Abstract
Metformin is the most used oral anti-diabetic drug in the world and consequently is commonly found in the aquatic environment. Some studies demonstrated that metformin may act as an endocrine-disrupting-chemical (EDC) in fish, although it does not have a classic EDC structure. In this sense, the aim of this work was to evaluate the potential disrupting effect of metformin in the cardiovascular system through in vitro, ex vivo, and in silico studies. For this purpose, human umbilical artery (HUA) and rat aorta artery (RAA) were used. The toxic concentrations of metformin were determined by a cytotoxicity assay and in silico simulations were performed to analyze the interactions of metformin with hormonal receptors. Our results show that metformin decreases viability of the smooth muscle cells. Moreover, metformin induces a vasorelaxant effect in rat aorta and human models by an endothelium-dependent and -independent pathways. Furthermore, docking simulations showed that metformin binds to androgen receptors (AR) and estrogen receptors (ERα and ERβ). In conclusion, the in silico assays suggested that metformin has the potential to be an endocrine disruptor, acting mainly on ERα. Further studies are needed to use metformin in pregnant women without impairing the cardiovascular health of the future generation.
1. Introduction
Metformin (3-(diaminomethylidene)-1,1-dimethylguanidine) belongs to the biguanide class—antidiabetic drugs with two guanidine rings connected—and derivates from galegine (isoamylene guanidine), a chemical found in the plant Galega officinalis [1,2]. This drug has a therapeutic potential well defined in several diseases besides Diabetes mellitus. Its effects seem to be related to the endocrine and cardiovascular systems, and its off-label use has been growing in these fields. The molecular targets of metformin are not clear, but it is already known that biguanides reduce the liver output of glucose, reduce gluconeogenesis, and stimulate glycolysis [3]. Metformin can also reduce glucose absorption in the gut [4]; increase oxidation of fatty acids [5]; reduce low-density-lipoproteins, very-low-density-lipoproteins cholesterol, and triglycerides [6,7,8]; increase high-density-lipoproteins cholesterol; and reduce blood pressure [8].
In this sense, metformin seems to have beneficial effects on the human cardiovascular system. In patients with diabetes mellitus, one of these effects is vascular endothelial protection [9,10], which consequently reduces the risk of atherosclerosis development [11] and cardiovascular diseases. Overall, metformin protect the endothelial cells by different mechanisms including, for example, an increase in nitric oxide (NO) production and an inhibition of inflammation and oxidative stress [10]. Moreover, some studies have reported that metformin has a protective role in hypertensive disorders of pregnancy (HDP) [12].
In a clinical practice, metformin is used during pregnancy as a safe drug for treatment of gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM). The main clinical benefits that support its use are the reduction in mothers’ weight, the adequate glycemic control, and a high degree of patient acceptability due to the oral administration [13,14]. Moreover, the use of this drug in women with HDP and with GDM seems to have beneficial effects in the mother, as it has been postulated that metformin has an anti-inflammatory effect and is protective for endothelium. In this sense, metformin may have an important role in the prevention and/or treatment of the HDP [12], manly pre-eclampsia (PE). The pathogenesis of PE is associated with the reduced AMPK pathway activity, and once this antidiabetic drug is an AMPK activator, it may be used in the treatment of PE. The α-subunit by liver kinase B1(LKB1) is a key molecule for AMPK activation, as recently reviewed by Shpakov (2021) [15]. However, the cellular mechanisms of metformin action remain unclear and future investigations are urgent to improve the clinical treatments. Furthermore, HDP are also associated with the increase in the anti-angiogenic factor, fms-like tyrosine kinase 1 (sFlt-1), and it seems that metformin can also decrease sFlt-1 production from placenta [16]. However, according to Poniedziałek-Czajkowska et al. there are several randomized controlled trials and meta-analyses which are ambiguous. Metabolic diseases, such as GDM or obesity, are well-known risk factors for HDP development, and the majority of the studies evaluated the effect of metformin on the incidence of HDP [12]. In this sense, this fact may be a confounding factor to establish the real effect of metformin in pregnant women.
Pregnant women are a susceptible population for endocrine disruption [17]. Worryingly, some studies in fish have reported that metformin can act as an endocrine-disrupting chemical (EDC) [18,19,20]. The effect of metformin in aquatic organisms seems to involve an effect on estrogen receptors with repercussions in the F1 generation [18,20,21]. These negative effects were also observed in pregnant mice where intrauterine exposure to metformin lead to reduced testicular size of offspring and reduced number of Sertolli cells [21]. However, there is still a lack of evidence about its potential effect as a human EDC. Although it does not structurally resemble identified EDCs [22], it has been recognized that endocrine disruption can occur by processes other than classic binding to endocrine receptors [23]. In this sense, identifying these agents is challenging because there are several mechanisms of endocrine disruption and the time interval that can occur between the exposure to an EDC and the triggering of symptoms/diseases can further confound these associations [24].
Due to this evidence, the main objective of this study was to analyze the potential disrupting effect of metformin in the cardiovascular system through in vitro, ex vivo, and in silico studies. For this purpose, two models were used: rat aorta arteries (RAA) and human umbilical arteries (HUA). RAA are low-cost model for studying several signaling pathways involved in the contractility response [25]. Moreover, RAA can simultaneously enable study of the smooth muscle cells and the endothelial cells that are primary constituents of vascular tone regulation [26]. On the other hand, the HUA is a good human model for studying the effects of EDCs in the vascular system of pregnant women. The use of human umbilical artery smooth muscle cells (HUASMC) allows us to perform arterial and cellular contractility studies, and to understand how exposome impairs the normal physiological regulation. Moreover, this human model also allows us to analyze the contribution of endothelium in vascular response SMC. Overall, the use of this model contributes to understanding how the pregnant exposome is related to cardiovascular and metabolic diseases [17].
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture of Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells (SMC)
The cells used to perform the viability assay were A7r5, a vascular smooth muscle cell line obtained from an embryonic rat aorta (Promochem, Barcelona, Spain). The cells were cultured according to Melissa et al. (2018) [27] in a 5% CO2 atmosphere at 37 °C. The composition of culture medium for cell growth was: DMEM-F12 (Sigma Aldrich, Lisboa, Portugal) supplemented with bovine serum albumin (0.5%; Sigma-Aldrich); heat-inactivated fetal bovine serum (FBS; 10%; Biochrom, Harvard, UK); and a mixture of penicillin (100 U/mL), streptomycin (100 g/mL), and amphotericin B (250 ng/mL) (Sigma-Aldrich).
2.2. Assessment of Viability (MTT Assay)
The MTT assay is established on the conversion of a substrate (tetrazolium salt–MTT) to a chromogenic product (purple formazan) by cellular dehydrogenase enzymes to evaluate the cell viability and proliferation in vitro in response to an external factor [28]. Briefly, the culture is more purple, which can be evaluated by spectrophotometry after dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) dilution of the crystals, as more viable cells exist.
Since vascular tonus response is due to smooth muscle cells, we placed confluent A7r5 cells in 96-well plates and exposed them to different metformin concentrations (0.0001 μmol/L, 0.001 μmol/L, 0.01 μmol/L, 0.1 μmol/L, 1 μmol/L, 10 μmol/L, 100 μmol/L, 1000 μmol/L, 10,000 μmol/L, 20,000 μmol/L and 100,000 μmol/L) for 24 h. After that period, 100 μL of MTT solution (0.5 mg/mL) was added to each well, and after 4 h (in a 5% CO2 atmosphere at 37 °C), this solution was removed. The culture was diluted in 100 μL of DMSO to solubilize the colored formazan crystals. The amount of formazan production was measured by absorbance at 570 nm with a photometer (EZ Read 400, Microplate Reader, Biochrom).
