Abstract
The ability for density functional theory with the B3LYP functional with the lanl2dz basis set to predict the 1st (Wave 1) and 2nd (Wave 2) reductions of the diazine ring in a series of thirty-seven (37) 1,4-di-N-oxide quinoxaline-2-carboxamide derivatives in dimethylformamide was examined. The B3LYP/lanl2dz method had a strong correlation and low correlation to the experimental potentials for Wave 1 and Wave 2, respectively. There are nine identifiable analogs based on similarities of structure. The predicted reduction potentials for the derivatives of each analog generally fit the modified Hammett equation. The B3LYP/lanl2dz method is shown to be useful in accurately predicting the Wave 1 potentials for quinoxaline-di-N-oxide derivatives. For derivatives with assessable anti-tuberculosis activity, the predicted Wave 1 potentials have a similar correlation with the bioactivity when compared to the experimental wave 1 potentials.
1. Introduction
Over the last several decades, scientists have been investigating quinoxaline derivatives for a variety of medical applications. Quinoxaline derivatives have been found to have medicinal effects including anti-cancer, anti-trypanosomal, anti-microbial and anti-viral activities [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16]. The biomechanisms for the medicinal applications is not known but is often linked to the ease of reduction of the quinoxaline derivatives [6,17,18]. In 2011, Crawford et. al. studied the electrochemical properties of a series of thirty-seven (37) 1,4-di-N-oxide quinoxaline-2-carboxamide derivatives shown in Table 1 [18]. The ease of reduction was compared to the molecular structure, and it was observed that the addition of an electron-withdrawing group resulted in a positive shift for the reduction potential. Likewise, the addition of an electron-donating group resulted in a negative shift in the reduction potential. The thirty-seven derivatives can be assigned to nine analogs based on similarities in structure. The anti-tuberculosis activities of the derivatives were measured and compared to the ease of reduction. The two analogs containing benzyl (compounds 1–5) and 2-phenylethyl (compounds 6–12) were previously found to have significant anti-tuberculosis activity. For these derivates, Crawford et al. demonstrated an exponential correlation between the anti-tuberculosis activity and the ease of reduction for this subset of derivatives [18].
The common correlation between bioactivity and ease of reduction has made cyclic voltammetry a common analytical technique to study quinoxaline derivatives [6,17,18,19,20,21]. We have proposed that simple computational methods provide a powerful tool allowing for the prediction of the electrochemical properties of quinoxaline derivatives. Furthermore, the ability to accurately predict the electrochemical properties could become a powerful tool to help synthetic chemists design potential derivatives. As a proposed tool for synthetic chemists, we are looking for the fastest reliable computational methods. Several computational studies have investigated the HOMO/LUMO gap in small organic molecules [20,22,23,24,25,26]. Additionally, studies have investigated electronic properties, thermodynamic properties, effects of substitutions, and polymerization of quinoxalines [20,24,27,28].
In our previous studies, we investigated twenty 3-aryl-quinoxaline-2-carbonitrile 1,4-di-N-oxide derivatives that demonstrated varying degrees of cytotoxic activity [29,30]. Voltametric methods were used to measure the electrochemical properties of the 20 quinoxaline derivatives in dimethylformamide (DMF) [30]. All but one of the first reductions of the n-oxide derivatives (Wave 1) were found to be reversible or quasireversible, while the second reductions (Wave 2) were found to be irreversible. There was good correlation between molecular structure and the reduction potential of these derivatives. Surprisingly, no correlation was found between the ease of reduction and the cytotoxic activity for the twenty 3-aryl-quinoxaline-2-carbonitrile 1,4-di-N-oxide derivatives studied [30]. We also tested the ability of DFT: B3LYP/6-31G [29], DFT: B3LYP/lanl2dz [29] and DFT: B3LYP/cc-pVTZ (unpublished) [31] to predict the electrochemical properties for the same twenty 3-aryl-quinoxaline-2-carbonitrile 1,4-di-N-oxide derivatives. For all basis sets, a strong correlation with similar R2 values and standard error was found between the predicted and experimental potentials for wave 1 when considering the sixteen derivatives without a nitro functional group. The main advantage of DFT: B3LYP/cc-pVTZ was the ability to predict wave 1 for four (4) derivatives with a nitro functional group. None of the methods were able to accurately predict the wave 2 or nitro wave reductions.
In this study, we investigate the ability for Density Functional Theory (DFT) [32] calculation at the B3LYP/lanl2dz level of theory to accurately predict the 1st (Wave 1) and 2nd (Wave 2) reduction potentials for the diazine ring for the thirty-seven (37) 1,4-di-N-oxide quinoxaline-2-carboxamide derivatives from the 2011 Crawford study [18]. The DFT: B3LYP/lanl2dz level of theory was used as none of the current derivatives contain a nitro functional group. The correlation between the DFT: B3LYP/lanl2dz predicted potentials and the anti-tuberculosis activity and compared the results to the correlation of the experimental potentials.


Table 1.
The parent structure of the 1,4-di-N-oxide quinoxaline-2-carboxamide derivative and the list of the R, R7, and R6 substituents [18,33]. 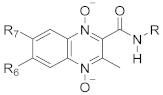

Table 1.
The parent structure of the 1,4-di-N-oxide quinoxaline-2-carboxamide derivative and the list of the R, R7, and R6 substituents [18,33]. 

