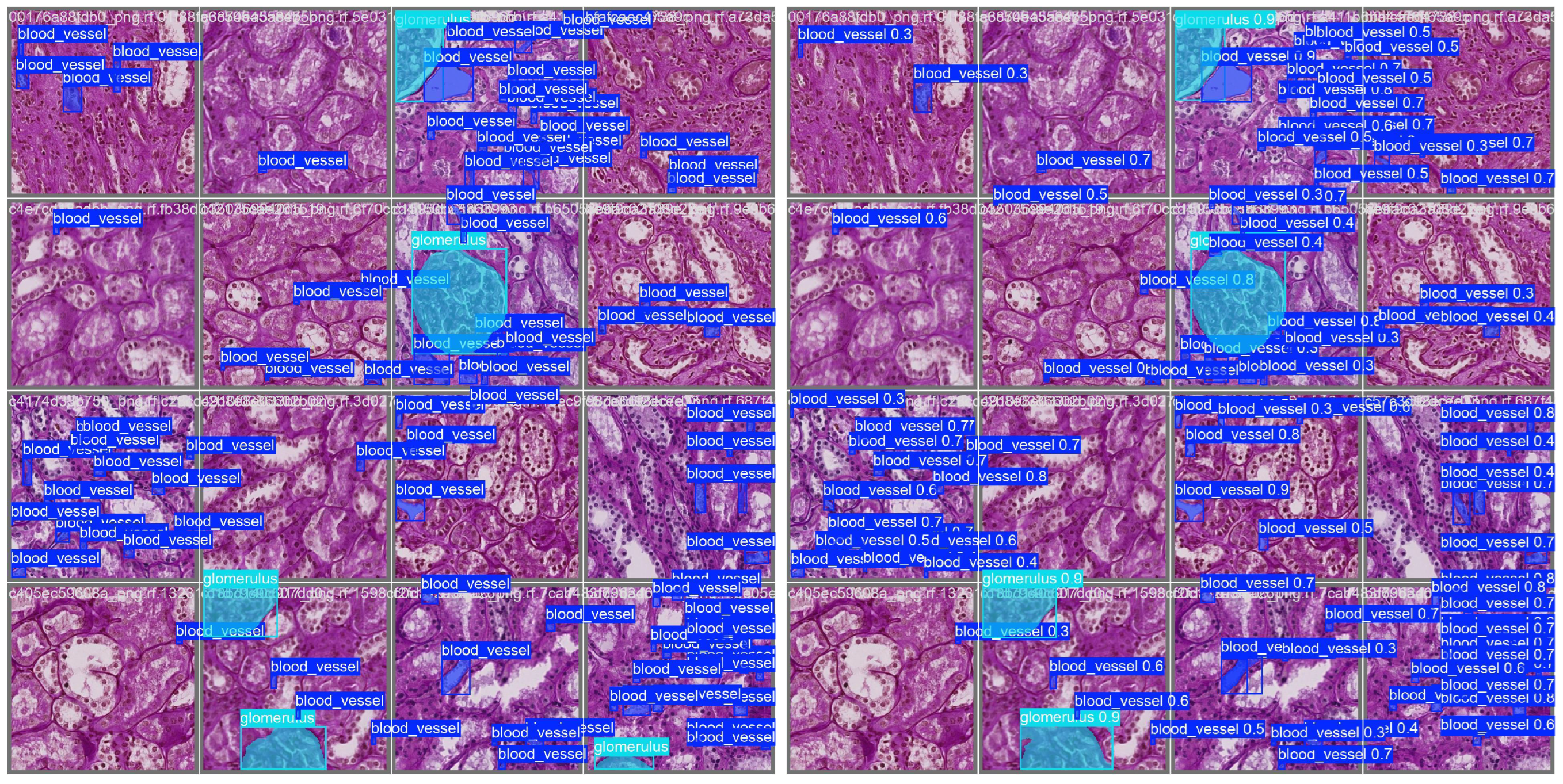
Figure 4 presents a representative validation example. The left panel shows ground truth masks for glomeruli and blood vessels overlaid on a histology tile, while the right panel displays YOLOv11s-seg’s predicted masks for the same region. Qualitatively, the model captures the boundaries and structure of glomeruli accurately, with reasonable performance on finer vascular elements.
