Skin Lesion Classification Using Hybrid Feature Extraction Based on Classical and Deep Learning Methods
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Section 2: Presents an overview of the related work in skin lesion classification.
- Section 3: Describes the proposed methodology, conventional feature extraction, feature extraction based on deep learning, and fusion feature.
- Section 4: Presents the experimental findings, with a comprehensive discussion.
- Section 5: Presents the conclusion of this study and suggests directions for future research.
2. Related Work
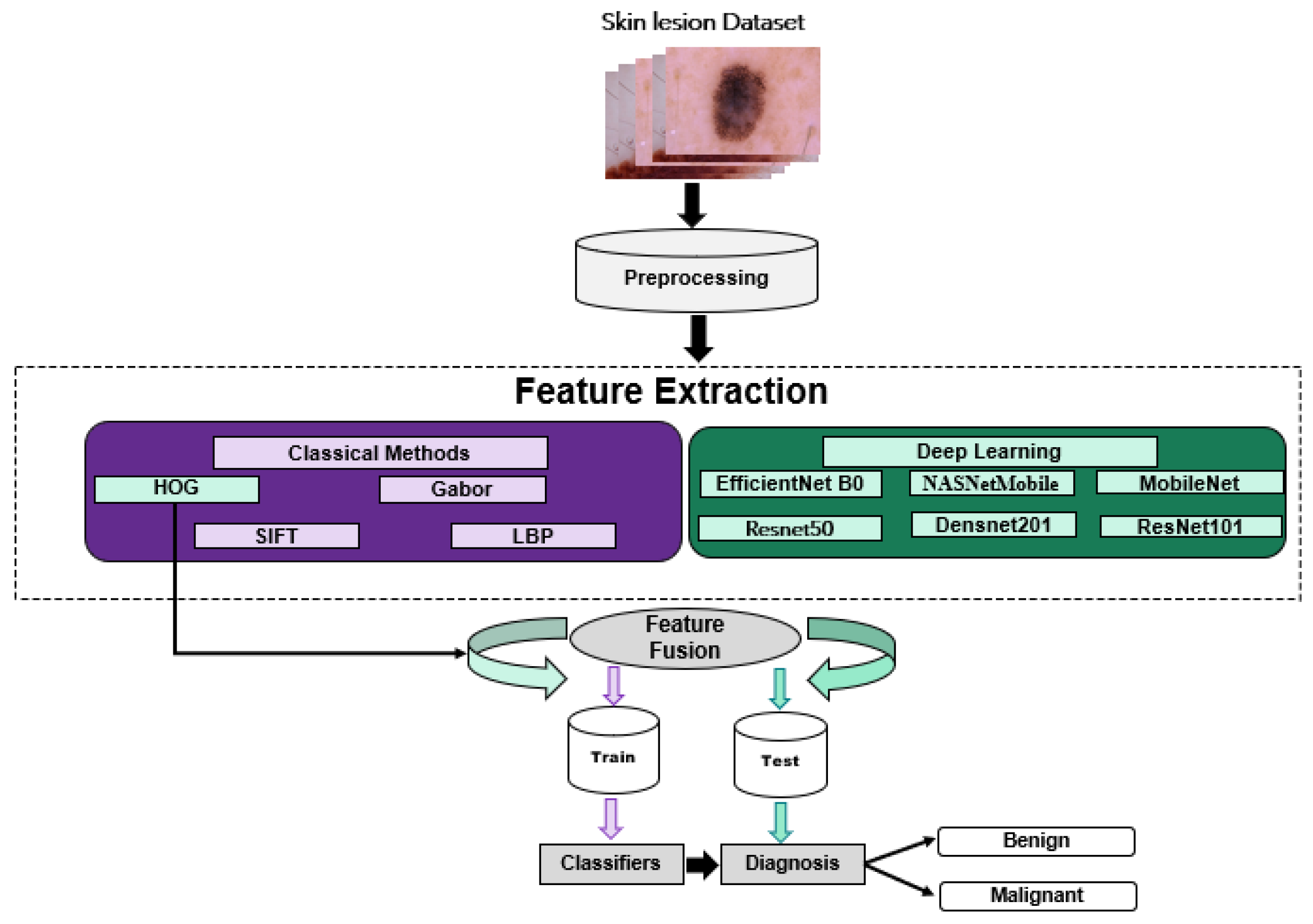
3. Methodology
3.1. Classical Methods
3.1.1. HOG-Based Method
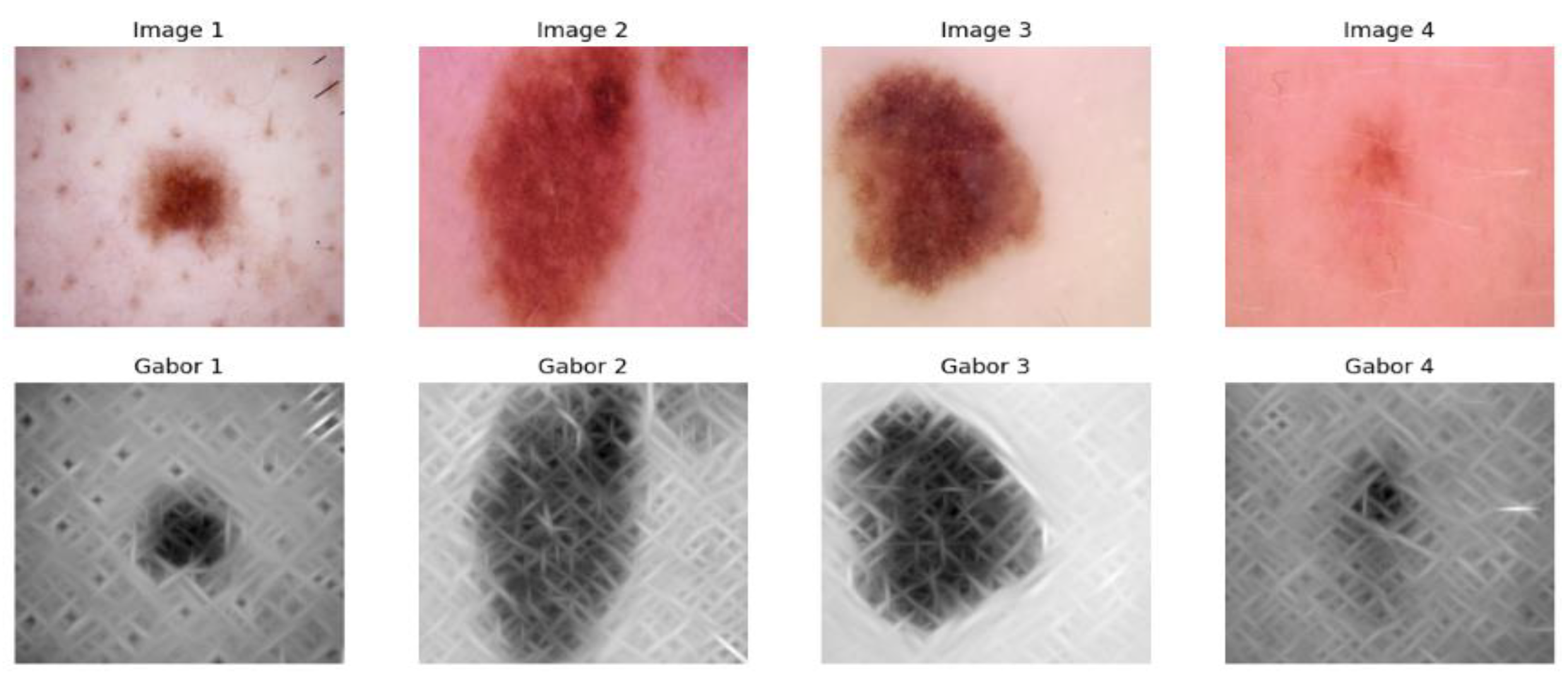
3.1.2. Gabor Filter Feature Extraction
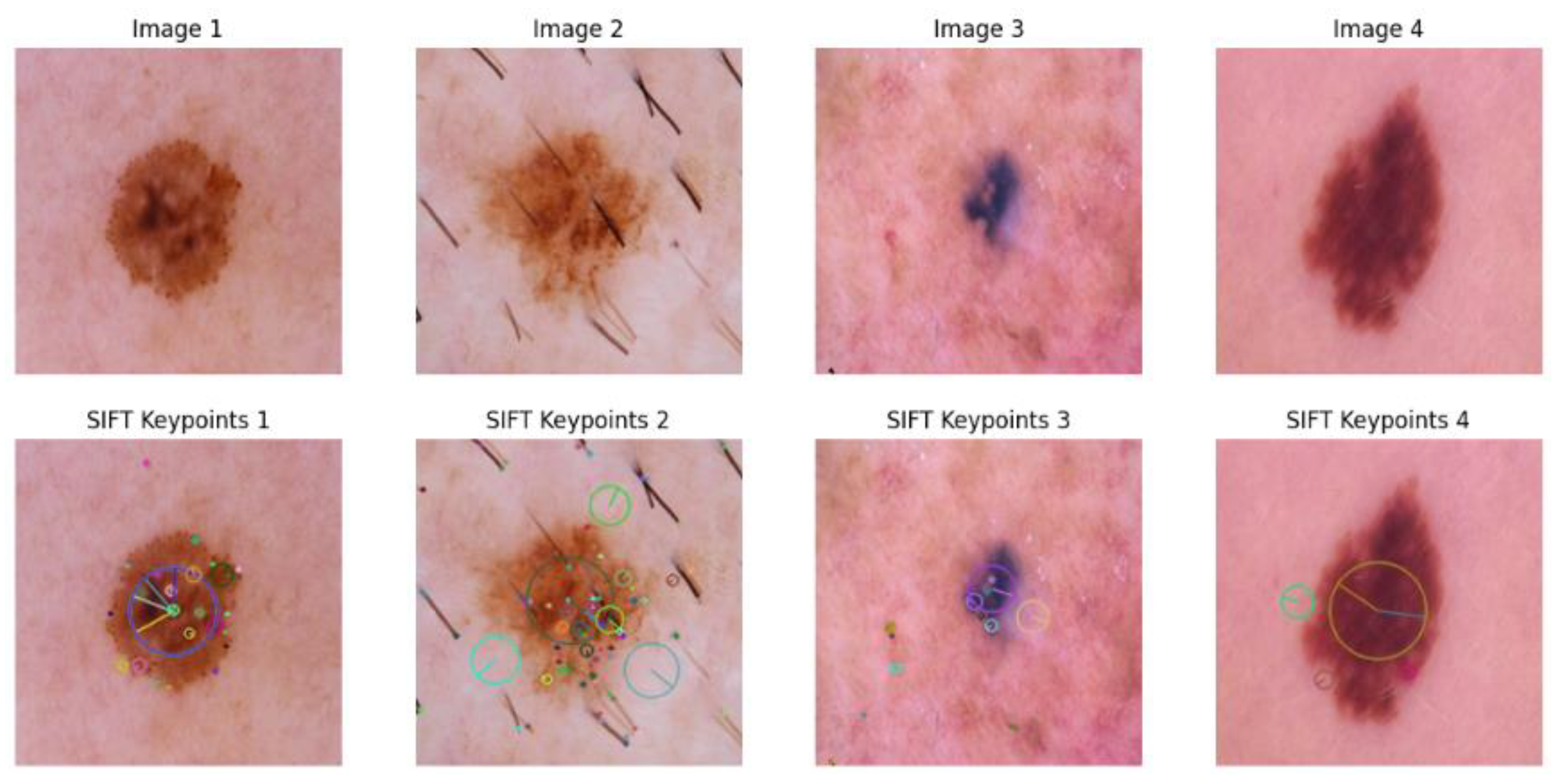
3.1.3. SIFT-Based Method
3.1.4. LBP-Based Method
3.2. Deep Learning Methods
3.2.1. EfficientNetB0-Based Method
3.2.2. ResNet-Based Method
3.2.3. NASNetMobile-Based Method
3.2.4. DenseNet201-Based Method
3.2.5. MobileNetV2-Based Method
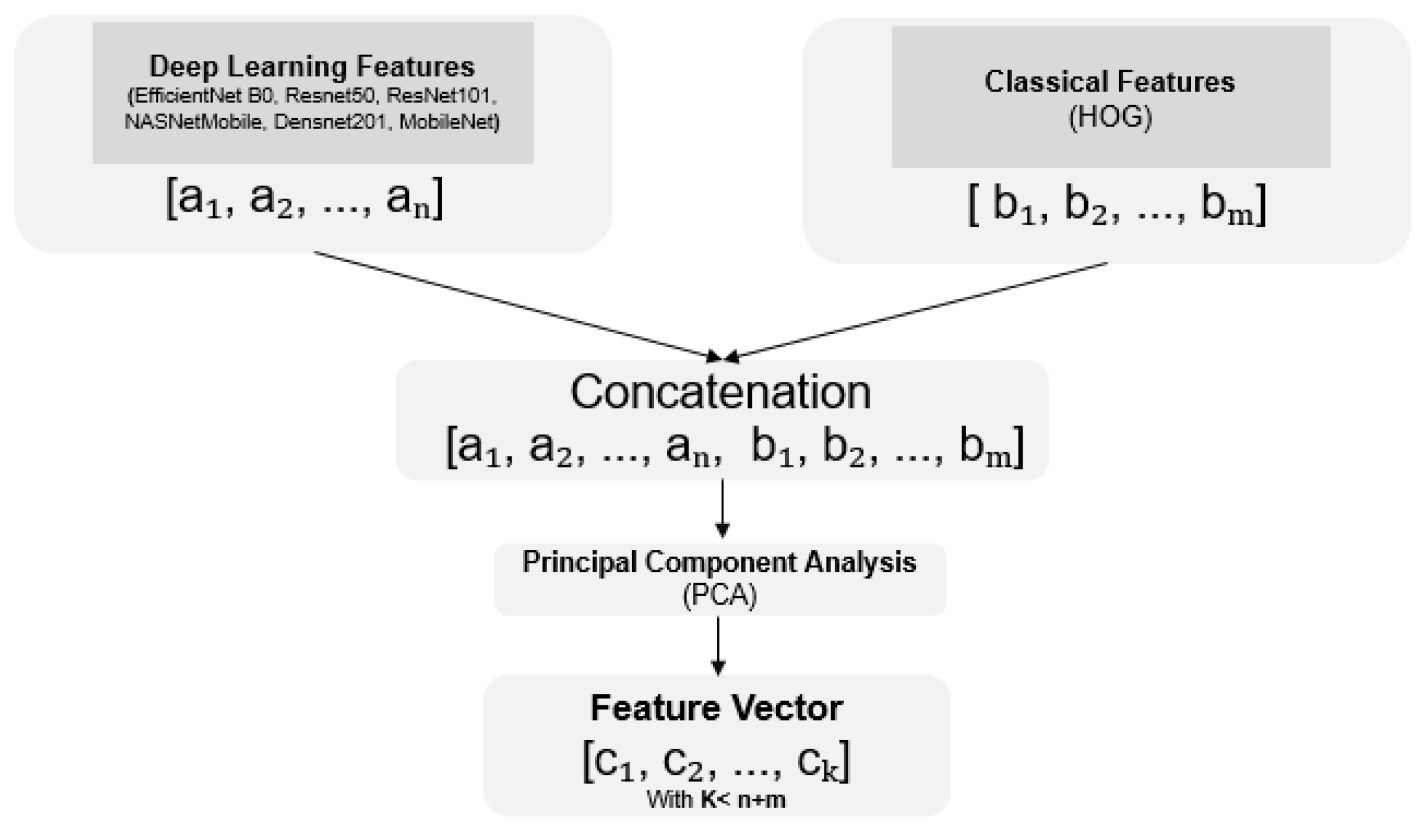
3.3. Fusion Methods
4. Experimental Results and Discussion
4.1. Dataset and Distribution
4.2. Evaluation Metrics
4.3. Results of Classical Methods
4.4. Results of Deep Learning Methods
4.5. Results of Fusion Methods
