Evaluation of ((La0.60Sr0.40)0.95Co0.20Fe0.80O3-x)-Ag Composite Anode for Direct Ammonia Solid Oxide Fuel Cells and Effect of Pd Impregnation on the Electrochemical Performance
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Methods
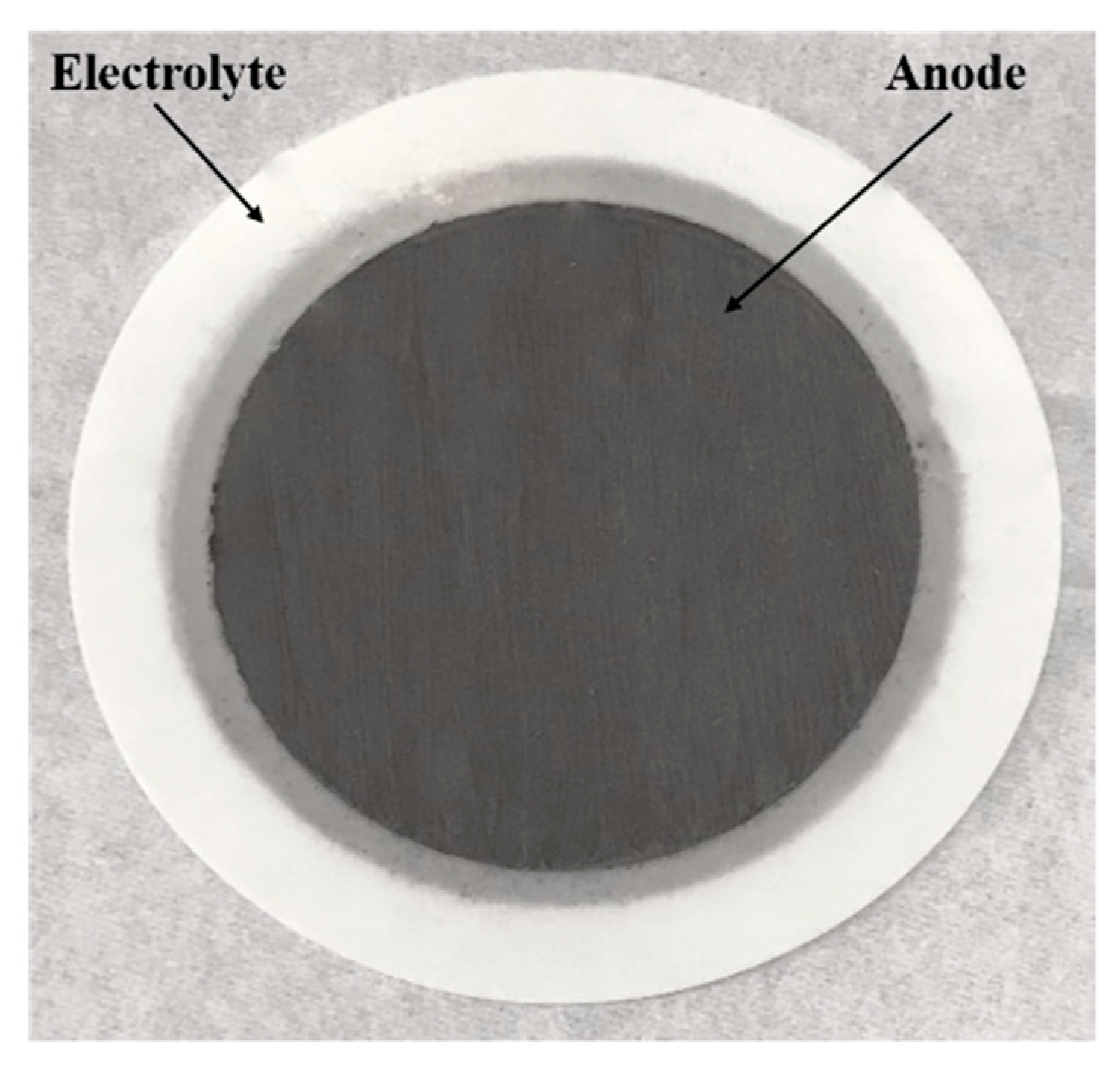
2.1. Materials and Cell Fabrication
2.2. Material Characterisation
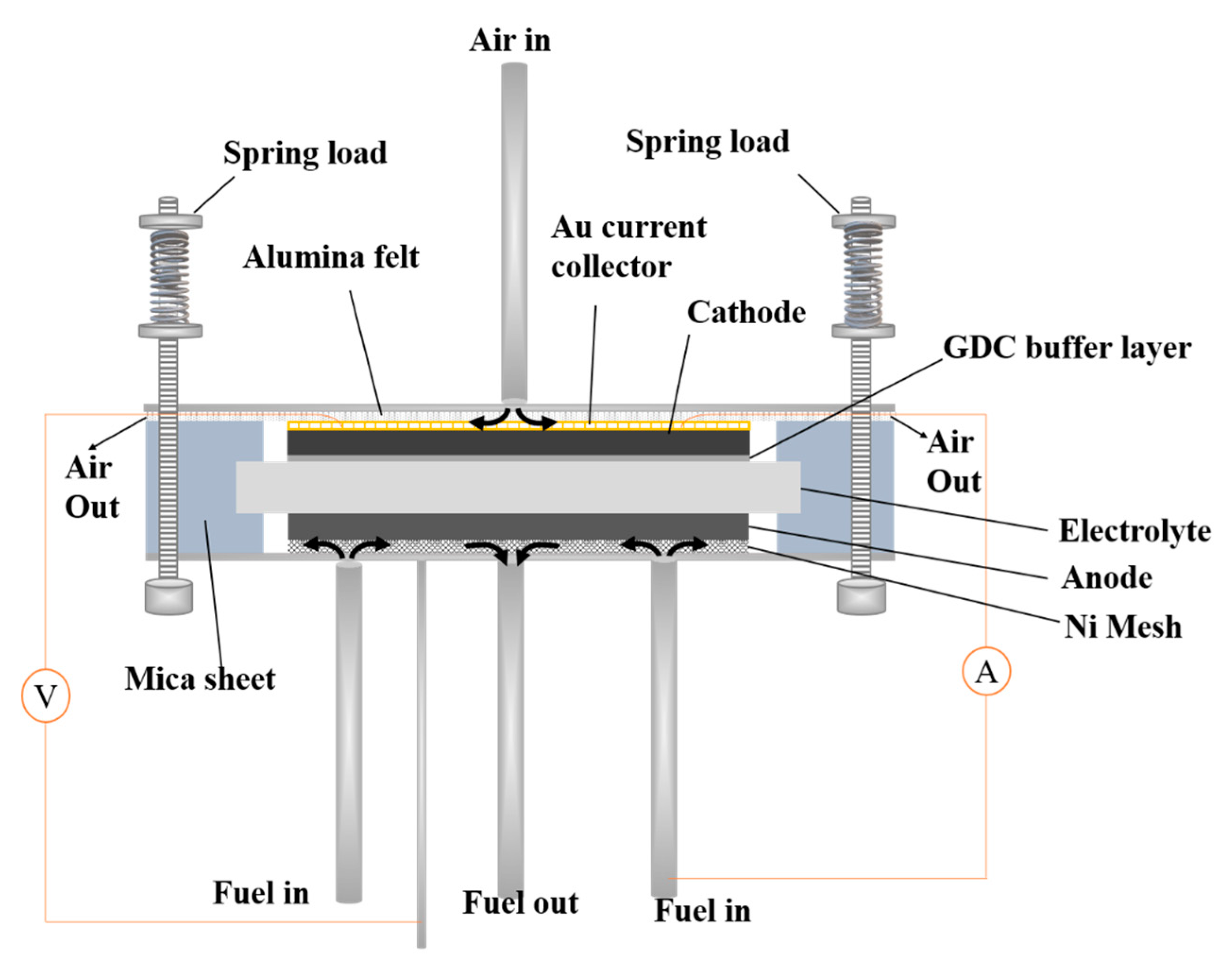
2.3. Cell Performance Evaluation
3. Result and Discussion
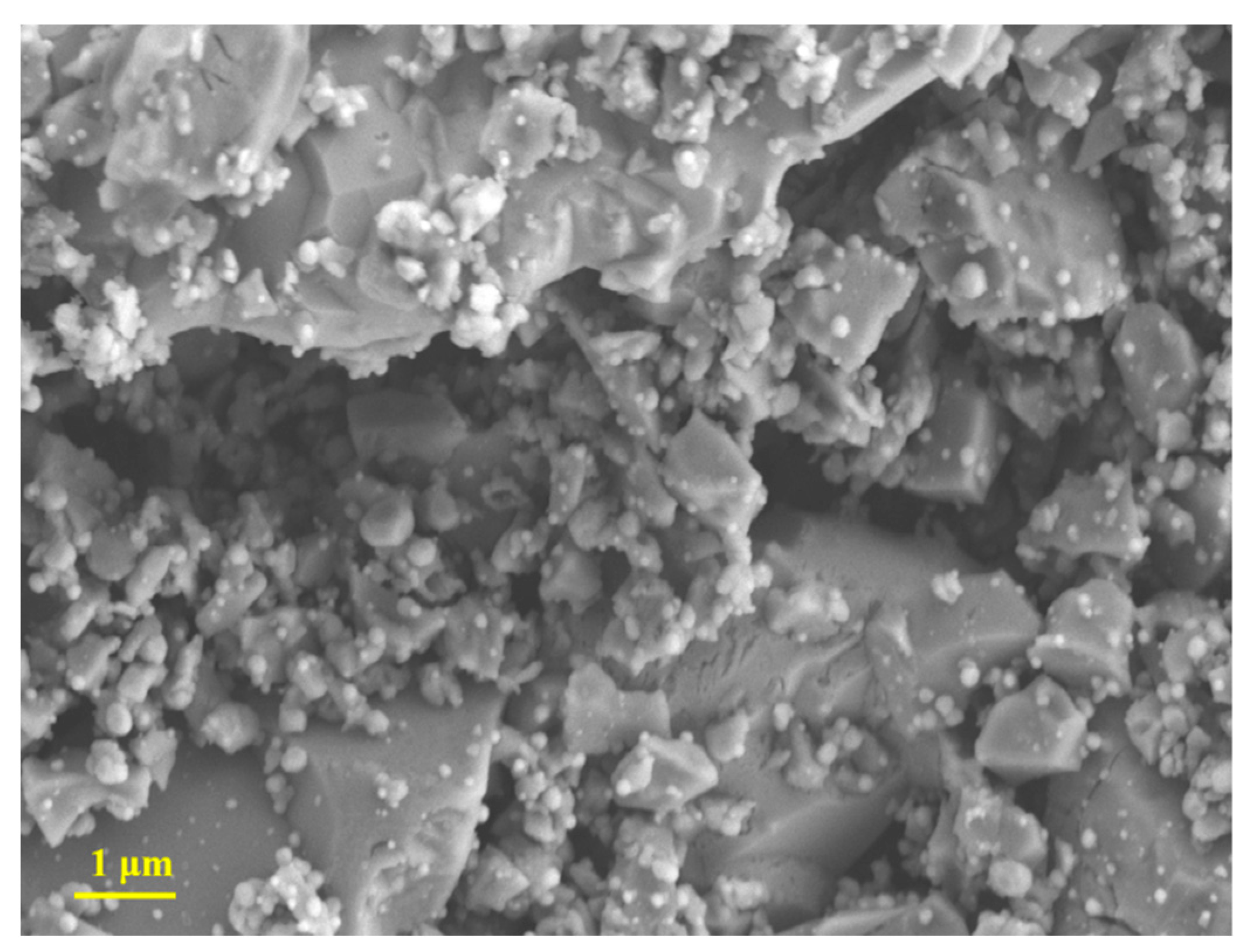
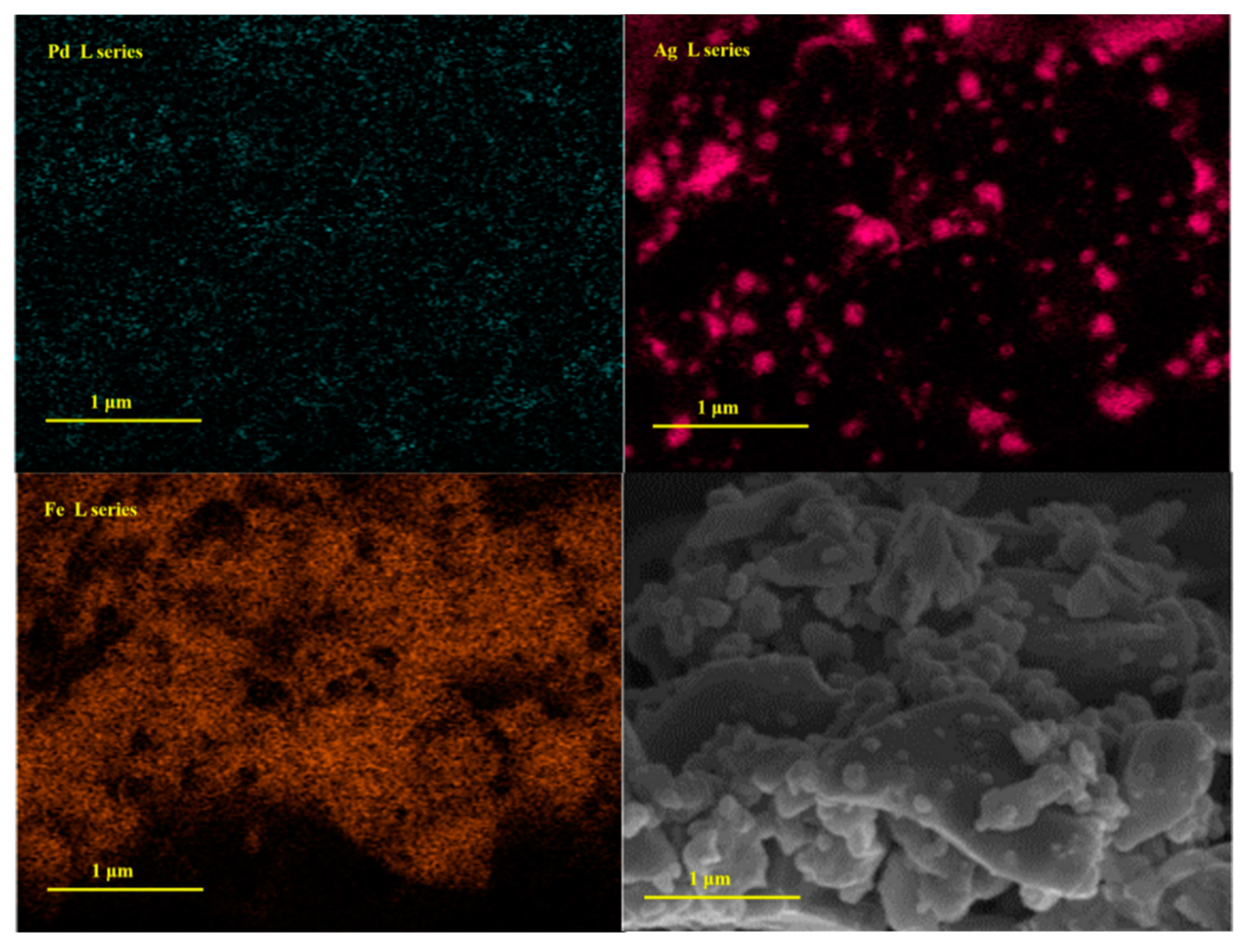
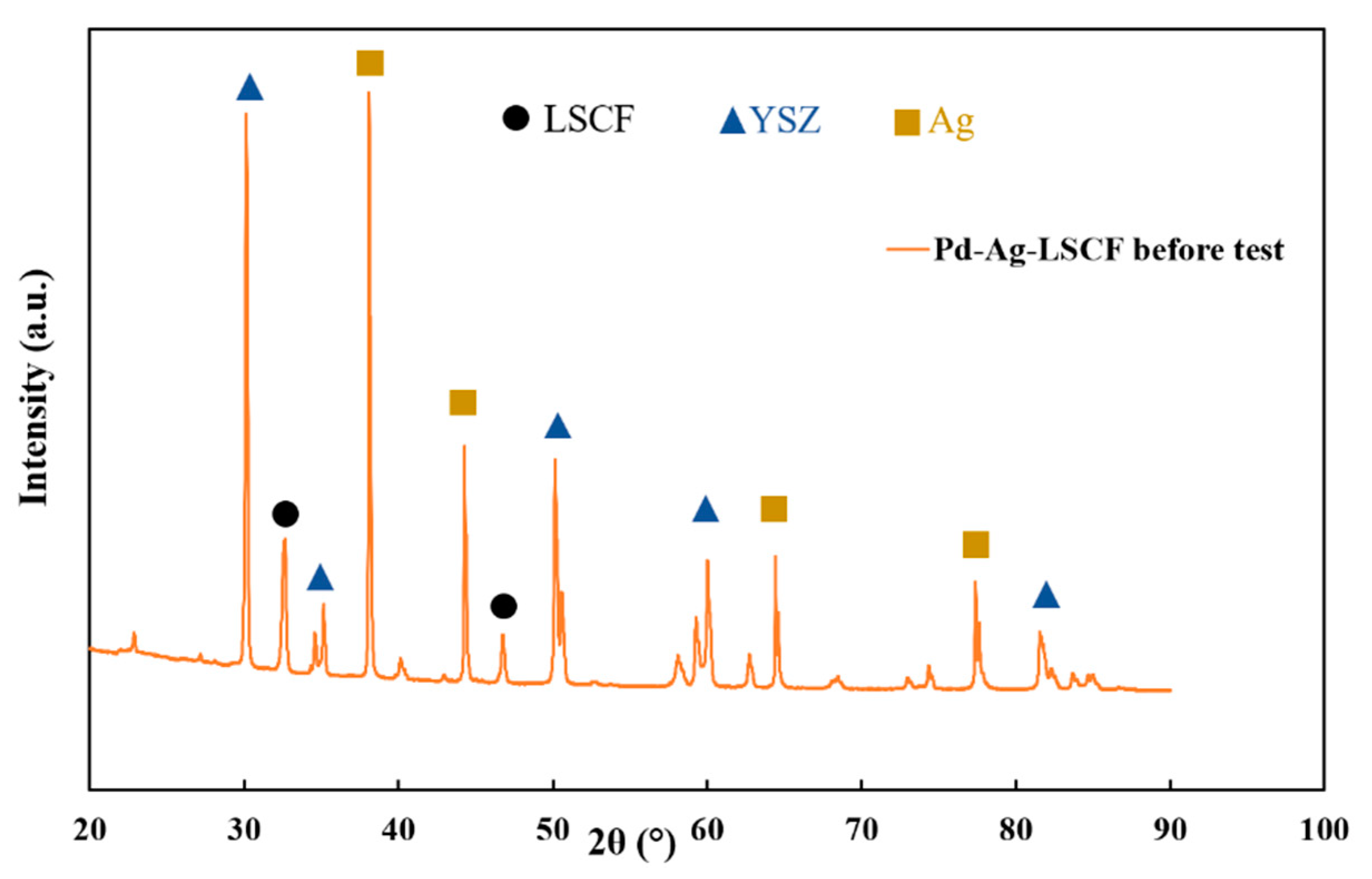
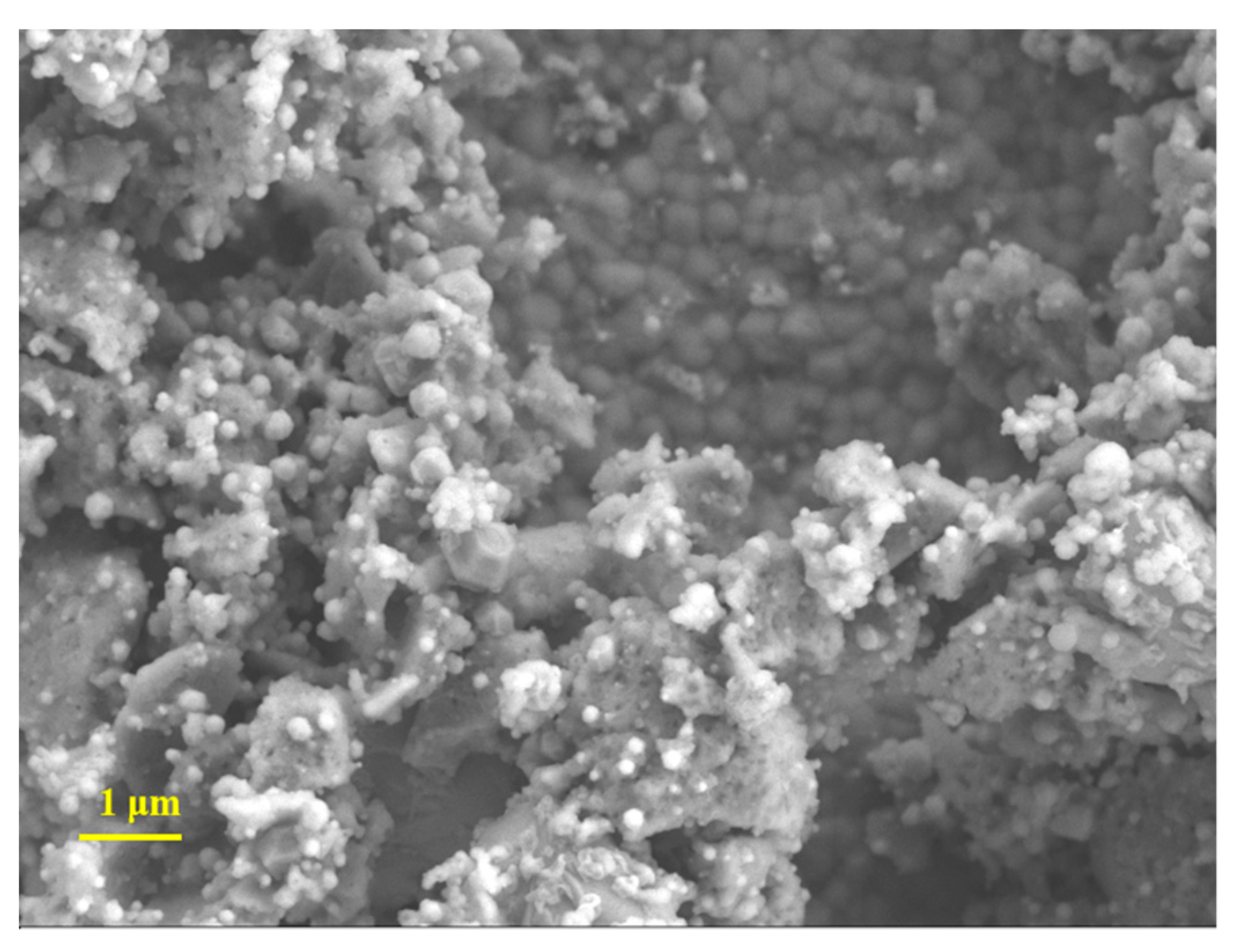
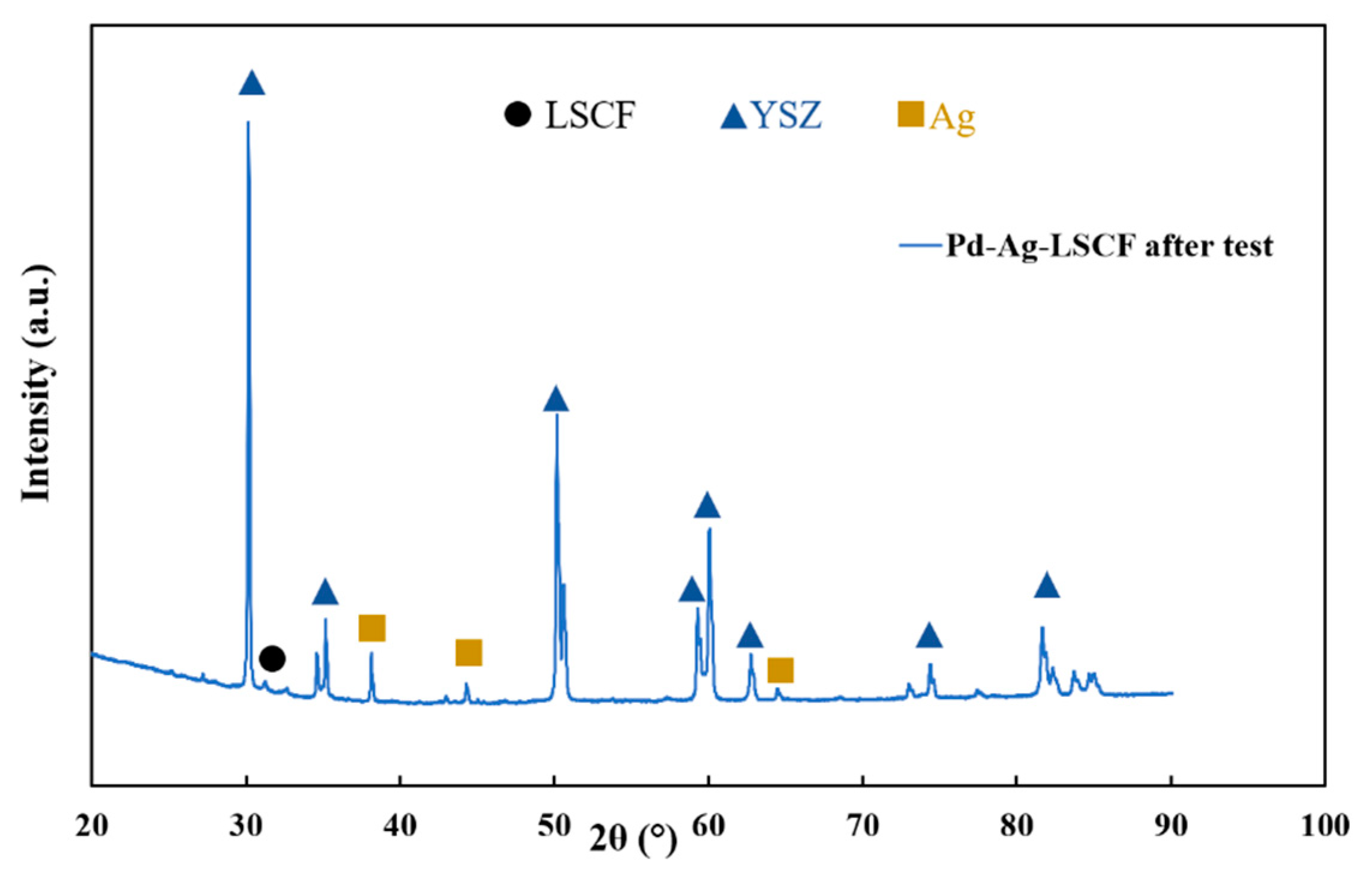
3.1. Materials Characterisation
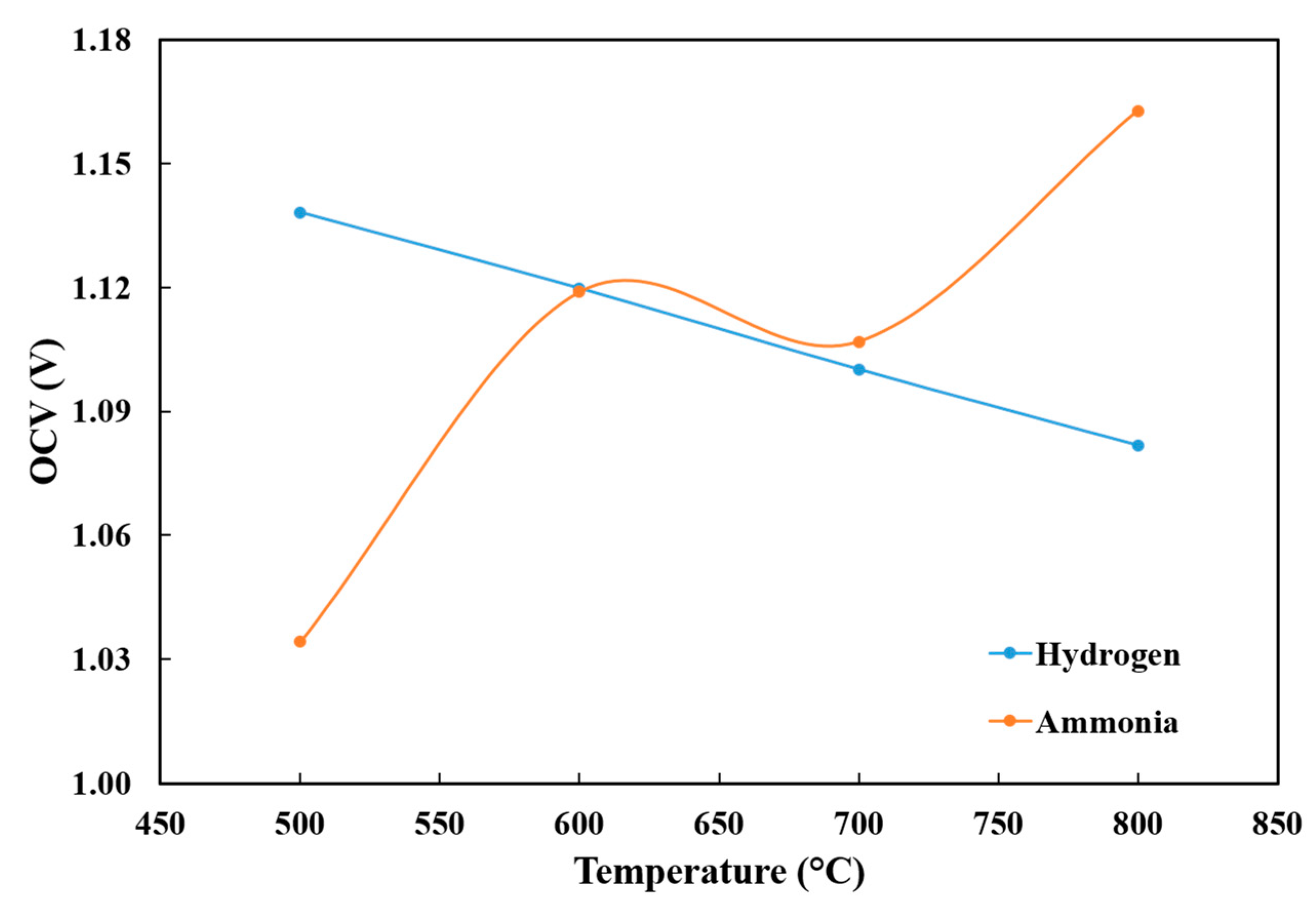
3.2. Temperature Effects on OCV and Performance
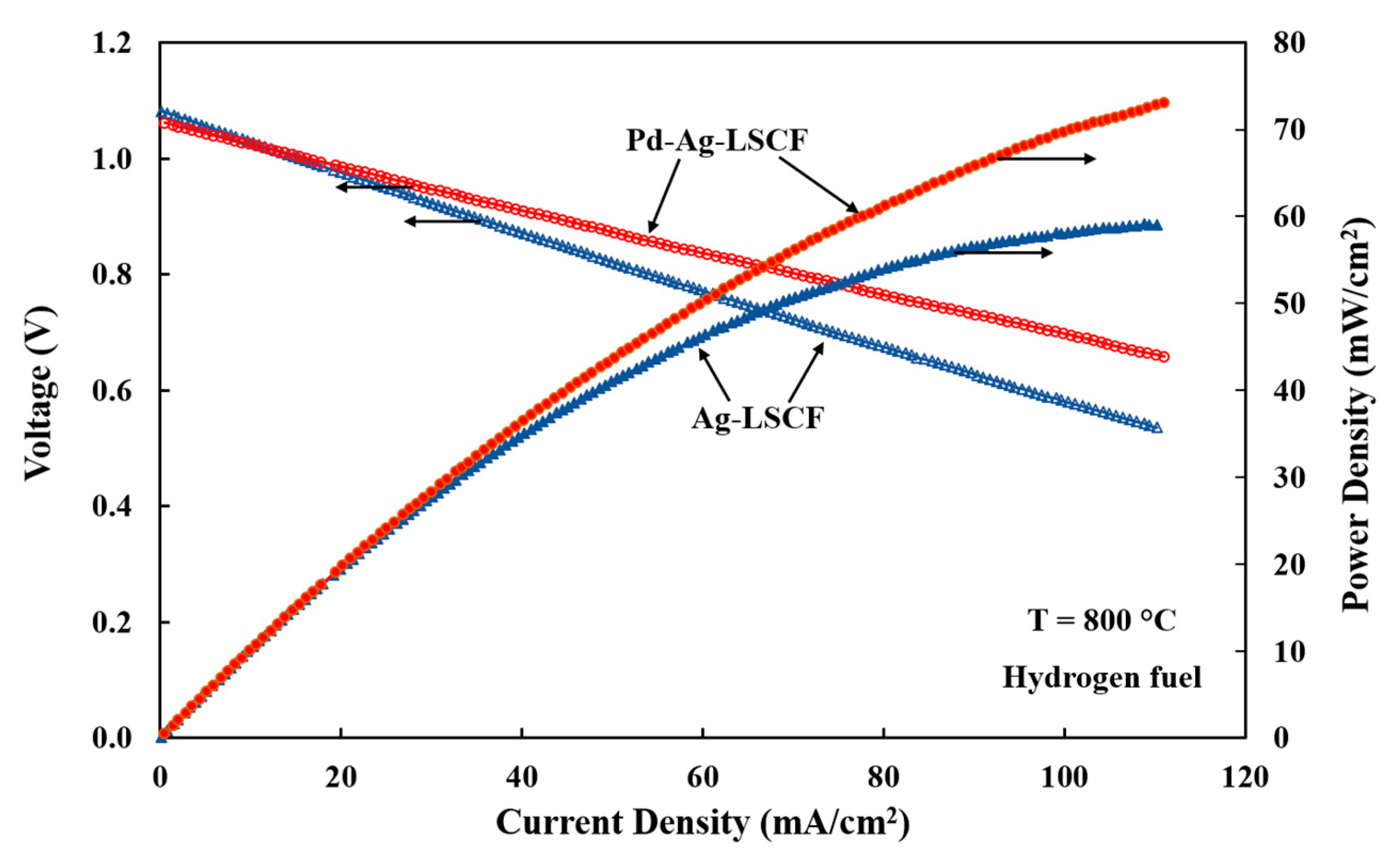
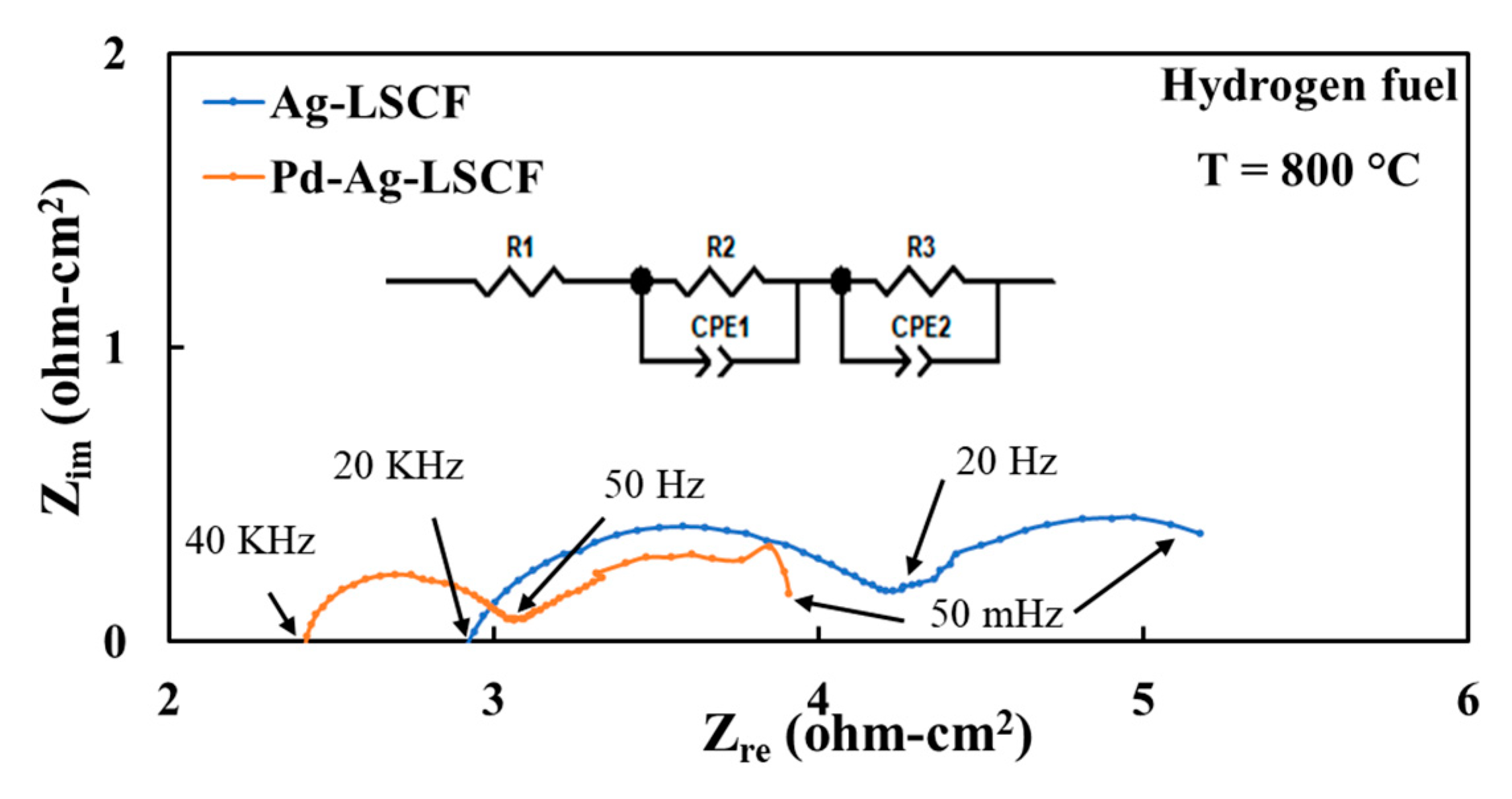
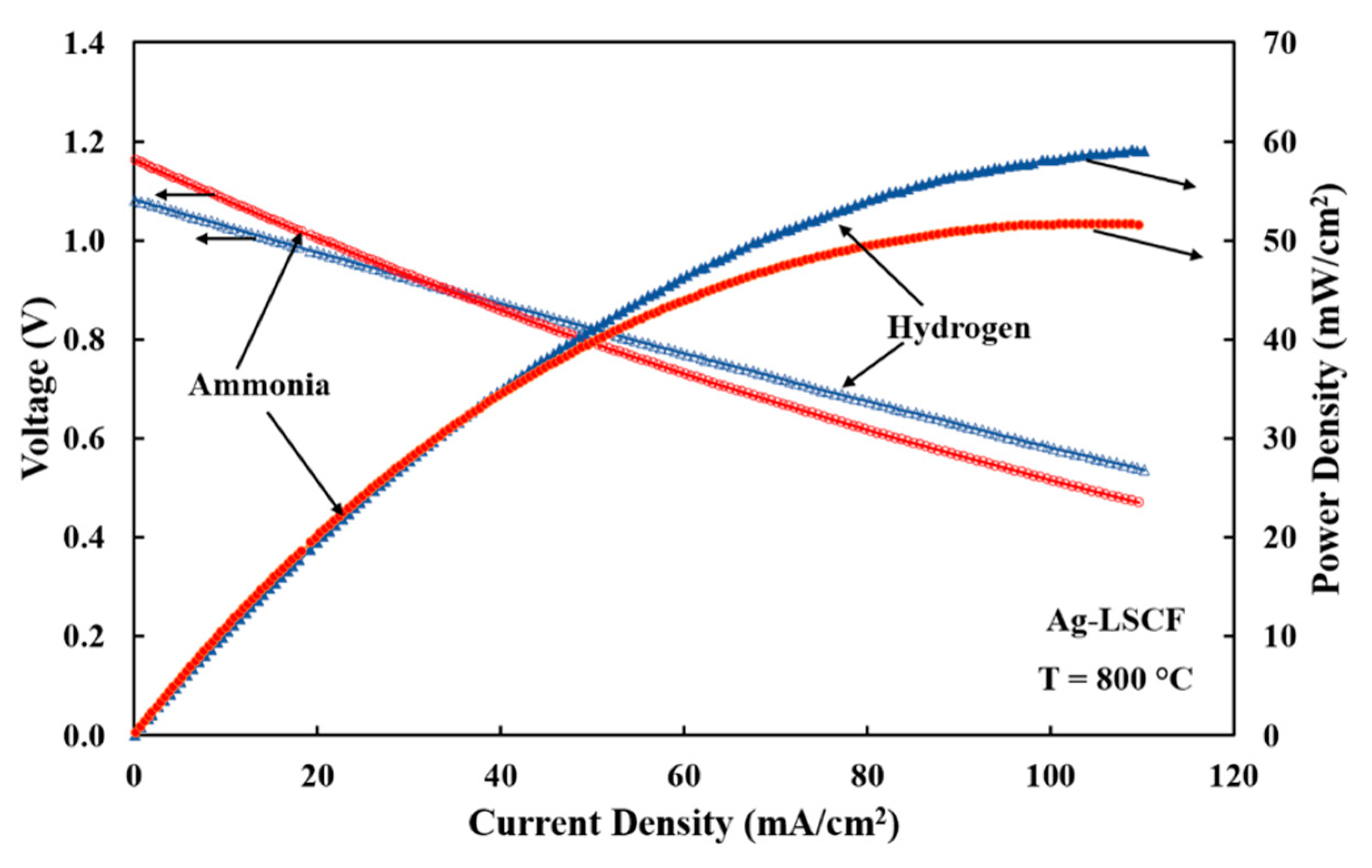
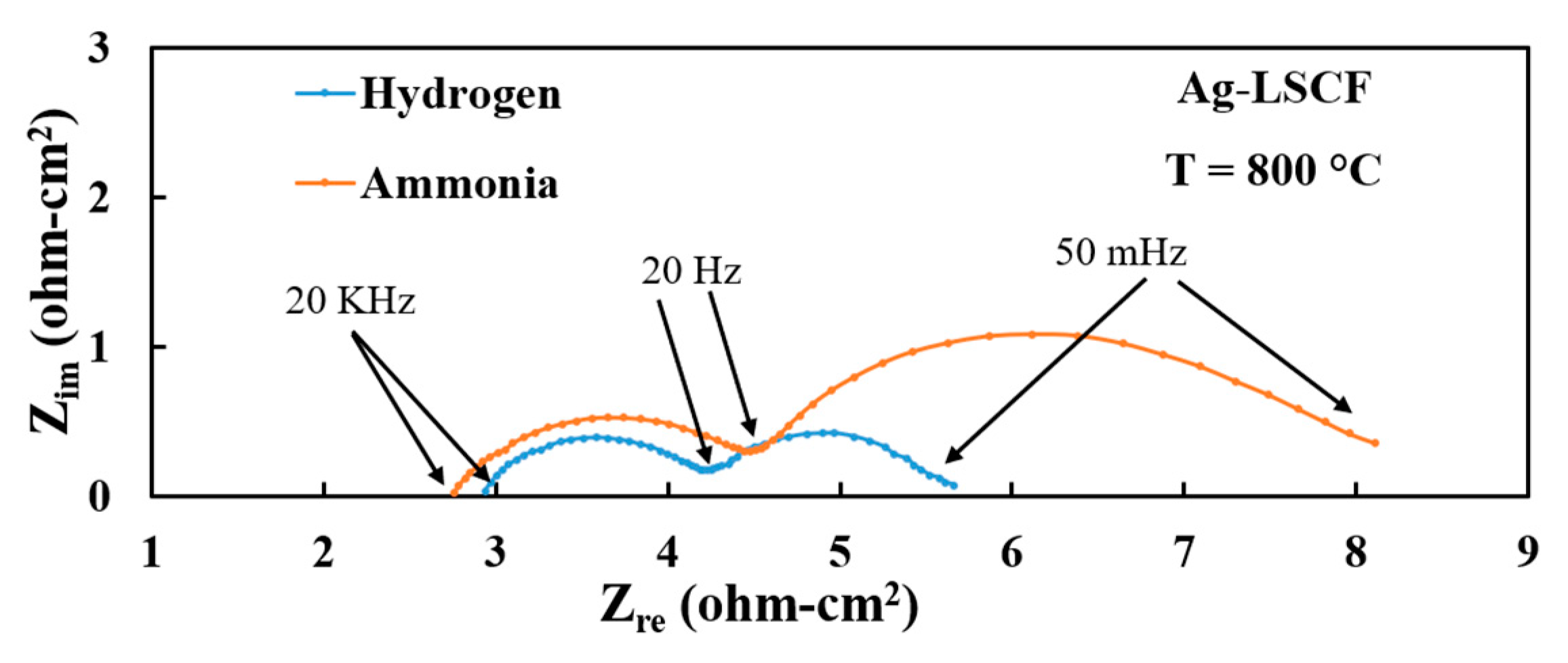
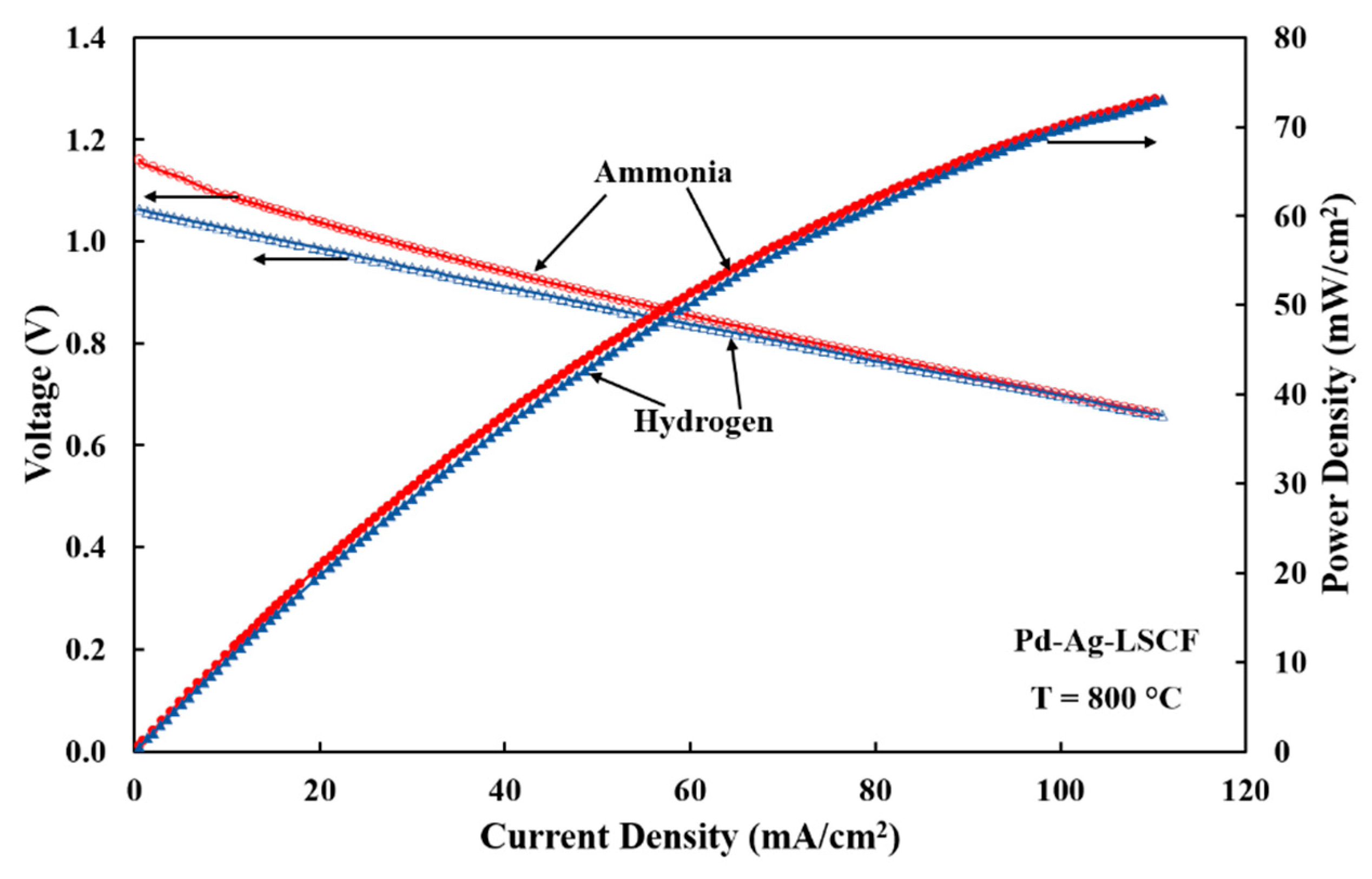
3.3. Electrode Performances with Hydrogen Fuel
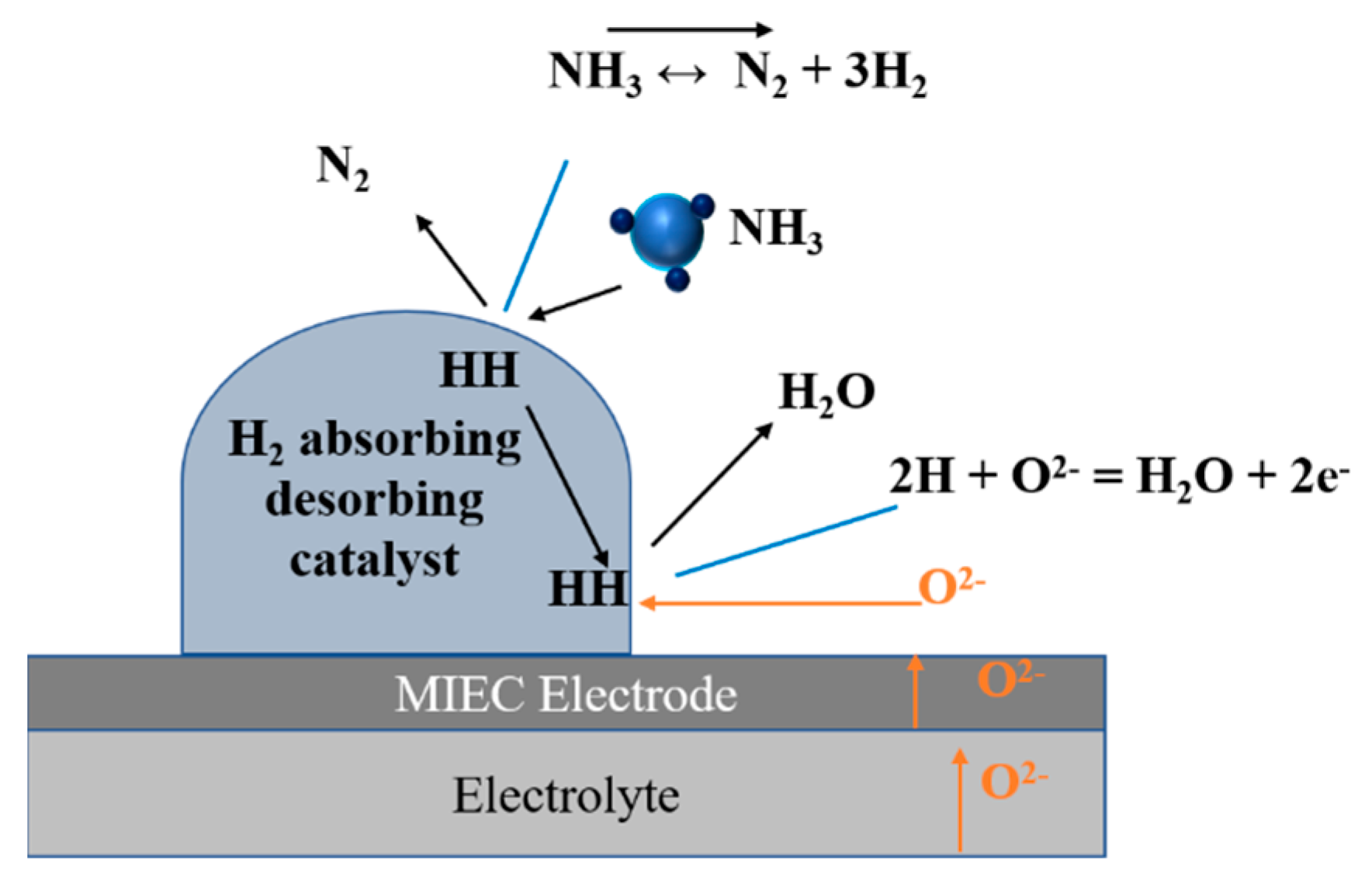
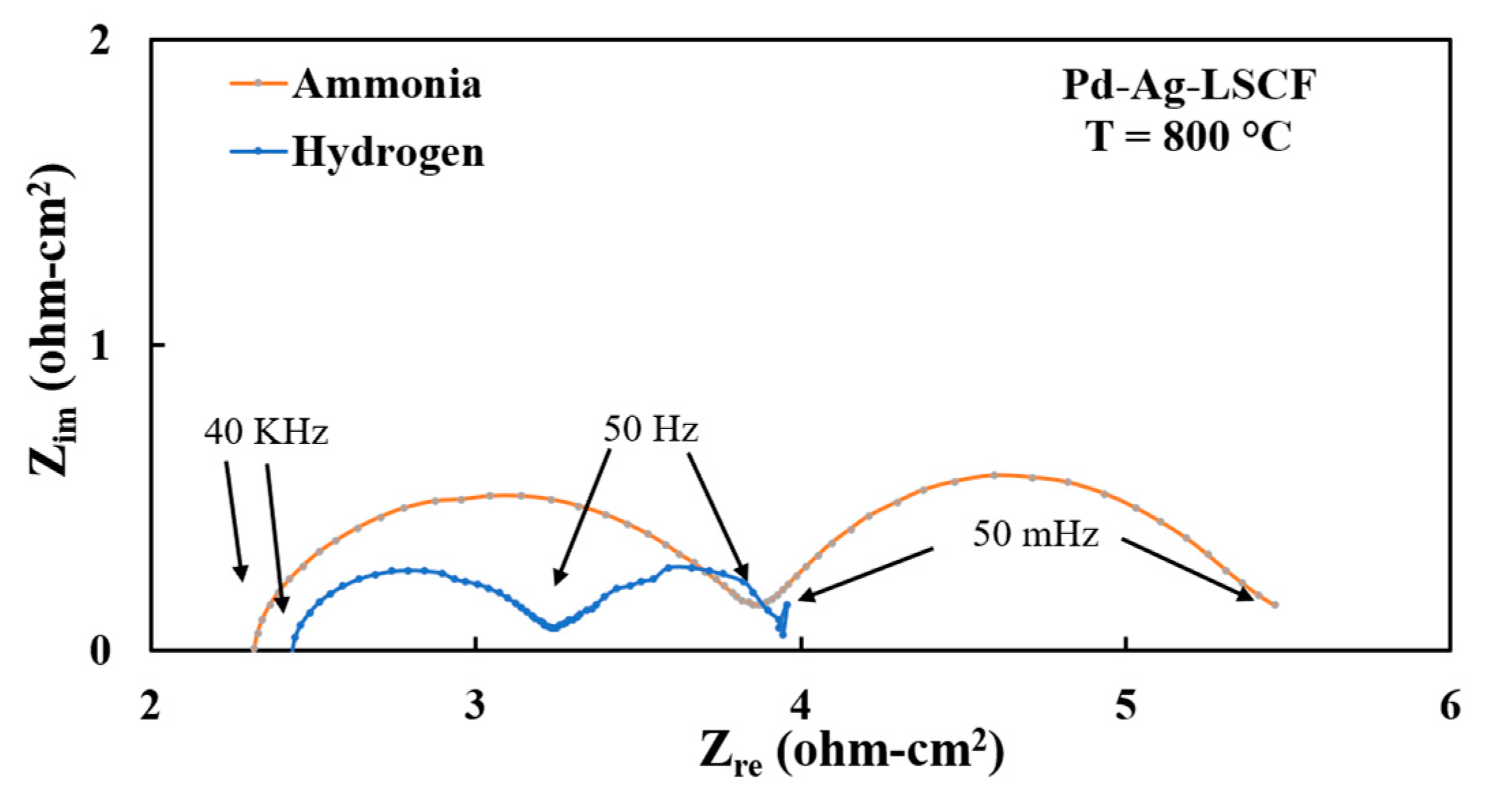
3.4. Electrode Performances with Ammonia Fuel
