The Effect of Pyrantel Pamoate Treatment on Fecal Pinworm (Leidynema appendiculata) Parasites of Dietary Dubia Roaches (Blaptica dubia): Efforts to Eliminate Passthrough Fecal Pseudoparasites in Lesser Hedgehog Tenrecs (Echinops telfairi)
Abstract
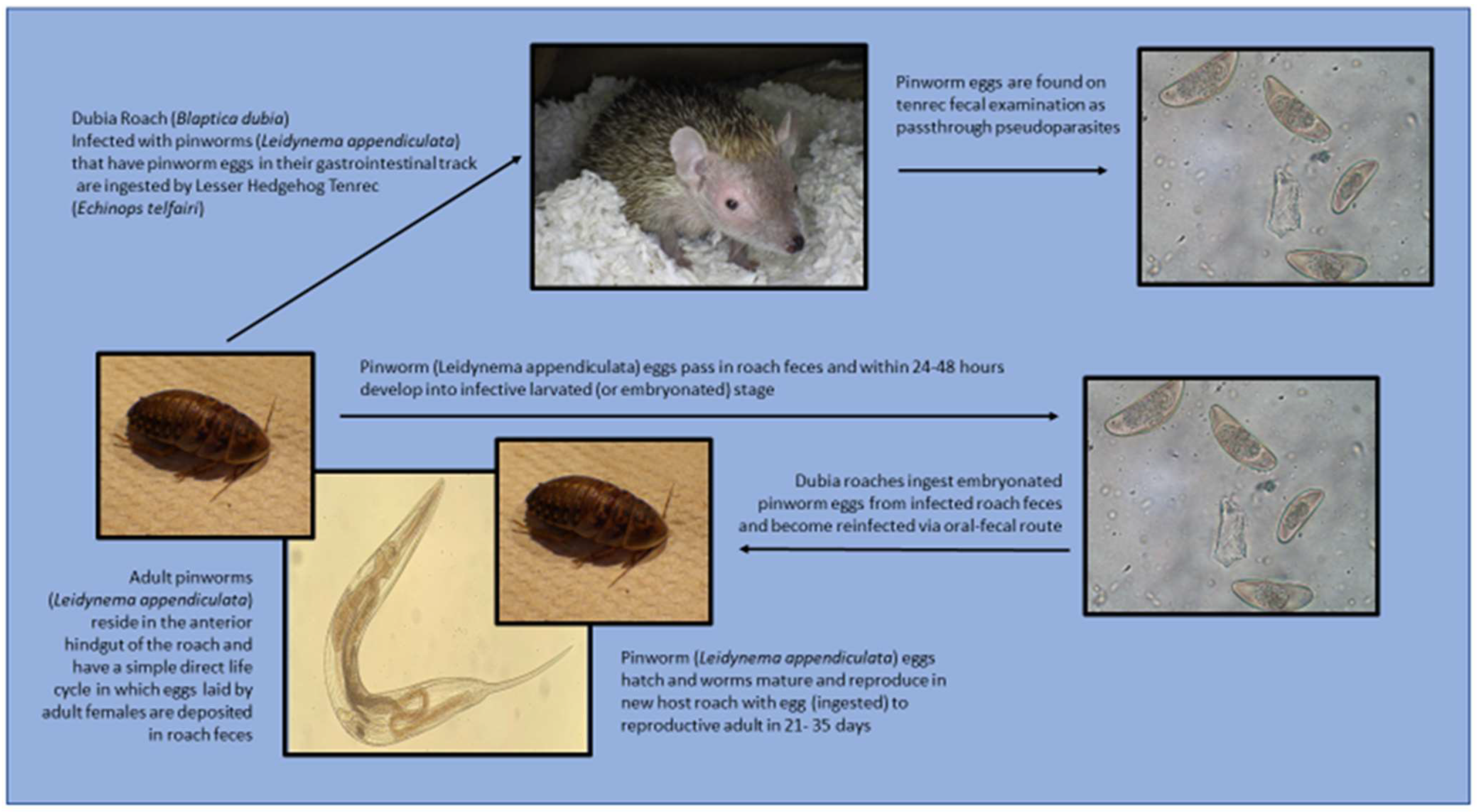
1. Introduction
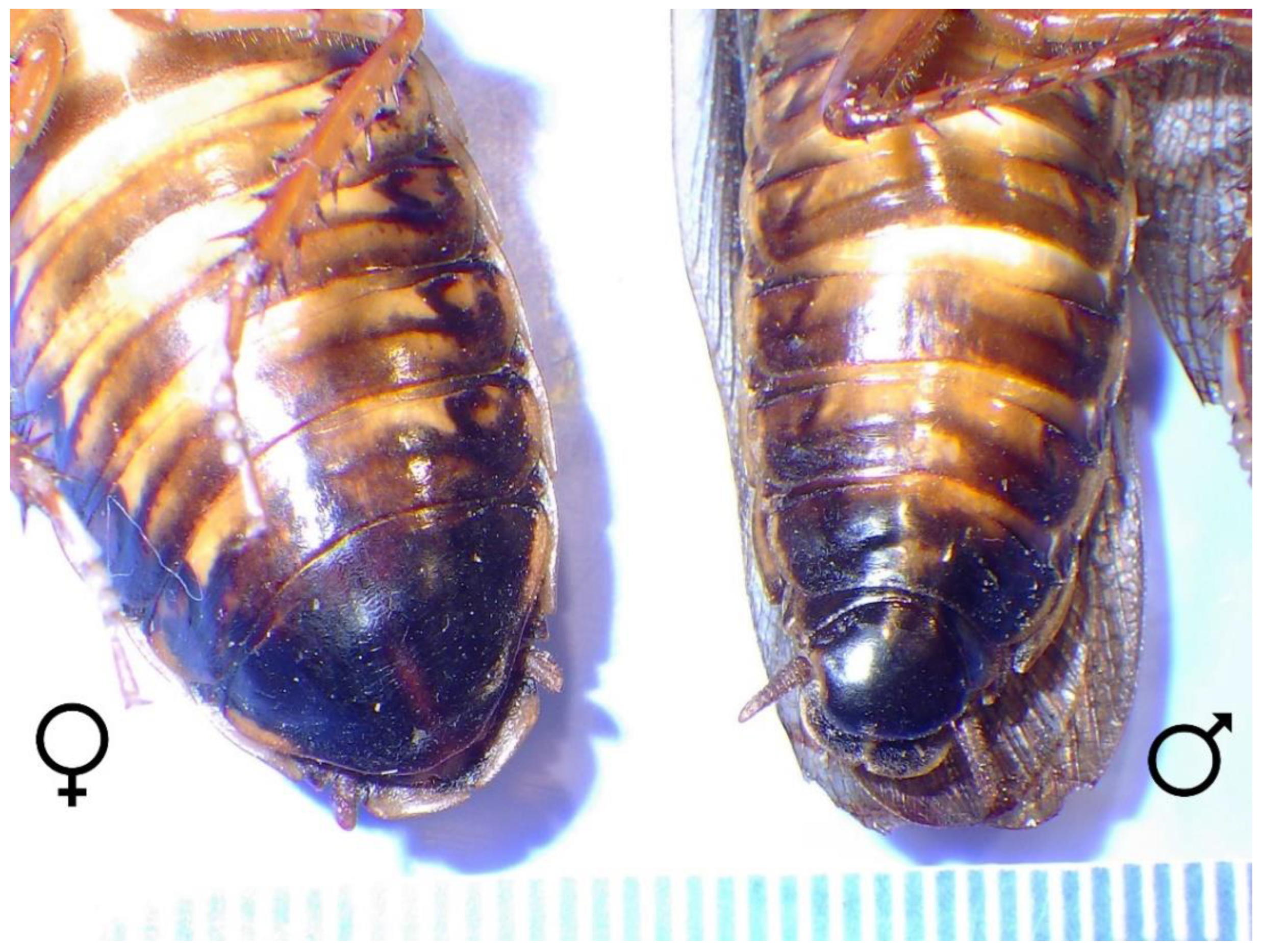
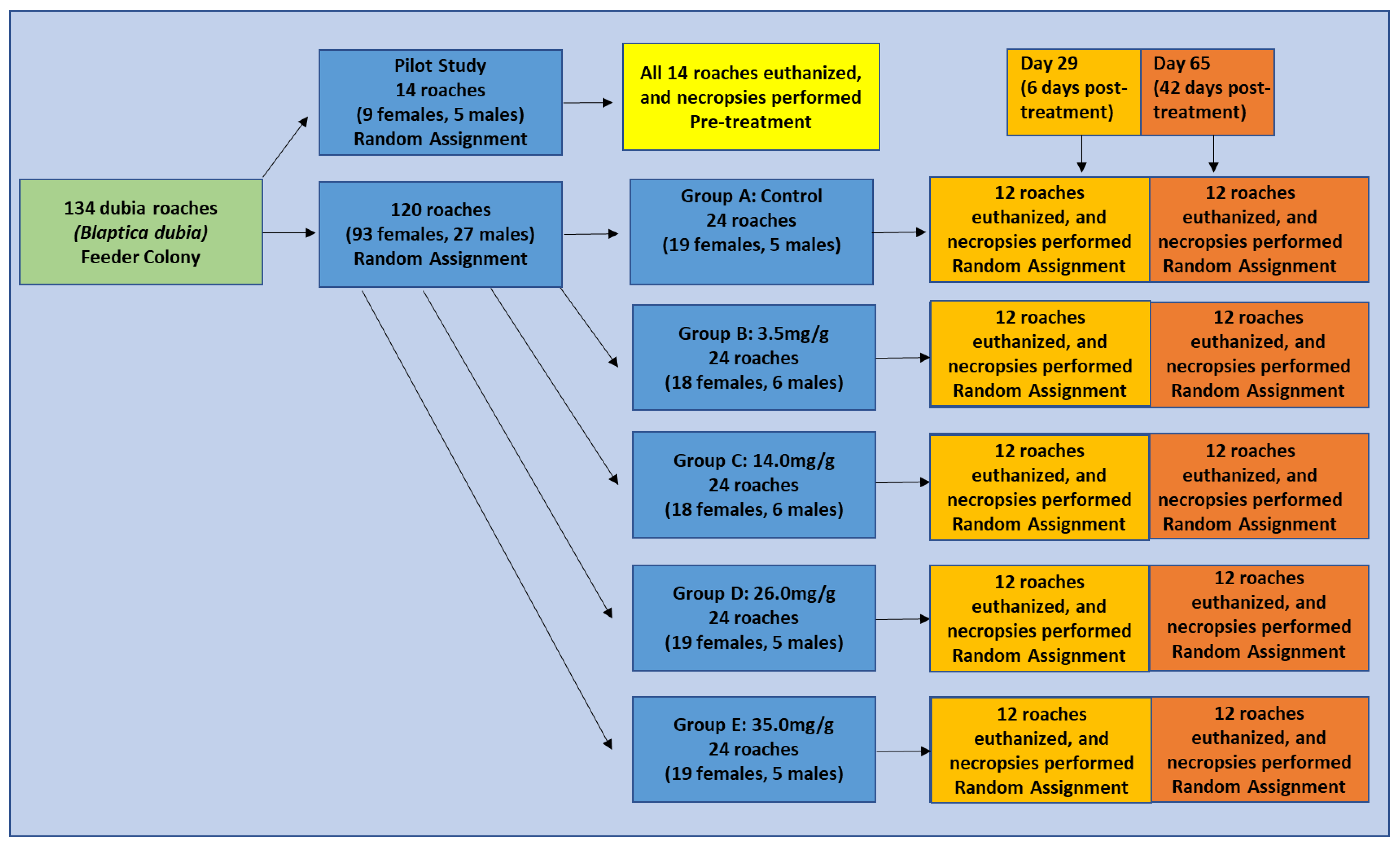
2. Materials and Methods
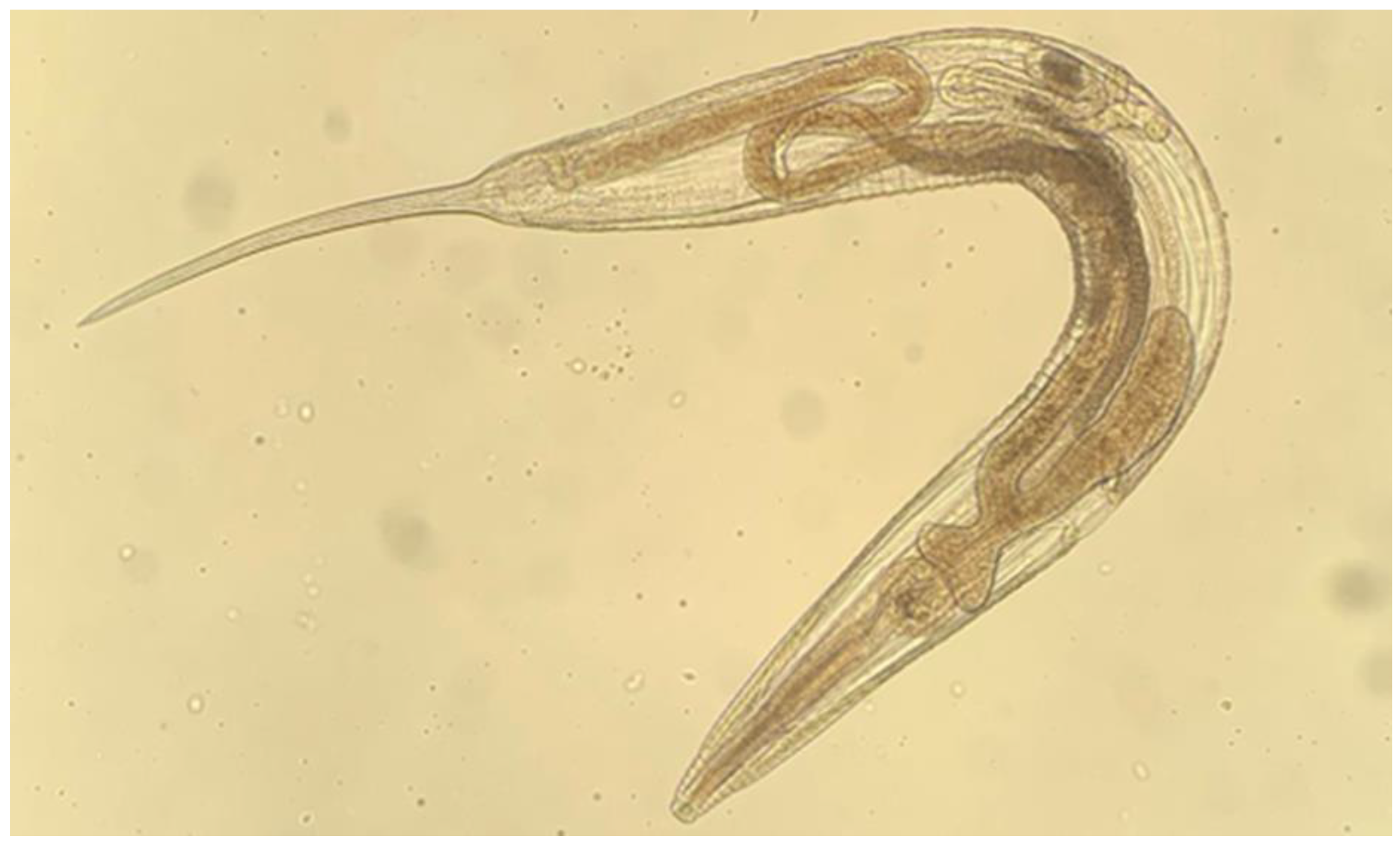
2.1. Pilot Study: Preliminary Roach Necropsy Findings
2.2. Pyrantel Pamoate Efficacy Study
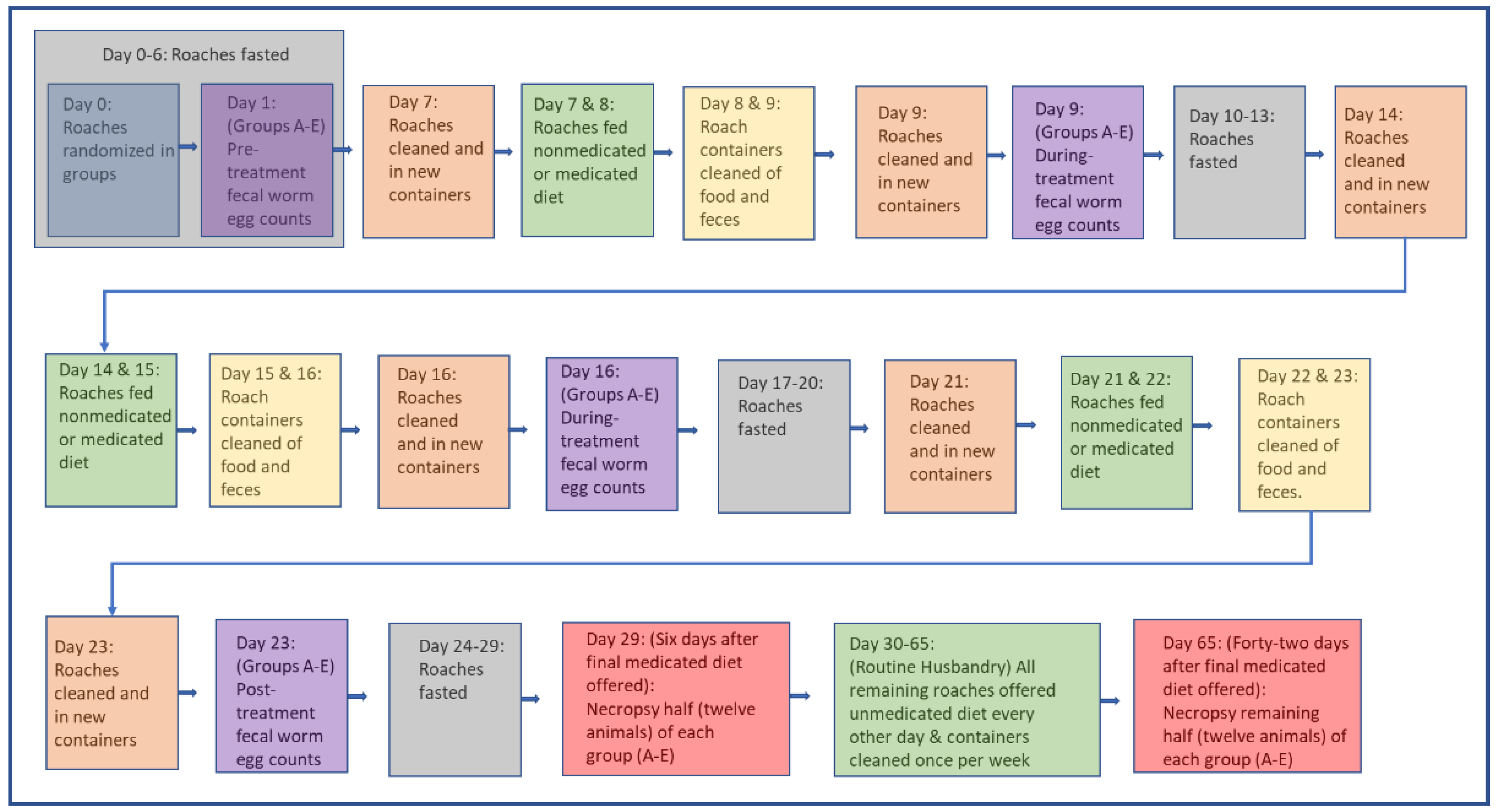
2.2.1. Group Randomization and Pre-Treatment Fecal Worm Ova Counts (Pre-FWOC)
