Machine Learning Tools and Platforms in Clinical Trial Outputs to Support Evidence-Based Health Informatics: A Rapid Review of the Literature
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- RQ1. What MLTs and platforms are reported in the literature to derive results through clinical trial implementations?
- RQ2. What are the main categories of these MLTs?
- RQ3. What are the results, benefits, and experience gained from their implementation and what are the inherent difficulties in implementing them and the main observations for future work and challenges to be overcome?
2. Related Work
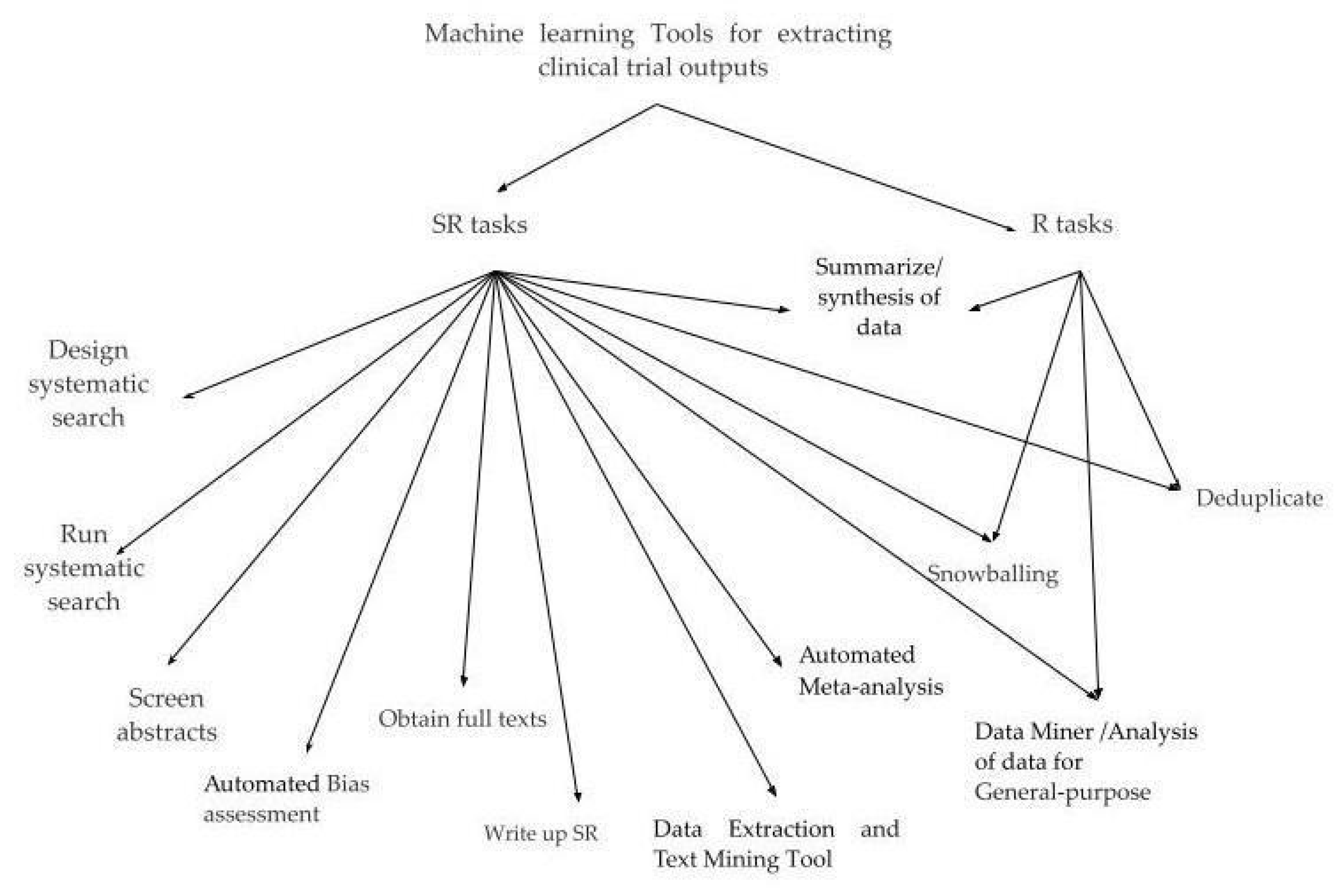
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Study Design
3.2. Search Strategy and Eligibility Criteria
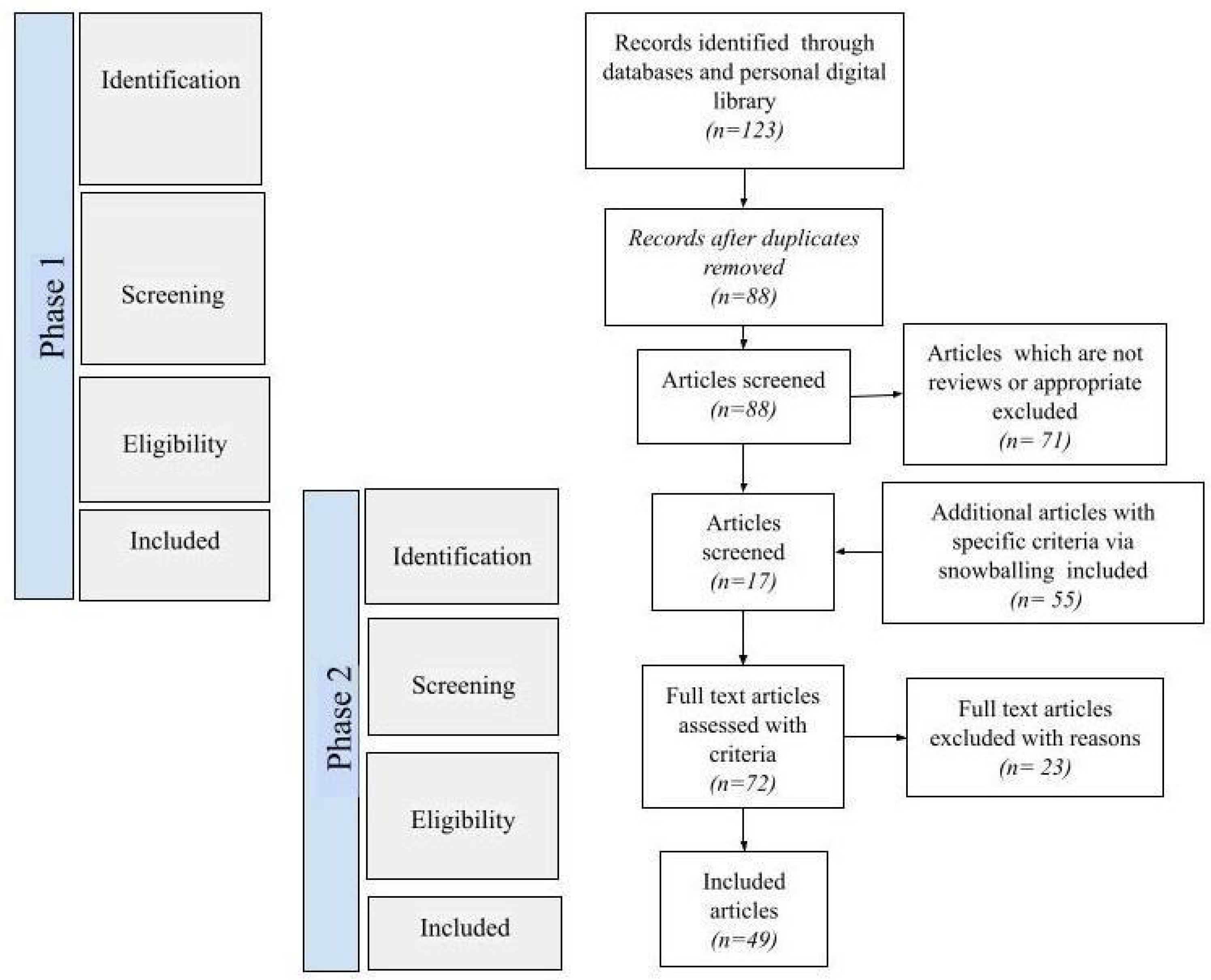
3.3. Data Screening
3.4. Data Extraction and Analyses
- Review (selected from the first phase);
- Tools assessment (selected from the first either second phase);
- Automated tool (article selected from the first phase);
- Book either book chapter (selected from the first or second phase).
