Composition and Interactions of the Oral–Gastrointestinal Microbiome Populations During Health, Disease, and Long-Duration Space Missions: A Narrative Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
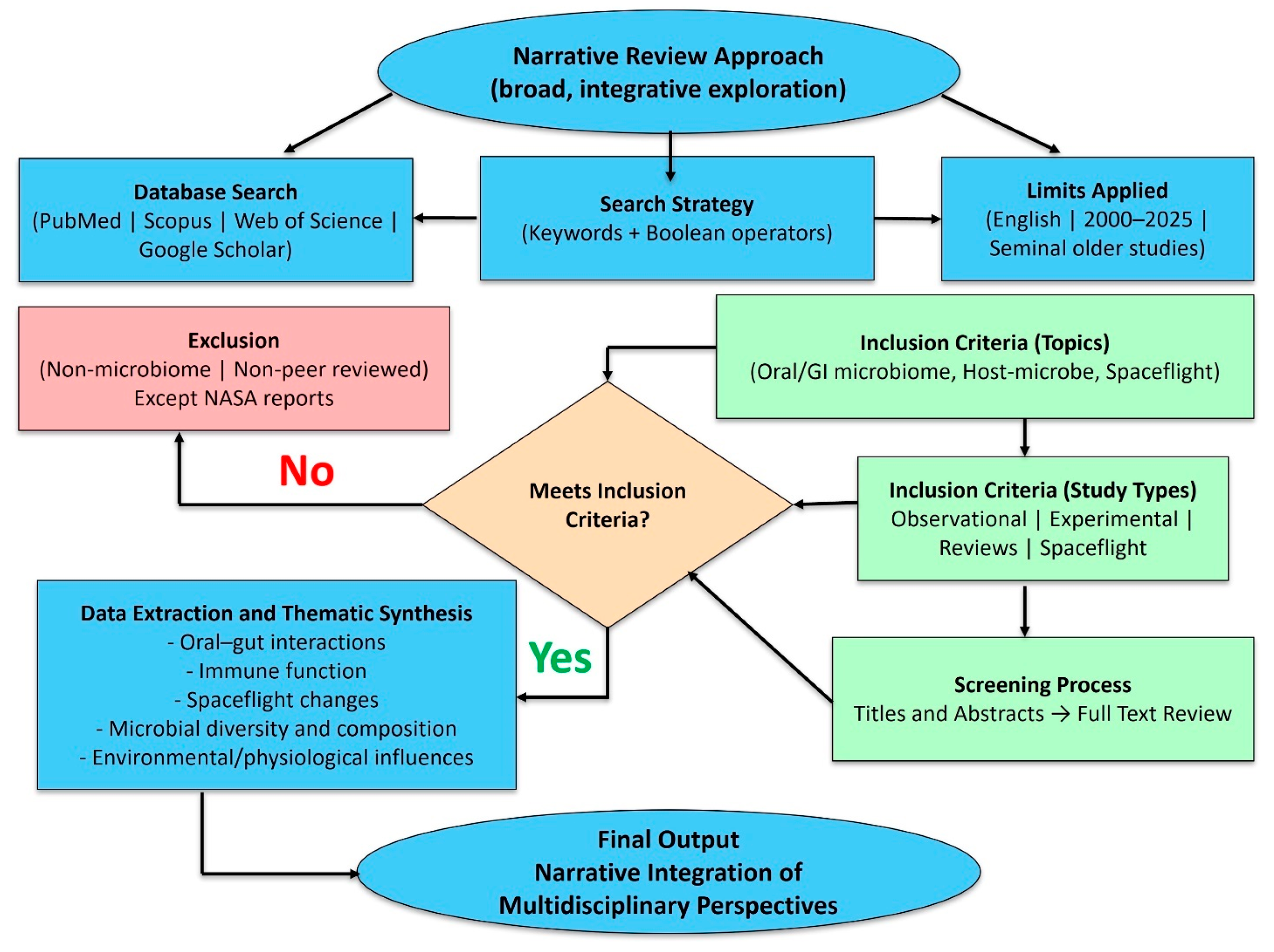
2. Methodology
- “oral microbiome” OR “gut microbiome” OR “gastrointestinal microbiota”;
- AND “health” OR “homeostasis”;
- AND “disease” OR “dysbiosis”;
- AND “prebiotics” OR “probiotics” OR “postbiotics”;
- AND “spaceflight” OR “microgravity” OR “long-duration space missions”.
3. Oral and Gastrointestinal Microbiome
3.1. Oral Microbiome Composition
3.2. Survival of Microorganisms in the Oral Cavity
3.3. Healthy Oral Microbiota
3.4. Oral Viral Microbiota
3.5. Oral and Other Microbiomes in the Human Body
3.6. Impacts on Oral Microbiota
3.7. The Gastrointestinal Microbiome Composition
3.8. The Gastrointestinal Microbiome in Health and Disease
4. Interactions Between Oral and Gastrointestinal Microbiomes
5. Effect of Systemic Diseases on the Oral Microbiome
5.1. Auto-Immune Diseases
5.2. Cognitive Decline
5.3. COVID-19
6. The Role of Prebiotics, Probiotics, and Postbiotics in Oral and Gastrointestinal Health
6.1. Prebiotics and Probiotics
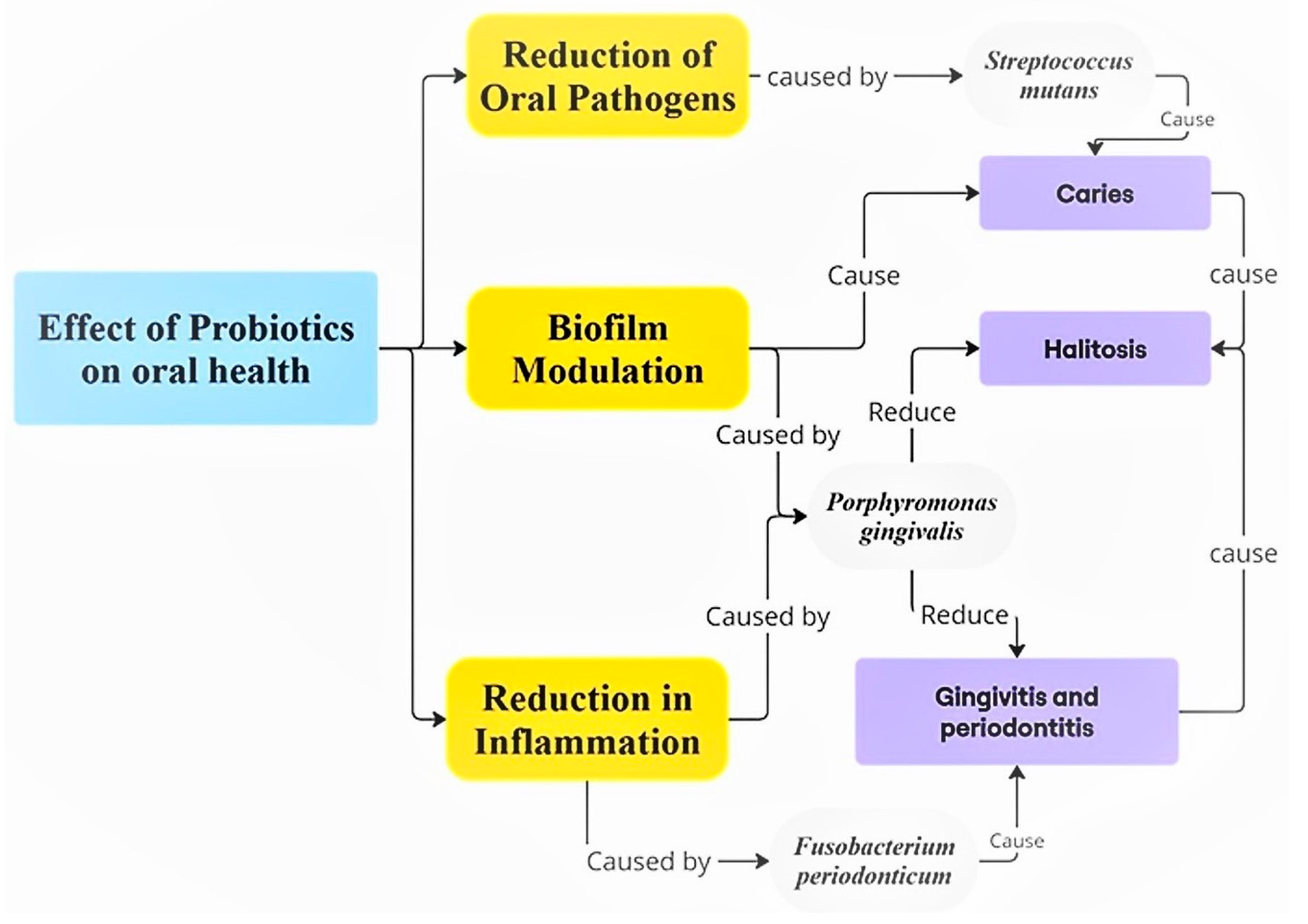
6.2. Prebiotics, Probiotics, and Their Applications in Oral Health
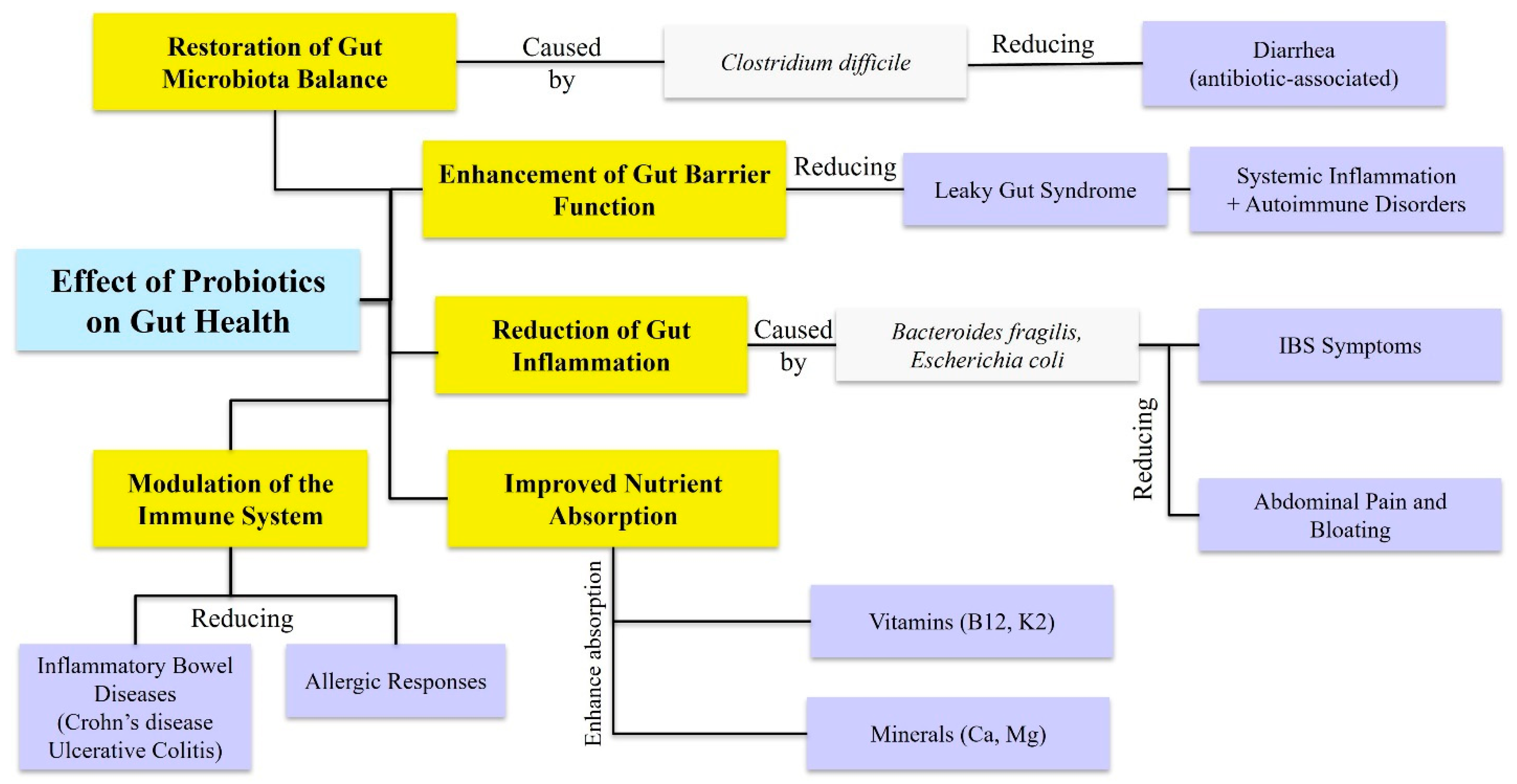
6.3. Prebiotics and Probiotics and Their Applications in Gastrointestinal Health
6.4. Prebiotics and Probiotics in Commercial Oral Health Products
6.5. Postbiotics and Their Applications in Oral and Gastrointestinal Health
7. Changes in Oral and Gut Microbiota During Long-Duration Space Missions
7.1. The Effect of Microgravity on the Oral–Gastrointestinal Microbiome
7.2. The Link Between the Oral and Gastrointestinal Microbiome
7.3. Innovative Approaches for Maintaining a Healthy Oral–Gastrointestinal Microbiome in Space Missions
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hou, K.; Wu, Z.X.; Chen, X.Y.; Wang, J.Q.; Zhang, D.; Xiao, C.; Zhu, D.; Koya, J.B.; Wei, L.; Li, J.; et al. Microbiota in health and diseases. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, E.P.; Gautam, Y.; Proctor, D.M.; Bhandari, D.; Tandukar, S.; Gupta, M.; Gautam, G.P.; Relman, D.A.; Shibl, A.A.; Sherchand, J.B.; et al. Nepali oral microbiomes reflect a gradient of lifestyles from traditional to industrialized. Microbiome 2024, 12, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeoman, C.J.; White, B.A. Gastrointestinal tract microbiota and probiotics in production animals. Annu. Rev. Anim. Biosci. 2014, 2, 469–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whipps, J.; Lewis, K.; Cooke, R. Fungi in Biological Control Systems; Manchester University Press: Manchester, UK, 1988; pp. 161–187. [Google Scholar]
- Berg, G.; Rybakova, D.; Fischer, D.; Cernava, T.; Verges, M.C.; Charles, T.; Chen, X.; Cocolin, L.; Eversole, K.; Corral, G.H.; et al. Microbiome definition re-visited: Old concepts and new challenges. Microbiome 2020, 8, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilian, M.; Chapple, I.L.; Hannig, M.; Marsh, P.D.; Meuric, V.; Pedersen, A.M.; Tonetti, M.S.; Wade, W.G.; Zaura, E. The oral microbiome—An update for oral healthcare professionals. Br. Dent. J. 2016, 221, 657–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Y.; Pedersen, O. Gut microbiota in human metabolic health and disease. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 19, 55–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deo, P.N.; Deshmukh, R. Oral microbiome: Unveiling the fundamentals. J. Oral Maxillofac. Pathol. 2019, 23, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davenport, E.R.; Sanders, J.G.; Song, S.J.; Amato, K.R.; Clark, A.G.; Knight, R. The human microbiome in evolution. BMC Biol. 2017, 15, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dewhirst, F.E.; Chen, T.; Izard, J.; Paster, B.J.; Tanner, A.C.; Yu, W.H.; Lakshmanan, A.; Wade, W.G. The human oral microbiome. J. Bacteriol. 2010, 192, 5002–5017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixit, K.; Chaudhari, D.; Dhotre, D.; Shouche, Y.; Saroj, S. Restoration of dysbiotic human gut microbiome for homeostasis. Life Sci. 2021, 278, 119622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.Y.; Tsolis, R.M.; Bäumler, A.J. The microbiome and gut homeostasis. Science 2022, 377, eabp9960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kutschera, U. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek (1632–1723): Master of Fleas and Father of Microbiology. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleinstein, S.E.; Nelson, K.E.; Freire, M. Inflammatory Networks Linking Oral Microbiome with Systemic Health and Disease. J. Dent. Res. 2020, 99, 1131–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tierney, B.T.; Kim, J.; Overbey, E.G.; Ryon, K.A.; Foox, J.; Sierra, M.A.; Bhattacharya, C.; Damle, N.; Najjar, D.; Park, J.; et al. Longitudinal multi-omics analysis of host microbiome architecture and immune responses during short-term spaceflight. Nat. Microbiol. 2024, 9, 1661–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aagaard, K.; Ma, J.; Antony, K.M.; Ganu, R.; Petrosino, J.; Versalovic, J. The placenta harbors a unique microbiome. Sci. Transl. Med. 2014, 6, 237ra265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arweiler, N.B.; Netuschil, L. The Oral Microbiota. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2016, 902, 45–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mady, E.A.; Doghish, A.S.; El-Dakroury, W.A.; Elkhawaga, S.Y.; Ismail, A.; El-Mahdy, H.A.; Elsakka, E.G.E.; El-Husseiny, H.M. Impact of the mother’s gut microbiota on infant microbiome and brain development. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2023, 150, 105195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Li, L.; Jin, B.; Xu, X.; Zuo, X.; Li, Y.; Li, Z. The Effects of Delivery Mode on the Gut Microbiota and Health: State of Art. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 724449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaan, A.M.M.; Kahharova, D.; Zaura, E. Acquisition and establishment of the oral microbiota. Periodontol. 2000 2021, 86, 123–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turunen, J.; Tejesvi, M.V.; Paalanne, N.; Hekkala, J.; Lindgren, O.; Kaakinen, M.; Pokka, T.; Kaisanlahti, A.; Reunanen, J.; Tapiainen, T. Presence of distinctive microbiome in the first-pass meconium of newborn infants. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 19449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ames, N.J.; Barb, J.J.; Ranucci, A.; Kim, H.; Mudra, S.E.; Cashion, A.K.; Townsley, D.M.; Childs, R.; Paster, B.J.; Faller, L.L.; et al. The oral microbiome of patients undergoing treatment for severe aplastic anemia: A pilot study. Ann. Hematol. 2019, 98, 1351–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellogg, J.A.; Manzella, J.P.; Bankert, D.A. Frequency of low-level bacteremia in children from birth to fifteen years of age. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2000, 38, 2181–2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caufield, P.W.; Cutter Gr Fau—Dasanayake, A.P.; Dasanayake, A.P. Initial acquisition of mutans streptococci by infants: Evidence for a discrete window of infectivity. J. Dent. Res. 1993, 72, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mills, J.G.; Bissett, A.; Gellie, N.J.C.; Lowe, A.J.; Selway, C.A.; Thomas, T.; Weinstein, P.; Weyrich, L.S.; Breed, M.F. Revegetation of urban green space rewilds soil microbiotas with implications for human health and urban design. Restor. Ecol. 2020, 28, S322–S334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.J.; Liao, Y.; He, Y.Q.; Zheng, M.Q.; Tong, X.T.; Xue, W.Q.; Zhang, J.B.; Yuan, L.L.; Zhang, W.L.; Jia, W.H. Association Between Oral Microbiota and Cigarette Smoking in the Chinese Population. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 658203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmer, R.J., Jr. Composition and development of oral bacterial communities. Periodontol. 2000 2014, 64, 20–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedghi, L.; DiMassa, V.; Harrington, A.; Lynch, S.V.; Kapila, Y.L. The oral microbiome: Role of key organisms and complex networks in oral health and disease. Periodontol. 2000 2021, 87, 107–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khelaifia, S.A.-O.; Virginie, P.; Belkacemi, S.A.-O.; Tassery, H.; Terrer, E.A.-O.X.; Aboudharam, G. Culturing the Human Oral Microbiota, Updating Methodologies and Cultivation Techniques. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demmitt, B.A.; Corley, R.P.; Huibregtse, B.M.; Keller, M.C.; Hewitt, J.K.; McQueen, M.B.; Knight, R.; McDermott, I.; Krauter, K.S. Genetic influences on the human oral microbiome. BMC Genom. 2017, 18, 659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Chu, M.; Huang, Z.; Yang, X.; Ran, S.; Hu, B.; Zhang, C.; Liang, J. Variations in oral microbiota associated with oral cancer. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 11773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultan, A.S.; Kong, E.F.; Rizk, A.M.; Jabra-Rizk, M.A. The oral microbiome: A Lesson in coexistence. PLoS Pathog. 2018, 14, e1006719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaura, E.; Keijser, B.J.; Huse, S.M.; Crielaard, W. Defining the healthy “core microbiome” of oral microbial communities. BMC Microbiol. 2009, 9, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghannoum, M.A.; Jurevic, R.J.; Mukherjee, P.K.; Cui, F.; Sikaroodi, M.; Naqvi, A.; Gillevet, P.M. Characterization of the oral fungal microbiome (mycobiome) in healthy individuals. PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6, e1000713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, J.H.; Lee, J.H. Probing the diversity of healthy oral microbiome with bioinformatics approaches. BMB Rep. 2016, 49, 662–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Brocal, V.; Moya, A. The analysis of the oral DNA virome reveals which viruses are widespread and rare among healthy young adults in Valencia (Spain). PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0191867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurek-Górecka, A.; Walczyńska-Dragon, K.; Felitti, R.; Nitecka-Buchta, A.; Baron, S.; Olczyk, P. The Influence of Propolis on Dental Plaque Reduction and the Correlation between Dental Plaque and Severity of COVID-19 Complications-A Literature Review. Molecules 2021, 26, 5516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, J.A.; Dupont, C.L. Microbial metagenomics: Beyond the genome. Annu. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2011, 3, 347–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdal Dayem, A.; Hossain, M.K.; Lee, S.B.; Kim, K.; Saha, S.K.; Yang, G.M.; Choi, H.Y.; Cho, S.G. The Role of Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) in the Biological Activities of Metallic Nanoparticles. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, C.C.; Shih, T.P.; Ko, W.C.; Tang, H.J.; Hsueh, P.R. Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) and coronavirus disease-2019 (COVID-19): The epidemic and the challenges. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2020, 55, 105924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medeiros da Silva, R.C.; Nogueira Marinho, L.C.; de Araújo Silva, D.N.; Costa de Lima, K.; Pirih, F.Q.; Luz de Aquino Martins, A.R. Saliva as a possible tool for the SARS-CoV-2 detection: A review. Travel Med. Infect. Dis. 2020, 38, 101920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poukka, E.; Mäkelä, H.; Hagberg, L.; Vo, T.; Nohynek, H.; Ikonen, N.; Liitsola, K.; Helve, O.; Savolainen-Kopra, C.; Dub, T. Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Gargle, Spit, and Sputum Specimens. Microbiol. Spectr. 2021, 9, e0003521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Cui, J.; Liu, Y.; Chen, K.; Huang, L.; Liu, Y. Oral, Tongue-Coating Microbiota, and Metabolic Disorders: A Novel Area of Interactive Research. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 8, 730203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foster, K.R.; Schluter, J.; Coyte, K.Z.; Rakoff-Nahoum, S. The evolution of the host microbiome as an ecosystem on a leash. Nature 2017, 548, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebersole, J.L.; Kirakodu, S.S.; Gonzalez, O.A. Oral microbiome interactions with gingival gene expression patterns for apoptosis, autophagy and hypoxia pathways in progressing periodontitis. Immunology 2021, 162, 405–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khor, B.; Snow, M.; Herrman, E.; Ray, N.; Mansukhani, K.; Patel, K.A.; Said-Al-Naief, N.; Maier, T.; Machida, C.A. Interconnections Between the Oral and Gut Microbiomes: Reversal of Microbial Dysbiosis and the Balance Between Systemic Health and Disease. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKeon, M.G.; Gallant, J.A.-O.; Kim, Y.J.; Das, S.A.-O. It Takes Two to Tango: A Review of Oncogenic Virus and Host Microbiome Associated Inflammation in Head and Neck Cancer. Cancers 2022, 14, 3120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radaic, A.; Ganther, S.; Kamarajan, P.; Grandis, J.; Yom, S.S.; Kapila, Y.L. Paradigm shift in the pathogenesis and treatment of oral cancer and other cancers focused on the oralome and antimicrobial-based therapeutics. Periodontol. 2000 2021, 87, 76–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yost, S.; Stashenko, P.; Choi, Y.; Kukuruzinska, M.; Genco, C.A.; Salama, A.; Weinberg, E.O.; Kramer, C.D.; Frias-Lopez, J. Increased virulence of the oral microbiome in oral squamous cell carcinoma revealed by metatranscriptome analyses. Int. J. Oral Sci. 2018, 10, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowińska, I.; Szyperska-Ślaska, A.; Zariczny, P.; Pasławski, R.; Kramkowski, K.; Kowalczyk, P. The Influence of Diet on Oxidative Stress and Inflammation Induced by Bacterial Biofilms in the Human Oral Cavity. Materials 2021, 14, 1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, V.S.M.; Azevedo, J.; Leal, H.F.; Queiroz, A.T.L.; da Silva Filho, H.P.; Reis, J.N. Bacterial diversity and prevalence of antibiotic resistance genes in the oral microbiome. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0239664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannella, L.; Grelloni, C.; Quintili, D.; Fiorelli, A.; Montironi, R.; Alia, S.; Delli Carpini, G.; Di Giuseppe, J.; Vignini, A.; Ciavattini, A. Microbiome Changes in Pregnancy Disorders. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, H.; Patoine, A.; Wu, T.T.; Castillo, D.A.; Xiao, J. Oral microflora and pregnancy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 16870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.H.; Chung, S.W.; Auh, Q.S.; Hong, S.J.; Lee, Y.A.; Jung, J.; Lee, G.J.; Park, H.J.; Shin, S.I.; Hong, J.Y. Progress in Oral Microbiome Related to Oral and Systemic Diseases: An Update. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abusleme, L.; Hoare, A.; Hong, B.Y.; Diaz, P.I. Microbial signatures of health, gingivitis, and periodontitis. Periodontol. 2000 2021, 86, 57–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtis, M.A.; Diaz, P.I.; Van Dyke, T.E. The role of the microbiota in periodontal disease. Periodontol. 2000 2020, 83, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Huang, Z.; Tang, Z.; Huang, Y.; Huang, M.; Liu, H.; Ziebolz, D.; Schmalz, G.; Jia, B.; Zhao, J. More Than Just a Periodontal Pathogen—The Research Progress on Fusobacterium nucleatum. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 815318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A. Persistence of Tannerella forsythia and Fusobacterium nucleatum in dental plaque: A strategic alliance. Curr. Oral Health Rep. 2020, 7, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Socransky, S.S.; Haffajee, A.D. Periodontal microbial ecology. Periodontol. 2000 2005, 38, 135–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loesche, W.J. Role of Streptococcus mutans in human dental decay. Microbiol. Rev. 1986, 50, 353–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowen, W.H.; Burne, R.A.; Wu, H.; Koo, H. Oral Biofilms: Pathogens, Matrix, and Polymicrobial Interactions in Microenvironments. Trends Microbiol. 2018, 26, 229–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kidd, E.A.; Fejerskov, O. What constitutes dental caries? Histopathology of carious enamel and dentin related to the action of cariogenic biofilms. J. Dent. Res. 2004, 83, C35–C38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spatafora, G.; Li, Y.; He, X.; Cowan, A.; Tanner, A.C.R. The Evolving Microbiome of Dental Caries. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havsed, K.; Stensson, M.; Jansson, H.; Carda-Diéguez, M.; Pedersen, A.; Neilands, J.; Svensäter, G.; Mira, A. Bacterial Composition and Metabolomics of Dental Plaque from Adolescents. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 716493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simón-Soro, A.; Mira, A. Solving the etiology of dental caries. Trends Microbiol. 2015, 23, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ertugrul, A.S.; Arslan, U.; Dursun, R.; Hakki, S.S. Periodontopathogen profile of healthy and oral lichen planus patients with gingivitis or periodontitis. Int. J. Oral Sci. 2013, 5, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, W.; Jang, S. Oral Microbiome Research on Oral Lichen Planus: Current Findings and Perspectives. Biology 2022, 11, 723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Liu, Y.; Zheng, H.J.; Zhang, C.P. The Oral Microbiota May Have Influence on Oral Cancer. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2019, 9, 476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sami, A.; Elimairi, I.; Stanton, C.; Ross, R.P.; Ryan, C.A. The Role of the Microbiome in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma with Insight into the Microbiome-Treatment Axis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, H.; Li, G.; Xu, X.; Zhang, C.; Zhong, W.; Xu, S.; Yin, Y.; Song, J. The role of oral microbiome in periodontitis under diabetes mellitus. J. Oral Microbiol. 2022, 14, 2078031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.P.; Bali, A.; Singh, N.; Jaggi, A.S. Advanced glycation end products and diabetic complications. Korean J. Physiol. Pharmacol. Off. J. Korean Physiol. Soc. Korean Soc. Pharmacol. 2014, 18, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thursby, E.; Juge, N. Introduction to the human gut microbiota. Biochem. J. 2017, 474, 1823–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donaldson, G.P.; Lee, S.M.; Mazmanian, S.K. Gut biogeography of the bacterial microbiota. Microbiome 2017, 5, 20–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lynch, S.V.; Pedersen, O. The Human Intestinal Microbiome in Health and Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 2369–2379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowland, I.; Gibson, G.; Heinken, A.; Scott, K.; Swann, J.; Thiele, I.; Tuohy, K. Gut microbiota functions: Metabolism of nutrients and other food components. Eur. J. Nutr. 2017, 57, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommer, F.; Bäckhed, F. The gut microbiota—Masters of host development and physiology. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2013, 11, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belkaid, Y.; Hand, T.W. Role of the microbiota in immunity and inflammation. Cell Host Microbe 2014, 157, 121–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buffie, C.G.; Pamer, E.G. Microbiota-mediated colonization resistance against intestinal pathogens. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2013, 13, 790–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cryan, J.F.; O’Riordan, K.J.; Cowan, C.S.M.; Sandhu, K.V.; Bastiaanssen, T.F.S.; Boehme, M.; Codagnone, M.G.; Cussotto, S.; Fulling, C.; Golubeva, A.V.; et al. The Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis. Physiol. Rev. 2019, 99, 1877–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kostic, A.D.; Xavier, R.J.; Gevers, D. The microbiome in inflammatory bowel disease: Current status and the future ahead. Gastroenterology 2014, 146, 1489–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menees, S.; Chey, W.A.-O. The gut microbiome and irritable bowel syndrome. F1000Research 2018, 7, 1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilg, H.; Moschen, A.R. Microbiota and diabetes: An evolving relationship. Gut 2014, 63, 1513–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turnbaugh, P.J.; Ley, R.E.; Mahowald, M.A.; Magrini, V.; Mardis, E.R.; Gordon, J.I. An obesity-associated gut microbiome with increased capacity for energy harvest. Nature 2006, 444, 1027–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesci, A.; Carnuccio, C.A.-O.; Ruggieri, V.; D’Alessandro, A.; Di Giorgio, A.; Santoro, L.A.-O.; Gasbarrini, A.A.-O.; Santoliquido, A.; Ponziani, F.A.-O. Gut Microbiota and Cardiovascular Disease: Evidence on the Metabolic and Inflammatory Background of a Complex Relationship. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 9087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cani, P.D.; Delzenne, N.M. The role of the gut microbiota in energy metabolism and metabolic disease. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2009, 15, 1546–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayer, E.A.-O.; Knight, R.; Mazmanian, S.K.; Cryan, J.A.-O.; Tillisch, K. Gut microbes and the brain: Paradigm shift in neuroscience. J. Neurosci. 2014, 34, 15490–15496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharon, G.; Cruz, N.J.; Kang, D.W.; Gandal, M.J.; Wang, B.; Kim, Y.M.; Zink, E.M.; Casey, C.P.; Taylor, B.C.; Lane, C.J.; et al. Human Gut Microbiota from Autism Spectrum Disorder Promote Behavioral Symptoms in Mice. Cell 2019, 177, 1600–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maki, K.A.; Kazmi, N.; Barb, J.J.; Ames, N. The Oral and Gut Bacterial Microbiomes: Similarities, Differences, and Connections. Biol. Res. Nurs. 2021, 23, 7–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; Xuan, S.; Wang, Z. Oral microbiota: A new view of body health. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2019, 8, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, N.; Yang, F.; Li, A.; Prifti, E.; Chen, Y.; Shao, L.; Guo, J.; Le Chatelier, E.; Yao, J.; Wu, L.; et al. Alterations of the human gut microbiome in liver cirrhosis. Nature 2014, 513, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abed, J.; Emgård, J.E.; Zamir, G.; Faroja, M.; Almogy, G.; Grenov, A.; Sol, A.; Naor, R.; Pikarsky, E.; Atlan, K.A.; et al. Fap2 Mediates Fusobacterium nucleatum Colorectal Adenocarcinoma Enrichment by Binding to Tumor-Expressed Gal-GalNAc. Cell Host Microbe 2016, 20, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zepeda-Rivera, M.; Minot, S.A.-O.; Bouzek, H.; Wu, H.; Blanco-Míguez, A.A.-O.; Manghi, P.A.-O.; Jones, D.S.; LaCourse, K.D.; Wu, Y.; McMahon, E.F.; et al. A distinct Fusobacterium nucleatum clade dominates the colorectal cancer niche. Nature 2024, 628, 424–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickard, J.M.; Zeng, M.Y.; Caruso, R.; Núñez, G. Gut microbiota: Role in pathogen colonization, immune responses, and inflammatory disease. Immunol. Rev. 2017, 279, 70–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakajima, M.; Arimatsu, K.; Kato, T.; Matsuda, Y.; Minagawa, T.; Takahashi, N.; Ohno, H.; Yamazaki, K. Oral Administration of P. gingivalis Induces Dysbiosis of Gut Microbiota and Impaired Barrier Function Leading to Dissemination of Enterobacteria to the Liver. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0134234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willis, J.R.; Gabaldón, T. The Human Oral Microbiome in Health and Disease: From Sequences to Ecosystems. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.S. Oral microbiota and systemic disease. Anaerobe 2013, 24, 90–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plachokova, A.S.; Andreu-Sánchez, S.; Noz, M.P.; Fu, J.; Riksen, N.P. Oral Microbiome in Relation to Periodontitis Severity and Systemic Inflammation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozak, M.; Pawlik, A. The Role of the Oral Microbiome in the Development of Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 5231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, X.; Alekseyenko, A.V.; Wu, J.; Peters, B.A.; Jacobs, E.J.; Gapstur, S.M.; Purdue, M.P.; Abnet, C.C.; Stolzenberg-Solomon, R.; Miller, G.; et al. Human oral microbiome and prospective risk for pancreatic cancer: A population-based nested case-control study. Gut 2018, 67, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudra, A.; Muszyński, D.; Sobocki, B.K.; Atzeni, A.; Carbone, L.; Kaźmierczak-Siedlecka, K.; Połom, K.; Kalinowski, L. Insights into oral microbiome and colorectal cancer—On the way of searching new perspectives. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1159822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Huang, X.; Huang, Y.; Zheng, J.; Lu, Y.; Mai, Z.; Zhao, X.; Cui, L.; Huang, S. The oral microbiome in autoimmune diseases: Friend or foe? J. Transl. Med. 2023, 21, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Meade, J.; Mankia, K.; Emery, P.; Devine, D.A. Periodontal disease and periodontal bacteria as triggers for rheumatoid arthritis. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 2017, 31, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, X.J.; Cao, N.W.; Zhou, H.Y.; Meng, X.; Guo, B.; Zhang, H.Y.; Li, B.Z. The oral and gut microbiome in rheumatoid arthritis patients: A systematic review. Rheumatology 2021, 60, 1054–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasinski-Bergner, S.; Mandelboim, O.; Seliger, B. Molecular mechanisms of human herpes viruses inferring with host immune surveillance. J. Immunother. Cancer 2020, 8, e000841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dziedzic, A. Is Periodontitis Associated with Age-Related Cognitive Impairment? The Systematic Review, Confounders Assessment and Meta-Analysis of Clinical Studies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, L.; Gupta, S.; Perambudhuru, Y. Association between periodontitis and cognitive impairment in adults. Evid.-Based Dent. 2023, 24, 123–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Said-Sadier, N.; Sayegh, B.; Farah, R.; Abbas, L.A.; Dweik, R.; Tang, N.; Ojcius, D.M. Association between Periodontal Disease and Cognitive Impairment in Adults. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 4707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Z.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y. No genetic causal associations between periodontitis and brain atrophy or cognitive impairment: Evidence from a comprehensive bidirectional Mendelian randomization study. BMC Oral Health 2024, 24, 571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayten, Ş.; Bilici, S. Modulation of Gut Microbiota Through Dietary Intervention in Neuroinflammation and Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s Diseases. Curr. Nutr. Rep. 2024, 13, 82–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Y.; Xiao, J.; Ma, L.; Wang, C.; Wang, X.; Huang, X.; Cao, Z. Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Periodontitis and Associated Systemic Diseases: Implications for Pathomechanisms and Therapeutic Strategies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbarisi, A.; Visconti, V.; Lauritano, D.; Cremonini, F.; Caccianiga, G.; Ceraulo, S. Correlation between Periodontitis and Onset of Alzheimer’s Disease: A Literature Review. Dent. J. 2024, 12, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gang, J.; Wang, H.; Xue, X.; Zhang, S. Microbiota and COVID-19: Long-term and complex influencing factors. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 963488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hazan, S.; Stollman, N.; Bozkurt, H.S.; Dave, S.A.-O.; Papoutsis, A.J.; Daniels, J.; Barrows, B.D.; Quigley, E.A.-O.; Borody, T.J. Lost microbes of COVID-19: Bifidobacterium, Faecalibacterium depletion and decreased microbiome diversity associated with SARS-CoV-2 infection severity. BMJ Open Gastroenterol. 2022, 9, e000871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, E.C.; Chiang, Y.C.; Lin, H.Y.; Tseng, S.Y.; Hsieh, Y.T.; Shieh, J.A.; Huang, Y.H.; Tsai, H.T.; Feng, S.A.-O.; Peng, T.A.-O.; et al. Unraveling the Link between Periodontitis and Coronavirus Disease 2019: Exploring Pathogenic Pathways and Clinical Implications. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 2789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swaney, R.; Jokomo-Nyakabau, R.; Nguyen, A.A.N.; Kenny, D.; Millner, P.G.; Selim, M.; Destache, C.A.-O.; Velagapudi, M.A.-O. Diagnosis and Outcomes of Fungal Co-Infections in COVID-19 Infections: A Retrospective Study. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaibani, P.; D’Amico, F.; Bartoletti, M.; Lombardo, D.; Rampelli, S.; Fornaro, G.; Coladonato, S.; Siniscalchi, A.; Re, M.C.; Viale, P.; et al. The Gut Microbiota of Critically Ill Patients With COVID-19. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 670424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roncati, L.; Lusenti, B.; Nasillo, V.; Manenti, A. Fatal SARS-CoV-2 coinfection in course of EBV-associated lymphoproliferative disease. Ann. Hematol. 2020, 99, 1945–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markowiak, P.; Śliżewska, K. Effects of Probiotics, Prebiotics, and Synbiotics on Human Health. Nutrients 2017, 9, 1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davani-Davari, D.; Negahdaripour, M.; Karimzadeh, I.; Seifan, M.; Mohkam, M.; Masoumi, S.J.; Berenjian, A.; Ghasemi, Y. Prebiotics: Definition, Types, Sources, Mechanisms, and Clinical Applications. Foods 2019, 8, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunningham, M.; Azcarate-Peril, M.A.; Barnard, A.; Benoit, V.; Grimaldi, R.; Guyonnet, D.; Holscher, H.D.; Hunter, K.; Manurung, S.; Obis, D.; et al. Shaping the Future of Probiotics and Prebiotics. Trends Microbiol. 2021, 29, 667–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hemarajata, P.; Versalovic, J. Effects of probiotics on gut microbiota: Mechanisms of intestinal immunomodulation and neuromodulation. Ther. Adv. Gastroenterol. 2013, 6, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaumont, M.; Roura, E.; Lambert, W.; Turni, C.; Michiels, J.; Chalvon-Demersay, T. Selective nourishing of gut microbiota with amino acids: A novel prebiotic approach? Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 1066898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tester, R.F.; Al-Ghazzewi, F.H. A preliminary study of the synbiotic effects of konjac glucomannan hydrolysates (GMH) and lactobacilli on the growth of the oral bacterium Streptococcus mutans. Nutr. Food Sci. 2011, 41, 234–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, B.; Li, D.; Zhao, J.; Liu, X.; Gu, Z.; Chen, Y.Q.; Zhang, H.; Chen, W. Metagenomic insights into the effects of fructo-oligosaccharides (FOS) on the composition of fecal microbiota in mice. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 856–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verspecht, T.; Van Holm, W.; Boon, N.; Bernaerts, K.; Daep, C.A.; Zayed, N.; Quirynen, M.; Teughels, W. Comparison of the modulatory effects of three structurally similar potential prebiotic substrates on an in vitro multi-species oral biofilm. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 15033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Z.T.; Huang, X.; Ellepola, K.; Liao, S.; Li, Y. Lactobacilli and human dental caries: More than mechanical retention. Microbiology 2022, 168, 001196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, Y.-D.; Kim, K.-H.; Lee, Y.-M.; Ku, Y.; Seol, Y.-J. Oral Microbiome and Host Health: Review on Current Advances in Genome-Wide Analysis. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 4050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inchingolo, F.; Inchingolo, A.M.; Malcangi, G.; De Leonardis, N.; Sardano, R.; Pezzolla, C.; de Ruvo, E.; Di Venere, D.; Palermo, A.; Inchingolo, A.D.; et al. The Benefits of Probiotics on Oral Health: Systematic Review of the Literature. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juneja, A.; Kakade, A. Evaluating the effect of probiotic containing milk on salivary mutans streptococci levels. J. Clin. Pediatr. Dent. 2012, 37, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NĘdzi-GÓra, M.; WrÓblewska, M.; GÓrska, R. The Effect of Lactobacillus salivarius SGL03 on Clinical and Microbiological Parameters in Periodontal Patients. Pol. J. Microbiol. 2020, 69, 441–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutula, J.; Coulthwaite, L.A.; Thomas, L.V.; Verran, J. The effect of a commercial probiotic drink containing Lactobacillus casei strain Shirota on oral health in healthy dentate people. Microb. Ecol. Health Dis. 2013, 24, 21003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toiviainen, A.; Jalasvuori, H.; Lahti, E.; Gursoy, U.; Salminen, S.; Fontana, M.; Flannagan, S.; Eckert, G.; Kokaras, A.; Paster, B.; et al. Impact of orally administered lozenges with Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG and Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis BB-12 on the number of salivary mutans streptococci, amount of plaque, gingival inflammation and the oral microbiome in healthy adults. Clin. Oral Investig. 2015, 19, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, M.; Charvat, J.; Zwart, S.R.; Mehta, S.; Crucian, B.E.; Smith, S.M.; He, J.; Piermarocchi, C.; Mias, G.I. Time-resolved molecular measurements reveal changes in astronauts during spaceflight. bioRxiv Prepr. Serv. Biol. 2023, 14, 1219221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niranjan, R.; Patil, S.; Dubey, A.; Lochab, B.; Priyadarshini, R. Small cyclic dipeptide produced by Lactobacillus rhamnosus with anti-biofilm properties against Streptococcus mutans biofilm. Biofilm 2024, 8, 100237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, P.; Sharma, P. Probiotics and Their Efficacy in Improving Oral Health: A Review. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2012, 2, 151–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.; Hamayun, M.; Siraj, M.; Khan, S.A.; Kim, H.-Y.; Lee, B. Recent advances in prebiotics: Classification, mechanisms, and health applications. Future Foods 2025, 12, 100680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, S.; Ma, Y.; Yan, B.; Pei, W.; Wu, Q.; Ding, C.; Huang, C. The promotion mechanism of prebiotics for probiotics: A review. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 1000517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruis, W.; Frič, P.; Pokrotnieks, J.; Lukáš, M.; Fixa, B.; Kaščák, M.; Kamm, M.A.; Weismueller, J.; Beglinger, C.; Stolte, M.; et al. Maintaining remission of ulcerative colitis with the probiotic Escherichia coli Nissle 1917 is as effective as with standard mesalazine. Gut 2004, 53, 1617–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, C.; Singh, A.; Singh, D.; Upadhyay, R. Potential therapeutic solution for Clostridioides difficile infection: Current scenario and future prospects. Med. Microecol. 2025, 24, 100121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanashat, M.; Abuelazm, M.; Abouzid, M.; Al-Ajlouni, Y.A.; Ramadan, A.; Alsalah, S.; Sharaf, A.; Ayman, D.; Elharti, H.; Zhana, S.; et al. Efficacy of probiotics regimens for Helicobacter pylori eradication: A systematic review, pairwise, and network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2025, 65, 424–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allaker, R.P.; Stephen, A.S. Use of Probiotics and Oral Health. Curr. Oral Health Rep. 2017, 4, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yelin, I.; Flett, K.B.; Merakou, C.; Mehrotra, P.; Stam, J.; Snesrud, E.; Hinkle, M.; Lesho, E.; McGann, P.; McAdam, A.J.; et al. Genomic and epidemiological evidence of bacterial transmission from probiotic capsule to blood in ICU patients. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 1728–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabahi, S.; Homayouni Rad, A.; Aghebati-Maleki, L.; Sangtarash, N.; Ozma, M.A.; Karimi, A.; Hosseini, H.; Abbasi, A. Postbiotics as the new frontier in food and pharmaceutical research. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 63, 8375–8402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manos, J. The human microbiome in disease and pathology. APMIS Acta Pathol. Microbiol. Immunol. Scand. 2022, 130, 690–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghazadeh, Z.; Pouralibaba, F.; Yari Khosroushahi, A. The prophylactic effect of Acetobacter syzygii probiotic species against squamous cell carcinoma. J. Dent. Res. Dent. Clin. Dent. Prospect. 2017, 11, 208–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar-Toalá, J.E.; Garcia-Varela, R.; Garcia, H.S.; Mata-Haro, V.; González-Córdova, A.F.; Vallejo-Cordoba, B.; Hernández-Mendoza, A. Postbiotics: An evolving term within the functional foods field. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 75, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plaza-Diaz, J.; Ruiz-Ojeda, F.J.; Gil-Campos, M.; Gil, A. Mechanisms of Action of Probiotics. Adv. Nutr. 2019, 10 (Suppl. S1), S49–S66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginsburg, I. Role of lipoteichoic acid in infection and inflammation. Lancet. Infect. Dis. 2002, 2, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, F.C.; Patangia, D.; Grimaud, G.; Lavelle, A.; Dempsey, E.M.; Ross, R.P.; Stanton, C. The interplay between diet and the gut microbiome: Implications for health and disease. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2024, 22, 671–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özdemir, V. Toward Next-Generation Phenomics: Precision Medicine, Spaceflight, Astronaut Omics, and Beyond. Omics J. Integr. Biol. 2024, 28, 377–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Douglas, G.L.; Zwart, S.R.; Smith, S.M. Space Food for Thought: Challenges and Considerations for Food and Nutrition on Exploration Missions. J. Nutr. 2020, 150, 2242–2244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etlin, S.; Rose, J.; Bielski, L.; Walter, C.; Kleinman, A.S.; Mason, C.E. The human microbiome in space: Parallels between Earth-based dysbiosis, implications for long-duration spaceflight, and possible mitigation strategies. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2024, 37, e0016322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siddiqui, R.; Akbar, N.; Khan, N.A. Gut microbiome and human health under the space environment. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2021, 130, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagpal, R.; Neth, B.J.; Wang, S.; Craft, S.; Yadav, H. Modified Mediterranean-ketogenic diet modulates gut microbiome and short-chain fatty acids in association with Alzheimer’s disease markers in subjects with mild cognitive impairment. eBioMedicine 2019, 47, 529–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandith, J.A.; Neekhra, S.; Ahmad, S.; Sheikh, R.A. Recent developments in space food for exploration missions: A review. Life Sci. Space Res. 2023, 36, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watkins, P.; Hughes, J.; Gamage, T.V.; Knoerzer, K.; Ferlazzo, M.L.; Banati, R.B. Long term food stability for extended space missions: A review. Life Sci. Space Res. 2022, 32, 79–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malla, M.A.; Dubey, A.; Kumar, A.; Yadav, S.; Hashem, A.; Abd Allah, E.F. Exploring the Human Microbiome: The Potential Future Role of Next-Generation Sequencing in Disease Diagnosis and Treatment. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dilmore, A.H.; Martino, C.; Neth, B.J.; West, K.A.; Zemlin, J.; Rahman, G.; Panitchpakdi, M.; Meehan, M.J.; Weldon, K.C.; Blach, C.; et al. Effects of a ketogenic and low-fat diet on the human metabolome, microbiome, and foodome in adults at risk for Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer Dement. J. Alzheimer Assoc. 2023, 19, 4805–4816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X. Research progress on the effects of microgravity and space radiation on astronauts’ health and nursing measures. Open Astron. 2022, 31, 300–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caswell, G.; Eshelby, B. Skin microbiome considerations for long haul space flights. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 956432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garrett-Bakelman, F.E.; Darshi, M.; Green, S.J.; Gur, R.C.; Lin, L.; Macias, B.R.; McKenna, M.J.; Meydan, C.; Mishra, T.; Nasrini, J.; et al. The NASA Twins Study: A multidimensional analysis of a year-long human spaceflight. Science 2019, 364, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urbaniak, C.; Lorenzi, H.; Thissen, J.; Jaing, C.; Crucian, B.; Sams, C.; Pierson, D.; Venkateswaran, K.; Mehta, S. The influence of spaceflight on the astronaut salivary microbiome and the search for a microbiome biomarker for viral reactivation. Microbiome 2020, 8, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burcham, Z.M.; Garneau, N.L.; Comstock, S.S.; Tucker, R.M.; Knight, R.; Metcalf, J.L. Patterns of Oral Microbiota Diversity in Adults and Children: A Crowdsourced Population Study. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rutter, L.A.; Cope, H.; MacKay, M.J.; Herranz, R.; Das, S.; Ponomarev, S.A.; Costes, S.V.; Paul, A.M.; Barker, R.; Taylor, D.M.; et al. Astronaut omics and the impact of space on the human body at scale. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 4952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pignatelli, P.; Romei, F.M.; Bondi, D.; Giuliani, M.; Piattelli, A.; Curia, M.C. Microbiota and Oral Cancer as A Complex and Dynamic Microenvironment: A Narrative Review from Etiology to Prognosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 8323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, B.; Tan, J.; Guo, G.; Li, Z.; Yang, L.; Lao, X.; Wang, D.; Ma, J.; Zhang, S.; Liao, G.; et al. The oral cancer microbiome contains tumor space-specific and clinicopathology-specific bacteria. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 942328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakr, M.M.; Caswell, G.M.; Hussein, H.; Shamel, M.; Al-Ankily, M.M. Considerations for oral and dental tissues in holistic care during long-haul space flights. Front. Physiol. 2024, 15, 1406631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloro, V.; Giovannoni, L.M.; Lozano-de Luaces, V.; Lloro, I.; Manzanares, M.C. Is oral health affected in long period space missions only by microgravity? A systematic review. Acta Astronaut. 2020, 167, 343–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, G.; Curtis, P.A.-O. The Impacts of Microgravity on Bacterial Metabolism. Life 2022, 12, 774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, S.K.; Laudenslager, M.L.; Stowe, R.P.; Crucian, B.E.; Feiveson, A.H.; Sams, C.F.; Pierson, D.L. Latent virus reactivation in astronauts on the international space station. NPJ Microgravity 2017, 3, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, P.; Green, S.J.; Chlipala, G.E.; Turek, F.W.; Vitaterna, M.A.-O. Reproducible changes in the gut microbiome suggest a shift in microbial and host metabolism during spaceflight. Microbiome 2019, 7, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tesei, D.A.-O.X.; Jewczynko, A.A.-O.; Lynch, A.M.; Urbaniak, C. Understanding the Complexities and Changes of the Astronaut Microbiome for Successful Long-Duration Space Missions. Life 2022, 12, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casero, D.; Gill, K.; Sridharan, V.; Koturbash, I.; Nelson, G.; Hauer-Jensen, M.; Boerma, M.; Braun, J.; Cheema, A.K. Space-type radiation induces multimodal responses in the mouse gut microbiome and metabolome. Microbiome 2017, 5, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Kim, H.D.; Barrila, J.; Lee, S.H.; Nickerson, C.A.; Ott, C.M.; Israel, S.A.; Choukér, A.A.-O.; Yang, J.Y. Navigating mental health in space: Gut-brain axis and microbiome dynamics. Exp. Mol. Med. 2025, 57, 1152–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierson, D.L. Microbial contamination of spacecraft. Gravit. Space Biol. Bull. 2001, 14, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Kuehnast, T.; Abbott, C.; Pausan, M.R.; Pearce, D.A.; Moissl-Eichinger, C.; Mahnert, A. The crewed journey to Mars and its implications for the human microbiome. Microbiome 2022, 10, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schultz, J.; Jamil, T.; Sengupta, P.; Sivabalan, S.K.M.; Rawat, A.; Patel, N.; Krishnamurthi, S.; Alam, I.; Singh, N.K.; Raman, K.; et al. Genomic insights into novel extremotolerant bacteria isolated from the NASA Phoenix mission spacecraft assembly cleanrooms. Microbiome 2025, 13, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nastasi, N.; Bope, A.; Meyer, M.E.; Horack, J.M.; Dannemiller, K.C. Predicting how varying moisture conditions impact the microbiome of dust collected from the International Space Station. Microbiome 2024, 12, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voorhies, A.; Lorenzi, H. The Challenge of Maintaining a Healthy Microbiome During Long-Duration Space Missions. Front. Astron. Space Sci. 2016, 3, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voorhies, A.A.; Mark Ott, C.; Mehta, S.; Pierson, D.L.; Crucian, B.E.; Feiveson, A.; Oubre, C.M.; Torralba, M.; Moncera, K.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Study of the impact of long-duration space missions at the International Space Station on the astronaut microbiome. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 9911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salido, R.A.; Zhao, H.N.; McDonald, D.; Mannochio-Russo, H.; Zuffa, S.; Oles, R.E.; Aron, A.T.; El Abiead, Y.; Farmer, S.; González, A.; et al. The International Space Station has a unique and extreme microbial and chemical environment driven by use patterns. Cell 2025, 188, 2022–2041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al, K.F.; Chmiel, J.A.-O.; Stuivenberg, G.A.-O.; Reid, G.A.-O.; Burton, J.A.-O. Long-Duration Space Travel Support Must Consider Wider Influences to Conserve Microbiota Composition and Function. Life 2022, 2, 1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, R.A.-O.; Qaisar, R.; Goswami, N.A.-O.; Khan, N.A.-O.; Elmoselhi, A.A.-O. Effect of Microgravity Environment on Gut Microbiome and Angiogenesis. Life 2021, 11, 1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharindwal, S.; Goswami, N.A.