Abstract
Current computer vision models require a significant amount of annotated data to improve their performance in a particular task. However, obtaining the required annotated data is challenging, especially in medicine. Hence, data augmentation techniques play a crucial role. In recent years, generative models have been used to create artificial medical images, which have shown promising results. This study aimed to use a state-of-the-art generative model, StyleGAN3, to generate realistic synthetic abdominal magnetic resonance images. These images will be evaluated using quantitative metrics and qualitative assessments by medical professionals. For this purpose, an abdominal MRI dataset acquired at Garcia da Horta Hospital in Almada, Portugal, was used. A subset containing only axial gadolinium-enhanced slices was used to train the model. The obtained Fréchet inception distance value (12.89) aligned with the state of the art, and a medical expert confirmed the significant realism and quality of the images. However, specific issues were identified in the generated images, such as texture variations, visual artefacts and anatomical inconsistencies. Despite these, this work demonstrated that StyleGAN3 is a viable solution to synthesise realistic medical imaging data, particularly in abdominal imaging.
1. Introduction
Nowadays, deep learning (DL) is one of the most studied tools for medical imaging analysis. Despite being a complex tool, viewing the DL models as closed black boxes that receive input and return a prediction is sufficient for most applications, bringing more efficiency and simplicity to medical imaging analysis. These models have promising results that even align with radiologists’ results in supervised tasks, like image classification, where we classify the type of the disease presented in the image; image segmentation, in which we segment and classify the region of interest (for example, an organ) in an image; and object detection, in which we detect and classify a relevant structure (e.g., a lesion) in a medical image [1].
However, the number of practical applications of DL in health facilities is minimal. Multiple challenges hinder the widespread application of DL in clinical practice. Data are the fundamental building blocks for developing high-performance DL models [2]. Nevertheless, acquiring and annotating large volumes of data for training models remains one of the foremost challenges in the medical domain due to its time-consuming nature and the necessity for domain expertise (unlike natural image labelling). In addition, the nature of medical data presents an issue due to its heterogeneity and inherent class imbalance [2]. Frequently, having enough patients for some diseases is a great challenge. In addition, there can be patients who do not allow their images to be used, or the desired images can be impossible to obtain. Due to these factors, the medical imaging datasets are usually small and imbalanced, causing the DL models to overfit and produce inaccurate results [3].
In this study, we aimed to create a realistic synthetic dataset of abdominal magnetic resonance images and evaluate their quality using a questionnaire designed for a medical expert.
1.1. Data Augmentation
Data augmentation techniques tackle these data-related challenges without collecting new data samples. These techniques aim to increase the number of samples and the diversity of the dataset, and they can be regarded as a form of regularisation because they increase the model’s capacity to generalise [4]. Following the taxonomy presented in the systematic review by Garcea et al., the data augmentation techniques can be divided into two broad categories: transformation of the original data and generation of artificial data [5]. The first consists of transforming the original data using, for example, affine or elastic transformations. This approach is the simplest to implement and fastest to compute and has become a common practice in medical imaging DL works; in some cases, its effect is not even assessed [4]. It is crucial to note that even though these augmentation techniques are widely used, they cannot improve the ability of a deep learning model to generalise beyond the data it was initially trained on. Also, these techniques may lead to the generation of samples that are highly correlated with each other.
Artificial data generation can create more diverse samples, overcoming the limitations of transformation-based augmentation. Generative networks are presented as the most common tool to create synthetic samples. Within these networks are the variational autoencoders, generative adversarial networks (GANs) [5], and the more recent diffusion models [6] and transformers [7]. The GAN is the most studied DL model for creating synthetic data [4].
1.2. Generative Adversarial Networks
A generative adversarial network (GAN) is a type of DL model that consists of two networks that are trained in parallel. These two networks are called the generator and the discriminator. The generator aims to create similar images to those of the training data from random noise. The discriminator has to distinguish whether a sample is real or generated. These two networks engage in a symbiotic training process, wherein the generator refines its output to generate increasingly realistic images, progressively blurring the distinction between real and synthetic ones. Meanwhile, the discriminator adjusts to the evolving capabilities of the generator. This training procedure resembles a min–max optimisation procedure. The discriminator seeks to maximise the discrepancy between real and synthetic data distributions, while the generator strives to minimise it. The training concludes when the discriminator cannot distinguish between real and generated images [8]. There are three common issues related to this training process: convergence, vanishing gradient and mode collapse. Convergence is a common issue related to any adversarial learning because these networks often suffer from a lack of a defined convergence state. For instance, the generator might become overly adept at deceiving the discriminator by producing inaccurate outputs. A vanishing gradient happens when the discriminator network outperforms the generator, resulting in near-zero backpropagated gradients, stalling the learning process. Finally, a mode collapse occurs when the generator only outputs a few modes of the input data distribution. Mode collapse contributes dearly to the loss of diversity of the synthetic dataset, and therefore, it will harm subsequent networks trained with that data [9].
