Silver Nanoparticles for Conductive Inks Functionalization on Paper Substrates
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Geometrical Characterization of Silver Nanoparticles
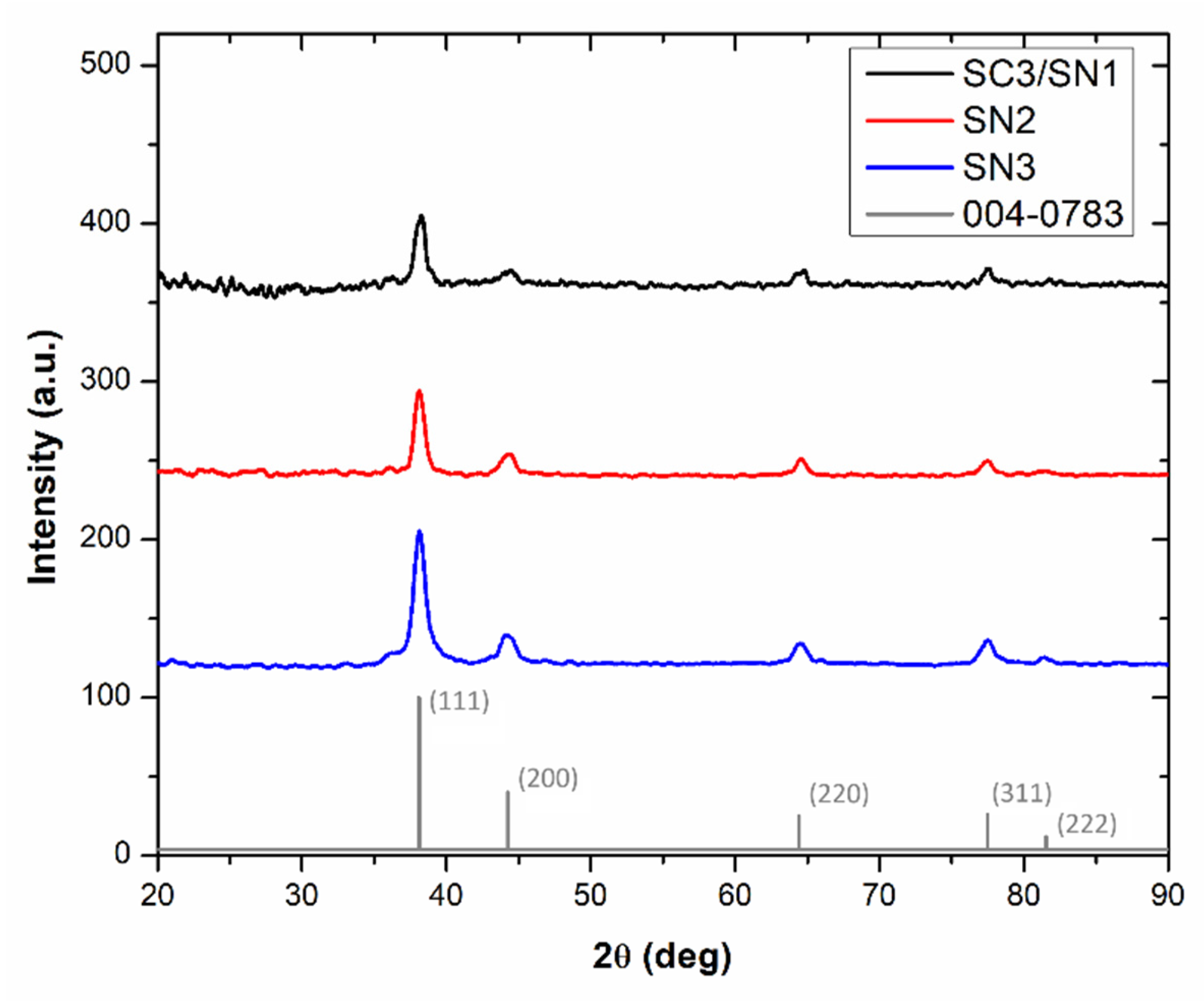
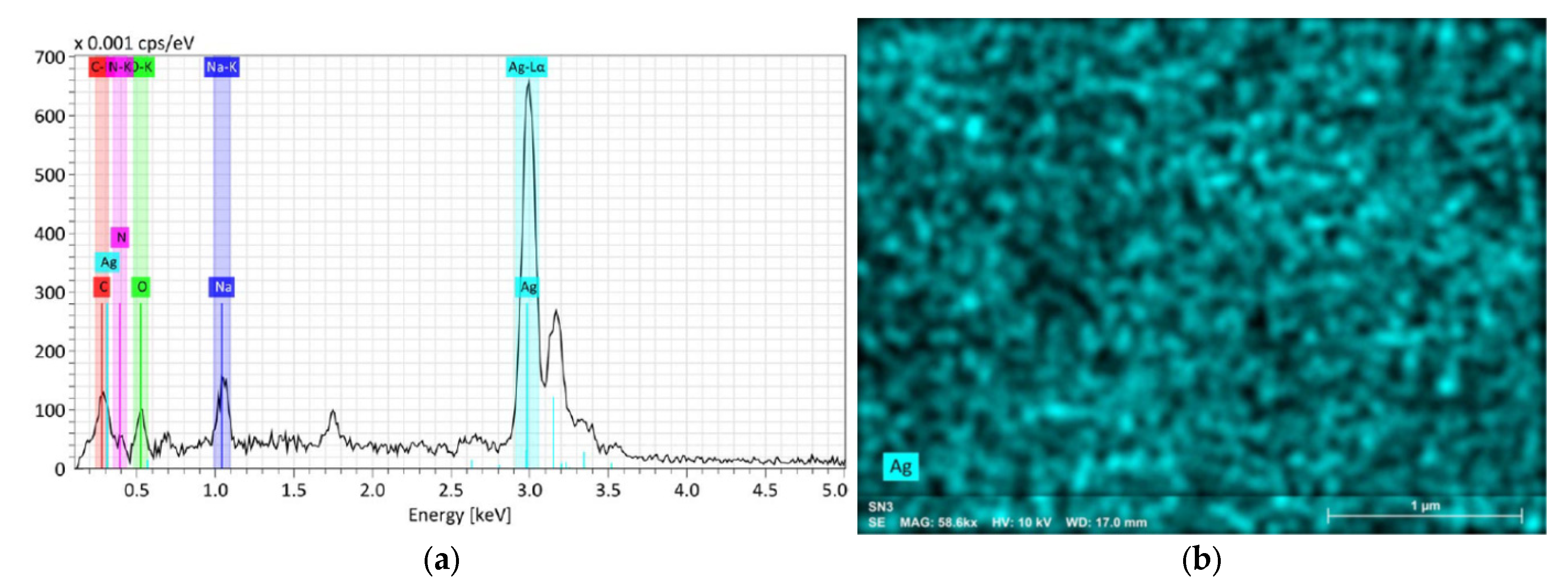
3.2. Chemical Composition Analyses
3.3. AgNPs Ink Density and Surface Morphology
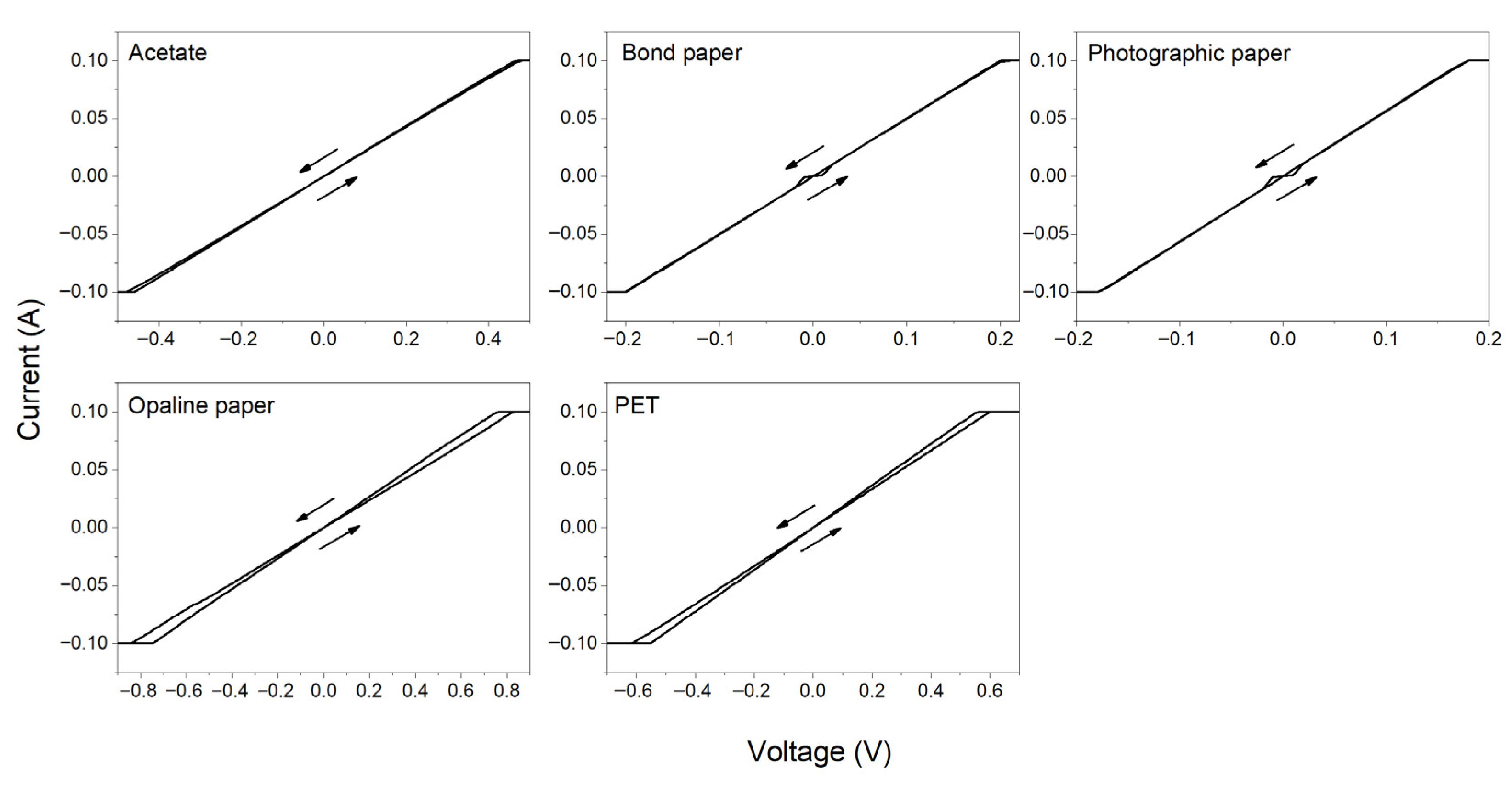
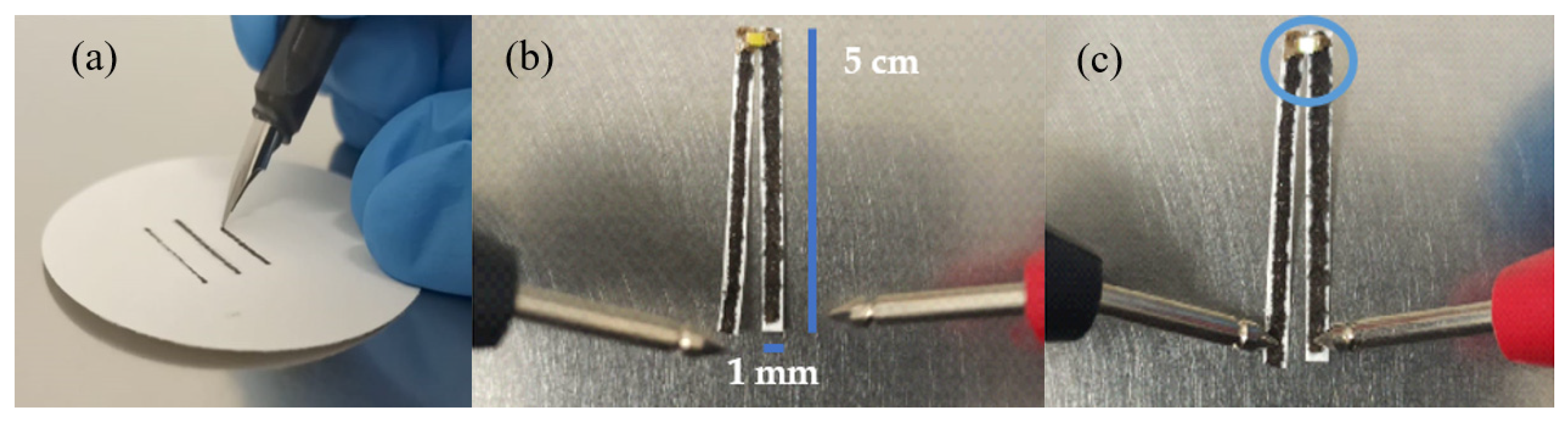
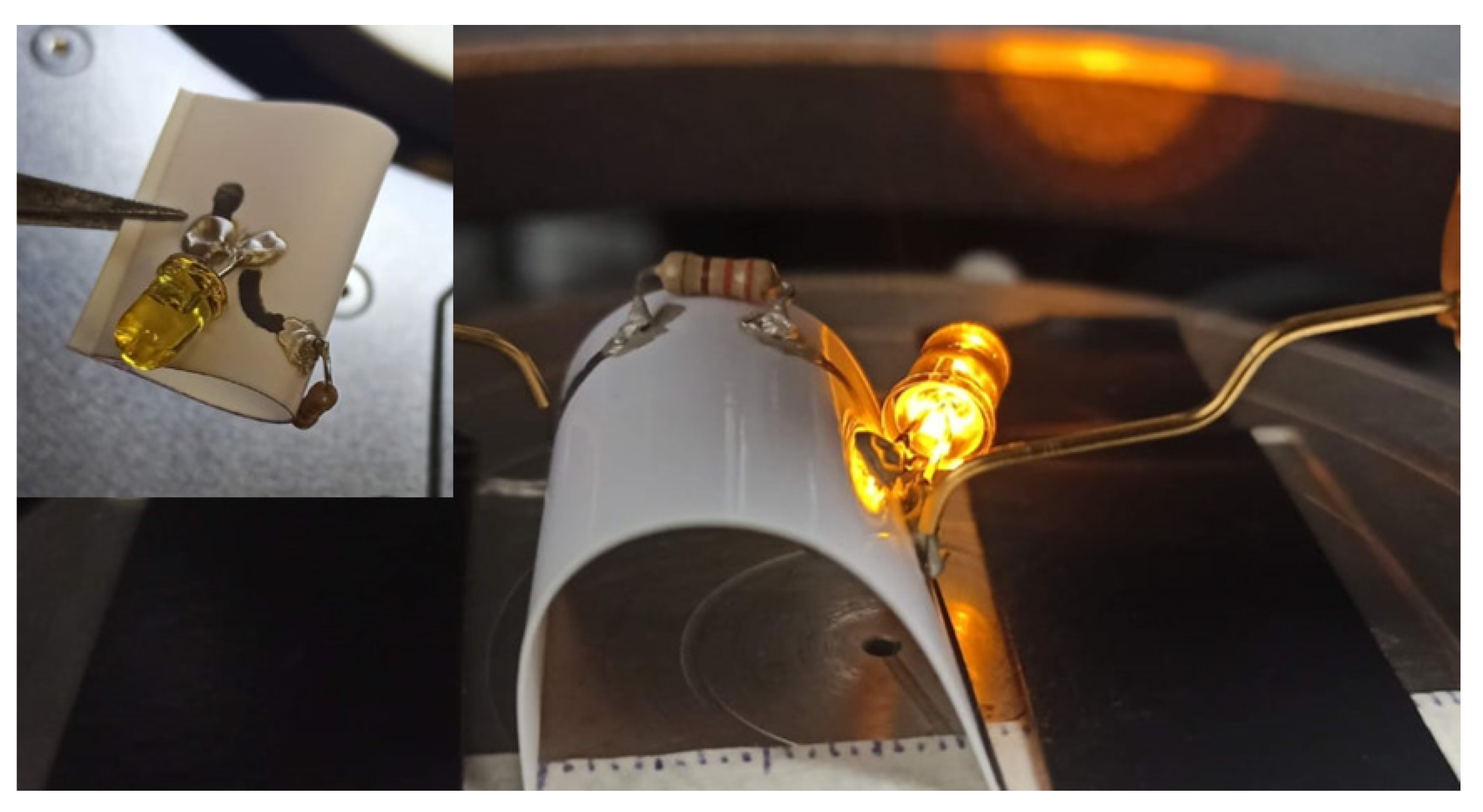
3.4. Electrical Measurements
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Williams, D.F.; Hemmati, S. An Overview of Silver Nanowire Polyol Synthesis Using Millifluidic Flow Reactors for Continuous Transparent Conductive Film Manufacturing by Direct Ink Writing. Nanomanufacturing 2025, 5, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, N.; Akindoyo, J.O.; Mariatti, M. Recent development in silver-based ink for flexible electronics. J. Sci. Adv. Mater. Devices 2022, 7, 100395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Shen, W.; Xu, Q.; Tan, R.; Song, W. Properties of polyacrylic acid-coated silver nanoparticle ink for inkjet printing conductive tracks on paper with high conductivity. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2014, 147, 550–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, I.J.; Aroche, A.F.; Schuck, A.; Lamberty, P.; Peter, C.R.; Hasenkamps, W.; Rocha, T.L.A.C. Silver nanoparticle conductive inks: Synthesis, characterization, and fabrication of inkjet-printed flexible electrodes. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 8878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawadi, S.; Katuwal, S.; Gupta, A.; Lamichhane, U.; Thapa, R.; Jaisi, S.; Lamichhane, G.; Bhattarai, D.P.; Parajuli, N. Current Research on Silver Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Characterization, and Applications. J. Nanomater. 2021, 2021, 6687290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Qiao, X.; Qiu, X. Synthesis and electrical properties of uniform silver nanoparticles for electronic applications. J. Mater. Sci. 2009, 44, 1076–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Yang, W.; Song, Y.; Shen, X.; Zhong, X.; Song, Y. A General Strategy for Nanohybrids Synthesis via Coupled Competitive Reactions Controlled in a Hybrid Process. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 9189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Guo, Q.; Dai, W.; Chen, J.L.; Mao, G.; Peng, Y.