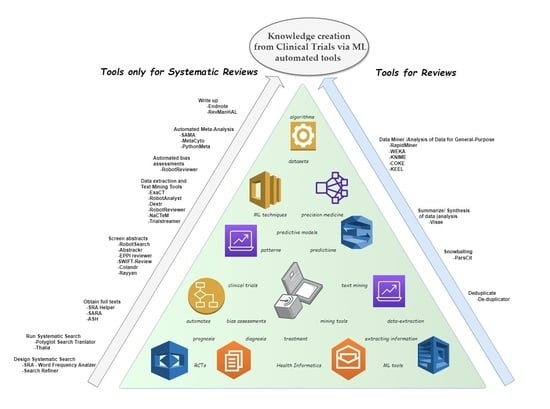
- Design systematic search
- Run systematic search
- Deduplicate
- Obtain full texts
- Snowballing
- Screen abstracts
- Data extraction and text mining tool
- Automated bias assessments
- Automated meta-analysis
- Summarize/synthesis of data (analysis)
- Write up
- Data miner/analysis of data for general purpose.
4. Results
4.1. Review Articles on MLTs for Extracting Clinical Trial Results
4.2. Articles Relative to MLTs for Extracting Clinical Trial Outputs
4.2.1. Design Systematic Search (Includes Two Tools)
- SRA—Word Frequency Analyzer [28], (http://sr-accelerator.com/#/help/wordfreq, accessed on 10 August 2022)
- The Search Refiner [28]
4.2.2. Run Systematic Search (Includes Two Tools)
- Polyglot Search Translator (http://sr-accelerator.com/#/polyglot, accessed on 10 August 2022), [28,40]
- Thalia (http://nactem-copious.man.ac.uk/Thalia/, accessed on 10 August 2022), [16]
4.2.3. Deduplicate (Includes One Tool)
- De-duplicator (http://sr-accelerator.com/#/help/dedupe, accessed on 8 August 2022)
4.2.4. Obtain Full Texts (Includes Three Tools)
- SRA Helper (http://sr-accelerator.com/#/sra-helper, accessed on 8 August 2022)
- SARA (http://sr-accelerator.com/, accessed on 8 August 2022)
- ASH [41]
4.2.5. Snowballing (Includes One Tool)
- ParsCit [42]
4.2.6. Screen Abstracts (Includes Six Tools)
- RobotSearch (https://robotsearch.vortext.systems/, accessed on 8 August 2022), [9]
- SWIFT-Review (https://www.sciome.com/swift-review/, accessed on 8 August 2022), [16]
- Colandr (https://www.colandrapp.com, accessed on 8 August 2022), [16]
4.2.7. Data Extraction and Text Mining Tool (Includes Six Tools)
- Dextr [47]
- RobotReviewer (https://robotreviewer.vortext.systems, accessed on 8 August 2022), [16]
- NaCTeM [16], (http://www.nactem.ac.uk/software.php, accessed on 8 August 2022)
- Trialstreamer [48]
4.2.8. Automated Bias Assessments (Includes One Tool)
4.2.9. Automated Meta-Analysis (Includes Three Tools)
- SAMA (Ajiji et al., 2022) [50]
- MetaCyto (http://bioconductor.org/packages/release/bioc/html/MetaCyto.html, accessed on 8 August 2022), [51]
- PythonMeta [4]
4.2.10. Summarize/Synthesis of Data (Analysis) (Includes One Tool)
- Visae [52]
4.2.11. Write Up (Includes Two Tools)
- Endnote (https://endnote.com/, accessed on 8 August 2022)
- RevManHAL [53]
4.2.12. Data Miner/Analysis of Data for General-Purpose (Includes Five Tools)
- Using MLTs to assist with data extraction resulted in performance gains compared with using manual extraction.
