Impacts of Maternal Noise Exposure on Risk of Stillbirth and Oxidative Stress-Induced Neurobehavioral Changes in Offspring
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Maternal Noise Exposure Altered the Gestational Length in Offspring
2.2. Maternal Noise Exposure Decreased the Body Weight and Discrete Regions of the Brain in Offspring
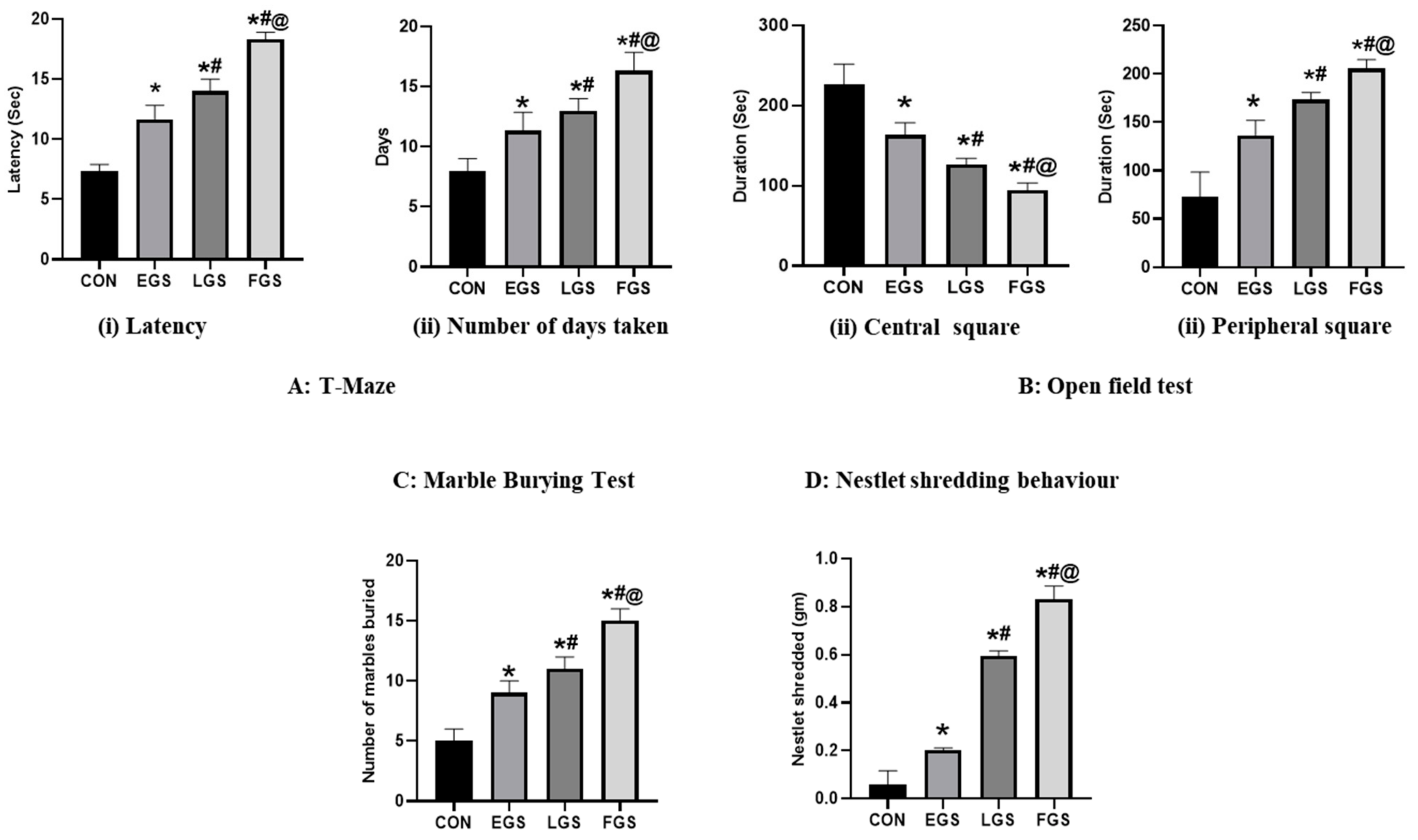
2.3. Maternal Noise Exposure Altered the Offspring’s Cognitive and Emotional Functioning
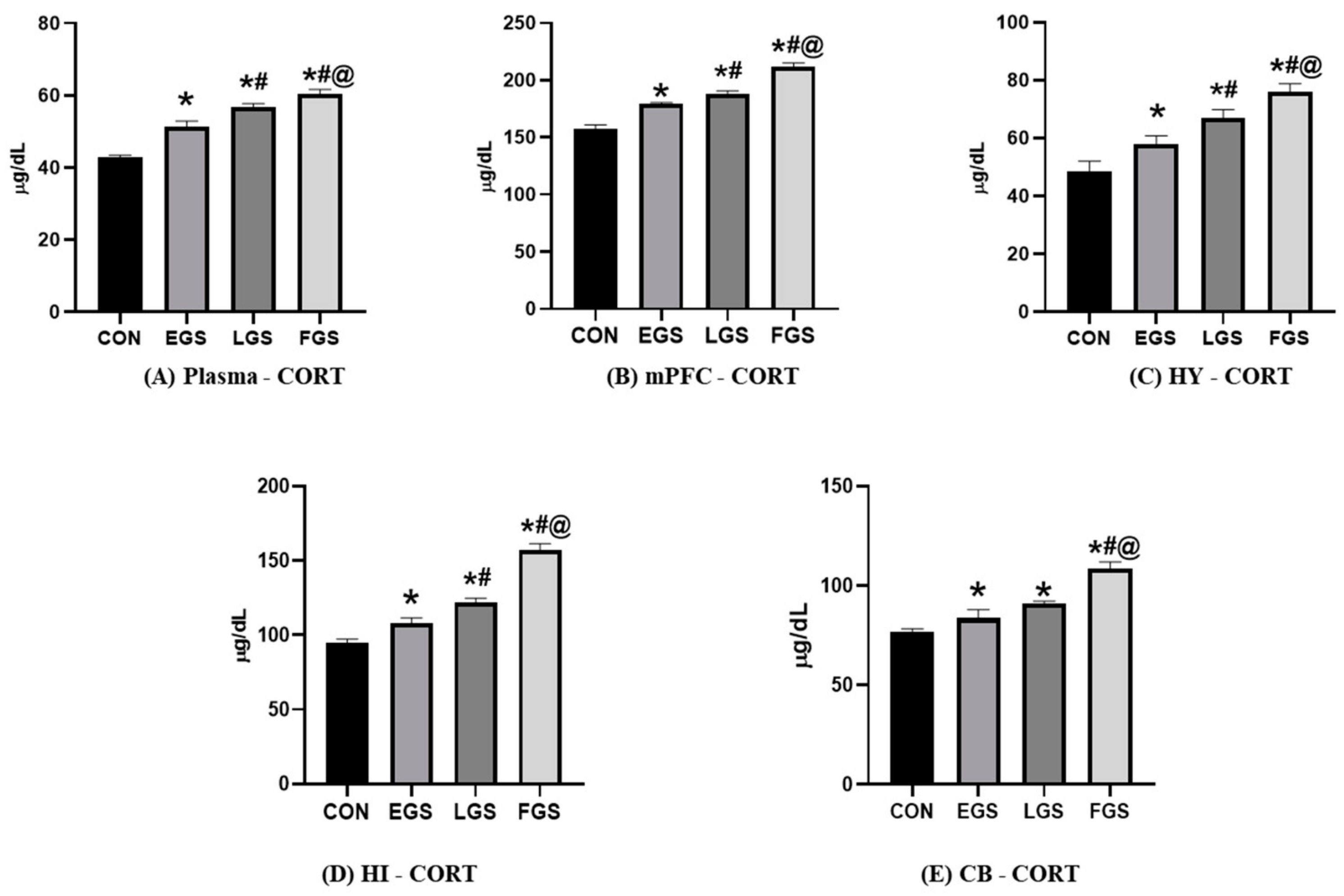
2.4. Maternal Noise Exposure Impairs Corticosterone and the Redox Balance in the Offspring’s Brain
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animal Maintenance
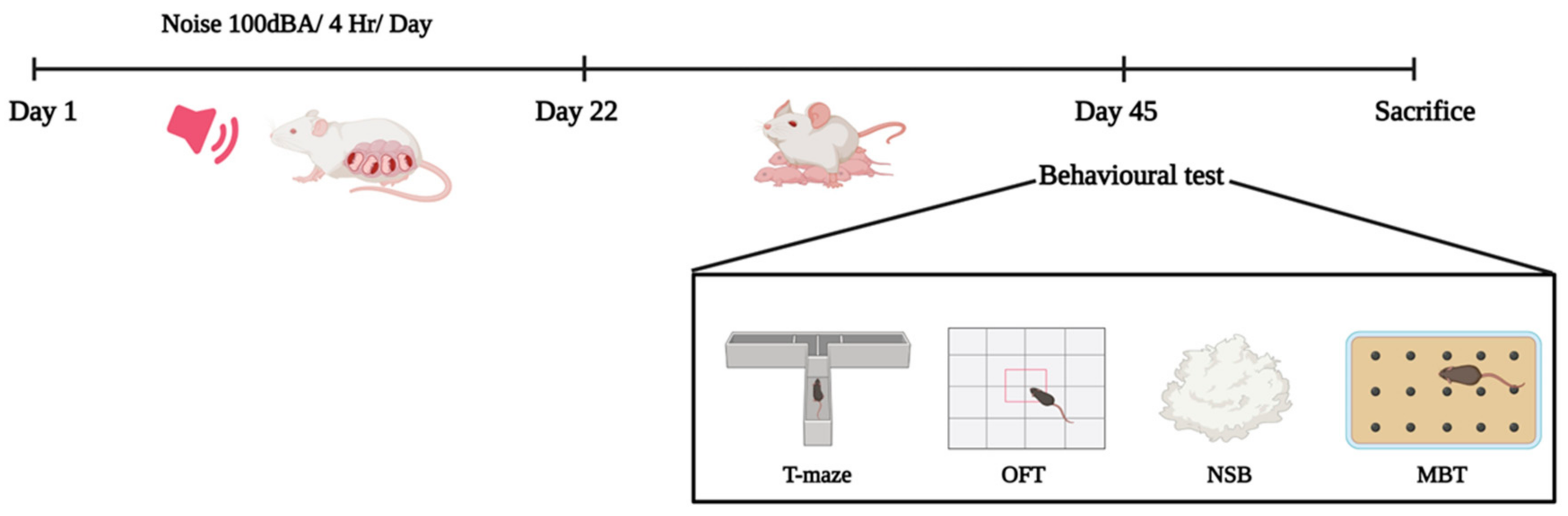
4.2. Experimental Design
4.3. Noise Exposure
4.4. Gestational Length
4.4.1. Stillbirth
4.4.2. Congenital Disabilities
4.4.3. Neonatal Mortality Rate
4.5. Measurement of Bodyweight
4.6. Behavioral Analysis
4.6.1. T-Maze
4.6.2. Open-Field Behavior
4.6.3. Marble-Burying Behavior Test
4.6.4. Nestlet-Shredding Behavior Test
4.7. Biochemical Assay
4.8. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jafari, Z.; Kolb, B.E.; Mohajerani, M.H. Noise exposure accelerates the risk of cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease: Adulthood, gestational, and prenatal mechanistic evidence from animal studies. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2020, 117, 110–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipschutz, R.; Kulesz, P.A.; Elgbeili, G.; Biekman, B.; Laplante, D.P.; Olson, D.M.; King, S.; Bick, J. Maternal mental health mediates the effect of prenatal stress on infant temperament: The Harvey Mom Study. Dev. Psychopathol. 2023, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergh, B.R.V.D.; Heuvel, M.I.V.D.; Lahti, M.; Braeken, M.; de Rooij, S.R.; Entringer, S.; Hoyer, D.; Roseboom, T.; Räikkönen, K.; King, S.; et al. Prenatal developmental origins of behavior and mental health: The influence of maternal stress in pregnancy. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2020, 117, 26–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, Q.; He, S.; Wu, K.; Ren, M.; Dong, H.; Di, J.; Yu, Z.; Huang, C. Ambient air pollution and gestational diabetes mellitus: A review of evidence from biological mechanisms to population epidemiology. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 719, 137349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ju, L.; Hua, L.; Xu, H.; Li, C.; Sun, S.; Zhang, Q.; Cao, J.; Ding, R. Maternal atmospheric particulate matter exposure and risk of adverse pregnancy outcomes: A meta-analysis of cohort studies. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 317, 120704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, T.H.; Chen, P.H.; Tung, T.H.; Hsu, J.; Hsu, T.Y.; Wan, G.H. Risks of preterm birth and low birth weight and maternal exposure to NO2/PM2. 5 acquired by dichotomous evaluation: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 30, 9331–9349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomson, E.M. Air Pollution, Stress, and Allostatic Load: Linking Systemic and Central Nervous System Impacts. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2019, 69, 597–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arjunan, A.; Rajan, R. Noise and brain. Physiol. Behav. 2020, 227, 113136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basner, M.; Babisch, W.; Davis, A.; Brink, M.; Clark, C.; Janssen, S.; Stansfeld, S. Auditory and non-auditory effects of noise on health. Lancet 2014, 383, 1325–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- I Stirrat, L.; Sengers, B.G.; E Norman, J.; Homer, N.Z.M.; Andrew, R.; Lewis, R.M.; Reynolds, R.M. Transfer and Metabolism of Cortisol by the Isolated Perfused Human Placenta. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 103, 640–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manikandan, S.; Devi, R.S. Antioxidant property of α-asarone against noise-stress-induced changes in different regions of rat brain. Pharmacol. Res. 2005, 52, 467–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samson, J.; Devi, R.S.; Ravindran, R.; Senthilvelan, M. Effect of noise stress on free radical scavenging enzymes in brain. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2005, 20, 142–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deacon, R.M.J.; Rawlins, J.N.P. T-maze alternation in the rodent. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seibenhener, M.L.; Wooten, M.C. Use of the open field maze to measure locomotor and anxiety-like behavior in mice. J. Vis. Exp. 2015, 96, e52434. [Google Scholar]
