Assessing Antipsoriatic Effects of Bitter Pu’er Tea and Its Three Major Compounds, Strictinin, Theacrine and Epigallocatechin Gallate, in Imiquimod-Treated Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
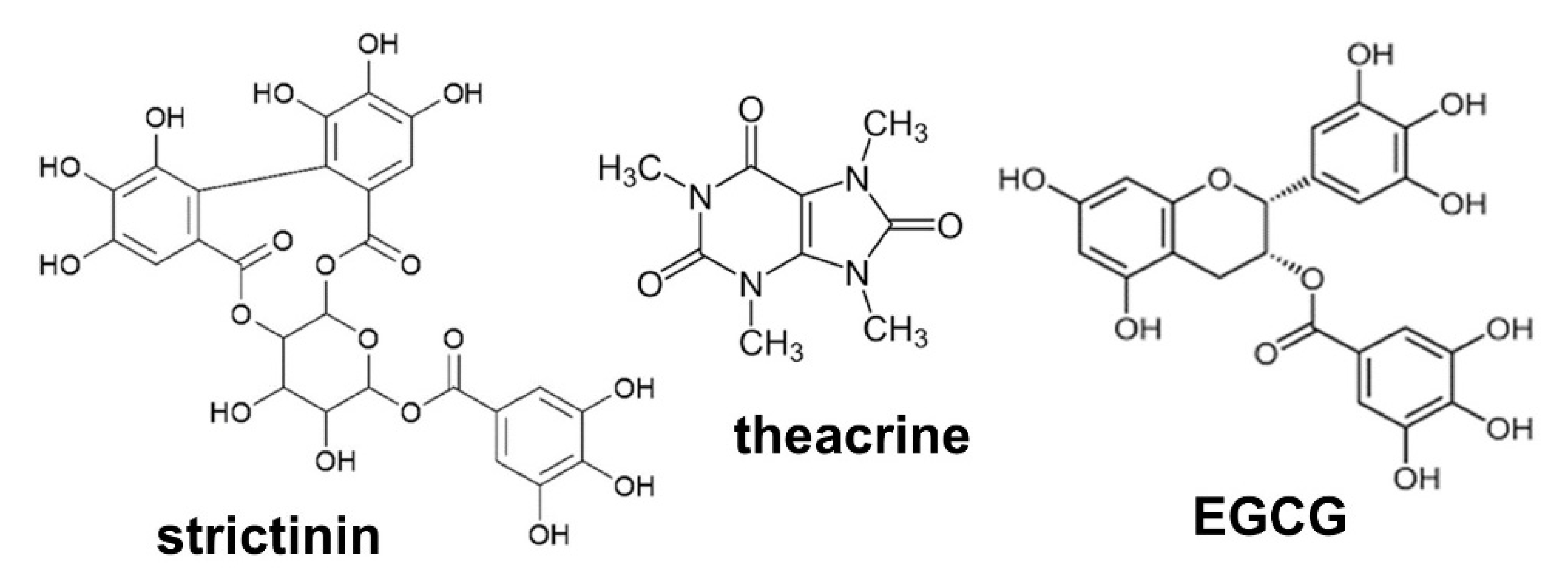
2.1. Chemicals and Materials
2.2. Animals and Experiment Design
2.3. Histological Analysis
2.4. Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR) Analysis
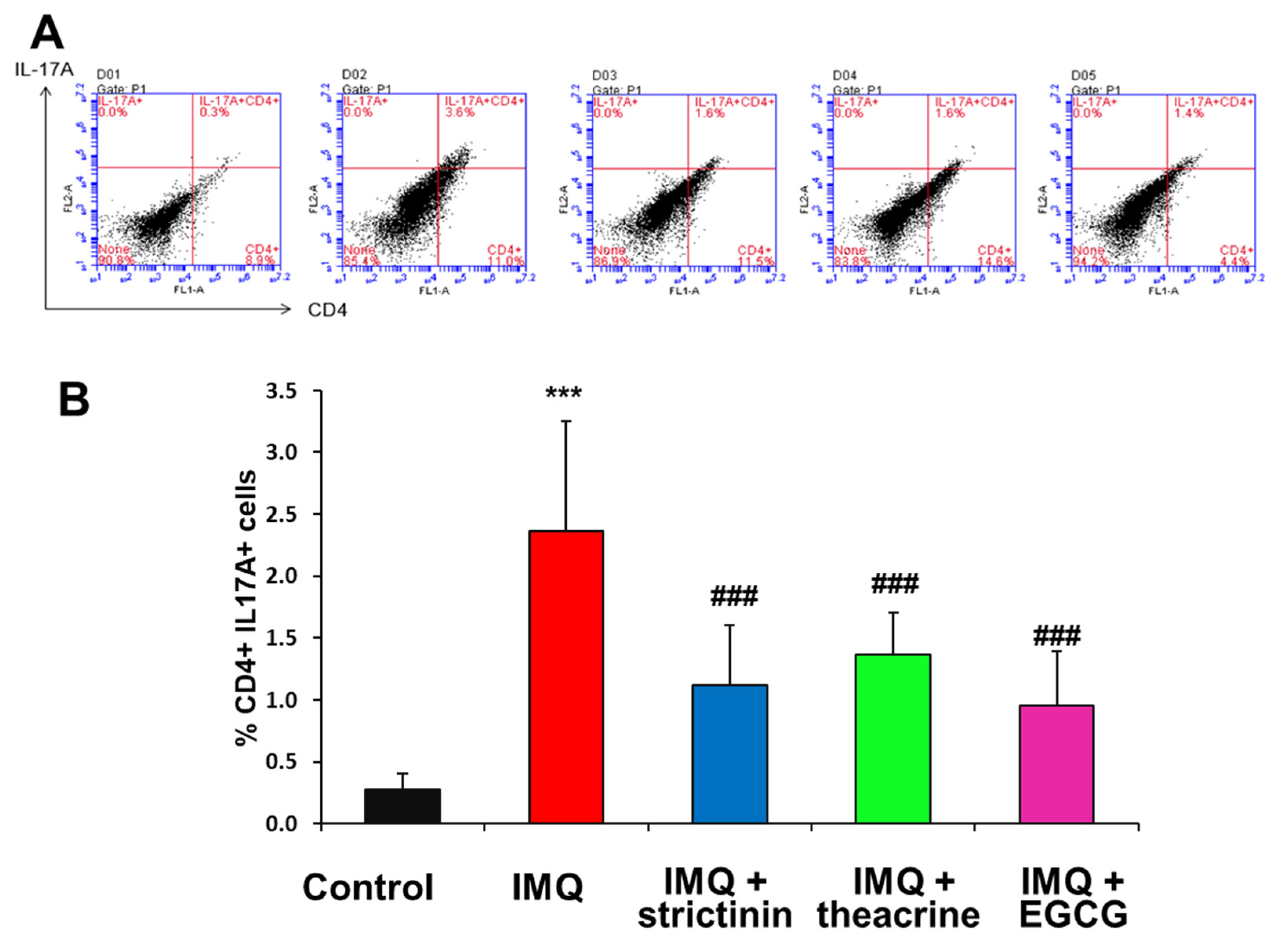
2.5. Flow Cytometric Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Effects of Bitter Pu’er Tea on Psoriasis-Like Dermatitis in IMQ-Treated Mice
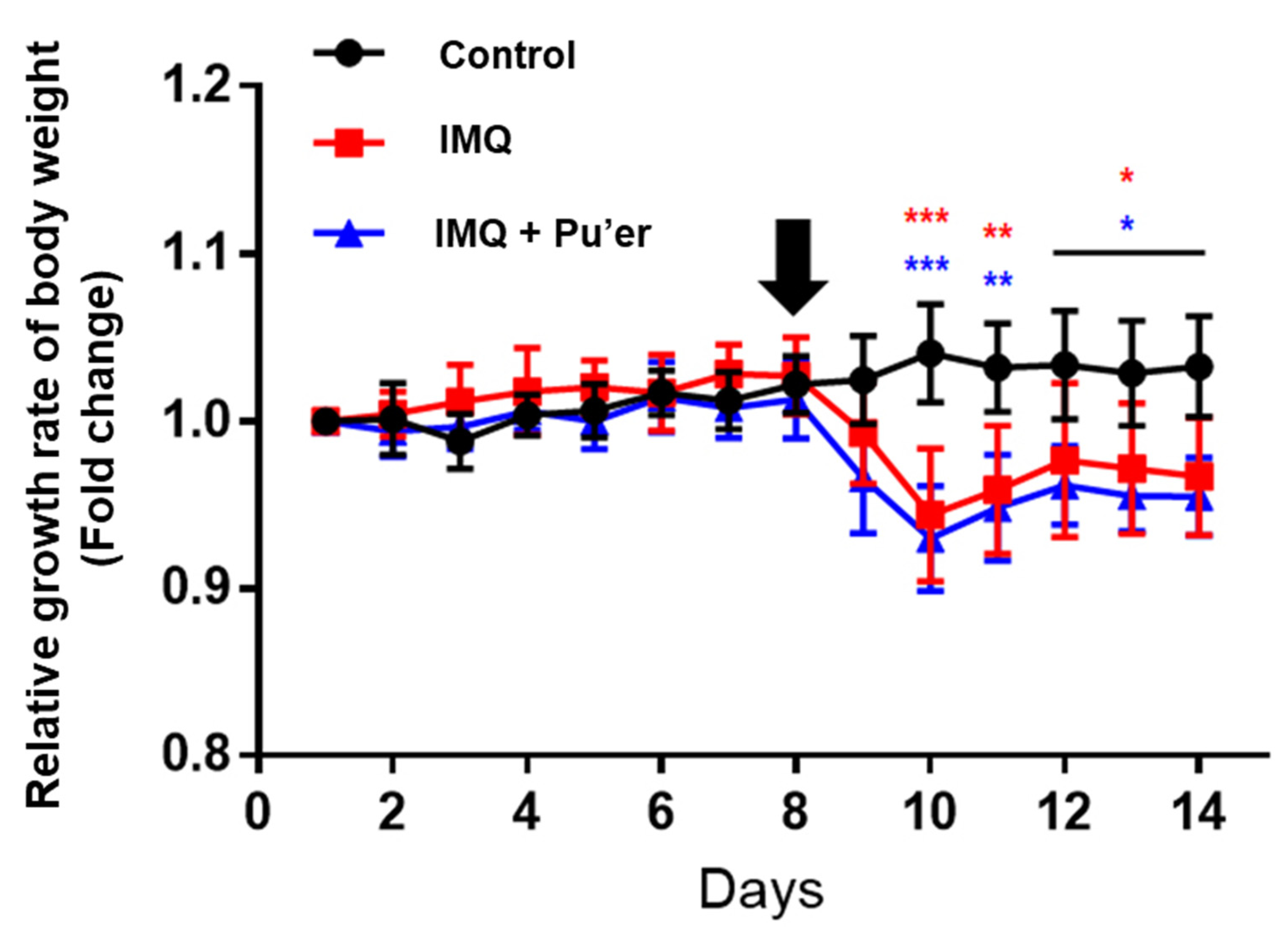
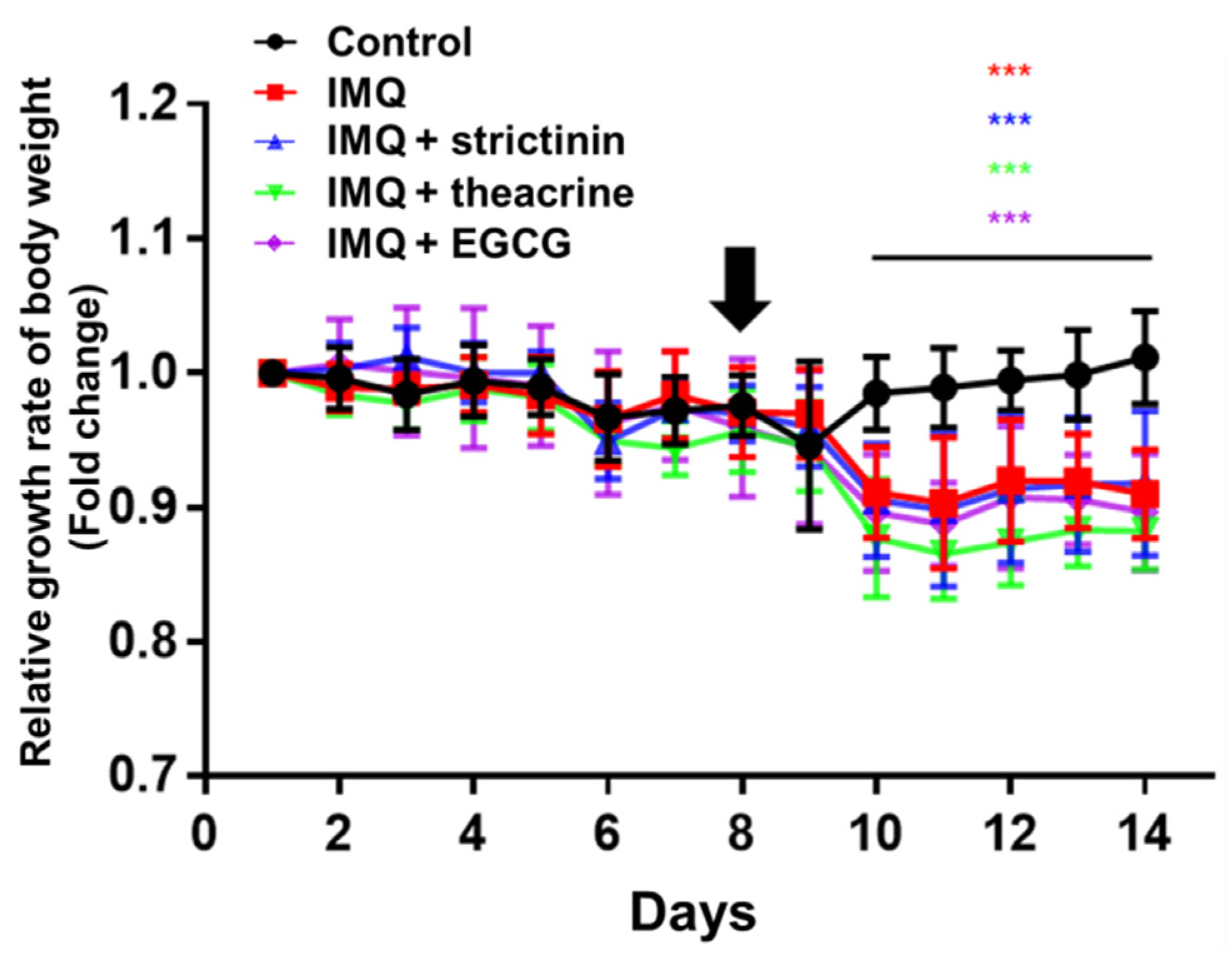
3.1.1. Effects on Body Weight of Mice after IMQ Treatment
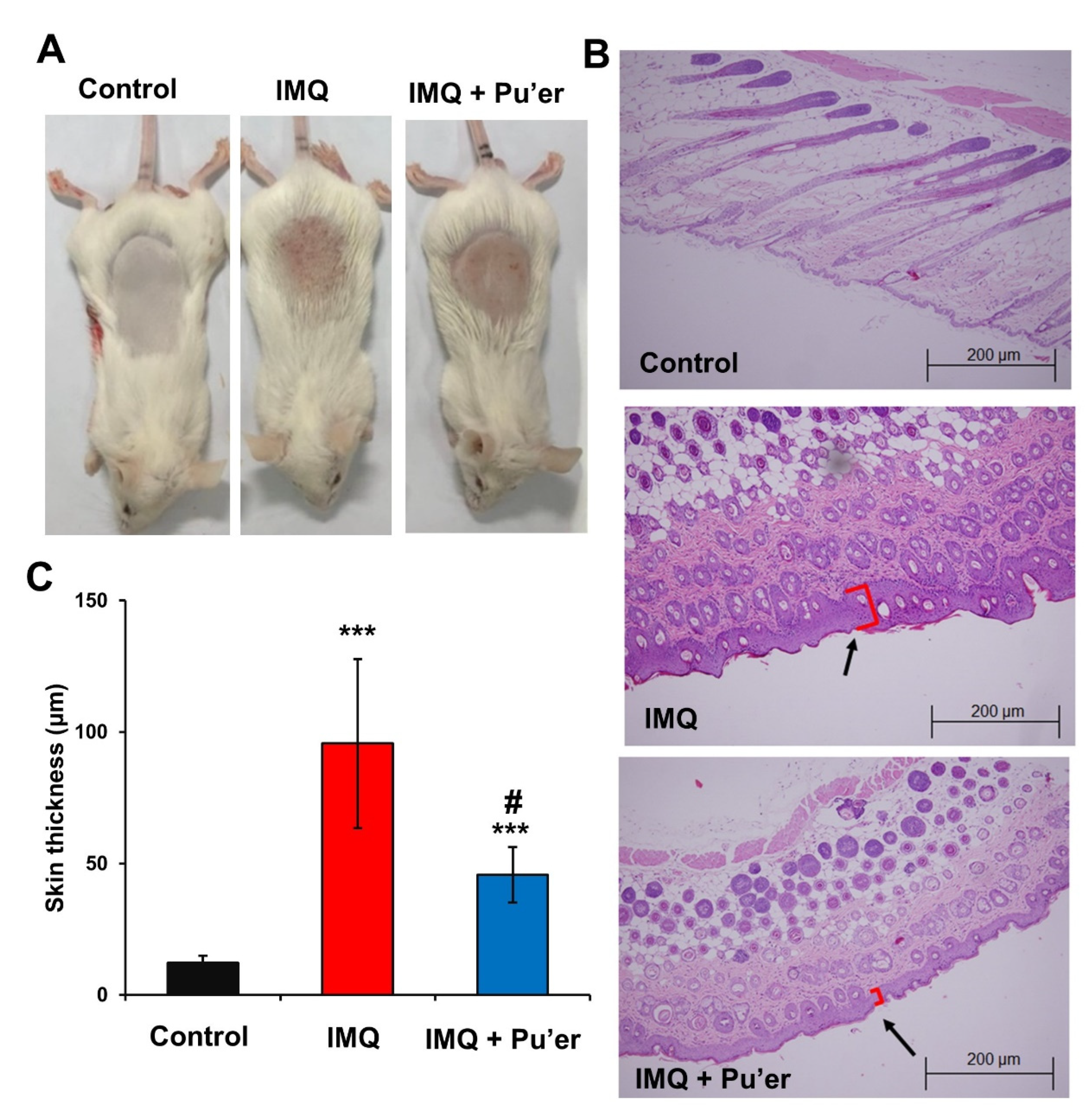
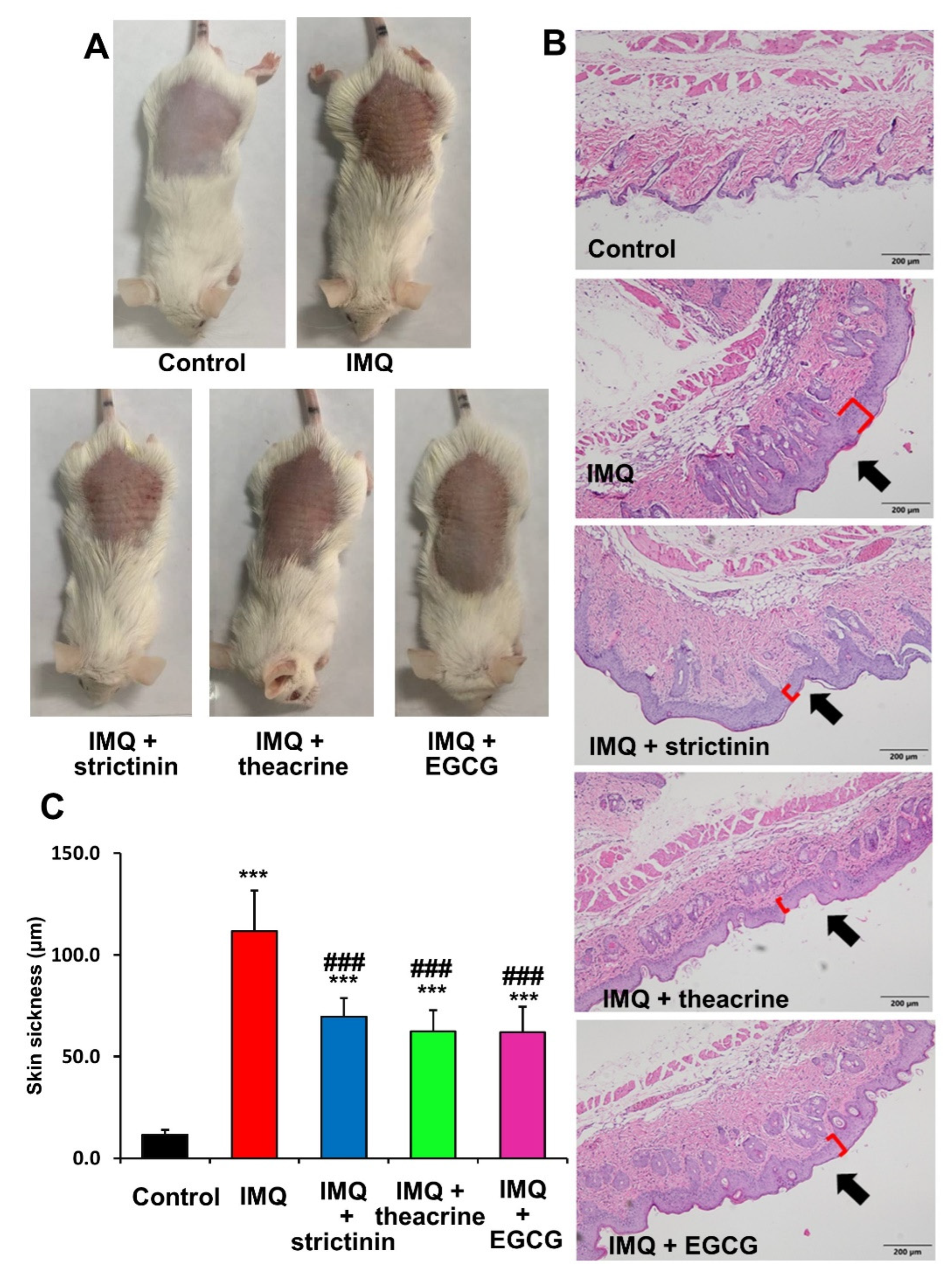
3.1.2. Reduction in Dorsal Skin Lesions in IMQ-Treated Mice by Bitter Pu’er Tea
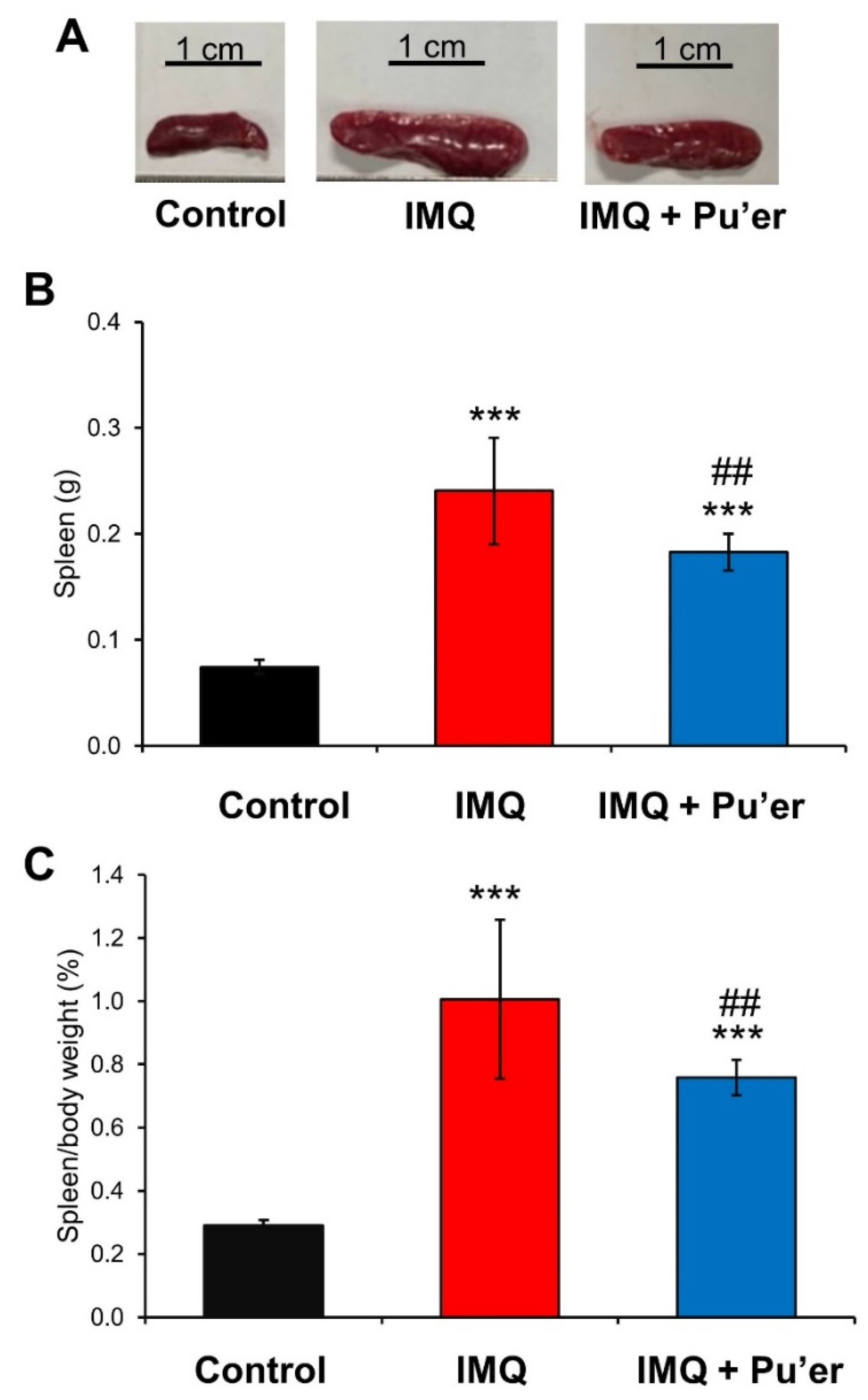
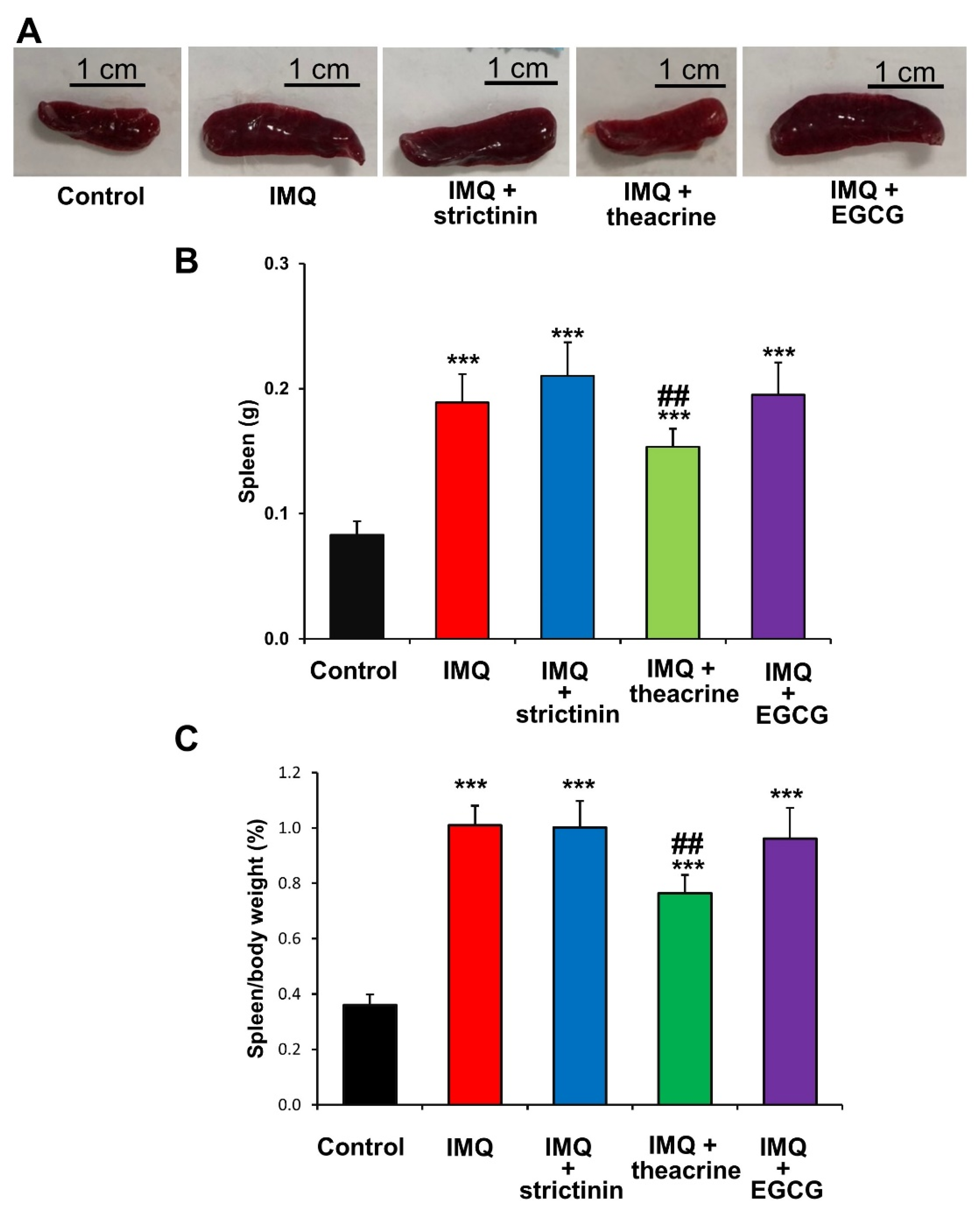
3.1.3. Attenuation of Splenomegaly in IMQ-Treated Mice by Bitter Pu’er Tea
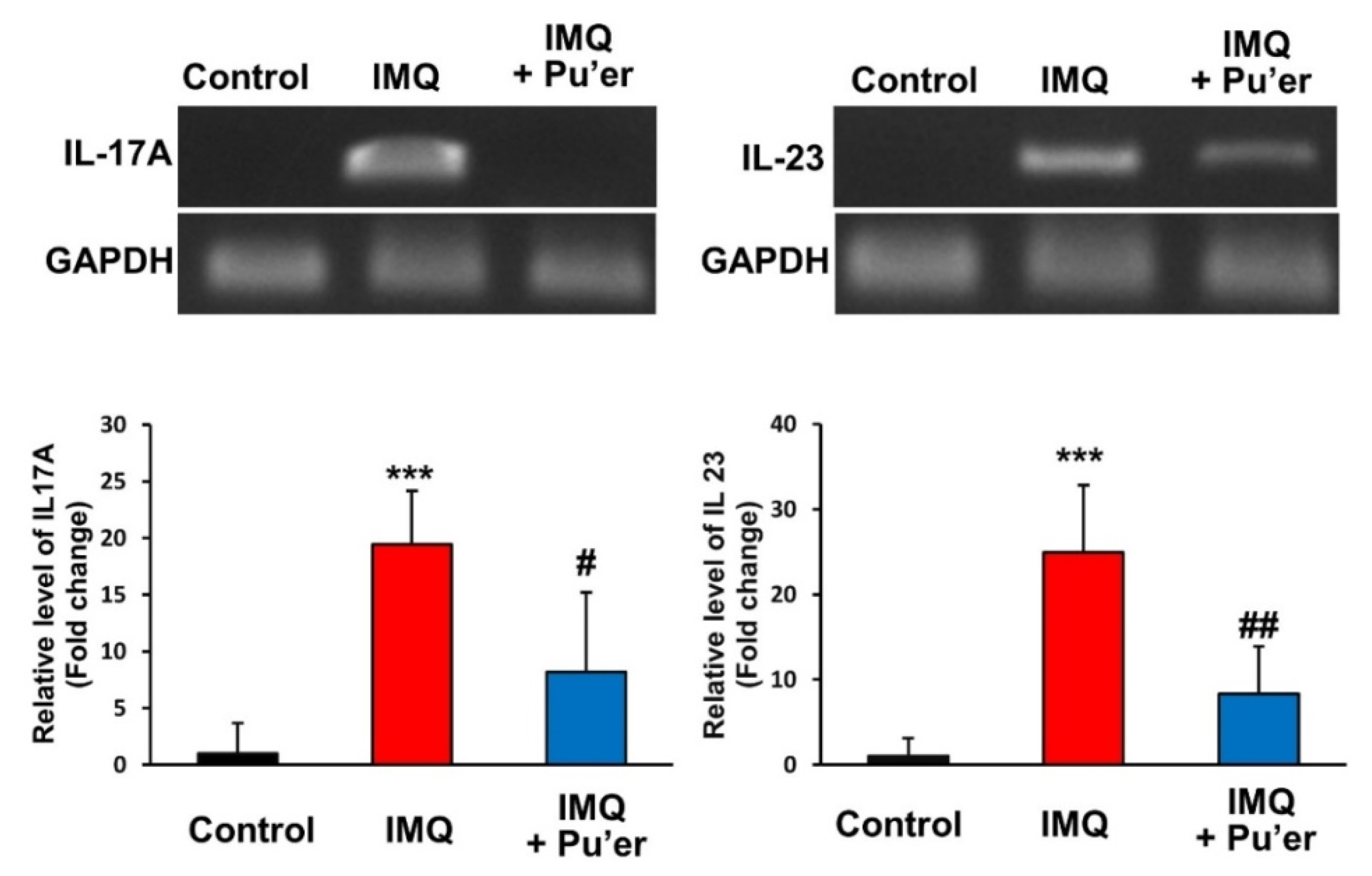
3.1.4. Effects of Bitter Pu’er Tea Supplementation on the mRNA Expression Levels of IL-17A and IL-23 in IMQ-Treated Mice
3.2. Effects of Strictinin, Theacrine and EGCG on Psoriasis-Like Dermatitis in IMQ-Treated Mice
3.2.1. Effects of Strictinin, Theacrine and EGCG on Body Weight of IMQ-Treated Mice
3.2.2. Effects of Strictinin, Theacrine and EGCG on Dorsal Skin Lesions of IMQ-Treated Mice
3.2.3. Effects of Strictinin, Theacrine and EGCG on Splenomegaly of IMQ-Treated Mice
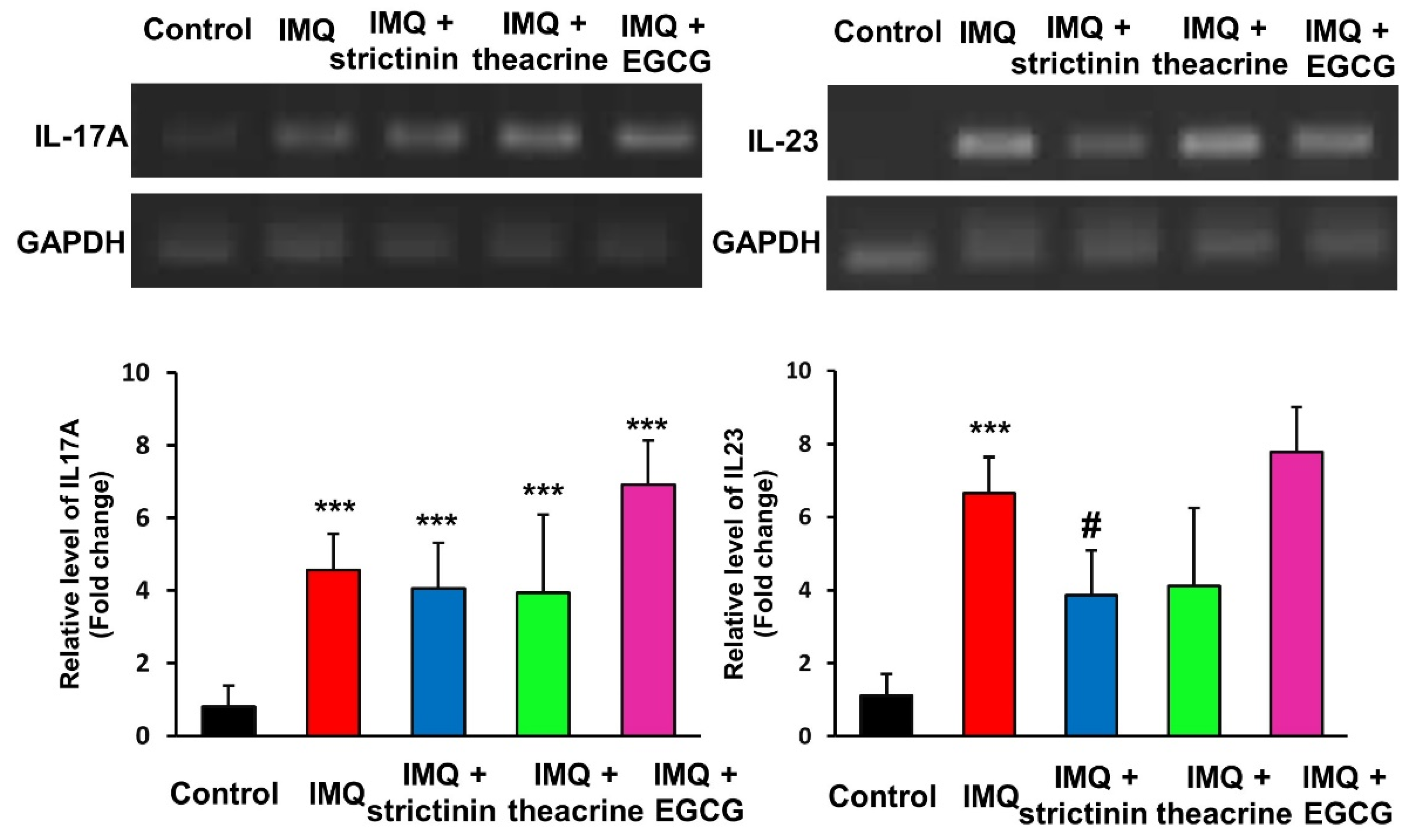
3.2.4. Effects of Strictinin, Theacrine and EGCG on the mRNA Expression Levels of IL-17A and IL-23 in IMQ-Treated Mice
