Sodium-Doped Carbon Dots as Fluorescent Sensor for Highly Selective Detection of TNP Explosives in the Environment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Procedure
2.1. Materials and Instruments
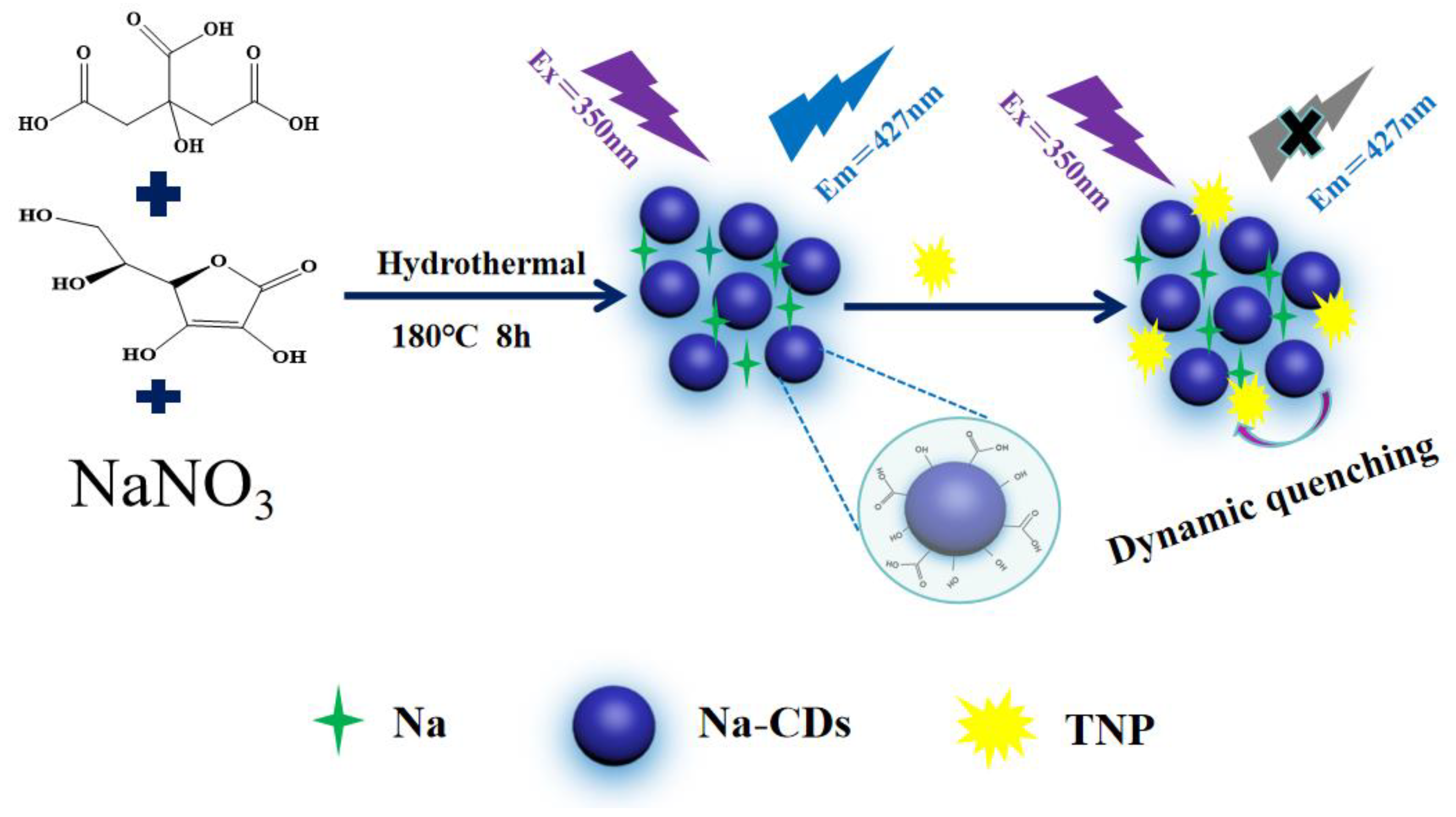
2.2. Preparation of Na-CDs
2.3. Study on the Fluorescence Sensing of TNP
3. Results and Discussion
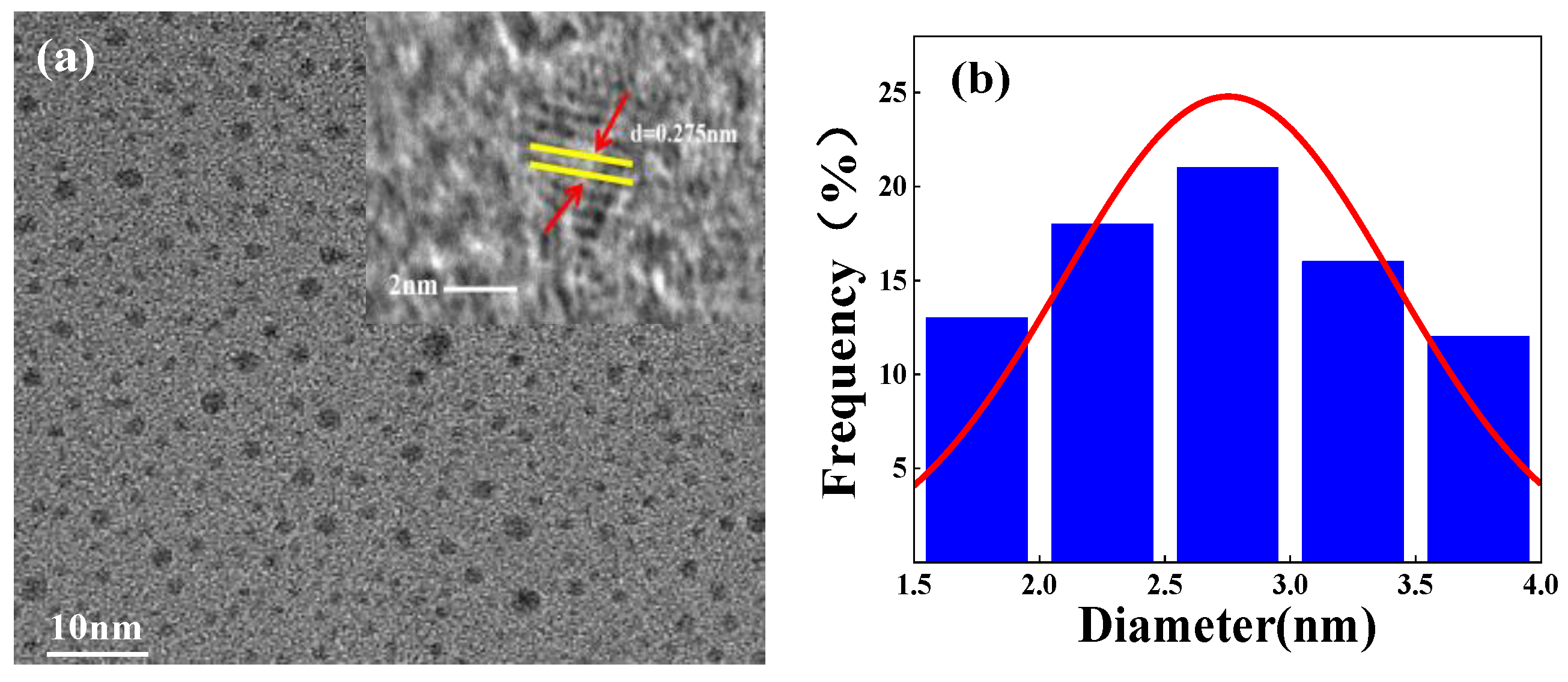
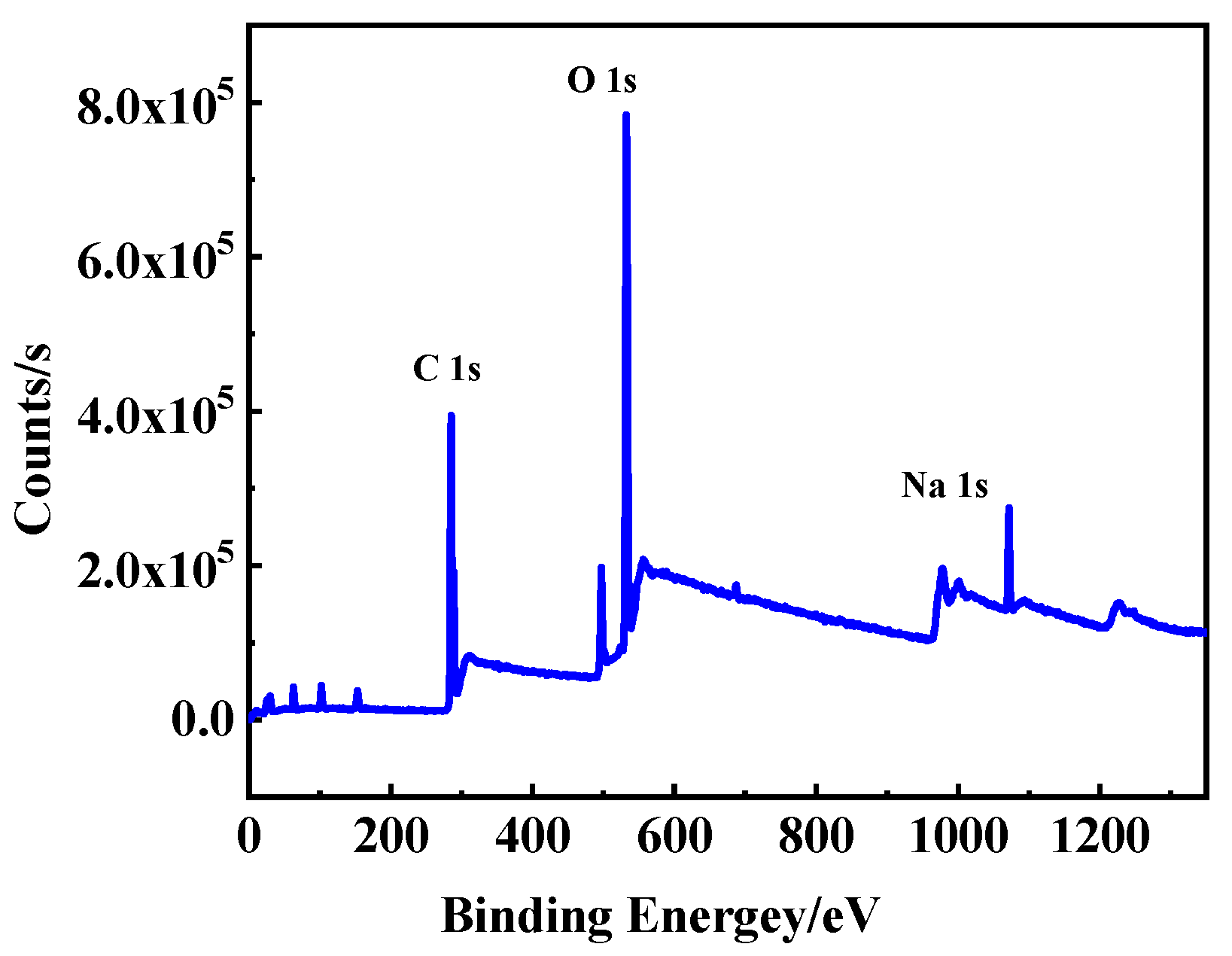
3.1. Characterization of Na-CDs
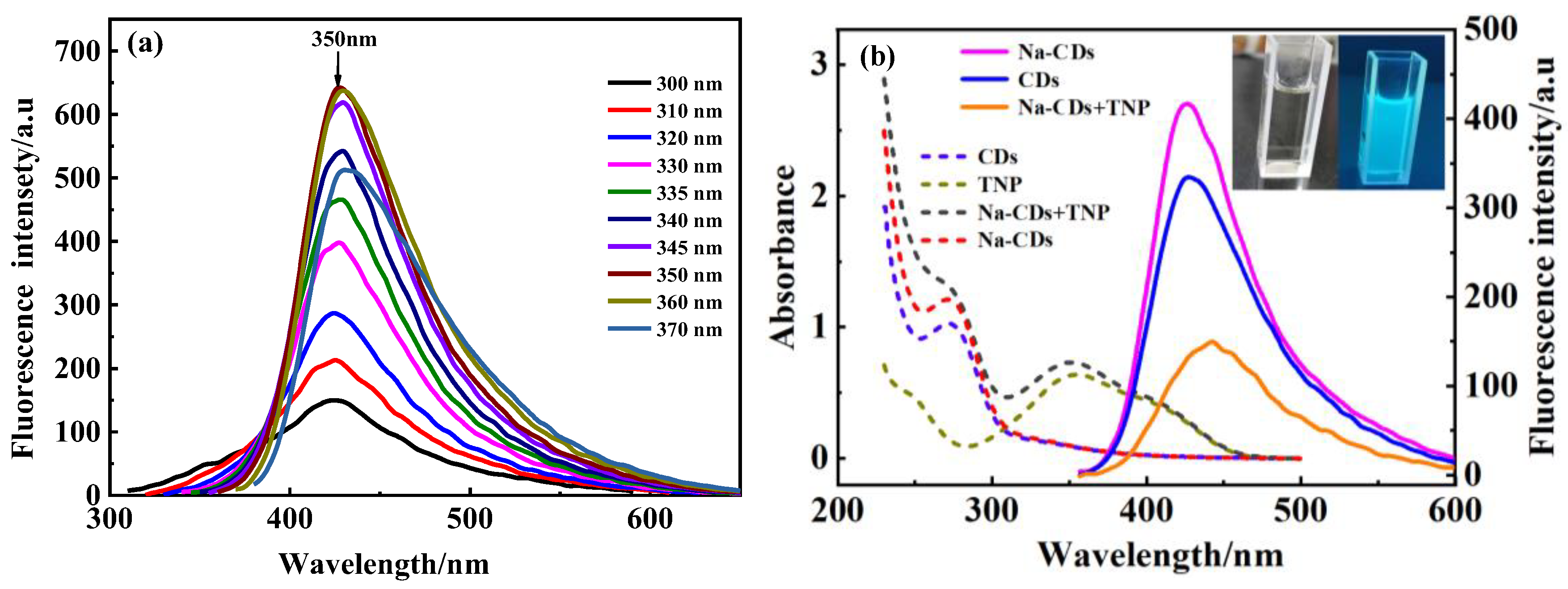
3.2. Optical Properties of Na-CQDs
3.3. Fluorescence Quantum Yield
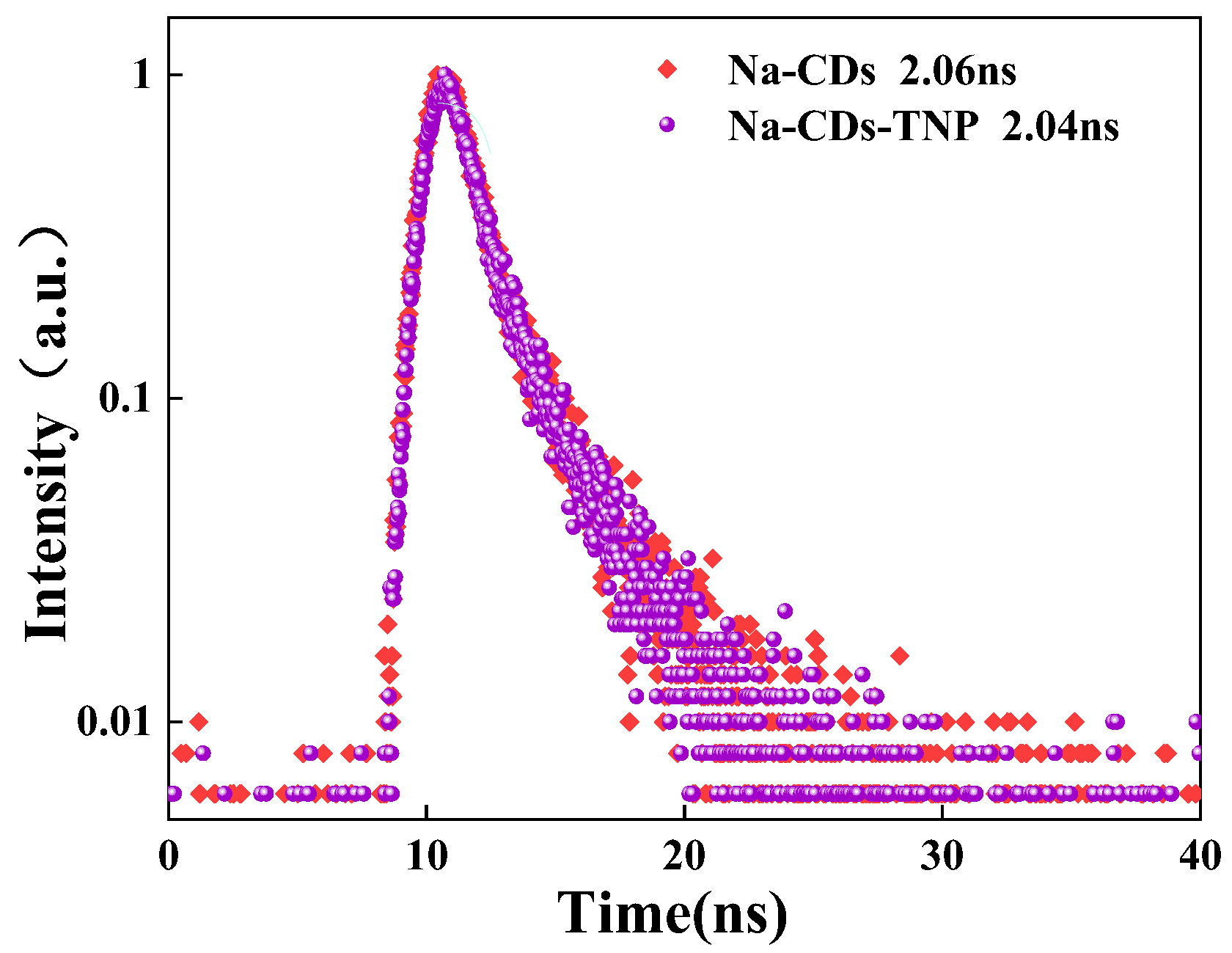
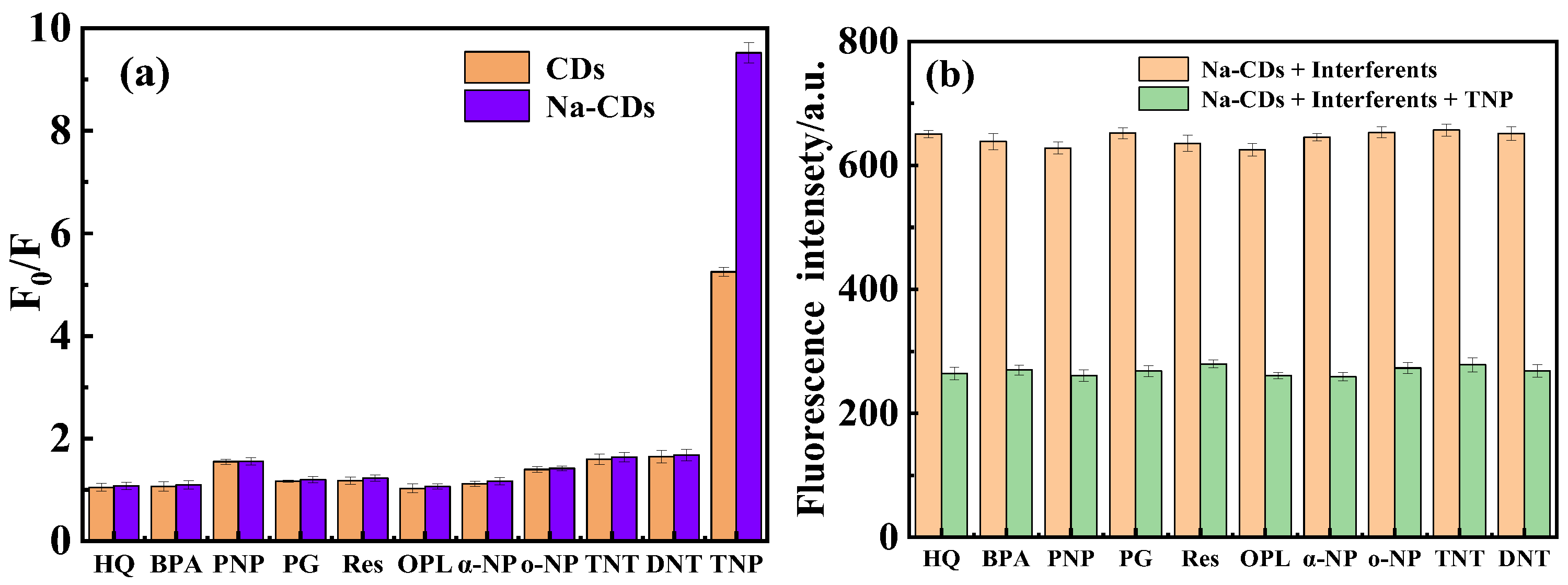
3.4. Sensing Mechanism
3.5. Optimization of Experimental Conditions
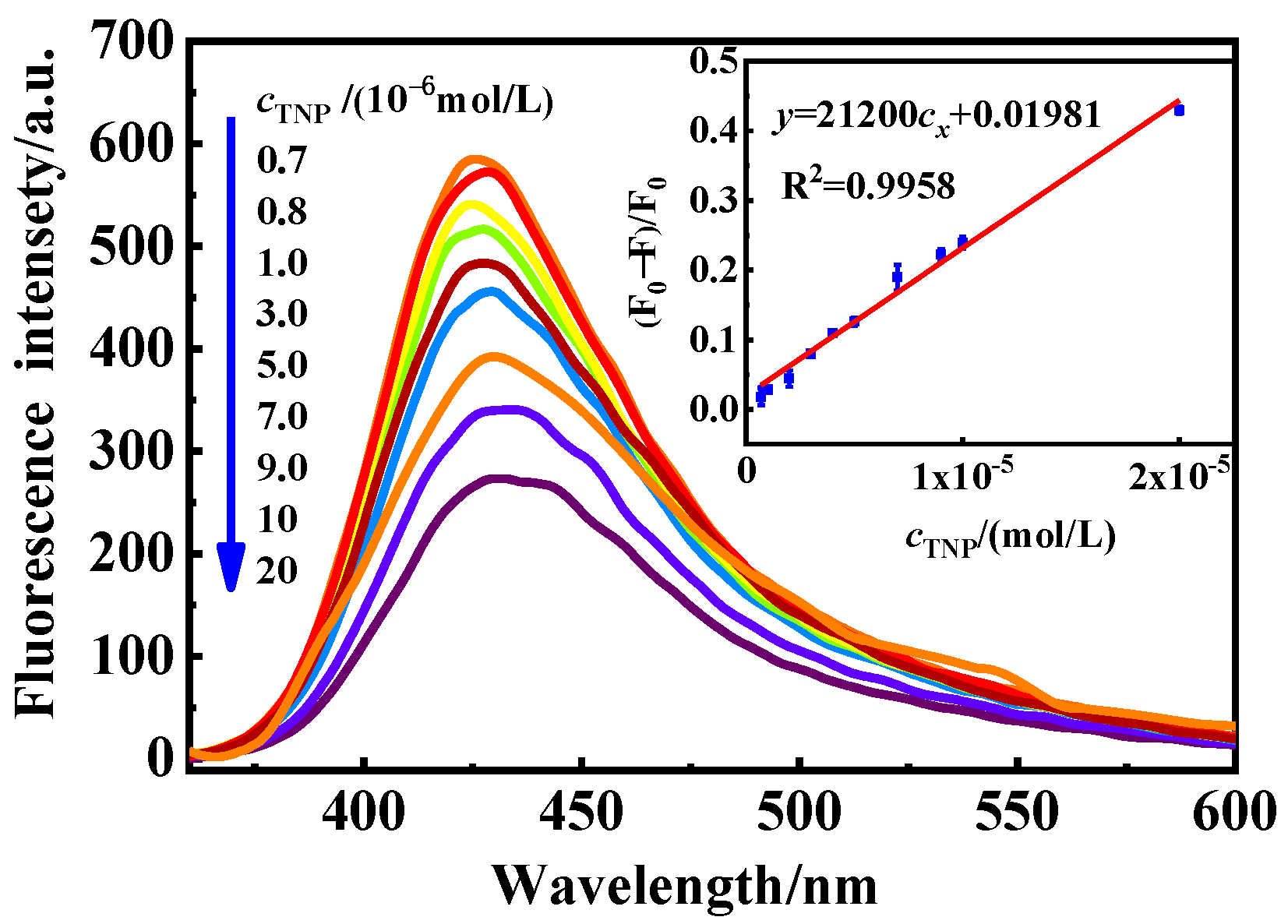
3.6. Standard Curve
3.7. Real Sample Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fu, Z.H.; Wang, Y.W.; Peng, Y. Two Fluorescein-Based Chemosensors for the Fast Detection of 2,4,6-Trinitrophenol (TNP) in Water. Chem. Commun. 2017, 53, 10524–10527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagarkar, S.S.; Desai, A.V.; Ghosh, S.K. Engineering Metal—Organic Frameworks for Aqueous Phase 2,4,6-Trinitrophenol (TNP) Sensing. CrystEngComm 2016, 18, 2994–3007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, H.; Shangguan, M.Q.; Guo, B.G.; Yang, H.J.; Hou, L.X. A Water-Soluble Fluorescent Probe for Selective Detection of 2,4,6-Trinitrophenol (TNP) in Real Samples. Microchem. J. 2020, 157, 10511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, D.S. Instrumentation for Trace Detection of Highexplosives. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2004, 75, 2499–2512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khezri, B.; Mousavi, S.M.B.; Sofer, Z.; Pumera, M. Recyclable Nanographene-Based Micromachines for the on-the-Fly Capture of Nitroaromatic Explosives. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 8825–8834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, Z.M.; Wang, A.J.; Tian, M.G.; Zuo, Y.J. Pyrene-Based Monomer-Excimer Dual Response Organosilicon Polymer for the Selective Detection of 2,4,6-Trinitrotoluene (TNT) and 2,4,6-Trinitrophenol (TNP). Mater. Chem. Front. 2022, 6, 607–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Pan, Z.-R.; Qi, Z.-P.; Sun, J. Three Luminescent Zn-MOFs Based on V-Shaped Ligands for Fluorescence Sensing of 2,4,6-Trinitrophenol and Fe3+ in Aqueous Solution. Chin. J. Inorg. Chem. 2022, 38, 2479–2490. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, I.; Sinha, R.K.; Shil, S.; Rani, S.; Anil Kumar, N.V. Novel Coumarin-Substituted Cyclophosphazene as a Fluorescent Probe for Highly Selective Detection of 2,4,6-Trinitrophenol. ACS Omega 2025, 10, 5312–5323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.Q.; Cheng, B.; Bu, Y.F.; Qian, J.F.; Liang, Q.; He, M.Y.; Chen, Q. Carbon Dots as Electron Acceptors Modified NH2-MIL-125 (Ti)/Cu2O Heterojunction for Highly Efficient Photocatalytic H2 Production. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2025, 127, 189–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrabi, F.; Hosseini, M.; Sadeghi, N.; Mohammadi, J.; Ganjali, M.R.; Ranjbar, B. Green Emitting Carbon Dots-Immunosensor on Magnetic Nanoparticles for Detection of Nanog Antigen as a Cancer Stem Cell Biomarker. Anal. Chim. Acta 2025, 1353, 343960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.H.; Ma, M.; Liu, J.T.; Tian, R.; Chai, H.M.; Cui, H.L.; Gao, L.J. Pr/N Co-Doped Biomass Carbon Dots with Enhanced Fluorescence for Efficient Detection of 2,4-Dinitrophenylhydrazine. Chin. J. Inorg. Chem. 2025, 41, 561–573. [Google Scholar]
- Koc, O.K.; Üzer, A.; Apak, R. High Quantum Yield Nitrogen-Doped Carbon Quantum Dot-Based Fluorescent Probes for Selective Sensing of 2,4,6-Trinitrotoluene. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2022, 5, 5868–5881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadian, S.; Kalkal, A.; Jain, V.; Shukla, S.; Narayan, R.J. Pomegranate leaf extract-based carbon dots for the selective detection of 2,4,6-trinitrophenol. MRS Commun. 2023, 13, 885–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iacovo, A.D.; Mitri, F.; Santis, S.D.; Giansante, C.; Colace, L. Colloidal Quantum Dots for Explosive Detection: Trends and Perspectives. ACS Sens. 2024, 9, 555–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.L.; Zheng, Y.X.; Moon, K.S.; Chen, Y.; Shi, D.C.; Chen, X.; Wong, C.P. Ambient-air