Impact of Walking Path Length on Gait Parameters During the 2-Minute Walk Test in Healthy Young Adults
Abstract
1. Introduction
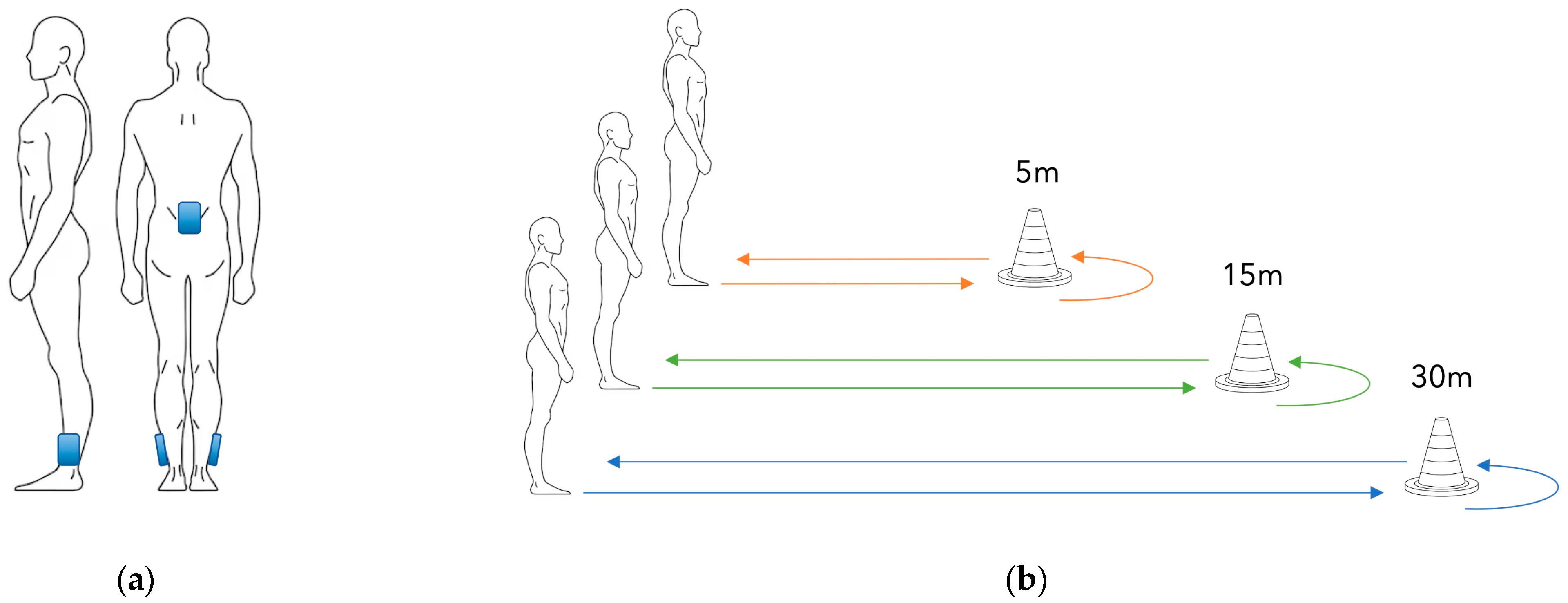
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 6MWT | 6-Minute Walk Test |
| 2MWT | 2-Minute Walk Test |
| IMUs | Inertial Measurement Units |
| WD | Walking Distance |
| WS | Walking Speed |
| SD | Standard Deviation |
References
- Hollman, J.H.; McDade, E.M.; Petersen, R.C. Normative spatiotemporal gait parameters in older adults. Gait Posture 2011, 34, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Thoracic Society. ATS Statement. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2002, 166, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butland, R.J.A.; Pang, J.; Gross, E.R.; Woodcock, A.A.; Geddes, D.M. Two-, six-, and 12-minute walking tests in respiratory disease. Br. Med. J. (Clin. Res. Ed.) 1982, 284, 1607–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wafi, A.; Ribeiro, L.; Kolli, V.; Azhar, B.; Budge, J.; Loftus, I.M.; Holt, P.J. Predicting Prosthetic Mobility at Discharge from Rehabilitation Following Major Amputation in Vascular Surgery. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2023, 66, 832–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, C.K.; Chihuri, S.T.; Santo, E.G.; White, R.A. Relevance of medical comorbidities for functional mobility in people with limb loss: Retrospective explanatory models for a clinical walking measure and a patient-reported functional outcome. Physiotherapy 2020, 107, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frlan-Vrgoc, L.; Vrbanić, T.S.L.; Kraguljac, D.; Kovacević, M. Functional outcome assessment of lower limb amputees and prosthetic users with a 2-minute walk test. Coll. Antropol. 2011, 35, 1215–1218. [Google Scholar]
- O’Keefe, J.A.; Guan, J.; Robertson, E.; Biskis, A.; Joyce, J.; Ouyang, B.; Liu, Y.; Carnes, D.; Purcell, N.; Berry-Kravis, E.; et al. The Effects of Dual Task Cognitive Interference and Fast-Paced Walking on Gait, Turns, and Falls in Men and Women with FXTAS. Cerebellum 2021, 20, 212–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, W.L.S.; Pin, T.W. Reliability, validity and minimal detectable change of 2-min walk test and 10-m walk test in frail older adults receiving day care and residential care. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2020, 32, 597–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kushioka, J.; Sun, R.; Zhang, W.; Muaremi, A.; Leutheuser, H.; Odonkor, C.A.; Smuck, M. Gait Variability to Phenotype Common Orthopedic Gait Impairments Using Wearable Sensors. Sensors 2022, 22, 9301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.Y.; Wang, Y.L.; Cheng, F.Y.; Chao, Y.H.; Chen, C.L.; Yang, Y.R. Effects of combined exercise on gait variability in community-dwelling older adults. AGE 2015, 37, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theunissen, K.; Plasqui, G.; Boonen, A.; Timmermans, A.; Meyns, P.; Feys, P.; Meijer, K. The increased perceived exertion during the six minute walking test is not accompanied by changes in cost of walking, gait characteristics or muscle fatigue in persons with multiple sclerosis. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2023, 70, 104479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grimpampi, E.; Oesen, S.; Halper, B.; Hofmann, M.; Wessner, B.; Mazzà, C. Reliability of gait variability assessment in older individuals during a six-minute walk test. J. Biomech. 