2.3. Rat Aorta Artery (RAA)
Six adult Wistar rats (3 to 5 months old) were used, after being hosted and acclimatized in cycles of light (12 h light/12 h darkness), with food and water ad libitum for at least 1 week before the experiment. The procedures with the animals were done according to the European guidelines for animal protection [29] and the “Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals” proclaimed by the USA National Institute of Health (NIH Publication No.85-23, revised 1996). First, the animals were euthanized with carbon monoxide. Afterward, to remove the aorta, a thoracotomy was performed in a Krebs-bicarbonate solution with a carbogen at 37 °C.
2.4. Human Umbilical Artery (HUA)
Eleven HUAs were provided from human umbilical cords, according to a procedure approved by the local ethics committee (CHUCB, No.33/2018, 18 July 2018, Centro Hospitalar Universitário da Cova da Beira E.P.E.). The samples were collected in the Obstetrics and Gynecology Service of CHUCB, resulting from eutocic deliveries at the end of pregnancy. The collection was carried out by the nurses of this service within intervals of no more than 30 min after the births. After obtaining 3 to 7 cm of the umbilical cord from the proximal half to the newborn, its integrity was preserved in a sterile saline solution (PSS) at 4 °C. The solution was enriched with antibiotics—penicillin (5 U/mL), streptomycin (5 µg/mL), and amphotericin B (12.5 ng/mL)—to avoid contamination and antiproteases—leupeptin (0.45 mg/L), benzamidine (26 mg/L), and trypsin inhibitor (10 mg/L)—to prevent cell degradation.
Healthy pregnant women gave written informed consent following the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki. All umbilical cords belonging to mothers who had pathologies during pregnancy were excluded. All donor mothers were supplemented with folic acid during the first trimester of gestation, and some of them also took iron supplementation throughout the pregnancy.
2.5. Arteries Isolation and Organ Bath
Both RAAs and HUAs were carefully isolated from rat tissue and umbilical cord, according to the methodology described by Mariana et al. (2017) [27] and Cairrão et al. (2008) [30] respectively. Briefly, the HUA isolation procedure was performed on ice, unlike the procedure with the rat aorta, which was always done with solutions heated to physiological temperature. Afterward, the isolated arteries were segmented into small vascular rings of 3 to 4 mm suitable for organ bath (LE01.004, Letica, Madrid, Spain) containing a 37 °C Krebs-bicarbonate solution continuously aerated with carbogen (95% O2 and 5% CO2). The vascular endothelium was mechanically removed by inserting a needle and a cotton thread in half of the samples in the arterial lumen. The solution for the HUA experiments was composed by NaCl 119 mmol/L, KCl 5.0 mmol/L, NaHCO3 25 mmol/L, KH2PO4 1.2 mmol/L, CaCl2 0.5 mmol/L, MgSO4 1.2 mmol/L, EDTA 0.03 mmol/L, and glucose 11 mmol/L (pH 7.4) [27,30]. For the RAA, the composition of the Krebs’ modified solution included an additional amount of CaCl2, making the final concentration 1.5 mmol/L.
2.6. Artery Tension Recordings
The artery rings were dipped in the organ bath and suspended between two parallel stainless-steel wires. The tension exerted by the rings was measured through isometric transducers (TRI201, Panlab SA, Spain), an amplifier (ML118/D Quad Bridge, ADInstruments, Oxford, UK), a PowerLab/4SP interface (ML750, ADInstruments, Oxford, UK), and a computer system with Chart5 PowerLab software (ADInstruments, Oxford, UK). The organ bath solution was changed every 15 min during the rest periods. This period of establishment of equilibrium (45 min) was performed to achieve a baseline tension of 0.025 N.
The first contraction of the aortic rings with noradrenaline was performed (NA 1 μmol/L) to check the viability of the arteries. The RAAs with contractions below 0.01 N were excluded according to the tensions used in previous works of Mariana et al., 2018 [27]. Then, the arteries were subjected to 1 μmol/L of acetylcholine (Ach) to check the functionality of the endothelium for relaxation. Rings with more than 90% of relaxation were considered intact-endothelium rings, whereas rings with less than 10% relaxation were deemed to be denuded-endothelium rings [31]. Afterward, the rings were washed for a minimum of 45 min before the next stimulus. In the rat aorta arteries, the contraction was induced with NA (1 μmol/L) to study if metformin has an indirect effect on the calcium channels [24] and KCl (60 mmol/L) to see if that effect is a direct one [32].
The first contraction of the HUA rings was done with serotonin (5-HT; 1 μmol/L) to check the viability of the arteries. The HUAs with contractions below 0.01 N were excluded according to the tensions used in previous works of Cairrao et al., 2008 [30]. These arteries were then contracted with different agents to evaluate possible mechanisms of actions of metformin in the vascular tonus: Hist (10 mmol/L), to study the involvement of metformin in the PLC/IP3 pathway (phospholipase C/inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate) [32,33]; KCl (60 mmol/L) to test the interaction with L-type voltage-dependent calcium channel (L-CDC) [32] and 5-HT (1 μmol/L) to study both phospholipase C pathway and adenylate cyclase/cAMP pathway [33].
After the contractions, the effect of metformin concentrations between 0.01 µmol/L and 2000 µmol/L was analyzed. In parallel, control measurements with solvent (water) were always performed. The concentrations used in this study were based on metformin concentrations in the umbilical cord plasma at the time of delivery [34].
2.7. Molecular Docking
In order to calculate the binding energy and to study the types of interaction of metformin with the androgen receptor (AR) and the estrogen alpha and beta receptor (ERα and ERβ), the Autodock4 program (http://autodock.scripps.edu/, accessed on 8 September 2021) was chosen. The 3D structure of the target proteins (sex hormone receptors) and the drug in a study (Metformin) were obtained from the Protein Data Bank (PDB): we downloaded the crystal structure of the AR (PDB ID: 2PKL) at 2.49 Å co-complexed with its natural ligand 5-alpha-dihydrotestosterone (DHT); the ERα (PBD ID: 1GWR) at 2.40 Å and the ERβ (PDB ID: 5TOA) at 2.10 Å co-complexed with their natural ligand estradiol (E2). The crystal structure of metformin (PDB ID: 5G5J) at 2.60 Å complexed to the structure of human CYP3A4 was also obtained from PDB.
The proteins and ligands downloaded were prepared for docking by removing water molecules, merging non-polar hydrogen atoms, and adding Gasteiger partial charges in the Autodock tools 1.5.6 and Chimera 1.15 software [35].
Autogrid 4 was used to perform the calculations of the grid map based on the coordinates of each crystal protein structure active center. The grid boxes were constructed with a grid spacing of 0.375 Å around the active site of AR, ERα, and ERβ with the dimension sizes of 20 × 26 × 10 Å (along with x, y, and z); 21 × 8 × 30 Å and 14 × 32 × 14 Å, respectively.