- Deacon, R.M.J. Digging and marble burying in mice: Simple methods for in vivo identification of biological impacts. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 122–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, S.L.; Welch, A.C.; Ho, E.V.; Bessa, J.M.; Portugal-Nunes, C.; Morais, M.; Young, J.W.; Knowles, J.A.; Dulawa, S.C. Btbd3 expression regulates compulsive-like and exploratory behaviors in mice. Transl. Psychiatry 2019, 9, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundareswaran, L.; Srinivasan, S.; Wankhar, W.; Sheeladevi, R. Effect of Scoparia dulcis on noise stress induced adaptive immunity and cytokine response in immunized Wistar rats. J. Ayurveda Integr. Med. 2017, 8, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gedzun, V.R.; Khukhareva, D.D.; Sarycheva, N.Y.; Kotova, M.M.; Kabiolsky, I.A.; Dubynin, V.A. Perinatal Stressors as a Factor in Impairments to Nervous System Development and Functions: Review of In Vivo Models. Neurosci. Behav. Physiol. 2023, 53, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarkar, T.; Patro, N.; Patro, I.K. Cumulative multiple early life hits- a potent threat leading to neurological disorders. Brain Res. Bull. 2019, 147, 58–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivakumaran, K.; Ritonja, J.A.; Waseem, H.; AlShenaibar, L.; Morgan, E.; Ahmadi, S.A.; Denning, A.; Michaud, D.; Morgan, R.L. Impact of Noise Exposure on Risk of Developing Stress-Related Obstetric Health Effects: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Noise Health 2022, 24, 137. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, C.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, J.; Qu, H.; Zhou, S.; Chen, M.; Xu, D.; Chen, L.; Wang, H. Paternal Nicotine/Ethanol/Caffeine Mixed Exposure Induces Offspring Rat Dysplasia and Its Potential “GC-IGF1” Programming Mechanism. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyadanu, S.D.; Tessema, G.A.; Mullins, B.; Kumi-Boateng, B.; Ofosu, A.A.; Pereira, G. Prenatal exposure to long-term heat stress and stillbirth in Ghana: A within-space time-series analysis. Environ. Res. 2023, 222, 115385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Flores, V.; Romero, R.; Furcron, A.-E.; Levenson, D.; Galaz, J.; Zou, C.; Hassan, S.S.; Hsu, C.-D.; Olson, D.; Metz, G.A.S.; et al. Prenatal Maternal Stress Causes Preterm Birth and Affects Neonatal Adaptive Immunity in Mice. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Xu, X.; Ren, Z.; Yang, J.; Kong, F. Maternal high-decibel acoustic exposure elevates prenatal stress, impairing postnatal hearing thresholds associated with decreasing ribbon synapses in young rats. Reprod. Toxicol. 