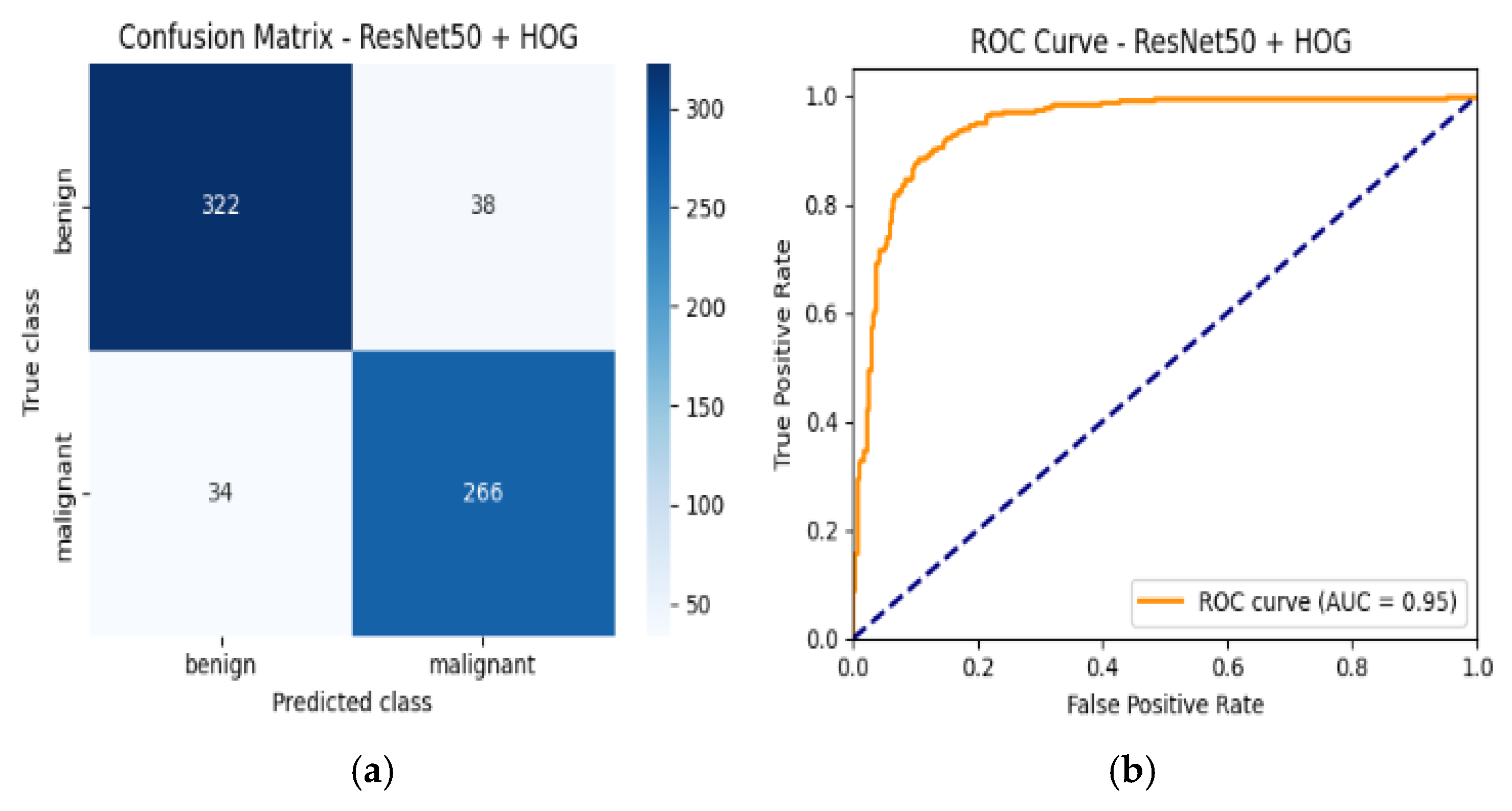
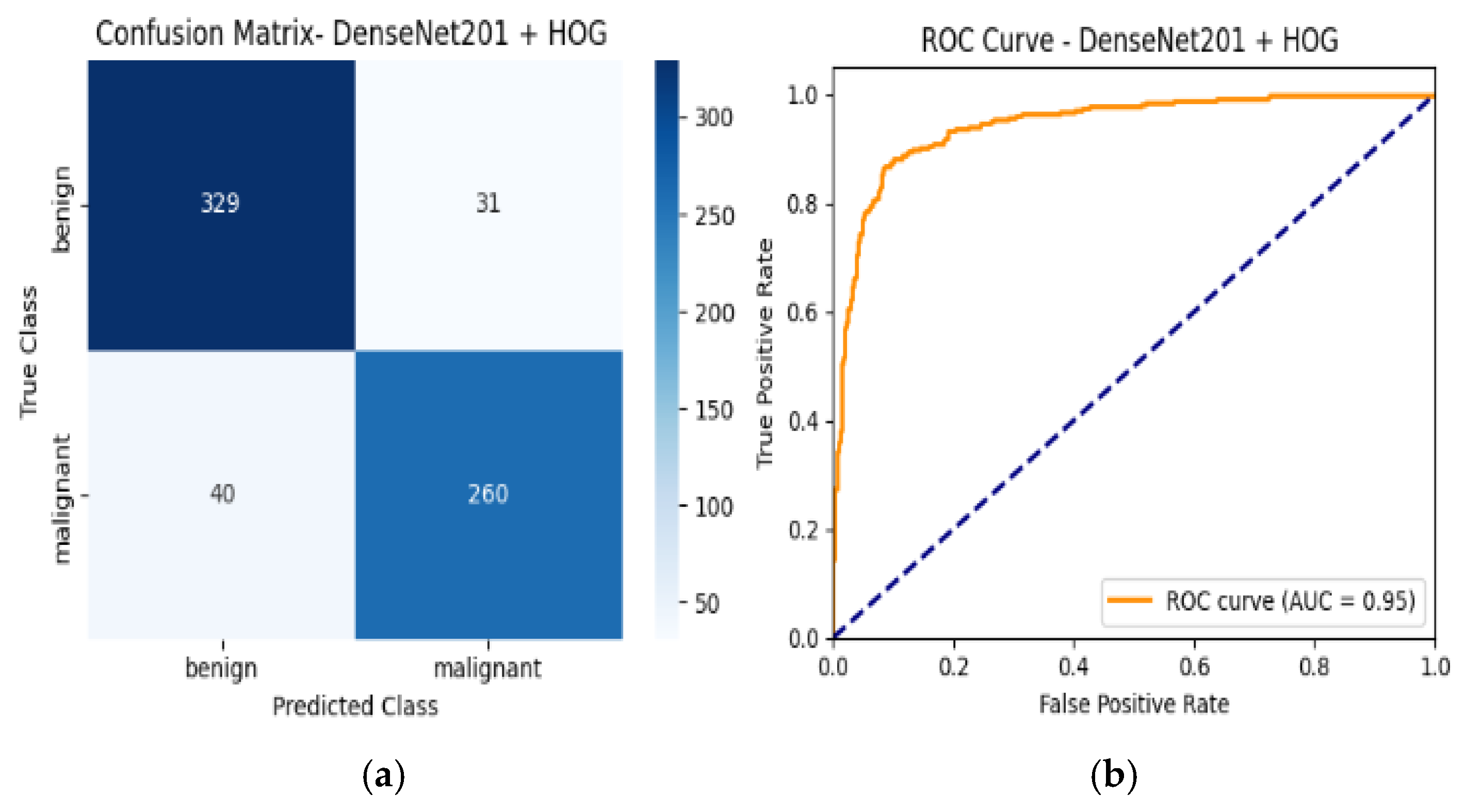
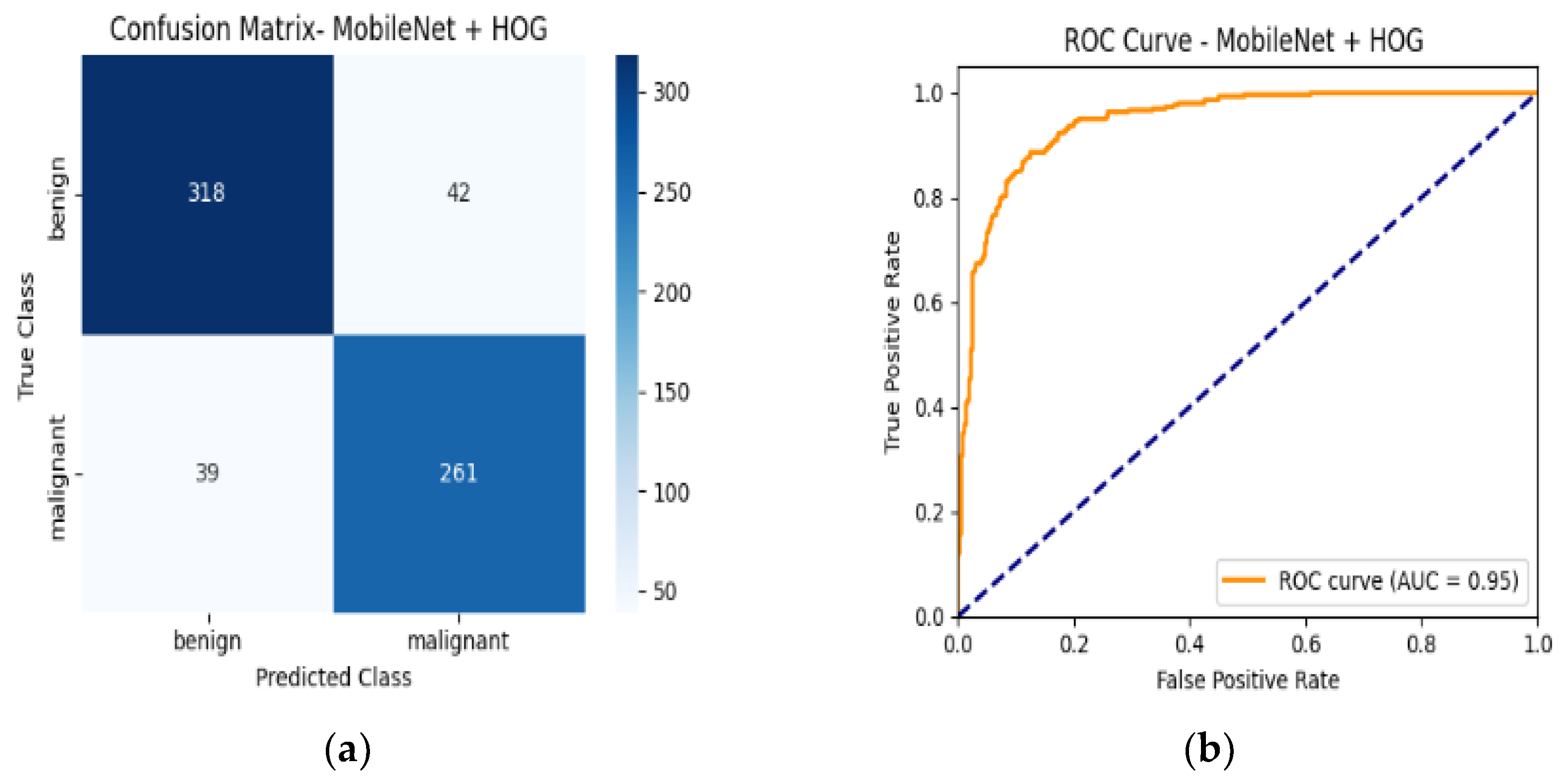
4.6. Confusion Matrix and ROC Curves
4.7. Performance Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Farkhod, F. Investigation of Ways to Improve the HOG Method in the Classification of Histological Images by Machine Learning Methods. Int. J. Multidiscip. Res. 2024, 6, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzakari, S.A.; Ojo, S.; Wanliss, J.; Umer, M.; Alsubai, S.; Alasiry, A.; Marzougui, M.; Innab, N. LesionNet: An Automated Approach for Skin Lesion Classification Using SIFT Features with Customized Convolutional Neural Network. Front. Med. 2024, 11, 1487270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1512.03385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoph, B.; Vasudevan, V.; Shlens, J.; Le, Q.V. Learning Transferable Architectures for Scalable Image Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 8697–8710. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, G.; Liu, Z.; Van Der Maaten, L.; Weinberger, K.Q. Densely Connected Convolutional Networks. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 4700–4708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandler, A.G.; Zhu, M.; Chen, B.; Kalenichenko, D.; Wang, W.; Weyand, T.; Andreetto, M.; Adam, H. MobileNets: Efficient Convolutional Neural Networks for Mobile Vision Applications. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1704.04861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, L.K.; Pooja, N.; Garg, H.; Khanna, M. Histogram of Oriented Gradients (HOG)-Based Artificial Neural Network (ANN) Classifier for Glaucoma Detection. Int. J. Swarm Intell. Res. 2022, 13, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stockmeier, H.G.; Bäcker, H.; Bäumler, W.; Lang, E.W. BSS-Based Feature Extraction for Skin Lesion Image Classification. Lect. Notes Comput. Sci. 2009, 5441, 467–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ajel, A.R.; Al-Dujaili, A.Q.; Hadi, Z.G.; Humaidi, A.J. Skin Cancer Classifier Based on Convolution Residual Neural Network. Int. J. Power Electron. Drive Syst./Int. J. Electr. Comput. Eng. 2023, 13, 6240–6248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, M.; Sethi, N.M.J.; Hussain, N.S.S. Artificial Intelligence-Based Skin Lesion Analysis and Skin Cancer Detection. Pak. J. Eng. Technol. 2025, 7, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, I.; Younus, M.; Walayat, K.; Kakar, M.U.; Ma, J. Automated Multi-Class Classification of Skin Lesions through Deep Convolutional Neural Network with Dermoscopic Images. Comput. Med. Imaging Graph. 