Abstract
Brazilian flora are highly diverse and have great potential for research into new medicines of plant origin. Platonia insignis Mart. is a fruit tree from the Amazon region with several potential pharmacological applications already demonstrated. The present study aimed to investigate the protective effect of a mixture of the biflavones volkensiflavone and moreloflavone obtained from P. insignis flowers against the lethality induced by ethidium bromide in efflux pump overproducer strains of Staphylococcus aureus. Microdilution tests were performed to determine the minimum inhibitory concentration of ethidium bromide in the absence or presence of biflavones. The addition of biflavones to the growth medium increased the minimum inhibitory concentration of ethidium bromide against all strains tested, indicating that biflavones protected the bacterial cells against cell damage induced by this biocide agent. Comparative analysis of the infrared absorption spectra of each isolated compound, as well as of the associated compounds, demonstrated the complexation reaction, indicating that there was a preferential interaction between the H2N- groups of primary amines of ethidium bromide with the carbonyls of biflavones that formed imines -C=NH. Such complexation could reduce the amount of free ethidium bromide molecules available for DNA intercalation, resulting in the observed protective effect. These results suggest a possible technological application of the biflavones from P. insignis as protective agents against cell damage induced by ethidium bromide.
1. Introduction
Ethidium bromide (EtBr) is a tricyclic aromatic compound of the phenanthridine class showing aniline groups on either side of a pyridine, represented by the formula C21H2OBrN3. It is also a strong DNA intercalating agent [1]. Intercalation of EtBr in the DNA double helix results in increased fluorescence emission, and for this reason, this compound is widely used as an organic fluorescent dye for visualizing DNA on agarose gel [2,3]. These changes in the spectrum contradict what was expected, which was that its fluorescence would be partially reduced by interactions with the solvent’s molecules when in solution [4]. Studies indicate that binding between EtBr and DNA occurs mainly through intercalation between base pairs in DNA, but electrostatic binding can also occur [5].
Despite its wide use, this molecule has high toxicity, mutagenic activity and ability to inhibit RNA synthesis [6]. Other studies report that EtBr is capable of inhibiting DNA synthesis as well as causing selective inhibition of mitochondrial DNA and kinetoplastic DNA. EtBr is able to inhibit the formation of mitochondrial cytochrome oxidase and to selectively inhibit specific phases of RNA synthesis or processing [7]. It is also an inhibitor of DNA polymerase enzyme and DNA-dependent RNA polymerase enzyme by binding to template DNA [2]. Furthermore, it inhibits cell growth in tissue cultures, induces mutation by altering the gene reading frame and causes the development of chromosomal abnormalities [6].
Species of Brazilian flora are widely evaluated in relation to the pharmacological effects of their plant extracts and essential oils as well as their isolated phytoconstituents, aiming at the development of new drugs. Platonia insignis Mart. (Clusiaceae) is a fruit and lumber plant from the Amazon rainforest, popularly known as bacurizeiro [8]. The distribution of this species was recorded in the states of Amazonas, Amapá, Pará, Maranhão, Piauí, Tocantins and Mato Grosso [9,10]. In Piauí, its occurrence was reported in a wide area of cerrado in the north-central region of the state [11].
Different biological activities were reported for the species P. insignis, such as leishmanicidal activity against Leishmania amazonensis [12], a hypotensive effect on the cardiovascular system of rats [13] and antioxidant activity [14]. It also has anticonvulsant, antidepressant, stimulatory and protective effects on the central nervous system [15,16] as well as cytotoxic activity [17].
In a previous study performed by our research group, we isolated and identified a mixture of biflavonoids (volkensiflavone and moreloflavone) from the hydroethanolic extract of the P. insignis flowers, which inhibited the efflux pumps NorA, QacA/B, TetK and MsrA and thereby enhanced the activity of norfloxacin, tetracycline and erythromycin against Staphylococcus aureus [18]. This mixture of biflavonoids also demonstrated antileishmanial activity and increased the lysosomal activity of macrophages against internalized amastigote forms of Leishmania amazonensis, suggesting a possible modulating effect [19]. Several biological activities are attributed to volkensiflavone, such as analgesic, antibacterial and antitumor activities [20]. Moreloflavone showed anti-viral [21], antioxidant [22], anti-inflammatory [23] and antiparasitic activities [24].
