Abstract
Toxoplasmosis in immunocompromised patients results in either reactivation of latent toxoplasmosis or acute infection. In the framework of the kidney transplantation program in Senegal, the serological screening of potential pre-transplant and transplanted patients can prevent the disease. This study aimed to assess the seroprevalence of toxoplasmosis in a cohort of hemodialysis patients, candidates for kidney transplantation. To this end, a multicentre cross-sectional study was conducted in 2020 in six dialysis units from five regions. Blood samples and sociodemographic data were collected from each patient. IgG and IgM against T. gondii antibodies were assessed by a chemiluminescent method using Architect ci4100, and statistical analysis was performed using R software. Overall, 211 hemodialysis patients aged from 18 to 77 years were enrolled. The mean age was 42.62 years ± 13.6, and the sex ratio M/F was 1.24. The overall seroprevalence of T. gondii was 41.7%, with the highest value being recorded in the region of Kaolack (44.4%). Patients aged over 60 years were more typically infected, at a proportion of 56.0%. Regarding sex, males elicited a higher prevalence (44.4.%) than females did. Patients of an upper socioeconomic status were less affected, and contact with cats was not associated with toxoplasmosis. By education level, the illiterate group was most affected one. Overall, this first study of toxoplasmosis among Senegalese hemodialysis patients indicates high seroprevalence.
1. Introduction
Toxoplasmosis is a widespread, cosmopolitan parasitic disease caused by an intracellular parasite: Toxoplasma gondii. It is mainly acquired through contact with newly infected cats or by consuming contaminated meat, unwashed fruit and vegetables, and sometimes, water contaminated with cat feces [1,2,3]. While acquired toxoplasmosis is generally benign in healthy humans, it can be fatal in immunocompromised individuals, including patients with cancer, organ transplant recipients, and those with HIV/AIDS [4,5,6,7]. Either reactivation of latent toxoplasmosis or acute infection can cause toxoplasmosis in immunocompromised patients such as organ transplant recipients. In both cases, various clinical manifestations, including neurological signs such as headaches, disorientation, and convulsions may be observed [2,8]. In northern countries, serological screening for toxoplasmosis among potential pre-transplant and transplant recipients is highly recommended. The primary goal is to identify patients with a chronic infection at risk of reactivation and to prevent the disease spreading to non-immunized patients by transplanting an infected organ [3,9,10,11,12,13].
In Senegal, hemodialysis is the only treatment for patients with chronic renal failure [14]. Nevertheless, organ transplantation is now allowed due to the adoption of the law on organ and human tissue transplantation in 2015. The National Committee for Donation and Transplantation is currently finalizing procedures for initiating kidney transplantation. Previous studies on toxoplasmosis in Senegal focused only on pregnant women with seroprevalence rates ranging from 31.15% to 35.4% [15,16,17]. So far, in the framework of kidney transplantation, there are no available data on toxoplasmosis in hemodialysis patients. This study aimed to assess the seroprevalence of toxoplasmosis in a cohort of hemodialysis patients in Senegal.
2. Results
2.1. Characteristics of the Study Participants
Cross-sectional blood sampling was carried out on 211 hemodialysis patients aged from 18 to 77 years. The mean age (±SD) was 42.62 years ± 13.6, and the sex (M/F) ratio was 1.24. By age, the most represented age group (years) was 31 to 45 with 37.9%, followed by 46–60 with 27%, 18–30 with 23%, and those over 60 were less represented with 12%. Patients from Dakar region were most represented ones with 41.2% (95% CI 35–48), followed by Kaolack and Thiès with 17.1% (95% CI 12–23) and 16.1% (95% CI 12–22), respectively. With regard to the education level, the proportions for primary, secondary, and university levels were 33% (95% CI 27–40), 27.8% (95% CI 22–34), and 14.4% (95% CI 10–20), respectively. According to socioeconomic status (SES), most of the patients (41.7% (95% CI, 35–49)) had a low SES. Those with moderate and upper SES were observed at proportions of 35.1% (95% CI, 29–42) and 23.2% (95% CI, 18–30), respectively. Contact with a cat was noted in 60 participants (28.4% (95% CI, 23–35)). Detailed characteristics of the cohort are summarized in Table 1.

Table 1.
Sociodemographic characteristics of hemodialysis patients (N = 221).