| Compounds Code | R | R7/R6 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Benzyl | CH3/H |
| 2 | Cl/H | |
| 3 | Cl/Cl | |
| 4 | F/H | |
| 5 | CF3/H | |
| 6 | 2-Phenylethyl | H/H |
| 7 | CH3/H | |
| 8 | Cl/H | |
| 9 | Cl/Cl | |
| 10 | CF3/H | |
| 11 | F/H | |
| 12 | F/F | |
| 13 | p-Methoxybenzyl | H/H |
| 14 | CH3/H | |
| 15 | Cl/H | |
| 16 | p-Trifluoromethylbenzyl | H/H |
| 17 | CH3/H | |
| 18 | Cl/H | |
| 19 | p-Chlorobenzyl | H/H |
| 20 | CH3/H | |
| 21 | Cl/H | |
| 22 | Cl/Cl | |
| 23 | p-Bromobenzyl | H/H |
| 24 | CH3/H | |
| 24 | Cl/H | |
| 26 | Cl/Cl | |
| 27 | p-Methylbenzyl | H/H |
| 28 | CH3/H | |
| 29 | Cl/H | |
| 30 | 2,2-Diphenylethel | H/H |
| 31 | CH3/H | |
| 32 | Cl/H | |
| 33 | Cl/Cl | |
| 34 | Benzo[d] [1,3] dioxol-5-ylmethyl | H/H |
| 35 | CH3/H | |
| 36 | Cl/H | |
| 37 | Cl/Cl |
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Drawing the Derivatives
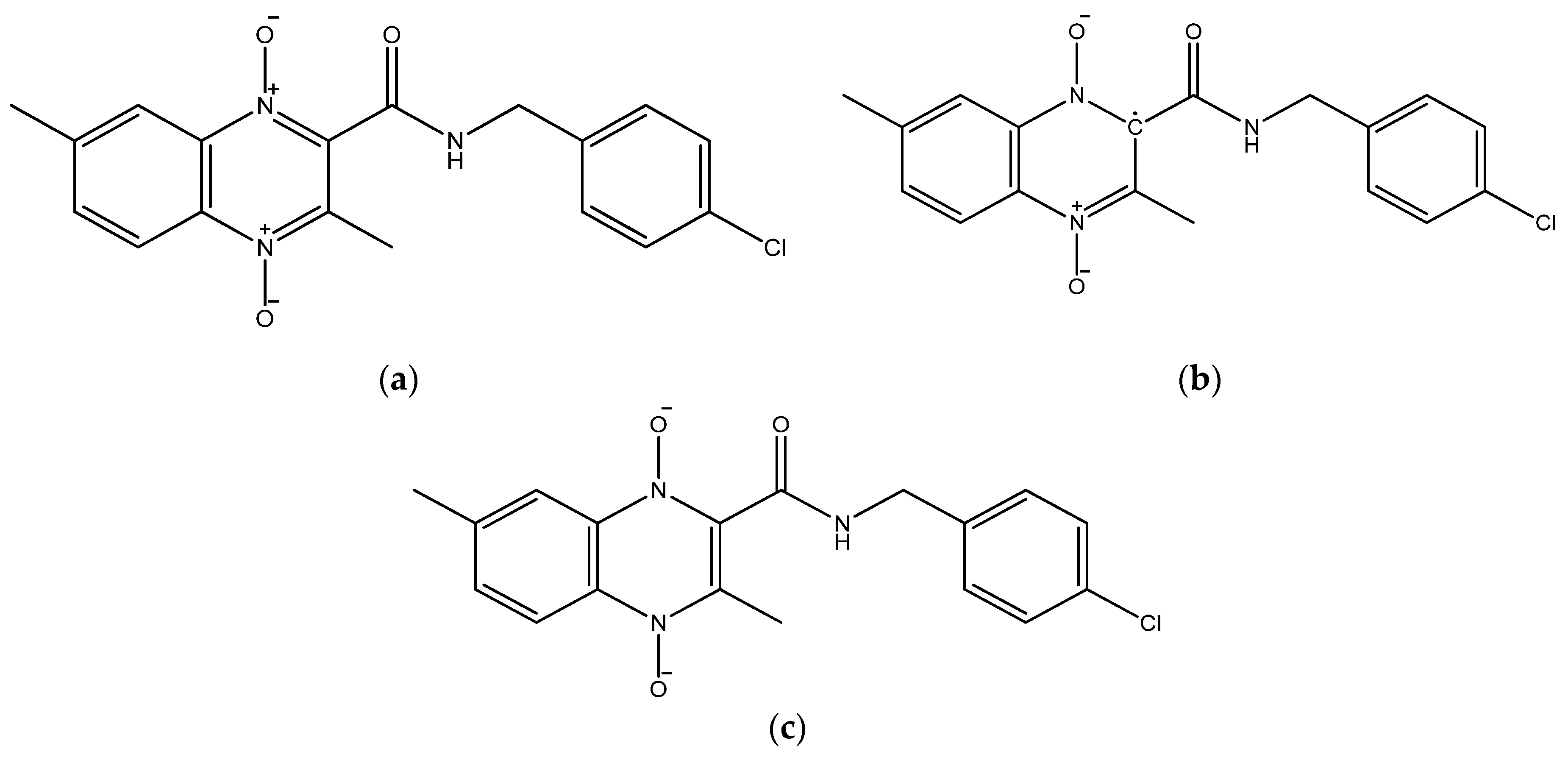
The molecular structures for the 1,4-di-N-oxide quinoxaline-2-carboxamide derivatives were drawn using GaussView 5 [34]. For each derivative, three structures were drawn including the original neutral molecule, the anion product from the first N-oxide reduction (Wave 1), and the dianion product from the second N-oxide reduction (Wave 2). Figure 1 shows 2D structures created with ChemDraw for the three individual structures for Compound 20 (Table 1). The original neutral molecule is shown in Figure 1a. The anion product structures for the product of wave 1 had the radical attached to the carbon adjacent to the amide group (Figure 1b). The dianion product from wave 2 is shown in Figure 1c.
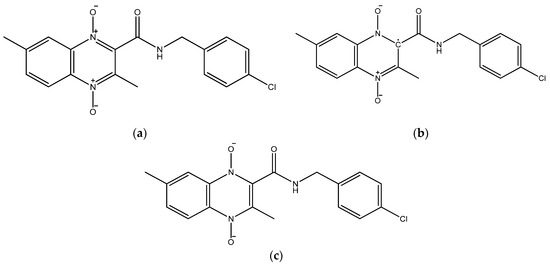
Figure 1.
The molecular structures of Compound 20 [18] in (a) neutral, (b) the anion product from the 1st N-oxide reduction (Wave 1), and (c) the dianion product from the 2nd N-oxide reduction (Wave 2) drawn with ChemDraw [33].
2.2. DFT Reduction Potential Predictions
All density functional theory (DFT) with the B3LYP functional and the lanl2dz basis set [35,36] calculations were carried out in Gaussian 09 [37] following the procedure outlined in our previous papers [29,30]. All the Gaussian 09 settings remained the default settings unless explicitly indicated. Each structure was optimized in the gas phase using the lanl2dz basis set to find the most stable configuration with the lowest energy (). Next, a frequency calculation was run from the optimized structures to determine the thermal correction factor () needed to correct for thermal artifacts. The energy of the structure in the gas phase () was determined by combining the and according to Equation (1).
The change in Gibbs Free Energy from the reduction of the derivative is found by comparing the energy of the structures in gas phase before and after the reduction of the derivative. For wave 1, the change in Gibbs Free Energy ( is the difference between the energy of the anion ( and neutral forms ( of the derivative (Equation (2)).
Energy calculations were run from the optimized structures in the gas phase in the solvent N, N-dimethylformamide (DMF) to find the solvated energy (). The default solvent in Gaussian 09 is the Integral equation formalism variant of the Polarizable Continuum Model (IEFPCM) [38,39,40]. The Gibbs Free Energy of Solvation was found by subtracting from (Equation (3)).
