Taxonomic Value of Leaf Epidermal Markers in Discriminating Some Medicinal Tree Species of Apocynaceae Juss †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sources of Plant Samples and Epidermal Peels Preparation
2.2. Preparation of Slides, Assessment of Epidermal Characters, and Data Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- El-Fiki, M.A.; El-Taher, A.M.; EL-Gendy, A.G.; Lila, M.I. Morphological and anatomical studies on some taxa of family Apocynaceae. Al-Azhar J. Agric. R. 2019, 44, 136–147. [Google Scholar]
- Endress, M.E.; Bruyns, P.V. A revised classification of Apocynaceae sl. Bot. Rev. 2000, 66, 1–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, S.K. Handbook of Aromatic Plants, 3rd ed.; Pointer Publisher: Jaipur, India, 2004; p. 403. [Google Scholar]
- Koyuncu, M. A new species of Vinca (Apocynaceae) from eastern Anatolia. Turk. J. Bot. 2012, 36, 247–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkateshwar, C.; Rao, S.G.; Kumar, R.S. Epidermal study of medicinal plants with special reference to identification, adulteration and authentification of crude leaf drugs. Ann. Phytomed. 2013, 2, 115–125. [Google Scholar]
- Kidyoo, M. Ceropegia suddeei sp. nov. (Apocynaceae, Asclepiadoideae) from northeastern Thailand. Nordic J. Bot. 2014, 32, 569–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bibi, H.; Afzal, M.; Kamal, M.; Sohail, I.U.; Khan, S.M.; Sher, A.A.; Ziaulhaq, I.U.; Ali, A.; Khan, S.A.; Ur Rahman, I. Morphological and anatomical characteristics of selected dicot xerophytes of district Karak, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan. Middle-East J. Sci. Res. 2015, 23, 545–557. [Google Scholar]
- Kannabiran, B.; Ramassamy, V. Foliar epidermis and taxonomy in Apocynaceae. Proe. Indian Acad. Sei. 1988, 98, 409–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashir, K.; Sohail, A.; Ali, U.; Ullah, A.; Ul Haq, Z.; Gul, B.; Ullah, I.; Sunera; Asghar, M. Foliar micromorphology and its role in identification of the Apocynaceae taxa. Microscopy Research and Technique 2020, 83, 755–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odugbemi, T.; Akinsulire, O. Medicinal Plants by Species Name. In Outlines and Pictures of Medicinal Plants from Nigeria, 1st ed.; Tolu Odugbemi ed.; University of Lagos press: Lagos, Nigeria, 2006; pp. 73–116. [Google Scholar]
- Fabeku, P.O. Traditional Medicine: The Arts, Ways and Practice. In Outlines and Pictures of Medicinal Plants from Nigeria, 1st ed.; Tolu Odugbemi ed.; University of Lagos press: Lagos, Nigeria, 2006; pp. 117–125. [Google Scholar]
- Olowokudejo, J.D.; Nyananyo, B.L. Epidermal morphology of the genus Khaya (Meliaceae) in West Africa. Feddes Rep. 1990, 101, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyedapo, O.A.; Agbedahunsi, J.M.; Illoh, H.C.; Akinloye, A.J. Comparative foliar anatomy of three Khaya species (Meliaceae) used in Nigeria as antisickling agent. Sci. Cold Arid Reg. 2018, 10, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, J.A.; Ayodele, A.E. Taxonomic Significance of Leaf Epidermal Characters of the Family Loranthaceae in Nigeria. World Appl. Sci. J. 2013, 24, 1172–1179. [Google Scholar]
