Instagram Engagement and Content Strategies of US and UK Legacy Media: A Quantitative Analysis of Five Leading News Outlets
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Audience Engagement and Participation in Social Media
2.2. Curated News Flows and News Distribution on Social Media
2.3. Instagram as a Visual and Strategic Communication Platform
2.4. News Media Strategies and Challenges on Instagram
2.5. Research Objectives and Questions
- RQ1: How do the analyzed media outlets differ in terms of posting frequency and content delivery rhythms on Instagram?
- RQ2: In what ways do audience engagement metrics (likes and comments) vary across outlets, and how might these variations reflect strategic or structural differences?
- RQ3: What patterns emerge in the use of hashtags, profile mentions, and geographic references, and how are these practices related to audience engagement and editorial positioning?
3. Materials and Methods
- From the United States: The Washington Post, The New York Times, and USA Today.
- From Great Britain: The Independent and The Guardian.
4. Results
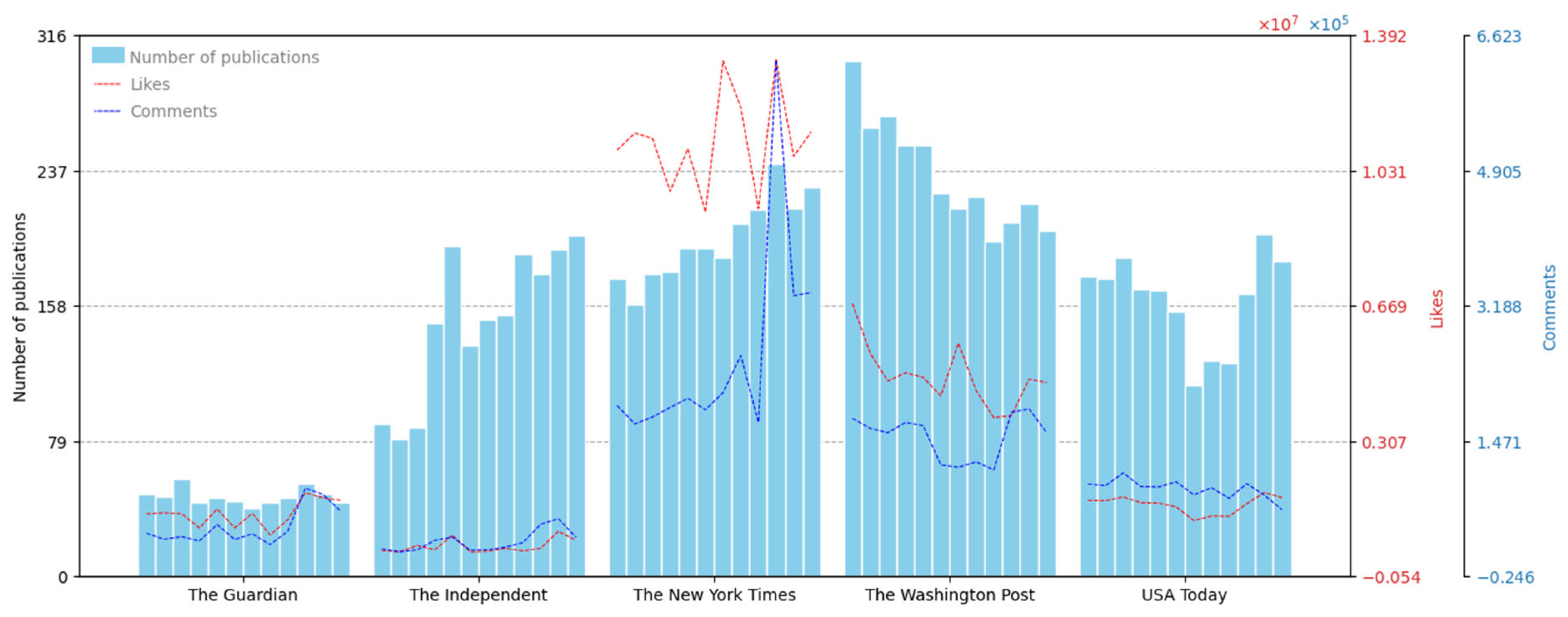
4.1. Posting Frequency and Interaction Volume
4.2. Proportional Engagement per Post
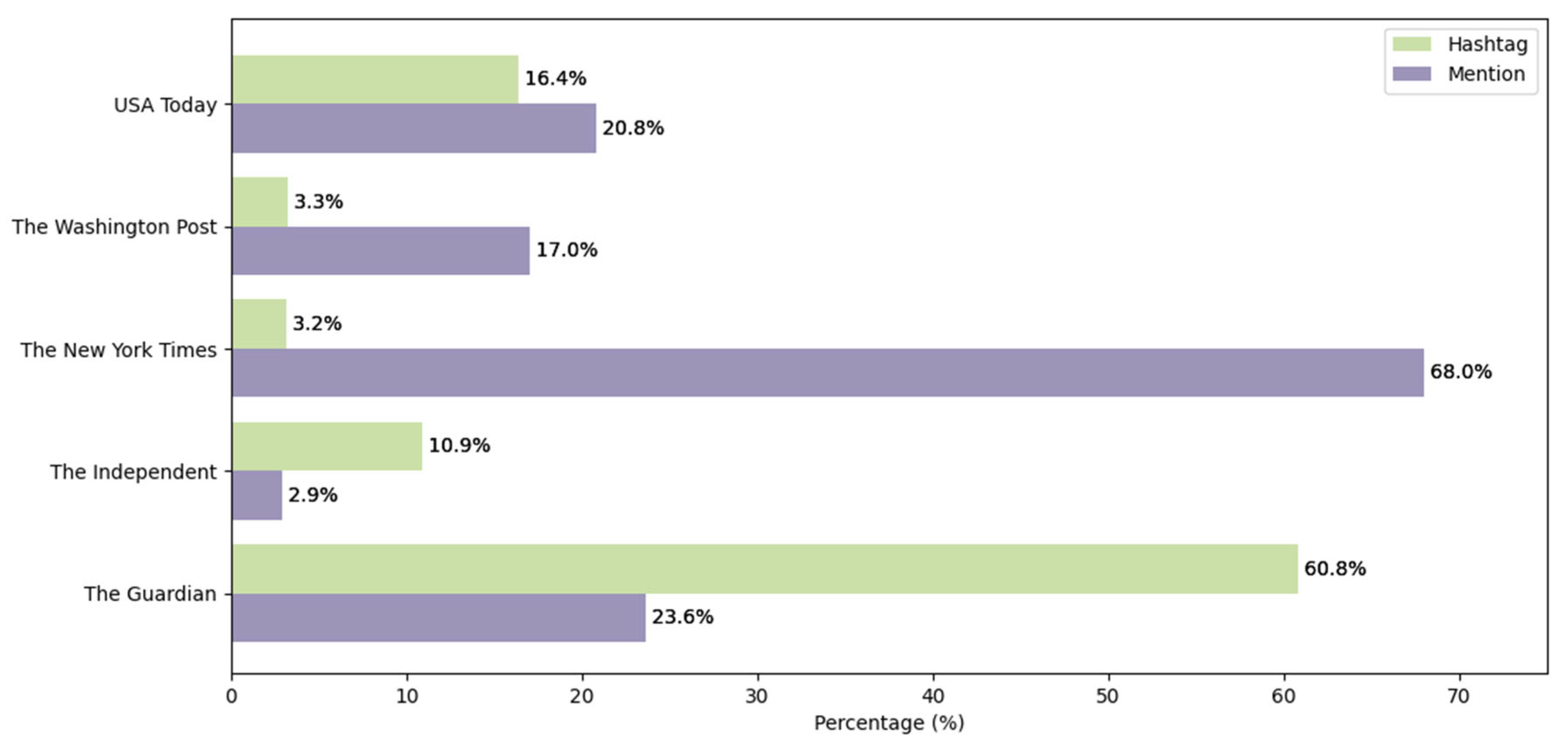
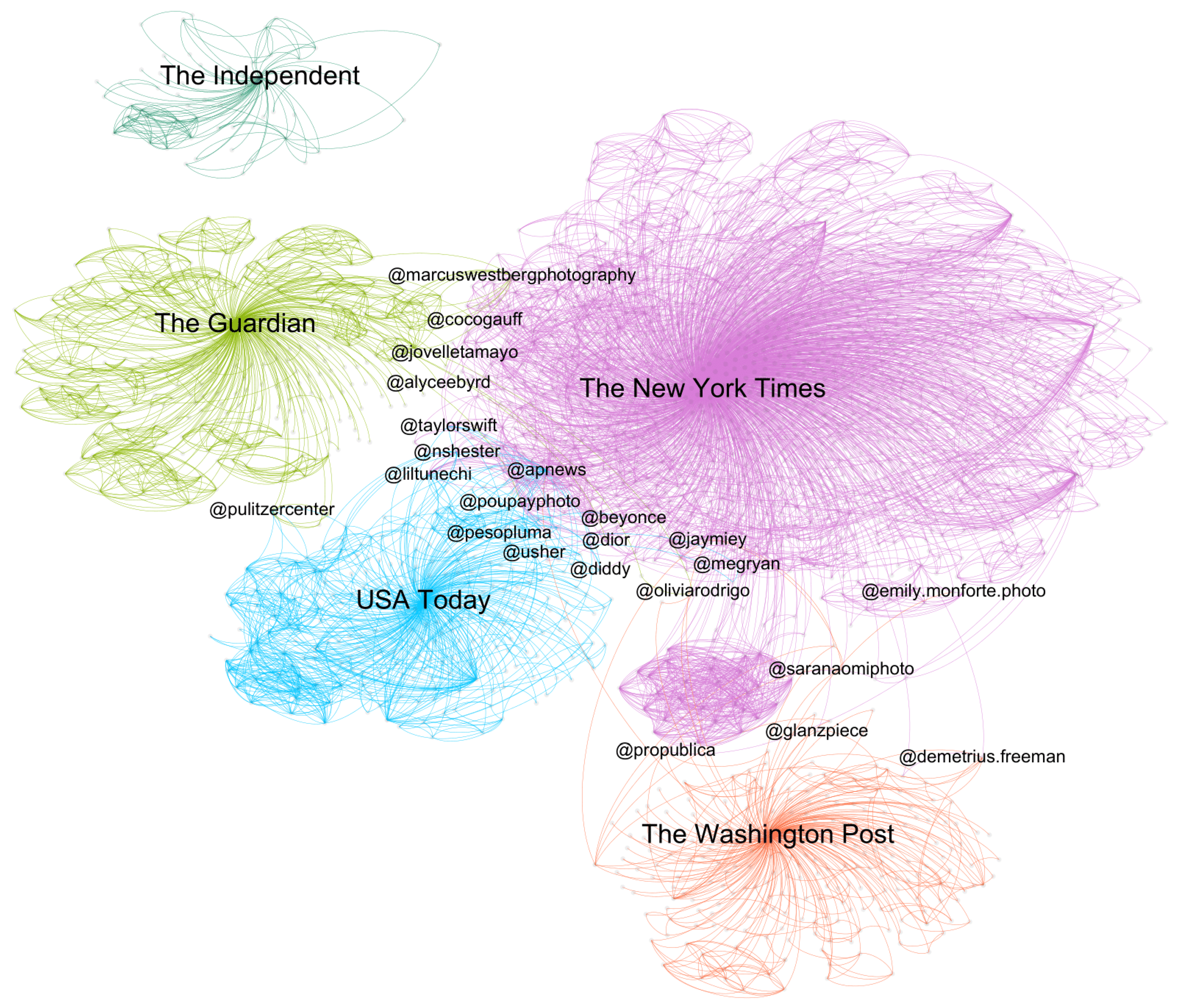
4.3. Hashtags and Mentions
4.4. Named Entities: People
4.5. Geographical Coverage
5. Discussion and Conclusions
5.1. Theoretical and Practical Implications
- Platform-specific strategy: Simply posting content is insufficient. Outlets should treat Instagram as a distinct publication space, using visual formats and analytics to maximize engagement.
- Audience interaction and community building: Features like Stories, polls, and Q&As offer ways to involve audiences without compromising editorial standards. Strategic mentions and user-generated content can enhance relevance and trust.
- Rethinking success metrics: Rather than focusing solely on external clicks, newsrooms should also track engagement rate, shares, and comment sentiment to evaluate performance within Instagram’s ecosystem.
- Ongoing newsroom adaptation: Journalists need support to interpret analytics and maintain editorial values amid algorithmic pressures. Editorial decisions must weigh-up both public interest and platform visibility, with ethical guidelines for content presentation.