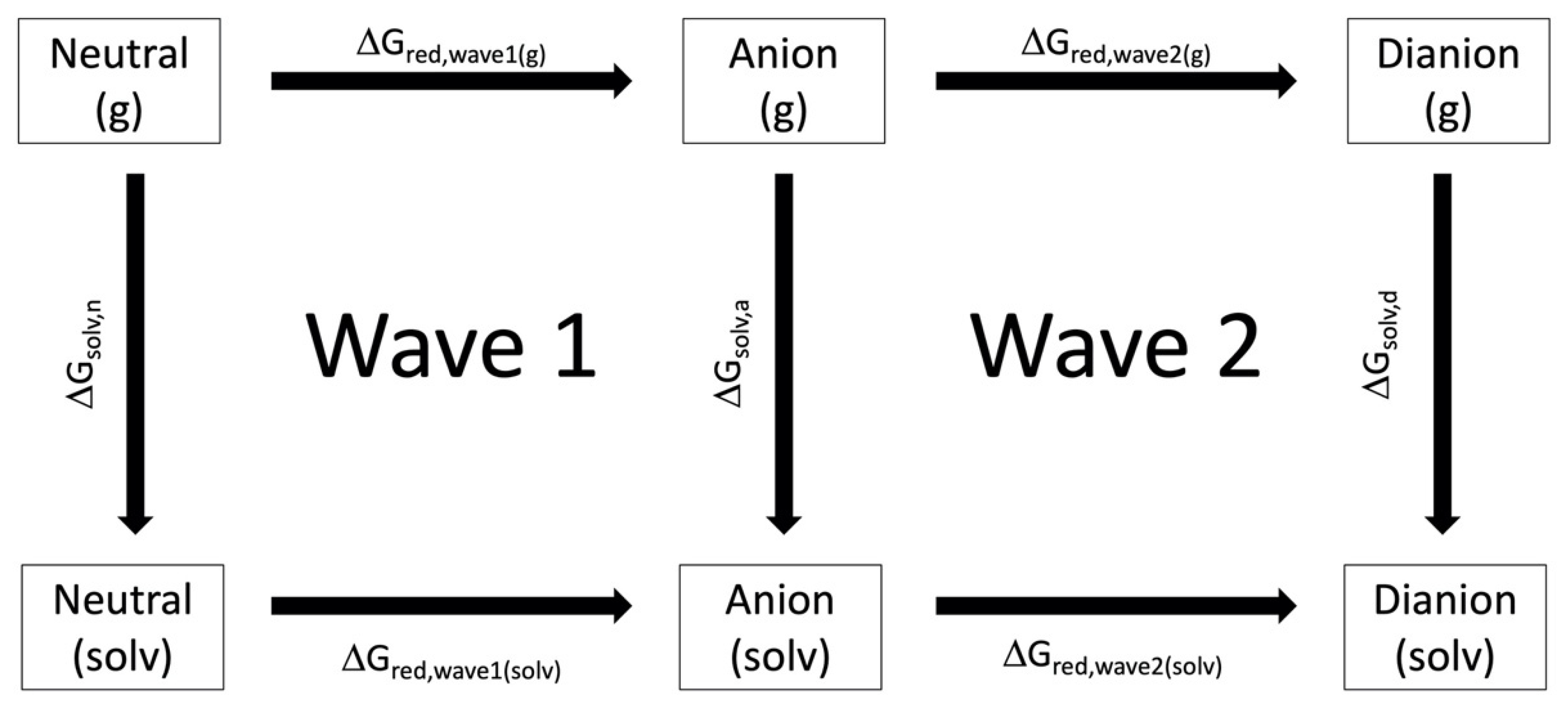
Figure 2 shows the thermodynamic cycle used to calculate the change in Gibbs Free energy associated with the reduction wave 1 and wave 2, and , respectively. For wave 1, is calculated from , and according to equation 4 where n is the neutral and a is the anion form of the derivative.
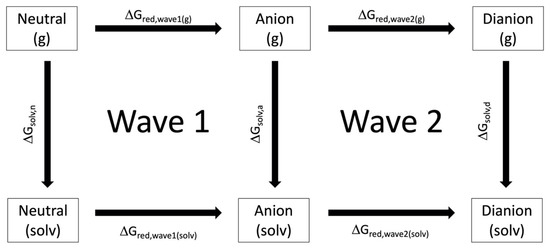
Figure 2.
The thermodynamic cycle used to calculate the electrochemical cell potentials for wave 1 and wave 2.
The change in Gibbs Free energy is converted to a half-cell reduction potential () using Equation (5),
where n is the number of electrons transferred and F is Faraday’s constant (96,485 C/mole). Computational values for the ferrocene (Fc) and ferrocenium (Fc+) ion reference system have been previously calculated [22] and were used in this study. The cell reduction potentials (were calculated by comparing the half-cell reduction potentials of the derivative and the Fc/Fc+ reference system (Equation (6)).
lastly, the reduction potential was modified to set the ferrocene/ferrocenium reference system to zero by subtracting 0.7 V, the difference between the ferrocene/ferrocenium reference system and the standard hydrogen electron in DMF (Equation (7)).
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Computational Raw Chemical Potentials
The B3LYP/lanl2dz predicted half-cell reduction potentials for the 1,4-di-N-oxide quinoxaline-2-carboxamide derivatives are shown in Table 2. The calculated reduction potentials were within the expected range. The appearance of the neutral and anion structures of the compounds appeared as expected. The dianion structures of some chlorine or Br containing derives is observed to have C−Cl or C−Br bond lengthening. For the derivatives with C−Cl bond lengthening, the C−Cl of the dianion was found to be between 1.87 Å and 1.89 Å. The derivatives with C−Br bond lengthening the C-Br in the dianion structure was between 2.05 Å and 2.3 Å.

Table 2.
The predicted half-cell reduction potentials for the 1,4-di-N-oxide quinoxaline-2-carboxamide derivatives calculated using Gaussian 09 at the DFT: B3LYP/lanl2dz level of theory [32,37].
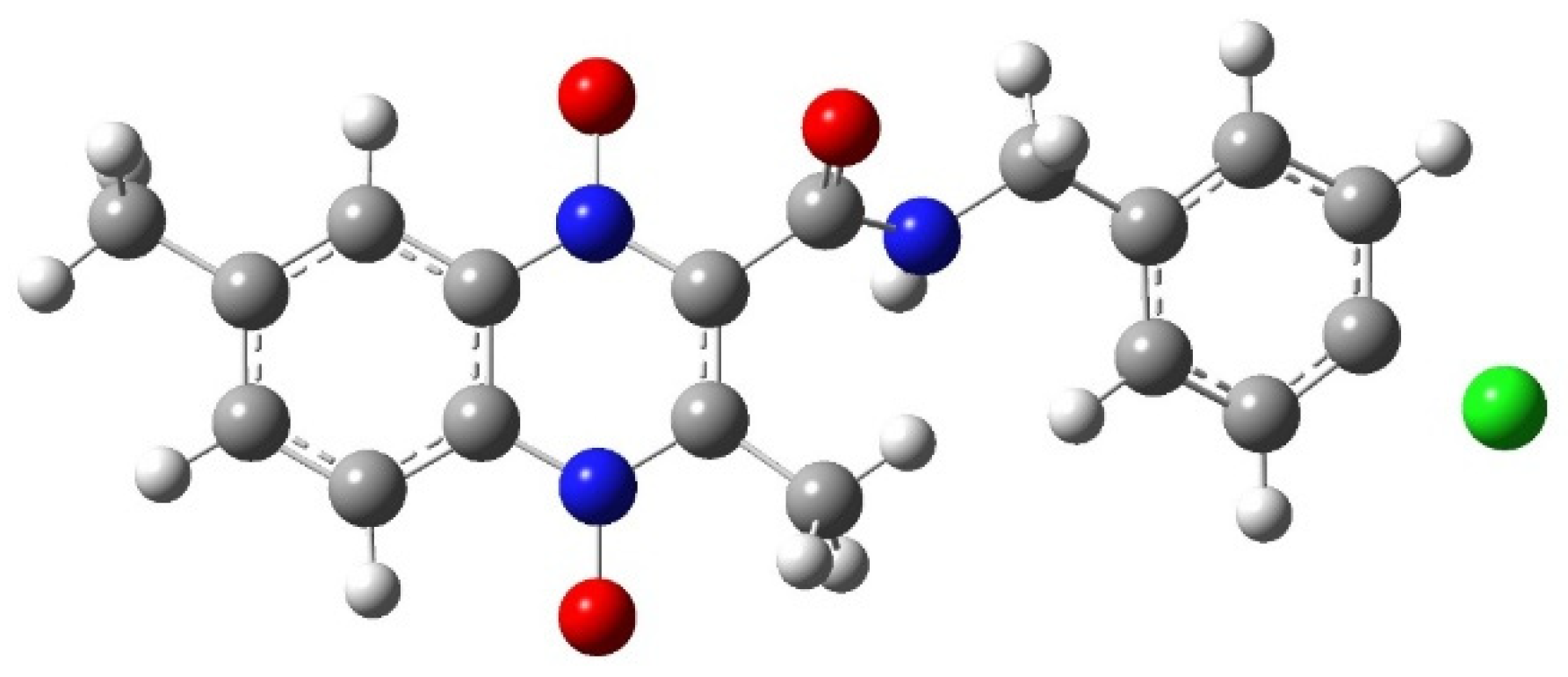
The optimized dianion structure of Compound 20 is shown in Figure 3. The C−Cl bond was missing, indicating that the chlorine atom had moved far enough away from the derivative that GaussView 5 [34] no longer draws the Cl as bonded. The C−Cl bond distance increases as the compound is reduced. After optimization the C-Cl bond length was found to be 1.76 Å, 1.837 Å, and 1.87 Å for the Compound 20 derivative, after wave 1, and after wave 2, respectively. This result was not totally unexpected, since we observed a the C−Cl bonding lengthening and even Cl atom dissociating from pyrazine in molecule E4 in our previous study [29]. In the 2019 study, the DFT: B3LYP/lanl2dz the C−Cl distance was found to be 1.81 Å, 1.83 Å, and 1.91 Å for the E4 before reduction, after wave 1, and after wave 2, respectively. The effect was more pronounced with the DFT: B3LYP/6-31g. The C−Cl distance was 1.81 Å, 1.84 Å, and 10.9 Å for the original E4 before reduction, after wave 1, and after wave 2, respectively [29]. Since the lengthening of the C−Cl bond is seen in more than one study across different quinoxaline analogs, this could indicate a real structural change. Given the electron withdrawing nature of chlorine, it is not unreasonable to think some C−Cl bond lengthening may occur as the molecule is reduced and has an increased electron density on the chlorine atom.