- Salisbury, E.J. On the cause and ecological significance of stomatal Frequency with special reference to the woodland Flora. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. B 1927, 216, 1–65. [Google Scholar]
- Fayose, O.H.; Freke, R.M. A study on the Floral and Epidermal characteristics of two species of Ixora. Int. J. Med. Plant Res. 2016, 5, 299–306. [Google Scholar]
- Shokefun, E.O.; Ayodele, A.E.; Orijemie, E.A. A preliminary leaf epidermal and pollen morphology of some West African species of Desplatsia Bocq. J. Med. Plant Res. Eco. Dev. 2017, 1, a4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogunkunle, A.T.J. The Value of Leaf Epidermal Characters in Diagnosing Some Nigerian Species of Ficus L. (Moraceae). Res. J. Bot. 2013, 8, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Haruna, H.; Ashir, H.I. Leaf Epidermal Structures and Stomata Ontogeny In Some Members of the Lamiaceae Family. Bayero J. Pure App. Sci. 2017, 10, 670–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omino, E. A Contribution to the Leaf Anatomy and Taxonomy of Apocynaceae in Africa: The Leaf Anatomy of Apocynaceae in East Africa: A Monograph of Pleiocarpinae (Series of Revisions of Apocynaceae XLI). Ph.D. Thesis, Landbouwuniversiteit, Wageningen, The Netherlands, April 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Hassiotou, F.; Evans, J.R.; Ludwig, M.; Veneklaas, E.J. Stomatal crypts may facilitate diffusion of CO2 to adaxial mesophyll cells in thick sclerophylls. Plant Cell Environ. 2009, 32, 1596–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu, N.E.; Ezeomeke, S.I.; Azegba, P.; Davidson, G.I. Phytochemical, nutritional and anti-nutritional properties of leaves, stems bark and roots of trees used in popular medicine for the treatment of malaria in South Eastern Nigeria. J. Med. Plants Res. 2016, 10, 662–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, D.; Singh, D.; Sharma, S.K.; Sharma, S.; Chandrawat, P.; Sharma, R. Epidermal Studies of Some Plants of Family Apocynaceae. As. J. Bioch. Pharm. Res. 2012, 2, 231–236. [Google Scholar]
- Ibrahim, J.A.; Ayodele, A.E.; Okhale, S.E.; Jegede, A.I.; Kunle, O.F. The taxonomic significance of Agelanthus dodoneifolius (DC.) Polh. & Wiens in relation to its hosts. Nig. J. Bot. 2009, 22, 89–101. [Google Scholar]
- Ayodele, A.E.; Olowokudejo, J.D. The family Polygonaceae in West Africa: Taxonomic Significance of Leaf Epidermal Characters. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2006, 72, 442–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, J.A.; Ayodele, A.E.; Jegede, A.I.; Kunle, Y.F. Comparative Studies on Khaya A. Juss. (Meliaceae) in Nigeria. Afr. J. Biot. 2006, 5, 1154–1160. [Google Scholar]
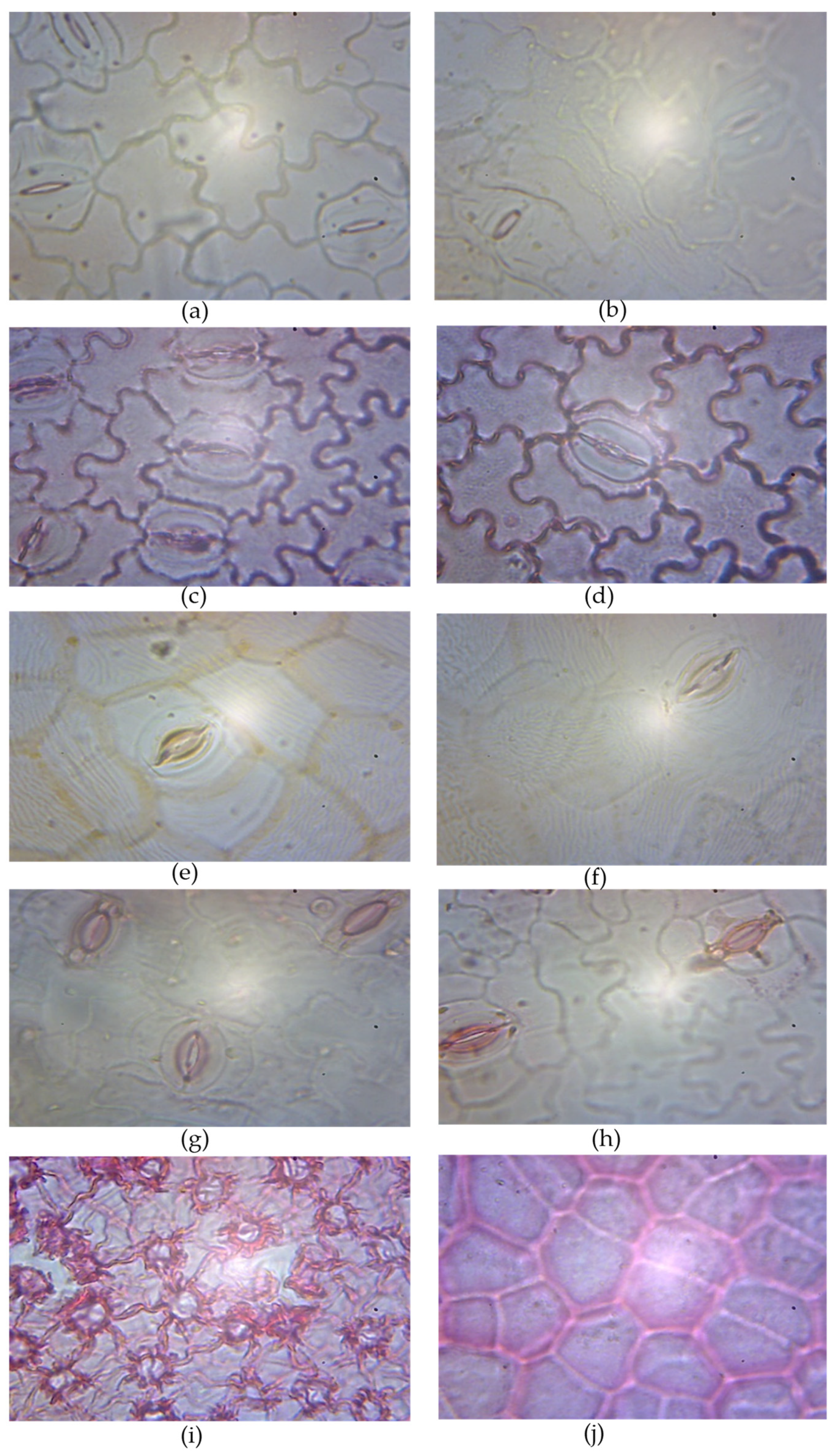
| Epidermal Markers | Leaf Surfaces | Rauvofia vomitoria | Holarhena floribunda | Vocanga africana | Thevetia nerifolia | Alstonia boonei |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stomata (P/A) | Abaxial | Present | Present | Present | Present | Present |
| Stomatal type | Abaxial | Paracytic | Paracytic | Paracytic | Paracytic | Stomatal crypts |
| Stomata abundance | Abaxial | Many | Many | Few | Many | Few |
