Determining Aligner-Induced Tooth Movements in Three Dimensions Using Clinical Data of Two Patients
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Intraoral Scanner
2.2. Fabrication of Optically Transparent Aligners with Cellulose Coating
2.3. Case Study with Two Patients
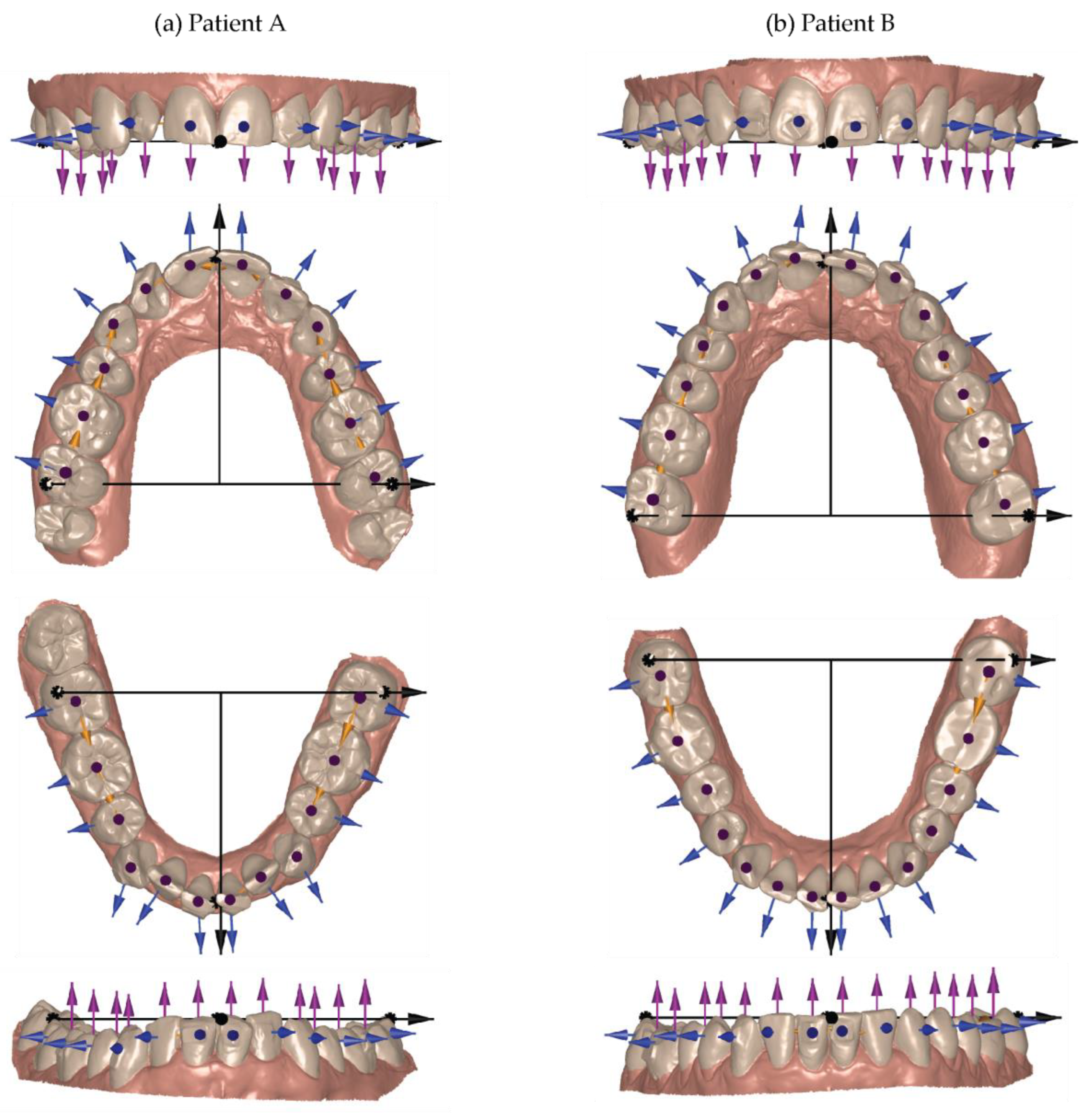
2.4. Selection of Global and Local Coordinate Systems
2.5. Data Evaluation
3. Results
3.1. Intraoral Scanner Selection
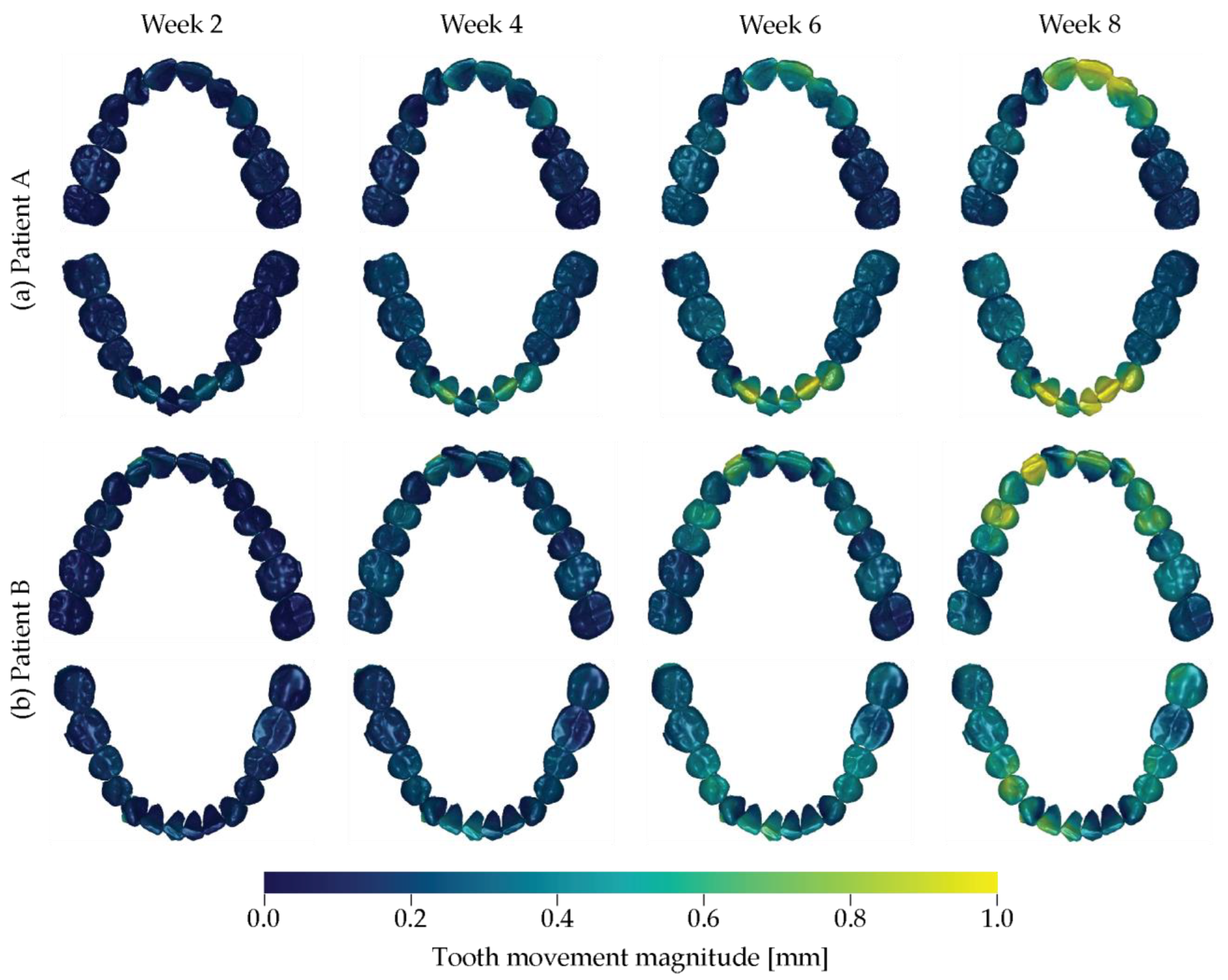
3.2. Tooth Movement Induced by a Series of Optically Transparent Aligners
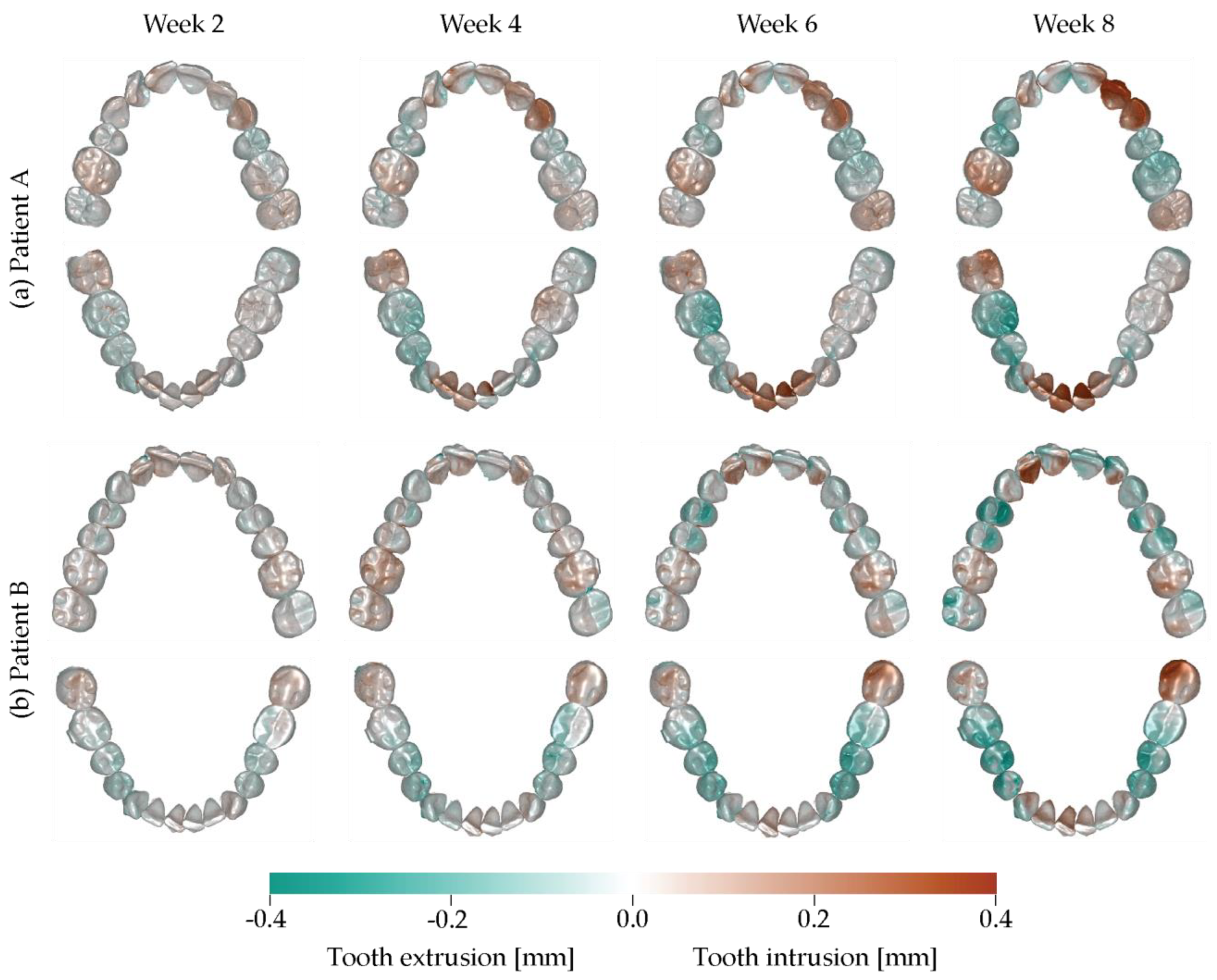
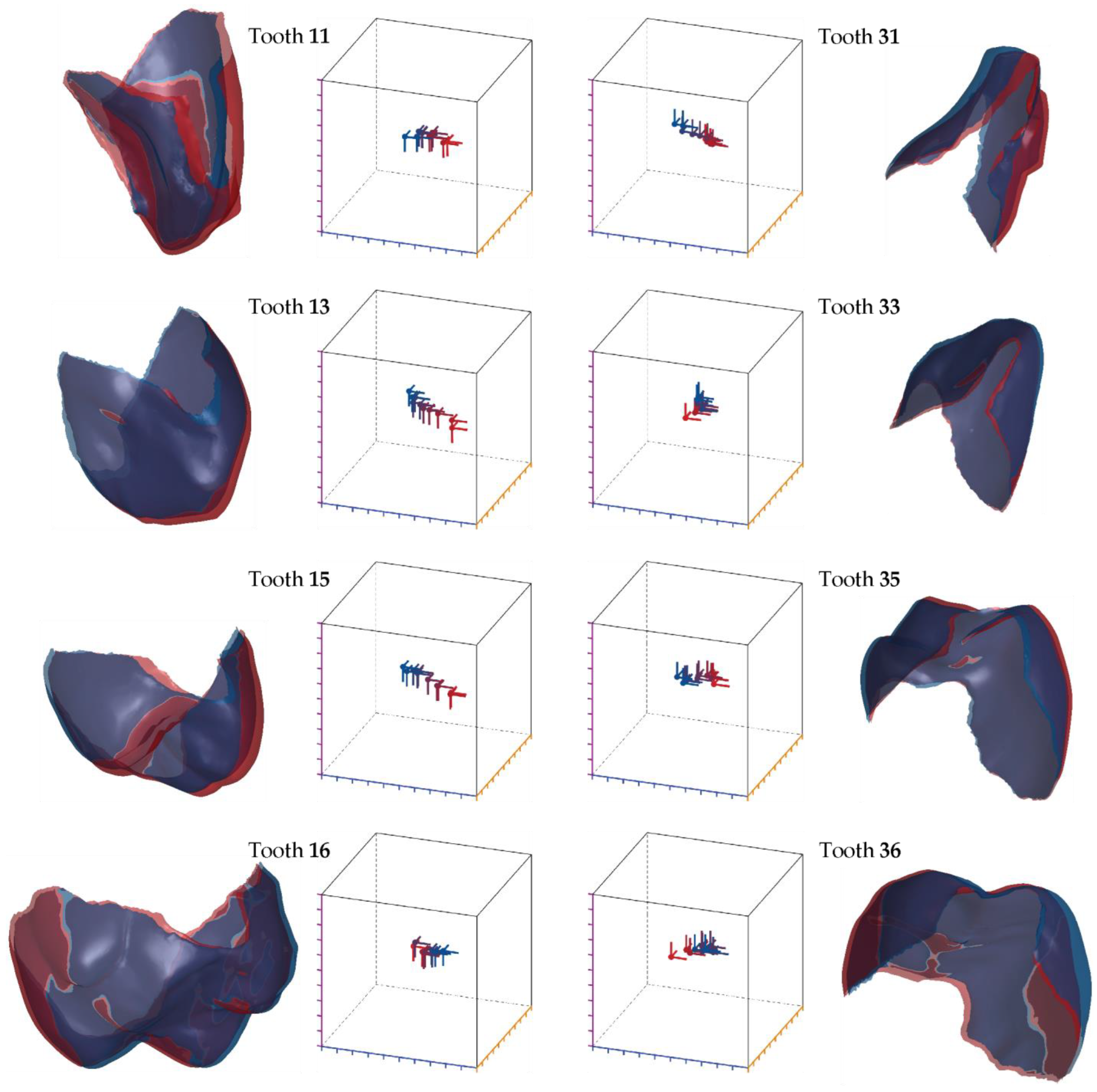
3.3. Intrusion–Extrusion Crown Displacements
3.4. Displacement of Individual Teeth
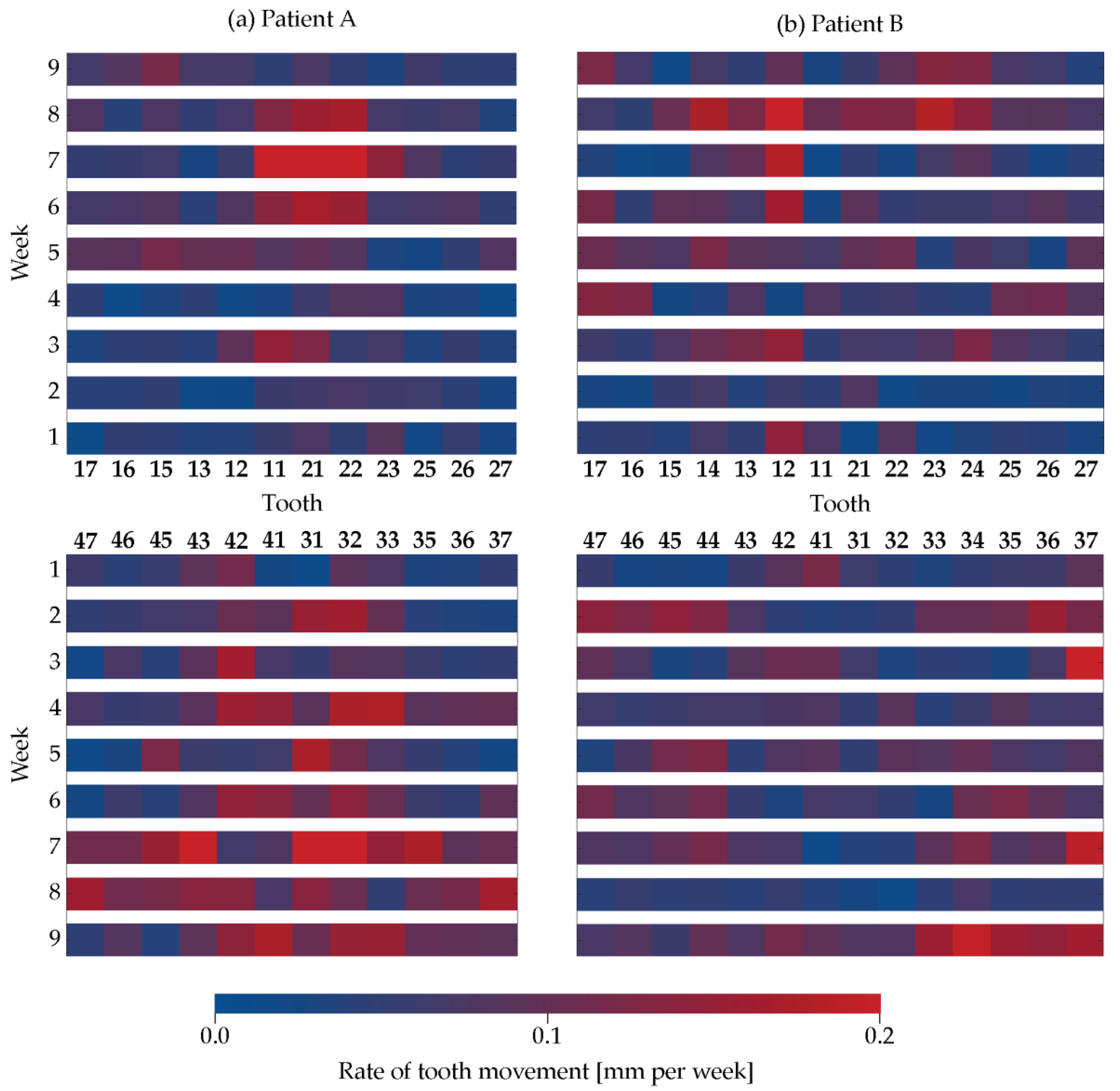
3.5. Rate of Tooth Movement
3.6. Tooth Displacement Difference to the Therapy Plan
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ke, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Zhu, M. A comparison of treatment effectiveness between clear aligner and fixed appliance therapies. BMC Oral Health 2019, 19, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papageorgiou, S.N.; Koletsi, D.; Iliadi, A.; Peltomaki, T.; Eliades, T. Treatment outcome with orthodontic aligners and fixed appliances: A systematic review with meta-analyses. Eur. J. Orthod. 2020, 42, 331–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Timm, L.H.; Farrag, G.; Baxmann, M.; Schwendicke, F. Factors influencing patient compliance during clear aligner therapy: A retrospective cohort study. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 3103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrivastava, A.; Mohanty, P.; Dash, B.P.; Jena, S.; Sahoo, N. Proficiency of clear aligner therapy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Cureus 2023, 15, e45072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Revilla-León, M.; Raney, L.; Cascón, W.; Barrington, J.; Zandinejad, A.; Özcan, M. Digital workflow for an esthetic rehabilitation using a facial and intraoral scanner and an additive manufactured silicone index: A dental technique. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2019, 123, 564–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kau, C.H.; Soh, J.; Christou, T.; Mangal, A. Orthodontic aligners: Current perspectives for the modern orthodontic office. Medicina 2023, 59, 1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinstein, T.; Marano, G.; Aulakh, R. Five-to-five clear aligner therapy: Predictable orthodontic movement for general dentist to achieve minimally invasive dentistry. BMC Oral Health 2021, 21, 671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elnagar, M.H.; Pan, A.Y.; Handono, A.; Sanchez, F.; Talaat, S.; Bourauel, C.; Kaboudan, A.; Kusnoto, B. Utilization of machine learning methods for predicting orthodontic treatment length. Oral 2022, 2, 263–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gay, G.; Ravera, S.; Castroflorio, T.; Garino, F.; Cugliari, G.; Deregibus, A. Root resorption in mandibular incisors during orthodontic treatment with Invisalign®: A radiometric study. Iran. J. Orthod. 