Cerium Oxide Nanoparticles: Synthesis and Characterization for Biosafe Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis of Cerium Oxide Nanoparticles
2.3. Characterization Techniques
2.3.1. Scanning Electron Microscopy
2.3.2. Field Emission Scanning Electron Microscopy
2.3.3. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy
2.3.4. X-ray Diffraction Spectroscopy
2.4. In Vitro Cell Culture and Experimental Conditions
2.5. Measurement of Cell Viability by MTT Assay
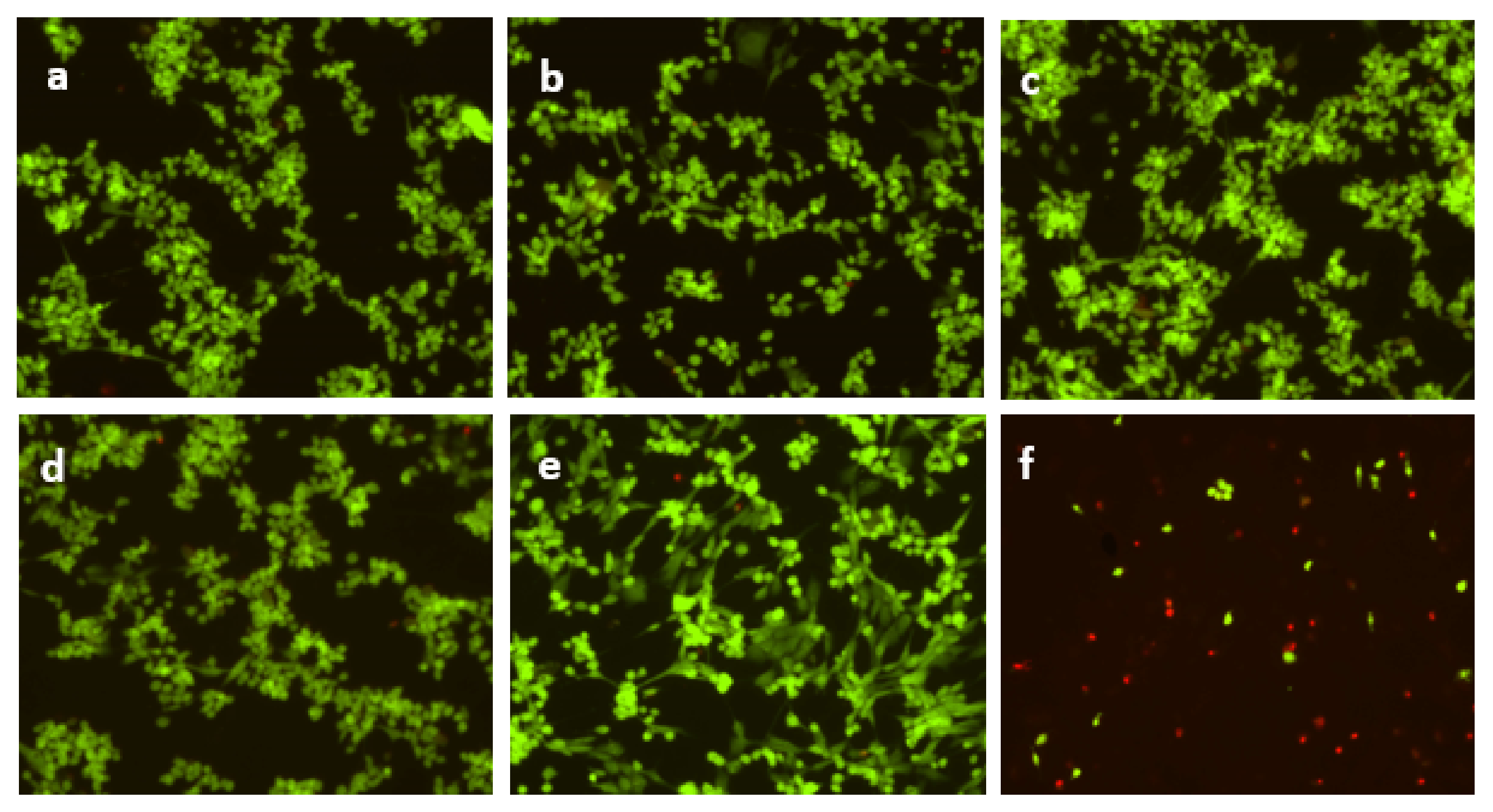
2.6. Live/Dead Cell Imaging Assay
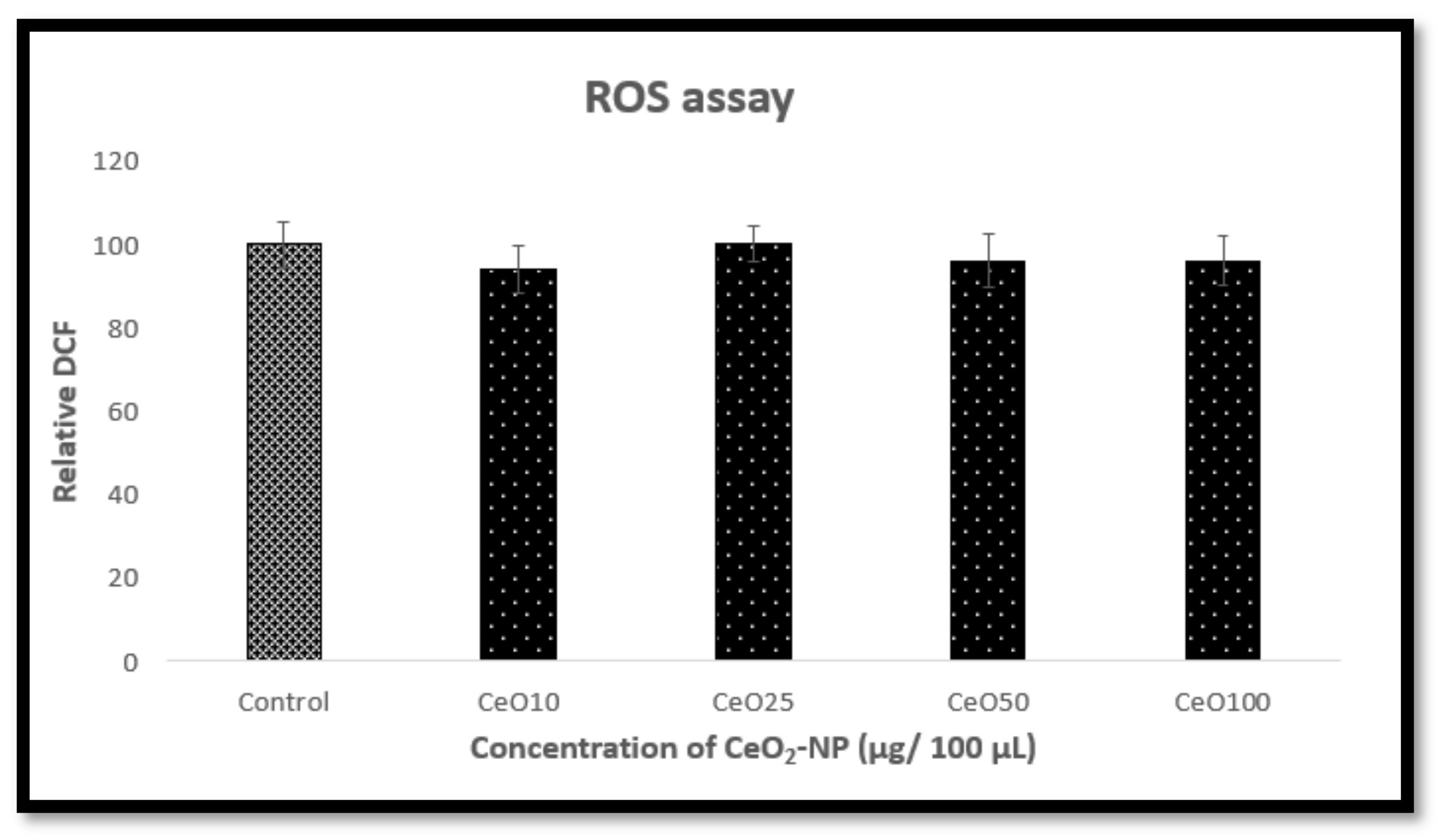
2.7. Detection of Reactive Oxygen Species by ROS Assay
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Synthesis
3.2. Characterization
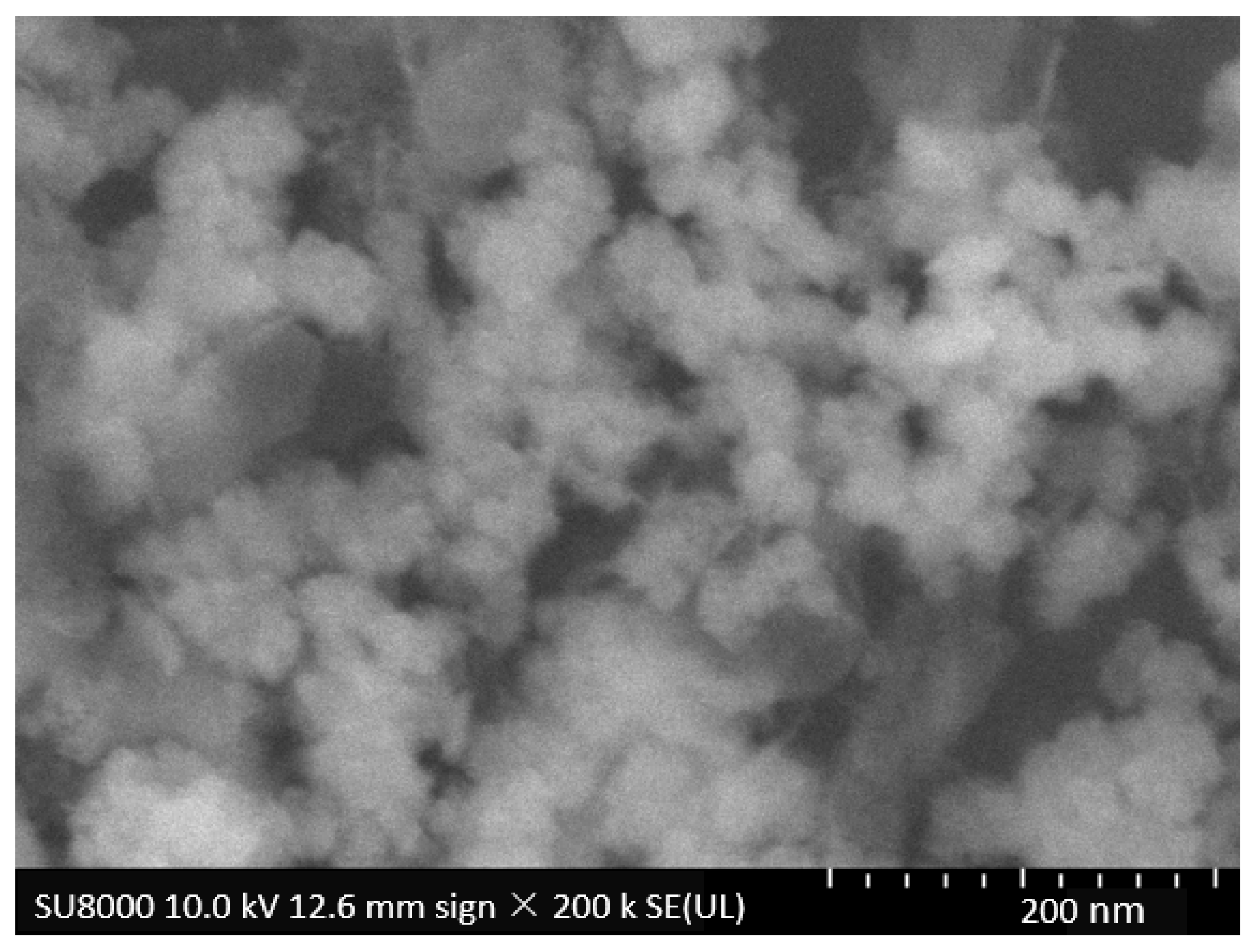
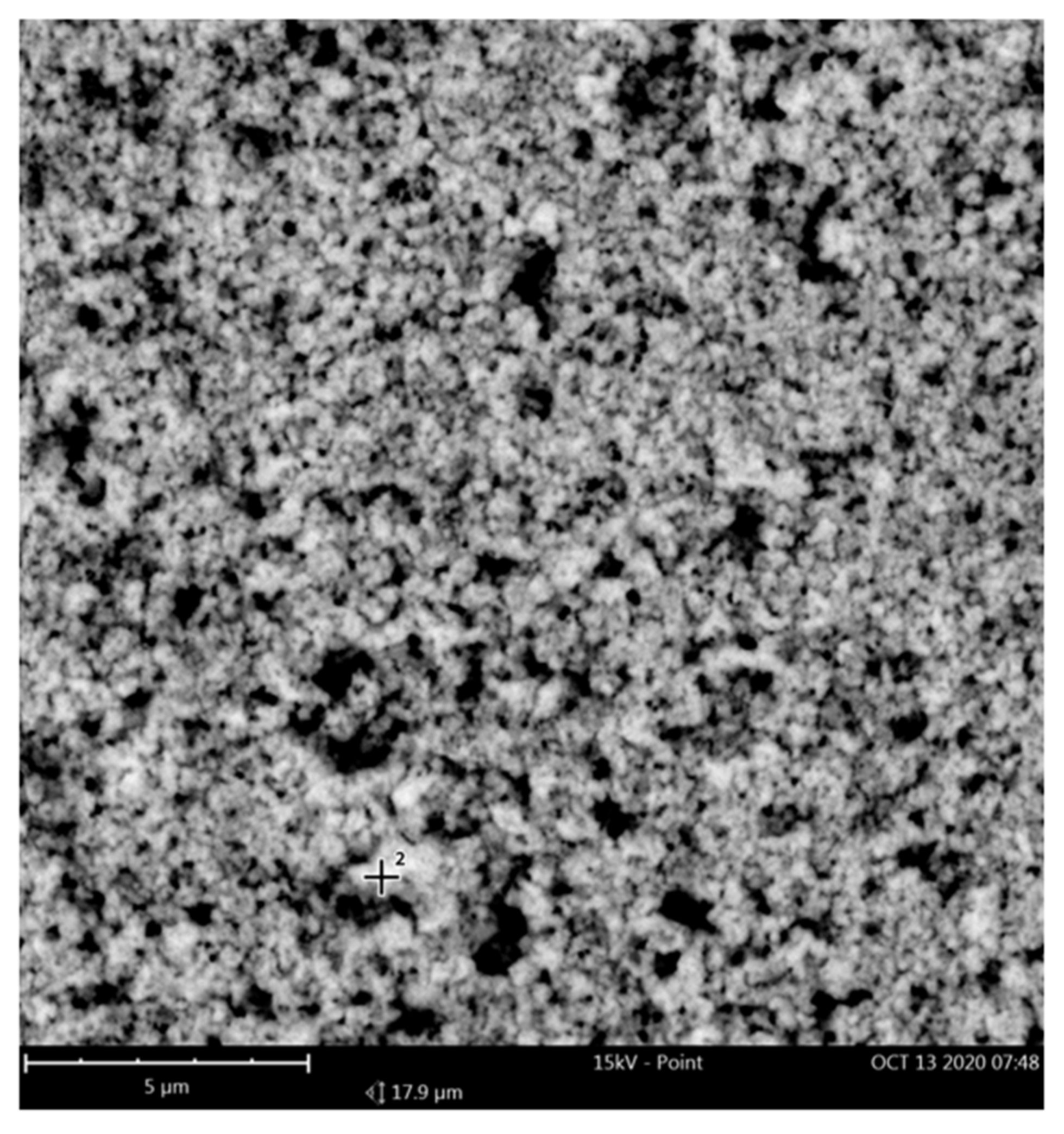
3.2.1. SEM Analysis
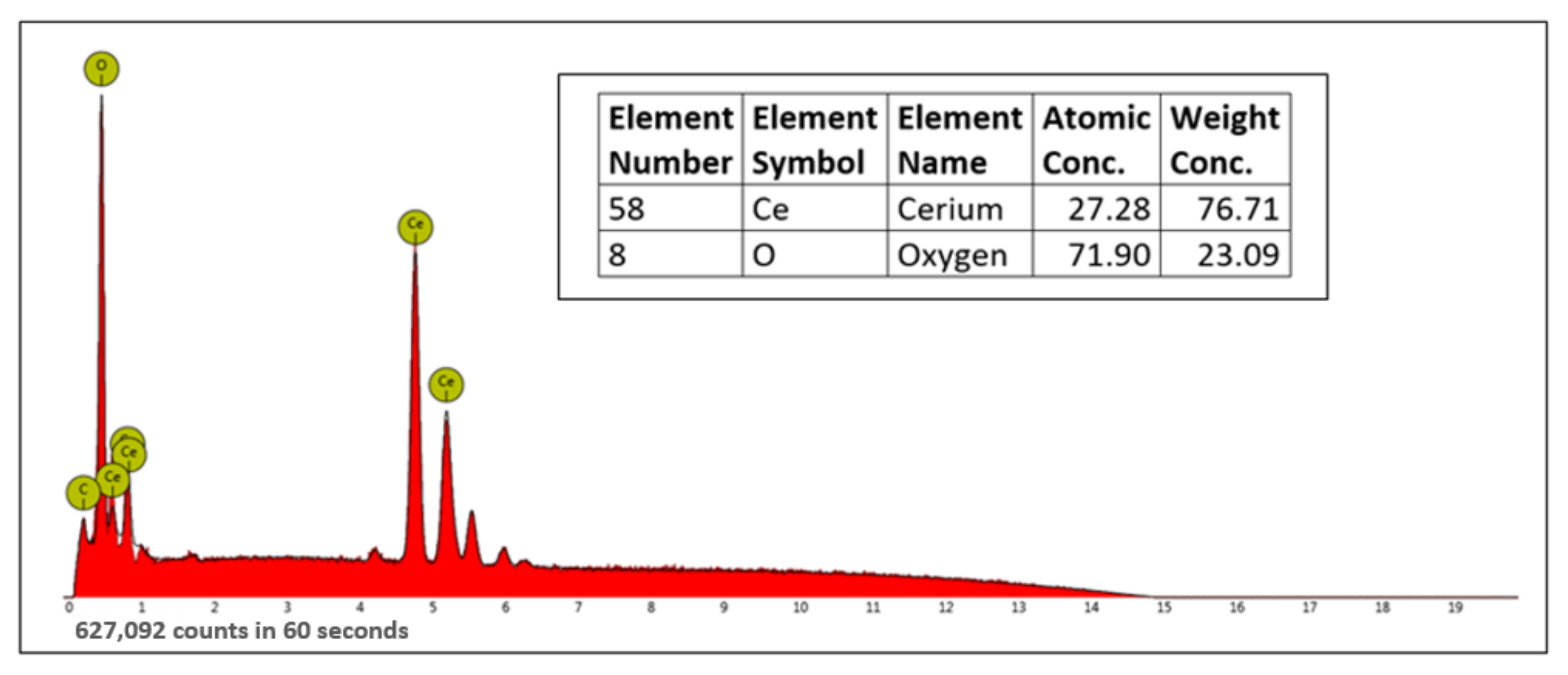
3.2.2. FESEM-EDX Analysis
3.2.3. FTIR Analysis
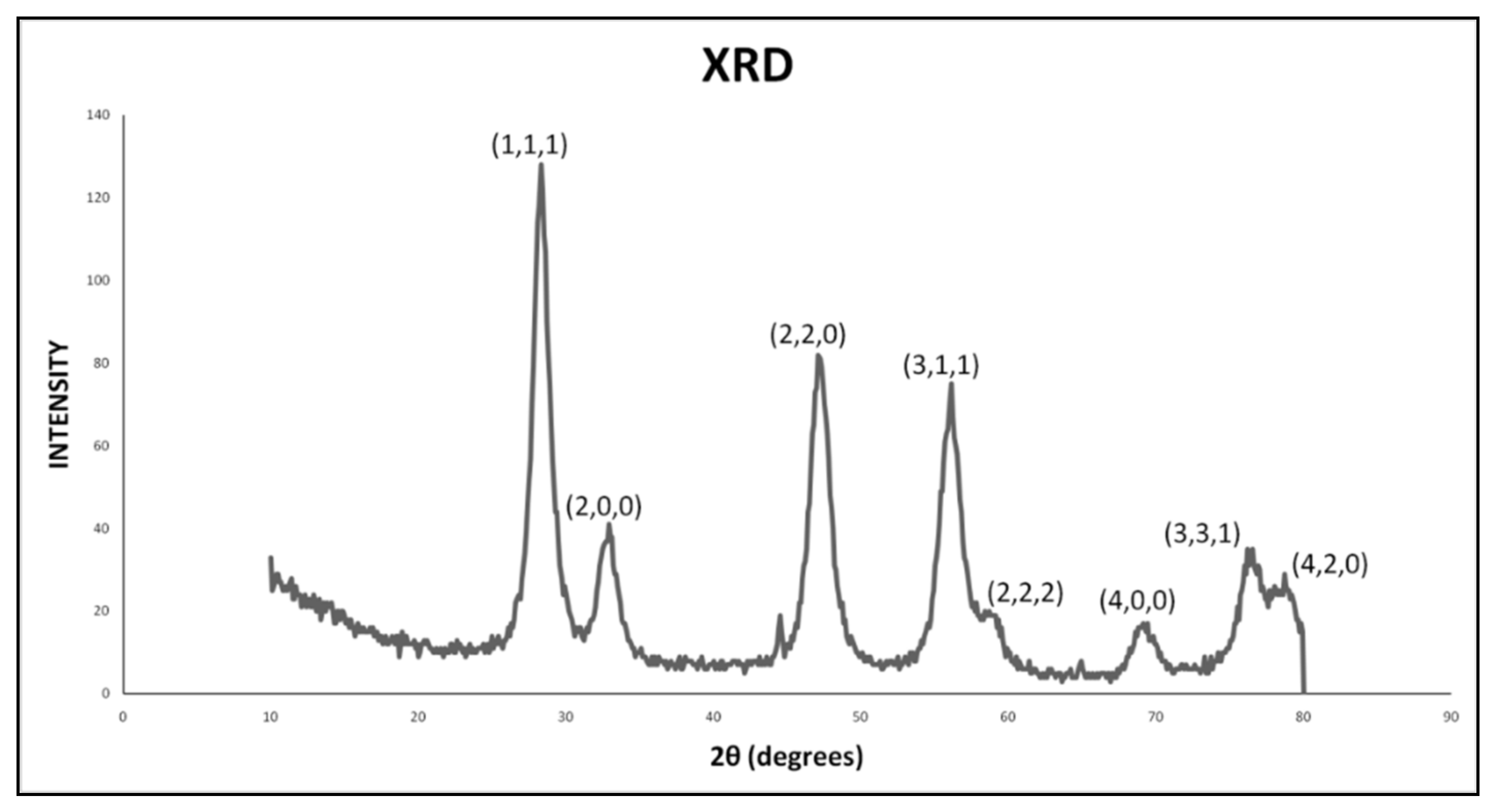
3.2.4. XRD Analysis
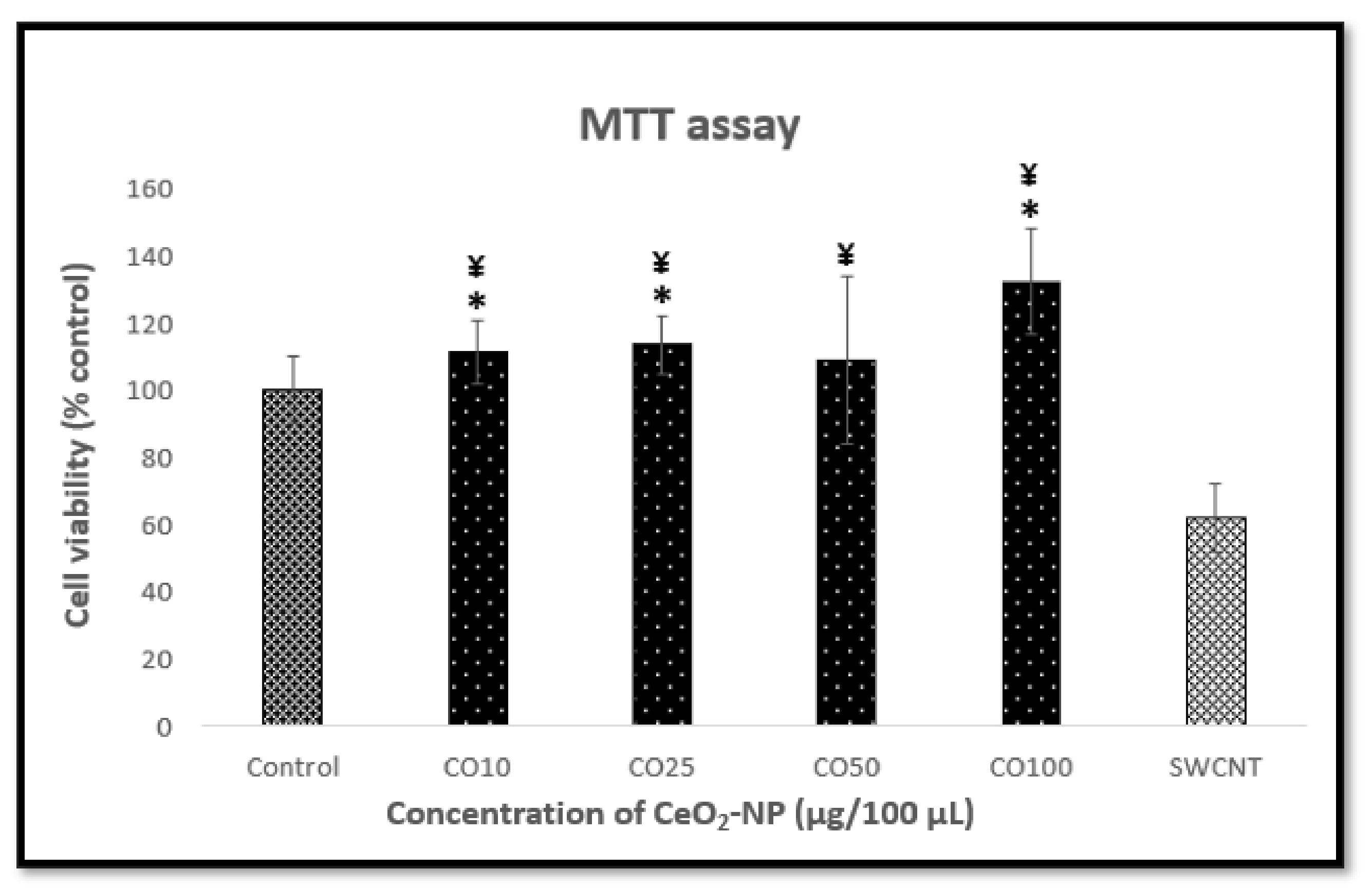
3.3. Effect of Cerium Oxide Nanoparticles on Cell Viability and Cytotoxicity
3.4. Effect of Cerium Oxide Nanoparticles on Oxidative Stress
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gazzi, A.; Fusco, L.; Orecchioni, M.; Ferrari, S.; Franzoni, G.; Yan, J.S.; Rieckher, M.; Peng, G.; Lucherelli, M.A.; Vacchi, I.A.; et al. Graphene, other carbon nanomaterials and the immune system: Toward nanoimmunity-by-design. J. Phys. Mater. 2020, 3, 034009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mai, H.D.; Rafiq, K.; Yoo, H. Nano Metal-Organic Framework-Derived Inorganic Hybrid Nanomaterials: Synthetic Strategies and Applications. Chem. A Eur. J. 2017, 23, 5631–5651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, L.; Craig, M.M.; Khang, D.; Chen, C. Applications of Nanomaterials in Biology and Medicine. J. Nanotechnol. 2012, 2012, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhtar, M.; Bilal, M.; Rahdar, A.; Barani, M.; Arshad, R.; Behl, T.; Brisc, C.; Banica, F.; Bungau, S. Nanomaterials for Diagnosis and Treatment of Brain Cancer: Recent Updates. Chemosensors 2020, 8, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamboj, V.K.; Kumar, A.; Hooda, M.S.; Sangwan, P. Nanotechnology: Various methods used for preparation of Nanomaterials. Asian J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2018, 4, 356–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimulescu, I.A.; Nechifor, A.C.; Bǎrdacǎ, C.; Oprea, O.; Paşcu, D.; Totu, E.; Albu, P.; Nechifor, G.; Bungău, S. Accessible Silver-Iron Oxide Nanoparticles as a Nanomaterial for Supported Liquid Membranes. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.Y.; Lee, S.H.; Bin Na, H.; An, K.; Hyeon, T.; Seo, T.S. In vitro cytotoxicity screening of water-dispersible metal oxide nanoparticles in human cell lines. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2009, 33, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younis, A.; Chu, D.; Li, S.; Younis, A.; Chu, D.; Li, S. Cerium Oxide Nanostructures and Their Applications. In Functionalized Nanomaterials; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2016; Available online: https://www.intechopen.com/chapters/52860 (accessed on 20 August 2021). [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, K.; Khan, S.A.; Khan, S.B.; Asiri, A.M. Scanning Electron Microscopy: Principle and Applications in Nanomaterials Characterization. In Handbook of Materials Characterization; Springer: Basingstoke, UK, 2018; ISBN 9783319929552. [Google Scholar]
- Asati, A.; Santra, S.; Kaittanis, C.; Perez, J.M. Surface-Charge-Dependent Cell Localization and Cytotoxicity of Cerium Oxide Nanoparticles. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 5321–5331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.L.; Yang, Z.M.; Ding, B.J. Synthesis of Cerium Oxide Nanoparticles by the Precipitation Method. Mater. Sci. Forum 2009, 610–613, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyoka, M.; Choonara, Y.E.; Kumar, P.; Kondiah, P.P.D.; Pillay, V. Synthesis of Cerium Oxide Nanoparticles Using Various Methods: Implications for Biomedical Applications. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhall, A.; Self, W. Cerium Oxide Nanoparticles: A Brief Review of Their Synthesis Methods and Biomedical Applications. Antioxidants 2018, 7, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Qu, X. Cerium oxide nanoparticle: A remarkably versatile rare earth nanomaterial for biological applications. NPG Asia Mater. 