Despite the architectural enhancements in YOLOv12s-seg, such as A2C2f blocks and deeper layer integration, the model underperformed YOLOv11s-seg in both segmentation quality and computational efficiency. Specifically, YOLOv11s-seg achieved higher mask mAP@0.5 (0.623 vs. 0.585) and overall better balance of precision and recall across key object classes. While glomerular segmentation performance remained strong in both models, YOLOv11s-seg showed slightly higher overall mAP and more consistent recall. The YOLOv12 model also incurred greater computational cost, with significantly slower inference (2×) and deeper network complexity. Moreover, YOLOv12s-seg required over 70% more training time and 47% more GPU memory, while offering no clear benefit in segmentation accuracy. Clearly, the additional complexity of YOLOv12s-seg does not translate into improved performance in this histological context, and simpler CNN-based models like YOLOv11s-seg remain more reliable for resource-constrained biomedical segmentation tasks.
The impact of tile overlap ratio on segmentation performance was evaluated. Experiments were conducted using varying overlap ratios ranging from 0% to 15% in steps of 2.5%. Performance was assessed using the
metric, computed as the mean F1 score across IoU thresholds 0.5–0.9 compared with ground truth.
Figure 5 illustrates how segmentation quality, measured via
, changes with increasing overlap. The performance improves steadily up to an overlap of approximately 7.5%, after which it plateaus or slightly declines. This suggests moderate overlap helped in restoring instance structures across tiles. As expected, inference time per image increases with larger overlaps due to redundant tile processing.
Figure 5 shows a near-linear increase in average runtime from 140 to over 210 s per image as the overlap increases from 7.5% to 15%. Based on the
results, the optimal overlap ratio was found to be approximately 7.5%.
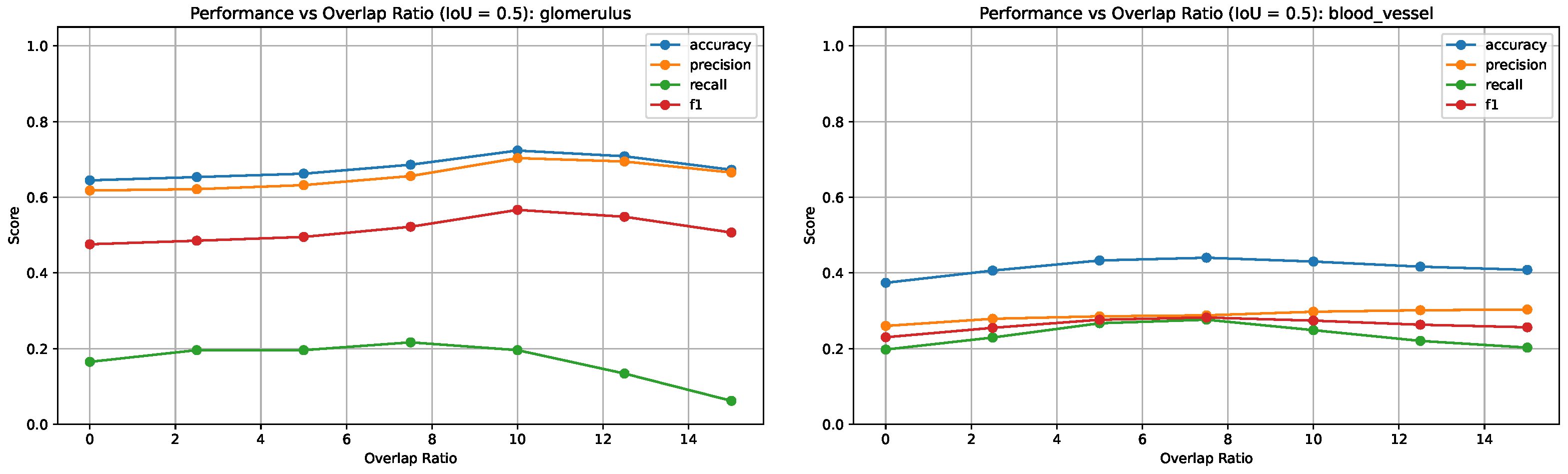
Figure 6 presents F1 scores across all IoU thresholds and overlap ratios for both blood vessels and glomeruli. These plots highlight how stricter IoU thresholds affect the precision/recall tradeoff differently across tissue types, with blood vessels showing more pronounced performance variations due to their elongated and fragmented morphology.