5.2. Limitations and Future Research
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Al Nashmi, E. (2018). From selfies to media events: How Instagram users interrupted their routines after the Charlie Hebdo shootings. Digital Journalism, 6(1), 98–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Rawi, A., Al-Musalli, A., & Fakida, A. (2021). News values on Instagram: A comparative study of international news. Journalism and Media, 2(2), 305–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altmeppen, K. D., Bieber, C., Filipović, A., Heesen, J., Neuberger, C., Röttger, U., & Stieglitz, S. (2019). Öffentlichkeit, Verantwortung und Gemeinwohl im digitalen Zeitalter. Publizistik, 64, 59–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anter, L., & Kümpel, A. S. (2023). Young Adults’ information needs, use, and understanding in the context of Instagram: A multi-method study. Digital Journalism, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berwin, K., Voronov, A., Schneider, M., Bornschlegl, M., Engel, F., Kaufmann, M., & Hemmje, M. (2017). Big data reference model. In A. K. Somani, & G. C. Deka (Eds.), Big data analytics: Tools and technology for effective planning (pp. 55–74). CRC Press. [Google Scholar]
- Bruns, A. (2015). Working the story: News curation in social media as a second wave of citizen journalism. In C. Atton (Ed.), The Routledge companion to alternative and community media (pp. 379–388). Routledge. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruns, A. (2018). Gatewatching and news curation: Journalism, social media, and the public sphere. Digital Formations. [Google Scholar]
- Carlson, M. (2016). Embedded links, embedded meanings: Social media commentary and news sharing as mundane media criticism. Journalism Studies, 17(7), 915–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenter, J., Morrison, S., Craft, M., & Lee, M. (2020). How and why are educators using Instagram? Teaching and Teacher Education, 96, 103149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denisova, A. (2023). Viral journalism. Strategy, tactics and limitations of the fast spread of content on social media: Case study of the United Kingdom quality publications. Journalism, 24(9), 1919–1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devlin, J., Chang, M., Lee, K., & Toutanova, K. (2018). BERT: Pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding. arXiv, arXiv:1810.04805. [Google Scholar]
- García-Ortega, A., & García-Avilés, J. A. (2023). Innovation in narrative formats redefines the boundaries of journalistic storytelling: Instagram stories, TikTok and comic journalism. In M. C. Negreira-Rey, J. Vázquez-Herrero, J. Sixto-García, & X. López-García (Eds.), Blurring boundaries of journalism in digital media (Vol. 140). Studies in Big Data. Springer. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimme, C., Assenmacher, D., & Adam, L. (2018). Changing perspectives: Is it sufficient to detect social bots? In G. Meiselwitz (Ed.), Social computing and social media: User experience and behavior (Vol. 10913, pp. 445–461). Springer. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M., & Sun, F. S. (2023). Local television news on Instagram: Exploring the effects of news values and post features on audience engagement. International Journal on Media Management, 25(1–2), 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hase, V., Boczek, K., & Scharkow, M. (2022). Adapting to affordances and audiences? A cross-platform, multi-modal analysis of the platformization of news on Facebook, Instagram, TikTok, and Twitter. Digital Journalism, 11(8), 1499–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendrickx, J. (2023). The rise of social journalism: An explorative case study of a youth-oriented Instagram news account. Journalism Practice, 17(8), 1810–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendrickx, J., & Vázquez-Herrero, J. (2024). Dissecting social media journalism: A comparative study across platforms, outlets and countries. Journalism Studies, 25(9), 1053–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermida, A., & Mellado, C. (2020). Dimensions of social media logics: Mapping Forms of journalistic norms and practices on twitter and Instagram. Digital Journalism, 8(7), 864–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hille, S., & Bakker, P. (2013). I like news. Searching for the ‘Holy Grail’ of social media: The use of Facebook by Dutch news media and their audiences. European Journal of Communication, 28(6), 663–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallio, S. M., & Mäenpää, J. (2025). Visuality as an affordance on Instagram news production. Digital Journalism, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlsson, M., Ferrer Conill, R., & Örnebring, H. (2023). Recoding journalism: Establishing normative dimensions for a twenty-first century news media. Journalism Studies, 24(5), 553–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleis Nielsen, R., & Ganter, S. A. (2018). Dealing with digital intermediaries: A case study of the relations between publishers and platforms. New Media & Society, 20(4), 1600–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsson, A. O. (2018). The news user on social media: A comparative study of interacting with media organizations on Facebook and Instagram. Journalism Studies, 19(15), 2225–2242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leaver, T., Highfield, T., & Abidin, C. (2020). Instagram: Visual social media cultures. John Wiley & Sons. [Google Scholar]
- Malik, M. M., & Pfeffer, J. (2016). A macroscopic analysis of news content in Twitter. Digital Journalism, 4(8), 955–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayerhöffer, E., Kristensen, J. B., & Ramsland, T. (2024). Curators of digital counterpublics: Mapping alternative news environments in Sweden and Denmark. Nordicom Review, 45(S1), 92–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nee, R. C. (2019). Youthquakes in a post-truth era: Exploring social media news use and information verification actions among global teens and young adults. Journalism & Mass Communication Educator, 74(2), 171–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuberger, C., Nuernbergk, C., & Langenohl, S. (2018). Journalism as multichannel communication: A newsroom survey on the multiple uses of social media. Journalism Studies, 20(9), 1260–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, N. (2023). Overview and key findings of the 2023 digital news report. Reuters Institute for the Study of Journalism. Available online: https://reutersinstitute.politics.ox.ac.uk/digital-news-report/2023/dnr-executive-summary (accessed on 20 April 2025).