2014, 6, e90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, N.; Manna, P.; Das, J. Synthesis and biomedical applications of nanoceria, a redox active nanoparticle. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2019, 17, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heckman, K.L.; DeCoteau, W.; Estevez, A.; Reed, K.J.; Costanzo, W.; Sanford, D.; Leiter, J.C.; Clauss, J.; Knapp, K.; Gomez, C.; et al. Custom Cerium Oxide Nanoparticles Protect against a Free Radical Mediated Autoimmune Degenerative Disease in the Brain. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 10582–10596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mourdikoudis, S.; Pallares, R.M.; Thanh, N.T.K. Characterization techniques for nanoparticles: Comparison and complementarity upon studying nanoparticle properties. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 12871–12934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baalousha, M.; Ju-Nam, Y.; Cole, P.A.; Gaiser, B.; Fernandes, T.F.; Hriljac, J.A.; Jepson, M.A.; Stone, V.; Tyler, C.R.; Lead, J.R. Characterization of cerium oxide nanoparticles-Part 1: Size measurements. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2012, 31, 983–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Q.; Saltsburg, H.; Flytzani-Stephanopoulos, M. Active Nonmetallic Au and Pt Species on Ceria-Based Water-Gas Shift Catalysts. Science 2003, 301, 935–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaspar, J.; Fornasiero, P.; Graziani, M. Use of CeO2-based oxides in the three-way catalysis. Catal. Today 1999, 50, 285–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Hui, R.; Roller, J. Cathode materials for solid oxide fuel cells: A review. J. Solid State Electrochem. 2010, 14, 1125–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasinski, P.; Suzuki, T.; Anderson, H.U. Nanocrystalline undoped ceria oxygen sensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2003, 95, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Sayle, D.C.; Wang, Z.L.; Paras, M.S.; Santora, B.; Sutorik, A.C.; Sayle, T.X.T.; Yang, Y.; Ding, Y.; Wang, X.; et al. Converting Ceria Polyhedral Nanoparticles into Single-Crystal Nanospheres. Science 2006, 312, 1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, X.; Hong, L.; Liu, Z.-L. Oxygen permeation through the LSCO-80/CeO2 asymmetric tubular membrane reactor. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 268, 2–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozer, N. Optical Properties and Electrochromic Characterization of Sol–Gel Deposited Ceria Films. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2001, 68, 391–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asati, A.; Santra, S.; Kaittanis, C.; Nath, S.; Perez, J.M. Oxidase-Like Activity of Polymer-Coated Cerium Oxide nanoparticles. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 2308–2312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarnuzzer, R.W.; Colon, J.; Patil, S.; Seal, S.; Cancer, M.D.A.; Healthcare, O.R. Vacancy Engineered Ceria Nanostructures for Protection from Radiation-Induced Cellular Damage. Nano Lett. 2005, 5, 2573–2577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalyanaraman, V.; Naveen, S.V.; Mohana, N.; Balaje, R.M.; Navaneethakrishnan, K.R.; Brabu, B.; Murugan, S.S.; Kumaravel, T.S. Biocompatibility studies on cerium oxide nanoparticles–combined study for local effects, systemic toxicity and genotoxicity via implantation route. Toxicol. Res. 2019, 8, 25–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urner, M.; Schlicker, A.; Z’Graggen, B.R.; Stepuk, A.; Booy, C.; Buehler, K.P.; Limbach, L.; Chmiel, C.; Stark, W.J.; Beck-Schimmer, B. Inflammatory Response of Lung Macrophages and Epithelial Cells after Exposure to Redox Active Nanoparticles: Effect of Solubility and Antioxidant Treatment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 13960–13968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisichella, M.; Berenguer, F.; Steinmetz, G.; Auffan, M.; Rose, J.; Prat, O. Toxicity evaluation of manufactured CeO2 nanoparticles before and after alteration: Combined physicochemical and whole-genome expression analysis in Caco-2 cells. BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franchi, L.P.; Manshian, B.B.; Souza, T.; Soenen, S.; Matsubara, E.Y.; Rosolen, J.M.; Takahashi, C.S. Cyto- and genotoxic effects of metallic nanoparticles in untransformed human fibroblast. Toxicol. Vitr. 2015, 29, 1319–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- RajeshKumar, S.; Naik, P. Synthesis and biomedical applications of Cerium oxide nanoparticles—A Review. Biotechnol. Rep. 2018, 17, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pešić, M.; Podolski-Renić, A.; Stojković, S.; Matovic, B.; Zmejkoski, D.; Kojić, V.; Bogdanovic, G.; Pavićević, A.; Mojovic, M.; Savic, A.; et al. Anti-cancer effects of cerium oxide nanoparticles and its intracellular redox activity. Chem. Interact. 