- At the same time, the use of MLTs has enough flexibility and can speed up and further improve the results of meta-analyses.
- In summary, there are a number of data mining tools available in the digital world that can help researchers with the evaluation of the clinical trials outputs [34]. Evaluations from applying ML to datasets and clinical studies show that this approach could yield promising results.
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions and Future Directions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AI | Artificial intelligence |
| ML | Machine learning |
| MLT | Machine learning tool |
| SE | Software engineering |
| SLR | Systematic literature review |
| SR | Systematic review |
| R | Review |
| RCT | Randomized controlled trial |
References
- Ammenwerth, E.; de Keizer, N. A viewpoint on evidence-based health informatics, based on a pilot survey on evaluation studies in health care informatics. J. Am. Med. Inform. Assoc. 2007, 14, 368–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sargeant, J.M.; Kelton, D.F.; O’Connor, A.M. Study Designs and Systematic Reviews of Interventions: Building Evidence Across Study Designs. Zoonoses Public Health 2014, 61, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, L.; Katz-Rogozhnikov, D.A.; Varshney, K.R.; Baldini, I. Automated meta-analysis: A causal learning perspective. arXiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masoumi, S.; Shahraz, S. Meta-analysis using Python: A hands-on tutorial. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2022, 22, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pynam, V.; Spanadna, R.R.; Srikanth, K. An Extensive Study of Data Analysis Tools (Rapid Miner, Weka, R Tool, Knime, Orange). Int. J. Comput. Sci. Eng. 2018, 5, 4–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinhubl, S.R.; Wolff-Hughes, D.L.; Nilsen, W.; Iturriaga, E.; Califf, R.M. Digital clinical trials: Creating a vision for the future. npj Digit. Med. 2019, 2, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, C.; Marsch, L.A.; Winstanley, E.L.; Brunner, M.; Campbell, A.N.C. Using digital technologies in clinical trials: Current and future applications. Contemp. Clin. Trials 2021, 100, 106219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inan, O.T.; Tenaerts, P.; Prindiville, S.A.; Reynolds, H.; Dizon, D.S.; Cooper-Arnold, K.; Turakhia, M.; Pletcher, M.J.; Preston, K.L.; Krumholz, H.M.; et al. Digitizing clinical trials. Npj Digit. Med. 2020, 3, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClendon, L.; Meghanathan, N. Using Machine Learning Algorithms to Analyze Crime Data. Mach. Learn. Appl. Int. J. 2015, 2, 2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habehh, H.; Gohel, S. Machine Learning in Healthcare. Curr. Genom. 2021, 22, 291–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, G.; Mendez, A.; Assi, E.B.; Zhao, B.; Sawan, M. Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare: Review and Prediction Case Studies. Engineering 2020, 6, 291–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, Y.; Mahajan, M. 5. Recent advancement of machine learning and deep learning in the field of healthcare system. In Computational Intelligence for Machine Learning and Healthcare Informatics; Walter de Gruyter GmbH & Co KG: Berlin, Germany, 2020; pp. 77–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonnalagadda, S.R.; Goyal, P.; Huffman, M.D. Automating data extraction in systematic reviews: A systematic review. Syst. Rev. 2015, 4, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Xie, H.; Cheng, G.; Poon, L.K.M.; Leng, M.; Wang, F.L. Trends and Features of the Applications of Natural Language Processing Techniques for Clinical Trials Text Analysis. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrer, S.; Shah, P.; Antony, B.; Hu, J. Artificial Intelligence for Clinical Trial Design. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2019, 40, 577–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, I.J.; Wallace, B.C. Toward systematic review automation: A practical guide to using machine learning tools in research synthesis. Syst. Rev. 2019, 8, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsafnat, G.; Glasziou, P.; Choong, M.K.; Dunn, A.; Galgani, F.; Coiera, E. Systematic review automation technologies. Syst. Rev. 2014, 3, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Carter, B.Z.; Li, Z.; Huang, X. Application of machine learning methods in clinical trials for precision medicine. JAMIA Open 2022, 5, ooab107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izonin, I.; Tkachenko, R.; Kryvinska, N.; Tkachenko, P. Multiple Linear Regression Based on Coefficients Identification Using Non-iterative SGTM Neural-like Structure. In Advances in Computational Intelligence; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 467–479. [Google Scholar]
- Felizardo, K.R.; Carver, J.C. Automating Systematic Literature Review. In Contemporary Empirical Methods in Software Engineering; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 327–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gates, A.; Gates, M.; Sim, S.; Elliott, S.A.; Pillay, J.; Hartling, L. Creating efficiencies in the extraction of data from randomized trials: A prospective evaluation of a machine learning and text mining tool. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2021, 21, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiritchenko, S.; De Bruijn, B.; Carini, S.; Martin, J.; Sim, I. ExaCT: Automatic extraction of clinical trial characteristics from journal publications. BMC Med. Inform. Decis. Mak. 2010, 10, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golinelli, D.; Nuzzolese, A.G.; Sanmarchi, F.; Bulla, L.; Mongiovì, M.; Gangemi, A.; Rucci, P. Semi-Automatic Systematic Literature Reviews and Information Extraction of COVID-19 Scientific Evidence: Description and Preliminary Results of the COKE Project. Information 2022, 13, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khangura, S.; Konnyu, K.; Cushman, R.; Grimshaw, J.; Moher, D. Evidence summaries: The evolution of a rapid review approach. Syst. Rev. 2012, 1, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenhalgh, T.; Peacock, R. Effectiveness and efficiency of search methods in systematic reviews of complex evidence: Audit of primary sources. BMJ 2005, 331, 1064–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manktelow, M.; Iftikhar, A.; Bucholc, M.; McCann, M.; O’Kane, M. Clinical and operational insights from data-driven care pathway mapping: A systematic review. BMC Med. Inform. Decis. Mak. 2022, 22, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christopoulou, S.C.; Kotsilieris, T.; Anagnostopoulos, I. Assessment of Health Information Technology Interventions in Evidence-Based Medicine: A Systematic Review by Adopting a Methodological Evaluation Framework. Healthcare 2018, 6, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, J.; McFarlane, C.; Cleo, G.; Ramos, C.I.; Marshall, S. The Impact of Systematic Review Automation Tools on Methodological Quality and Time Taken to Complete Systematic Review Tasks: Case Study. JMIR Med. Educ. 2021, 7, e24418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, J.; Glasziou, P.; del Mar, C.; Bannach-Brown, A.; Stehlik, P.; Scott, A.M. A full systematic review was completed in 2 weeks using automation tools: A case study. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2020, 121, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, H.; Ameen, D.; Zarnegar, A. Tools to support the automation of systematic reviews: A scoping review. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2022, 144, 22–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erickson, B.J.; Korfiatis, P.; Akkus, Z.; Kline, T.; Philbrick, K. Toolkits and Libraries for Deep Learning. J. Digit. Imaging 2017, 30, 400–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cleo, G.; Scott, A.M.; Islam, F.; Julien, B.; Beller, E. Usability and acceptability of four systematic review automation software packages: A mixed method design. Syst. Rev. 2019, 8, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shravan, I.V. Top 10 Open Source Data Mining Tools. Open Source For You, CreateSpace Independent Publishing Platform, Delhi NCR, India. 2017. Available online: https://www.opensourceforu.com/2017/03/top-10-open-source-data-mining-tools/ (accessed on 1 September 2022).