The validation of molecular docking was obtained if root mean square deviation (RMSD) values were less than 2 Å for the complex between the receptor and the natural ligand [36]. Then, the results were confirmed with AutoDock Vina. All docking calculations were performed with the Lamarckian genetic algorithm (from Autodock 4), and docking parameters were established by default. For each simulation, we obtained 10 hybrid runs and analyzed the dominating configuration of the binding complex—the one with the minimum binding energy (ΔG, expressed in kcal/mol). Chimera 1.15 was used to analyze the interactions (amino acid residues, hydrogen bonds, and hydrophobic environment) between metformin and the receptors. The atomic interactions were analyzed using PMV (v. 1.5.6) tool and the visualization of the main interactions was achieved with the Discovery Studio Visualizer software (BIOVIA, v. 21.1.0.20298) [37].
All files to open and visualize these in silico simulations can be found in Supplementary Materials and GitHub repository (https://github.com/ecairrao/Molecular-Docking-of-Metformin.git, accessed on 17 March 2022).
2.8. Drugs
All drugs and chemicals used were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich Química (Sintra, Portugal). Metformin was kindly offered by AcoFarma (metformin hydrochloride 95% (Lot: 171569, Barcelona, Spain). The stock solutions were dissolved in distilled and demineralized water. For each experiment, the different dilutions of metformin in the study were prepared daily.
2.9. Statistical Analysis
The SigmaStat Statistical Analysis System, version 3.5 (2005), was used to perform the statistical treatment. The results were expressed as mean ± standard deviation (SD) of 6 rats and 11 umbilical cords. These homoscedasticity and normality were evaluated by Levene’s mean test [38] and the Kolmogorov–Smirnov [39], respectively.
The Student’s t-test [40] was used for different metformin concentrations and to compare the presence of endothelium. This statistical test was used since the number of samples was less than 100, and for this reason it is considered the most robust test for analyzing statistical differences between more than two groups. The corresponding non-parametric method, Mann–Whitney rank sum test [41] were also used when the criteria of normality and/or homoscedasticity were not achieved. Probability levels below 5% were considered significant (p < 0.05).
The cell viability after the incubation with metformin was calculated through the absorbance’s values obtained at the end of the MTT assay, according to the following formula: cell viability (%) = x/y × 100%, where x and y were averages of the absorbances after incubation with metformin and averages of the absorbances of the control, respectively. The Student’s t-test was used to compare the cellular viability of the control and treated groups (p < 0.05).
3. Results
3.1. Assessment of Viability (MTT Assay)
To investigate the cellular viability of A7r5 cells under the effect of metformin, MTT assay was performed. As shown in Figure 1, the cellular viability decreased at the highest concentrations of metformin (10,000; 20,000; and 100,000 μmol/L) used.
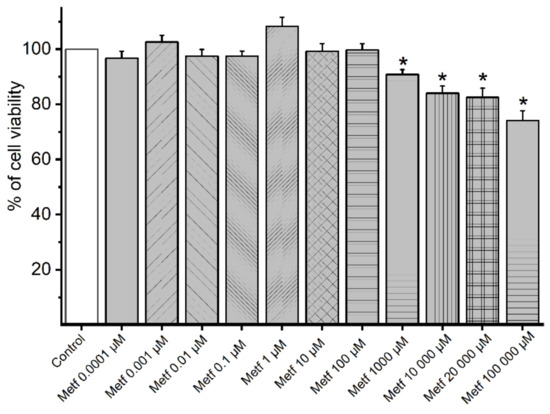
Figure 1.
MTT assay results. Percentage of cell viability of A7r5 cells (n = 12) under the effect of metformin (Metf). The bars represent the mean and the lines of the SD. * p < 0.05 versus control performed with the vehicle, Student’s t-test.
3.2. Rat Aorta
The metformin effect in the rat aorta artery is shown in Figure 2. The control group was subjected only to the solvent (water), and there was not a significant change in the contractile response (data not shown).
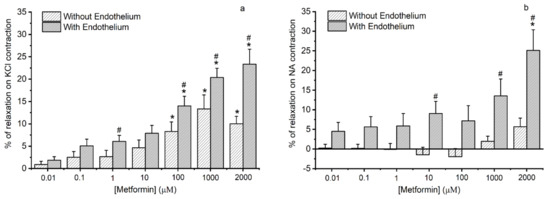
Figure 2.
Vasorelaxant effects of metformin on rat aorta artery. Vasorelaxant effects of metformin (0.01–2000 μmol/L) on with and without endothelium aorta rings contracted with (a) potassium chloride (KCl, 60 mmol/L) and (b) noradrenaline (NA, 1 μmol/L). Data are expressed as a percentage (%) of relaxation on contractile effects. The bars represent the mean values and the lines of the SD at least three different rats. * p < 0.05 versus different metformin concentrations, Student’s t-test and # p < 0.05 with versus without endothelium, Student’s t-test, and Mann–Whitney test.
After contraction with KCl 60 mmol/L (Figure 2a) and subsequent addition of cumulative concentrations of metformin (from 0.01 μmol/L to 2000 μmol/L), there was a significant relaxation in arteries without endothelium from the concentration greater than 100 μmol/L. Conversely, in the arteries with endothelium, metformin induces a greater relaxation effect. Moreover, at concentrations of 1, 100, 1000, and 2000 μmol/L, it was found that there is a significant difference in metformin response between arteries with and without endothelium.
In Figure 2b, we can observe the relationship between metformin concentration with the average percentages of relaxation in the rat aorta previously contacted with NA 1 μmol/L. In arteries without endothelium, metformin did not induce a significative contractility response. Concerning the arteries with endothelium, metformin in 2000 μmol/L induces a significant relaxation effect. Significant differences in the metformin responses between arteries with and without endothelium were verified for the concentrations of 10, 1000, and 2000 μmol/L of metformin.
3.3. Human Umbilical Artery
The metformin effect in the HUA is shown in Figure 3. The control group was subjected only to the solvent (water), and there was not a significant change in the contractile response (data not shown).
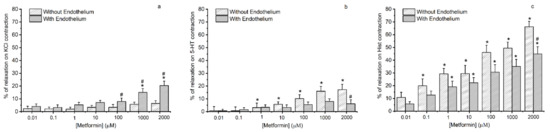
Figure 3.
Vasorelaxant effects of metformin on human umbilical artery. Vasorelaxant effects of metformin (0.01–2000 μmol/L) on with and without endothelium human umbilical artery rings contracted with (a) potassium chloride (KCl, 60 mmol/L), (b) serotonin (5-HT, 1 μmol/L), and (c) histamine (Hist, 10 μmol/L). Data are expressed as a percentage (%) of relaxation on contractile effects. The bars represent the mean values and the lines of the SD at least three different umbilical cords. * p < 0.05 versus different metformin concentrations, Student’s t-test and # p < 0.05 with versus without endothelium, Student’s t-test and Mann–Whitney test.
The arteries with endothelium contracted with KCl relaxed significantly in the highest concentrations of metformin tested, unlike the arteries without endothelium. There was a significant difference in the percentages of relaxation of the HUAs with and without endothelium at metformin 100, 1000, and 2000 μmol/L (Figure 3a).
The HUA without endothelium and contracted with 5-HT (Figure 3b) relaxed significantly in response to the highest five concentrations of metformin tested (1, 10, 100, 1000, and 2000 μmol/L). However, HUA with endothelium showed little response to metformin concentrations (p > 0.05). In addition, there was a statistically significant difference between the percentage of relaxation of the HUAs with and without endothelium at 2000 μmol/L.