2021, 88, 101843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iqbal, I.; Walayat, K.; Kakar, M.U.; Ma, J. Automated Identification of Human Gastrointestinal Tract Abnormalities Based on Deep Convolutional Neural Network with Endoscopic Images. Intell. Syst. Appl. 2022, 16, 200149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Shuai, R.; Ma, L.; Liu, W.; Hu, D.; Wu, M. Dermoscopy Image Classification Based on StyleGAN and DenseNet201. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 8659–8679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasu, P.N.; SivaSai, J.G.; Ijaz, M.F.; Bhoi, A.K.; Kim, W.; Kang, J.J. Classification of Skin Disease Using Deep Learning Neural Networks with MobileNet V2 and LSTM. Sensors 2021, 21, 2852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Wu, Y.; Lu, Y. A Study on Skin Lesions Classification Based on Improved EfficientNetB0 Network. In Proceedings of the 2024 International Conference on New Trends in Computational Intelligence (NTCI), Qingdao, China, 18–20 October 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, M.U.; Nizami, I.F.; Ullah, F.; Hussain, I. IQA Vision Transformed: A Survey of Transformer Architectures in Perceptual Image Quality Assessment. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 183369–183399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaw, K.P.; Mon, A. Enhanced Multi-Class Skin Lesion Classification of Dermoscopic Images Using an Ensemble of Deep Learning Models. J. Comput. Theor. Appl. 2024, 2, 256–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Yu, L.; Tian, S.; Cheng, J.; Guo, Z.; Zhang, Y. Serial Attention Network for Skin Lesion Segmentation. J. Ambient Intell. Humaniz. Comput. 2021, 13, 799–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aditi, N.; Nagda, M. K.; Eswaran, P. Image Classification Using a Hybrid LSTM-CNN Deep Neural Network. Int. J. Eng. Adv. Technol. 2019, 8, 1342–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thirumaladevi, S.; Veeraswamy, K.; Sailaja, M.; Shaik, S. Synergistic Feature Fusion for Accurate Skin Cancer Classification. Int. J. Pharm. Res. Technol. 2024, 14, 79–86. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.; Wang, W.; Liu, Y.; Bäckemo, J.; Heuchel, M.; Wang, W.; Yan, N.; Iqbal, I.; Kratz, K.; Lendlein, A. Substrates Mimicking the Blastocyst Geometry Revert Pluripotent Stem Cell to Naivety. Nat. Mater. 