2.2.2. Medicated Diet
2.2.3. Anthelmintic Oral Treatments via Medicated Gel Diet
2.2.4. Post-Treatment Fecal Worm Ova Counts (Post-FWOC)
2.2.5. Post-Treatment Necropsies
2.3. Data Analysis
3. Results
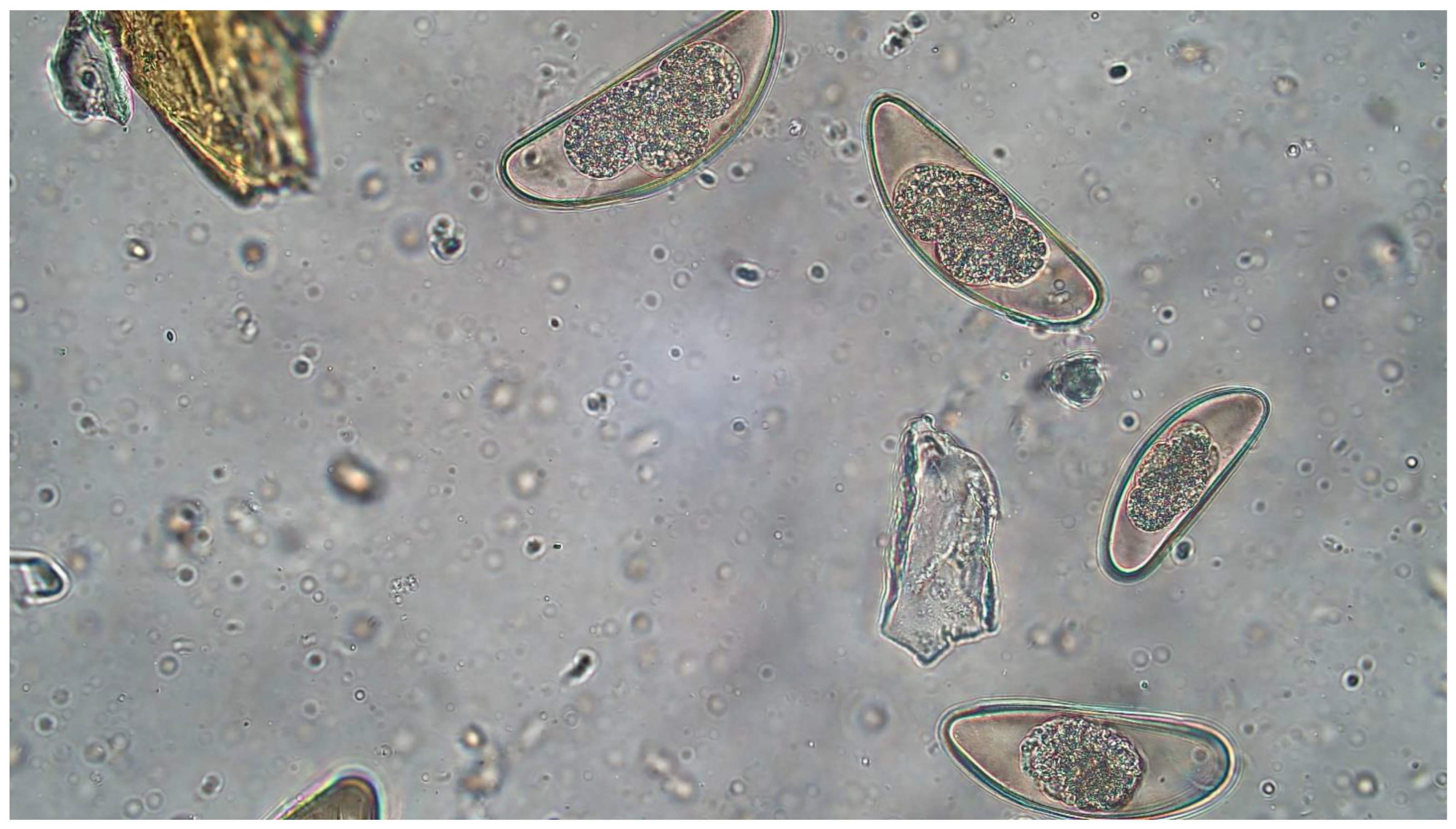
3.1. Pilot Roach Fecal Examinations and Necropsies
3.2. Pyrantel Pamoate Efficacy Study
3.2.1. Pyrantel Pamoate Consumed
3.2.2. Fecal Pinworm Ova Counts
3.2.3. 6 Days Post-Treatment Hindgut Examination for Pinworms
3.2.4. Forty-Two Day Post-Treatment Hindgut Examination for Pinworms
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Olson, L.E. Tenrecs. Curr. Biol. 2013, 23, R5–R8. Available online: https://www.cell.com/current-biology/pdf/S0960-982201324-3.pdf (accessed on 31 December 2022). [CrossRef]