Several variants of GAN aim to solve the basic GAN’s main issues, altering, for example, the objective function or even the structure of the basic GAN but maintaining its adversarial nature [10]. These variants can be applied to specific tasks in the context of medical imaging synthesis.
1.3. Medical Image Synthesis with GANs
According to a review by Yi et al., medical image synthesis can be divided into three types: unconditional synthesis, cross-modality synthesis and other conditional synthesis. Unconditional synthesis is the process of creating images from random noise without any additional input, and it is commonly accomplished using GAN variations, such as deep convolution GAN (DCGAN), Wasserstein GAN (WGAN), progressive GAN (ProGAN) and StyleGANs, which are known for their stable training. Creating images of one medical modality using training data from another modality is called cross-modality synthesis, for example, generating synthetic CT (computed tomography) images from real MR (magnetic resonance) images. One of the most common GAN variations used for this type of synthesis is the CycleGAN. Finally, it is beneficial to incorporate additional types of conditional information when generating images in atypical circumstances. Conditional generative adversarial networks (cGANs) allow for applying constraints based on segmentation maps, text or specific locations [11].
1.4. Evaluation of Synthetic Datasets
Assessing the generated datasets is of utmost importance in determining the value of the synthetic images created by GANs. There are multiple approaches to evaluate the generated datasets, which can be broadly categorised into three groups: evaluation using downstream tasks, quantitative metrics and visual inspection by experts.
Following the generation of synthetic samples, evaluating their impact on the performance of another deep learning (DL) model for tasks such as classification, segmentation or detection is standard practice. These assessments, referred to as downstream tasks, typically involve two approaches. First, one can exclusively employ the generated dataset as the training dataset for these models and compare the performance results with models trained solely on the original dataset. Alternatively, synthetic samples can be added to the original dataset, allowing for an examination of any potential enhancement in the model’s overall performance.
In terms of quantitative metrics, it is common to utilise conventional metrics, like the peak signal-to-noise ratio (PSNR) or structural similarity index measure (SSIM); however, with the advancements in the field, DL-specific metrics have been presented that are more appropriate to evaluate synthetic images created with DL models in specific GANs [9]. The most commonly known metric of that category is the Fréchet inception distance (FID), which measures the distance between the feature representation (obtained from an inception network) of sampled images and real images [12]. Another metric was presented by Karras et al. called the kernel inception distance (KID) [13]. This metric only differs from the FID in how it computes the distance between feature representations; instead of the Fréchet distance, the KID uses kernel methods. The authors stated that this metric is more suited to smaller datasets than the FID [13]. The FID metric is the most widely accepted benchmark for evaluating the performance of state-of-the-art GAN models. However, since it depends on a DL model pre-trained with the ImageNet dataset, some authors advise caution when evaluating medical image synthesis with the FID [14]. The KID has the same issue because it depends on an ImageNet pre-trained model. A study by Skandari et al. corroborated the idea that the FID is not entirely adequate for the medical imaging field. The authors endeavoured to validate the medical suitability of GAN-generated images by independently training a secondary network for semantic segmentation on the generated images and comparing the outcomes with the original dataset. The findings demonstrated that although the FID score consistently improves (its value decreases) throughout GAN training, a lower FID score does not necessarily lead to better performance in image segmentation tasks, even when the generated images closely resemble real data [9].
1.5. Related Work
The review papers [4,5] provide a thorough analysis and discussion on data augmentation tools, specifically GAN-based augmentation, for medical imaging analysis with deep learning. The articles [10,11,15,16,17] provide comprehensive discourses on the applications of GANs in the medical imaging analysis field across various stages of maturity. GANs have been applied to a plethora of imaging modalities and anatomies.
Frid-Adar et al. made the first breakthrough in applying GANs to abdominal images. In their study, GANs were used to generate liver CT images to enhance data for downstream tasks. The study focused on classifying three types of liver lesions and employed DCGANs to augment the training dataset. The team generated new images using three DCGANs separately, one per lesion type: cysts, metastases and hemangiomas. The results indicated that combining the generated images with the real training data improved CNN performance in the medical image classification [18].