2017, 12, e7915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaddam, R.; Freer, E.; Kerr, B.; Weir, T. Reliability of torque expression by the Invisalign appliance: A retrospective study. Australas. Orthod. J. 2021, 37, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Mei, L.; Long, H.; Jian, F.; Lai, W. Changing clear aligners every 10 days or 14 days? A randomised controlled trial. Australas. Orthod. J. 2023, 39, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grassia, V.; d’Apuzzo, F.; Alansari, R.A.; Jamilian, A.; Sayahpour, B.; Adel, S.M.; Nucci, L. Instagram and clear aligner therapy: A content analysis of patient perspectives. Semin. Orthod. 2024; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopinath, P.M.; Parvathi, V.D.; Yoghalakshmi, N.; Kumar, S.M.; Athulya, P.A.; Mukherjee, A.; Chandrasekaran, N. Plastic particles in medicine: A systematic review of exposure and effects to human health. Chemosphere 2022, 303, 135227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quinzi, V.; Orilisi, G.; Vitiello, F.; Notarstefano, V.; Marzo, G.; Orsini, G. A spectroscopic study on orthodontic aligners: First evidence of secondary microplastic detachment after seven days of artificial saliva exposure. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 866, 161356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ammann, R.; Tanner, C.; Schulz, G.; Osmani, B.; Nalabothu, P.; Töpper, T.; Müller, B. Three-dimensional analysis of aligner gaps and thickness distributions, using hard X-ray tomography with micrometer resolution. J. Med. Imaging 2022, 9, 031509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asiry, M.A. Biological aspects of orthodontic tooth movement: A review of literature. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2018, 25, 1027–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacher, M.; Schulz, G.; Deyhle, H.; Jäger, K.; Müller, B. Accuracy of commercial intraoral scanners. J. Med. Imaging 2021, 8, 035501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vögtlin, C.; Schulz, G.; Jäger, K.; Müller, B. Comparing the accuracy of master models based on digital intra-oral scanners with conventional plaster casts. Phys. Med. 2016, 1, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, G.; Thalmann, P.; Khimchenko, A.; Müller, B. Grating-based tomography applications in biomedical engineering. Proc. SPIE 2017, 10391, 1039117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.Y.; Choi, S.-H.; Yu, H.-S.; Kim, S.-J.; Kim, H.; Kim, K.B.; Cha, J.-Y. Comparison of translucency, thickness, and gap width of thermoformed and 3D-printed clear aligners using micro-CT and spectrophotometer. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 10921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, D.; Mohammed, H.; Koo, S.H.; Kang, K.H.; Kim, S.C. Three-dimensional evaluation of tooth movement in Class II malocclusions treated without extraction by orthodontic mini-implant anchorage. Korean J. Orthod. 2016, 46, 280–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amberg, B.; Romdhani, S.; Vetter, T. Optimal Step Nonrigid ICP Algorithms for Surface Registration. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 17–22 June 2007; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Kabsch, W. A solution for the best rotation to relate two sets of vectors. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. A 1976, 32, 922–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, A.; Collard, A.; Monteiro, F.; Matos, D.; Carvalho, Ó.; Azevedo, R.; Silva, F.S.; Pinho, T. Accuracy of Invisalign(®) on upper incisors: A systematic review. Turk. J. Orthod. 2023, 36, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inchingolo, A.M.; Inchingolo, A.D.; Carpentiere, V.; Del Vecchio, G.; Ferrante, L.; Di Noia, A.; Palermo, A.; Di Venere, D.; Dipalma, G.; Inchingolo, F. Predictability of dental distalization with clear aligners: A systematic review. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AlMogbel, A. Clear Aligner Therapy: Up to date review article. J. Orthod. Sci. 2023, 12, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamberland, S.; Nataf, N. Noninvasive conservative management of anterior open bite treated with TADs versus clear aligner therapy. Clin. Oral Investig. 