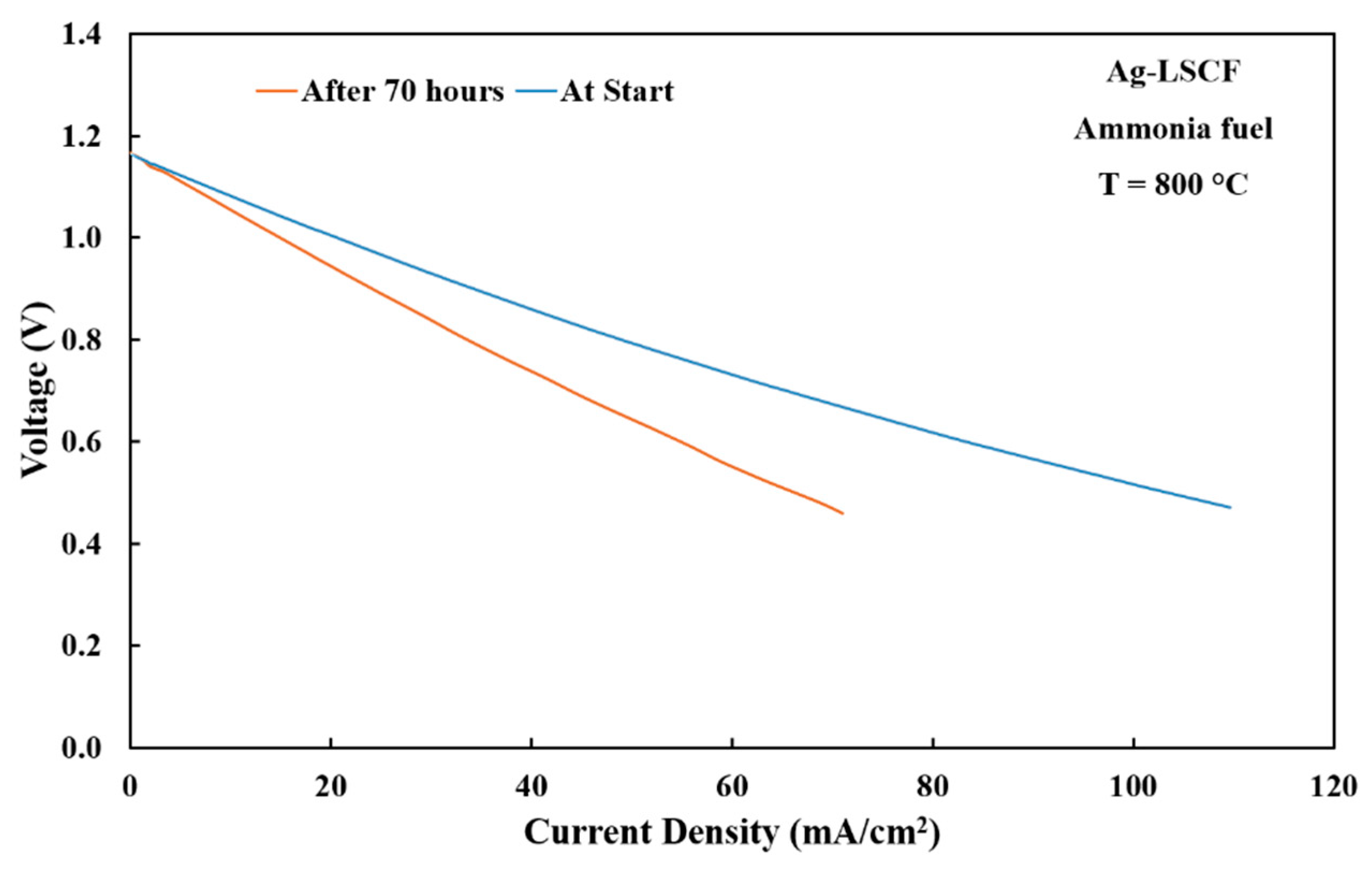
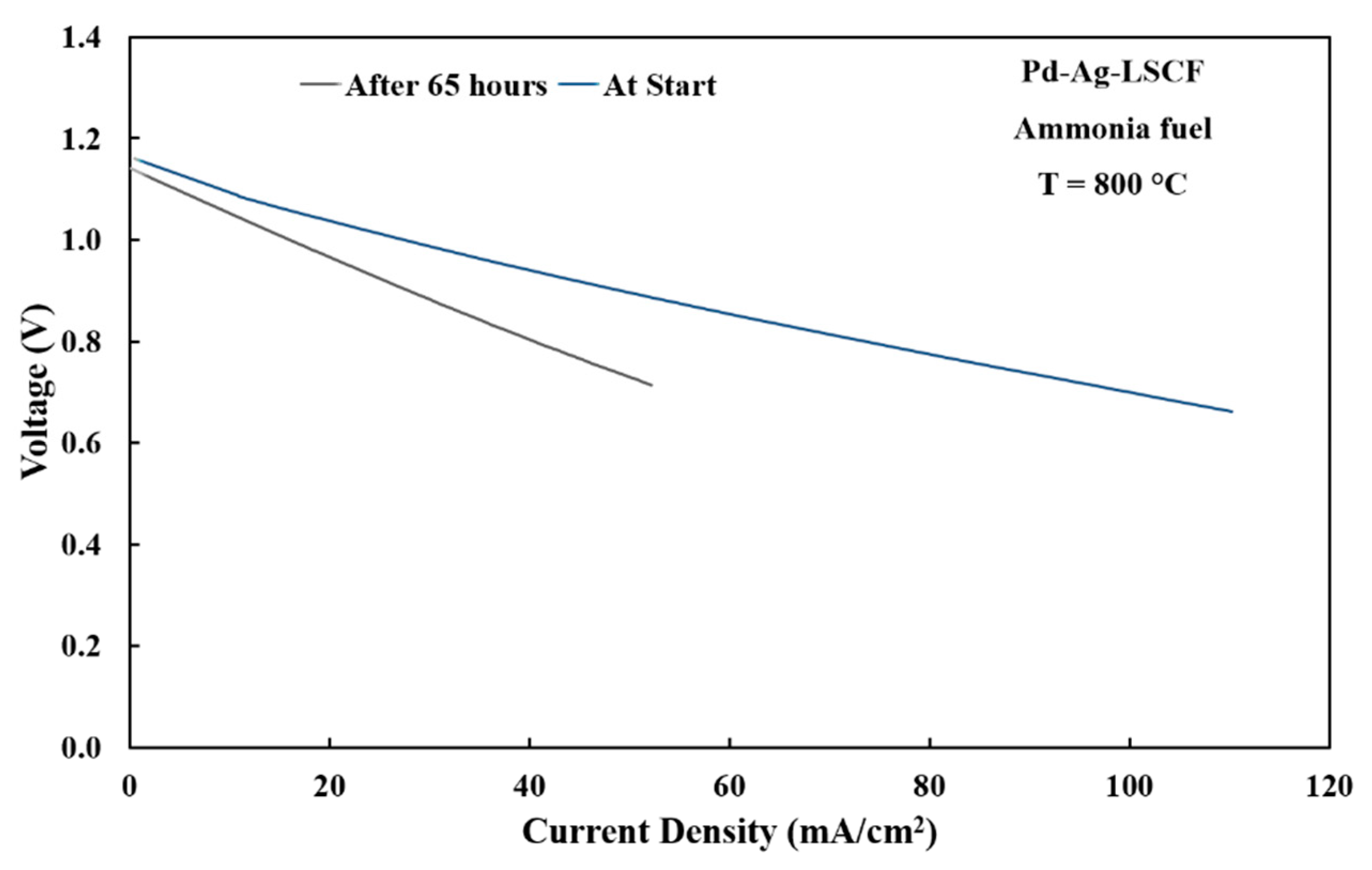
3.5. Short-Term Stability Testing of Anode Materials
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Glenk, G.; Reichelstein, S. Economics of converting renewable power to hydrogen. Nat. Energy 2019, 4, 216–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, T.; Pachfule, P.; Wu, H.; Xu, Q.; Chen, P. Hydrogen carriers. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2016, 1, 16059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giddey, S.; Badwal, S.P.S.; Munnings, C.; Dolan, M. Ammonia as a Renewable Energy Transportation Media. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 10231–10239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Peng, R.; Tian, L.; Meng, G. Direct utilization of ammonia in intermediate-temperature solid oxide fuel cells. Electrochem. Commun. 2006, 8, 1791–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dekker, N.J.J.; Rietveld, G. Highly Efficient Conversion of Ammonia in Electricity by Solid Oxide Fuel Cells. J. Fuel Cell Sci. Technol. 