2024, 23, 1748–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirmozaffari, M.; Yazdani, R.; Shadkam, E.; Khalili, S.M.; Tavassoli, L.S.; Boskabadi, A. A Novel Hybrid Parametric and Non-Parametric Optimisation Model for Average Technical Efficiency Assessment in Public Hospitals during and Post-COVID-19 Pandemic. Bioengineering 2022, 9, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, M.; Le, Q. EfficientNet: Rethinking Model Scaling for Convolutional Neural Networks. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1905.11946. [Google Scholar]
- Kaggle. Skin Cancer: Malignant vs Benign. Available online: https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/fanconic/skin-cancer-malignant-vs-benign (accessed on 14 April 2023).



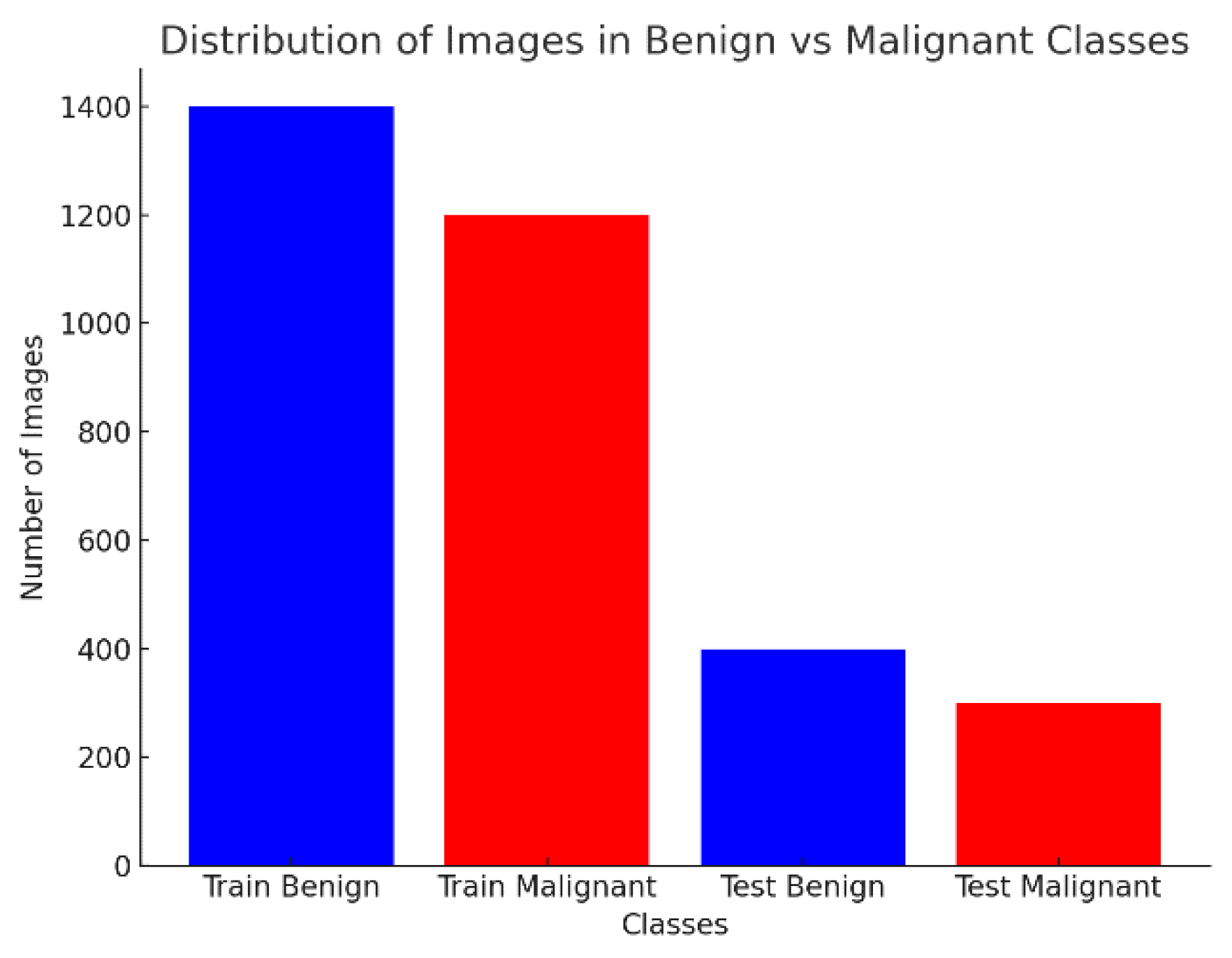

| Class | Train Images | Test Images |
|---|---|---|
| Benign | 1440 | 360 |
| Malignant | 1197 | 300 |
| Total | 2637 | 660 |
| Model | Accuracy | Class | Precision | Recall | F1-Score | ROC-AUC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HOG | 80% | Benign | 0.82 | 0.80 | 0.81 | 0.87 |
| Malignant | 0.77 | 0.79 | 0.78 | |||
| Gabor | 79% | Benign | 0.77 | 0.86 | 0.81 | 0.87 |
| Malignant | 0.81 | 0.70 | 0.75 | |||
| SIFT | 78% | Benign | 0.80 | 0.78 | 0.79 | 0.85 |
| Malignant | 0.75 | 0.77 | 0.76 | |||
| LBP | 76% | Benign | 0.76 | 0.81 | 0.79 | 0.82 |