-K. Conductive Coatings on PDMS, PMMA, and Glass: Comparative Study of Graphene, Graphene Oxide, and Silver Nanoparticle Composites. Electrochem 2024, 5, 380–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sati, A.; Ranade, T.N.; Mali, S.N.; Ahmad Yasin, H.K.; Pratap, A. Silver Nanoparticles (AgNPs): Comprehensive Insights into Bio/Synthesis, Key Influencing Factors, Multifaceted Applications, and Toxicity—A 2024 Update. CS Omega 2025, 10, 7549–7582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velgosova, O.; Mačák, L.; Čižmárová, E.; Mára, V. Influence of Reagents on the Synthesis Process and Shape of Silver Nanoparticles. Materials 2022, 15, 6829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turkevich, J.; Stevenson, P.C.; Hillier, J. A study of the nucleation and growth processes in the synthesis of colloidal gold. Discuss. Faraday Soc. 1951, 11, 55–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinescu, L.; Ficai, D.; Ficai, A.; Oprea, O.; Nicoara, A.I.; Vasile, B.S.; Boanta, L.; Marin, A.; Andronescu, E.; Holban, A.-M. Comparative Antimicrobial Activity of Silver Nanoparticles Obtained by Wet Chemical Reduction and Solvothermal Methods. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Budlayan, M.L.; Lagare-Oracion, J.P.; Dela Rosa, L.; Rodriguez, M.J.; Capangpangan, R.Y.; Manigo, J.; Alguno, A.; Austria, E.; Arco, S.; Patricio, J. A Facile Route in Crontolling the Optical Absorbance of Polyvinylpyrrolidone-Capped Silver Nanoparticles Via Chemical Reduction Technique. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 925, 012050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velgosova, O.; Mačák, L.; Lisnichuk, M.; Vojtko, M. Synthesis and Analysis of Polymorphic Silver Nanoparticles and Their Incorporation into the Polymer Matrix. Polymers 2022, 14, 2666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S.A.; Das, S.S.; Khatoon, A.; Ansari, M.T.; Afzal, M.; Hasnain, M.S.; Nayak, A.K. Bactericidal activity of silver nanoparticles: A mechanical review. Mater. Sci. Energy Technol. 2020, 3, 756–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Reddy, G.B. Effect of atmospheric exposure on the growth of citrate-capped silver nanoparticles. Phys. E Low Dimens. Syst. Nanostruc. 