Concerning the HUA with and without endothelium contracted by histamine (Figure 3c), metformin at a concentration of 100 μmol/L has become sufficient to produce significant relaxation. Additionally, we found a significant difference in the contractile response of the arteries in the presence and absence of endothelium at the highest concentration.
3.4. Molecular Docking Simulations
Rigid docking of metformin was performed with the active site of AR, Erα, and ERβ. The molecular docking results are present in Table 1, and the docking views are shown in Figure 4, Figure 5 and Figure 6.

Table 1.
Binding energies (kcal/mol) of ligands 5-alpha-dihydrotestosterone (DHT), estradiol (E2), and metformin (1–10) calculated from molecular docking studies.
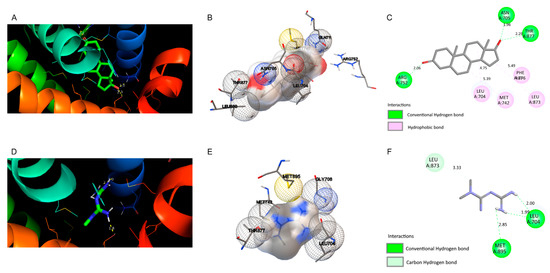
Figure 4.
Docking views of the complex between the ligands with androgen receptor (AR). (A–C) show the interaction between natural 5-alpha-dihydrotestosterone (DHT) and (D–F) metformin within the AR active center. (A,D) 3D representations of the interactions and preferred conformation, using PyMOL 2.3.2 software. (B,E) Interaction of the amino acid residues in the AR active center, using Autodock. (C,F) Atomic interactions, using Discovery Studio.
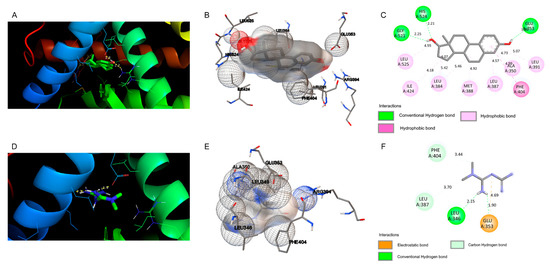
Figure 5.
Docking views of the complex between the ligands with estrogen receptor alpha (ERα). (A–C) Interaction between natural ligand E2 and (D–F) metformin within the ERα active center. (A,D) 3D representations of the interactions and preferred conformation, using PyMOL 2.3.2 software. (B,E) Interaction of the amino acid residues in the ERα active center, using Autodock. (C,F) Atomic interactions, using Discovery Studio.
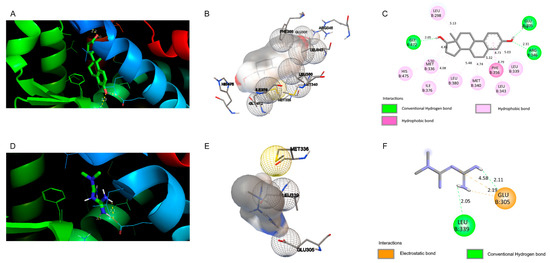
Figure 6.
Docking views of the complex between the ligands with estrogen receptor beta (ERβ). (A–C) Interaction between natural E2 and (D–F) metformin within the ERβ active center. (A,D) 3D representations of the interactions and preferred conformation, using PyMOL 2.3.2 software. (B,E) Interaction of the amino acid residues in the ERβ active center, using Autodock. (C,F) Atomic interactions, using Discovery Studio.
As shown in Figure 4, the molecular docking of natural ligand DHT with AR shows that this molecule involves hydrophobic interactions with amino acid residues Leu 704, Met 742, Leu 873, and Phe 876. DHT formed three H-bonds with residues Arg 752 at 2.06 Å, Asn 705 at 1.96 Å, and Thr 877 at 2.29 Å, and is in a hydrophobic environment. Compared with the control, the molecular docking of metformin with the AR does not show hydrophobic interactions. However, there are three H-bonds between metformin and the AR at Leu 704 (distances of 2.00 and 1.99 Å) and at Met 895 with distance of 2.85 Å. Moreover, a carbon hydrogen bond was observed for Leu 873 at 3.33 Å. The binding energies of DHT and metformin to the active center of AR were −11.28 and −2.7 kcal/mol, respectively.
As shown in Figure 5, the molecular docking of natural ligand E2 with ERα shows that this molecule involves hydrophobic interactions with amino acid residues Leu 525, Ile 424, Leu 384, Leu 387, Leu 391, Ala 350, Met 388, and Phe 404. E2 formed three H-bonds with residues Gly 521 at 2.25 Å, His 524 at 2.21 Å, and Glu 353 at 1.85 Å, and is in a hydrophobic environment. Compared to the control, the molecular docking of metformin with the ERα does not show hydrophobic interactions. However, there are two H-bonds between metformin and the ERα at Leu 346 (distance of 2.15 Å) and at Glu 353 with distance of 1.90 Å. Moreover, two carbon hydrogen bonds were observed for Phe 404 at 3.44 Å and Leu 387 at 3.70 Å. Furthermore, one electrostatic bond was observed for Glu 353 with distance of 4.69 Å. The binding energies of E2 and metformin to the active center of ERα were −10.24 and −4.34 kcal/mol, respectively.
As shown in Figure 6, the molecular docking of natural ligand E2 with ERβ shows that this molecule involves hydrophobic interactions with amino acid residues Leu 298, His 475, Met 336, ILe 376, Leu 380, Met 340, Leu 343, Leu 339, and Phe 356. E2 formed three H-bonds with residues Gly 472 at 2.05 Å, Glu 305 at 1.79 Å, and Arg 346 at 2.31 Å, and is in a hydrophobic environment. Compared to the control, the molecular docking of metformin with the ERβ do not show hydrophobic interactions. However, there are two H-bonds between metformin and the ERβ at Leu 339 (distance of 2.05 Å) and at Glu 305 with distance of 2.11 Å. Moreover, two electrostatic bonds were observed for Glu 305 with distances of 2.19 Å and 4.58 Å. The binding energies of E2 and metformin to the active center of ERβ were −10.24 and −3.55 kcal/mol, respectively.
4. Discussion
In the present study, we analyzed the mechanisms of the cardiovascular and endocrine effects of metformin through in vitro, ex vivo, and in silico studies. Firstly, we evaluated the effect of metformin in SMC viability with the MTT assay, and a decrease of 20% in the viability of this cells in the supra-therapeutic dosages (10,000; 20,000; and 100,000 μmol/L). Moreover, metformin is a hydrophilic cationic base at physiological pH that crosses the placenta. At the time of delivery, the umbilical cord concentrations are at least half of the maternal ones [2,34]. In one study, metformin blood levels found in the umbilical cord were higher than maternal levels (3.16 µmol/L vs. 1.50 µmol/L) [34]. In this sense, the maximum metformin concentration used in the organ bath was determined. Using this technique, the contractile response of RAA and HUA were also analyzed, and metformin causes vasorelaxation in these two different models and this effect in the vascular tonus was more prominent in 5-HT-contracted HUA and NA-contracted RAA. The in silico studies showed metformin’s ability to compete with sex hormones for the binding to their receptors, which may suggest that this oral antidiabetic may have an endocrine disruptive effect.