2024, 28, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elshazly, T.M.; Bourauel, C.; Ismail, A.; Ghoraba, O.; Aldesoki, M.; Salvatori, D.; Elattar, H.; Alhotan, A.; Alkabani, Y. Effect of material composition and thickness of orthodontic aligners on the transmission and distribution of forces: An in vitro study. Clin. Oral Investig. 2024, 28, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalaie, K.; Fatemi, S.M.; Ghaffari, S. Dynamic mechanical and thermal properties of clear aligners after thermoforming and aging. Prog. Orthod. 2021, 22, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meade, M.J.; Weir, T.; Seehra, J.; Fleming, P.S. Clear aligner therapy practice among orthodontists in the United Kingdom and the Republic of Ireland: A cross-sectional survey of the British Orthodontic Society membership. J. Orthod. 2024, 51, 120–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tüfekçi, E.; Carrico, C.K.; Gordon, C.B.; Lindauer, S.J. Does crown, root, and bone visualization in a clear aligner virtual setup impact treatment decisions? Am. J. Orthod. Dentofacial Orthop. 2024, 165, 671–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Worafi, N.A.; Zheng, B.; Al-Warafi, L.A.; Alyafrusee, E.S.; Alsomairi, M.A.A.; Liu, Y. Impact of molar teeth distalization by clear aligners on maxillary alveolar bone thickness and root resorption: A three-dimensional study. BMC Oral Health 2024, 24, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woo, H.; Jha, N.; Kim, Y.