2010, 42, 1940–1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Affonso de Oliveira, J.F.; Borba Cardoso, M. Partial aggregation of silver nanoparticles induced by capping and reducing agents competition. Langmuir 2013, 30, 4879–4886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Spina, R.; Mehn, D.; Fumagalli, F.; Holland, M.; Reniero, F.; Rossi, F.; Gilliland, D. Synthesis of Citrate-Stabilized Silver Nanoparticles Modified by Thermal and pH Preconditioned Tannic Acid. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Ji, X.; Jing, J.; Li, M.; Li, J.; Yang, W. Synthesis of Triangular Silver Nanoprisms by Stepwise Reduction of Sodium Borohydride and Trisodium Citrate. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 2070–2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zielińska, A.; Skwarek, E.; Zaleska, A.; Gazda, M.; Hupka, J. Preparation of silver nanoparticles with controlled particle size. Procedia Chem. 2009, 1, 1560–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, S.; Yu, Z.; Zhang, R.; Fan, B.; Wang, Q.; Guang, J.; Wang, S.; Zhang, X.; Hou, C.; Wang, C.; et al. Transformation of silver nanospheres into triangular nanoplates through a photoinduced process. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 2023, 27, 101610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaseen, M.; Akhter, Z.; Li, W.; Yarali, E.; Anthopoulos, T.D.; Shamim, A. High-conductivity screen-printable silver nanowire ink for optically transparent flexible radio frequency electronics. Flex. Print. Electron. 2022, 7, 044001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, M.A.; Kanwal, Z.; Rauf, A.; Sabri, A.N.; Riaz, S.; Naseem, S. Size-and Shape-Dependent Antibacterial Studies of Silver Nanoparticles Synthesized by Wet Chemical Routes. Nanomaterials 2016, 6, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monowar, T.; Rahman, S.; Bhore, S.J.; Raju, G.; Sathasivam, K.V. Silver Nanoparticles Synthesized by Using the Endophytic Bacterium Pantoea ananatis are Promising Antimicrobial Agents agains Multidrug Resistant Bacteria. Molecules 2018, 23, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kora, A.J.; Manjusha, R.; Arunachalam, J. Superior bactericidal activity of SDS capped silver nanoparticles: Synthesis and characterization. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2009, 29, 2104–2109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ImageJ. Image Processing and Analysis in Java. Available online: https://imagej.net/ij/ (accessed on 30 April 2024).