- Harrison, T.M.; Harrison, S.H. Evaluation of husbandry and mortality in lesser hedgehog tenrecs (Echinops telfairi). J. Zoo Wildl. Med. 2017, 48, 440–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leidy, J. Description of some nematoid entozoa infesting insects. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1850, 5, 100–102. [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi, M.; Ooi, H.; Taira, K. Effects of anthelmintics on the pinworm Blatticola blattae in laboratory-reared German cockroaches Blatella germanica. Parasitol. Res. 2020, 119, 3093–3097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adamson, M.L.; Van Waerebeke, D. Revision of the Thelastomatoidea, Oxyurida of invertebrate hosts. I. Thelastomatidae. Syst. Parasitol. 1992, 21, 21–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozawa, S.; Vicent, C.S.L.; Sato, K.; Yoshiga, T.; Kanzaki, N.; Hasegawa, K. First report of the nematode Leidynema appendiculata from Periplaneta fuliginosa. Acta Parasitol. 2014, 59, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pawlik, J. Control of the nematode Leidynema appendiculata (Leidy) (Nemata: Rhabditida: Thelastomatidae) in laboratory cultures of the American cockroach. J. Econ. Entomol. 1966, 59, 468–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizzi, R.; Carta, L.; George, S. Oral nematode infection of tarantulas. Vet. Rec. 2003, 152, 695. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12803400/ (accessed on 31 December 2022). [PubMed]
- Ozawa, S.; Hasegawa, K. Broad infectivity of Leidynema appendiculatum (Nematoda: Oxyurida: Thelastomatidae) parasite of the smoky brown cockroach Periplaneta fuliginosa (Blattodea: Blattidae). Ecol. Evol. 2018, 8, 3908–3918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dryden, M.W.; Payne, P.A.; Ridley, R.; Smith, V. Comparison of common fecal flotation techniques for the recovery of parasite eggs and oocysts. J. Vet. Pharmacol. 2005, 6, 15–28. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15906267/ (accessed on 31 December 2022).
- Lewbart, G.A.; Mosley, C. Clinical anesthesia and analgesia in invertebrates. J. Exot. Pet Med. 2012, 21, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pritchard, M.H.; Kruse, G.O.W. The Collection and Preservation of Animal Parasites; University of Nebraska Press: Lincoln, NE, USA, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Chitwood, B.G. A synopsis of the nematodes parasitic in insects of the family Blattidae. Z. Parasitenkd. 1932, 5, 14–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobrovolny, C.G.; Ackert, J.E. The life history of Leidynema appendiculata (Leidy), a nematode parasite of cockroaches. Parasitol. Res. 1934, 26, 468–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nixon, S.A.; Welz, C.; Woods, D.J.; Costa-Junior, L.; Zamanian, M.; Martin, R.J. Where are all the anthelmintics? Challenges and opportunities on the path to new anthelmintics. Int. J. Parasitol. Drugs Drug. Resist. 2020, 14, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pyrantel. In LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury [Internet]; National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2012. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK548238/ (accessed on 20 July 2020).