2006, 3, 499–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staniforth, J.; Ormerod, R.M. Clean destruction of waste ammonia with consummate production of electrical power within a solid oxide fuel cell system. Green Chem. 2003, 5, 606–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Ma, J.; Zhou, S.; Yan, R.; Gao, J.; Meng, G. A high-performance ammonia-fueled SOFC based on a YSZ thin-film electrolyte. J. Power Sour. 2007, 164, 86–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Sun, K.; Wu, X.; Li, X.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, N.; Zhou, X. Improved performance of ammonia-fueled solid oxide fuel cell with SSZ thin film electrolyte and Ni-SSZ anode functional layer. Int. J. Hydr. Energy 2012, 37, 10857–10865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Molouk, A.F.S.; Okanishi, T.; Muroyama, H.; Matsui, T.; Eguchi, K. A Stability Study of Ni/Yttria-Stabilized Zirconia Anode for Direct Ammonia Solid Oxide Fuel Cells. ACS Appl. Mater. Interf. 2015, 7, 28701–28707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, R.; Tao, S. Ammonia as a Suitable Fuel for Fuel Cells. Front. Energy Res. 2014, 2, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, A.; Ciacchi, F.T.; Giddey, S.; Munnings, C.; Badwal, S.P.S.; Kimpton, J.A.; Fini, D. Mixed ionic electronic conducting perovskite anode for direct carbon fuel cells. Int. J. Hydr. Energy 2012, 37, 19092–19102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, A.P.; Giddey, S.; Badwal, S.P.S. Efficient conversion of CO2 in solid oxide electrolytic cells with Pd doped perovskite cathode on ceria nanofilm interlayer. J. CO2 Util. 2017, 17, 180–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, J.C.; Chuang, S.S.C. Investigating the CH4 reaction pathway on a novel LSCF anode catalyst in the SOFC. Catal. Commun. 2009, 10, 772–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, B.-K.; Kerman, K.; Ramanathan, S. Nanostructured La0.6Sr0.4Co0.8Fe0.2O3/Y0.08Zr0.92O1.96/La0.6Sr0.4Co0.8Fe0.2O3 (LSCF/YSZ/LSCF) symmetric thin film solid oxide fuel cells. J. Power Source 2011, 196, 1826–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, A.; Giddey, S.; Badwal, S.P.S. Yttria-doped ceria anode for carbon-fueled solid oxide fuel cell. J. Solid State Electrochem. 