2.2. Toxoplasmosis Seroprevalence
The overall seroprevalence of T. gondii was 41.7% (95% CI 35–49). Only four patients were positive for IgM toxoplasma antibodies (1.9%, (95% CI 0.61–5.1)). The distribution of antibody response by region showed the highest seroprevalence in Kaolack (44.4%, (95% CI 28–62)), followed by Dakar (43.7%, (95% CI 33–55)), Thies (41.2%, (95% CI 25–59)), Ziguinchor (40.7%, (95% CI 23–61)), and Saint-Louis (33.3%, (95% CI 17–54)). By age group, the highest seroprevalence was found among patients aged over 60 years with 56.0% (95% CI 35–75), followed by the age groups 46–60 years (41.4%, (95% CI 29–55)), 31–45 years (41.2%, (95% CI 31–53)), and decreasing to 35.4% (95% CI 23–51) among patients aged between 18 and 30 years old. Overall, the positive antibody response was higher in males (44.4.%, (95% CI 35–54)) compared to that in females (38.3%, (95% CI 29–49)), although the difference was not significant (p = 0.37). According to the education level, the highest seroprevalence was recorded in the illiterate group with 57.7% (95% CI 43–71) and the lowest was recorded in patients with secondary education at 31.0% (95% CI 20–45). Although there was no significant difference in the seroprevalence according to SAS (p = 0.7), patients with high SAS were less affected (36.7%, (95% CI 24–52)) than those with low (43.1%, (95% CI 33–54)) and moderate (43.2%, 95% CI 32–55) SAS were. Similarly, contact with a cat did not show any significant difference in the prevalence between the two groups (p > 0.9) (Table 2).

Table 2.
Seroprevalence of toxoplasmosis by sociodemographic characteristics of hemodialysis patients.
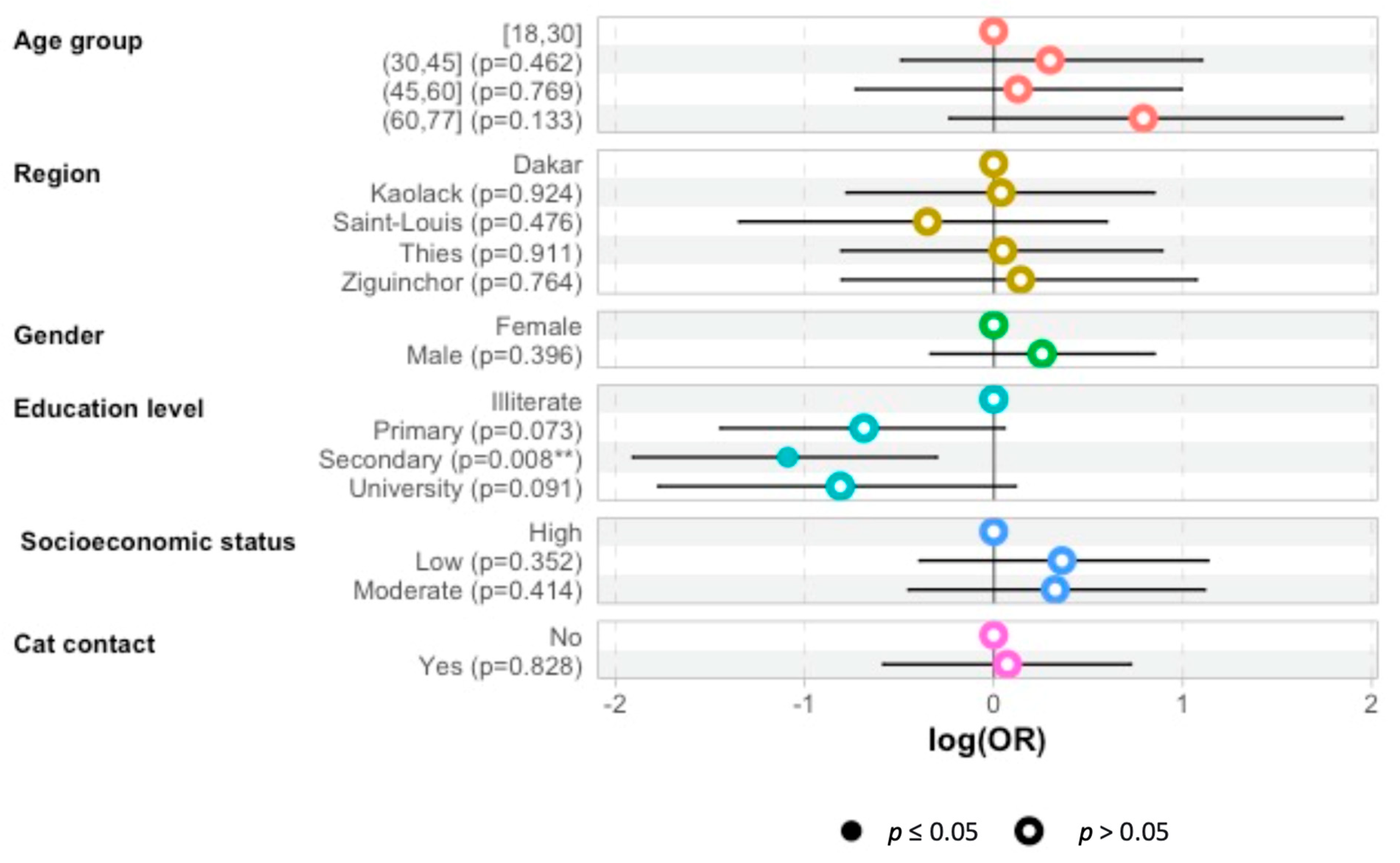
The multivariate logistic regression analysis has shown that patients with secondary education levels were less affected by toxoplasmosis than the illiterate group was: odds ratio—1.1 (95%CI 1.9–0.28; p = 0.009) (Figure 1).