- Wu, W.; Wang, Z.; Jiang, P.; Tang, Z. Effect of Electroplating Variables on Electrodeposition of Ni Rich Ni-Ir Alloys from Citrate Aqueous Solutions. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2017, 164, D985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharjee, S. DLS and zeta potential—What they are and what they are not? J. Control. Release 2016, 235, 337–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, V.; Trivedi, P. Chapter 15—In vitro and in vivo characterization of pharmaceutical topical nanocarriers containing anticancer drugs for skin cancer treatment. In Lipid Nanocarriers for Drug Targeting; Grumezescu, A.M., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 563–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raval, N.; Maheshwari, R.; Kalyane, D.; Youngren-Ortiz, S.R.; Chougule, M.B.; Tekade, R.K. Chapter 10—Importance of Physicochemical Characterization of Nanoparticles in Pharmaceutical Product Development. In Basic Fundamentals of Drug Delivery; Advances in Pharmaceutical Product Development and Research; Takade, R.K., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; pp. 369–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vokhidova, N.R.; Rashidova, S.S. The influence of synthesis conditions on the film morphology of chitosan-stabilized silver nanoparticles. Polym. Bull. 2022, 79, 3419–3436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shikha, S.; Dureja, S.; Sapra, R.; Babu, J.; Haridas, V.; Pattanayek, S.K. Interaction of borohydride stabilized silver nanoparticles with sulfer-containing organophosphates. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 32286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gakiya-Teruya, M.; Palomino-Marcelo, L.; Rodriguez-Reyes, J.C.F. Synthesis of Highly Concentrated Suspensions of Silver Nanoparticles by Two Versions of the Chemical Reduction Method. Methods Protoc. 2019, 2, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, A.; Murray, S.; Bell, S.E.J. Simple preparation of positively charged silver nanoparticles for detection of anions by surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Analyst 2015, 140, 2988–2994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ider, M.; Abderrafi, K.; Eddahbi, A.; Ouaskit, S.; Kassiba, A. Silver Metallic Nanoparticles with Surface Plasmon Resonance: Synthesis and Characterizations. J. Clust. Sci. 2017, 28, 1051–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El-Aziz, S.M.; Farahat, E.A. The Activity of Vossia cuspidata Polysaccharides-Derived Monometallic CuO, Ag, Au, and Trimetallic CuO-Ag-Au Na noparticles Against Cancer, Inflammation, and Wound Healing. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 2023, 33, 853–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Lei, Z.; Zhao, M.; Si, P. Facile macro fabrication of ultra-fine, ultra-long silver nanowire and growth mechanism. Synth. Met. 2023, 292, 117244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutus, B.; Dudás, C.; Friesen, S.; Peintler, G.; Pálinkó, I.; Sipos, P.; Buchner, R. Equilibria and Dynamics of Sodium Citrate Aqueous Solutions: The Hydration of Citrate and Formation of the Na3Cit0 Ion Aggregate. J. Phys. Chem. B 2020, 124, 9604–9614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, C.-t.F.; Karan, K.; Davis, B.R. Kinetic Studies of Reaction between Sodium Borohydride and Methanol, Water, and Their Mixtures. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2007, 46, 5478–5484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrad, M.; Aliyeva, M.; Martins, M.A.R.; Thomsen, K.; Pinho, S.P. Thermodynamic description of aqueous solutions of silver nitrate: Experimental and modeling. Fluid Phase Equilib. 2025, 597, 114459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janz, G.J.; Lakshminarayanan, G.R.; Klotzkin, M.P.; Mayer, G.E. Diffusion of Silver Nitrate in Concentrated Aqueous Solutions. J. Phys. Chem. 1966, 70, 536–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.-f.; Yu, S.-j.; Yin, Y.-g.; Chao, J.-b. Methods for separation, identification, characterization and quantification of silver nanoparticles. Trends. Analyt. Chem. 2012, 33, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, R.; Mankad, V.; Gupta, S.K.; Jha, P.K. Size Distribution of Silver Nanoparticles: UV-Visible Spectroscopic Assessment. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. Lett. 2012, 4, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, R.B.; Chougale, A.D. Analytical methods for the identification and characterization of silver nanoparticles: A brief review. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 47, 5520–5532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semchuk, O.Y.; Biliuk, A.A.; Havryliuk, O.O.; Biliuk, A.I. Kinetic theory of electroconductivity of metal nanoparticles in the condition of surface plasmon resonance. Appl. Surf. Sci. Adv. 2021, 3, 100057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintero-Quiroz, C.; Acevedo, N.; Zapata-Giraldo, J.; Botero, L.E.; Quintero, J.; Zárate-Triviño, D.; Saldarriaga, J.; Pérez, V.Z. Optimization of silver nanoparticle synthesis by chemical reduction and evaluation of its antimicrobial and toxic activity. Biomater. Res. 2019, 23, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, A.E.F.; Pereira, A.C.; Asevedo Campos de Resende, M.; Franco Ferreira, L. Synthesis of a silver nanoparticles ink for fabrication of reference electrodes. Talanta Open 2022, 5, 100085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agnihotri, S.; Mukherji, S.; Mukherji, S. Size-controlled silver nanoparticles synthesized over the range 5–100 nm using the same protocol and their antibacterial efficacy. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 3974–3983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, A.; Qian, H.; Chen, H.; Anker, J.N. One-pot hydrothermal synthesis of silver nanowires via citrate reduction. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 352, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranoszek-Soliwoda, K.; Tomaszewska, E.; Socha, E.; Krzyczmonik, P.; Ignaczak, A.; Orlowski, P.; Krzyzowska, M.; Celichowski, G.; Grobelny, J. The role of tannic acid and sodium citrate in the synthesis of silver nanoparticles. J. Nanopart. Res. 2017, 19, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piñero, S.; Camero, S.; Blanco, S. Silver nanoparticles: Influence of the temperature synthesis on the particles morphology. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2017, 786, 012020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, K.C.; Lee, S.M.; Park, T.S.; Lee, B.S. Preparation of colloidal silver nanoparticles by chemical reduction method. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2009, 26, 153–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smitha, S.L.; Nissamudeen, K.M.; Philip, D.; Gopchandran, K.G. Studies on surface plasmon resonance and photoluminescence of silver nanoparticles. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2008, 71, 186–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krukowski, S.; Karasiewicz, M.; Kolodziejski, W. Convenient UV-spectrophotometric determination of citrates in aqueous solutions with applications in the pharmaceutical analysis of oral electrolyte formulations. J. Food Drug Anal. 2017, 25, 717–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Indana, M.K.; Gangapuram, B.R.; Dadigala, R.; Bandi, R.; Guttena, V. A novel green synthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticles using gum tragacanth and evaluation of their potential catalytic reduction activities with methylene blue and Congo red. J. Anal. Sci. Technol. 2016, 7, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, A.; Paul, A.; Chattopadhyay, A. The effect of temperature on the aggregation kinetics of partially bare gold nanoparticles. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 82138–82149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afshinnia, K.; Baalousha, M. Effect of phosphate buffer on aggregation kinetics of citrate-coated silver nanoparticles induced by monovalent and divalent electrolytes. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 581–582, 268–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, W.; Zhang, X.; Huang, Q.; Xu, Q.; Song, W. Preparation of solid silver nanoparticles for inkjet printed flexible electronics with high conductivity. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 1622–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grabill, C.N.; Freppon, D.; Hettinger, M.; Kuebler, S.M. Nanoscale morphology of electrolessly deposited silver metal. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 466, 230–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceran, Ö.B.; Şimşek, B.; Doruk, S.; Uygunoğlu, T.; Şara, O.N. Effects of dispersed and powdered silver nanoparticles on the mechanical, thermal, electrical and durability properties of cementitious composites. Constr. Build Mater. 2019, 222, 152–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhao, X.L.T.; Hu, Y.; Zhu, P.; Sun, R. Facile synthesis of monodisperse silver nanoparticles for screen printing conductive inks. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2017, 28, 16939–16947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, F.; Razwan, M.; Shabbir, S. Microstructure and Resistivity Analysis of Silver Nanoparticle-Based Crystalline Conductive Films Synthesized using PEG Surfactant. Processes 2019, 7, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhadra, J.; Al-Thani, N.J.; Karmakar, S.; Madi, N.K. Photo-reduced route of polyaniline nanofiber synthesis with embedded silver nanoparticles. Arab. J. Chem. 2019, 12, 4848–4860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.-Y.; Ren, X.-L.; Zheng, M.-L.; Jin, F.; Liu, J.; Dong, X.-Z.; Zhao, Z.-S.; Duan, X.-M. Plasmon-enhanced nanosoldering of silver nanoparticles for high-conductive nanowires electrodes. Opto Electron. Adv. 2021, 4, 200101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chettri, P.; Tripathi, A.; Tiwari, A. Effect of silver nanoparticles on electrical and magnetic properties of reduced graphene oxide. Mater. Res. Bull. 2022, 150, 111752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Männl, U.; van den Berg, C.; Magunje, B.; Härting, M.; Britton, D.T.; Jones, S.; van Staden, M.J.; Scriba, M.R. Nanoparticle composites for printed electronics. Nanotechnology 2014, 25, 094004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominguez, M.; Sosa, J. Copper phthalocyanine buffer interlayer film incorporated in paper substrates for printed circuit boards and dielectric applications in flexible electronics. Solid State Electron. 2020, 172, 107898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedrosa, J.F.S.; Alves, L.; Neto, C.P.; Rasteiro, M.G.; Ferreira, P.J.T. Assessment of the Performance of Cationic Cellulose Derivatives as Calcium Carbonate Flocculant for Papermaking. Polymers 2022, 14, 3309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasmee, S.; Omar, G.; Masripan, N.A.B.; Kamarolzaman, A.A.; Ashikin, A.S.; Che Ani, F. Hydrophobicity performance of polyethylene terephthalate (PET) and thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU) with thermal effect. Mater. Res. Express 2018, 5, 096304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silver Nanoparticle Ink. Available online: https://www.sigmaaldrich.com/CA/en/product/aldrich/798738?srsltid=AfmBOorU4Qo-Lq6LYVYUdyRBCASjh46s6iT7Jj-nLsIsV03ecwJaft_mYiI (accessed on 16 September 2025).