4.1. Effects of Metformin in Arterial Contractility
The vasorelaxation effect of metformin in RAA and HUA was observed for the first time. The contractility studies performed with the organ bath aimed to clarify the mechanism behind the cardiovascular effects of metformin. For this purpose, two different models (RAA and HUA) were chosen to study the mode of action of this oral antidiabetic. The RAA is considered a good model which enables the separate study of endothelial and smooth muscle pathways [42]. Regarding the HUA, this human vessel has recently been described as an excellent model for studying endocrine-disrupting chemicals (EDC) in the vascular system of pregnant women and fetuses [17]. Moreover, these two arteries were already used to study the cardiovascular effects of different EDCs [28,36,43,44].
Smooth muscle cells (SMC) are highly specialized in the contraction and regulation of vascular tonus, blood pressure, and circulation. In the blood vessels, they maintain the tonus in response to different stimuli—the autonomic nervous system, the endocrine system, and local mediators of paracrine action through chemical vasodilating and vasoconstricting agents such as serotonin (5-HT) and histamine (His), and physical stimuli [43,45]. Endothelial cells regulate vascular tone through production of vasoactive substances (such as NO, hydrogen sulfide (H2S) and carbon monoxide (CO), angiotensin II (AngII), endothelin 1 (ET-1), thromboxane A2 (TXA2), and thrombin) [10]. In this sense, endothelium can interact with SMC to produce a contractile or relaxant response: the increase in intracellular calcium in SMC induces vasoconstriction, while the increase in calcium in endothelial cells causes vasorelaxation of SMC [25], by increase the NO production. The production of basal NO levels by endothelial cells contributes to the regulation of vascular tone and the preservation of a non-thrombogenic behavior of the vasculature [11].
Regarding the experiment with rat aorta, with and without endothelium, the data show that metformin causes vasodilation via endothelium-dependent and endothelium-independent mechanisms in the contraction with KCL. The endothelium-dependent mechanism may be related to the activation of AMPK and eNOS [1] but also with the expression of vasoconstrictive molecules (namely Endothelin-1, Angiotensin II, and tissue factors) [10]. On the other hand, the endothelium-independent mechanisms may be related to a decrease in the intracellular calcium levels (by influx decrease and/or by the release of the intracellular reserves), inhibition of phospholipase C pathways, the opening of potassium channels, direct inhibition of soluble guanylate cyclase or the contractile apparatus, as has been observed in a similar study with sodium ferulate [44]. However, the contraction induced by KCl in rat aorta is mainly due to the depolarization of SMC and consequent calcium influx through the L-CDC [32].
The vasorelaxant metformin effect in the arteries previously contracted with NA was only observed in arteries with endothelium. It has been previously described that metformin was more powerful in relaxing SMC contractions induced by adrenergic vasoactive agents [46], but to our knowledge the importance of endothelial cells in this effect was never reported. This vasorelaxant effect induced by metformin may be due to the activation of the adrenergic aorta receptors present in the endothelium [25], which induced the production of NO or the activation of the soluble guanylate cyclase (sGC) and consequently led to the SMC relaxation. The activation of β2 and β3-adrenoceptors, which are present in endothelium, may cause stimulation of the eNOS activity, which may increase the release of endothelial NO. This mechanism may explain the vasorelaxant effect of metformin observed in RAA with intact endothelium [47,48].
In conclusion, these data suggest that the endothelium-independent mechanism of metformin seems to be related to calcium channel inhibition since it was only observed on the contractions triggered by KCl. The NA capacity to activate the L-CDC is lower and only an indirect consequence of the phospholipase C pathway [48]. Regarding the endothelium-dependent mechanism of metformin, and in accordance with Matsuda et al., the NO release is dependent from vasocontractile agents used [49].
Regarding the experiments with HUA, metformin caused significant vasorelaxation of the HUA contacted with KCl in the presence of endothelium. These results are according to Vitale et al., who demonstrated the improvement of metformin-induced vasodilatation by an endothelial-dependent mechanism in patients with metabolic syndrome [48]. It should be noted that the presence of an healthy endothelium is mandatory to keep normal vascular tonus responses, since the balance between secreted vasoconstrictors and vasodilators is essential [10,50,51]. Concerning the serotonin contraction in HUA, this contractile agent acts by activating the 5-HT2A and 5-HT1B/1D receptors, favoring the phospholipase C pathway and inhibiting the adenylyl cyclase/cAMP pathway, respectively [33]. Our results show that the five highest concentrations of metformin used were able to significantly relax HUA without endothelium, and the arteries with endothelium did not experience any effect. Concerning histamine, its contractile effect is mainly due to the activation of H1 receptor that is coupled to the Gq-protein, which activates the phospholipase C/IP3 cascade and increases intracellular calcium [33,52]. After histamine-triggered contraction, a relaxation was observed from metformin 100 μmol/L in all the arteries (with and without endothelium). This vasorelaxant effect is higher than that observed with serotonin, and this fact may be due to the differences in the number of receptors that trigger vasoconstriction and vasodilation. In this sense, the activation of 5-HT7 receptors, H2-receptors, and H3-receptors are linked to the vasoresponse in the HUA [28,30]. Moreover, Sharma et al. suggested that metformin induced the vasorelaxant effects due to inhibition of some contractile agents that increase intracellular calcium—such as the platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) pathway and angiotensin II pathway [53]. In this case, metformin could be interacting with serotonin or histamine receptors and, consequently, disfavoring the phospholipase C and activating the adenyl cyclase/cAMP pathway. As it has already been found, metformin increases active AMPK by increasing circulating cAMP [54], so the hypothesis that seems more plausible is that metformin has caused vasorelaxation in arteries without endothelium by interfering with the cAMP/adenyl cyclase pathway. The endothelium response in the histamine and serotonin contracted HUA are in accordance, and may suggest that endothelium can release some vasocontractile agents (endothelin [55], urotensin [56], adenosine [57], angiotensin II (ANG-II), thromboxane A2 (TxA2), prostacyclin H2 [12], and even some reactive oxygen species (ROS) [58]) which may inhibit the metformin vasorelaxant response. However, further investigation will be necessary to understand the molecular pathway involved in this response.
In summary, and comparing these two ex vivo models, different effects of metformin were obtained. A much more significant relaxation in the HUA (the maximum percentage was around 65%) than in the RAA (the maximum percentage was around 25%) was observed. However, in the potassium chloride contraction, which were tested in both models, the highest relaxation was observed in the RAA. The effect of the endothelium was similar in both vessels, thus—as expected—metformin in the presence of the endothelium induced a greater relaxing effect. In conclusion, these results demonstrate that RAA and HUA are good models for the study of the contractile response of metformin. Thus, we can infer that although the results are not the same, they are complementary and suggest the same vasorelaxant response to metformin. However, HUA presents a larger number of advantages over RAA; namely, HUA is a human tissue obtained from a safe, painless, and easy procedure for both mother and fetus; the collection of the tissue is very cheap because it does not require any special material and allows accurate results in the study of the arterial tonus, determining the adverse outcome pathways.
4.2. Interaction of Metformin with Steroid Hormone Receptors
According to the last scientific statement of the International Endocrine Society about EDCs, it is now accepted that an EDC does not have to be obesogenic or diabetogenic to predispose to cardiovascular disease (and they give the example of Bisphenol A) [23]. Therefore, despite the beneficial effects of metformin in diabetes, obesity, lipid metabolism, and even hypertension [44,58], some studies in fish have already reported that metformin can act as an EDC [17,18,19]. The hypothesis is that metformin alters the gene expression of ERs in a sex-dependent manner, probably via the hypothalamus–pituitary–gonadal axis, instead of direct binding to the receptors [17]. The results obtained by Ayas et al. (2020) and Mansfield (2003) are in agreement with this hypothesis, that show that metformin affects the estradiol production in the ovaries [59,60]. However, the in silico interaction between metformin and the steroid hormones has never been demonstrated. In this sense, our in silico data could give a new perspective about the receptor binding of metformin.