- Hofer, R.; Forstner, H.; Rettenwander, R. Duration of gut passage and its dependence on temperature and food consumption in roach, Rutilus rutilus L: Laboratory and field experiments. J. Fish Biol. 1982, 20, 289–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente, C.S.; Ozawa, S.; Hasegawa, K. Composition of the cockroach gut microbiome in the presence of parasitic nematodes. Microbes Environ. 2016, 31, 314–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Roach Number (n = 14) | Weight of Feces (g) | Oxyurid Ova (#) | Pinworms (#) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.011 | 90 | 2 |
| 2 | 0.014 | 71 | 4 |
| 3 | 0.022 | 0 | 0 |
| 4 | 0.039 | 0 | 0 |
| 5 | 0.016 | 62 | 2 |
| 6 | 0.017 | 117 | 4 |
| 7 | 0.009 | 777 | 7 |
| 8 | 0.026 | 38 | 7 |
| 9 | 0.027 | 0 | 0 |
| 10 | 0.012 | 416 | 7 |
| 11 | 01 | NA | 3 |
| 12 | 0.008 | 0 | 0 |
| 13 | 0.012 | 750 | 2 |
| 14 | 0 1 | NA | 0 |
| Pyrantel Pamoate (mg/g) | Day 1: Total Fecal Ova | Day 9: Total Fecal Ova | Day 16: Total Fecal Ova | Day 23: Total Fecal Ova |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group A—0.0 (control) | 620 | 596 | 444 | 636 |
| Group B—3.5 | 509 | 210 | 390 | 160 |
| Group C—14.0 | 461 | 553 | 480 | 172 |
| Group D—26.0 | 1501 | 160 | 46 | 225 |
| Group E—35.0 | 510 | 176 | 358 | 194 |
| Group (n = 12 Roaches Each) | Pyrantel Pamoate in Gel Diet (mg/g) | Day 29: 6 Days Post-Treatment Total Pinworms | Day 65: 42 Days Post-Treatment Total Pinworms |
|---|---|---|---|
| A (control) | 0.0 | 143 | 106 |
| B | 3.5 | 130 | 49 |
| C | 14.0 | 34 1 | 74 |
| D | 26.0 | 25 2 | 69 |
| E | 35.0 | 10 3 | 36 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Browder, E.; Kapp, S.; Ange-van Heugten, K.; Flowers, J.; Christian, L.S.; Dombrowski, D.S. The Effect of Pyrantel Pamoate Treatment on Fecal Pinworm (Leidynema appendiculata) Parasites of Dietary Dubia Roaches (Blaptica dubia): Efforts to Eliminate Passthrough Fecal Pseudoparasites in Lesser Hedgehog Tenrecs (Echinops telfairi). J. Zool. Bot. Gard. 2023, 4, 146-157. https://doi.org/10.3390/jzbg4010015
Browder E, Kapp S, Ange-van Heugten K, Flowers J, Christian LS, Dombrowski DS. The Effect of Pyrantel Pamoate Treatment on Fecal Pinworm (Leidynema appendiculata) Parasites of Dietary Dubia Roaches (Blaptica dubia): Efforts to Eliminate Passthrough Fecal Pseudoparasites in Lesser Hedgehog Tenrecs (Echinops telfairi). Journal of Zoological and Botanical Gardens. 2023; 4(1):146-157. https://doi.org/10.3390/jzbg4010015
Chicago/Turabian StyleBrowder, Elizabeth, Sabrina Kapp, Kimberly Ange-van Heugten, James Flowers, Larry S. Christian, and Daniel S. Dombrowski. 2023. "The Effect of Pyrantel Pamoate Treatment on Fecal Pinworm (Leidynema appendiculata) Parasites of Dietary Dubia Roaches (Blaptica dubia): Efforts to Eliminate Passthrough Fecal Pseudoparasites in Lesser Hedgehog Tenrecs (Echinops telfairi)" Journal of Zoological and Botanical Gardens 4, no. 1: 146-157. https://doi.org/10.3390/jzbg4010015
APA StyleBrowder, E., Kapp, S., Ange-van Heugten, K., Flowers, J., Christian, L. S., & Dombrowski, D. S. (2023). The Effect of Pyrantel Pamoate Treatment on Fecal Pinworm (Leidynema appendiculata) Parasites of Dietary Dubia Roaches (Blaptica dubia): Efforts to Eliminate Passthrough Fecal Pseudoparasites in Lesser Hedgehog Tenrecs (Echinops telfairi). Journal of Zoological and Botanical Gardens, 4(1), 146-157. https://doi.org/10.3390/jzbg4010015