2015, 232, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lord, M.S.; Jung, M.; Teoh, W.Y.; Gunawan, C.; Vassie, J.; Amal, R.; Whitelock, J.M. Cellular uptake and reactive oxygen species modulation of cerium oxide nanoparticles in human monocyte cell line U937. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 7915–7924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenkranz, P.; Fernandez-Cruz, M.L.; Conde, E.; Ramírez-Fernández, M.; Flores, J.C.; Navas, J.M. Effects of cerium oxide nanoparticles to fish and mammalian cell lines: An assessment of cytotoxicity and methodology. Toxicol. Vitr. 2012, 26, 888–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, T.; Kovochich, M.; Liong, M.; Mädler, L.; Gilbert, B.; Shi, H.; Yeh, J.I.; Zink, J.I.; Nel, A.E. Comparison of the Mechanism of Toxicity of Zinc Oxide and Cerium Oxide Nanoparticles Based on Dissolution and Oxidative Stress Properties. ACS Nano 2008, 2, 2121–2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.M.; Mahdi, H.S.; Parveen, A.; Azam, A. Mediated Method Optical properties of cerium oxide (CeO2) nanoparticles synthesized by hydroxide mediated method. In AIP Conference Proceedings; AIP Publishing: Melville, NY, USA, 2018; Volume 1953, p. 030044. [Google Scholar]
- Reshma, P. Molecular Nanotechnology Cerium Oxide Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Characterization and Study of Antimicrobial Activity. J. Nanomater. Mol. Nanotechnol. 2017, 6, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tumkur, P.P.; Bayon, N.N.; Gunasekaran, N.K.; Lamani, B.R.; Prabhakaran, K.; Hall, J.C.; Ramesh, G.T. Evaluation of Cellulose Nanoparticles Synthesized by Acid Hydrolysis for Safe Applications. J. Nanosci. Res. Rep. 2020, 2, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutalib, M.A.; Rahman, M.A.; Othman, M.H.D.; Ismail, A.F.; Jaafar, J. Chapter 9-Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) and Energy-Dispersive X-ray (EDX) Spectroscopy. In Membrane Characterization; Elsevier B.V.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; ISBN 9780444637765. [Google Scholar]