Fetty et al. [12] utilised StyleGAN2 to produce synthetic pelvic MR and CT images. This study showed that the StyleGAN is a promising model for generating medical MR and CT images. The researchers also introduced an innovative approach to manipulating the latent space, which allowed them to define the modality of the image (CT or MR), the patient’s gender and the position of the slice of the generated image [19].
A study compared traditional image augmentation techniques with GAN-based augmentation techniques on an image classification task. The study used progressive GANs and StyleGANs’ architectures to synthesise a dataset of 25k melanoma images. The results showed that StyleGAN2-ADA was the GAN that produced higher-quality images despite exhibiting some discrepancies, such as a checkerboard pattern covering the lesion and an image with mixed modes. Combining the StyleGAN2-generated images with the original dataset improved the balanced accuracy of the CNN model by 2.1% compared with the same CNN model without any augmentation [20].
In a study conducted by Karras et al. (where StyleGAN2-ADA was presented), a comparative analysis of the quality of the generated images was made. StyleGAN2, StyleGAN2-ADA and other models were utilised to create synthetic images from multiple small datasets, one of which was the public BreCaHAD dataset, which consisted of only 162 breast cancer histopathology images. The team computed both the FID and KID for all datasets and concluded that the KID was more appropriate for small datasets than the FID, including the medical BreCAHD dataset. However, they acknowledged that further studies in the medical field need to be conducted to validate this conclusion [13].
Skandarani et al. conducted an empirical study, already mentioned above, to assess the effectiveness of GANs in medical imaging. They applied different GAN architectures to three medical datasets and concluded that not all GANs are suitable for medical imaging applications. While some top-performing GANs, such as style-based GANs, can generate realistic samples for image synthesis tasks, no GAN could provide the richness of medical datasets for segmentation tasks. The study revealed that StyleGAN and SPADE GAN are the best models, while simpler GANs, such as DCGANs and WGANs, performed poorly with all datasets [9].
Some studies performed visual inspection of the generated images. These evaluations were focused on the capability to distinguish between a generated sample and a real sample. Han et al. [21] and Kazuhiro et al. [22] generated brain MR images using a cGAN and a DCGAN, respectively, and stated that the medical experts could not distinguish between the generated and real samples. Another study performed the same type of evaluation but with synthetic CT patches with lung nodules created with a DCGAN. The authors stated that the synthetic dataset managed to deceive the experts [23]. Korkinof et al. surveyed experts and non-experts about the high-resolution synthetic mammograms generated using a ProGAN. The authors reported that most participants could not reliably distinguish real from synthetic mammograms [24]. Similarly, Levine et al. utilised a ProGAN to synthesise high-resolution histological images. The medical assessment concluded that the synthetic dataset was visually undistinguishable from real images and had a comparable classification accuracy [25]. The work conducted by Chorbani et al. generated skin lesions with a custom GAN called DermGAN and concluded that the synthetic datasets not only exhibited visual similarity to real images but also accurately represented various skin conditions as perceived by dermatologists [26].
Woodland et al. focused on evaluating synthetic datasets generated by StyleGAN2-ADA. They utilised four public datasets and a CT liver dataset, assessing quality quantitatively with the FID and qualitatively through visual inspection. The results demonstrate StyleGAN2-ADA’s effectiveness in synthesising high-quality medical images without extensive hyperparameter tuning [27].
1.6. Goals
This study aimed to create a realistic synthetic dataset of complete abdominal images capable of achieving good results on a medical evaluation task via a self-made questionnaire. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first work where a medical assessment of complete synthetic MRI abdominal images was performed. This work is a continuation of our previous work [28]. In that study, we created a synthetic MRI dataset using a small public MRI dataset and StyleGAN2-ADA. The current work improved the latter in three main aspects: (1) Instead of a small public dataset, we used our private dataset acquired at the Garcia de Orta Hospital in Almada, Portugal, which has more samples and improved quality. (2) Also, instead of using the StyleGAN2-ADA, we used the state-of-the-art StyleGAN—StyleGAN3. (3) Finally, instead of just assessing the images using quantitative metrics, we created a visual assessment questionnaire to be answered by a medical expert.
GANs can potentially create synthetic MRI images that are indistinguishable from real data. While these tools hold promise for various medical applications, concerns exist regarding their misuse for generating fabricated patient data. Here, we emphasise the ethical use of GAN-generated MRIs in this work. Our sole focus was just on evaluating the quality of synthetic images to ensure their suitability for deep learning training purposes.
2. Materials and Methods
Figure 1 presents a flowchart representing this study’s applied methodology. This section details each step of the flowchart.