Another study verified that a higher concentration of EtBr was needed to inhibit S. aureus strains when quercetin was added in the growth medium, suggesting a protector effect caused by this flavonoid against cell damage induced by EtBr [25]. Hesperetin and naringenin were able to displace EtBr complexed to calf-thymus DNA [26], indicating that the molecular interactions of these flavonoids with EtBr could result in DNA protection. However, there are no data available in the literature demonstrating that biflavonoids volkensiflavone and moreloflavone could protect prokaryotic cells against cell damage induced by EtBr. In the present study, we investigated the protective effect of the mixture of biflavones (BFs) volkensiflavone and moreloflavone (Figure 1) obtained from the P. insignis flowers against the lethality induced by ethidium bromide in efflux pump-producing Staphylococcus aureus strains.
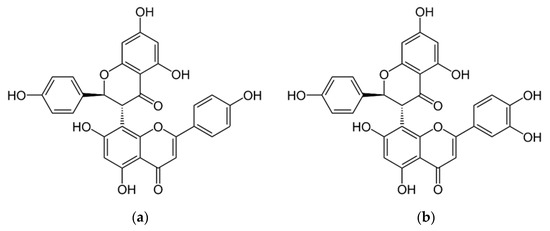
Figure 1.
Chemical structure of the biflavones mixture obtained from the hydroethanolic extract of Platonia insignis flowers: (a) volkensiflavone and (b) moreloflavone.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strains and Chemical Compounds
Assays to evaluate the protective effect against the antibacterial activity of EtBr were carried out with the following strains of Staphylococcus aureus: SA1199B (overproducer of the NorA efflux pump), strain SA1199 (parental wild-type producer of NorA at basal levels), IS-58 (producer of the TetK efflux pump), K2068 (producer of the MepA efflux pump), K4100 (producer of the QacC efflux pump) and RN4220 (producer of the MsrA efflux pump). These strains were kindly provided by Dr. Glenn W. Kaatz, John Dingell VA Medical Center, Detroit, MI, USA. Bacterial strains were maintained in Brain Heart Infusion Agar (BHIA, Himedia, Mumbai, India) slanted at 4 °C. Prior to assays, cells were subcultured into tubes containing Brain Heart Infusion medium (BHI, Himedia, Mumbai, India) and incubated at 37 °C for 24 h. EtBr and chlorpromazine (CPZ) were obtained from Sigma Chemical Corp., St. Louis, MO, USA. EtBr and CPZ were dissolved in sterile distilled water.
2.2. Extraction of the Biflavones Mixture
The biflavones mixture (BFs) used to perform the biological assays was obtained from the hydroethanolic extract of the P. insignis flowers by developing the work of Silva et al. [18]. The flowers of Platonia insignis Mart. were collected in the municipality of Parnarama, Maranhão state, in August 2014. The exsiccatae were deposited in the Graziella Barroso Herbarium of the Federal University of Piauí (UFPI) under the ICN number TEPB 27174. The petals of fresh flowers of P. insignis were ground and macerated in a solvent mixture EtOH/H2O in the ratio of 7:3 (m/v) and in the ratio of 1:5 plant material/solvent (m/v) at room temperature for 9 days. Subsequently, the hydroalcoholic extract (EHPi) was rotaevaporated and lyophilized. The EHPi was resuspended in MeOH/H2O 9:1 (v/v) and subjected to liquid–liquid partitioning with solvents in increasing order of polarity. The ethyl acetate fraction, FAcOEt, was obtained with a mass of 3.82 g and η = 26.56%. From mass spectrometry with electrospray ionization in negative mode coupled with a mass spectrometer (ion trap hybrid) (ESI-IT-MS) in scan mode, a mixture of biflavonoids, moreloflavone and volkensiflavone, stood out as majorities in the hydroalcoholic extract. To identify the constituents present in the FAcOEt fraction, silica dry column chromatography was performed, thereby obtaining a subfraction eluted with MeOH/H2O 1:1 (v/v) and presenting as a yellow amorphous solid. After ESI-MS analysis in the negative ionization mode and NMR, the moreloflavone compounds were identified, with the majority molecular form being C30H19O11; the volkensiflavone was also identified, and its molecular form was C30H19O10.
2.3. Determination of the Minimum Inhibitory Concentration
Test solutions of BFs and CPZ were prepared in DMSO, which was followed by dilution in sterile distilled water to a final concentration of 1024 μg/mL. Minimal inhibitory concentrations (MIC) were determined using a microdilution assay in BHI broth with bacterial suspensions of approximately 105 CFU/mL and test product ranging from 8 to 512 μg/mL. Microtiter plates were incubated at 37 °C for 24 h, and then 20 μL of resazurin (0.01 % w/v in sterile distilled water) was added to each well to detect bacterial growth as indicated by a color change from blue to pink. MIC was defined as the lowest concentration at which no bacterial growth was observed.