Figure 7 shows the variation in segmentation metrics at IoU = 0.5 for both tissue types, highlighting the effect of overlap ratio on detection performance.
Figure 8 illustrates the impact of tile overlap on segmentation quality. The no-overlap result shows fragmented and incomplete segmentations, especially at tile boundaries, while the overlap result yields more continuous and accurate detections. As seen in the figure, the central glomerulus (red) on the left has lost its upper left corner due to the tile boundary truncation. This demonstrates that moderate overlap improves prediction quality and also suggests that further postprocessing is necessary to consolidate segments across tiles, motivating our proposed enhanced mask merging method.
Based on these findings, an overlap ratio in the range of 5–7.5% is recommended for most use cases, as this range offers a favorable balance between segmentation accuracy and inference time. Overlaps within this range consistently improved object continuity across tile boundaries without introducing significant computational overhead for large-scale whole slide image processing. To further refine the segmentation results, postprocessing optimization was conducted using a tile overlap of 7.5%.
Table 4 presents the best performing hyperparameter configurations, both overall and separately for each class, as determined by peak
score. The values listed in
Table 4 represent the PSO optimized parameters used in the algorithm, with rounded values shown for implementation and original outputs provided in parentheses for reference.
The results show that glomeruli segmentation achieved near-optimal performance with minimal missed instances, while vessel detection remained more challenging due to under-segmentation and fragmentation. The optimized morphological kernel sizes fall within the lower end of their respective ranges, suggesting that moderate morphological closing is generally effective. Polygon approximation parameters (
epsilon) support preserving shape detail, with vessels favoring higher values than glomeruli. Clustering thresholds reflect the fragmentary nature of instance predictions: low
bbox_iou_thresh values (0.12–0.21) allow for permissive spatial merging, while moderate
cosine_sim_thresh values maintain conservative shape agreement. Specifically, a low
bbox_iou_thresh value (0.12) allows for permissive spatial merging of partially overlapping vessel fragments, compensating for breakage across tile boundaries. At the same time, a relatively high
cosine_sim_thresh (0.91) ensures that only geometrically similar fragments are merged, thus guarding against the erroneous fusion of unrelated vessels. The
contour_proximity_thresh values indicate that a spatial clustering radius in the 45–56 pixel range is effective. Importantly, all optimized parameters remained within the empirically defined hyperparameter bounds (
Table 1), validating the suitability of the selected search space.