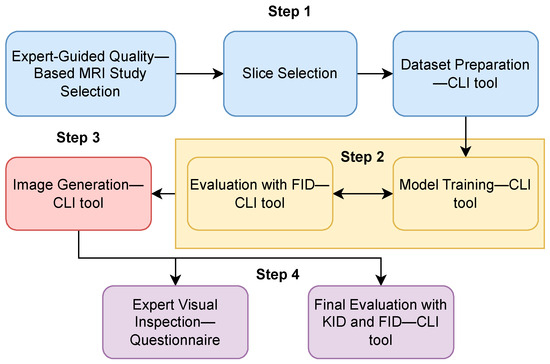
Figure 1.
Flowchart: synthetic data generation methodology applied in this study. The process began with preparing the training data (step 1), followed by the model’s training (step 2). Then, synthetic data were generated (step 3), and finally, the synthetic dataset was evaluated (step 4).
2.1. Dataset Description and Preparation
The base dataset used in this work was acquired at the Garcia de Orta Hospital in Almada, Portugal, from 2008 to 2019. Table 1 shows the dataset characterisation. In total, the dataset had 211 patients with known adrenal pathologies. The most common lesions in the dataset were adenomas, followed by metastases. The patients’ median age was 65. Each patient’s study comprised axial and coronal images, with both gadolinium-enhanced and non-enhanced scans. A medical expert selected the best MRI study for each patient based on the image quality, conducting a visual inspection of each study for the analysis.

Table 1.
Dataset characterisation.
From the expert-filtered studies, we selected only the gadolinium-enhanced axial slices to train our generative model because they provided more anatomical and visual details of the adrenal region. The MR studies were converted from DICOM to PNG images sized at 512 × 512 pixels. Our final dataset had 19,433 slices with and without adrenal lesions.
2.2. Model Selection and Training
As highlighted in the preceding section, our choice for this project was a GAN model. Drawing from the findings reported by [9], which demonstrate the efficacy of StyleGAN in medical imaging synthesis, and considering our objective of MR unconditional synthesis, we opted for the StyleGAN, specifically for the StyleGAN3 [16], which is the latest iteration of this model. The StyleGAN model, which Nvidia’s researchers first presented in 2018, is appropriate for unconditional synthesis [29]. This model merged the strengths of ProGANs [30] and neural style transfer [31]. The training process starts with low-resolution images and progressively adds details to the images while manipulating “style vectors” that control aspects like the pose, expression and fine textures. This new approach and adding the AdaIN operation meant a new architecture of the generator network: a style-based generator [29]. This model has three improved versions: StyleGAN2, StyleGAN2-ADA and StyleGAN3. Overall, StyleGAN2 improves the training speed of the original network and decreases the appearance of some image artefacts [32]. The StyleGAN2-ADA proposed an adaptive discriminator augmentation mechanism to enhance the training with small datasets [13]. Finally, the StyleGAN3, which is the most recent version of the model, was an improvement in the model generator that is most significant to the video and animation synthesis [33]. Finally, another aspect that influenced our decision was the ease of use of this model due to the existence of an official PyTorch implementation (https://github.com/NVlabs/stylegan3 (accessed on 26 February 2024)). This GitHub repository offers several CLI (command line interface) tools for preparing the dataset, training the model, evaluating the results and generating synthetic images.
The model training was conducted on a computer with an Intel Xeon CPU, an Nvidia GeForce GTX 1080Ti GPU and 32 GB of RAM. We utilised Python 3.8, along with PyTorch 1.9.0 and CUDA toolkit 11.1, for the implementation.
The StyleGAN3 implementation offers guidance for selecting suitable training options across various scenarios, ranging from high-level to low-level configurations. The three main configurations include StyleGAN3-T (translation equivariance), StyleGAN3-R (translation and rotation equivariance) or StyleGAN2.
2.3. Quality Assessment
The quality assessment of the generated images was done using quantitative metrics and a questionnaire.
Throughout the training process, the FID metric was computed to monitor the temporal progression of the process. Then, the best model was evaluated with the KID. Following the repository’s terminology, the computed metrics were fid50k_full and kid50k_full, which are part of the recommended quality metrics. These metrics were computed by comparing 50k synthetic samples and the full real dataset.
Recognising the significance of clinical expertise in thoroughly evaluating the authenticity of synthesised images, medical feedback was solicited through a questionnaire. With the questionnaire, we aimed to gauge how much these images conformed to the natural standards observed in abdominal MRI exams. The survey included ten sets of four images displayed in a grid-like fashion. Each set encompassed a blend of real and synthesised images, and the participant was asked to identify which images were synthetic. Following the initial phase of identifying synthetic images, participants were prompted to identify and classify the significance of visual features that led to suspicion regarding the nature of the images.