-O.; Jha, P.A.-O.; Pandey, S.A.-O.; Jobby, R. Prospective Use of Probiotics to Maintain Astronaut Health during Spaceflight. Life 2023, 13, 727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turroni, S.; Magnani, M.; Kc, P.; Lesnik, P.; Vidal, H.; Heer, M. Gut Microbiome and Space Travelers’ Health: State of the Art and Possible Pro/Prebiotic Strategies for Long-Term Space Missions. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 553929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crucian, B.E.; Choukèr, A.; Simpson, R.J.; Mehta, S.; Marshall, G.; Smith, S.M.; Zwart, S.R.; Heer, M.; Ponomarev, S.; Whitmire, A.; et al. Immune System Dysregulation During Spaceflight: Potential Countermeasures for Deep Space Exploration Missions. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Sui, L.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, W.; Gao, L.; Hu, W.; Song, M.; Liu, X.; Kong, F.; Gong, Y.; et al. Differences in the Establishment of Gut Microbiota and Metabolome Characteristics Between Balb/c and C57BL/6J Mice After Proton Irradiation. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 874702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Zhou, Q.; Qiao, P.; Zhu, D.; Xin, B.; Wu, B.; Tang, C. Short-term head-down bed rest microgravity simulation alters salivary microbiome in young healthy men. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1056637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minoretti, P.; Fontana, J.M.; Yilmaz, Y. Pilots, Astronauts, and the Aerospace Microbiota: A Narrative Review of Occupational Impact. Cureus 2024, 16, e72268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chhabrani, A.; Bs, A.; Bharadwaj, R.S.; Kale, R.; Kathuria, A. ‘Microgravity’s dental dilemma: Navigating oral health challenges in space, from effect on bone to therapeutic frontiers—A review’. Acta Astronaut. 2024, 219, 363–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Liu, S.; Chen, L.; Zhou, Z.; Ma, M.; Li, J.; Lu, Y.; Shi, Y.; Yao, T.; Feng, R.; et al. Spaceflight redefines ageing-associated microbiota. Imeta 2025, 4, e70023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.; Gao, X.; Wei, D.; Ge, J.; Deng, X.; Chen, H.; Yang, H.; Gao, J.; Yang, J. The digestive system under microgravity environment: Changes, mechanisms and the prospects of the future. Gastroenterol. Endosc. 2025, 3, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Guo, J.; Yu, W.; Zeng, D.; Song, C.; Zhou, L.; Anatolyevna, N.A.-O.; Baranenko, D.A.-O.; Xiao, D.; Zhou, Y.; et al. Molecular Mechanism of Microgravity-Induced Intestinal Flora Dysbiosis on the Abnormalities of Liver and Brain Metabolism. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 3094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, Z.; Khan, N.A.; Siddiqui, R.; Qaisar, R.; Marzook, H.; Soares, N.C.; Elmoselhi, A.B. Gut matters in microgravity: Potential link of gut microbiota and its metabolites to cardiovascular and musculoskeletal well-being. Nutr. Metab. 2024, 21, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galčenko, K.; Bourdakou, M.M.; Spyrou, G.A.-O. Exploring the Impact of Microgravity on Gene Expression: Dysregulated Pathways and Candidate Repurposed Drugs. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapoor, P.; Yadav, R.B.; Agrawal, N.; Gaur, S.; Arora, R. Long duration space missions: Challenges and prospects in sustaining humans in space. Life Sci. Space Res. 2025, 47, 14–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cutigni, M.; Cucina, G.; Galante, E.; Cerri, M.; Bizzarri, M. Microgravity impairs endocrine signaling and reproductive health of women. A narrative review. Sec. Environ. Aviat. Space Physiol. 2025, 6, 1558711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De la Torre, G.G.; Groemer, G.; Diaz-Artiles, A.; Pattyn, N.; Van Cutsem, J.; Musilova, M.; Kopec, W.; Schneider, S.; Abeln, V.; Larose, T.; et al. Space Analogs and Behavioral Health Performance Research review and recommendations checklist from ESA Topical Team. NPJ Microgravity 2024, 10, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Wu, T.; Han, Y.; Wang, F.; Zhao, D.; Fang, Z.; Pan, L.; Tang, C. Advancements in Mars Habitation Technologies and Terrestrial Simulation Projects: A Comprehensive Review. Aerospace 2025, 12, 510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortazavi, S.M.J.; Said-Salman, I.; Mortazavi, A.R.; El Khatib, S.; Sihver, L. How the adaptation of the human microbiome to harsh space environment can determine the chances of success for a space mission to Mars and beyond. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1237564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chugh, P.; Dutt, R.; Sharma, A.; Bhagat, N.; Dhar, M.S. A critical appraisal of the effects of probiotics on oral health. J. Funct. Foods 2020, 70, 103985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.; Guo, Y.; Fang, T.; Jiang, X.; Wang, D.; Li, D.; Bai, P.; Zhang, B.; Wang, J.; Liu, C. Effects of Simulated Microgravity on the Physiology of Stenotrophomonas maltophilia and Multiomic Analysis. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 701265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jasemi, S.; Simula, E.R.; Yasushi, K.; Sechi, L.A. Unveiling the impact of simulated microgravity on HSV-1 infection, neuroinflammation, and endogenous retroviral activation in SH-SY5Y cells. J. Neurovirol. 2025, 31, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mednieks, M.; Hand, A. Oral Tissue Responses to Travel in Space. In Beyond LEO—Human Health Issues for Deep Space Exploration; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Charan Teja, G.V.; Nandana Raju, M.R.; Neelima Reddy, U.L.; UV, V.S.; Praneeth, D.; Maheswari, K. An In Vitro Evaluation of the Antimicrobial Activity of Probiotics Against Endodontic Pathogens. Cureus 2022, 14, e26455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Chen, X.; Yu, H.; Zhou, H.; Xu, S. Oral Microbiota as Promising Diagnostic Biomarkers for Gastrointestinal Cancer: A Systematic Review. OncoTargets Ther. 2019, 12, 11131–11144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fragkioudakis, I.; Riggio, M.P.; Apatzidou, D.A. Understanding the microbial components of periodontal diseases and periodontal treatment-induced microbiological shifts. J. Med. Microbiol. 2021, 70, 001247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, G.R.; Roberfroid, M.B. Dietary modulation of the human colonic microbiota: Introducing the concept of prebiotics. J. Nutr. 1995, 125, 1401–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negrini, T.C.; Carlos, I.Z.; Duque, C.; Caiaffa, K.S.; Arthur, R.A. Interplay Among the Oral Microbiome, Oral Cavity Conditions, the Host Immune Response, Diabetes Mellitus, and Its Associated-Risk Factors-An Overview. Front. Oral Health 2021, 2, 697428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulkarni, M.S.; Miller, B.A.-O.X.; Mahani, M.; Mhaskar, R.; Tsalatsanis, A.; Jain, S.; Yadav, H.A.-O. Poor Oral Health Linked with Higher Risk of Alzheimer’s Disease. Brain Sci. 2023, 13, 1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyedmoalemi, M.A.; Saied-Moallemi, Z. Association between periodontitis and Alzheimer’s disease: A narrative review. IBRO Neurosci. Rep. 2025, 18, 360–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gianos, E.; Jackson, E.A.; Tejpal, A.; Aspry, K.; O’Keefe, J.; Aggarwal, M.; Jain, A.; Itchhaporia, D.; Williams, K.; Batts, T.; et al. Oral health and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease: A review. Am. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2021, 7, 100179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carding, S.; Verbeke, K.; Vipond, D.T.; Corfe, B.M.; Owen, L.J. Dysbiosis of the gut microbiota in disease. Microb. Ecol. Health Dis. 2015, 26, 26191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotillard, A.; Kennedy, S.P.; Kong, L.C.; Prifti, E.; Pons, N.; Le Chatelier, E.; Almeida, M.; Quinquis, B.; Levenez, F.; Galleron, N.; et al. Dietary intervention impact on gut microbial gene richness. Nature 2013, 500, 585–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajasekaran, J.J.; Krishnamurthy, H.A.-O.; Bosco, J.; Jayaraman, V.; Krishna, K.; Wang, T.; Bei, K. Oral Microbiome: A Review of Its Impact on Oral and Systemic Health. Microorganisms 2024, 2, 1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shayista, H.; Prasad, M.N.N.; Raj, S.N.; Prasad, A.; Lakshmi, S.; Ranjini, H.K.; Manju, K.; Ravikumara; Chouhan, R.S.; Khohlova, O.Y.; et al. Complexity of antibiotic resistance and its impact on gut microbiota dynamics. Eng. Microbiol. 2025, 5, 100187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinon, P.; Fraticelli, L.; Giboreau, A.; Dussart, C.; Bourgeois, D.; Carrouel, F. Nutrition as a Key Modifiable Factor for Periodontitis and Main Chronic Diseases. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLean, J.S. Advancements toward a systems level understanding of the human oral microbiome. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2014, 4, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patini, R.; Staderini, E.; Lajolo, C.; Lopetuso, L.; Mohammed, H.; Rimondini, L.; Rocchetti, V.; Franceschi, F.; Cordaro, M.; Gallenzi, P. Relationship between oral microbiota and periodontal disease: A systematic review. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2018, 22, 5775–5788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, K.; Rodriguez, M.; Paul, Z.; Gordon, E.; Gu, T.; Rice, K.; Triplett, E.W.; Keller-Wood, M.; Wood, C.E. Transfer of oral bacteria to the fetus during late gestation. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez, L.A.; De Avila, J.; Castillo, D.M.; Montenegro, D.A.; Trujillo, T.G.; Suárez, L.J.; Lafaurie, G.I. Porphyromonas gingivalis Placental Atopobiosis and Inflammatory Responses in Women with Adverse Pregnancy Outcomes. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 591626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thienngern, P.; Panichuttra, A.; Ratisoontorn, C.; Aumnate, C.; Matangkasombut, O. Efficacy of chitosan paste as intracanal medication against Enterococcus faecalis and Candida albicans biofilm compared with calcium hydroxide in an in vitro root canal infection model. BMC Oral Health 2022, 22, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, Y.C.; Yang, B.Y.; Lu, J.; Zhang, S.W.; Liu, L.; Nassar, K.; Xu, X.X.; Pang, X.Y.; Lv, J.P. Metabolite secretions of Lactobacillus plantarum YYC-3 may inhibit colon cancer cell metastasis by suppressing the VEGF-MMP2/9 signaling pathway. Microb. Cell Factories 2020, 19, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, F.; Polk, D.B. Probiotics and immune health. Curr. Opin. Gastroenterol. 2011, 27, 496–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coblentz, M.; Evans, J.D.; Kothe, C.I.; Mak, T.; Valerón, N.R.; Chwalek, P.; Wejendorp, K.; Garg, S.; Pless, L.; Mak, S.; et al. Food fermentation in space: Opportunities and challenges. iScience 2025, 28, 112189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Phylum | Main Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Bacillota | Common in the mouth and include many Gram-positive bacteria |
| Fusobacteriota | Linked to periodontal disease |
| Pseudomonadota | Diverse group; some species associated with inflammation |
| Actinomycetota | Include beneficial and pathogenic species |
| Bacteroidota | Abundant in the gut and oral microbiome |
| Chlamydiota | Less common; intracellular pathogens |
| Chloroflexota | Rare in the oral cavity |
| Spirochaetota | Includes some pathogens like Treponema species |
| Synergistota | Anaerobic bacteria; some linked to periodontitis |
| Saccharibacteria | Part of the TM7 group; difficult to culture |
| Gracilibacteria | Uncultivated; found in various environments |
| Candidate division SR1 | Uncultivated; detected via sequencing in oral and marine settings |
| Type of Interaction | Oral Bacteria | Gut Bacteria | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mutualism | Lactobacillus spp. | Bifidobacterium spp. | Symbiosis in which both bacteria are beneficial to each other. |
| Antagonism | Streptococcus mutans | Lactobacillus rhamnosus | Beneficial gut bacteria can be hostile to oral bacteria. |
| Immune Modulation | Veillonella | Bacteroidota fragilis | Oral and gut bacteria can change immune responses in the body. |
| Dysbiosis | Treponema denticola | Clostridium difficile | Bacteria are out of balance. |
| Translocation | Enterococcus faecalis | E. coli | Oral bacteria can change the location to the gut and vice versa, affecting gut flora. |
| Metabolite Exchange | Actinomycetota spp. | Bifidobacterium longum | Exchange of molecular factors produced by gut bacteria can influence oral bacteria and vice versa. |
| Competition for Nutrients | Porphyromonas gingivalis | Faecalibacterium prausnitzii | Both compete for nutrient supplies, thus can affect overall health. |
| Feature | Healthy Earth Oral Microbiome | Dysbiotic Space Oral Microbiome | Healthy Earth GI Microbiome | Dysbiotic Space GI Microbiome |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diversity | High and balanced | Reduced and pathogen-dominated | High and balanced | Reduced and pathogen-dominated |
| Dominant taxa | Streptococcus Actinomycetota Veillonella | P. gingivalis F. nucleatum Candida overgrowth | Faecalibacterium Bifidobacterium Akkermansia | Enterobacteriaceae Clostridioides Opportunistic E. coli |
| Biofilm | Stable and protective | Unstable and pathogenic | N/A | N/A |
| Key functions | pH balance Metabolism Immune tolerance | Acid production Inflammation Immune resistance | Short-Chain Fatty Acids Vitamin synthesis Immune tolerance | Reduced Short Chain Fatty Acids Increased pro-inflammatory metabolites Immune resistance |
| Host effects | Oral health maintenance Systemic benefits | Caries Periodontal disease Systemic inflammation | Intact mucus Strong epithelial integrity | Leaky gut syndrome Impaired gut barrier |
| Drivers/systemic effects | Salivary flow Diet Immune system | Microgravity Radiation Immune suppression Altered diet | Metabolic balance Immune regulation Gut–brain signaling | Inflammation Malabsorption Metabolic and immune dysfunction |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bakr, M.M.; Caswell, G.M.; Al Ankily, M.; Zeitoun, S.I.; Ahmed, N.; Meer, M.; Shamel, M. Composition and Interactions of the Oral–Gastrointestinal Microbiome Populations During Health, Disease, and Long-Duration Space Missions: A Narrative Review. Oral 2025, 5, 66. https://doi.org/10.3390/oral5030066
Bakr MM, Caswell GM, Al Ankily M, Zeitoun SI, Ahmed N, Meer M, Shamel M. Composition and Interactions of the Oral–Gastrointestinal Microbiome Populations During Health, Disease, and Long-Duration Space Missions: A Narrative Review. Oral. 2025; 5(3):66. https://doi.org/10.3390/oral5030066
Chicago/Turabian StyleBakr, Mahmoud M., Gabrielle M. Caswell, Mahmoud Al Ankily, Sarah I. Zeitoun, Nada Ahmed, Mohammed Meer, and Mohamed Shamel. 2025. "Composition and Interactions of the Oral–Gastrointestinal Microbiome Populations During Health, Disease, and Long-Duration Space Missions: A Narrative Review" Oral 5, no. 3: 66. https://doi.org/10.3390/oral5030066
APA StyleBakr, M. M., Caswell, G. M., Al Ankily, M., Zeitoun, S. I., Ahmed, N., Meer, M., & Shamel, M. (2025). Composition and Interactions of the Oral–Gastrointestinal Microbiome Populations During Health, Disease, and Long-Duration Space Missions: A Narrative Review. Oral, 5(3), 66. https://doi.org/10.3390/oral5030066