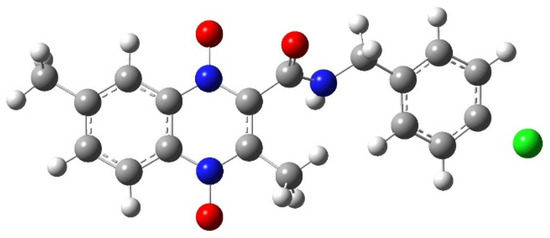
Figure 3.
The carbon—chlorine bond length increases to 1.87 Å for Compound 20 during the optimization of the dianion species. Chemical structure created in GaussView 5 [34] and optimized in Gaussian 09 [37]. Carbon is shown in grey, hydrogen in white, nitrogen in blue, oxygen in red, and chlorine in green.
3.2. Computationally Predicted Electrochemical Cell Reaction Potentials
The calculated and experimental electrochemical cell potentials () versus Fc/Fc+ with the Fc/Fc+ potential set to zero are shown in Table 3. The comparison of the calculated electrochemical cell potentials () with the ferrocene/ferrocenium electrode (Fc/Fc+) reduction potential adjusted to zero for wave 1 is between −1.1261 and −1.5159 V but for wave 2 is in a lower range, from −2.3236 to −3.3491 V (Table 3).

Table 3.
The DFT: B3LYP/lanl2dz-predicted electrochemical potential, experimental [18] electrochemical cell potentials, and anti-tuberculosis activities [18] for the 1,4-di-N-oxide quinoxaline-2-carboxamide derivatives.
3.3. Comparison to Experimental Reduction Potentials
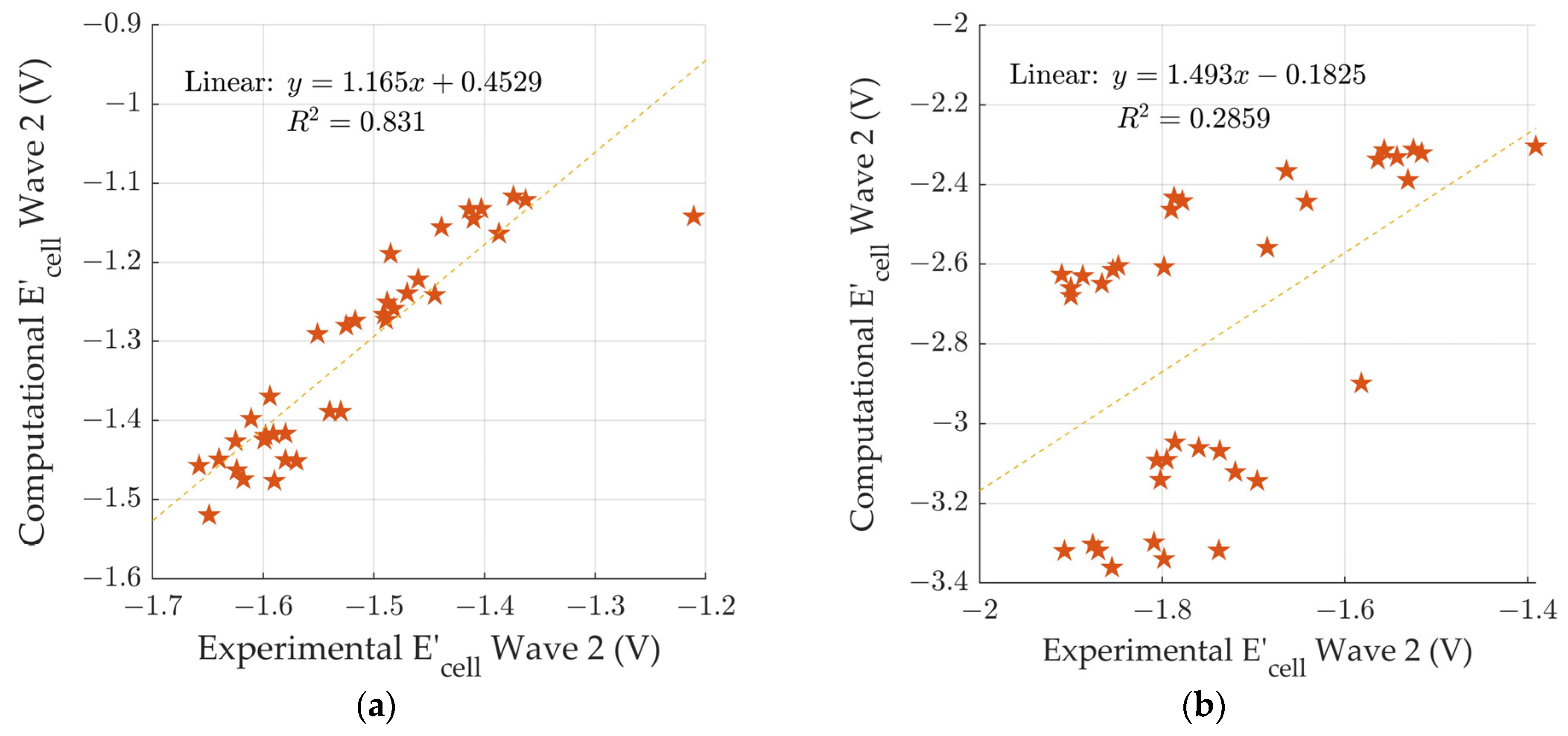
To investigate any correlation between calculated and experimental data, two diagrams based on the electrochemical cell potentials () were plotted for both wave 1 and wave 2. Figure 4a is a comparison between the experimental [18] and calculated electrochemical potentials for wave 1. The wave 1 slope has a value of 1.16 ± 0.09 (slope ± standard error of slope) and has an R2 value of 0.831, indicating a significant correlation between the calculated and experimental data. However, the slope value is greater than 1 meaning that the computational values are changing in response to the chemical differences more than the experimental values. Additionally, we observed that calculated values are more positive than the experimental values. In Table 3, the calculated electrochemical cell potentials () for wave 1 lie in the range of −1.12 and −1.52 V. In contrast, the experimental values ranged from −1.211 to −1.658 V [18].