in situ fabrication of high-surface-area, superhydrophilic, and microporous few-layer activated graphene films by ultrafast ultraviolet laser for enhanced energy storage. Nano Energy 2022, 94, 106902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.H.; Ma, M.; Tian, R.; Chai, H.M.; Wang, J.W.; Gao, L.J. One-Pot Hydrothermal Method Preparation of Cerium—Nitrogen Codoped Carbon Quantum Dots from Waste Longan Nucleus as a Fluorescent Sensor for Sensing Drug Rifampicin. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 34859–34867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Fan, Z.F. Application of cerium—Nitrogen co-doped carbon quantum dots to the detection of tetracyclines residues and bioimaging. Microchem. J. 2021, 165, 106139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Xu, M.H.; Liu, Y.; He, F.J.; Gao, F.; Su, Y.J.; Wei, H.; Zhang, Y.F. Nitrogen-Doped, Carbon-Rich, Highly Photoluminescent Carbon Dots from Ammonium Citrate. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 1890–1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walekar, L.S.; Zheng, M.D.; Zheng, L.H.; Long, M.C. Selenium and nitrogen co-doped carbon quantum dots as a fluorescent probe for perfluorooctanoic acid. Microchim. Acta 2019, 186, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.R.; Zhao, D.L.; Chung, T.S. Na+ functionalized carbon quantum dot incorporated thin-film