2019, 89, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oinam, B.; Anand, V.; Kajal, R.K. A geospatial based hotspot and regression analysis of abortion and stillbirth prevalence in Manipur, India. Women Health 2021, 61, 599–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzhambov, A.M.; Dimitrova, D.D.; Dimitrakova, E.D. Noise Exposure During Pregnancy, Birth Outcomes And Fetal Development: Meta-Analyses Using Quality Effects Model. Folia Med. 2014, 56, 204–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gjerstad, J.K.; Lightman, S.L.; Spiga, F. Role of glucocorticoid negative feedback in the regulation of HPA axis pulsatility. Stress 2018, 21, 403–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nepomnaschy, P.A.; Sheiner, E.; Mastorakos, G.; Arck, P.C. Stress, immune function and reproduction. Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 2007, 1113, 350–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fe’Li, S.N.; Esmaielpour, M.R.M.; Hokmabadi, R.; Rezaei-Hachesu, V. Effect of occupational noise exposure on cortisol hormone level: A systematic review. Noise Vib. Worldw. 2022, 53, 579–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafari, Z.; Okuma, M.; Karem, H.; Mehla, J.; Kolb, B.E.; Mohajerani, M.H. Prenatal noise stress aggravates cognitive decline and the onset and progression of beta amyloid pathology in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol. Aging 2019, 77, 66–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanafi, S.; Zulkifli, I.; Ramiah, S.; Chung, E.; Kamil, R.; Awad, E. Prenatal auditory stimulation induces physiological stress responses in developing embryos and newly hatched chicks. Poult. Sci. 2023, 102, 102390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafari, Z.; Mehla, J.; Kolb, B.E.; Mohajerani, M.H. Prenatal noise stress impairs HPA axis and cognitive performance in mice. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 10560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barzegar, M.; Sajjadi, F.S.; Talaei, S.A.; Hamidi, G.; Salami, M. Prenatal exposure to noise stress: Anxiety, impaired spatial memory, and deteriorated hippocampal plasticity in postnatal life. Hippocampus 2015, 25, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, T.-W.; Shin, M.-S.; Park, J.-K.; Shin, M.-A.; Lee, H.-H.; Lee, S.-J. Treadmill exercise alleviates prenatal noise stress-induced impairment of spatial learning ability through enhancing hippocampal neurogenesis in rat pups. J. Exerc. Rehabil. 