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhong, L.; Luo, N.; Zhong, X.; Xu, T.; Hao, P. The immunoregulatory effects of natural products on psoriasis via its action on Th17 cells versus regulatory T cells balance. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2022, 110, 109032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nadeem, A.; Ahmad, S.F.; Al-Harbi, N.O.; Fardan, A.S.; El-Sherbeeny, A.M.; Ibrahim, K.E.; Attia, S.M. IL-17A causes depression-like symptoms via NFkappaB and p38MAPK signaling pathways in mice: Implications for psoriasis associated depression. Cytokine 2017, 97, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Cai, X.C.; Sun, X.Y.; Zhou, Y.Q.; Jin, M.Z.; Wang, J.; Ma, T.; Li, B.; Li, X. Global prevalence of metabolic syndrome in patients with psoriasis in the past two decades: Current evidence. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2022, 36, 1969–1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, J.; Zhu, Q.; Wang, S.; Li, X.; Sun, Z.; Li, N.; Feng, J.; Ding, H.; Dong, S.; Wang, H. Clinical efficacy and safety of using calcipotriol-betamethasone compounding agent for psoriasis treatment: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2022, 314, 633–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hari, G.; Kishore, A.; Karkala, S.R.P. Treatments for psoriasis: A journey from classical to advanced therapies. How far have we reached? Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2022, 929, 175147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diotallevi, F.; Paolinelli, M.; Radi, G.; Offidani, A. Latest Combination Therapies in Psoriasis: Narrative Review of The Literature. Dermatol Ther. 2022, 11, e15759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevagamoorthy, A.; Sockler, P.; Akoh, C.; Takeshita, J. Racial and ethnic diversity of us participants in clinical trials for acne, atopic dermatitis, and psoriasis: A comprehensive review. J. Dermatolog. Treat. 2022, 18, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Yang, X.Q.; Cheng, J.; Hui, R.S.; Gao, T.W. Increased Th17 cells are accompanied by FoxP3+ Treg cell accumulation and correlated with psoriasis disease severity. Clin. Immunol. 2010, 135, 108–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Awasthi, A.; Yosef, N.; Quintana, F.J.; Xiao, S.; Peters, A.; Wu, C.; Kleinewietfeld, M.; Kunder, S.; Hafler, D.A. Induction and molecular signature of pathogenic TH 17 cells. Nat. Immunol. 2012, 13, 991–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, T.C.; Hawkes, J.E.; Krueger, J.G. Interleukin 23 in the skin: Role in psoriasis pathogenesis and selective interleukin 23 blockade as treatment. Ther. Adv. Chronic Dis. 2018, 9, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunte, K.; Beikler, T. Th17 cells and the IL-23/IL-17 axis in the pathogenesis of periodontitis and immune-mediated inflammatory diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, S.; Ghilardi, N.; Xie, M.H.; de Sauvage, F.J.; Gurney, A.L. Interleukin-23 promotes a distinct CD4 T cell activation state characterized by the production of interleukin-17. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 1910–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imiquimod Topical. MedlinePlus. National Library of Medicine; January 2018. Available online: https://medlineplus.gov/druginfo/meds/a698010.html (accessed on 26 September 2022).