nanocomposite membranes for selenium and arsenic removal. J. Membrane Sci. 2018, 564, 483–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.B.; Chen, D.Q.; Fang, G.L.; Yuan, S.; Chen, X.; Zhong, J.S. Excellent Luminescence Films of Excitation-Independent Carbon Quantum Dots Toward Non-Rare-Earth Phosphor-Based White Light-Emitting Diodes. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 764, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.L.; He, M.Y.; Yan, X.Y.; Xiang, G.Q.; Jiang, X.M.; He, L.J. Preparation of Boron-Doped Carbon Dots with High Fluorescence Quantum Yield and Its Application for Determination of 2,4,6-Trinitrophenol in Water. J. Inst. Anal. 2023, 42, 1127–1133. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.Y.; Long, C.C.; Zhang, L.; Qing, T.P.; Zhang, P.; Qing, Z.H.; Feng, B. Carbon Dots for All-in-One Detection and Degradation: The Role of Photoinduced Electron Transfer. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 108951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhang, H.Y.; Yu, D.M.; Qin, W.; Wu, X.H. Ultra-Sensitive and Stable N-Doped Carbon Dots for Selective Detection of Uranium Through Electron Transfer Induced UO2+(V) Sensing Mechanism. Carbon 2022, 198, 162–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshmukh, A.; Bandyopadhyay, S.; Jamesa, A.; Patra, A. Trace Level Detection of Nitroanilines Using a Solution Processable Fluorescent Porous Organic Polymer. J. Mater. Chem. C 