2013, 9, 451–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadizadeh, M.; Hamidi, G.; Salamim, M. Probiotic supplementation improves the cognitive function and the anxiety-like behaviors in the stressed rats. Iran. J. Basic Med. Sci. 2019, 22, 506–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badache, S.; Bouslama, S.; Brahmia, O.; Baïri, A.M.; Tahraoui, A.K.; Ladjama, A. Prenatal noise and restraint stress interact to alter exploratory behavior and balance in juvenile rats, and mixed stress reverses these effects. Stress 2017, 20, 320–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dowell, J.; Elser, B.A.; Schroeder, R.E.; Stevens, H.E. Cellular stress mechanisms of prenatal maternal stress: Heat shock factors and oxidative stress. Neurosci. Lett. 2019, 709, 134368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernhardt, L.K.; Madhyastha, S.; Bairy, L.; Kishore, A. Status of the brain antioxidant system at different growing periods after prenatal stress and N -acetyl cysteine administration. Folia Neuropathol. 2017, 1, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, H.; Phillips, T.J.; Sze, Y.; Alfieri, A.; Rogers, M.F.; Volpato, V.; Case, C.P.; Brunton, P.J. Maternal antioxidant treatment prevents the adverse effects of prenatal stress on the offspring’s brain and behavior. Neurobiol. Stress 2020, 13, 100281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juarez, P.; Cerdeño, V.M. Parvalbumin and parvalbumin chandelier interneurons in autism and other psychiatric disorders. Front. Psychiatry 2022, 13, 913550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teimouri, M.; Heidari, M.H.; Amini, A.; Sadeghi, Y.; Abdollahifar, M.-A.; Aliaghaei, A.; Khavanin, A.; Nadri, F.; Danyali, S.; Sanchooli, T. Neuroanatomical changes of the medial prefrontal cortex of male pups of Wistar rat after prenatal and postnatal noise stress. Acta Histochem. 2020, 122, 151589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sajjadi, F.; Aghighi, F.; Vahidinia, Z.; Azami-Tameh, A.; Salami, M.; Talaei, S. Prenatal urban traffic noise exposure impairs spatial learning and memory and reduces glucocorticoid receptor expression in the hippocampus of male rat offspring. Physiol. Int. 2020, 107, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soares-Cunha, C.; Coimbra, B.; Borges, S.; Domingues, A.V.; Silva, D.; Sousa, N.; Rodrigues, A.J. Mild Prenatal Stress Causes Emotional and Brain Structural Modifications in Rats of Both Sexes. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Discrete Regions | mPFC | HI | HY | CB |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CON | 0.225 ± 0.353 | 0.189 ± 0.007 | 0.091 ± 0.002 | 0.461 ± 0.038 |