- Hemmi, H.; Kaisho, T.; Takeuchi, O.; Sato, S.; Sanjo, H.; Hoshino, K.; Horiuchi, T.; Tomizawa, H.; Takeda, K.; Akira, S. Small anti-viral compounds activate immune cells via the TLR7 MyD88-dependent signaling pathway. Nat. Immunol. 2002, 3, 196–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Fits, L.; Mourits, S.; Voerman, J.S.; Kant, M.; Boon, L.; Laman, J.D.; Cornelissen, F.; Mus, A.M.; Florencia, E.; Prens, E.P. Imiquimod-induced psoriasis-like skin inflammation in mice is mediated via the IL-23/IL-17 axis. J. Immunol. 2009, 182, 5836–5845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.H.; Lin, Y.L.; Hsu, W.L.; Hsieh, S.K.; Tzen, J.T.C. Significant elevation of antiviral activity of strictinin from Pu’er tea after thermal degradation to ellagic acid and gallic acid. J. Food Drug Anal. 2015, 23, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, P.R.; Kuo, P.C.; Li, Y.C.; Jhuo, C.F.; Hsu, W.L.; Tzen, J.T.C. Theacrine and strictinin, two major ingredients for the anti-influenza activity of Yunnan Kucha tea. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020, 262, 113190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.C.; Yen, G.C.; Wang, B.S.; Chiu, C.K.; Yen, W.J.; Chang, L.W.; Duh, P.D. Antimutagenic and antimicrobial activities of pu-erh tea. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2007, 40, 506–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Shao, W.; Xiao, R.; Xu, K.; Ma, Z.; Johnstone, B.H.; Du, Y. Pu-erh tea aqueous extracts lower atherosclerotic risk factors in a rat hyperlipidemia model. Exp. Gerontol. 