2016, 4, 4427–4433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, S.R.; Patel, S.; Vaidyanathan, S. Imidazole-Based Fluorescent Probes: Concomitant Effects of N1 Substitution and Lone Pair on Selective Recognition of Picric Acid. New J. Chem. 2023, 47, 3524–3534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.; Chu, H.T.; Chen, J.Q.; Gao, L.D.; Zong, W.; Han, S.; Li, J.L. Dual-Emission Ratiometric Fluorescence Probe Based on Copper Nanoclusters for the Detection of Rutin and Picric Acid. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2022, 270, 120829–120841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatappa, L.; Ture, S.A.; Yelamaggad, C.V.; Sundaram, V.N.N.; Martínez-Máñez, R.; Abbaraju, V. Mechanistic Insight into the Turn-off Sensing of Nitroaromatic Compounds Employing Functionalized Polyaniline. Chemistryselect 2020, 5, 6321–6330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Huang, X.M.; Chen, W.; Zhao, H.L. Preparation Novel Fluorescent Carbon Dots and Its Application in 2,4,6-Trinitrophenol Detection. Laser Optoelectron. Prog. 2022, 59, 2130002. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, C.; Wang, J.Y.; Lin, J.R.L.; Huang, W.; He, Y. Improved colorimetric detection of 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene through γ-cyclodextrin complexation. Forensic Chem. 2022, 30, 100444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.Q.; Zheng, F.R.; Zou, Y.J.; Yang, Y.J.; Zhang, J.; Li, D.P.; Li, Y.X. Crown-like Cd(II) metallocycle as effective fluorescent sensor for detection of 2,4,6-trinitrophenol. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2025, 582, 122653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, R.H.; Bu, Y.M.; Zhu, H.J.; Su, P.C.; Ye, E.Y.; Li, Z.B.; Loh, X.J.; Yuan, C.; Wang, S.H. Simultaneous detection and removal of 2,4,6-trinitrophenyl phenol and dichromate by metal-organic framework. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2023, 297, 122735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, K.; Khan, M.Q.; Khan, R.A.; Kim, H. Preparation of Mo-doped WO3 as Catalyst for Electrochemical Sensing of 2,4,6-Trinitrophenol. Top. Catal. 2025, 68, 307–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Fluorescent Probe | Detection Method | Detection Range (μmol/L) | Detection Limit (μmol/L) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CuNCs | Fluorescence | 5–50 | 0.27 | [27] |
| Functionalized polyaniline | Fluorescence | 0.6–2.2 | 0.61 | [28] |
| New fluorescent carbon quantum dots | Fluorescence | 0.8–80 | 0.16 | [29] |
| γ-cyclodextrin complexation | Colorimetry | 0–200 | 0.80 | [30] |
| Metallocycle | Fluorescence | 0–25 | 0.91 | [31] |
| Metal–organic framework | Fluorescence | 0–15 | 0.68 | [32] |
| Mo@WO3 | Electrochemical Sensing | 0.3–200 | 0.30 | [33] |
| Na-CDs | Fluorescence | 0.7–20 | 0.035 | This paper |