- Conductive Ink Silver-Based. Available online: https://caig.com/product/circuitwritertm-pen-cw100p/ (accessed on 16 September 2025).
- Conductive Silver Printing Ink. Available online: https://www.sigmaaldrich.com/CA/en/product/aldrich/791881?srsltid=AfmBOooBnLce0N3RCWVodZQ0rdRv-DEKRzAB6ECxZkZokcgSZkGzcM381t8 (accessed on 16 September 2025).
- Silver Nanoparticles Ink for Inkjet Printing. Available online: https://www.sigmaaldrich.com/CA/en/product/aldrich/901083?srsltid=AfmBOoqEq5L0qXHyS3piA9rWbZg4E6dXMqJy3k6cfspZPSBTUZeb-KwsL8 (accessed on 16 September 2025).
- Silver Nanoparticles Ink. Available online: https://www.sigmaaldrich.com/CA/en/product/aldrich/796042?srsltid=AfmBOoohu5ieGSeMrTuBnczdD7twtahYUc5J_YE2cTzh5McU-7PcXUYMGQ (accessed on 16 September 2025).
- Gao, H.; Liao, Y.Q.; Wang, Y.Y.; Zhu, J.; Liu, P.; Ding, R.; Guo, D.M.; Wang, F.; Song, F.; Wang, Y. Conductive Superhydrophobic Smart Coatings Based on Speherical Silver Nanoparticles and Waterbone Polyurethane for Flexible and Wearable. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 16, 65553–65564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russo, A.; Ahn, B.Y.; Adams, J.J.; Duoss, E.B.; Bernhard, J.T.; Lewis, J.A. Pen-on-Paper Flexible Electronics. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 3426–3430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naderi-Samani, E.; Razavi, R.S.; Nekouee, K.; Naderi-Samani, H. Synthesis of silver nanoparticles for use in conductive inks by Chemical reduction