2.4. Evaluation of the Protective Effect of BFs against Lethality Induced by EtBr in Staphylococcus aureus
To assess whether BFs were able to protect S. aureus strains against the lethal effect induced by EtBr, bacterial cells were treated with EtBr in the presence or absence of BFs at subinhibitory concentrations (MIC 1/8, 128 μg/mL). EtBr concentrations ranged from 0.125 to 128 μg/mL. Microtiter plates were incubated at 37 °C for 24 h, and readings were performed with resazurin as described above. As a control, assays were performed replacing BFs with CPZ (MIC 1/8, 8 μg/mL), a known inhibitor of the NorA efflux pump [27].
2.5. Spectroscopic Analysis in the Infrared Region
Absorption spectra of EtBr, BFs and EtBr/BFs (1:1, m/m) in the infrared region were obtained with a Cary 630 FTIR spectrometer and ATR accessory (both from Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA).
2.6. Statistical Analysis
The experiments were performed in triplicate, and the results were normalized by calculating the geometric mean of the MICs. The standard error and standard deviation of the geometric mean were determined. Statistical analyses were performed using the GraphPad Prism program, version 5.02 (San Diego, CA, USA). The occurrence of differences between EtBr treatment in the absence or presence of BF was examined using one-step analysis of variance (ANOVA). The differences mentioned above were analyzed using the Bonferroni post-test and were considered statistically significant when p < 0.05.
3. Results and Discussion
Figure 2 shows the results of the assays for comparing the antibacterial activity of EtBr either alone or associated with BFs against the SA1199B strain that overproduces the NorA efflux pump. It can be verified that the MIC value obtained for EtBr isolated against this strain was 64 μg/mL. On the other hand, when the SA1199B strain was treated with EtBr associated with the BFs in subinhibitory concentration, the EtBr MIC increased to 128 μg/mL (a 2× increase), indicating that the BFs protected the SA1199B strain against the lethal effect of EtBr. Such protection was not exercised by CPZ in subinhibitory concentrations, which, unlike BFs, potentiated the action of EtBr, possibly by inhibiting the NorA efflux pump.
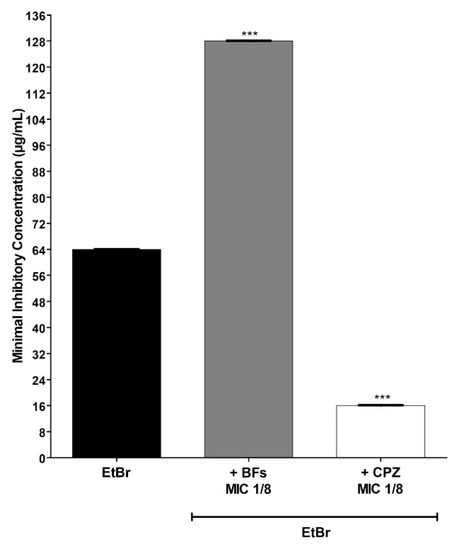
Figure 2.
MIC (minimum inhibitory concentration) values of ethidium bromide (EtBr) against S. aureus SA1199-B (NorA+++) in the absence or presence of biflavones (BF, 128 μg/mL) or chlorpromazine (CPZ, 8 μg/mL). Each result represents the geometric mean of three simultaneous experiments. (***) Statistically significant values (p < 0.0001).
Similar results were obtained with the wild-type parent SA1199 strain that produced the NorA efflux pump at baseline levels (Figure 3). For this strain, the MIC value obtained for EtBr isolated against the strain was 16 μg/mL, whereas for EtBr combined with the BFs, the MIC value was raised to 32 μg/mL (a 2× increase). On the other hand, these results suggest that the protective effect exerted by the BFs against EtBr-induced lethality in S. aureus occurs independently of the NorA efflux pump’s expression level. Such protection was not exercised by CPZ, which, unlike BFs, potentiated the action of EtBr against the SA1199B strain, possibly by inhibiting the NorA efflux pump.