The endocrine disruptor effects are related to their interaction with different nuclear receptors (by mimicking or blocking natural ligands): ERα and ERβ, AR, the pregnane X receptor (PXR), the peroxisome proliferator activated receptors α and γ (PPARα, PPARγ), thyroid receptors α and β (TRα and TRβ), retinoid X receptors (RXRα, RXRβ and RXRγ), constitutive androstane receptor (CAR), and the estrogen related receptor γ (ERRγ) [61]. The ERα, Erβ, and AR were the chosen receptors for in silico simulations, which are the most important in endocrine disruptor effects.
Our results show that metformin interacts with AR (binding energy = −2.7 kcal/mol), ERα (binding energy = −4.34 kcal/mol), and ERβ (binding energy = −3.55 kcal/mol). However, the binding energies between metformin and the receptors are too high when compared to the binding energies for the natural ligands (−11.28, −10.24, and −10.24 kcal/mol). We cannot exclude that metformin binds to these receptors, because metformin is a polypharmacological agent with multiple weak binding partners [62]. Indeed, polypharmacology is a common phenomenon, when weak interactions with many targets contribute to the final effect of a specific drug [63], such as has already been demonstrated with metformin in cancer [61].
Considering in silico simulations for AR, our results show that DHT forms H-bond interactions with Thr877, Arg752, and Asn705. These results are in accordance with previous studies performed by Sakkiah et al. (2018). Moreover, the authors also show that DHT is an AR agonist that binds mainly through van der Waals interactions, and the remaining polar amino acids forms H-bonds [64]. The 3D structures of the complex AR-natural ligand reveal interactions with AR active sites through hydrophobic amino acids [64]. Our results show that DHT interact with AR active site through hydrophobic interactions, but the same results were not observed for metformin. Thus, these results suggest that metformin may have a weak agonist activity on AR, even if metformin forms H-bonds to AR with Leu 704 and at Met 895, and a weak interaction of a carbon hydrogen bond with Leu 873.
Considering in silico simulations for ERα, our results show that metformin forms two H-bond interactions with Leu 346 and Glu 353. Moreover, two carbon H-bonds for Phe 404 and Leu 387, and one electrostatic bond for Glu 353 were observed. The H-bond interactions with Glu 353 and Leu 387 in ERα are indicative of the “active” binding mode of EDCs to active this receptor [65]. Thus, these results show that metformin may act as EDC by an agonist of ERα. Moreover, compared to the control, the interactions with Glu 353 and Leu 387 were increased, with the interaction with Glu 353 being the strongest interaction (electrostatic bond). Concordantly, other authors have also shown that metformin heightened bonding preference toward Glu residues [65].
Considering in silico simulations for ERβ, our results show that metformin forms two H-bond interactions with Leu 339 and Glu 305. Moreover, two electrostatic bonds for Glu 305 were observed. Compared to the control, and similarly to the data obtained for ERα, the interactions with Glu 305 were strong (electrostatic bonds), which shows again the binding preference of metformin for Glu residues.
In summary, the conformational changes observed in the binding of metformin to steroid receptors may explain the metformin-induced contractility changes observed in this study [62]. Although metformin does not have a classic structure of EDC, nor does it have a very similar structure to DHT or E2 [22]. Its activity as a polypharmacological agent—acting weakly on multiple targets—induces a strong end effect, which may be the explanation for its adverse effects on human reproductive health. Moreover, the preferential binding of metformin to ERα points to an estrogenic activity, which agrees with the effects of other EDCs at the vascular level [66,67]. Regarding its androgenic activity, this effect seems to be weaker, explaining the dissonance of the data between the animal and human models. Concordantly, similar results were obtained for testosterone in rat aortic artery [68] and human umbilical artery [69], suggesting also a possible agonist effect of metformin.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, this study enabled an understanding of the potential mechanism of metformin cytotoxicity, by ex vivo assays and a cell viability analysis together with in silico studies. Our results showed that metformin induces a vasorelaxant effect in rat aorta and human models by an endothelium-dependent and -independent pathways. The in silico assays suggested that metformin has a potential to be an endocrine disruptor acting mainly in ERα. Future evidence will allow us to confirm the use of metformin in pregnant women without impairing the cardiovascular health of the future generation. The knowledge of metformin’s effect in the cardiovascular and endocrine systems will be decisive in approving metformin’s off-label uses and in determining whether it is more beneficial when compared with the classic therapeutics, mainly for women with gestational diabetes, where insulin remains the first line of treatment.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/biomedinformatics2020014/s1 and GitHub repository (https://github.com/ecairrao/Molecular-Docking-of-Metformin.git, accessed on 17 March 2022).
Author Contributions
M.B.: conceptualization; formal analysis; investigation; methodology; roles/writing—original draft; writing—review and editing. M.L.: investigation; methodology; roles/writing—original draft; writing—review and editing. E.C.: conceptualization; funding acquisition; investigation; methodology; project administration; supervision; visualization; writing—review and editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was financed by the Foundation for Science and Technology (FCT), through funds from the State Budget, and by the European Regional Development Fund (ERDF), under the Portugal 2020 Program, through the Regional Operational Program of the Center (Centro2020), through the project with the reference no. UIDB/00709/2020. M.L. acknowledges the Ph.D. fellowship from FCT (reference no. 2020.06616.BD). This work was also supported by the European Regional Development Fund through the “Programa Operacional Regional do Centro (Centro 2020)—Sistema de Apoio à Investigação Científica e Tecnológica—Programas Integrados de IC&DT” (Project Centro-01-0145-FEDER-000019—C4—Centro de Competências em Cloud Computing).
Institutional Review Board Statement
All experimental protocols and procedures with human samples described above were in accordance with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki and were approved by the Ethics Committees to the health of the Centro Hospitalar Universitário da Cova da Beira E.P.E. (CHUCB, No.33/2018, 18 July 2018). All experiments with rats conformed to the guidelines for animal care endorsed by the University of Beira Interior and to the Directive 2010/63/EU of the European Parliament on the protection of animals used for scientific purposes.
Informed Consent Statement
Healthy pregnant women gave written informed consent following the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki.
Data Availability Statement
Detailed information on Molecular Docking Simulations is given in the Supplementary Materials and GitHub repository (https://github.com/ecairrao/Molecular-Docking-of-Metformin.git, accessed on 17 March 2022).
