Evaluation of CloudSat Products with ACTRIS Lidar/Radar Measurements over the Eastern Mediterranean †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Data and Methodology
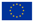
2.1. Ground-Based Measurements
2.2. Satellite-Based Observations
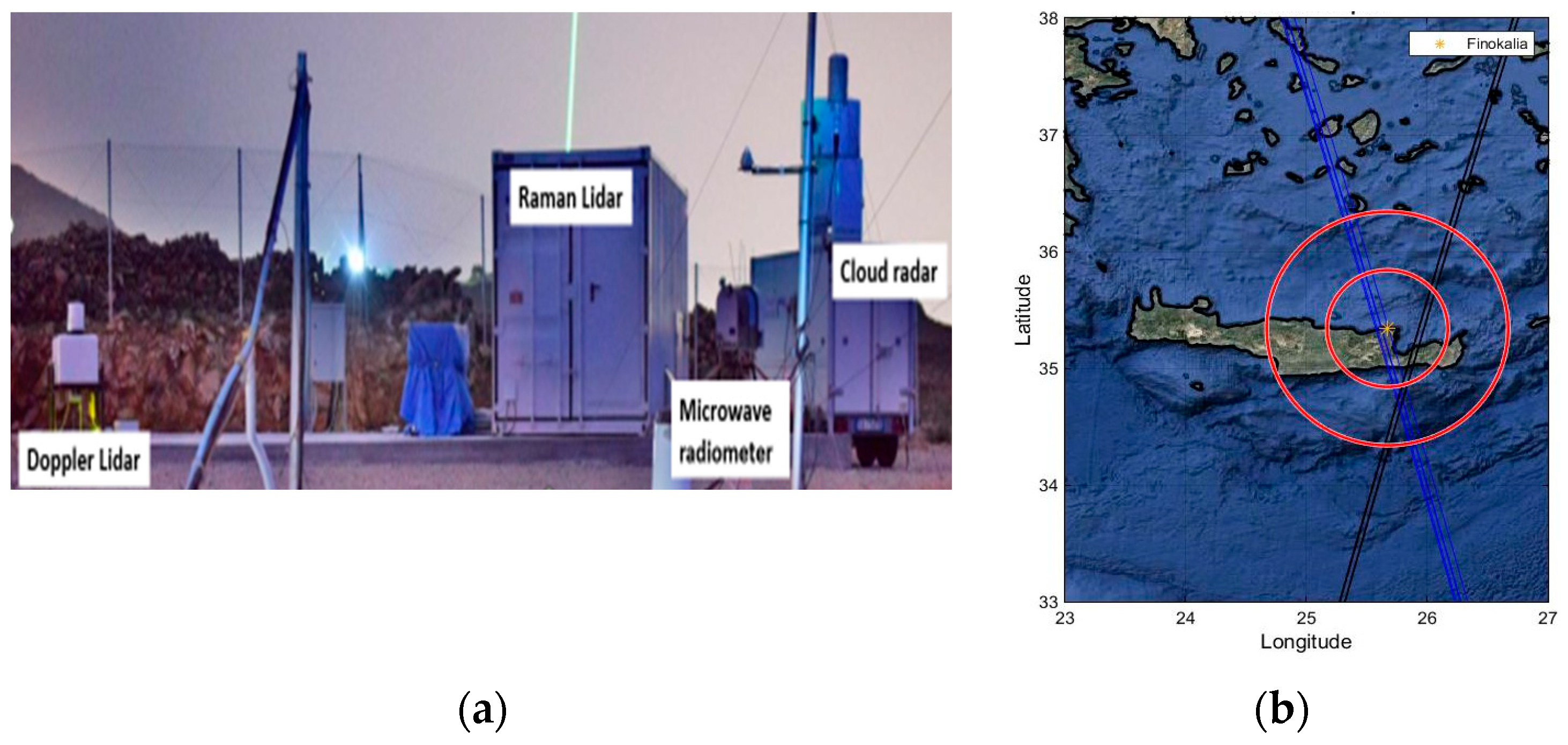
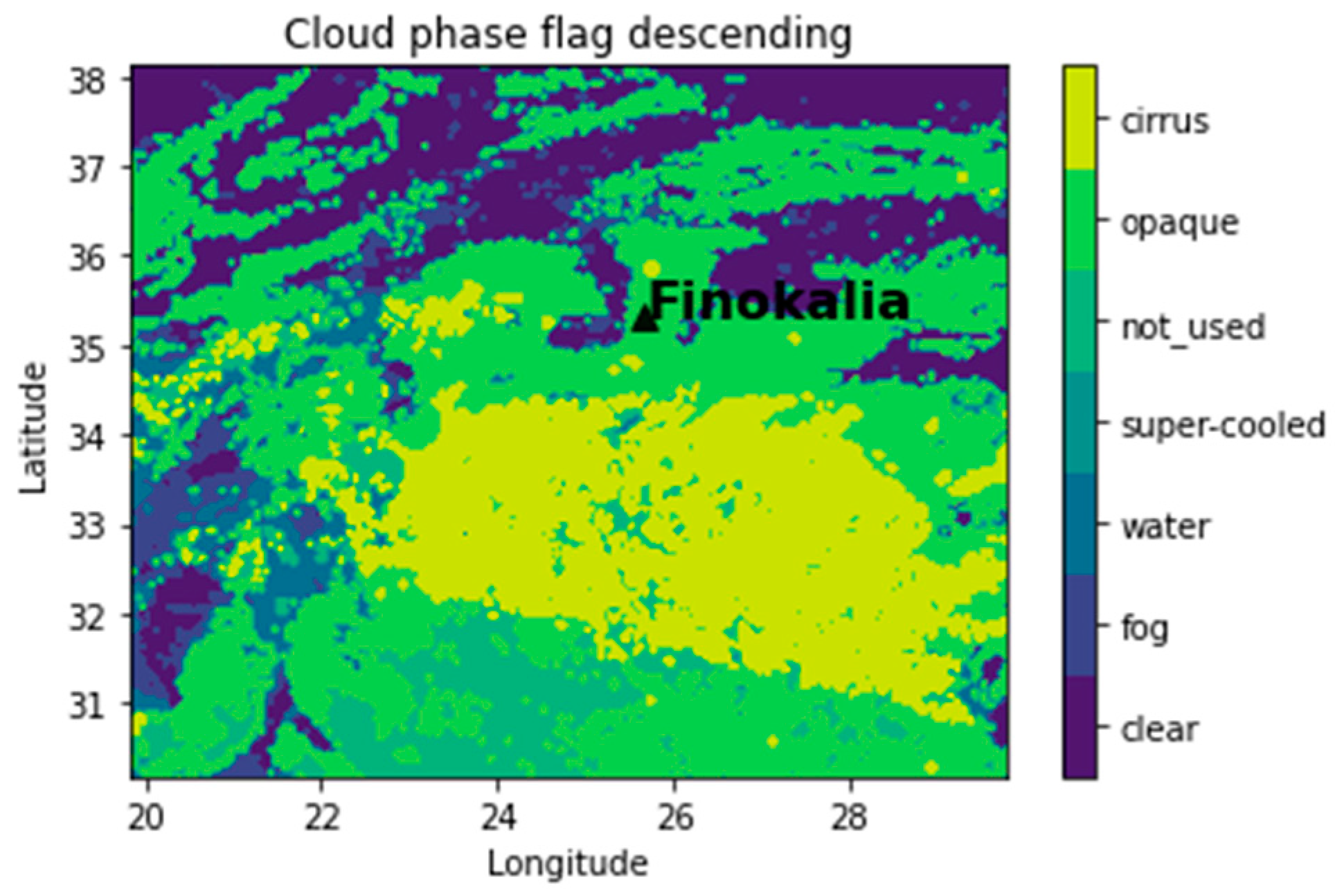
3. Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
 . E.M. and I.K. acknowledge support by the Hellenic Foundation for Research and Innovation (H.F.R.I.) under the “3rd Call for H.F.R.I. Research Projects to support Post-Doctoral Researchers” (Project Acronym: REVEAL, Project Number: 07222).
. E.M. and I.K. acknowledge support by the Hellenic Foundation for Research and Innovation (H.F.R.I.) under the “3rd Call for H.F.R.I. Research Projects to support Post-Doctoral Researchers” (Project Acronym: REVEAL, Project Number: 07222).Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- IPCC. Climate Change 2014: Synthesis Report. Contribution of Working Groups I, II and III to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Pachauri, R.K., Meyer, L.A., Eds.; IPCC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014; p. 151. [Google Scholar]
- Delanoë, J.; Hogan, R.J. A variational scheme for retrieving ice cloud properties from combined radar, lidar, and infrared radiometer. J. Geophys. Res. 2008, 113, D07204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The PRE-TECT Experimental Campaign. Available online: http://PRE-TECT.space.noa.gr/ (accessed on 30 May 2023).