- Ratra, R.; Gulia, P. Experimental Evaluation of Open Source Data Mining Tools (WEKA and Orange). Int. J. Eng. Trends Technol. 2020, 68, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altalhi, A.H.; Luna, J.M.; Vallejo, M.A.; Ventura, S. Evaluation and comparison of open source software suites for data mining and knowledge discovery. WIREs Data Min. Knowl. Discov. 2017, 7, e1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwivedi, S.; Kasliwal, P.; Soni, S. Comprehensive study of data analytics tools (RapidMiner, Weka, R tool, Knime). In Proceedings of the 2016 Symposium on Colossal Data Analysis and Networking (CDAN), Indore, India, 18–19 March 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naik, A.; Samant, L. Correlation Review of Classification Algorithm Using Data Mining Tool: WEKA, Rapidminer, Tanagra, Orange and Knime. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2016, 85, 662–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zippel, C.; Bohnet-Joschko, S. Rise of Clinical Studies in the Field of Machine Learning: A Review of Data Registered in ClinicalTrials.gov. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 5072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, C.; Sutton, A. Systematic Review Toolbox. Value Health 2016, 19, A398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, J.M.; Sanders, S.; Carter, M.; Honeyman, D.; Cleo, G.; Auld, Y.; Booth, D.; Condron, P.; Dalais, C.; Bateup, S.; et al. Improving the translation of search strategies using the Polyglot Search Translator: A randomized controlled trial. J. Med. Libr. Assoc. 2020, 108, 195–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sośnicki, M.; Madeyski, L. ASH: A New Tool for Automated and Full-Text Search in Systematic Literature Reviews. In Computational Science—ICCS 2021; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 362–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choong, M.K.; Galgani, F.; Dunn, A.G.; Tsafnat, G. Automatic evidence retrieval for systematic reviews. J. Med. Internet Res. 2014, 16, e223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wallace, B.C.; Small, K.; Brodley, C.E.; Lau, J.; Trikalinos, T.A. Deploying an interactive machine learning system in an evidence-based practice center. In Proceedings of the 2nd ACM SIGHIT symposium on International health informatics—IHI ’12, Miami, FL, USA, 28–30 January 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shemilt, I.; Khan, N.; Park, S.; Thomas, J. Use of cost-effectiveness analysis to compare the efficiency of study identification methods in systematic reviews. Syst. Rev. 2016, 5, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouzzani, M.; Hammady, H.; Fedorowicz, Z.; Elmagarmid, A. Rayyan—a web and mobile app for systematic reviews. Syst. Rev. 2016, 5, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Przybyła, P.; Brockmeier, A.J.; Kontonatsios, G.; Le Pogam, M.-A.; McNaught, J.; von Elm, E.; Nolan, K.; Ananiadou, S. Prioritising references for systematic reviews with RobotAnalyst: A user study. Res Synth. Methods 2018, 9, 470–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, V.R.; Schmitt, C.P.; Wolfe, M.S.; Nowak, A.J.; Kulesza, K.; Williams, A.R.; Shin, R.; Cohen, J.; Burch, D.; Stout, M.D.; et al. Evaluation of a semi-automated data extraction tool for public health literature-based reviews: Dextr. Environ. Int. 2022, 159, 107025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, I.J.; Nye, B.; Kuiper, J.; Noel-Storr, A.; Marshall, R.; Maclean, R.; Soboczenski, F.; Nenkova, A.; Thomas, J.; Wallace, B.C. Trialstreamer: A living, automatically updated database of clinical trial reports. J. Am. Med. Inform. Assoc. 2020, 27, 1903–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soboczenski, F.; Trikalinos, T.A.; Kuiper, J.; Bias, R.G.; Wallace, B.C.; Marshall, I.J. Machine learning to help researchers evaluate biases in clinical trials: A prospective, randomized user study. BMC Med. Inform. Decis. Mak. 2019, 19, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajiji, P.; Cottin, J.; Picot, C.; Uzunali, A.; Ripoche, E.; Cucherat, M.; Maison, P. Feasibility study and evaluation of expert opinion on the semi-automated meta-analysis and the conventional meta-analysis. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2022, 78, 1177–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Jujjavarapu, C.; Hughey, J.J.; Andorf, S.; Lee, H.-C.; Gherardini, P.F.; Spitzer, M.H.; Thomas, C.G.; Campbell, J.; Dunn, P.; et al. MetaCyto: A Tool for Automated Meta-analysis of Mass and Flow Cytometry Data. Cell Rep. 2018, 24, 1377–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diniz, M.A.; Gresham, G.; Kim, S.; Luu, M.; Henry, N.L.; Tighiouart, M.; Yothers, G.; Ganz, P.A.; Rogatko, A. Visualizing adverse events in clinical trials using correspondence analysis with R-package visae. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2021, 21, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, M.T.; Adams, C.E. RevManHAL: Towards automatic text generation in systematic reviews. Syst. Rev. 2017, 6, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, E.; Hall, M.; Trigg, L.; Holmes, G.; Witten, I.H. Data mining in bioinformatics using Weka. Bioinformatics 2004, 20, 2479–2481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witten, I.H.; Frank, E.; Hall, M.A.; Pal, C.J. Data Mining: Practical Machine Learning Tools and Techniques; Morgan Kaufmann: Burlington, MA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Witten, I.H.; Frank, E.; Trigg, L.; Hall, M.; Holmes, G.; Cunningham, S.J. Weka: Practical Machine Learning Tools and Techniques with Java Implementations; University of Waikato, Department of Computer Science: Hamilton, New Zealand, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Weka 3—Data Mining with Open Source Machine Learning Software in Java. Available online: www.cs.waikato.ac.nz/ml/weka/ (accessed on 14 August 2022).