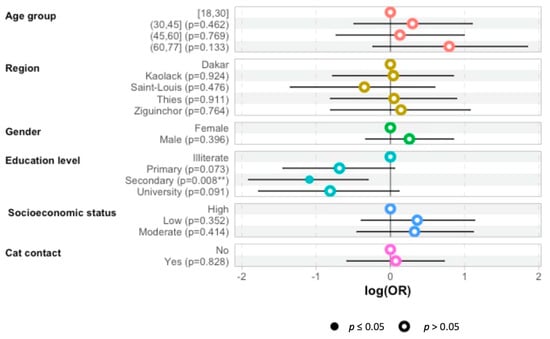
Figure 1.
Odds ratio (OR) predictions for the probability of toxoplasmosis seropositivity according to age group, region, sex, education level, SAS, of hemodialysis patients and whether they had contact with a cat. The plot presents OR points estimates with 95% CI. (**: p < 0.05).
3. Discussion
Our objective was to determine the seroprevalence of toxoplasmosis among hemodialysis patients for the first time. Indeed, toxoplasmosis is an opportunistic disease, in which the reactivation of a past infection can occur during immunosuppressive treatment. In the framework of renal transplantation in Senegal, it is crucial to evaluate the seropositivity rate in patients undergoing hemodialysis.
In our series, a positivity rate of IgG antibodies of 41.71% was recorded, and four patients were IgM positive (1.9%). However, a second sample was not collected from the four patients with patterns compatible with a recent infection (IgG +/IgM +) to investigate the course of the disease. Comparing our results to those found in hemodialysis patients in other countries, our seroprevalence rate was lower than those recorded in Malaysia (56.7%) [18], Turkey (76.6%) [19], and Iran (80.8%) [20]. These wide variations in seroprevalence across countries may be attributed to socio-economic or cultural factors (cat ownership, personal hygiene, and eating habits) and climatic factors.
In Senegal, as in most West African countries, data regarding toxoplasmosis are exclusively available for pregnant women. Therefore, our findings are compared with previous data regarding pregnant women in Dakar.
In 2010, Lô et al. reported a seroprevalence rate of 31.15% in their study among pregnant women referred to the laboratory of the Military Hospital of Ouakam [15]. Five years later, Seck et al. still reported a slightly increased seroprevalence rate of 32.70% in the same laboratory [17]. In addition, in 2017, Tine et al. reported a seroprevalence of 35.4% among pregnant women attending the Fann Teaching Hospital in Dakar [16]. These findings indicate that the seroprevalence of toxoplasmosis is highest in hemodialysis patients compared to that in the pregnant women population. This same pattern was observed by comparing the specific results from dialysis units of Dakar with the previous data on pregnant women. However, comparing the seroprevalence rate of toxoplasmosis among females in this study (38.3%) with those previously recorded in Dakar shows that it remains higher, even if the difference is insignificant.
In Africa, toxoplasma seroprevalence has been highly variable from country to country. Indeed, rates above 50% were recorded in Côte d’Ivoire (60%) [7], Gabon (56%) [21], Central African Republic (47.9%) [22], and Morocco (50.6%) [23]. However, they are much lower in Nigeria and Algeria, at 43.7% and 47.8%, respectively [24,25].