3. Results
3.1. Training Monitoring and Quantitative Evaluation
Several training experiments of the StyleGAN3 model on our abdominal MRI dataset of gadolinium-enhanced axial slices with adrenal lesions were done in order to find the optimal values for the network’s hyperparameters. Table 2 presents the optimal values of the tuned hyperparameters. The gamma value or R1 regularisation weight is a discriminator network parameter that determines the strength of regularisation for training stabilisation. Kimgs denotes the number of images (in thousands) shown to the discriminator, defining the duration of training. The augmentation mode turns the adaptive discriminator augmentation (ADA) [13] on or off, controlling the generator at each convolutional layer using adaptive instance normalisation (AdaIN) [29]. The batch size refers to the number of images used in each iteration during training. Snap configures the frequency at which the network saves snapshots.

Table 2.
Model hyperparameters and their best values.
The experiments that yielded the best results were conducted using the default parameters of the StyleGAN3-R implementation with three modifications:
- As suggested in [33], the R1 gamma value was tailored to the training dataset’s image resolution and batch size.
- For smaller datasets with fewer than 30k images, it is advised to keep the adaptive augmentations (ADA) enabled.
Figure 2 presents the progression of the FID across the network training. This metric was computed periodically to monitor the training progress and determine the appropriate timing to stop the training process. Each FID computation required approximately one hour. The total training time was 6 h, reaching a total of 1000 kimgs. At this point, as shown in Figure 2, we could confirm that the model had reached a plateau in terms of the FID, prompting us to halt the training process and use the last network checkpoint as our best model. Overall, Figure 2 illustrates a declining trend in the FID scores, consistent with the anticipated behaviour of this metric, which ideally converges to a value of 0. This trend towards lower FID scores suggests an enhancement in the quality and fidelity of the synthetic images.
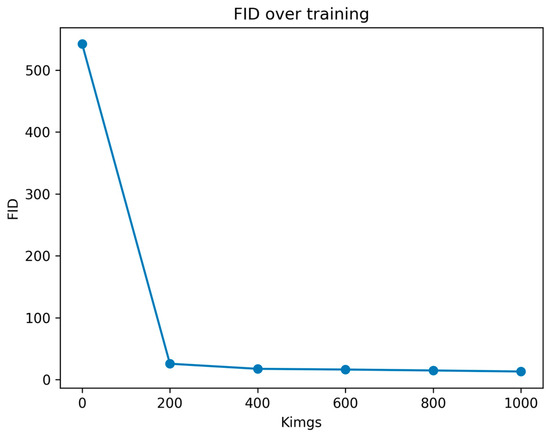
Figure 2.
Evolution of FID values across consequent training checkpoints. Kimgs is the number of images shown to the discriminator.
After the completion of the training process, we extracted the latest checkpoint of our model and used it to compute the quality metrics and a synthetic dataset. Table 3 presents the obtained values of the FID and KID of our best model. These values were compared with those obtained in other related studies.

Table 3.
Evaluation metrics of our best model.
3.2. Visual Inspection
This section presents examples of synthetic MR images alongside real abdominal MRI from our training dataset to perform a highly subjective analysis of the quality of the synthetic images. The aim was to exemplify the realism and diversity of our synthetic dataset. However, the anatomical complexity and high variability in abdominal MR hindered this type of analysis. Figure 3 showcases four samples from the real dataset in the left column and four samples from the generated dataset in the right column. Overall, the synthetic images demonstrated good intensity contrast and accurately represented the anatomical structures. However, there was a noticeable difference in texture: the real images exhibited a typical granular texture, whereas the generated ones lacked this texture, occasionally resulting in distorted areas.