| Samples | Determination Result (µmol/L) | Added (µmol/L) | Found (µmol/L) | Recovery (%) | RSD (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| River water | 0 | 15.0 | 14.52 | 97.60 | 1.22 |
| 10.0 | 10.13 | 102.0 | 1.63 | ||
| 5.00 | 5.22 | 104.0 | 1.50 | ||
| Industrial wastewater | 0 | 15.0 | 15.26 | 101.7 | 1.40 |
| 10.0 | 9.54 | 95.40 | 1.14 | ||
| 5.00 | 5.19 | 103.8 | 2.02 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, T.; Sun, X.; Chai, H. Sodium-Doped Carbon Dots as Fluorescent Sensor for Highly Selective Detection of TNP Explosives in the Environment. Nanomanufacturing 2025, 5, 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/nanomanufacturing5040016
Gao T, Sun X, Chai H. Sodium-Doped Carbon Dots as Fluorescent Sensor for Highly Selective Detection of TNP Explosives in the Environment. Nanomanufacturing. 2025; 5(4):16. https://doi.org/10.3390/nanomanufacturing5040016
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Tianyu, Xuehua Sun, and Hongmei Chai. 2025. "Sodium-Doped Carbon Dots as Fluorescent Sensor for Highly Selective Detection of TNP Explosives in the Environment" Nanomanufacturing 5, no. 4: 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/nanomanufacturing5040016
APA StyleGao, T., Sun, X., & Chai, H. (2025). Sodium-Doped Carbon Dots as Fluorescent Sensor for Highly Selective Detection of TNP Explosives in the Environment. Nanomanufacturing, 5(4), 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/nanomanufacturing5040016