- Panditrao, M. P. (2021). A python guide for web scraping. BPB Publications. [Google Scholar]
- Perreault, G. P., & Hanusch, F. (2023). Normalizing Instagram. Digital Journalism, 12(4), 413–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Planer, R., Godulla, A., Wolf, C., Bürzle, L., Grobb, J., Henke, A., & Ötting, H. L. (2022). Storys told, storys linked: Die Instagram-Nutzung deutscher, britischer und US-amerikanischer Medienunternehmen. In J. Schützeneder, & M. Graßl (Eds.), Journalismus und Instagram. Springer. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saks, J., & Hopkins, A. (2023). US regional newspapers and Instagram: A content analysis. Electronic News, 18(1), 49–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saks, J., & Hopkins, A. (2024). Insta-news: How the New York Times and Washington Post Use Instagram. Journalism Practice, 18(3), 456–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scharkow, M., Mangold, F., Stier, S., & Breuer, J. (2020). How social network sites and other online intermediaries increase exposure to news. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 117(6), 2761–2763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sixto-García, J., Silva-Rodríguez, A., Rodríguez-Vázquez, A. I., & López-García, X. (2023). Redefining journalism narratives, distribution strategies, and user involvement based on innovation in digital native media. Journalism, 24(6), 1322–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tandoc, E. C. (2014). Journalism is twerking? How web analytics is changing the process of gatekeeping. New Media & Society, 16(4), 559–575, (Original work published 2014). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tandoc, E. C., & Vos, T. P. (2016). The journalist is marketing the news: Social media in the gatekeeping process. Journalism Practice, 10(8), 950–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorson, K., & Wells, C. (2015). How gatekeeping still matters: Understanding media effects in an era of curated flows. In T. P. Vos, & F. Heinderyckx (Eds.), Gatekeeping in transition (pp. 25–44). Routledge. [Google Scholar]
- Thorson, K., & Wells, C. (2016). Curated flows: A Framework for mapping media exposure in the digital age. Communication Theory, 26(3), 309–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Dijck, J. (2013). The culture of connectivity: A critical history of social media. Oxford University Press. [Google Scholar]
- Vállez, M., Boté-Vericad, J. J., Guallar, J., & Bastos, M. (2024). Indifferent about online traffic: The posting strategies of five news outlets during musk’s acquisition of Twitter. Journalism Studies, 25(11), 1249–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez-Herrero, J., Direito-Rebollal, S., & López-García, X. (2019). Ephemeral journalism: News distribution through Instagram stories. Social Media + Society, 5(4), 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J., Huang, J. X., Tu, X., Wang, J., Huang, A. J., Laskar, M. T. R., & Bhuiyan, A. (2024). Utilizing BERT for information retrieval: Survey, applications, resources, and challenges. ACM Computing Surveys, 56(7), 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L. (2021). Understanding college students’ news sharing experience on Instagram. In Companion publication of the 2021 conference on computer supported cooperative work and social computing (pp. 187–190). Association for Computing Machinery. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanti, N., & Dewi, L. (2021). Application of Instagram media for ‘no club’ business growth. Primanomics: Jurnal Ekonomi & Bisnis, 19(2), 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, D., Klee, A., & Kaspar, K. (2023). Political news on Instagram: Influencer versus traditional magazine and the role of their expertise in consumers’ credibility perceptions and news engagement. Frontiers in Psychology, 14, 1257994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, D., Noll, C., Gräßer, L., Hugger, K., Braun, L. M., Nowak, T., & Kaspar, K. (2022). Influencers on YouTube: A quantitative study on young people’s use and perception of videos about political and societal topics. Current Psychology, 41, 6808–6824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| The Guardian | The Independent | The New York Times | The Washington Post | USA Today | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total Volume | 559 | 1790 | 2361 | 2820 | 1937 |
| Estimated Followers (Dec 23) | 5.7 M | 796 K | 17.6 M | 6.6 M | 3.4 M |
| Monthly Volume | 46.58 (10.37%) | 149.17 (29.24%) | 196.75 (12.29%) | 235.00 (13.57%) | 161.42 (16.81%) |
| Monthly Likes Number | 1,135,659.50 (29.96%) | 265,309.58 (69.90%) | 11,083,485.00 (11.91%) | 4,814,903.42 (17.40%) | 1,374,207.75 (16.79%) |
| Monthly Comments Number | 38,797.17 (61.05%) | 19,719.08 (68.99%) | 254,329.92 (51.95%) | 152,249.42 (18.80%) | 86,427.08 (13.86%) |
| Monthly Proportional Engagement | 25,141.98 (28.49%) | 1888.56 (52.55%) | 58,222.56 (15.02%) | 21,172.60 (11.90%) | 9062.62 (1.22%) |
| Daily Volume | 1.59 (48.85%) | 5.10 (52.42%) | 6.47 (23.05%) | 7.73 (30.40%) | 5.31 (32.30%) |
| Daily Likes Number | 38,715.66 (151.29%) | 9070.41 (327.09%) | 364,388.55 (51.95%) | 158,298.19 (83.90%) | 45,179.43 (32.29%) |
| Daily Comments Number | 1322.63 (180.93%) | 674.16 (206.65%) | 8361.53 (87.10%) | 5005.46 (63.16%) | 2841.44 (38.23%) |
| Daily Proportional Engagement | 24,597.54 (127.86%) | 1860.77 (262.98%) | 58,035.36 (46.80%) | 21,306.05 (76.93%) | 9065.44 (1.96%) |
| Monthly Engagement Rate (%) | 20.75 | 35.81 | 64.59 | 75.40 | 43.36 |
| The Guardian | The Independent | The New York Times | The Washington Post | USA Today | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hashtags and no mentions | −19.70% | −33.36% | −41.43% | −2.70% | +0.26% |
| Mentions and no hashtags | +6.47% | −86.66% | +12.06% | −22.56% | −0.18% |
| Hashtags and mentions | −21.23% | −50.52% | −22.69% | −34.24% | −0.85% |
| The Guardian | The Independent | The New York Times | The Washington Post | USA Today fzi | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| @guardian_us | 14 (10.61%) | @the.independent | 20 (38.46%) | @apnews | 67 (4.17%) | @postclimate | 39 (8.12%) | @apnews | 111 (27.54%) |
| @guardianaustralia | 9 (6.82%) | @emelisande | 4 (7.69%) | @nytopinion | 44 (2.74%) | @mattmcclainphoto | 23 (4.79%) | @usatoday | 111 (27.54%) |
| @bjennigsuk | 4 (3.03%) | @hannahgrae | 4 (7.69%) | @nytmag | 40 (2.49%) | @eatvoraciously | 22 (4.58%) | @gettyimages | 93 (23.08%) |
| @chantayyjayy | 4 (3.03%) | @lookfantastic | 4 (7.69%) | @nytcooking | 29 (1.81%) | @washingtonpost | 20 (4.17%) | @afpphoto | 41 (10.17%) |
| @christophcherry | 4 (3.03%) | @damianlewisreallyofficial | 3 (5.77%) | @amirbangs | 24 (1.49%) | @jabinbotsford | 19 (3.96%) | @usatodaysports | 21 (5.21%) |
| The Guardian | The Independent | The New York Times | The Washington Post | USA Today | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| #ClimateCrisis | 27 (7.94%) | #news | 27 (13.85%) | #nytopinion | 44 (58.67%) | #thelilycomics | 29 (31.52%) | #sports | 23 (7.26%) |