| Cell shape | Abaxial | Polygonal | Polygonal | Polygonal | Polygonal | Polygonal |
| Anticlinal wall | Abaxial | Straight-wavy | Sinuated | Straight | Sinuated | Straight |
| Crystal type | Abaxial | Druses | Druses | Raphides | Druses | Raphides |
| Stomata (P/A) | Adaxial | Present | Present | Present | Present | Absent |
| Stomatal type | Adaxial | Paracytic | Paracytic | Paracytic | Paracytic | Nil |
| Stomata abundance | Adaxial | Few | Few | Few | Few | None |
| Cell shape | Adaxial | Polygonal | Polygonal | Polygonal | Polygonal | Polygonal |
| Anticlinal wall | Adaxial | Straight-wavy | Sinuated | Straight | Sinuated | Straight |
| Crystal type | Adaxial | Druses | Druses | Raphides | Druses | Raphides |
| Tree Species | LE (μm) | BE (μm) | LS (μm) | BS (μm) | LGC (μm) | WGC (μm) | GCA (μm2) | SD (mm2) | SI (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rauvolfia vomitoria | 24.00 | 11.04 | 20.88 | 11.76 | 20.4 | 4.32 | 68.98 | 137.32 | 36.84 |
| Hollarhena floribunda | 34.32 | 20.64 | 22.08 | 21.6 | 20.35 | 9.12 | 146.66 | 88.41 | 30.00 |
| Vocanga africana | 31.44 | 20.63 | 21.93 | 12.72 | 21.84 | 4.44 | 80.75 | 122.79 | 28.57 |
| Thevetia neriifolia | 29.52 | 18.00 | 25.92 | 12.00 | 24.48 | 4.80 | 93.19 | 110.51 | 46.34 |
| Alstonia boonei | 19.44 | 10.08 | 22.80 | 9.60 | 19.87 | 4.08 | 65.73 | 85.95 | 35.35 |
| p-value | 0.000 * | 0.000 * | 0.182 ns | 0.000 * | 0.217 ns | 0.000 * | 0.008 * | 0.000 * | 0.041 * |
| Tree Species | LE (μm) | BE (μm) | LS (μm) | BS (μm) | LGC (μm) | WGC (μm) | GCA (μm2) | SD (mm2) | SI (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rauvolfia vomitoria | 24.00 | 13.68 | 18.97 | 10.46 | 18.96 | 6.38 | 95.77 | 98.23 | 38.83 |
| Hollarhena floribunda | 30.48 | 21.12 | 24.00 | 19.68 | 21.36 | 14.64 | 249.04 | 29.47 | 23.07 |
| Vocanga africana | 26.16 | 12.48 | 29.28 | 12.96 | 28.32 | 6.48 | 142.95 | 39.29 | 29.00 |
| Thevetia neriifolia | 30.00 | 18.24 | 26.64 | 16.56 | 26.16 | 5.66 | 116.26 | 186.64 | 44.44 |
| Alstonia boonei | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| p-value | 0.030 * | 0.001 * | 0.001 * | 0.000 * | 0.002 * | 0.012 * | 0.049 * | 0.000 * | 0.000 * |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Onefeli, A.O.; Kehinde, L.P. Taxonomic Value of Leaf Epidermal Markers in Discriminating Some Medicinal Tree Species of Apocynaceae Juss. Environ. Sci. Proc. 2021, 3, 91. https://doi.org/10.3390/IECF2020-07982
Onefeli AO, Kehinde LP. Taxonomic Value of Leaf Epidermal Markers in Discriminating Some Medicinal Tree Species of Apocynaceae Juss. Environmental Sciences Proceedings. 2021; 3(1):91. https://doi.org/10.3390/IECF2020-07982
Chicago/Turabian StyleOnefeli, Alfred O., and Lekan P. Kehinde. 2021. "Taxonomic Value of Leaf Epidermal Markers in Discriminating Some Medicinal Tree Species of Apocynaceae Juss" Environmental Sciences Proceedings 3, no. 1: 91. https://doi.org/10.3390/IECF2020-07982
APA StyleOnefeli, A. O., & Kehinde, L. P. (2021). Taxonomic Value of Leaf Epidermal Markers in Discriminating Some Medicinal Tree Species of Apocynaceae Juss. Environmental Sciences Proceedings, 3(1), 91. https://doi.org/10.3390/IECF2020-07982