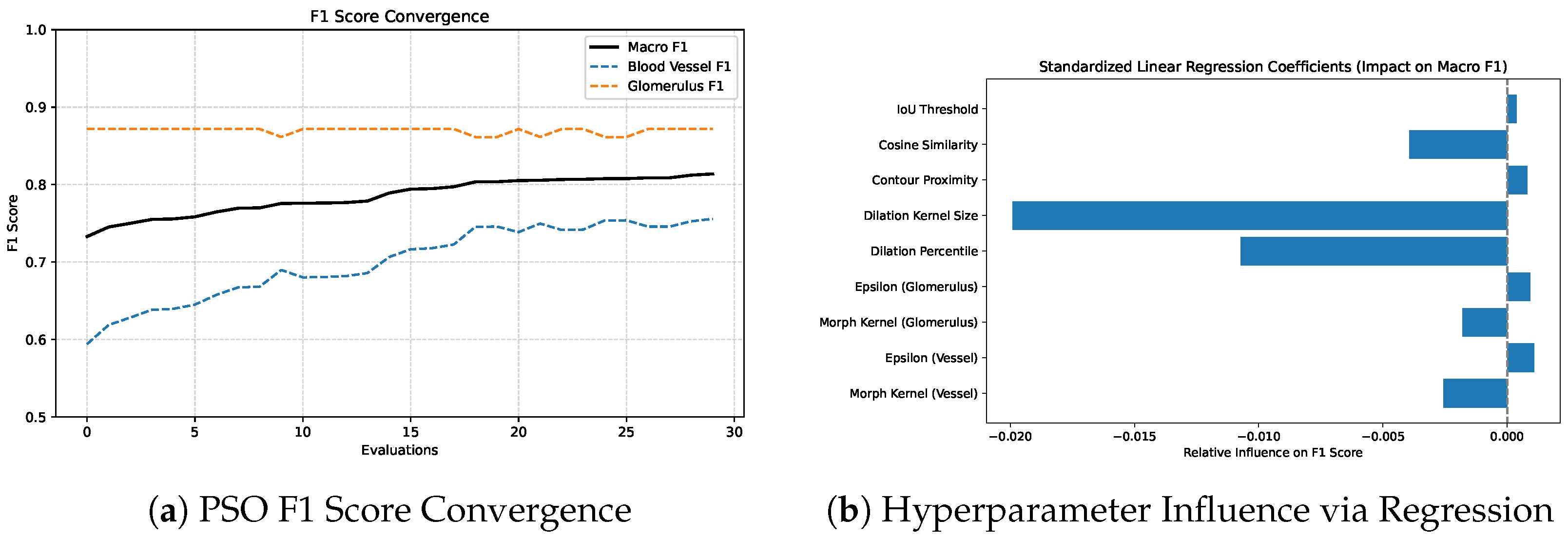
Figure 9 illustrates the convergence of F1 scores during PSO optimization (left) and the relative influence of each hyperparameter on macro F1 as determined by standardized linear regression (right). Regression analysis revealed that dilation_kernel, dilation_percentile and cosine_similarity had the strongest negative influence on macro
. In contrast, parameters such as morphological_kernel (glomerulus), epsilon (glomerulus) and IoU_threshold showed minimal impact within the tested range. The sensitivity analysis and convergence behavior observed in this study not only validate the effectiveness of our optimization strategy but also highlight the practical application of the proposed postprocessing algorithm. By identifying a small subset of hyperparameters with high impact, future tuning efforts can be confidently prioritized around these parameters.
Additionally, qualitative and quantitative evaluations were performed using the best-scoring image from each class.
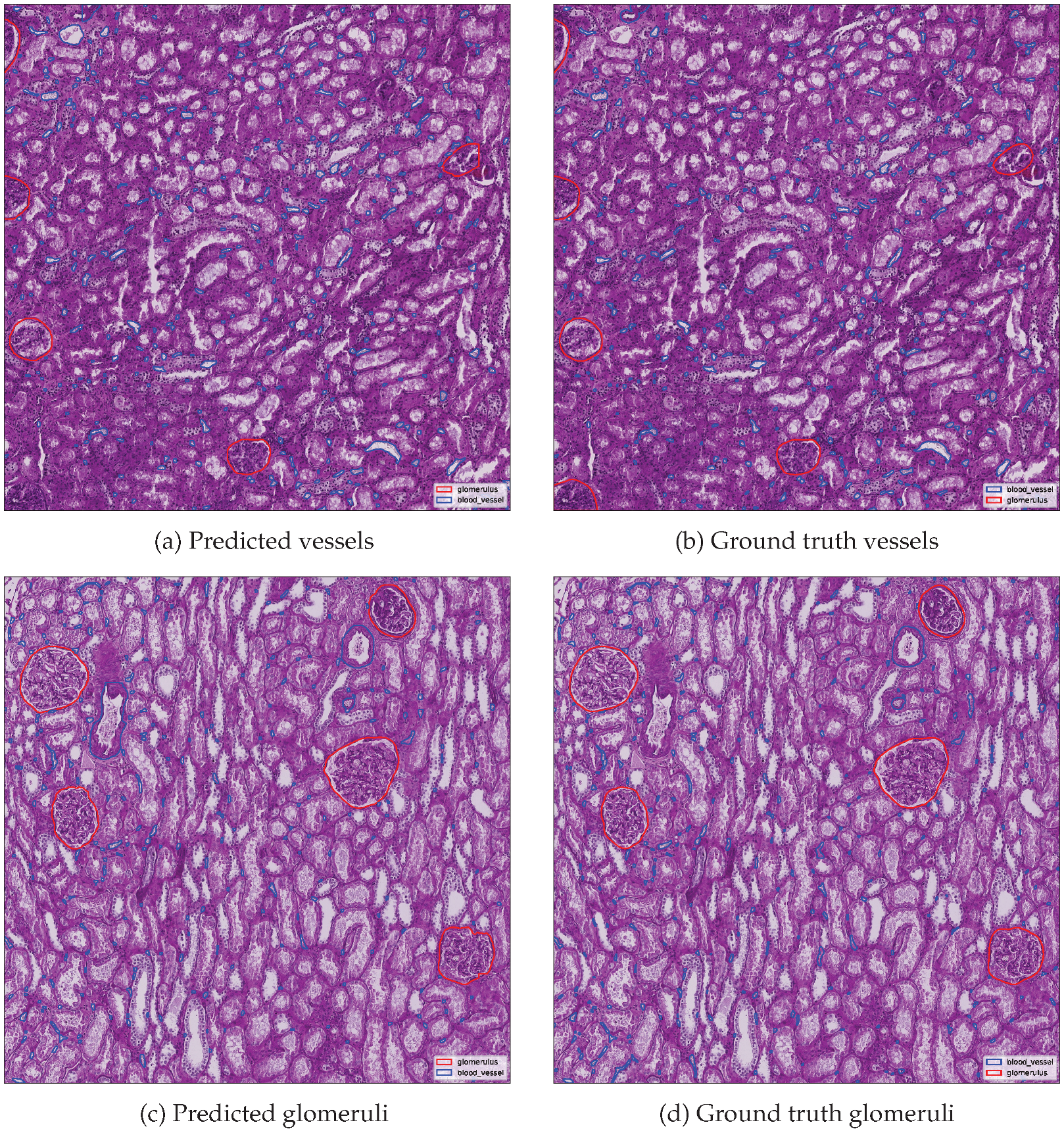
Figure 10 presents side-by-side comparisons between predicted and ground truth instance segmentations for the top-performing image in each class.
Metrics are summarized in
Table 5, including detection counts and evaluation metrics. Ground truth and predicted instance counts are reported separately, while derived metrics such as precision, recall and F1 score were computed against the reference annotations. The results demonstrate the fitness of the proposed merging and cleaning algorithm. Glomerulus segmentation achieved perfect agreement with the ground truth in the best-performing image, whereas blood vessel segmentation, although highly accurate, exhibited slightly lower performance due to the greater structural complexity and fragmentary nature of vascular objects.
Finally,
Table 6 summarizes the average and maximum improvements (denoted as
) in segmentation performance metrics when comparing the proposed optimized pipeline against baseline predictions produced by YOLOv11s-seg without postprocessing. Consistent performance gains were observed across both tissue classes. Notably, glomerulus detection benefited the most, with an average
improvement of 35.7% and a precision gain of 48.3%. These improvements were primarily driven by effective mask merging across tile boundaries, particularly in fragmented or partially visible instances. In contrast, blood vessel segmentation achieved a more moderate average precision gain of 8.15%, while recall decreased slightly by 0.58%, suggesting improved boundary specificity at the cost of missing some peripheral detections. As most vessels were centrally located within tiles, the merging strategy primarily enhanced boundary alignment rather than correcting tile edge artifacts. In contrast, glomeruli more frequently spanned tile borders and thus benefited more substantially from reconstruction. Overall, the strategy proved most beneficial for glomeruli, where mask resolution across tiles had a stronger effect.