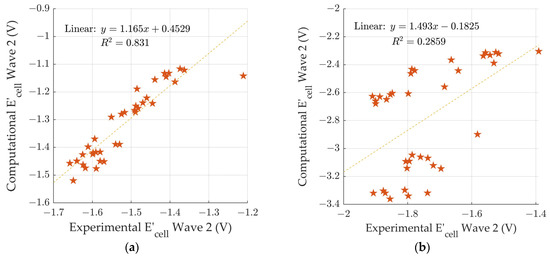
Figure 4.
Comparison of computational electrochemical cell potentials vs. experimental electrochemical cell potentials [18] for (a) wave 1, and (b) wave 2.
Figure 4b is a comparison between the experimental [18] and calculated electrochemical potentials for wave 2. The wave 2 comparison has a slope of 1.5 ± 0.5 (slope ± standard error of slope) and an R2 value of 0.285, indicating little to no correlation between the experimental and computational waves to electrochemical potentials. For wave 2, we observed that the calculated electrochemical cell potentials () were significantly more negative than the experimental values (Table 3). The calculated electrochemical cell potentials () for wave 2 lie in the range −2.30 V to −3.36 V. In contrast, the experimental values ranged from −1.391 V to −1.91 V [18].
The inability for DFT: B3LYP/lanl2dz to predict the electrochemical potentials for wave 2 was also observed in our previous study [29]. We have also tested the ability for DFT: B3LYP/cc-pVTZ to predict the electrochemical potentials for the twenty (20) 3-aryl-quinoxaline-2-carbonitrile 1,4-di-N-oxide derivatives from our 2019 study (unpublished) [31]. The DFT calculations with the higher B3LYP/cc-pVTZ level of theory is also unable to accurately predict the wave 2 electrochemical potentials. Given the combination of our studies on both sets of derivatives, we hypothesize that the inability to predict the wave 2 potentials is an indication that there are likely other structural changes during reduction. It would be expected that the addition of the second electron leads a highly reactive species that could react with solvent, an electrolyte, or another quinoxaline molecule. Unfortunately, structural changes during reduction were not investigated by the experimentalists.
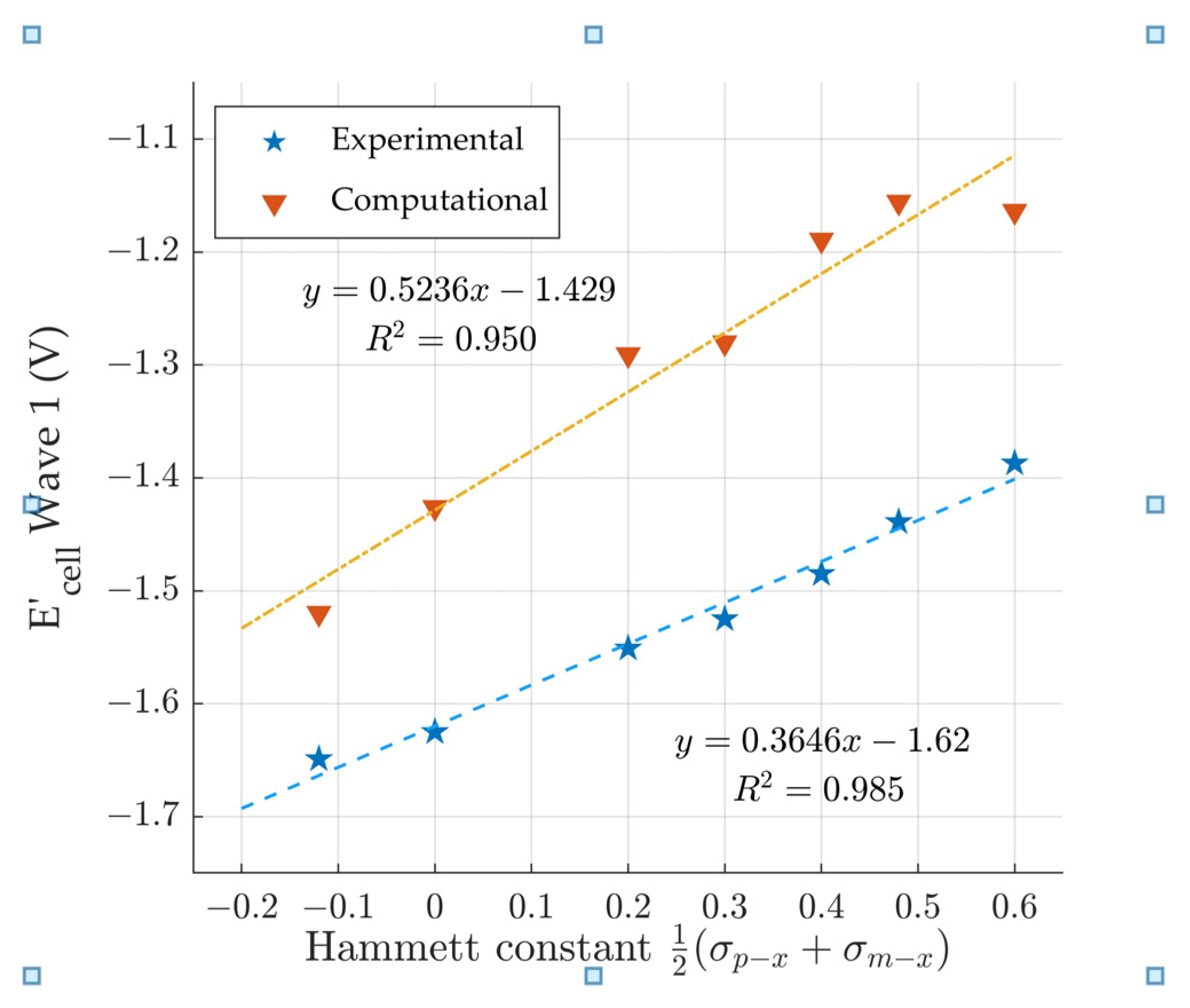
3.4. Comparison to the Modified Hammett Equation
The Hammett Equation is used to model the impact of the substitution of hydrogens with electron withdrawing or electron donating groups on the reaction constant for the reduction of the aromatic ring system [41]. The predicted Wave 1 potentials generally fits the modified Hammett equation for the different homologous series. The modified Hammett equation (Equation (8)) shows the relationship between change in electrochemical potentials with , the reaction constant, and , the polar inductive electronic substituent constant. It is recommended to use the average of the para position polar inductive substituent constant, , and the meta position polar inductive substituent constant, , for quinoxalines, [42]. The Hammett constants are listed in Table 4.

Table 4.
Hammett substituent constants [41].
The derivatives within each analog generally fit the modified Hammett equation. Figure 5 shows the comparison between the Hammett constant [41] and the electrochemical potentials. This analysis was repeated for all the analogs. For the DFT: B3LYP/lanl2dz predicted electrochemical potentials, the R2 values range between 0.8873 and 0.9972 for series with at least four (4) derivatives. Although the qualitative trend is observed for the series with three derivatives, the R2 was not calculated due to a lack of data points. The correlation between DFT: B3LYP/lanl2dz predicted wave 2 electrochemical potentials and the Hammett constants [41] weakens drastically when compared to wave 1. Compounds 6–12 have a R2 of 0.950 (Figure 5) for wave 1 but only an R2 = 0.502 for wave 2 (not shown). This correlation decrease is not observed with the experimental data [18] as the wave 2 R2 remains >0.9.