- Marinou, E.; Voudouri, K.A.; Tsikoudi, I.; Drakaki, E.; Tsekeri, A.; Rosoldi, M.; Ene, D.; Baars, H.; O’Connor, E.; Amiridis, V.; et al. Geometrical and Microphysical Properties of Clouds Formed in the Presence of Dust above the Eastern Mediterranean. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 5001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelmann, R.; Kanitz, T.; Baars, H.; Heese, B.; Althausen, D.; Skupin, A.; Wandinger, U.; Komppula, M.; Stachlewska, I.S.; Amiridis, V.; et al. The automated multiwavelength Raman polarization and water-vapor lidar PollyXT: The neXT generation. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2016, 9, 1767–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madonna, F.; Amodeo, A.; Boselli, A.; Cornacchia, C.; Cuomo, V.; D’Amico, G.; Giunta, A.; Mona, L.; Pappalardo, G. CIAO: The CNR-IMAA advanced observatory for atmospheric research. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2011, 4, 1191–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manninen, A.J.; O’Connor, E.J.; Vakkari, V.; Petäjä, T. A generalised background correction algorithm for a Halo Doppler lidar and its application to data from Finland. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2016, 9, 817–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephens, G.; Wood, N. Properties of tropical convection observed by millimeter-wave radar systems. Mon. Weather Rev. 2007, 135, 821–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephens, G.L.; Vane, D.G.; Tanelli, S.; Im, E.; Durden, S.; Rokey, M.; Reinke, D.; Partain, P.; Mace, G.G.; Austin, R.; et al. CloudSat mission: Performance and early science after the first year of operation. J. Geophys. Res. 2008, 113, D00A18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mace, G.; Marchand, R.; Zhang, Q.; Stephens, G. Global hydro-meteor occurrence as observed by CloudSat: Initial observations from summer 2006. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, L09808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchand, R.; Mace, G.G.; Ackerman, T.; Stephens, G. Hydro-meteor detection using CloudSat an Earth-orbiting 94-GHz cloud radar. J. Atmos. Oceanic Technol. 2008, 25, 519–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sassen, K.; Wang, Z. Classifying clouds around the globe with the CloudSat radar: 1-year of results. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35, L04805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voudouri, K.A.; Giannakaki, E.; Komppula, M.; Balis, D. Variability in cirrus cloud properties using a PollyXT Raman lidar over high and tropical latitudes. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 4427–4444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battaglia, A.; Kollias, P.; Dhillon, R.; Roy, R.; Tanelli, S.; Lamer, K.; Grecu, M.; Lebsock, M.; Watters, D.; Mroz, K.; et al. Spaceborne Cloud and Precipitation Radars: Status, Challenges, and Ways Forward. Rev. Geophys. 2020, 58, e2019RG000686. Available online: https://hdl.handle.net/2381/13133234.v1 (accessed on 22 August 2023). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
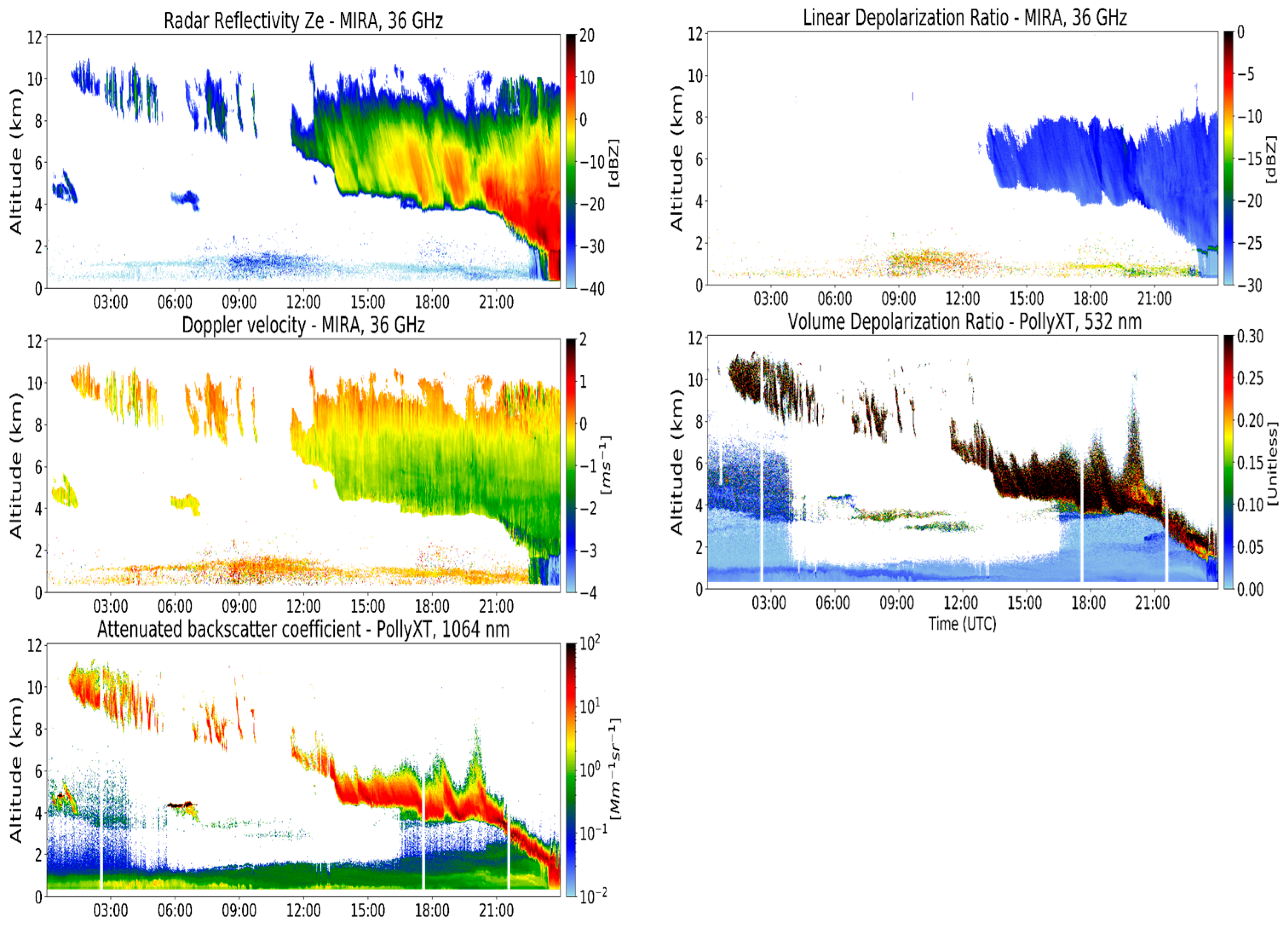

| Instrumentation | Base | Top |
|---|---|---|
| MIRA36 | 7.2 ± 0.1 km | 8.4 ± 0.35 km |
| PollyXT | 6.5 km | 8.3 km |
| CloudSat | 7.1 ± 1.1 km | 9.0 ± 1.4 km |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Voudouri, K.A.; Marinou, E.; Koutsoupi, I.; Koukouli, M.-E.; Tsikoudi, I.; Battaglia, A.; Kollias, P. Evaluation of CloudSat Products with ACTRIS Lidar/Radar Measurements over the Eastern Mediterranean. Environ. Sci. Proc. 2023, 26, 194. https://doi.org/10.3390/environsciproc2023026194
Voudouri KA, Marinou E, Koutsoupi I, Koukouli M-E, Tsikoudi I, Battaglia A, Kollias P. Evaluation of CloudSat Products with ACTRIS Lidar/Radar Measurements over the Eastern Mediterranean. Environmental Sciences Proceedings. 2023; 26(1):194. https://doi.org/10.3390/environsciproc2023026194
Chicago/Turabian StyleVoudouri, Kalliopi A., Eleni Marinou, Iliana Koutsoupi, Maria-Elissavet Koukouli, Ioanna Tsikoudi, Alessandro Battaglia, and Pavlos Kollias. 2023. "Evaluation of CloudSat Products with ACTRIS Lidar/Radar Measurements over the Eastern Mediterranean" Environmental Sciences Proceedings 26, no. 1: 194. https://doi.org/10.3390/environsciproc2023026194
APA StyleVoudouri, K. A., Marinou, E., Koutsoupi, I., Koukouli, M.-E., Tsikoudi, I., Battaglia, A., & Kollias, P. (2023). Evaluation of CloudSat Products with ACTRIS Lidar/Radar Measurements over the Eastern Mediterranean. Environmental Sciences Proceedings, 26(1), 194. https://doi.org/10.3390/environsciproc2023026194