Analyzing seroprevalence of toxoplasma by age did not reveal any significant difference in our study (p = 0.49), even though the highest rates were reported among patients aged over 60 and between 30 and 45. Contrary to our findings, Lô showed a significant difference with increasing seropositivity with the age of the patients (p < 0.05) [15]. The same trends were observed in Iran in series by Rostami et al. in 2006 and Mostafavi et al. in 2011 [26,27].
The seroprevalence of toxoplasmosis in our study indicated that men are more affected than women are, although the difference was not statistically significant (p = 0.37). These findings suggest a comparable infection risk level between men and women. Indeed, toxoplasmosis is mainly contracted by ingesting oocysts buried in the soil or cysts in animal meat (sheep). Senegalese cooking habits, with temperatures above 70 °C, make contamination by the ingestion of cysts unusual. Therefore, cyst ingestion remains the main route of contamination in this context, with similar levels of risk for both sexes. The same finding was reported in the series by Nissapatorn in 2003 by ELISA [19] and Alvarado-Esquivel et al. in Mexico in 2014 [28]. Meanwhile, Saadat et al. showed the highest seroprevalence in women in Iran [29].
In this study, the seroprevalence of toxoplasmosis in hemodialysis patients differed between regions, although it was not significant. The region of Kaolack recorded the highest seroprevalence rate, followed by Dakar, Thiès, and Ziguinchor, respectively, without any significance. The northern region of Saint-Louis had the lowest seroprevalence trend. These findings are not in line with evidence from the literature that suggests that toxoplasmosis is more common in humid areas. The region Ziguinchor, located in the southern province of Senegal with the highest humidity level, is expected to record the highest seroprevalence. However, the low sample sizes in the different study areas may explain such results.
According to the education level, illiterate patients were more affected by toxoplasmosis than the other groups were. In a study in Malaysia, the highest prevalence was noted in patients with a primary level of education [19].
In our series, any significant difference was noted in seroprevalence based on contact with cats. In contrast, in Iran, Soltani et al. found a significant association between seroprevalence of T. gondii infection and contact with cats (OR 3.73 (95% CI 2.00–6.95)) [30]. Additionally, an association between Toxoplasma infection, contact with cats, and socioeconomic status was reported in Zambia by Frimpong et al. [31].