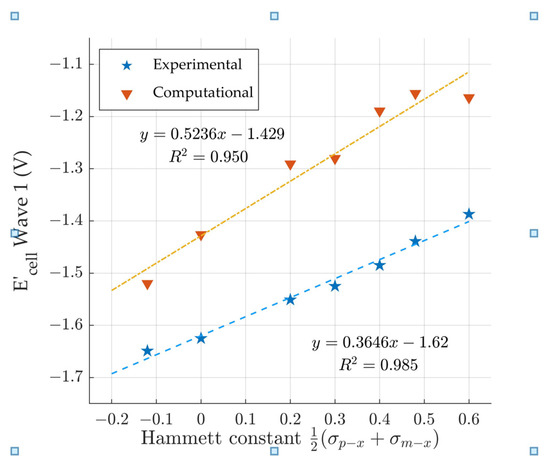
Figure 5.
Comparison of the Hammett constant [41] vs computationally predicted and experimental [18] electrochemical wave 1 cell potentials.
3.5. Comparison to Experimental Anti-Tuberculosis Data
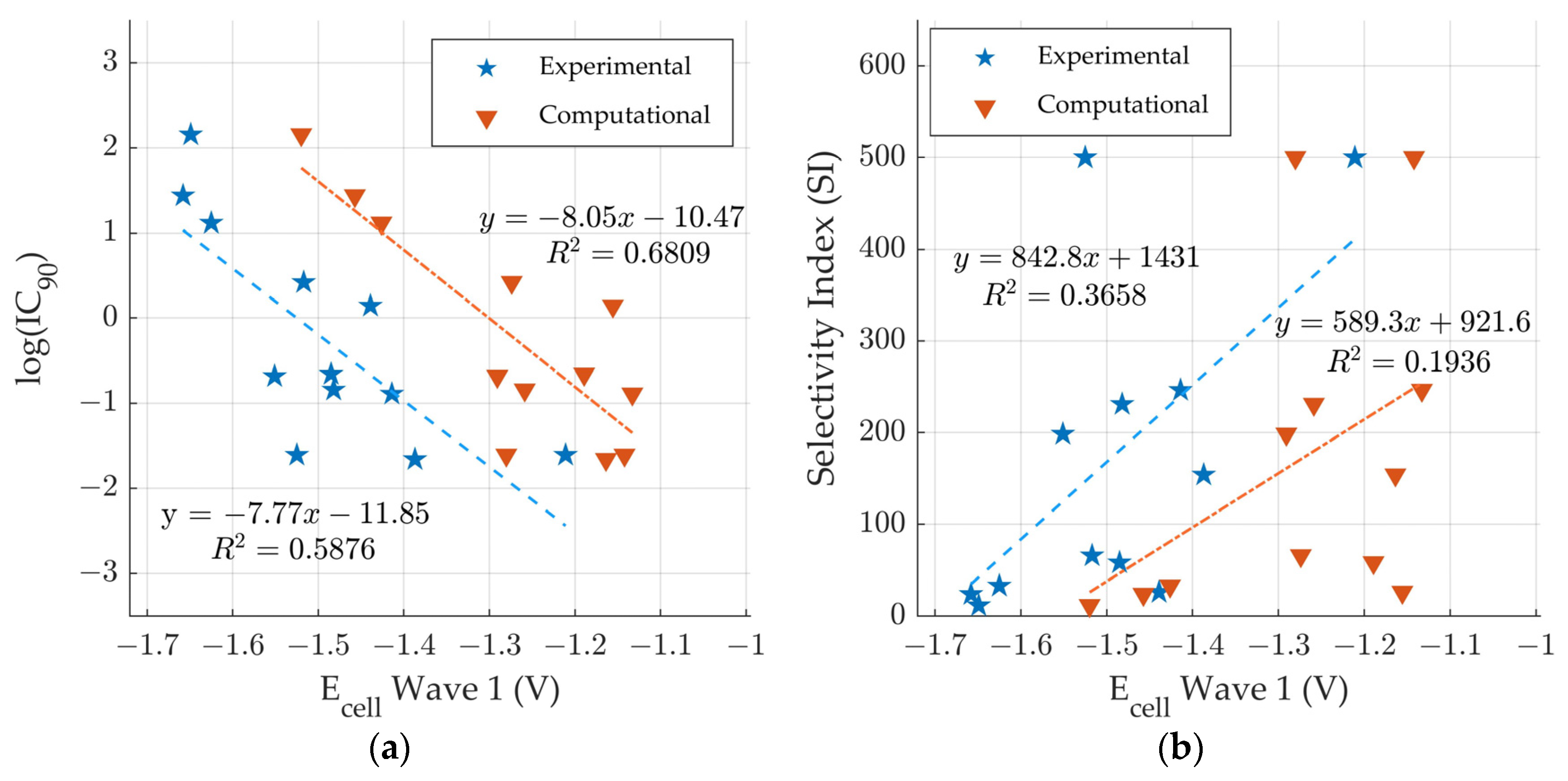
In 2011, Crawford et al. used IC90 and CC50 assays to quantify the anti-tuberculosis activity of these compounds [18]. The IC90 was defined as a reduction in fluorescence of 90% compared to a control against M. tuberculosis H37Rv (ATCC 27294) using the Microplate Alamar Blue Assay. Compounds with IC90 10 μg/mL were considered “active” for anti-tuberculosis activity and evaluated with the CC50 assay. The CC50 was determined using the VERO cell cytotoxicity assay. A selectivity index (SI) value was found by dividing CC50 by IC90 and SI values 10 were recommended for further anti-tuberculosis activity testing. The thirty-seven (37) derivatives were assigned to nine (9) analogs based on their structures and attached R-group. For two of the analogs (Compounds 1–5 and Compounds 6–12), all the derivatives were considered “active.” For these 12 compounds, a correlation was observed between the ease of reduction and the anti-tuberculosis activity [18].
Figure 6 shows the comparison of predicted and experimental potentials [18] with the measured anti-tuberculosis activity [18]. In Figure 6a, the predicted and experimental potentials are plotted versus log(IC90). The R2 values are determined to be 0.6 and 0.7 respectively, demonstrating that there is a moderate exponential correlation between the ease of reduction and the IC90. The correlation between predicted ease of reduction and IC90 suggests that DFT: B3LYP/lanl2dz can moderately predict anti-tuberculous activity for some derivates with new R6/R7 variations. Figure 6b shows comparison of the predicted and experimental potentials and the selectivity index (SI). The R2 values are determined to be 0.2 and 0.4 respectively, demonstrating that there is low correlation between the ease of reduction and the selectivity index. The SI values are reported as a range. The range is necessary as SI is a ratio of CC50 and IC90. The CC50 values are reported versus a concentration maximum [18]. The CC50 values are listed as >100 for Compounds 1–8 and 11 [18]. Given the lower certainty of the SI values, it is not surprising that there is less correlation with the ease of reduction.
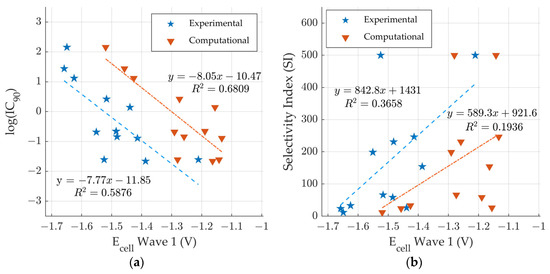
Figure 6.