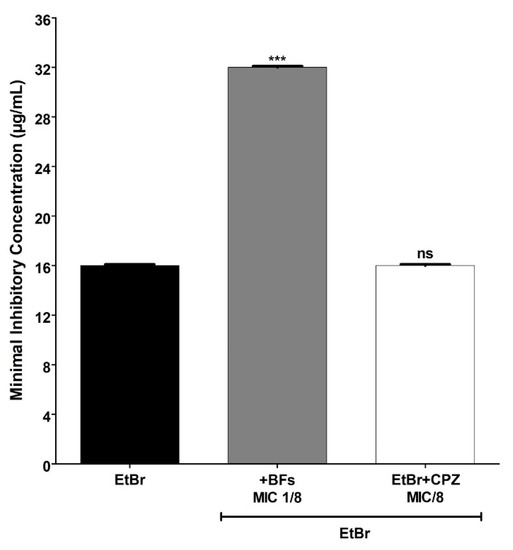
Figure 3.
MIC (minimum inhibitory concentration) values of ethidium bromide (EtBr) against S. aureus SA1199 (NorA+) in the absence or presence of biflavones (BFs, 128 μg/mL) or chlorpromazine (CPZ, 8 μg/mL). Each result represents the geometric mean of three simultaneous experiments. (***) Statistically significant values (p < 0.0001). ns: not significant.
The BFs also increased by 2× the concentration of EtBr necessary to inhibit the growth of the IS-58 strain overproducer of the efflux pump TetK (Figure 4), the strain K2068 overproducer of the efflux pump MepA (Figure 5) and the strain K4100 overproducer of the efflux pump QacC (Figure 6) as well as the strain RN4220 overproducer of MsrA efflux pump (Figure 7). The NorA and TetK proteins are proton-motive force-dependent efflux pumps and members of the MFS (Major Facilitator superfamily) [28]. The MepA efflux pump is a proton-motive force-dependent transporter of the MATE superfamily (Multidrug and toxin Extrusion), whereas the QacC protein is a carrier protein belonging to the SMR (Small multidrug Resistance) [29]. On the other hand, the MsrA efflux pump is ATP-dependent and belongs to the ABC superfamily [30]. These results indicate that the protective effect exerted by the BFs against EtBr-induced lethality in S. aureus occurs regardless of the type of efflux pump expressed by this pathogen.
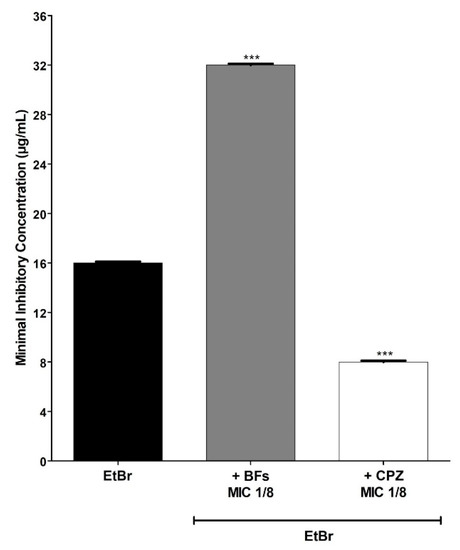
Figure 4.
MIC (minimum inhibitory concentration) values of ethidium bromide (EtBr) against S. aureus IS-58 (tetK) in the absence or presence of biflavones (BFs, 128 μg/mL) or chlorpromazine (CPZ, 8 μg/mL). Each result represents the geometric mean of three simultaneous experiments. (***) Statistically significant values (p < 0.0001).
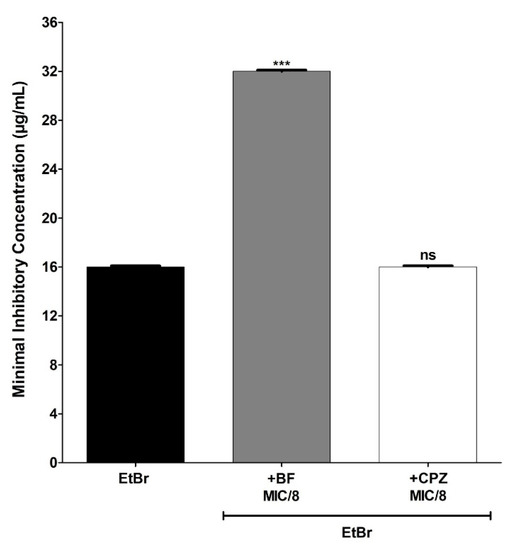
Figure 5.
MIC (minimum inhibitory concentration) values of ethidium bromide (EtBr) against S. aureus K2068 (MepA) in the absence or presence of biflavones (BFs, 128 μg/mL) or chlorpromazine (CPZ, 8 μg/mL). Each result represents the geometric mean of three simultaneous experiments. (***) Statistically significant values (p < 0.0001). ns: not significant.