Socioeconomic status has been identified as a factor influencing toxoplasmosis prevalence. Though the difference was not statistically significant, our results agree with this trend. Patients with high SAS are less affected than those with moderate and low socioeconomic status are. A similar trend was observed in Brazil, where the seroprevalences were 23% in the upper socioeconomic groups, 62% in the middle socioeconomic groups, and 84% in the lower socioeconomic groups [32]. Similarly, Yasodhara et al. reported, in India, a higher seropositivity rate among patients with low SES compared to that of those with high SES [33]. These findings are consistent with the hypothesis that toxoplasmosis is more prevalent in people of a low socioeconomic status.
Our study remains two limitations. First, the study’s small size was due to the low number of hemodialysis patients attending dialysis units. Nevertheless, all the patients consenting to be included were enrolled.
Second, there are no available data on toxoplasmosis for the general population in Senegal that has been used for comparison with the prevalence among hemodialysis patients. The only available data concern pregnant women.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Areas
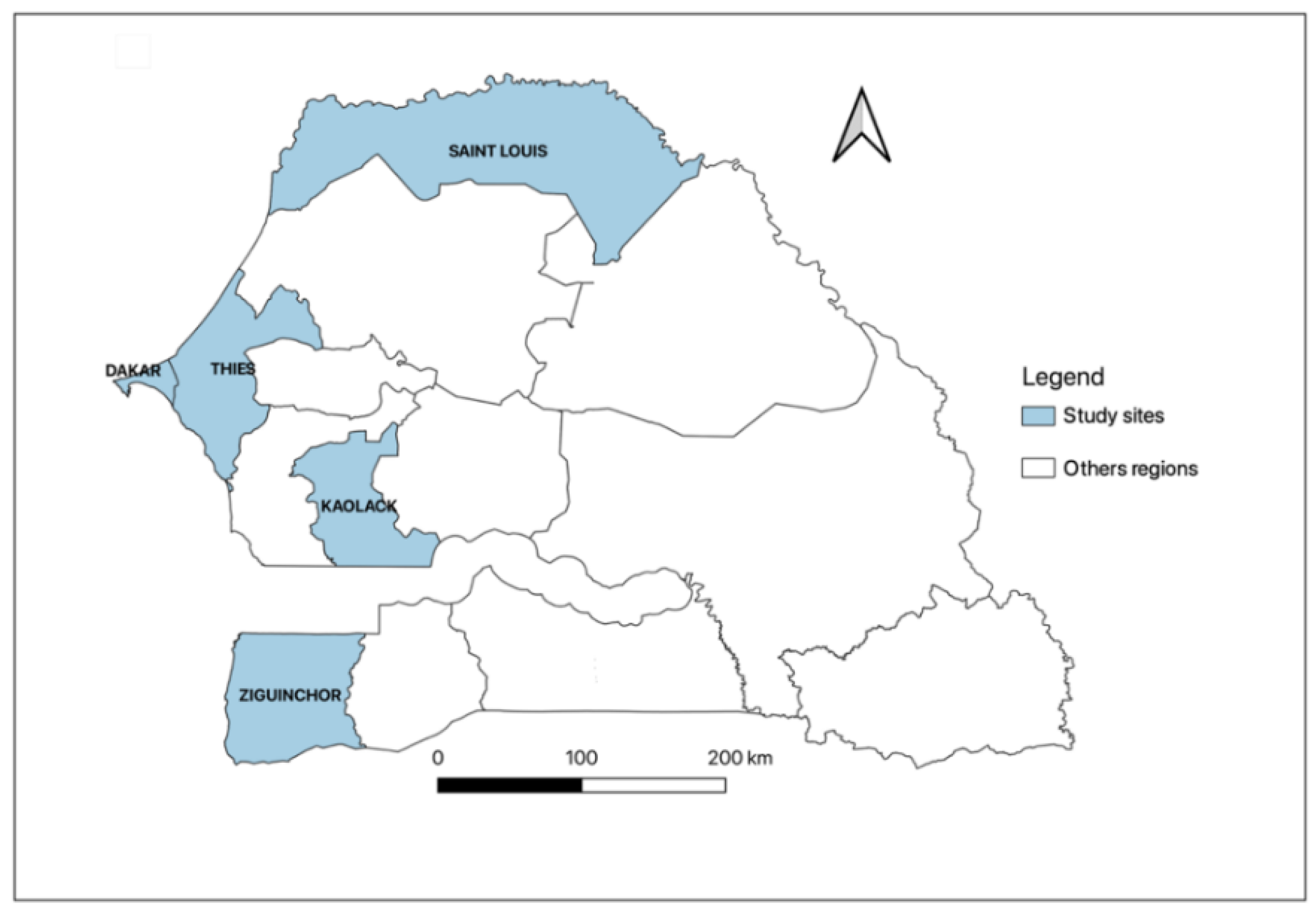
This is a cross-sectional multicentre study carried out between June and September 2020 in six dialysis units in five regions of Senegal, including Dakar, Thiès, Kaolack, Saint-Louis, and Ziguinchor. Two dialysis units in Dakar (Military hospital of Ouakam and Idrissa Pouye Hospital), and one in each other region: Thiès (Amadou Sakhir Ndieguene Hospital), Kaolack (El hadji Ibrahima Niass Regional Hospital), Saint-Louis (Regional Hospital of Saint-Louis), and Ziguinchor (Regional Hospital of Ziguinchor) (Figure 2). Patients aged ≥18 years and undergoing chronic hemodialysis for at least three months were included. Signed informed consent was obtained from all the study participants before enrolment. Non-consenting patients and those diagnosed with an acute kidney injury were excluded. We collected 5 mL of venous blood for each patient and recorded clinical symptoms for the last three months and dialysis parameters from the medical records. Serum samples were obtained by centrifugation of the whole blood at 3000 rpm for 5 min and stored at −20 °C until used.
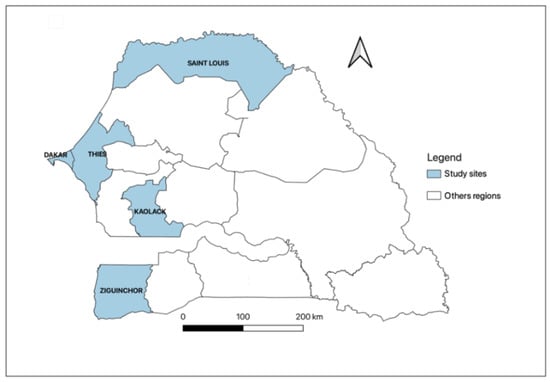
Figure 2.
Senegalese regions included the five study sites.