2015, 19, 325–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giddey, S.; Kulkarni, A.; Munnings, C.; Badwal, S.P.S. Composite anodes for improved performance of a direct carbon fuel cell. J. Power Sour. 2015, 284, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, G.; Kulkarni, A.P.; Giddey, S.; Badwal, S.P.S. Ceramic composite cathodes for CO2 conversion to CO in solid oxide electrolysis cells. Appl. Energy 2018, 221, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akimoto, W.; Saito, M.; Inaba, M.; Yoshida, H.; Inagaki, T. The Mechanism of Ammonia Oxidation at Ni-Fe-SDC Anode in Ammonia-Fueled SOFCs. ECS Trans. 2013, 57, 1639–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkler, W.; Nehter, P. Thermodynamics of Fuel Cells. In Modeling Solid Oxide Fuel Cells: Methods, Procedures and Techniques; Bove, R., Ubertini, S., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2008; pp. 13–50. [Google Scholar]
- Clarke, R.E.; Kulkarni, A.; Giddey, S.; Badwal, S.P.S. Evaluation of solid electrolyte cells with a versatile electrochemical technique. Ionics 2013, 19, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babaei, A.; Jiang, S.P. Analysis of fuel oxidation reaction steps in Ni/GDC anode electrode of solid oxide fuel cells by using palladium nanoparticles. In Proceedings of the Southeast Asian International Advances in Micro/Nano-technology, Bangkok, Thailand, 19 May 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Kalinci, Y.; Dincer, I. Analysis and performance assessment of NH3 and H2 fed SOFC with proton-conducting electrolyte. Int. J. Hydr. Energy 2018, 43, 5795–5807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akimoto, W.; Fujimoto, T.; Saito, M.; Inaba, M.; Yoshida, H.; Inagaki, T. Ni–Fe/Sm-doped CeO2 anode for ammonia-fueled solid oxide fuel cells. Solid State Ionics 2014, 256, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, F.A. Solubility of hydrogen in metals. Pure Appl. Chem. 1990, 62, 2091–2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashinokuchi, M.; Zhang, M.; Doi, T.; Inaba, M. Enhancement of anode activity and stability by Cr addition at Ni/Sm-doped CeO2 cermet anodes in NH3-fueled solid oxide fuel cells. Solid State Ionics 2018, 319, 180–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Temperature (°C) | Hydrogen Fuel | Ammonia Fuel | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ΔG (KJ/mol) | E° (V) | ΔG (KJ/mol) | E° (V) | |