2015, 48, 4185–4189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Troosters, T.; Gosselink, R.; Decramer, M. Six minute walking distance in healthy elderly subjects. Eur. Respir. J. 1999, 14, 270–274. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10515400/ (accessed on 13 December 2023). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipkin, D.P.; Scriven, A.J.; Crake, T.; Poole-Wilson, P.A. Six minute walking test for assessing exercise capacity in chronic heart failure. Br. Med. J. (Clin. Res. Ed.) 1986, 292, 653–655. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/3081210/ (accessed on 13 December 2023). [CrossRef]
- Barnett, C.T.; Bisele, M.; Jackman, J.S.; Rayne, T.; Moore, N.C.; Spalding, J.L.; Richardson, P.; Plummer, B. Manipulating walking path configuration influences gait variability and six-minute walk test outcomes in older and younger adults. Gait Posture 2016, 44, 221–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaunaurd, I.; Kristal, A.; Horn, A.; Krueger, C.; Muro, O.; Rosenberg, A.; Gruben, K.; Kirk-Sanchez, N.; Pasquina, P.; Gailey, R. The Utility of the 2-Minute Walk Test as a Measure of Mobility in People with Lower Limb Amputation. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2020, 101, 1183–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pin, T.W. Psychometric Properties of 2-Minute Walk Test: A Systematic Review. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2014, 95, 1759–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shank, C.; Kristal, A.; Van Veld, R.; Applegate, B.; Gaunaurd, I.; Gailey, R. Variations in 2-Minute Walk Test outcomes for people with lower limb amputation in the outpatient clinic and research settings. Prosthet. Orthot. Int. 2022, 46, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saggio, G.; Tombolini, F.; Ruggiero, A. Technology-Based Complex Motor Tasks Assessment: A 6-DOF Inertial-Based System Versus a Gold-Standard Optoelectronic-Based One. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 21, 1616–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricci, M.; Terribili, M.; Giannini, F.; Errico, V.; Pallotti, A.; Galasso, C.; Tomasello, L.; Sias, S.; Saggio, G. Wearable-based electronics to objectively support diagnosis of motor impairments in school-aged children. J. Biomech. 2019, 83, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middleton, A.; Fritz, S.L.; Lusardi, M. Walking Speed: The Functional Vital Sign. J. Aging Phys. Act. 2015, 23, 314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bohannon, R.W.; Glenney, S.S. Minimal clinically important difference for change in comfortable gait speed of adults with pathology: A systematic review. J. Eval. Clin. Pract. 2014, 20, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnston, K.N.; Potter, A.J.; Phillips, A.C. Minimal important difference and responsiveness of 2-minute walk test performance in people with COPD undergoing pulmonary rehabilitation. Int. J. Chronic Obstr. Pulm. Dis. 2017, 12, 2849–2857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowman, T.; Mestanza Mattos, F.G.; Allera Longo, C.; Bocini, S.; Gennuso, M.; Marazzini, F.; Materazzi, F.G.; Pelosin, E.; Putzolu, M.; Salvalaggio, S.; et al. The minimally clinically important difference in the 2-minute walk test for people in the subacute phase after a stroke. Top. Stroke Rehabil. 