| EGS | 0.189 ± 0.007 * | 0.179 ± 0.001 * | 0.090 ± 0.001 * | 0.439 ± 0.142 * |
| LGS | 0.183 ± 0.002 *# | 0.168 ± 0.002 *# | 0.092 ± 0.002 *# | 0.436 ± 0.013 *# |
| FGS | 0.173 ± 0.002 *#@ | 0.159 ± 0.002 *#@ | 0.091 ± 0.012 *#@ | 0.439 ± 0.023 *#@ |
| A: LPO | ||||
| Discrete regions | mPFC | HI | HY | CB |
| CON | 6.05 ± 0.353 | 5.90 ± 0.785 | 5.84 ± 0.552 | 5.16 ± 0.101 |
| EGS | 7.40 ± 0.141 * | 7.34 ± 0.152 * | 7.12 ± 0.314 * | 6.70 ± 0.364 * |
| LGS | 7.62 ± 0.247 *# | 7.99 ± 0.135 *# | 8.34 ± 0.146 *# | 7.27 ± 0.254 *# |
| FGS | 8.78 ± 0.632 *#@ | 9.31 ± 0.300 *#@ | 10.4 ± 0.707 *#@ | 9.49 ± 0.236 *#@ |
| B: SOD | ||||
| Discrete regions | mPFC | HI | HY | CB |
| CON | 20.05 ± 0.098 | 17.56 ± 0.470 | 24.92 ± 0.671 | 19.83 ± 0.651 |
| EGS | 19.62 ± 0.558 * | 16.11 ± 0.141 * | 24.60 ± 0.527 | 19.18 ± 0.219 * |
| LGS | 18.78 ± 0.629 *# | 15.46 ± 0.247 *# | 24.27 ± 2.870 | 18.87 ± 0.749 *# |
| FGS | 16.76 ± 0.664 *#@ | 14.51 ± 0.579 *#@ | 23.67 ± 3.152 *#@ | 19.56 ± 0.374 *#@ |
| C: Catalase | ||||
| Discrete regions | mPFC | HI | HY | CB |
| CON | 1.452 ± 0.025 | 0.941 ± 0.064 | 0.839 ± 0.010 | 1.492 ± 0.028 |
| EGS | 1.358 ± 0.043 * | 0.840 ± 0.019 * | 0.830 ± 0.017 * | 1.450 ± 0.025 * |
| LGS | 1.169 ± 0.057 *# | 0.752 ± 0.059 *# | 0.810 ± 0.018 *# | 1.451 ± 0.042 *# |
| FGS | 0.896 ± 0.062 *#@ | 0.661 ± 0.002 *#@ | 0.834 ± 0.024 *#@ | 1.465 ± 0.021 *#@ |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Arjunan, A.; Sah, D.K.; Rajan, R. Impacts of Maternal Noise Exposure on Risk of Stillbirth and Oxidative Stress-Induced Neurobehavioral Changes in Offspring. Stresses 2023, 3, 529-540. https://doi.org/10.3390/stresses3030037
Arjunan A, Sah DK, Rajan R. Impacts of Maternal Noise Exposure on Risk of Stillbirth and Oxidative Stress-Induced Neurobehavioral Changes in Offspring. Stresses. 2023; 3(3):529-540. https://doi.org/10.3390/stresses3030037
Chicago/Turabian StyleArjunan, Archana, Dhiraj Kumar Sah, and Ravindran Rajan. 2023. "Impacts of Maternal Noise Exposure on Risk of Stillbirth and Oxidative Stress-Induced Neurobehavioral Changes in Offspring" Stresses 3, no. 3: 529-540. https://doi.org/10.3390/stresses3030037
APA StyleArjunan, A., Sah, D. K., & Rajan, R. (2023). Impacts of Maternal Noise Exposure on Risk of Stillbirth and Oxidative Stress-Induced Neurobehavioral Changes in Offspring. Stresses, 3(3), 529-540. https://doi.org/10.3390/stresses3030037