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank all donors’ mothers who agreed to participate in this study and all the technical staff from Gynecology–Obstetrics Department staff of “Centro Hospitalar Universitário da Cova da Beira E.P.E.” (CHUCB, Covilhã, Portugal), mainly to all doctors, nurses, and health technicians for their disinterested collaboration. Moreover, the authors are grateful to the technical staff of “Centro de investigação de animais do CICS-UBI, Biotério” (Covilhã, Portugal) for their disinterested collaboration, particularly to Maria José Pinto, for the daily treatment and care of the animals.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Foretz, M.; Guigas, B.; Bertrand, L.; Pollak, M.; Viollet, B. Metformin: From mechanisms of action to therapies. Cell Metab. 2014, 20, 953–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Graham, G.G.; Punt, J.; Arora, M.; Day, R.O.; Doogue, M.P.; Duong, J.K.; Furlong, T.J.; Greenfield, J.R.; Greenup, L.C.; Kirkpatrick, C.M.; et al. Clinical pharmacokinetics of metformin. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2011, 50, 81–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plutzky, J.; Viberti, G.; Haffner, S. Atherosclerosis in type 2 diabetes mellitus and insulin resistance: Mechanistic links and therapeutic targets. J. Diabetes Complicat. 2002, 16, 401–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Xie, C.; Wu, H.; Jones, K.L.; Horowitz, M.; Rayner, C.K. Metformin reduces the rate of small intestinal glucose absorption in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2017, 19, 290–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viollet, B.; Guigas, B.; Sanz Garcia, N.; Leclerc, J.; Foretz, M.; Andreelli, F. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of metformin: An overview. Clin. Sci. 2012, 122, 253–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xu, T.; Brandmaier, S.; Messias, A.C.; Herder, C.; Draisma, H.H.M.; Demirkan, A.; Yu, Z.; Ried, J.S.; Haller, T.; Heier, M.; et al. Effects of metformin on metabolite profiles and LDL cholesterol in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2015, 38, 1858–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schneider, J.; Erren, T.; Zöfel, P.; Kaffarnik, H. Metformin-induced changes in serum lipids, lipoproteins, and apoproteins in non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Atherosclerosis 1990, 82, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howes, L.G.; Sundaresan, P.; Lykos, D. Cardiovascular effects of oral hypoglycaemic drugs. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 1996, 23, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maruhashi, T.; Higashi, Y. Pathophysiological Association between Diabetes Mellitus and Endothelial Dysfunction. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Ling, P.; Feng, X.; Luo, S.; Zheng, X.; Little, P.J.; Xu, S.; Weng, J. Metformin in cardiovascular diabetology: A focused review of its impact on endothelial function. Theranostics 2021, 11, 9376–9396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gimbrone, M.A.; García-Cardeña, G. Endothelial Cell Dysfunction and the Pathobiology of Atherosclerosis. Circ. Res. 2016, 118, 620–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Poniedziałek-Czajkowska, E.; Mierzyński, R.; Dłuski, D.; Leszczyńska-Gorzelak, B. Prevention of Hypertensive Disorders of Pregnancy—Is There a Place for Metformin? J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 2805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gui, J.; Liu, Q.; Feng, L. Metformin vs Insulin in the Management of Gestational Diabetes: A Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e64585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hyer, S.; Balani, J.; Shehata, H. Metformin in pregnancy: Mechanisms and clinical applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shpakov, A.O.; Sechenov, I.M. Improvement Effect of Metformin on Female and Male Reproduction in Endocrine Pathologies and Its Mechanisms. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalafat, E.R.K.A.N.; Sukur, Y.E.; Abdi, A.; Thilaganathan, B.; Khalil, A. Metformin for prevention of hypertensive disorders of pregnancy in women with gestational diabetes or obesity: Systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized trials. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. Off. J. Int. Soc. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2018, 52, 706–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lorigo, M.; Cairrao, E. Fetoplacental vasculature as a model to study human cardiovascular endocrine disruption. Mol. Asp. Med. 2021, 2021, 101054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.W.; Shin, Y.J.; Kim, H.; Kim, H.; Kim, J.; Min, S.A.; Kim, P.; Yu, S.D.; Park, K. Metformin-induced endocrine disruption and oxidative stress of Oryzias latipes on two-generational condition. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 367, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheurer, M.; Michel, A.; Brauch, H.J.; Ruck, W.; Sacher, F. Occurrence and fate of the antidiabetic drug metformin and its metabolite guanylurea in the environment and during drinking water treatment. Water Res. 2012, 46, 4790–4802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niemuth, N.J.; Klaper, R.D. Emerging wastewater contaminant metformin causes intersex and reduced fecundity in fish. Chemosphere 2015, 135, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tartarin, P.; Moison, D.; Guibert, E.; Dupont, J.; Habert, R.; Rouiller-Fabre, V.; Frydman, N.; Pozzi, S.; Frydman, R.; Lecureuil, C.; et al. Metformin exposure affects human and mouse fetal testicular cells. Hum. Reprod. 2012, 27, 3304–3314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tan, H.; Wang, X.; Hong, H.; Benfenati, E.; Giesy, J.P.; Gini, G.C.; Shi, W. Structures of Endocrine-Disrupting Chemicals Determine Binding to and Activation of the Estrogen Receptor α and Androgen Receptor. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 11424–11433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gore, A.C.; Chappell, V.A.; Fenton, S.E.; Flaws, J.A.; Nadal, A.; Prins, G.S.; Toppari, J.; Zoeller, R.T. EDC-2: The Endocrine Society’s Second Scientific Statement on Endocrine-Disrupting Chemicals. Endocr. Rev. 2015, 36, 1–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabir, E.R.; Rahman, M.S.; Rahman, I. A review on endocrine disruptors and their possible impacts on human health. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2015, 40, 241–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rameshrad, M.; Babaei, H.; Azarmi, Y.; Fouladi, R.F. Rat aorta as a pharmacological tool for in vitro and in vivo studies. Life Sci. 2016, 145, 190–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sturtzel, C. Endothelial cells. In Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2017; Volume 1003, pp. 71–91. [Google Scholar]
- Mariana, M.; Feiteiro, J.; Cairrao, E. Cardiovascular Response of Rat Aorta to Di-(2-ethylhexyl) Phthalate (DEHP) Exposure. Cardiovasc. Toxicol. 2018, 18, 356–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Nagarajan, A.; Uchil, P.D. Analysis of cell viability by the MTT assay. Cold Spring Harb. Protoc. 2018, 2018, 469–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Directive 2010/63/EU of the European Parliament and of the Council of 22 September 2010 on the Protection of Animals Used for Scientific Purposes. Off. J. Eur. Union 2010, 53, 33–79.