| Malignant | 0.76 | 0.69 | 0.72 |
| Model | Accuracy | Class | Precision | Recall | F1-Score | ROC-AUC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EfficientNetB0 | 82% | Benign | 0.86 | 0.80 | 0.83 | 0.91 |
| Malignant | 0.78 | 0.84 | 0.81 | |||
| Resnet50 | 82% | Benign | 0.85 | 0.82 | 0.84 | 0.91 |
| Malignant | 0.79 | 0.82 | 0.81 | |||
| ResNet101 | 83% | Benign | 0.88 | 0.81 | 0.84 | 0.92 |
| Malignant | 0.79 | 0.86 | 0.82 | |||
| NASNetMobile | 85% | Benign | 0.84 | 0.89 | 0.86 | 0.93 |
| Malignant | 0.86 | 0.79 | 0.82 | |||
| Densnet201 | 88% | Benign | 0.88 | 0.90 | 0.89 | 0.95 |
| Malignant | 0.87 | 0.85 | 0.86 | |||
| MobileNet | 88% | Benign | 0.89 | 0.88 | 0.89 | 0.95 |
| Malignant | 0.86 | 0.87 | 0.86 |
| Model | Accuracy | Class | Precision | Recall | F1-Score | ROC-AUC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EfficientNetB0 + HOG | 87% | Benign | 0.90 | 0.86 | 0.88 | 0.95 |
| Malignant | 0.84 | 0.88 | 0.86 | |||
| Resnet50 + HOG | 89% | Benign | 0.90 | 0.89 | 0.90 | 0.95 |
| Malignant | 0.88 | 0.89 | 0.88 | |||
| ResNet101 + HOG | 88% | Benign | 0.88 | 0.90 | 0.89 | 0.95 |
| Malignant | 0.87 | 0.86 | 0.87 | |||
| NASNetMobile + HOG | 86% | Benign | 0.86 | 0.89 | 0.87 | 0.94 |
| Malignant | 0.86 | 0.82 | 0.84 | |||