Comparison of computationally predicted and experimental electrochemical cell potentials [18] vs. anti-tuberculosis activity for compounds 1–12 [18]. (a) logIC90 vs wave 1 and (b) SI vs wave 1.
While it is likely that the ease of reduction is important for the mechanism for reaction for the quinoxaline derivatives through the formation of the free radical in wave 1 [18], an expectation for a “perfect” correlation between ease of reduction and activity would be unrealistic. For in vivo systems, additional factors including solubility, membrane permeability, absorption, stereochemistry, and active site binding will play a role in observed anti-tuberculosis activity.
4. Conclusions
For the 1st n-oxide reduction (wave 1), the DFT: B3LYP/lanl2dz calculations were able to predict the electrochemical properties for thirty-seven 1,4-di-N-oxide quinoxaline-2-carboxamide derivatives with good agreement to the experimental electrochemical potentials. The correlation was improved over our original study of twenty 3-aryl-quinoxaline-2-carbonitrile 1,4-di-N-oxide derivatives that includes some derivatives with a nitro group [29]. The lanl2dz basis set is a useful computational tool for making a first-level prediction for electrochemical properties for quinoxaline 1,4-di-N-oxide derivatives without attached nitro-groups. The predicted wave 1 electrochemical potentials had a moderate exponential correlation to the experimental IC90 values similar to the experimental potentials. This correlation suggests that DFT: B3LYP/lanl2dz predictions of the wave 1 electrochemical potentials could moderately predict new R6/R7 derivates with anti-tuberculosis activity.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, F.P., P.W.C. and C.M.R.; methodology, F.P. and C.M.R.; software, F.P., J.M.K. and C.M.R.; validation, F.P.; formal analysis, F.P., P.W.C., J.M.K. and C.M.R.; investigation, F.P., J.M.K. and C.M.R.; resources P.W.C., J.M.K. and C.M.R.; data curation, F.P., J.M.K. and C.M.R.; writing—original draft preparation F.P., P.W.C., J.M.K., G.R.C. and C.M.R.; writing—review and editing F.P., P.W.C., J.M.K., G.R.C. and C.M.R.; visualization, F.P., J.M.K. and C.M.R.; supervision, P.W.C. and C.M.R.; project administration, C.M.R. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available due to data size.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge Victor Batista from Yale University for his guidance. Some of the computation for this work was performed on the high-performance computing infrastructure provided by Research Support Solutions and in part by the National Science Foundation under grant number CNS-1429294 at the University of Missouri, Columbia MO. DOI: https://doi.org/10.32469/10355/69802.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Pereira, J.A.; Pessoa, A.M.; Cordeiro, M.N.; Fernandes, R.; Prudêncio, C.; Noronha, J.P.; Vieira, M. Quinoxaline, its derivatives and applications: A State of the Art review. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 97, 664–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zarranz, B.; Jaso, A.; Aldana, I.; Monge, A. Synthesis and anticancer activity evaluation of new 2-alkylcarbonyl and 2-benzoyl-3-trifluoromethyl-quinoxaline 1,4-di-N-oxide derivatives. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2004, 12, 3711–3721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amin, K.M.; Ismail, M.M.F.; Noaman, E.; Soliman, D.H.; Ammar, Y.A. New quinoxaline 1,4-di-N-oxides. Part 1: Hypoxia-selective cytotoxins and anticancer agents derived from quinoxaline 1,4-di-N-oxides. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2006, 14, 6917–6923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estevez, Y.; Quiliano, M.; Burguete, A.; Cabanillas, B.; Zimic, M.; Málaga, E.; Verástegui, M.; Pérez-Silanes, S.; Aldana, I.; Monge, A.; et al. Trypanocidal properties, structure–activity relationship and computational studies of quinoxaline 1,4-di-N-oxide derivatives. Exp. Parasitol. 2011, 127, 745–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ancizu, S.; Moreno, E.; Torres, E.; Burguete, A.; Pérez-Silanes, S.; Benítez, D.; Villar, R.; Solano, B.; Marín, A.; Aldana, I.; et al. Heterocyclic-2-carboxylic Acid (3-Cyano-1,4-di-N-oxidequinoxalin-2-yl)amide Derivatives as Hits for the Development of Neglected Disease Drugs. Molecules 2009, 14, 2256–2272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, E.; Moreno-Viguri, E.; Galiano, S.; Devarapally, G.; Crawford, P.W.; Azqueta, A.; Arbillaga, L.; Varela, J.; Birriel, E.; Di Maio, R.; et al. Novel quinoxaline 1,4-di-N-oxide derivatives as new potential antichagasic agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 66, 324–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carta, A.; Paglietti, G.; Rahbar Nikookar, M.E.; Sanna, P.; Sechi, L.; Zanetti, S. Novel substituted quinoxaline 1,4-dioxides with in vitro antimycobacterial and anticandida activity. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2002, 37, 355–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente, E.; Pérez-Silanes, S.; Lima, L.M.; Ancizu, S.; Burguete, A.; Solano, B.; Villar, R.; Aldana, I.; Monge, A. Selective activity against Mycobacterium tuberculosis of new quinoxaline 1,4-di-N-oxides. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2009, 17, 385–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Lu, Q.; Zhang, J.; Qu, W.; Xie, S.; Huang, L.; Yuan, Z.; Pan, Y. Discovery of novel nitrogenous heterocyclic-containing quinoxaline-1,4-di-N-oxides as potent activator of autophagy in M.tb-infected macrophages. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 223, 113657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, N.; Bhardwaj, A. An appraisal on synthetic and pharmaceutical perspectives of quinoxaline 1,4-di-N-oxide scaffold. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2022, 100, 346–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, R.F.; Yadav, P.; Shinde, S.S.; Hong, C.R.; Pullen, S.M.; Reynisson, J.; Wilson, W.R.; Hay, M.P. Radical Chemistry and Cytotoxicity of Bioreductive 3-Substituted Quinoxaline Di-N-Oxides. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2016, 29, 1310–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Divya, K.M.; Savitha, D.P.; Krishna, G.A.; Dhanya, T.M.; Mohanan, P.V. Crystal structure, DFT studies, Hirshfeld surface and energy framework analysis of 4-(5-nitro-thiophen-2-yl)-pyrrolo [1, 2-a] quinoxaline: A potential SARS-CoV-2 main protease inhibitor. J. Mol. Struct. 2022, 1251, 131932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucuk, C.; Yurdakul, S.; Celik, S.; Erdem, B. Experimental and DFT studies of 2-methyl-quinoxaline and its silver (I) complex: Non-covalent interaction analysis, antimicrobial activity and molecular docking study. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2022, 145, 109935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouanane, Z.; Bounekhel, M.; Elkolli, M.; Abrigach, F.; Khoutoul, M.; Bouyala, R.; Touzani, R.; Hellal, A. Synthesis, structural, catecholase, tyrosinase and DFT studies of pyrazoloquinoxaline derivatives. J. Mol. Struct. 