method. Heliyon 2023, 9, e20548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iram, N.; Khan, S.N.; Ahmed, M.; Mir, A.; Anwar, N.; Naeem, M.; Nguyen, V.H.; Pham, P.V. Synthesis and characterizations of silver nanoparticles-based conductive ink for high-frequency electronics. Phys. Scr. 2024, 99, 0589a8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.J.; Jong-Man, K.; Jaworski, J. Progression in the Fountain Pen Approach: From 2D Writing to 3D Free-Form Micro/Nanofabrication. Small 2017, 13, 1600137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceron, S.; Barba, D.; Dominguez, M.A. Solution-Processable and Eco-Friendly Functionalization of Conductive Silver Nanoparticles Inks for Printable Electronics. Electron. Mater. 2024, 5, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
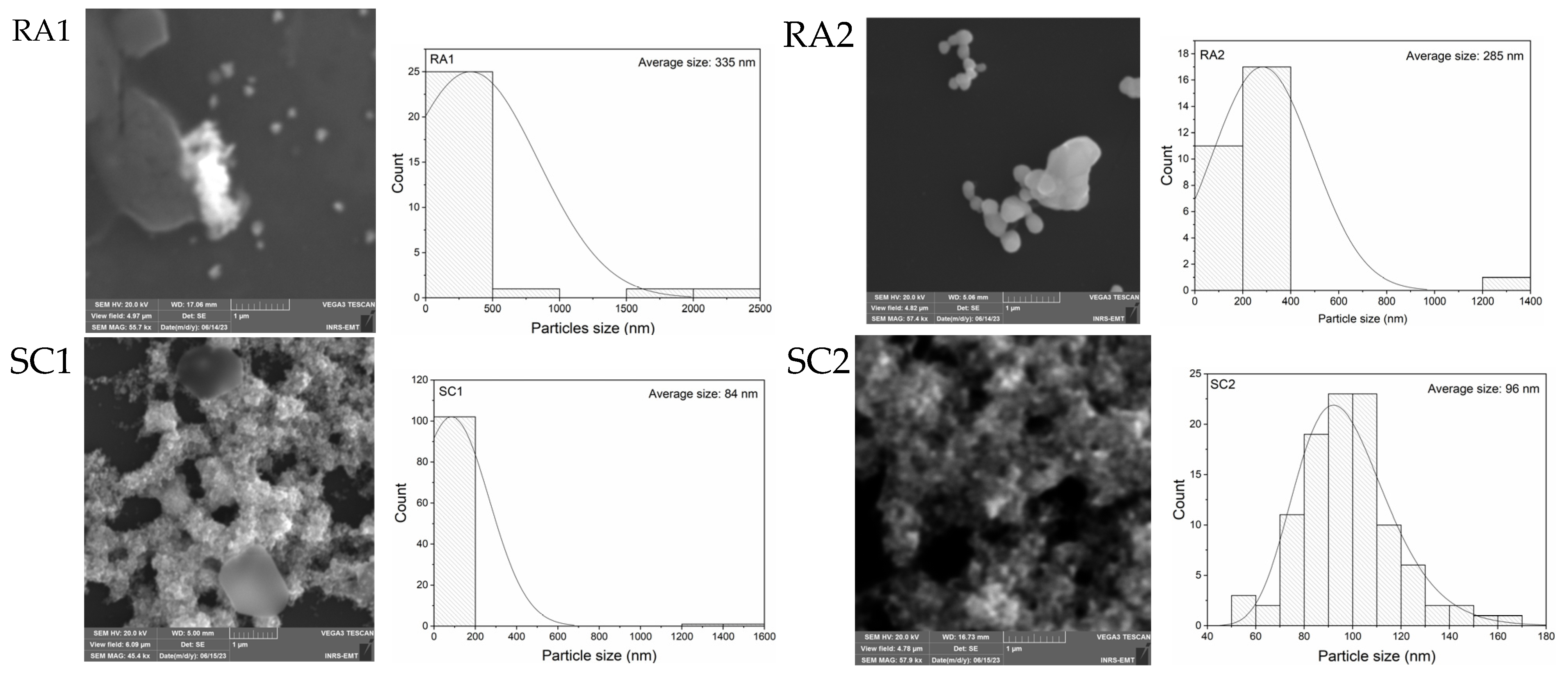
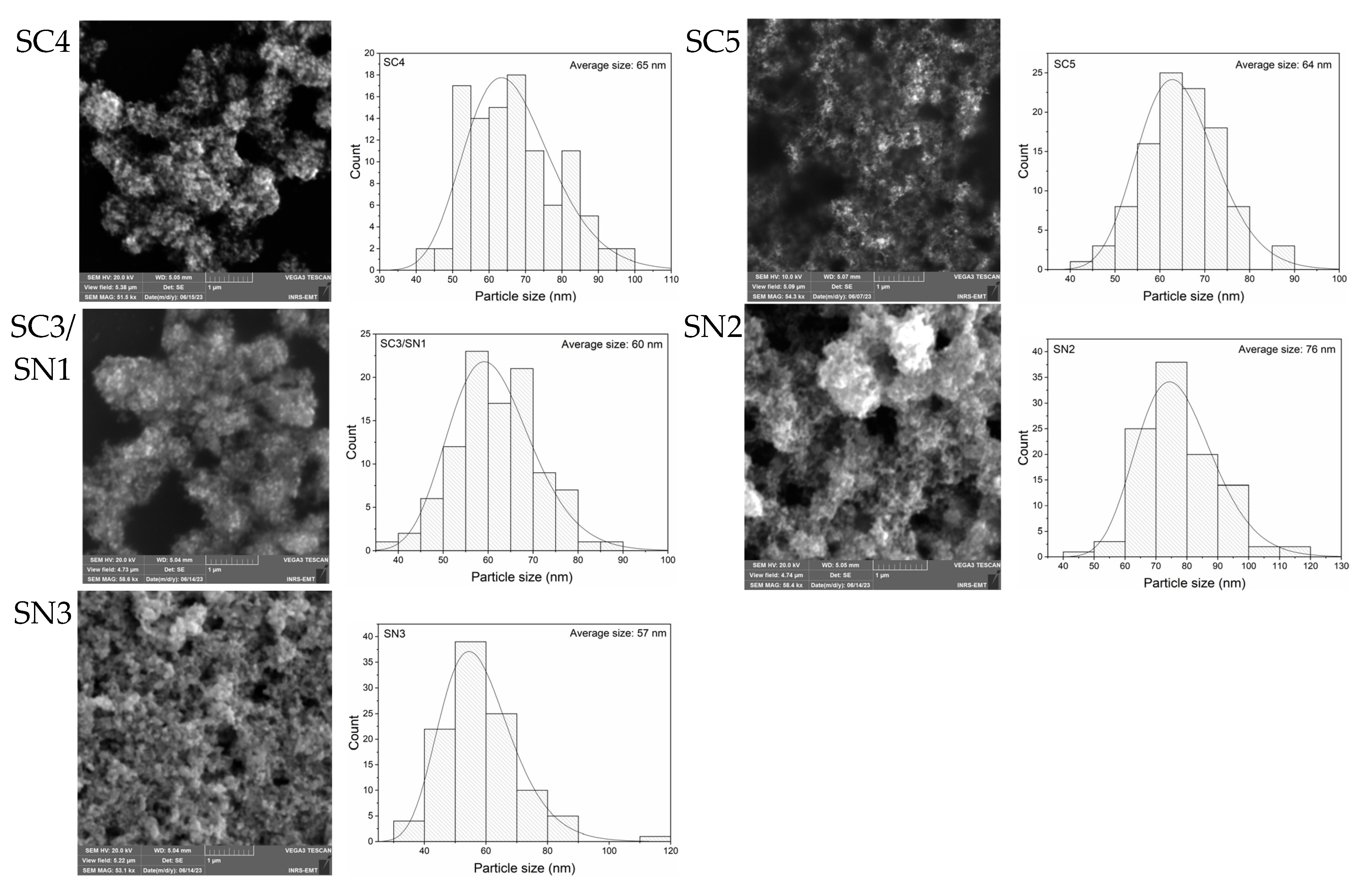
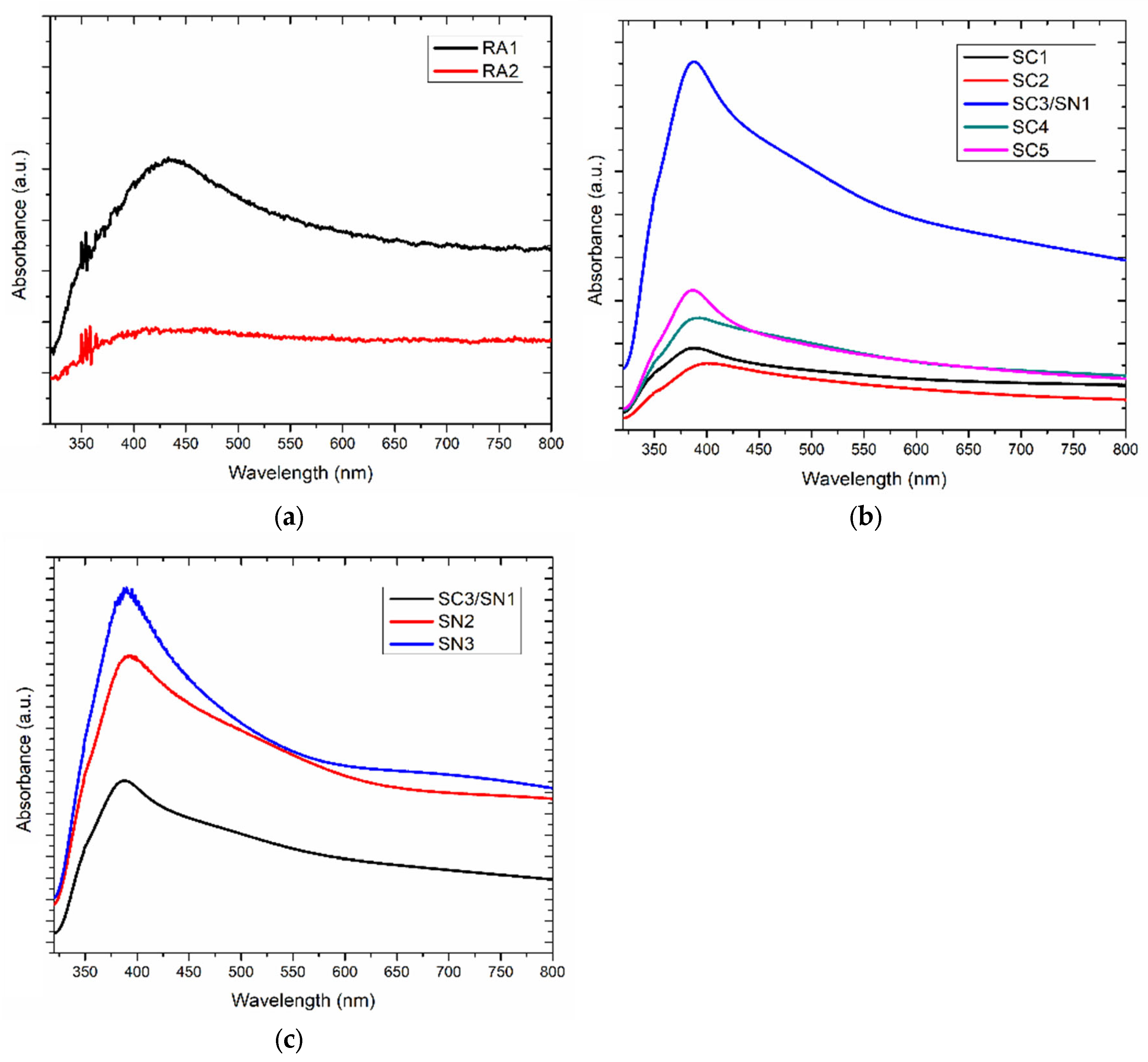
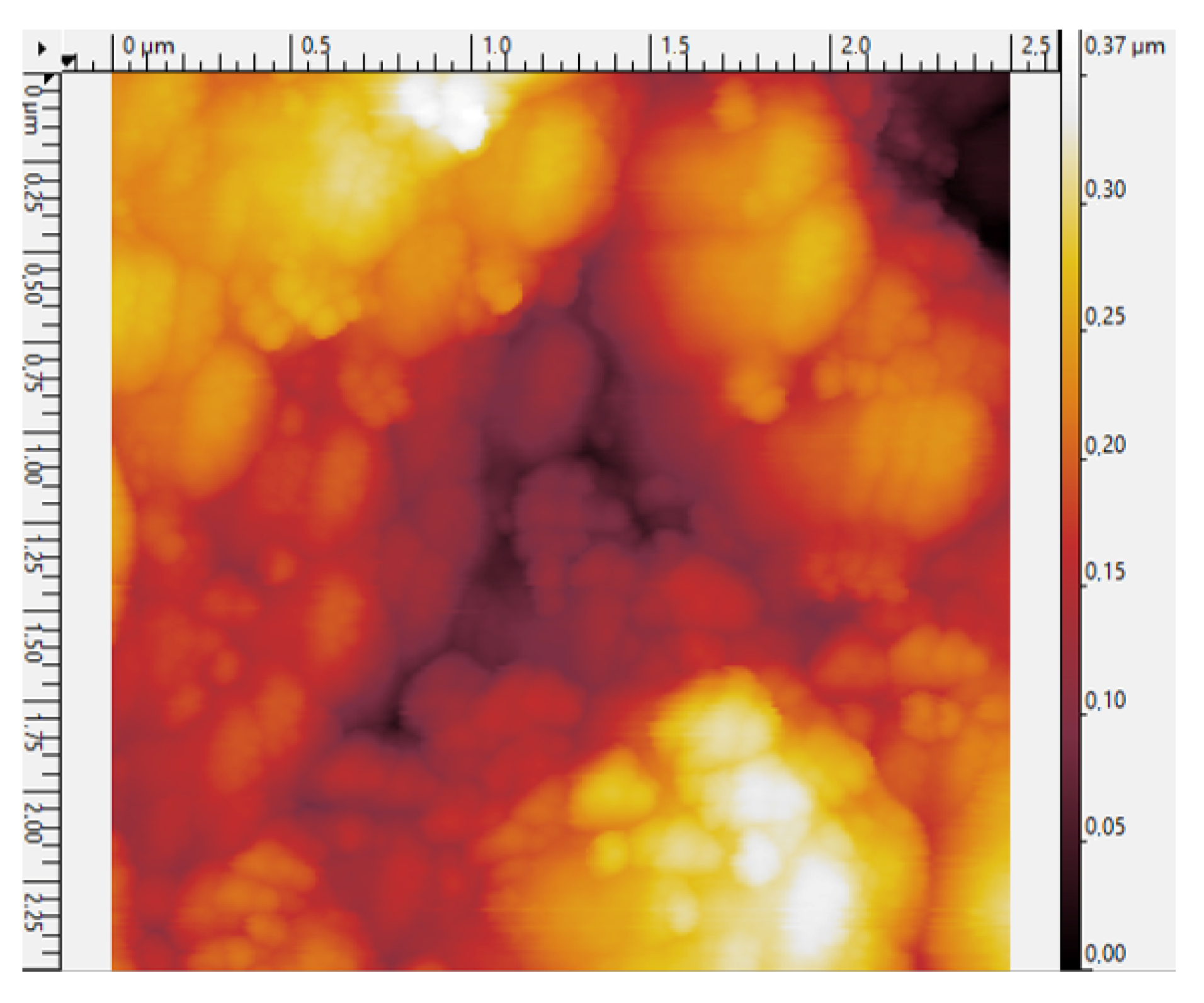
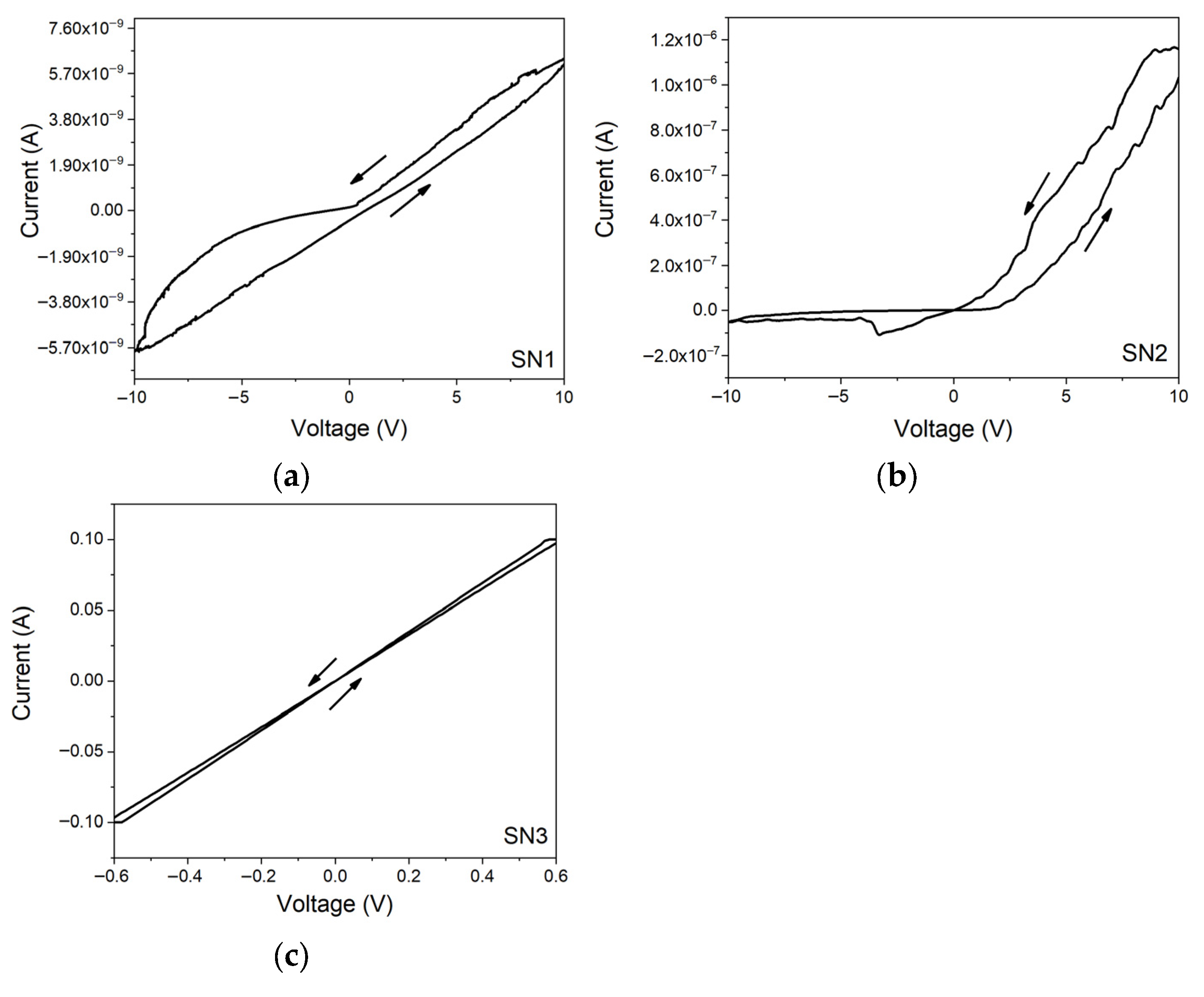
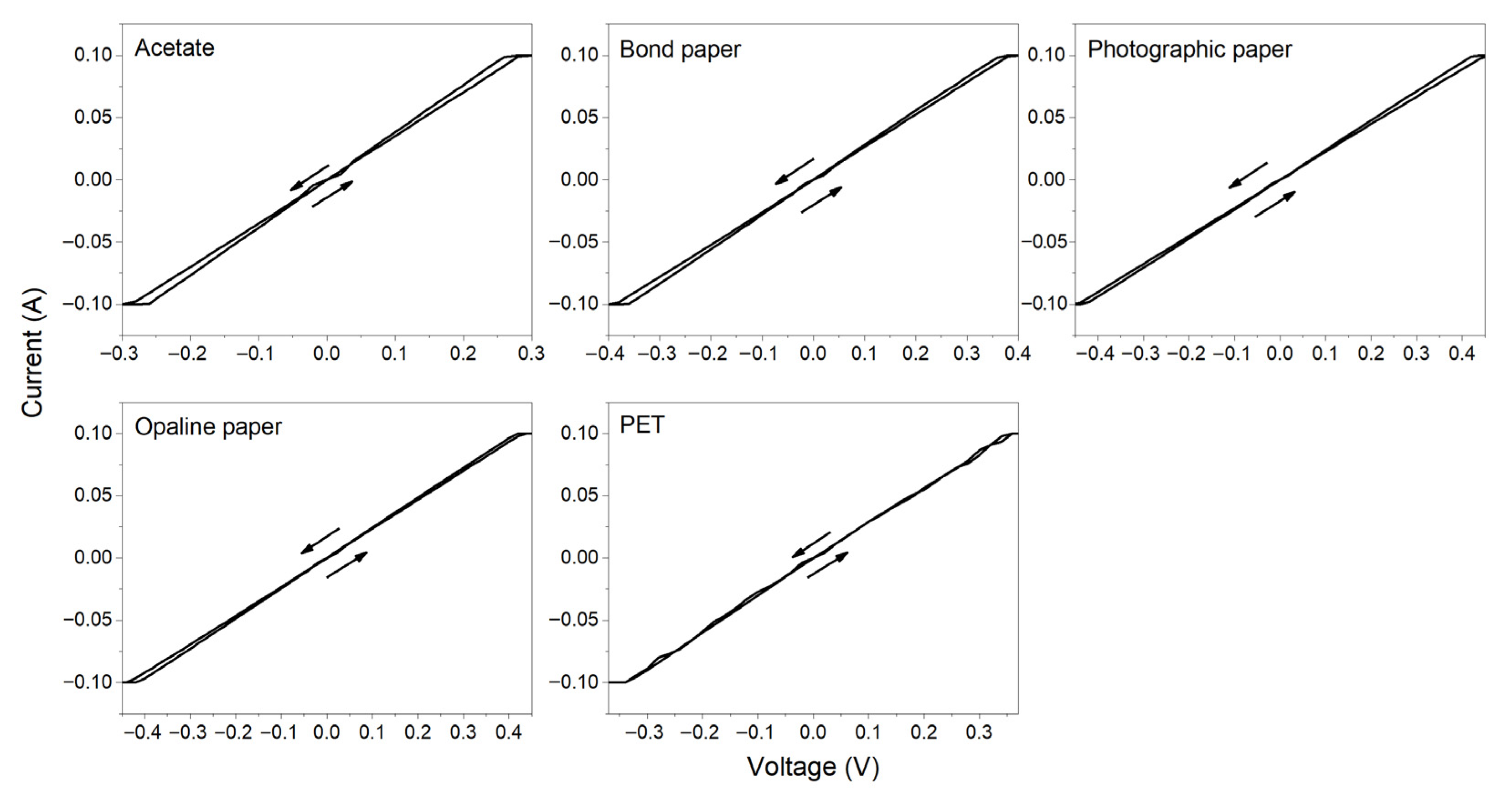
| Sample Set | Agents in the Reaction | Sample |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | AgNO3 0.05 M, C6H5Na3O7 0.05 M | RA1 |
| AgNO3 0.05 M, NaBH4 0.05 M | RA2 | |
| 2 | AgNO3 0.05 M, NaBH4 0.05 M, C6H5Na3O7 0.01 M | SC1 |
| AgNO3 0.05 M, NaBH4 0.05 M, C6H5Na3O7 0.02 M | SC2 | |
| AgNO3 0.05 M, NaBH4 0.05 M, C6H5Na3O7 0.03 M | SC3 | |
| AgNO3 0.05 M, NaBH4 0.05 M, C6H5Na3O7 0.04 M | SC4 | |
| AgNO3 0.05 M, NaBH4 0.05 M, C6H5Na3O7 0.05 M | SC5 | |