A direct comparison with standard NMS or Syncretic-NMS approaches was not included, as these methods are not directly applicable to overleaped tiling pipelines and do not include morphological postprocessing. Similarly, full-resolution inference on high-resolution images was excluded from comparative evaluation, since the underlying models were trained exclusively on smaller tiles extracted from whole slide images and are not optimized for global context.
4. Discussion
The results confirm that the proposed pipeline provides an effective and efficient solution for instance segmentation in tiled kidney whole slide images. Key contributions include adapting YOLO-based segmentation to high-resolution tile inference, incorporating overlap strategies and introducing a PSO-optimized mask merging algorithm.
The proposed framework addresses two major challenges in histological segmentation: object fragmentation across tile borders and morphological variability. By introducing a novel, enhanced mask merging algorithm that extends Syncretic-NMS with shape similarity and contour proximity, the merging step improves instance continuity across tiles. PSO optimization reduces manual tuning by efficiently exploring the postprocessing parameter space. Additionally, SAHI-based tiling enables efficient model training and inference on high-resolution WSIs, while overlap evaluation helps identify optimal configurations for accurate segmentation of complex microvascular structures. These combined strategies lead to substantial improvements in segmentation performance, with notable increases in both precision and F1 score, particularly for instances spanning tile boundaries.
Evaluation was conducted on 15 representative whole slide crops, covering over 600 tiles, which limits statistical generalizability. The merging strategy was tuned at a fixed tile overlap ratio and its sensitivity to this parameter remains untested. Reported gains, including improved glomerular precision, were measured against baseline predictions without postprocessing and were not statistically validated against alternative segmentation or merging baselines.
Despite these limitations, the pipeline’s modular design, low computational overhead and refinement strategy tailored to tiled inference make it broadly applicable to biomedical segmentation tasks. It is compatible with high-resolution WSIs and adaptable to various instance segmentation models, enabling seamless integration into existing workflows across diverse tissue types and imaging conditions. The proposed pipeline is not limited to kidney histology and can be applied to other tiled WSI domains where irregularly shaped or sparsely distributed structures, such as tumors, lesions or vascular abnormalities, require accurate reconstruction across tile boundaries. Its modular architecture allows replacement of the base model and adjustment of mask merging parameters for different tissues, imaging modalities and staining protocols. The low computational cost supports large-scale deployment on clinical repositories and research biobanks, facilitating high-precision segmentation in oncology, neuropathology, dermatopathology and other medical imaging fields where fragmented object detection remains a challenge.
Prior methods have explored tiling [
8] or postprocessing [
11] independently, but no complete histology-optimized pipeline has been proposed that integrates both. Universal medical segmentation models have been developed to handle diverse modalities, yet tiling-induced inconsistencies remain unresolved [
29]. A one-stage framework eliminating grouping postprocessing has been proposed, but it does not address boundary-crossing artifacts [
30], while evaluation approaches focusing on precise boundary accuracy do not offer corrective strategies [
31]. A scalable tile-based framework for region-merging segmentation in remote sensing images has been introduced, focusing on ensuring result equivalence rather than reconstructing fragmented structures in tiled inference [
32]. Object-based tile positioning has been proposed to reduce tile-induced truncation during training on diatom datasets, but this mainly mitigates training artifacts and does not resolve postprocessing inconsistencies during inference [
33].
In contrast, this study introduces a tailored segmentation pipeline for renal WSIs that combines YOLO-based tiling inference, a novel syncretic mask merging algorithm and adaptive PSO-driven parameter optimization to directly address spatial fragmentation and boundary inconsistencies, providing a principled and scalable alternative to existing heuristic postprocessing solutions.