2017, 1139, 238–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maltsev, D.V.; Skripka, M.O.; Spasov, A.A.; Vassiliev, P.M.; Perfiliev, M.A.; Divaeva, L.N.; Zubenko, A.A.; Morkovnik, A.S.; Klimenko, A.I.; Miroshnikov, M.V.; et al. Design, Synthesis and Pharmacological Evaluation of Novel C2,C3-Quinoxaline Derivatives as Promising Anxiolytic Agents. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 14401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, D.; Liu, P.; Jiang, Y.; He, X.; Zhang, L.; Wang, L.; Yang, T. Discovery and SAR Study of Quinoxaline–Arylfuran Derivatives as a New Class of Antitumor Agents. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 2420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawford, P.W.; Scamehorn, R.G.; Hollstein, U.; Ryan, M.D.; Kovacic, P. Cyclic voltammetry of phenazines and quinoxalines including mono- and di-N-oxides. Relation to structure and antimicrobial activity. Chem.-Biol. Interact. 1986, 60, 67–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, E.; Pérez-Silanes, S.; Gouravaram, S.; Macharam, A.; Ancizu, S.; Torres, E.; Aldana, I.; Monge, A.; Crawford, P.W. 1,4-Di-N-oxide quinoxaline-2-carboxamide: Cyclic voltammetry and relationship between electrochemical behavior, structure and anti-tuberculosis activity. Electrochim. Acta 2011, 56, 3270–3275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Silanes, S.; Devarapally, G.; Torres, E.; Moreno-Viguri, E.; Aldana, I.; Monge, A.; Crawford, P.W. Cyclic Voltammetric Study of Some Anti-Chagas-Active 1,4-Dioxidoquinoxalin-2-yl Ketone Derivatives. Helv. Chim. Acta 2013, 96, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbitskiy, E.V.; le Poul, P.; Bureš, F.; Achelle, S.; Barsella, A.; Kvashnin, Y.A.; Rusinov, G.L.; Charushin, V.N. Push-Pull Derivatives Based on 2,4′-Biphenylene Linker with Quinoxaline, [1,2,5]Oxadiazolo[3,4-B]Pyrazine and [1,2,5]Thiadiazolo[3,4-B]Pyrazine Electron Withdrawing Parts. Molecules 2022, 27, 4250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rupar, J.; Aleksić, M.M.; Nikolić, K.; Popović-Nikolić, M.R. Comparative electrochemical studies of kinetic and thermodynamic parameters of Quinoxaline and Brimonidine redox process. Electrochim. Acta 2018, 271, 220–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar-Martínez, M.; Cuevas, G.; Jiménez-Estrada, M.; González, I.; Lotina-Hennsen, B.; Macías-Ruvalcaba, N. An Experimental and Theoretical Study of the Substituent Effects on the Redox Properties of 2-[(R-phenyl)amine]-1,4-naphthalenediones in Acetonitrile. J. Org. Chem. 1999, 64, 3684–3694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hodgson, J.L.; Namazian, M.; Bottle, S.E.; Coote, M.L. One-Electron Oxidation and Reduction Potentials of Nitroxide Antioxidants: A Theoretical Study. J. Phys. Chem. A 2007, 111, 13595–13605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro da Silva, M.D.M.C.; Gomes, J.R.B.; Gonçalves, J.M.; Sousa, E.A.; Pandey, S.; Acree, W.E. Thermodynamic Properties of Quinoxaline-1,4-Dioxide Derivatives: A Combined Experimental and Computational Study. J. Org. Chem. 2004, 69, 2785–2792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhilshath Raihana, H.; Karthick, K.; Shankar, T.; Kamalesu, S.; Anish Babu, A.; Swarnalatha, K. A new tetradentate Schiff base of N,N′-bis(3,5-diiodosalicylidene)-1,2-phenylenediamine: Spectral aspects, Hirshfield surfaces, DFT computations and molecular docking. J. Mol. Struct. 2022, 1264, 133217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucuk, C.; Yurdakul, S.; Erdem, B. Spectroscopic characterization, DFT calculations, and microbiological activity of 5-iodoindole. J. Mol. Struct. 2022, 1252, 132125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, A.; Verma, C.; Srivastava, V.; Lgaz, H.; Quraishi, M.A.; Ebenso, E.E.; Chung, I.-M. Chemical, Electrochemical and Computational Studies of Newly Synthesized Novel and Environmental Friendly Heterocyclic Compounds as Corrosion Inhibitors for Mild Steel in Acidic Medium. J. Bio-Tribo-Corros. 2018, 4, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauria, A.; Almerico, A.M.; Barone, G. The influence of substitution in the quinoxaline nucleus on 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition reactions: A DFT study. Comput. Theor. Chem. 2013, 1013, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, E.M.; Brazel, C.J.; Brillos-Monia, K.A.; Crawford, P.W.; Hufford, H.C.; Loncaric, M.R.; Mruzik, M.N.; Nenninger, A.W.; Ragain, C.M. Reduction Potential Predictions for Some 3-Aryl-Quinoxaline-2-Carbonitrile 1,4-Di-N-Oxide Derivatives with Known Anti-Tumor Properties. Computation 2019, 7, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, M.E.; Xia, Q.; Cella, E.M.; Nenninger, W.A.; Mruzik, N.M.; Brillos-Monia, A.K.; Hu, Z.Y.; Sheng, R.; Ragain, M.C.; Crawford, W.P. Voltammetric Study of Some 3-Aryl-quinoxaline-2-carbonitrile 1,4-di-N-oxide Derivatives with Anti-Tumor Activities. Molecules 2017, 22, 1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattarai, S.; Mareta, P.; Crawford, P.W.; Kessler, J.M.; Ragain, C.M. Improved Computational Prediction of the Electrochemical Reduction Potential of Twenty 3-Aryl-Quinoxaline-2-Carbonitrile 1,4-Di-N-Oxide Derivatives. Computation 2023, 11, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaefer, H.F. (Ed.) Applications of Electronic Structure Theory; Plenum Press: New York, NY, USA, 1977; Volume 4. [Google Scholar]
- ChemDraw. Available online: https://perkinelmerinformatics.com/products/research/chemdraw (accessed on 30 November 2022).
- Dennington, R.; Keith, T.A.; Millam, J.M. GaussView 5; Semichem Inc.: Shawnee Mission, KS, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Hay, P.J.; Wadt, W.R. Ab initio effective core potentials for molecular calculations. Potentials for the transition metal atoms Sc to Hg. J. Chem. Phys. 1985, 82, 270–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becke, A.D. Density-functional thermochemistry. III. The role of exact exchange. J. Chem. Phys. 1993, 98, 5648–5652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisch, M.J.; Trucks, G.W.; Schlegel, H.B.; Scuseria, G.E.; Robb, M.A.; Cheeseman, J.R.; Scalmani, G.; Barone, V.; Petersson, G.A.; Nakatsuji, H.; et al. Gaussian 09; Gaussian, Inc.: Wallingford, CT, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Miertuš, S.; Scrocco, E.; Tomasi, J. Electrostatic interaction of a solute with a continuum. A direct utilizaion of AB initio molecular potentials for the prevision of solvent effects. Chem. Phys. 1981, 55, 117–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miertuš, S.; Tomasi, J. Approximate evaluations of the electrostatic free energy and internal energy changes in solution processes. Chem. Phys. 1982, 65, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascual-ahuir, J.L.; Silla, E.; Tuñon, I. GEPOL: An improved description of molecular surfaces. III. A new algorithm for the computation of a solvent-excluding surface. J. Comput. Chem. 1994, 15, 1127–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuman, P. Substituent Effects in Organic Polarography; Plenum Press: New York, NY, USA, 1967. [Google Scholar]
- Strier, M.P.; Cavagnol, J.C. The Polarography of Quinoxaline. II. 6-Substituted Derivatives. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1958, 80, 1565–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).