- Cairrão, E.; Álvarez, E.; Santos-Silva, A.J.; Verde, I. Potassium channels are involved in testosterone-induced vasorelaxation of human umbilical artery. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 2008, 376, 375–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pantan, R.; Onsa-Ard, A.; Tocharus, J.; Wonganan, O.; Suksamrarn, A.; Tocharus, C. Endothelium-independent vasorelaxation effects of 16-O-acetyldihydroisosteviol on isolated rat thoracic aorta. Life Sci. 2014, 116, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oloyo, A.K.; Sofola, O.A.; Nair, R.R.; Harikrishnan, V.S.; Fernandez, A.C. Testosterone relaxes abdominal aorta in male Sprague-Dawley rats by opening potassium (K+) channel and blockade of calcium (Ca2+) channel. Pathophysiology 2011, 18, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos-Silva, A.J.; Cairrão, E.; Marques, B.; Verde, I. Regulation of human umbilical artery contractility by different serotonin and histamine receptors. Reprod. Sci. 2009, 16, 1175–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eyal, S.; Easterling, T.R.; Carr, D.; Umans, J.G.; Miodovnik, M.; Hankins, G.D.V.; Clark, S.M.; Risler, L.; Wang, J.; Kelly, E.J.; et al. Pharmacokinetics of metformin during pregnancy. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2010, 38, 833–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lorigo, M.; Quintaneiro, C.; Breitenfeld, L.; Cairrao, E.; Altieri, F. UV-B Filter Octylmethoxycinnamate Alters the Vascular Contractility Patterns in Pregnant Women with Hypothyroidism. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazurek, A.H.; Szeleszczuk, Ł.; Simonson, T.; Pisklak, D.M. Application of Various Molecular Modelling Methods in the Study of Estrogens and Xenoestrogens. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruz-Vicente, P.; Gonçalves, A.M.; Ferreira, O.; Queiroz, J.A.; Silvestre, S.; Passarinha, L.A.; Gallardo, E. Discovery of Small Molecules as Membrane-Bound Catechol-O-methyltransferase Inhibitors with Interest in Parkinson’s Disease: Pharmacophore Modeling, Molecular Docking and In Vitro Experimental Validation Studies. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levene, H. Robust Tests for Equality of Variances; Contributions to Probability and Statistics: Essays in Honor of Harold Hotelling; Stanford University Press: Redwood City, CA, USA, 1960; Volume 1, pp. 278–292. [Google Scholar]
- Smirnov, N.V. Estimate of deviation between empirical distribution functions in two independent samples. Bull. Mosc. Univ. 1939, 2, 3–14. [Google Scholar]
- Student, W.S.G. The probable error of a mean. Biometrika 1908, 6, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, H.B.; Whitney, D.R. On a Test of Whether one of Two Random Variables is Stochastically Larger than the Other. Ann. Math. Stat. 1947, 18, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsang, H.G.; Rashdan, N.A.; Whitelaw, C.B.A.; Corcoran, B.M.; Summers, K.M.; MacRae, V.E. Large animal models of cardiovascular disease. Cell Biochem. Funct. 2016, 34, 113–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Owens, G.K.; Kumar, M.S.; Wamhoff, B.R. Molecular regulation of vascular smooth muscle cell differentiation in development and disease. Physiol. Rev. 2004, 84, 767–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.P.; Ye, Y.; Li, L.; Yang, Y.; Bin Qian, A.; Hu, S.J. Endothelium-independent vasorelaxant effect of sodium ferulate on rat thoracic aorta. Life Sci. 2009, 84, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorigo, M.; Mariana, M.; Feiteiro, J.; Cairrao, E. How is the human umbilical artery regulated? J. Obstet. Gynaecol. Res. 2018, 44, 1193–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.H.M.; Peuler, J.D. Acute vasorelaxant effects of metformin and attenuation by stimulation of sympathetic agonist release. Life Sci. 1998, 64, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conti, V.; Russomanno, G.; Corbi, G.; Izzo, V.; Vecchione, C.; Filippelli, A. Adrenoreceptors and nitric oxide in the cardiovascular system. Front. Physiol. 2013, 4, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Piascik, M.T.; Perez, D.M. Alpha1-adrenergic receptors: New insights and directions. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2001, 298, 403–410. [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda, K.; Sekiguchi, F.; Miyake, Y.; Inoue, S.; Shimamura, K.; Sunano, S. Influences of endothelium on the time course of noradrenaline-, 5-HT-, prostaglandin F(2a)- and high-K+-induced contractions in aortae of WKY and SHRSP. J. Smooth Muscle Res. 1998, 34, 207–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panfoli, I.; Puddu, A.; Bertola, N.; Ravera, S.; Maggi, D. The Hormetic Effect of Metformin: “Less Is More”? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morton, J.S.; Davidge, S.T. Arterial endothelium-derived hyperpolarization: Potential role in pregnancy adaptations and complications. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2013, 61, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hawley, J.; Rubin, P.C.; Hill, S.J. Distribution of receptors mediating phosphoinositide hydrolysis in cultured human umbilical artery smooth muscle and endothelial cells. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1995, 49, 1005–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.V.; Bhalla, R.C. Metformin attenuates agonist-stimulated calcium transients in vascular smooth muscle cells. Clin. Exp. Hypertens. 1995, 17, 913–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawley, S.A.; Ross, F.A.; Chevtzoff, C.; Green, K.A.; Evans, A.; Fogarty, S.; Towler, M.C.; Brown, L.J.; Ogunbayo, O.A.; Evans, A.M.; et al. Use of cells expressing γ subunit variants to identify diverse mechanisms of AMPK activation. Cell Metab. 2010, 11, 554–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Furchgott, R.; Vanhoutte, P. Endothelium-derived relaxing and contracting factors. FASEB J. 1989, 3, 2007–2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maguire, J.J.; Kuc, R.E.; Wiley, K.E.; Kleinz, M.J.; Davenport, A.P. Cellular distribution of immunoreactive urotensin-II in human tissues with evidence of increased expression in atherosclerosis and a greater constrictor response of small compared to large coronary arteries. Peptides 2004, 25, 1767–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, L.; Subiabre, M.; Araos, J.; Sáez, T.; Salsoso, R.; Pardo, F.; Leiva, A.; San Martín, R.; Toledo, F.; Sobrevia, L. Insulin/adenosine axis linked signalling. Mol. Asp. Med. 2017, 55, 45–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suresh, K.; Shimoda, L.A. Endothelial cell reactive oxygen species and Ca2+ signaling in pulmonary hypertension. In Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2017; Volume 967, pp. 299–314. [Google Scholar]
- Ayas, B.; Kırmızıkan, S.; Kocaman, A.; Avcı, B. The effects of metformin treatment on the ovaries and uterus of offspring. Gynecol. Endocrinol. 2020, 37, 624–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansfield, R.; Galea, R.; Brincat, M.; Hole, D.; Mason, H. Metformin has direct effects on human ovarian steroidogenesis. Fertil. Steril. 2003, 79, 956–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toporova, L.; Balaguer, P. Nuclear receptors are the major targets of endocrine disrupting chemicals. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2020, 502, 110665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, T.; Dider, S.; Han, W.; Xu, H.; Zhao, Z.; Xie, L. Toward Repurposing Metformin as a Precision Anti-Cancer Therapy Using Structural Systems Pharmacology. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 20441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, L.; Xie, L.; Kinnings, S.L.; Bourne, P.E. Novel computational approaches to polypharmacology as a means to define responses to individual drugs. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2012, 52, 361–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakkiah, S.; Wang, T.; Zou, W.; Wang, Y.; Pan, B.; Tong, W.; Hong, H. Endocrine Disrupting Chemicals Mediated through Binding Androgen Receptor Are Associated with Diabetes Mellitus. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 15, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tan, H.; Chen, Q.; Hong, H.; Benfenati, E.; Gini, G.C.; Zhang, X.; Yu, H.; Shi, W. Structures of Endocrine-Disrupting Chemicals Correlate with the Activation of 12 Classic Nuclear Receptors. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 16552–16562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorigo, M.; Quintaneiro, C.; Maia, C.J.; Breitenfeld, L.; Cairrao, E. UV-B filter octylmethoxycinnamate impaired the main vasorelaxant mechanism of human umbilical artery. Chemosphere 2021, 277, 130302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glória, S.; Marques, J.; Feiteiro, J.; Marcelino, H.; Verde, I.; Cairrão, E. Tributyltin role on the serotonin and histamine receptors in human umbilical artery. Toxicol. Vitr. 2018, 50, 210–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Álvarez, E.; Cairrao, E.; Morgado, M.; Morais, C.; Verde, I. Testosterone and cholesterol vasodilation of rat aorta involves L-type calcium channel inhibition. Adv. Pharmacol. Sci. 2010, 2010, 534184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cairrão, E.; Santos-Silva, A.J.; Verde, I. PKG is involved in testosterone-induced vasorelaxation of human umbilical artery. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2010, 640, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).