4.2. Toxoplasma gondii Antibodies Detection
Using serum samples, quantitative analysis of anti-T. gondii IgG and IgM antibodies was carried out at the laboratory of the Military Hospital of Ouakam by a chemiluminescent microparticle immunoassay (CMIA) according to the manufacturer’s instructions using Architect ci4100 (Abbott). Briefly, The ARCHITECT Toxo IgG and IgM assay is a two-step immunoassay for the quantitative determination of IgG and qualitative detection of IgM antibodies to T. gondii in human serum and plasma using CMIA technology with flexible assay protocols, referred to as Chemiflex. To quantitatively determine IgG, a pre-diluted sample, assay diluent, and paramagnetic microparticles coated with recombinant T. gondii antigens (containing recombinant antigens P30 (SAG1) and P35 (GRA8)) were combined in the first step. T. gondii specific antibodies in the sample bound to microparticles coated with recombinant T. gondii antigens. After washing, murine acridinium-labeled anti-human IgG conjugate was added to create a reaction mixture in the second step. After another wash cycle, pre-trigger and trigger solutions were added to the reaction mixture. There is a direct relationship between the amount of anti-Toxo IgG in the sample and the relative light units (RLU) detected by the ARCHITECT i System optics. The IgG antibody test was considered to be non-reactive (<1.6 IU/mL), grey zone (1.6 to <3.0 IU/mL), and reactive (≥3.0 IU/mL). For the qualitative detection of IgM, in the first step, we combined the pre-diluted sample and paramagnetic microparticles coated with anti-human IgM mouse monoclonal antibodies. The specific anti-toxoplasma IgM in the sample was bound to the anti-human IgM mouse monoclonal antibody-coated microparticles. After washing, a conjugate complex consisting of an acridinium labeled anti-mouse monoclonal antigen p30 F(ab’)2 fragment and a native T. gondii lysate containing the p30 antigen was added to create a reaction mixture in the second step. In the first step, this conjugate complex was bound to the specific anti-Toxo IgM captured by the microparticles coated with a mouse monoclonal anti-human IgM antibody. After another wash cycle, pre-trigger and trigger solutions were added to the reaction mixture. The ARCHITECT i system calculated the average chemiluminescent signal from Calibrator 1; the default result unit for the ARCHITECT Toxo IgM test is the index. The IgM antibody was considered to be non-reactive (<0.50 Index), grey zone (0.50 ≤ x < 0.60 Index), and reactive (≥0.60 Index).
4.3. Statistical Analysis
Data were analyzed using R software (R 4.1.2). Continuous variables are described as mean and standard deviation. Normally distributed variables were compared using the Student t-test, and abnormally distributed data were compared with the nonparametric Mann–Whitney U test. Categorical variables are presented as percentages, and Fisher exact or chi-squared tests were used for proportional assessments. Univariate logistic regression analysis was used to assess the association between the related risk factors and seropositivity. Four age groups were defined for analysis, i.e., from 18 to 30 years; from 31 to 45 years; from 46 to 60 years; from 61 to 77 years. Socioeconomic status (SES) was based on a combination of occupation, education level, monthly income, and living area [34]. For all the statistical tests, we accepted a two-sided level of significance at p ≤ 0.05.
5. Conclusions
This study is the first one regarding toxoplasmosis in hemodialysis patients in Senegal, and it revealed higher seroprevalence compared with the previous data recorded in pregnant women. This finding indicates an increased risk of potential transplant recipients harboring Toxoplasma gondii cysts, which could lead to re-activation after immunosuppressive treatments. In addition, almost 60% of hemodialysis patients are not immunized against toxoplasmosis, highlighting a risk of infection due to the transplantation of an infected organ. These findings suggest systematic screening for toxoplasmosis in future pre-transplant patients and among organ donor patients in Senegal.