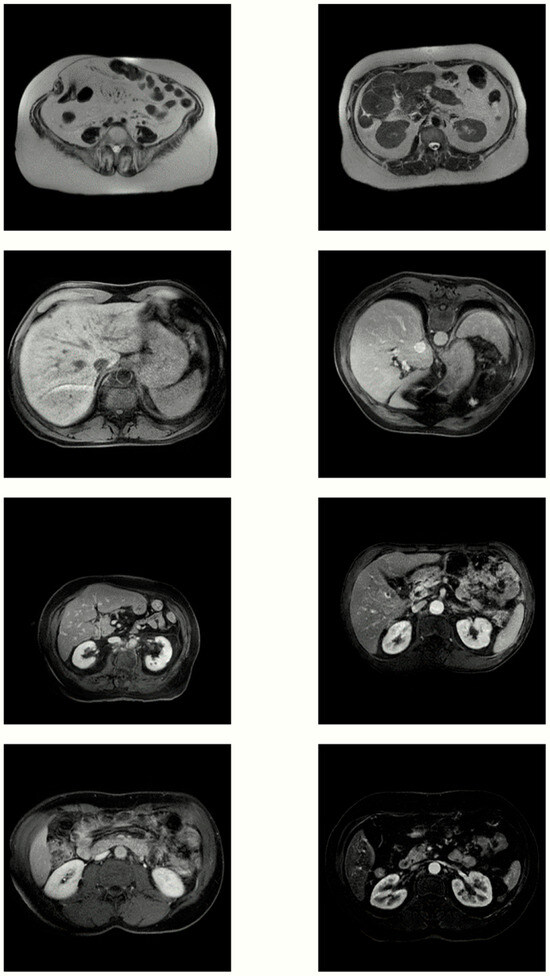
Figure 3.
Four pairs of real MR images (left) and images generated by our best model (right).
3.3. Medical Assessment
The self-made questionnaire was answered by one medical expert. Table 4 summarises the expert’s responses to the questionnaire that assessed the synthetic and real images. Regarding the overall performance, the radiologist accurately identified 14 out of 36 images. Specifically, only 4 out of 21 images from the synthetic dataset were correctly identified, whereas a higher accuracy rate was achieved for the real image set, with 10 out of 15 correctly identified. Notably, 17 synthetic images were identified as real, and five real images were identified as synthetic, indicating that the radiologist encountered difficulty in distinguishing between the real and generated images.

Table 4.
Radiologist’s assessment of image origin.
In the survey’s concluding questions, the radiologist was asked about the characteristics of the selected images that aroused suspicion of being artificially generated. Table 5 outlines the selected options.

Table 5.
Image characteristics that indicate their artificial nature to the medical expert.
Two characteristics were identified: visual artefacts, such as irregular edges and areas of distortion, rated with a relevance of 3 on a scale of 1–4. The other characteristic was anatomical inconsistencies, encompassing anatomical features that did not align with typical human anatomy, which were deemed highly relevant (rating 4).
4. Discussion
In this work, we trained StyleGAN3 with our abdominal MR dataset and then generated a synthetic dataset. The obtained dataset was evaluated using quantitative metrics, such as the FID and KID, and qualitatively assessed via a self-made medical questionnaire.
In [17], it is noted that while some researchers suggest 25,000 kimgs for convergence during network training, achieving convergence is feasible with just 5000 kimgs. In our study, we achieved FID stability with only 1000 kimgs, likely due to the size and nature of our dataset.
Our study’s FID and KID values aligned with those of other related works, as demonstrated in Table 6. For this comparison, we selected works that employed StyleGAN architectures with medical datasets. It is essential to highlight that lower values of these metrics indicate a better performance.

Table 6.
Comparison of metrics between related works.
The comparison of the qualitative evaluation by medical experts posed challenges due to variations in evaluation conditions and the diverse nature of data types. Table 7 provides a quantitative approach to the comparison of medical visual assessments conducted in various studies. For this, we used two metrics: the percentage of synthetic images classified by the medical experts as real images and the percentage of images that were correctly classified by the medical experts (accuracy). In studies with multiple participants, the table presents an average of their performances. Overall, the accuracy of the medical experts was generally low, indicating difficulty in discerning between real and generated images.

Table 7.
Comparison of the visual inspection evaluation between related works.
Throughout the project execution, we encountered difficulties finding appropriate image evaluation metrics for medical data. Existing metrics, which were initially trained on natural image data, may not fully capture the variability and richness of medical data. This challenge was previously noted in other studies, where authors concluded that images with the best metrics, such as FID, did not consistently enhance the performance of medical segmentation or classification models [9]. Additionally, our search for metrics beyond the FID in image synthesis studies yielded very few records related to medical data.
Given the challenge of finding appropriate evaluation metrics, the utilisation of synthetic data in downstream tasks becomes increasingly essential. In this study, we could not evaluate our synthetic data with a downstream task because we lacked the ground truth for our training data. In the future, after labelling the training data, it will be important to analyse the synthesis of adrenal lesions in a classification pipeline and assess their medical utility through visual inspection by medical experts. Another crucial step to enhance our current work is to increase the number of participants in the visual inspection of our synthetic dataset.