- Meinl, T.; Jagla, B.; Berthold, M.R. Integrated data analysis with KNIME. In Open Source Software in Life Science Research; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 151–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcalá-Fdez, J.; Sánchez, L.; García, S.; Del Jesus, M.J.; Ventura, S.; Garrell, J.M.; Otero, J.; Romero, C.; Bacardit, J.; Rivas, V.M.; et al. KEEL: A software tool to assess evolutionary algorithms for data mining problems. Soft Comput. 2009, 13, 307–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, A.; Luengo, J.; Derrac, J.; Alcalá-Fdez, J.; Herrera, F. Implementation and Integration of Algorithms into the KEEL Data-Mining Software Tool. In Intelligent Data Engineering and Automated Learning—IDEAL 2009; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 2009; pp. 562–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcala-Fdez, J.; Garcia, S.; Berlanga, F.J.; Fernandez, A.; Sanchez, L.; del Jesus, M.; Herrera, F. KEEL: A data mining software tool integrating genetic fuzzy systems. In Proceedings of the 2008 3rd International Workshop on Genetic and Evolving Systems, Witten-Bommerholz, Germany, 4–7 March 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triguero, I.; González, S.; Moyano, J.M.; García, S.; Alcalá-Fdez, J.; Luengo, J.; Fernández, A.; del Jesús, M.J.; Sánchez, L.; Herrera, F. KEEL 3.0: An Open Source Software for Multi-Stage Analysis in Data Mining. Int. J. Comput. Intell. Syst. 2017, 10, 1238–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: http://www.keel.es/software/KEEL_template.zip (accessed on 10 August 2022).
- Rashid, S.; Kathuria, N. Machine Learning in Clinical Trials. In Big Data and Artificial Intelligence for Healthcare Applications; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2021; pp. 69–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margulis, E.; Dagan-Wiener, A.; Ives, R.S.; Jaffari, S.; Siems, K.; Niv, M.Y. Intense bitterness of molecules: Machine learning for expediting drug discovery. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2021, 19, 568–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, L.; Olorisade, B.K.; McGuinness, L.A.; Thomas, J.; Higgins, J.P.T. Data extraction methods for systematic review (semi)automation: A living systematic review. F1000Research 2021, 10, 401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holzinger, A. Machine Learning for Health Informatics: State-of-the-Art and Future Challenges; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
| Author(s) | Tools |
|---|---|
| (J. Clark et al., 2021) [28] | Polyglot Search, Translator, Deduplicator, SRA-Helper, and SARA |
| (Clark et al., 2020) [29] | Word Frequency Analyzer, The Search Refiner, Polyglot Search Translator, De-duplicator, SRA Helper, RobotSearch, Endnote, SARA, RobotReviewer, SRA—RevMan Replicant |
| (Marshall & Wallace, 2019) [16] | RobotSearch, Cochrane, Register of Studies, RCT tagger, Thalia, Abstrackr, EPPI reviewer, RobotAnalyst, SWIFT-Review, Colandr, Rayyan, ExaCT, RobotReviewer, NEMine, Yeast MetaboliNER, AnatomyTagger |
| (Khalil et al., 2022) [30] | LitSuggest, Rayyan, Abstractr, BIBOT, R software, RobotAnalyst, DistillerSR, ExaCT and NetMetaXL |