Author Contributions
M.C.S., M.M., S.M.S., Y.K., M.M.C., K.D., M.A.D., A.D., S.M. and D.N. conceived and designed the study. M.M., S.M.S., S.M., A.D., Y.K., M.M.C., Y.A.D., B.C. and A.K. contributed to the sample collection. M.C.S., V.D., P.A.T.G., C.F., M.C., I.D., M.N. and M.G. performed the laboratory analyses. M.C.S., A.S.B., M.N. and M.G. analyzed the data and drafted the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The original survey from which samples were collected was funded by Fund O-COVID-19 (number 016/2020) from the Senegalese Ministry of High Education and Scientific and IRESSEF.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Patients were recruited under the study SEN20/56 approved by the Senegalese National Ethics Committee of Research and Health (Number: 00000159/MSAS/CNERS/Sec).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all participants.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets used and analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to the hemodialysis patients who participated in this study. We want to acknowledge all the staff of the dialysis units who participated in this study (HMO, HOGIP, Kaolack, Saint-Louis, and Ziguinchor) and the laboratory staff of the Military hospital of Ouakam, where the analyses were performed.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
References
- Skariah, S.; McIntyre, M.K.; Mordue, D.G. Toxoplasma gondii: Determinants of tachyzoite to bradyzoite conversion. Parasitol. Res. 2010, 107, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robert-Gangneux, F.; Dardé, M.L. Epidemiology of and diagnostic strategies for toxoplasmosis. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2012, 25, 264–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montoya, J.G.; Liesenfeld, O. Toxoplasmosis. Lancet 2004, 363, 1965–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pott, H.; Castelo, A. Isolated cerebellar toxoplasmosis as a complication of HIV infection. Int. J. STD AIDS 2013, 24, 70–72. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Agrawal, S.R.; Singh, V.; Ingale, S.; Jain, A.P. Toxoplasmosis of spinal cord in acquired immunodeficiency syndrome patient presenting as paraparesis: A rare entity. J. Glob. Infect. Dis. 2014, 6, 178–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da Cunha, S.; Ferreira, E.; Ramos, I.; Martins, R.; De Freitas, L.; Borges, J.L. Cerebral toxoplasmosis after renal transplantation. Case report and review. Acta Med. Port. 1994, 7 (Suppl. 1), S61–S66. [Google Scholar]
- AdouBryn, K.D.; Ouhon, J.; Nemer, J.; Yapo, C.G.; Assoumou, A. Serological survey of acquired toxoplasmosis in women of child-bearing age in Yopougon (Abidjan, Côte d’Ivoire). Bull. Soc. Pathol. Exot. 2004, 97, 345–348. [Google Scholar]
- Barratt, J.L.N.; Harkness, J.; Marriott, D.; Ellis, J.T.; Stark, D. Importance of nonenteric protozoan infections in immunocompromised people. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2010, 23, 795–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murat, J.B.; Hidalgo, H.F.; Brenier-Pinchart, M.P.; Pelloux, H. Human toxoplasmosis: Which biological diagnostic tests are best suited to which clinical situations? Expert Rev. Anti Infect. Ther. 2013, 11, 943–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contini, C. Clinical and diagnostic management of toxoplasmosis in the immunocompromised patient. Parassitologia 2008, 50, 45–50. [Google Scholar]
- Bessières, M.H. Les infections parasitaires chez les transplantés. RFL 2008, 2008, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patrat-Delon, S.; Gangneux, J.P.; Lavoué, S.; Lelong, B.; Guiguen, C.; Le Tulzo, Y. Correlation of parasite load determined by quantitative PCR to clinical outcome in a heart transplant patient with disseminated toxoplasmosis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2010, 48, 2541–2545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desoubeaux, G.; Perret-Gallix, K.; MacHet, M.C.; Sirinelli, A.; Bailly, É.; Van Langendonck, N. Toxoplasmic cyst and heart transplant: A case report of serological reactivation in an acute graft rejection context. Ann. Biol. Clin. 2012, 70, 323–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seck, S.M.; Mbow, M.; Kane, Y.; Cisse, M.M.; Faye, G.; Kama, A. Prevalence of SARS-CoV-2 antibodies in hemodialysis patients in Senegal: A multicenter cross-sectional study. BMC Nephrol. 2021, 22, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, G.; Diouf, N.N.; Faye, B.; Seck, M.C.; Diawara, P.S.; Ba, I. Toxoplasmosis prevalence among pregnant women attending at the Military hospital of Ouakam Laboratory, Dakar. MAN 2012, 59, 7. [Google Scholar]