2025, 32, 553–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.J.J.; Lemaire, E.D. Temporal-spatial gait parameter models of very slow walking. Gait Posture 2018, 61, 125–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziegler, J.; Gattringer, H.; Müller, A. On the relation between gait speed and gait cycle duration for walking on even ground. J. Biomech. 2024, 164, 111976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Retory, Y.; David, P.; Niedzialkowski, P.; de Picciotto, C.; Bonay, M.; Petitjean, M. Gait Monitoring and Walk Distance Estimation with an Accelerometer During 6-Minute Walk Test. Respir. Care 2019, 64, 923–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| 5 m | 15 m | 30 m | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | ±SD | Mean | ±SD | Mean | ±SD | p-Value | Effect Size | |
| Walking Distance (m) | 123.69 a,b | 14.36 | 161.77 a,c | 14.67 | 179.37 b,c | 19.42 | <0.001 | ηρ2 = 0.952 |
| Walking Speed (m/s) | 1.62 a,b | 0.17 | 1.69 a,c | 0.16 | 1.76 b,c | 0.16 | <0.001 | W = 0.473 |
| Stride Duration (s) | 1.05 a,b | 0.07 | 1.01 | 0.06 | 1.00 | 0.06 | <0.001 | ηρ2 = 0.625 |
| Stance Time (s) | 0.61 | 0.06 | 0.60 | 0.05 | 0.59 | 0.05 | 0.01 | ηρ2 = 0.268 |
| Swing Time (s) | 0.43 a,b | 0.03 | 0.41 | 0.02 | 0.41 | 0.02 | <0.001 | ηρ2 = 0.561 |
| Single Support Time (s) | 0.42 a,b | 0.02 | 0.41 | 0.02 | 0.41 | 0.02 | <0.001 | ηρ2 = 0.508 |
| Double Support Time (s) | 0.19 | 0.05 | 0.19 | 0.04 | 0.18 | 0.04 | 0.265 | ηρ2 = 0.067 |
| Cadence (steps/min) | 115.48 a,b | 7.30 | 119.05 | 6.66 | 119.97 | 6.76 | <0.001 | ηρ2 = 0.658 |
| Underestimation Level of: | Difference (%) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 m Compared to 15 m | 5 m Compared to 30 m | 15 m Compared to 30 m | 5 m Compared to 15 m | 5 m Compared to 30 m | 15 m Compared to 30 m | |
| Walking Distance (m) | −38.07 | −55.68 | −17.61 | −23.5% | −31.0% | −9.8% |
| Walking Speed (m/s) | −0.06 | −0.14 | −0.07 | −3.7% | −7.8% | −4.2% |
| Stride Duration (s) | 0.03 | 0.04 | 0.01 | 3.3% | 4.1% | 0.8% |
| Stance Time (s) | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 2.1% | 3.1% | 1.0% |
| Swing Time (s) | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.00 | 4.9% | 5.5% | 0.5% |
| Single Support Time (s) | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 2.3% | 2.8% | 0.4% |
| Double Support Time (s) | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 1.6% | 3.9% | 2.3% |
| Cadence (steps/min) | −3.57 | −4.49 | −0.92 | −3.0% | −3.7% | −0.8% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lo Zoppo, C.; Belluscio, V.; Vannozzi, G. Impact of Walking Path Length on Gait Parameters During the 2-Minute Walk Test in Healthy Young Adults. Biomechanics 2025, 5, 82. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomechanics5040082
Lo Zoppo C, Belluscio V, Vannozzi G. Impact of Walking Path Length on Gait Parameters During the 2-Minute Walk Test in Healthy Young Adults. Biomechanics. 2025; 5(4):82. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomechanics5040082
Chicago/Turabian StyleLo Zoppo, Cecilia, Valeria Belluscio, and Giuseppe Vannozzi. 2025. "Impact of Walking Path Length on Gait Parameters During the 2-Minute Walk Test in Healthy Young Adults" Biomechanics 5, no. 4: 82. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomechanics5040082
APA StyleLo Zoppo, C., Belluscio, V., & Vannozzi, G. (2025). Impact of Walking Path Length on Gait Parameters During the 2-Minute Walk Test in Healthy Young Adults. Biomechanics, 5(4), 82. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomechanics5040082