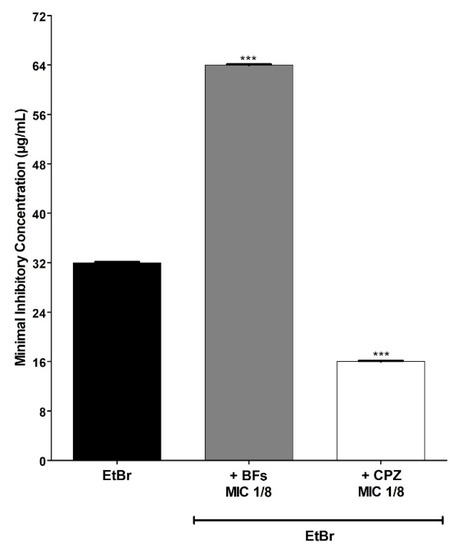
Figure 6.
MIC (minimum inhibitory concentration) values of ethidium bromide (EtBr) against S. aureus K4100 (QacC) in the absence or presence of biflavones (BFs, 128 μg/mL) or chlorpromazine (CPZ, 8 μg/mL). Each result represents the geometric mean of three simultaneous experiments. (***) Statistically significant values (p < 0.0001).
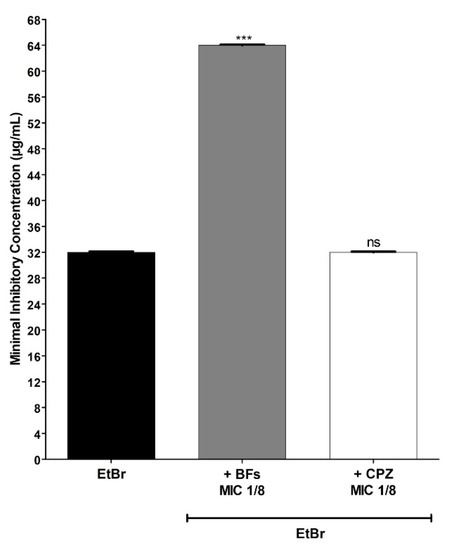
Figure 7.
MIC (minimum inhibitory concentration) values of ethidium bromide (EtBr) against S. aureus RN4220 (MsrA) in the absence or presence of biflavones (BFs, 128 μg/mL) or chlorpromazine (CPZ, 8 μg/mL). Each result represents the geometric mean of three simultaneous experiments. (***) Statistically significant values (p < 0.0001). ns: not significant.
To test the hypothesis that the protective effect exerted by the BFs could be due to a possible interaction between these compounds and EtBr, the spectra in the infrared region of EtBr, the BFs and the mixture of EtBr + BFs (1:1, m/m) were analyzed (Figure 8).
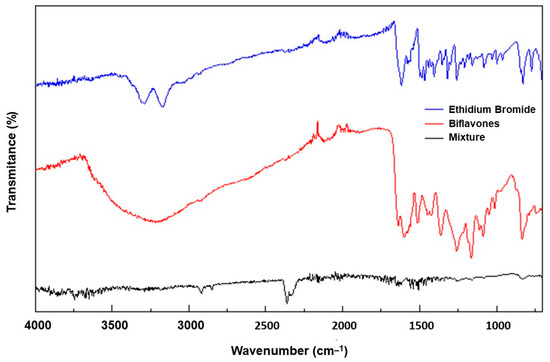
Figure 8.
Infrared spectra of ethidium bromide (EtBr), biflavones (BFs) and EtBr + BFs mixture.
In the spectrum of EtBr, it can be seen that NH stretching of primary amines occurred in the region between 3540–3380 cm−1. OH stretching of phenols occurred between 3676–3584 cm−1, and both bands had varying intensities. Observing the spectra of ethidium bromide isolated and the spectra of the mixture of biflavones, these bands appear well-defined; however, in the spectrum of the mixture of biflavones with ethidium bromide, these absorptions disappear, and two new absorption bands appear at 2368 cm−1 and 2335 cm−1, characteristics of –C=N + –H (stretch =CN + –H).
The disappearance of the 1600 cm−1 peak, which corresponds to carbonyls (C=O), when ethidium bromide is mixed with biflavones may be related to a possible complexation between the two compounds, indicating that there was a preferential interaction between the H2N– groups of primary amines of ethidium bromide with the carbonyls of biflavones that formed imines –C=NH (Figure 9). These imines can be protonated by acidic phenolic hydrogens, causing a change in the carbonyl peak.