2009, 44, 434–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Chiou, Y.S.; Pan, M.H.; Shahidi, F. Anti-inflammatory activity of lipophilic epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) derivatives in LPS-stimulated murine macrophages. Food Chem. 2012, 134, 742–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jhuo, C.F.; Hsu, Y.Y.; Chen, W.Y.; Tzen, J.T.C. Attenuation of tumor development in mammary carcinoma rats by theacrine, an antagonist of adenosine 2A receptor. Molecules 2021, 26, 7455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Liu, X.; Mei, L.; Wang, H.; Fang, F. Epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) inhibits imiquimod-induced psoriasis-like inflammation of BALB/c mice. BMC Complement Altern. Med. 2016, 16, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alashqar, M.B. Caffeine in the treatment of atopic dermatitis and psoriasis: A review. SKIN J. Cutan. Med. 2019, 3, 59–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Lu, C.; Liu, H.; Wang, M.; Zhao, H.; Yan, Y.; Han, L. Quercetin ameliorates imiquimod-induced psoriasis-like skin inflammation in mice via the NF-κB pathway. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2017, 48, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Liu, W.; Gao, S.; Mao, Y.; Xin, Y. Application of imiquimod-induced murine psoriasis model in evaluating interleukin-17A antagonist. BMC Immunol. 2021, 22, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardiff, R.D.; Miller, C.H.; Munn, R.J. Manual hematoxylin and eosin staining of mouse tissue sections. Cold Spring Harb. Protoc. 