| 500 | −204.93 | 1.06 | −342.94 | 1.18 |
| 600 | −199.54 | 1.03 | −346.14 | 1.20 |
| 700 | −194.06 | 1.00 | −349.86 | 1.21 |
| 800 | −188.52 | 0.98 | −353.26 | 1.22 |
| Electrode | Fuel | RLF(Ω-cm2) | RHF(Ω-cm2) | RE(Ω-cm2) | Peak Power Density(mW/cm2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ag-LSCF | Hydrogen | 5.66 | 4.25 | 2.93 | 59 |
| Ammonia | 8.11 | 4.54 | 2.76 | 51 | |
| Pd-Ag-LSCF | Hydrogen | 4.03 | 3.10 | 2.42 | 73 |
| Ammonia | 5.46 | 3.97 | 2.32 | 73 |
| Electrode | Phase | a-Parameter (Å) | c-Parameter (Å) | wt% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pd-Ag-LSCF anode before test | Silver | - | - | 50 ± 1 |
| Hexagonal LSCF | 5.48 ± 0.001 | 13.502 ± 0.003 | 50 ± 1 | |
| Pd-Ag-LSCF anode after test | Silver | - | - | 45 ± 6 |
| Hexagonal LSCF | 5.511 ± 0.02 | 13.65 ± 0.08 | 15 ± 8 | |
| Tetragonal LSCF | 3.875 ± 0.002 | 12.72 ± 0.01 | 40 ± 6 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rathore, S.S.; Kulkarni, A.P.; Fini, D.; Giddey, S.; Seeber, A. Evaluation of ((La0.60Sr0.40)0.95Co0.20Fe0.80O3-x)-Ag Composite Anode for Direct Ammonia Solid Oxide Fuel Cells and Effect of Pd Impregnation on the Electrochemical Performance. Solids 2021, 2, 177-191. https://doi.org/10.3390/solids2020012