-J.; Sung, S.-J. Evaluating the accuracy of automated orthodontic digital setup models. Semin. Orthod. 2023, 29, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adobes-Martin, M.; Montoya-Morcillo, M.L.; Zhou-Wu, A.; Garcovich, D. Invisalign treatment from the patient perspective: A Twitter content analyses. J. Clin. Exp. Dent. 2021, 13, e376–e382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fialho, T.; de Freitas, K.M.S.; Ohira, E.T.B.; de Souza, J.E.P.; de Oliveira, R.C.G.; de Oliveira, R.C.G.; Valarelli, F.P.; Pinzan-Vercelino, C.R.M.; Cotrin, P. Comparison of the efficiency of initial dental alignment with Invisalign® aligners changed every 7 or 14 days in mature adults: Randomized clinical trial. Orthod. Craniofac. Res. 2024, 27, 544–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moradinejad, M.; Harrell, R.E.; Mousavi, S.M.; Alavi, M.; Basseri, A.D.; Feiz, A.; Daryanavard, H.; Rakhshan, V. Effects of clear aligners on the vertical position of the molar teeth and the vertical and sagittal relationships of the face: A preliminary retrospective before-after clinical trial. BMC Oral Health 2024, 24, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, L.; Kaur, H.; Fagundes, N.C.F.; Romanyk, D.; Major, P.; Flores Mir, C. Effectiveness of clear aligner therapy for orthodontic treatment: A systematic review. Orthod. Craniofac. Res. 2020, 23, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