5. Conclusions
This work demonstrated that the StyleGAN3 network is a viable solution for generating realistic medical images without an extensive hyperparameter search, especially in abdominal imaging. The generated images’ evaluation metrics aligned with those found in state-of-the-art results. Additionally, the quality of the synthesised images was medically evaluated. When presented with a set of images containing both real and synthesised ones, the inquired radiologist found it challenging to distinguish between them, suggesting that the synthesised images adhered to the realism standards observed in abdominal magnetic resonance imaging.
Author Contributions
Conceptualisation, B.G. and M.S.; methodology, M.S.; software, M.S.; validation, B.G.; formal analysis, M.S.; investigation, M.S. and B.G.; resources, B.G. and P.V.; data curation, B.G. and M.S.; writing—original draft preparation, B.G.; writing—review and editing, P.V. and L.V.; visualisation, B.G.; supervision, B.G., L.V. and P.V.; project administration, B.G., P.V. and L.V. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was funded by the FCT—Portuguese Foundation for Science and Technology and Bee2Fire SA under a PhD grant with reference PD/BDE/150624/2020.
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Ethics Committee Hospital Garcia de Orta (Almada–Portugal), accepted on 31 August 2020.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in this study.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
We would like to acknowledge Miguel Ramalho and Gonçalo Saldanha from Hospital Garcia de Orta for their help.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Anaya-Isaza, A.; Mera-Jiménez, L.; Zequera-Diaz, M. An overview of deep learning in medical imaging. Inform. Med. Unlocked 2021, 26, 100723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elyan, E.; Vuttipittayamongkol, P.; Johnston, P.; Martin, K.; Sarker, M.M.K. Computer vision and machine learning for medical image analysis: Recent advances, challenges, and way forward. Artif. Intell. Surg. 2022, 2, 24–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goceri, E. Medical image data augmentation: Techniques, comparisons and interpretations. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2023, 56, 12561–12605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chlap, P.; Min, H.; Vandenberg, N.; Dowling, J.; Holloway, L.; Haworth, A. A review of medical image data augmentation techniques for deep learning applications. J. Med. Imaging Radiat. Oncol. 2021, 65, 545–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcea, F.; Serra, A.; Lamberti, F.; Morra, L. Data augmentation for medical imaging: A systematic literature review. Comput. Biol. Med. 2023, 152, 106391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazerouni, A.; Aghdam, E.K.; Heidari, M.; Azad, R.; Fayyaz, M.; Hacihaliloglu, I.; Merhof, D. Diffusion models in medical imaging: A comprehensive survey. Med. Image Anal. 2023, 88, 102846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shamshad, F.; Khan, S.; Zamir, S.W.; Khan, M.H.; Hayat, M.; Khan, F.S.; Fu, H. Transformers in medical imaging: A survey. Med. Image Anal. 2023, 88, 102802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodfellow, I.J.; Pouget-Abadie, J.; Mirza, M.; Xu, B.; Warde-Farley, D.; Ozair, S.; Courville, A.; Bengio, Y. Generative Adversarial Networks. arXiv 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skandarani, Y.; Jodoin, P.-M.; Lalande, A. GANs for Medical Image Synthesis: An Empirical Study. J. Imaging Sci. Technol. 2023, 9, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.-W.; Ko, J.-S.; Huh, J.-H.; Kim, J.-C. Review on Generative Adversarial Networks: Focusing on Computer Vision and Its Applications. Electronics 2021, 10, 1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, X.; Walia, E.; Babyn, P. Generative adversarial network in medical imaging: A review. Med. Image Anal. 2019, 58, 101552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borji, A. Pros and cons of GAN evaluation measures. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2019, 179, 41–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karras, T.; Aittala, M.; Hellsten, J.; Laine, S.; Lehtinen, J.; Aila, T. Training Generative Adversarial Networks with Limited Data. arXiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tronchin, L.; Sicilia, R.; Cordelli, E.; Ramella, S.; Soda, P. Evaluating GANs in Medical Imaging. In Deep Generative Models, and Data Augmentation, Labelling, and Imperfections; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 112–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazeminia, S.; Baur, C.; Kuijper, A.; van Ginneken, B.; Navab, N.; Albarqouni, S.; Mukhopadhyay, A. GANs for medical image analysis. Artif. Intell. Med. 2020, 109, 101938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorin, V.; Barash, Y.; Konen, E.; Klang, E. Creating Artificial Images for Radiology Applications Using Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs)—A Systematic Review. Acad. Radiol. 2020, 27, 1175–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osuala, R.; Kushibar, K.; Garrucho, L.; Linardos, A.; Szafranowska, Z.; Klein, S.; Glocker, B.; Díaz, O.; Lekadir, K. A Review of Generative Adversarial Networks in Cancer Imaging: New Applications, New Solutions. arXiv 2021. Available online: https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/35d2f0eb6e3c2ff7f61434231f4a59c1f4c9a49b (accessed on 12 May 2024).