| Densnet201 + HOG | 89% | Benign | 0.89 | 0.90 | 0.90 | 0.95 |
| Malignant | 0.88 | 0.87 | 0.87 | |||
| MobileNetV2 + HOG | 89% | Benign | 0.89 | 0.90 | 0.90 | 0.95 |
| Malignant | 0.88 | 0.87 | 0.88 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zahid, M.; Rziza, M.; Alaoui, R. Skin Lesion Classification Using Hybrid Feature Extraction Based on Classical and Deep Learning Methods. BioMedInformatics 2025, 5, 41. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedinformatics5030041
Zahid M, Rziza M, Alaoui R. Skin Lesion Classification Using Hybrid Feature Extraction Based on Classical and Deep Learning Methods. BioMedInformatics. 2025; 5(3):41. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedinformatics5030041
Chicago/Turabian StyleZahid, Maryem, Mohammed Rziza, and Rachid Alaoui. 2025. "Skin Lesion Classification Using Hybrid Feature Extraction Based on Classical and Deep Learning Methods" BioMedInformatics 5, no. 3: 41. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedinformatics5030041
APA StyleZahid, M., Rziza, M., & Alaoui, R. (2025). Skin Lesion Classification Using Hybrid Feature Extraction Based on Classical and Deep Learning Methods. BioMedInformatics, 5(3), 41. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedinformatics5030041