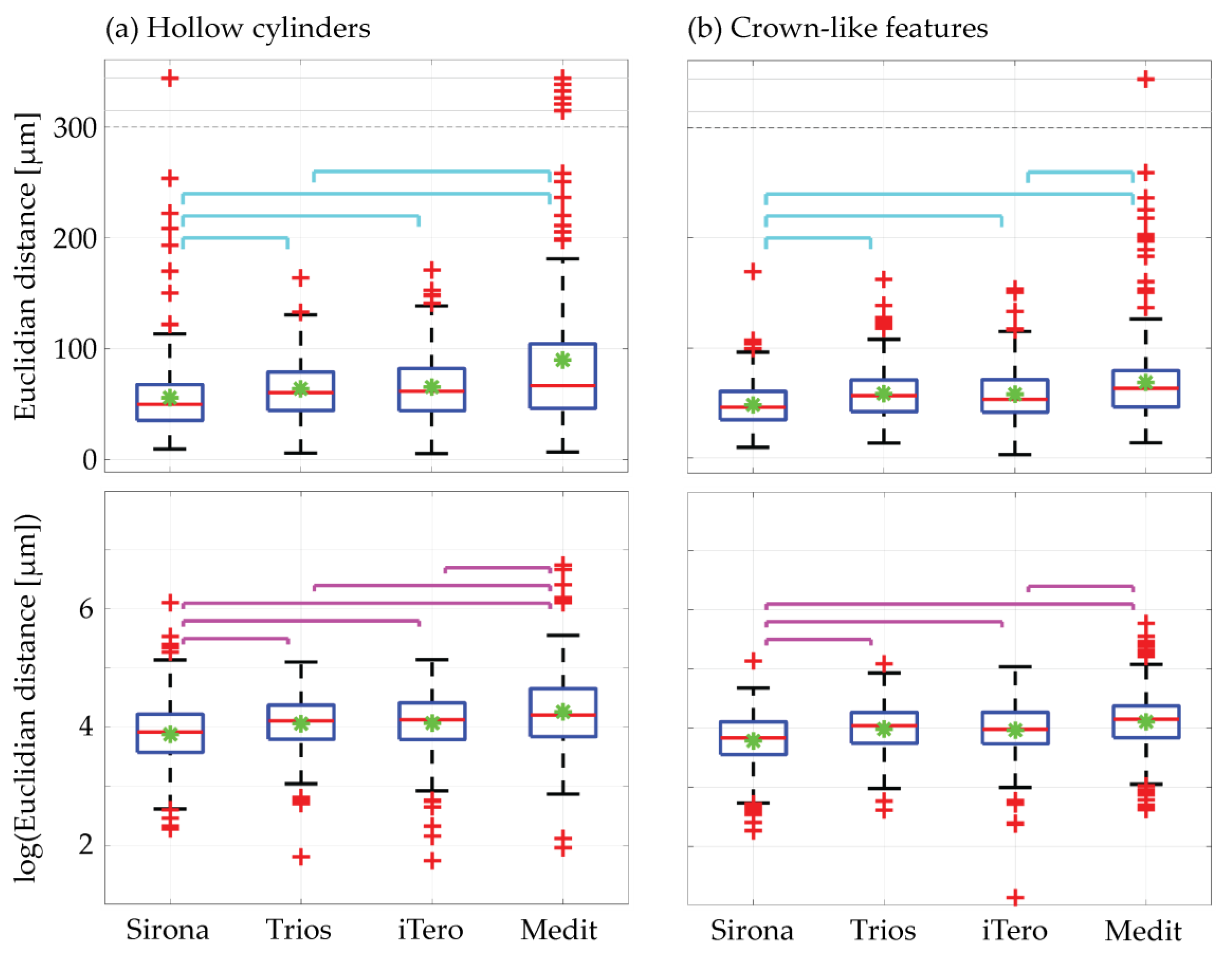


| Scanner | Cylinder Centers | Hollow Cylinders | Crown-Like Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sirona | 14 ± 8 | 55 ± 35 (56 ± 38) | 50 ± 25 (48 ± 21) |
| Trios | 24 ± 15 | 63 ± 26 (64 ± 28) | 58 ± 24 (58 ± 24) |
| iTero | 25 ± 15 | 65 ± 28 (66 ± 30) | 60 ± 26 (58 ± 24) |
| Medit | 43 ± 22 | 91 ± 90 (90 ± 91) | 70 ± 49 (69 ± 40) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Filippon, I.; Tanner, C.; von Jackowski, J.A.; Schulz, G.; Töpper, T.; Müller, B. Determining Aligner-Induced Tooth Movements in Three Dimensions Using Clinical Data of Two Patients. Oral 2024, 4, 487-504. https://doi.org/10.3390/oral4040039
Filippon I, Tanner C, von Jackowski JA, Schulz G, Töpper T, Müller B. Determining Aligner-Induced Tooth Movements in Three Dimensions Using Clinical Data of Two Patients. Oral. 2024; 4(4):487-504. https://doi.org/10.3390/oral4040039
Chicago/Turabian StyleFilippon, Ignacio, Christine Tanner, Jeannette A. von Jackowski, Georg Schulz, Tino Töpper, and Bert Müller. 2024. "Determining Aligner-Induced Tooth Movements in Three Dimensions Using Clinical Data of Two Patients" Oral 4, no. 4: 487-504. https://doi.org/10.3390/oral4040039
APA StyleFilippon, I., Tanner, C., von Jackowski, J. A., Schulz, G., Töpper, T., & Müller, B. (2024). Determining Aligner-Induced Tooth Movements in Three Dimensions Using Clinical Data of Two Patients. Oral, 4(4), 487-504. https://doi.org/10.3390/oral4040039