- Frid-Adar, M.; Diamant, I.; Klang, E.; Amitai, M.; Goldberger, J.; Greenspan, H. GAN-based Synthetic Medical Image Augmentation for increased CNN Performance in Liver Lesion Classification. arXiv 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fetty, L.; Bylund, M.; Kuess, P.; Heilemann, G.; Nyholm, T.; Georg, D.; Löfstedt, T. Latent space manipulation for high-resolution medical image synthesis via the StyleGAN. Z. Med. Phys. 2020, 30, 305–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonçalves, G.M. A Comparative Study of Data Augmentation Techniques for Image Classification: Generative Models vs. Classical Transformations. 2020. Available online: https://ria.ua.pt/handle/10773/30759 (accessed on 12 May 2024).
- Han, C.; Hayashi, H.; Rundo, L.; Araki, R.; Shimoda, W.; Muramatsu, S.; Furukawa, Y.; Mauri, G.; Nakayama, H. GAN-based synthetic brain MR image generation. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 15th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI 2018), Washington, DC, USA, 4–7 April 2018; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA; pp. 734–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazuhiro, K.; Werner, R.A.; Toriumi, F.; Javadi, M.S.; Pomper, M.G.; Solnes, L.B.; Verde, F.; Higuchi, T.; Rowe, S.P. Generative Adversarial Networks for the Creation of Realistic Artificial Brain Magnetic Resonance Images. Tomography 2018, 4, 159–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chuquicusma, M.J.M.; Hussein, S.; Burt, J.; Bagci, U. How to Fool Radiologists with Generative Adversarial Networks? A Visual Turing Test for Lung Cancer Diagnosis. arXiv 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korkinof, D.; Harvey, H.; Heindl, A.; Karpati, E.; Williams, G.; Rijken, T.; Kecskemethy, P.; Glocker, B. Perceived Realism of High-Resolution Generative Adversarial Network-derived Synthetic Mammograms. Radiol Artif. Intell. 2021, 3, e190181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levine, A.B.; Peng, J.; Farnell, D.; Nursey, M.; Wang, Y.; Naso, J.R.; Ren, H.; Farahani, H.; Chen, C.; Chiu, D.; et al. Synthesis of diagnostic quality cancer pathology images by generative adversarial networks. J. Pathol. 2020, 252, 178–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghorbani, A.; Natarajan, V.; Coz, D.; Liu, Y. DermGAN: Synthetic Generation of Clinical Skin Images with Pathology. In Proceedings of the Machine Learning for Health NeurIPS Workshop; Dalca, A.V., McDermott, M.B.A., Alsentzer, E., Finlayson, S.G., Oberst, M., Falck, F., Beaulieu-Jones, B., Eds.; PMLR: Cambridge, UK, 2020; Volume 116, pp. 155–170. Available online: https://proceedings.mlr.press/v116/ghorbani20a.html (accessed on 23 February 2024).
- Woodland, M.; Wood, J.; Anderson, B.M.; Kundu, S.; Lin, E.; Koay, E.; Odisio, B.; Chung, C.; Kang, H.C.; Venkatesan, A.M.; et al. Evaluating the Performance of StyleGAN2-ADA on Medical Images. arXiv 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, B.; Vieira, P.; Vieira, A. Abdominal MRI Synthesis using StyleGAN2-ADA. In Proceedings of the 2023 IST-Africa Conference (IST-Africa), Tshwane, South Africa, 31 May–2 June 2023; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2023; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karras, T.; Laine, S.; Aila, T. A Style-Based Generator Architecture for Generative Adversarial Networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2021, 43, 4217–4228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karras, T.; Aila, T.; Laine, S.; Lehtinen, J. Progressive Growing of GANs for Improved Quality, Stability, and Variation. arXiv 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatys, L.A.; Ecker, A.S.; Bethge, M. A Neural Algorithm of Artistic Style. arXiv 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karras, T.; Laine, S.; Aittala, M.; Hellsten, J.; Lehtinen, J.; Aila, T. Analyzing and Improving the Image Quality of StyleGAN. arXiv 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karras, T.; Aittala, M.; Laine, S.; Härkönen, E.; Hellsten, J.; Lehtinen, J.; Aila, T. Alias-Free Generative Adversarial Networks. arXiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).