2014, 2014, 655–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.M.; Ma, M.; Li, H.; Qi, Q.; Liu, Y.T.; Yan, Y.X.; Shen, Y.F.; Yang, X.Q.; Zhu, F.H.; He, S.J. Topical administration of reversible SAHH inhibitor ameliorates imiquimod-induced psoriasis-like skin lesions in mice via suppression of TNF-α/IFN-γ-induced inflammatory response in keratinocytes and T cell-derived IL-17. Pharmacol. Res. 2018, 129, 443–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Zhong, D.; Chen, H.; Ma, S.; Sun, Y.; Wang, M.; Liu, Q.; Li, G. Pivotal role of cerebral interleukin-23 during immunologic injury in delayed cerebral ischemia in mice. Neuroscience 2015, 290, 321–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Sun, J.; Fan, X.; Guan, L.; Li, D.; Zhou, Y.; Zeng, X.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, H.; Xu, L. Schisandrol B promotes liver regeneration after partial hepatectomy in mice. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2018, 818, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.R.; Shi, Y.; Jiang, J.L.; Luo, L.Y.; Zeng, L. Discriminant analysis of Pu-erh tea of different raw materials based on phytochemicals using chemometrics. Foods 2022, 11, 680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feduccia, A.A.; Wang, Y.; Simms, J.A.; Henry, Y.Y.; Li, R.; Bjeldanes, L.; Ye, C.; Bartlett, S.E. Locomotor activation by theacrine, a purine alkaloid structurally similar to caffeine: Involvement of adenosine and dopamine receptors. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2012, 102, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vali, A.; Asilian, A.; Khalesi, E.; Khoddami, L.; Shahtalebi, M.; Mohammady, M. Evaluation of the efficacy of topical caffeine in the treatment of psoriasis vulgaris. J. Dermatolog. Treat. 