| #news | 26 (7.65%) | #Trump | 17 (8.72%) | #YearInPictures | 12 (16.00%) | #wapocomics | 22 (23.91%) | #california | 10 (3.15%) |
| #Environment | 23 (6.76%) | #fyp | 13 (6.67%) | #metoo | 9 (12.00%) | #BTW | 18 (19.57%) | #Biden | 9 (2.84%) |
| #worldnews | 23 (6.76%) | #tv | 10 (5.13%) | #Covid | 1 (1.33%) | #BTWComics | 4 (4.35%) | #Politics | 9 (2.84%) |
| #UK | 22 (6.47%) | #Politics | 9 (4.62%) | #culture | 1 (1.33%) | #thelilynews | 4 (4.35%) | #nfl | 8 (2.52%) |
| The Guardian | The Independent | The New York Times | The Washington Post | USA Today | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Donald Trump | 20 (4.26%) | Rishi Sunak | 55 (5.91%) | Donald Trump | 119 (7.76%) | Donald Trump | 141 (8.73%) | Joe Biden | 67 (6.49%) |
| Boris Johnson | 10 (2.13%) | Donald Trump | 48 (5.16%) | Eric Adams | 22 (1.44%) | Kevin McCarthy | 35 (2.17%) | Donald Trump | 50 (4.84%) |
| António Guterres | 9 (1.91%) | Joe Biden | 21 (2.26%) | Kevin McCarthy | 19 (1.24%) | Ron DeSantis | 27 (1.67%) | Taylor Swift | 24 (2.33%) |
| Benjamin Netanyahu | 8 (1.70%) | Keir Starmer | 21 (2.26%) | Ron DeSantis | 16 (1.04%) | George Santos | 19 (1.18%) | Kevin McCarthy | 15 (1.45%) |
| Tyre Nichols | 8 (1.79%) | Boris Johnson | 18 (1.94%) | Volodymyr Zelensky | 16 (1.04%) | Taylor Swift | 17 (1.05%) | Tyre Nichols | 15 (1.45%) |
| Media | Number of Countries Mentioned | Percentage of Coverage * |
|---|---|---|
| The Guardian | 84 | 43.08% |
| The Independent | 96 | 49.23% |
| The New York Times | 132 | 67.69% |
| The Washington Post | 128 | 65.64% |
| USA Today | 95 | 48.72% |
| The Guardian | The Independent | The New York Times | The Washington Post | USA Today | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| United Kingdom | 126 (22.54%) | United States of America | 611 (34.13%) | United States of America | 1359 (57.56%) | United States of America | 1752 (62.13%) | United States of America | 1342 (62.28%) |
| United States of America | 114 (20.39%) | United Kingdom | 460 (25.70%) | Ukraine | 106 (4.49%) | Ukraine | 87 (3.09%) | United Kingdom | 41 (2.12%) |
| Palestine | 47 (8.41%) | Australia | 57 (3.18%) | Palestine | 73 (3.09%) | Palestine | 82 (2.91%) | Chile | 41 (2.12%) |
| Australia | 26 (4.65%) | Chile | 57 (3.18%) | France | 58 (2.46%) | China | 78 (2.77%) | Mexico | 40 (2.07%) |
| Israel | 20 (3.58%) | Canada | 45 (2.51%) | Israel | 58 (2.46%) | Mexico | 58 (2.06%) | Ukraine | 37 (1.91%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cordeiro, D.F.; Vállez, M.; Font-Julian, C.I.; Guallar, J. Instagram Engagement and Content Strategies of US and UK Legacy Media: A Quantitative Analysis of Five Leading News Outlets. Journal. Media 2025, 6, 89. https://doi.org/10.3390/journalmedia6020089
Cordeiro DF, Vállez M, Font-Julian CI, Guallar J. Instagram Engagement and Content Strategies of US and UK Legacy Media: A Quantitative Analysis of Five Leading News Outlets. Journalism and Media. 2025; 6(2):89. https://doi.org/10.3390/journalmedia6020089
Chicago/Turabian StyleCordeiro, Douglas Farias, Mari Vállez, Cristina I. Font-Julian, and Javier Guallar. 2025. "Instagram Engagement and Content Strategies of US and UK Legacy Media: A Quantitative Analysis of Five Leading News Outlets" Journalism and Media 6, no. 2: 89. https://doi.org/10.3390/journalmedia6020089
APA StyleCordeiro, D. F., Vállez, M., Font-Julian, C. I., & Guallar, J. (2025). Instagram Engagement and Content Strategies of US and UK Legacy Media: A Quantitative Analysis of Five Leading News Outlets. Journalism and Media, 6(2), 89. https://doi.org/10.3390/journalmedia6020089