- Tine, R.C.K.; Dieng, T.; Sylla, K.; Sow, D.; Lelo, S.; Dia, M. Trends in toxoplasmosis seroprevalence among pregnant women attending the Fann Teaching Hospital in Dakar Senegal. JPVB 2017, 9, 146–152. [Google Scholar]
- Seck, M.C.; Faye, B.; Mbow, M.; Ndiaye, M.; Badiane, A.S.; Diongue, K. Serological study on toxoplasmosis among pregnant women attending at military hospital of Ouakam, Dakar. Dakar Med. 2015, 60, 7. [Google Scholar]
- Nissapatorn, V.; Leong, T.H.; Lee, R.; Init, I.; Ibrahim, J.; Yen, T.S. Seroepidemiology of toxoplasmosis in renal patients. Southeast Asian J. Trop. Med. 2011, 42, 237–247. [Google Scholar]
- Ocak, S.; Duran, N.; Eskiocak, A.F.; Aytac, H. Anti-Toxoplasma gondii antibodies in hemodialysis patients receiving long-term hemodialysis therapy in Turkey. Saudi Med. J. 2005, 26, 1378–1382. [Google Scholar]
- Seyyedpour, S.H.; Afshar, P.; Barzegarnejad, A.; Kalhori, S.; Agah, R. Evaluation of Anti-Toxoplasma gondii Antibodies in Hemodialysis Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease in Sari, Iran. Nephrourol. Mon. 2016, 8, e40182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mpiga Mickoto, B.; Mickoto, B.M.; Akue, J.P.; Bisvigou, U.; Tsonga, S.M.; Nkoghe, D. Étude sérologique de la toxoplasmose chez les femmes enceintes de Franceville, Gabon. Bull. Soc. Pathol. Exot. 2010, 103, 41–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gamba, E.P.; Nambei, W.S.; Kamandji, L. Integrated screening for HIV, syphilis, and toxoplasmosis among pregnant women in the Central African Republic. Med. Sante Trop. 2013, 23, 421–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Mansouri, B.; Rhajaoui, M.; Sebti, F.; Amarir, F.; Laboudi, M.; Bchitou, R.; Hamad, M.; Lyagoubi, M. Seroprevalence of toxoplasmosis in pregnant women in Rabat, Morocco. Bull. Soc. Pathol. Exot. 2007, 100, 289–290. [Google Scholar]
- Olusi, T.; Groß, U.; Ajayi, J. High incidence of toxoplasmosis during pregnancy in Nigeria. Scand. J. Infect. Dis. 1996, 28, 645–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messerer, L.; Bouzbid, S.; Gourbdji, E.; Mansouri, R.; Bachi, F. Seroprevalence of toxoplasmosis in pregnant women in Annaba, Algeria. Rev. Epidemiol. Sante Publique 2014, 62, 160–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostami, M.N.; Eskandari, E.; Garoosi, Z.; Mohajeri, N.; Rezaian, M.; Keshavarz, H. Serological Study of Toxoplasma gondii Infection Using IFA Method in Renal Transplant Recipients. IJP 2006, 1, 31–39. [Google Scholar]
- Mostafa, N.E.S.; Abdel Hamed, E.F.; Rashed, H.E.S.; Mohamed, S.Y.; Abdelgawad, M.S.; Elasbali, A.M. The relationship between toxoplasmosis and different types of human tumors. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries. 2018, 12, 137–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarado-Esquivel, C.; Pacheco-Vega, S.J.; Hernández-Tinoco, J.; Sánchez-Anguiano, L.F.; Berumen-Segovia, L.O.; Rodríguez-Acevedo, F.J.I.; Beristain-García, I.; Rábago-Sánchez, E.; Liesenfeld, O.; Campillo-Ruiz, F.; et al. Seroprevalence of Toxoplasma gondii infection and associated risk factors in Huicholes in Mexico. Parasites Vectors 2014, 7, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saadat, F.; Mahmoudi, M.R.; Rajabi, E.; Roshan, Z.A.; Shad, B.M.; Karanis, P. Seroepidemiology and Associated Risk Factors of Toxoplasma gondii in Hemodialysis Patients. Acta Parasitol. 2020, 65, 906–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltani, S.; Kahvaz, M.S.; Soltani, S.; Maghsoudi, F.; Foroutan, M. Seroprevalence and associated risk factors of Toxoplasma gondii infection in patients undergoing hemodialysis and healthy group. BMC Res. Notes 2020, 13, 551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frimpong, C.; Makasa, M.; Sitali, L.; Michelo, C. Seroprevalence and determinants of toxoplasmosis in pregnant women attending antenatal clinic at the university teaching hospital, Lusaka, Zambia. BMC Infect. Dis. 2017, 17, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Malki, E.S. Toxoplasmosis: Stages of the protozoan life cycle and risk assessment in humans and animals for an enhanced awareness and an improved socio-economic status. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 28, 962–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasodhara, P.; Ramalakshmi, B.; Lakshmi, V.; Krishna, T. Socioeconomic status and prevalence of toxoplasmosis during pregnancy. IJMM 2004, 22, 241–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oakes, J.M.; Rossi, P.H. The measurement of SES in health research: Current practice and steps toward a new approach. Soc. Sci. Med. 2003, 56, 769–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).