| 3 | NaBH4 0.05 M, C6H5Na3O7 0.03 M, AgNO3 0.05 M | SN1 |
| NaBH4 0.05 M, C6H5Na3O7 0.03 M, AgNO3 0.10 M | SN2 | |
| NaBH4 0.05 M, C6H5Na3O7 0.03 M, AgNO3 0.15 M | SN3 |
| AgNP Size from SEM (nm) | Standard Deviation (nm) | Size from DLS (nm) | Polydispersity Index (PDI) | Zeta Potential (mV) | pH | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RA1 | 335 | 506 | 312 | 0.38 | −24.5 | 7–7.1 |
| RA2 | 285 | 210 | 304 | 1.00 | −24.3 | 7–7.1 |
| SC1 | 84 | 182 | 85 | 0.63 | −30.9 | 7.5–7.7 |
| SC2 | 96 | 19 | 106 | 0.44 | −30.9 | 7.5–7.7 |
| SC4 | 65 | 12 | 69 | 0.58 | −31.1 | 7.5–7.7 |
| SC5 | 64 | 8 | 62 | 0.50 | −30.0 | 7.5–7.7 |
| SC3/SN1 | 60 | 9 | 52 | 0.53 | −31.7 | 7.5–7.7 |
| SN2 | 76 | 12 | 71 | 0.69 | −31.2 | 7.5–7.7 |
| SN3 | 57 | 12 | 64 | 0.57 | −32.2 | 7.5–7.7 |
| SN1 | SN2 | SN3 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| wt.% | at.% | Abs. Error % | wt.% | at.% | Abs. Error % | wt.% | at.% | Abs. Error % | |||
| Ag | 81.6 | 41.1 | 2.1 | Ag | 88.8 | 55.1 | 2.8 | Ag | 88.8 | 55.5 | 3.2 |
| N | 0.16 | 0.6 | 0.3 | N | 0.35 | 1.7 | 0.4 | N | 1.0 | 5.0 | 0.8 |
| C | 2.5 | 11.2 | 0.6 | C | 1.95 | 10.9 | 0.5 | C | 1.3 | 7.4 | 0.6 |
| O | 9.5 | 32.1 | 1.7 | O | 5.1 | 21.4 | 1.3 | O | 4.8 | 20.4 | 1.7 |
| Na | 6.3 | 14.9 | 0.4 | Na | 3.8 | 11.0 | 0.3 | Na | 4.0 | 11.7 | 0.4 |
| Ag | 81.6 | 41.1 | 2.1 | Ag | 88.8 | 55.1 | 2.8 | Ag | 88.8 | 55.5 | 3.2 |
| N | 0.16 | 0.6 | 0.3 | N | 0.35 | 1.7 | 0.4 | N | 1.0 | 5.0 | 0.8 |