- Baudot, C.; Tan, C.M.; Kong, J.C. FTIR spectroscopy as a tool for nano-material characterization. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2010, 53, 434–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sehar, S.; Naz, I.; Rehman, A.; Sun, W.; Alhewairini, S.S.; Zahid, M.N.; Younis, A. Shape-controlled synthesis of cerium oxide nanoparticles for efficient dye photodegradation and antibacterial activities. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2021, 35, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Na, T.; Wu, T.; Yuan, B.-Z. Human lung epithelial BEAS-2B cells exhibit characteristics of mesenchymal stem cells. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0227174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tumkur, P.P.; Praful, T.R.; Lamani, B.R.; Bayón, N.N. Enzymatic Synthesis, Characterization and Biocompatibility Studies of Cellulose Nanoparticles from Cotton Fibers. Adv. Nat. Sci. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2018, 2, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Chacon, E.; Acosta, D.; Lemasters, J. Primary Cultures of Cardiac Myocytes as In Vitro Models for Pharmacological and Toxicological Assessments. In In Vitro Methods in Pharmaceutical Research; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1996; ISBN 012163390X. [Google Scholar]
- Goornavar, V.; Biradar, S.; Ezeagwu, C.; Ezeagwu, D.; Hall, J.C.; Ramesh, G.T. Toxicity of Raw and Purified Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes in Rat’s Lung Epithelial and Cervical Cancer Cells. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2015, 15, 2105–2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopes, V.R.; Sanchez-Martinez, C.; Strømme, M.; Ferraz, N. In vitro biological responses to nanofibrillated cellulose by human dermal, lung and immune cells: Surface chemistry aspect. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2017, 14, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartati, Y.W.; Topkaya, S.N.; Gaffar, S.; Bahti, H.H.; Cetin, A.E. Synthesis and characterization of nanoceria for electrochemical sensing applications. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 16216–16235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tumkur, P.P. Study on toxicity, biocompatibility and antioxidant property of cerium oxide nanoparticles in human lung epithelial cells. In Proceedings of the SPIE BiOS, San Francisco, CA, USA, 2–7 February 2019; Volume 10893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chelliah, M.; Rayappan, J.B.B.; Krishnan, U.M. Synthesis and Characterization of Cerium Oxide Nanoparticles by Hydroxide Mediated Approach. J. Appl. Sci. 2012, 12, 1734–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farahamndjou, M.; Zarinkamar, M.; Firoozabadi, T. Synthesis of Cerium Oxide (CeO(2)) Nanoparticles Using Simple CO-Precipitation Method. Rev. Mex. De Física 2016, 62, 496–499. [Google Scholar]
- Deori, K.; Gupta, D.; Saha, B.; Awasthi, S.K.; Deka, S. Introducing nanocrystalline CeO2 as heterogeneous environmental friendly catalyst for the aerobic oxidation of para-xylene to terephthalic acid in water. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 7091–7099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pujar, M.S.; Hunagund, S.M.; Desai, V.R.; Patil, S.; Sidarai, A.H. One-step synthesis and characterizations of cerium oxide nanoparticles in an ambient temperature via Co-precipitation method. In AIP Conference Proceedings; AIP Publishing: Melville, NY, USA, 2018; Volume 1942, p. 050026. [Google Scholar]
- Van Tonder, A.; Joubert, A.M.; Cromarty, A.D. Limitations of the 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyl-2H-tetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay when compared to three commonly used cell enumeration assays. BMC Res. Notes 2015, 8, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riss, T.L.; Moravec, R.A.; Niles, A.L.; Duellman, S.; Benink, H.A.; Worzella, T.J.; Minor, L. Cell Viability Assays. In Assay Guidance Manual; National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2004; pp. 1–25. [Google Scholar]
- Lü, L.; Zhang, L.; Wai, M.S.M.; Yew, D.T.W.; Xu, J. Exocytosis of MTT formazan could exacerbate cell injury. Toxicol. Vitr. 2012, 26, 636–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jabbar, S.A.; Twentyman, P.R.; Watson, J.V. The MTT assay underestimates the growth inhibitory effects of interferons. Br. J. Cancer 1989, 60, 