2005, 16, 234–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voorhees, J.J.; Duell, E.A.; Bass, L.J.; Powell, J.A.; Harrell, E.R. Decreased cyclic AMP in the epidermis of lesions of psoriasis. Arch. Dermatol. 1972, 105, 695–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinno-Hashimoto, H.; Eguchi, A.; Sakamoto, A.; Wan, X.; Hashimoto, Y.; Fujita, Y.; Mori, C.; Hatano, M.; Matsue, H.; Hashimoto, K. Effects of splenectomy on skin inflammation and psoriasis-like phenotype of imiquimod-treated mice. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 1473835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyazawa, T. Absorption, metabolism and antioxidative effects of tea catechin in humans. Biofactors 2000, 13, 55–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Z.Y.; Li, X.M.; Liang, J.P.; Xiang, L.P.; Wang, K.R.; Shi, Y.L.; Yang, R.; Shi, M.; Ye, J.H.; Lu, J.L.; et al. Bioavailability of tea catechins and its improvement. Molecules 2018, 23, 2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Chen, P.; Lin, L.Z.; Yu, L.; Li, Z. Tentative identification, quantitation, and principal component analysis of green pu-erh, green, and white teas using UPLC/DAD/MS. Food Chem. 2011, 126, 1269.e77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitley, A.C.; Stoner, G.D.; Darby, M.V.; Walle, T. Intestinal epithelial cell accumulation of the cancer preventive polyphenol ellagic acid—Extensive binding to protein and DNA. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2003, 66, 907–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landete, J. Ellagitannins, ellagic acid and their derived metabolites: A review about source, metabolism, functions and health. Food Res. Int. 2011, 44, 1150–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornélio Favarin, D.; Martins Teixeira, M.; Lemos de Andrade, E.; de Freitas Alves, C.; Lazo Chica, J.E.; Artério Sorgi, C.; Faccioli, L.H.; Paula Rogerio, A. Anti-inflammatory effects of ellagic acid on acute lung injury induced by acid in mice. Mediators Inflamm. 2013, 2013, 164202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, P.-Y.; Jhuo, C.-F.; Lin, N.-H.; Chen, W.-Y.; Tzen, J.T.C. Assessing Antipsoriatic Effects of Bitter Pu’er Tea and Its Three Major Compounds, Strictinin, Theacrine and Epigallocatechin Gallate, in Imiquimod-Treated Mice. Compounds 2022, 2, 293-306. https://doi.org/10.3390/compounds2040024
Lin P-Y, Jhuo C-F, Lin N-H, Chen W-Y, Tzen JTC. Assessing Antipsoriatic Effects of Bitter Pu’er Tea and Its Three Major Compounds, Strictinin, Theacrine and Epigallocatechin Gallate, in Imiquimod-Treated Mice. Compounds. 2022; 2(4):293-306. https://doi.org/10.3390/compounds2040024
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Pei-Yi, Cian-Fen Jhuo, Nan-Hei Lin, Wen-Ying Chen, and Jason T. C. Tzen. 2022. "Assessing Antipsoriatic Effects of Bitter Pu’er Tea and Its Three Major Compounds, Strictinin, Theacrine and Epigallocatechin Gallate, in Imiquimod-Treated Mice" Compounds 2, no. 4: 293-306. https://doi.org/10.3390/compounds2040024
APA StyleLin, P.-Y., Jhuo, C.-F., Lin, N.-H., Chen, W.-Y., & Tzen, J. T. C. (2022). Assessing Antipsoriatic Effects of Bitter Pu’er Tea and Its Three Major Compounds, Strictinin, Theacrine and Epigallocatechin Gallate, in Imiquimod-Treated Mice. Compounds, 2(4), 293-306. https://doi.org/10.3390/compounds2040024