| C | 2.5 | 11.2 | 0.6 | C | 1.95 | 10.9 | 0.5 | C | 1.3 | 7.4 | 0.6 |
| Substrate | Deposited at RT | Deposited at 60 °C | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drying Time of Deposited NPs | Resistance (Ω) | Drying Time of Deposited NPs | Resistance (Ω) | |
| Acetate | 2 h 30 min | 2.86 ± 0.2 | 5 min | 4.73 ± 0.3 |
| Bond paper | 20 min | 3.80 ± 0.3 | 5 min | 2.00 ± 0.2 |
| Photographic | 15 min | 4.35 ± 0.2 | 5 min | 1.80 ± 0.1 |
| Opaline paper | 25 min | 4.00 ± 0.3 | 5 min | 4.73 ± 0.3 |
| PET | 2 h | 3.60 ± 0.2 | 5 min | 5.57 ± 0.3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ceron, S.; Barba, D.; Dominguez, M.A. Silver Nanoparticles for Conductive Inks Functionalization on Paper Substrates. Nanomanufacturing 2025, 5, 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/nanomanufacturing5040019
Ceron S, Barba D, Dominguez MA. Silver Nanoparticles for Conductive Inks Functionalization on Paper Substrates. Nanomanufacturing. 2025; 5(4):19. https://doi.org/10.3390/nanomanufacturing5040019
Chicago/Turabian StyleCeron, Sonia, David Barba, and Miguel A. Dominguez. 2025. "Silver Nanoparticles for Conductive Inks Functionalization on Paper Substrates" Nanomanufacturing 5, no. 4: 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/nanomanufacturing5040019
APA StyleCeron, S., Barba, D., & Dominguez, M. A. (2025). Silver Nanoparticles for Conductive Inks Functionalization on Paper Substrates. Nanomanufacturing, 5(4), 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/nanomanufacturing5040019