523–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renu, G.; Rani, V.V.D.; Nair, S.V.; Subramanian, K.R.V.; Lakshmanan, V.K. Development of Cerium Oxide Nanoparticles and Its Cytotoxicity in Prostate Cancer Cells. Adv. Sci. Lett. 2012, 6, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nourmohammadi, E.; Khoshdel-Sarkarizi, H.; Nedaeinia, R.; Sadeghnia, H.R.; Hasanzadeh, L.; Darroudi, M.; Oskuee, R.K. Evaluation of anticancer effects of cerium oxide nanoparticles on mouse fibrosarcoma cell line. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 4987–4996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayir, H. Reactive oxygen species. Crit. Care Med. 2005, 33, S498–S501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thannickal, V.J.; Fanburg, B.L. Reactive oxygen species in cell signaling. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2000, 279, L1005–L1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, S.; Pandey, A.K. Cerium Oxide Nanoparticles Induced Toxicity in Human Lung Cells: Role of ROS Mediated DNA Damage and Apoptosis. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tumkur, P.P.; Gunasekaran, N.K.; Lamani, B.R.; Nazario Bayon, N.; Prabhakaran, K.; Hall, J.C.; Ramesh, G.T. Cerium Oxide Nanoparticles: Synthesis and Characterization for Biosafe Applications. Nanomanufacturing 2021, 1, 176-189. https://doi.org/10.3390/nanomanufacturing1030013
Tumkur PP, Gunasekaran NK, Lamani BR, Nazario Bayon N, Prabhakaran K, Hall JC, Ramesh GT. Cerium Oxide Nanoparticles: Synthesis and Characterization for Biosafe Applications. Nanomanufacturing. 2021; 1(3):176-189. https://doi.org/10.3390/nanomanufacturing1030013
Chicago/Turabian StyleTumkur, Prathima Prabhu, Nithin Krisshna Gunasekaran, Babu R. Lamani, Nicole Nazario Bayon, Krishnan Prabhakaran, Joseph C. Hall, and Govindarajan T. Ramesh. 2021. "Cerium Oxide Nanoparticles: Synthesis and Characterization for Biosafe Applications" Nanomanufacturing 1, no. 3: 176-189. https://doi.org/10.3390/nanomanufacturing1030013
APA StyleTumkur, P. P., Gunasekaran, N. K., Lamani, B. R., Nazario Bayon, N., Prabhakaran, K., Hall, J. C., & Ramesh, G. T. (2021). Cerium Oxide Nanoparticles: Synthesis and Characterization for Biosafe Applications. Nanomanufacturing, 1(3), 176-189. https://doi.org/10.3390/nanomanufacturing1030013