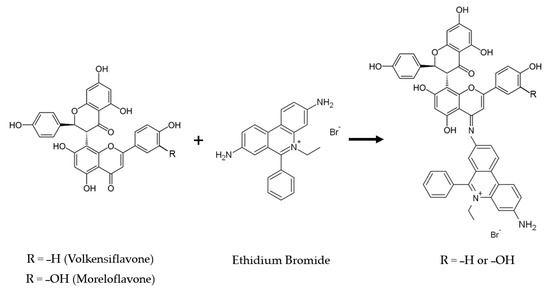
Figure 9.
Proposed reaction of the NH2 (amine) group of ethidium bromide on the C=O (carbonyl) group of biflavones.
These results suggest that the protective effect exerted by the BFs could be related to their ability to covalently bind EtBr, forming complexes of higher molecular weight in the extracellular medium that would not be assimilated by bacterial cells. In this way, the BFs would be reducing the entry of isolated EtBr molecules into the cell, which would reduce the cell damage induced by this compound.
A previous study with the same S. aureus strains tested in the present study verified that the BFs volkensiflavone and moreloflavone inhibited the NorA, QacA/B, TetK and MsrA efflux pumps, promoting greater accumulation of EtBr in these strains [18]. Therefore, despite the observed complexation, isolated molecules of EtBr and the BFs can be absorbed by bacterial cells. However, the complexes formed in the intracellular medium, due to their higher molecular weight and structure incompatible with the diameter of the DNA, would not be able to intercalate into the double helix, which would also contribute to reducing the cell damage induced by EtBr.
The cytoprotective activity of flavonoids was previously reported in eukaryotic cells. The dietary flavonoid quercetin showed a cytoprotective effect against benzo[a]pyrene-induced toxicity [31] and a cytoprotective effect in epithelial cells against Pseudomonas aeruginosa virulence factors [32]. Dihydromyricetin, a natural flavonoid extracted from Ampelopsis grossedentata, showed a cytoprotective effect on dairy cow mammary epithelial cells by suppressing mitochondrial membrane depolarization caused by heat stress and mitochondrial dysfunction as well as by modulating oxidative enzymes; thus, it prevented the production of oxygen-reactive species [33]. Hesperetin, a flavonoid derived from citrus fruits, exhibited cytoprotective action, protecting against hypoxia/reoxygenation injuries and doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity [34]. Because EtBr is a mutagenic and carcinogenic agent, the results obtained in the present study with prokaryotic cells are promising and open the horizon for future investigations of the protective effect of these BFs against the damage induced by EtBr in eukaryotic cells.
4. Conclusions
The results obtained indicate that the mixture of biflavones volkensiflavone and moreloflavone obtained from the P. insignis flowers shows a protective effect against EtBr-induced damage in S. aureus, suggesting a possible application of these compounds as cytoprotective agents. Future studies will be needed to investigate whether these compounds exert this same protective effect in eukaryotic cells.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, H.M.B., and H.D.M.C.; methodology, A.S.G.M., J.d.A.F.B., A.K.F.e.S., M.L.L.B.d.N., E.E.A.P., A.K.S.M. and J.d.S.L.-N.; validation, H.M.B., J.M.d.C.e.S. and A.M.d.G.L.C.; resources, H.M.B., J.M.d.C.e.S. and A.M.d.G.L.C.; writing—original draft preparation, A.S.G.M.; writing—review and editing, H.M.B. and H.D.M.C.; supervision, A.M.d.G.L.C. and H.M.B.; project administration, H.M.B.; funding acquisition, H.M.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was funded by the Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado do Piauí (grant number: 050/2019) and Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico-CNPq.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Galindo-Murillo, R.; Cheatham, T.E. Ethidium bromide interactions with DNA: An exploration of a classic DNA-ligand complex with unbiased molecular dynamics simulations. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, 3735–3747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LePecq, J.B.; Paoletti, C.A. Fluorescent complex between ethidium bromide and nucleic acids: Physical-chemical characterization. J. Mol. Biol. 1967, 27, 87–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burns, V.W.F. Fluorescence decay time characteristics of the complex between ethidium bromide and nucleic acids. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1969, 133, 420–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Possato, B.; Dalmolin, L.F.; Pereira, L.M.; Alves, J.Q.; Silva, R.T.C.; Gelamo, R.V.; Yatsuda, A.P.; Lopez, R.F.V.; Albuquerque, S.D.; Leite, N.B.; et al. Gold (III) complexes with thiosemicarbazonate ligands as potential anticancer agents: Cytotoxicity and interactions with biomolecular targets. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 162, 105834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burns, V.W.F. Fluorescence polarization characteristics of the complexes between ethidium bromide and rRNA, tRNA, and DNA. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1971, 145, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alnajrani, M.N.; Alsager, O.A. Decomposition of DNA staining agent ethidium bromide by gamma irradiation: Conditions, kinetics, by-products, biological activity, and removal from wastewater. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 389, 122142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, V.W.F. Location and molecular characteristics of fluorescent complexes of ethidium bromide in the cell. Exp. Cell Res. 1972, 75, 200–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braga, R. Plantas do Nordeste: Especialmente do Ceará, 2nd ed.; Imprensa Official: Fortaleza, Brazil, 1960; 540p. [Google Scholar]
- Cavalcante, P.B. Frutas Comestíveis da Amazônia, 1st ed.; Museu Paraense Emílio Goeldi: Pará, Brazil, 1996; 279p. [Google Scholar]
- Nascimento, W.M.O.D.; Carvalho, J.E.U.D.; Muller, C.H. Ocorrência e distribuição geográfica do bacurizeiro. Rev. Bras. Frutic. 2007, 29, 657–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinimbú-Neto, F.D.A.; Martins, A.B.G.; Barbosa, J.C. Viabilidade in vitro de grãos de pólen de bacurizeiro—Clusiaceae. Rev. Bras. Frutic. 2011, 33, 593–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, A.C.; Alves, M.M.D.M.; Brito, L.M.; Oliveira, L.G.D.C.; Sobrinho-Júnior, E.P.C.; Costa, I.C.G.; Freitas, S.D.L.; Rodrigues, K.A.D.F.; Chaves, M.H.; Arcanjo, D.D.R.; et al. Platonia insignis Mart., a Brazilian Amazonian plant: The stem barks extract and its main constituent lupeol exert antileishmanial effects involving macrophages activation. eCAM 2017, 2017, 3126458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes, M.B.; Silva-Filho, J.C.; Sabino, C.K.B.; Arcanjo, D.D.R.; Sousa, C.M.M.; Costa, I.C.G.; Chaves, M.H.; Oliveira, R.D.C.M.; Oliveira, A.P. Pharmacological evidence of 2-adrenergic receptors in the hypotensive effect of Platonia insignis Mart. J. Med. Food 2014, 17, 1079–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa-Júnior, J.S.; de Almeida, A.A.C.; Costa, J.P.; Citó, A.M.G.L.; Saffi, J.; de Freitas, R.M. Superoxide dismutase and catalase activities in rat hippocampus pretreated with garcinielliptone FC from Platonia insignis. Pharm. Biol. 2012, 50, 453–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa-Júnior, J.S.; Freitas, R.M.; Citó, A.M.G.L.; Henriques, J.A.P.; Saffi, J. Evaluation of effects of ethanolic extract (EE) from Platonia insignis Mart. on pilocarpine-induced seizures. J. Biol. Sci. 2010, 10, 747–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa-Júnior, J.S.; Ferraz, A.B.; Feitosa, C.M.; Citó, A.M.G.L.; Freitas, R.M.; Saffi, J. Evaluation of antioxidant effects in vitro of garcinielliptone FC (GFC) isolated from Platonia insignis Mart. J. Med. Plants Res. 2011, 5, 293–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa-Junior, J.S.; de Almeida, A.A.C.; Ferraz, A.D.B.F.; Rossatto, R.R.; Silva, T.G.; Silva, P.B.N.; Militão, G.C.G.; Citó, A.M.G.L.; Santana, L.C.L.R.; Carvalho, F.A.D.A.; et al. Cytotoxic and leishmanicidal properties of garcinielliptone FC, a prenylated benzophenone from Platonia insignis. Nat. Prod. Res. 2013, 27, 470–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.K.F.; Reis, A.C.; Pinheiro, E.E.A.; Sousa, J.N.; Oliveira, F.A.A.; Moura, A.K.S.; Lima-neto, J.S.; Citó, A.M.G.L.; Siqueira-Júnior, J.P.; Kaatz, G.W.; et al. Modulation of the drug resistance by Platonia insignis Mart. extract, ethyl acetate fraction and Morelloflavone/Volkensiflavone (Biflavonoids) in Staphylococcus aureus strains overexpressing efflux pump genes. Curr. Drug Metab. 2021, 21, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezerra, E.A.; Alves, M.M.M.; Lima, S.K.R.; Pinheiro, E.E.A.; Amorim, L.V.; Lima Neto, S.K.R.; Carvalho, F.A.A.; Citó, A.M.G.L.; Arcanjo, D.D.R. Biflavones from Platonia insignis Mart. Flowers promote In Vitro antileishmanial and immunomodulatory effects Against internalized amastigote forms of Leishmania amazonensis. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdi, L.G.; Pizzolatti, M.G.; Montanher, A.B.P.; Brighente, I.M.C.; Smânia Júnior, A.; Smânia, E.D.F.A.; Simionatto, E.L.; Monache, F.D. Antibacterial and brine shrimp lethality tests of biflavonoids and derivatives of Rheedia gardneriana. Fitoterapia 2004, 75, 360–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.M.; Anderson, H.; Flavin, M.T.; Pai, Y.H.S.; Mata-Greenwood, E.; Pengsuparp, T.; Pezzuto, J.M.; Schinazi, R.F.; Hughes, S.H.; Chen, F.C. In Vitro anti-HIV activity of biflavonoids isolated from Rhus succedanea and Garcinia multiflora. J. Nat. Prod. 1997, 60, 884–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gontijo, V.S.; De Souza, T.C.; Rosa, I.A.; Soares, M.G.; Da Silva, M.A.; Vilegas, W.; Viegas, C.; Dos Santos, M.H. Isolation and evaluation of the antioxidant activity of phenolic constituents of the Garcinia brasiliensis epicarp. Food Chem. 2012, 132, 1230–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otuki, M.F.; Bernardi, C.A.; Prudente, A.S.; Laskoski, K.; Gomig, F.; Horinouchi, C.D.S.; Guimarães, C.L.; Ferreira, J.; Delle-Monache, F.; Cechinel-Filho, V.; et al. Garcinia gardneriana (Planchon & Triana) Zappi. (Clusiaceae) as a topical anti-inflammatory alternative for cutaneous inflammation. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2011, 109, 56–62. [Google Scholar]
- Tuansulong, K.A.; Hutadilok-Towatana, N.; Mahabusarakam, W.; Pinkaew, D.; Fujise, K. Morelloflavone from Garcinia dulcis as a novel biflavonoid inhibitor of HMG-CoA reductase. Phyther. Res. 2011, 25, 424–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, J.F.S.; Tintino, S.R.; Silva, A.R.P.; Barbosa, C.R.S.; Scherf, J.R.; Silveira, Z.S.; Freitas, T.S.; Lacerda-Neto, L.J.; Barros, L.M.; Menezes, I.R.A.; et al. Enhancement of the antibiotic activity by quercetin against Staphylococcus aureus efflux pumps. J. Bioenerg. Biomembr. 2021, 53, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedge, A.H.; Prashanth, S.N.; Seetharamappa, J. Interaction of antioxidant flavonoids with calf thymus DNA analyzed by spectroscopic and electrochemical methods. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2012, 63, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neyfakh, A.A.; Borsch, C.M.; Kaatz, G.W. Fluoroquinolone resistance protein NorA of Staphylococcus aureus is a multidrug efflux transporter. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1993, 37, 128–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schindler, B.D.; Kaatz, G.W. Multidrug efflux pumps of Gram-positive bacteria. Drug Resist. Updat. 2016, 27, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, D.; Wang-Kan, X.; Neuberger, A.; van Veen, H.W.; Pos, K.M.; Piddock, L.J.; Luisi, B.F. Multidrug efflux pumps: Structure, function and regulation. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 16, 523–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shriram, V.; Khare, T.; Bhagwat, R.; Shukla, R.; Kumar, V. Inhibiting bacterial efflux pumps via phyto-therapeutics to combat threatening antimicrobial resistance. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Jee, S.C.; Kim, K.S.; Kim, H.S.; Yu, K.N.; Sung, J.S. Quercetin and Isorhamnetin Attenuate Benzo [a] pyrene-Induced Toxicity by Modulating Detoxification Enzymes through the AhR and NRF2 Signaling Pathways. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vipin, C.; Mujeeburahiman, M.; Ashwini, P.; Arun, A.B.; Rekha, P.D. Antibiofilm and cytoprotective activities of quercetin against Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2019, 68, 464–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.L.; Xing, G.D.; Qian, Y.; Sun, X.F.; Zhong, J.F.; Chen, K.L. Dihydromyricetin attenuates heat stress-induced apoptosis in dairy cow mammary epithelial cells through suppressing mitochondrial dysfunction. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 214, 112078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, Y.; Wu, Z.; Buist-Homan, M.; Blokzijl, H.; Moshage, H. Hesperetin protects against palmitate-induced cellular toxicity via induction of GRP78 in hepatocytes. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2020, 404, 115183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).