| (Erickson et al., 2017) [31] | Caffe, Deeplearning4j, Tensorflow, Theano, Keras, MXNet, Lasagne, Cognitive Network Toolkit (CNTK), DIGITS, Torch, PyTorch, Pylearn2, Chainer, Nolearn, Sklearn-theano and scikit-learn to work with the Theano library, Paddle, H2O |
| (Pynam et al., 2018) [5] | RapidMiner, Weka, R Tool, KNIME and Orange |
| (Cleo et al., 2019) [32] | Covidence, SRA-Helper for EndNote, Rayyan and RobotAnalyst |
| (Wang et al., n.d.) [18] | The authors selected nine mainstream ML algorithms and implemented them in the response-adaptive randomization (RAR) design to predict treatment response. |
| (Tsafnat et al., 2014) [17] | Quick Clinical, Sherlock, Metta, ParsCit, Abstrackr, ExaCT, WebPlotDigitizer, Meta-analyst, RevMan-HAL, PRISMA Flow Diagram Generator |
| (Shravan, 2017) [33] | Weka, Rapid Miner, Orange, Knime, DataMelt, Apache Mahout, ELKI, MOA, KEEL, Rattle Mining tasks: Pre-processing, Clustering, Classification, Outlier analysis, Regression, Summarisation Techniques: pattern recognition, statistics, ML, etc. |
| (Ratra & Gulia, 2020) [34] | WEKA and Orange |
| (Altalhi et al., 2017) [35] | ADaM, ADAMS, AlphaMiner, CMSR, D.ESOM DataMelt, ELKI, GDataMine, KEEL, KNIME, MiningMart, ML-Flex, Orange RapidMiner, Rattle, SPMF, Tanagra, V.Wabbit, WEKA |
| (Dwivedi et al., 2016) [36] | WEKA and Salford System |
| (Naik & Samant, 2016) [37] | RapidMiner, Weka, R Tool:, KNIME and Orange |
| (Zippel & Bohnet-Joschko, 2021) [38] | RobotSearch, Cochrane Register of Studies, RCT tagger, Thalia, Abstrackr, EPPI reviewer, RobotAnalyst, SWIFT-Review, Colandr, Rayyan, ExaCT, RobotReviewer, NEMine.Yeast MetaboliNER, AnatomyTagger |
| Systematic Review Toolbox (Marshall and Sutton 2016) [39] | Many tools are presented on web (http://systematicreviewtools.com/about.php, accessed on 5 August 2022) |
| (Felizardo and Carver 2020) [20] | An overview of strategies researchers have developed to automate the Systematic Literature Review (SLR) process. We used a systematic search methodology to survey the literature about the strategies used to automate the SLR process in SE |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Christopoulou, S.C. Machine Learning Tools and Platforms in Clinical Trial Outputs to Support Evidence-Based Health Informatics: A Rapid Review of the Literature. BioMedInformatics 2022, 2, 511-527. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedinformatics2030032
Christopoulou SC. Machine Learning Tools and Platforms in Clinical Trial Outputs to Support Evidence-Based Health Informatics: A Rapid Review of the Literature. BioMedInformatics. 2022; 2(3):511-527. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedinformatics2030032
Chicago/Turabian StyleChristopoulou, Stella C. 2022. "Machine Learning Tools and Platforms in Clinical Trial Outputs to Support Evidence-Based Health Informatics: A Rapid Review of the Literature" BioMedInformatics 2, no. 3: 511-527. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedinformatics2030032
APA StyleChristopoulou, S. C. (2022). Machine Learning Tools and Platforms in Clinical Trial Outputs to Support Evidence-Based Health Informatics: A Rapid Review of the Literature. BioMedInformatics, 2(3), 511-527. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedinformatics2030032