Rathore SS, Kulkarni AP, Fini D, Giddey S, Seeber A. Evaluation of ((La0.60Sr0.40)0.95Co0.20Fe0.80O3-x)-Ag Composite Anode for Direct Ammonia Solid Oxide Fuel Cells and Effect of Pd Impregnation on the Electrochemical Performance. Solids. 2021; 2(2):177-191. https://doi.org/10.3390/solids2020012
Chicago/Turabian StyleRathore, Shambhu Singh, Aniruddha P. Kulkarni, Daniel Fini, Sarbjit Giddey, and Aaron Seeber. 2021. "Evaluation of ((La0.60Sr0.40)0.95Co0.20Fe0.80O3-x)-Ag Composite Anode for Direct Ammonia Solid Oxide Fuel Cells and Effect of Pd Impregnation on the Electrochemical Performance" Solids 2, no. 2: 177-191. https://doi.org/10.3390/solids2020012
APA StyleRathore, S. S., Kulkarni, A. P., Fini, D., Giddey, S., & Seeber, A. (2021). Evaluation of ((La0.60Sr0.40)0.95Co0.20Fe0.80O3-x)-Ag Composite Anode for Direct Ammonia Solid Oxide Fuel Cells and Effect of Pd Impregnation on the Electrochemical Performance. Solids, 2(2), 177-191. https://doi.org/10.3390/solids2020012






