Abstract
Constructed wetlands (CWs) are eco-technologies used for wastewater treatment, where vegetation is a key component. In recent decades, the adaptability and phytoremediation functions of ornamental plants (OPs)—which are not typically found in natural wetlands—have been tested. However, few comprehensive studies address the processes or mechanisms by which these OPs enhance pollutant removal in CWs and their artisanal applications. It is also vital to understand the most used OP species in CWs and their advantages in phytoremediation. Thus, this study enhances the understanding of the processes involved in pollutant degradation within CWs, specifically focusing on absorption, adsorption, translocation, radial oxygen loss, and root exudates. It reaffirms the essential role that plants play in these systems, as suggested in previous scientific reports, and discusses some potential applications for the ornamental plants produced in CWs, such as flower arrangements and crafts. This also includes the social aspect, emphasizing community engagement through social capital initiatives for the adoption and appropriation of the ecotechnology. Additionally, a bibliometric analysis revealed that Mexico is among the countries with the most significant research on OPs in CWs, particularly concerning commercially valuable species, followed by India and China. These findings can be instrumental in planning future community projects focused on wastewater treatment using CWs using OPs.
1. Introduction
In the face of environmental degradation, the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development states that “We are determined to protect the planet from further degradation, including through sustainable consumption and production and the sustainable management of its natural resources, so that it can meet the needs of present and future generations” [1]. The agenda also acknowledges that sustainable management and development are essential for improving the quality of life. It proposes collaboration with authorities and communities to revitalize and plan human settlements, fostering community cohesion. One of the key actions highlighted in Goal 6 is the enhancement of local community participation in improving water and sanitation management [1,2].
In 2010, the United Nations recognized access to water and sanitation as a human right [3]. The World Health Organization (WHO) reports that over 80% of all diseases worldwide can be linked to poor water quality [4]. This situation highlights the impact of environmental degradation and emphasizes the urgent need for strategies to reduce water pollution. The problem is further complicated by population growth and its associated activities. It is projected that by 2050, one in four people will lack access to water [5]. According to data from UN-Habitat and the World Health Organization, 44% of household wastewater generated globally is discharged without safe treatment [6].
Wastewater treatment plays a vital role in sustainable resource management by enhancing the availability of clean water, reducing pressure on natural resources, recovering energy, and supporting agriculture [7]. However, the installation of treatment systems is often inadequate, particularly in rural areas where high construction and operational costs make it challenging to allocate financial resources for such projects [8].
In this context, CWs offer a sustainable alternative for wastewater treatment in rural settings. As a nature-based solution (NbS), they are easier to build and operate compared to traditional treatment systems like upflow anaerobic reactors or activated sludge systems [9]. Despite their benefits, the adoption of CWs remains low. This is mainly due to the need for knowledge regarding their functionality and operation, as well as the requirement for residents to engage with and maintain them. Encouraging community involvement is essential for promoting the long-term use and benefits of these systems.
Wetland treatment systems have primarily been implemented at the laboratory or pilot scale, with very few established on a full scale, particularly for addressing communal water pollution issues [10]. It is important to highlight the large-scale systems that have already been installed, as they can serve as models for tackling common water pollution problems. These systems can provide insights into replicability based on their removal efficiencies and the ideal vegetation employed in their processes. CWs form unique ecosystems that host specific biodiversity of microorganisms within the system and a variety of vegetation.
In CWs, vegetation is one of the key components alongside the substrate, microorganisms, and water. Plants play a crucial role in the purification of wastewater. Initially, only vegetation typical of natural wetlands—such as Typha spp., Phragmites spp., and Scirpus spp.—was used in wastewater treatment systems [11,12,13]. However, in recent decades, various terrestrial ornamental plants have been evaluated for their phytoremediation potential. This approach offers more aesthetically pleasing systems by incorporating floral ornamental plants, making them more acceptable to the public.
Hernández and Marín-Muñiz [14] evaluated CWs for treating domestic water and wastewater from student dormitories in a university area in the State of Veracruz, Mexico. In both cases, they observed varied flower production from species such as Hedychium coronarium, Canna hybrids, Alpinia purpurata, Zantedeschia aethiopica, and Anthurium andreanum, which was influenced by the organic load in the system. They proposed that these CWs can enhance water quality while simultaneously producing an important diversity of flowers.
Similarly, Méndez-Mendoza [15] studied two CWs using commercial ornamental plants including Heliconia stricta, Heliconia psittacorum, and Alpinia purpurata, which adapted well to wetland conditions, although the effectiveness of pollutant removal varied depending on the species used. In Chile, Vera-Puerto et al. [16] highlighted the potential of using CWs with Z. aethiopica for wastewater treatment in rural areas, emphasizing the possibility of reusing the treated effluents for irrigation purposes.
These findings demonstrate the usefulness of ornamental plants in wastewater treatment, but also highlight a gap in research regarding the identification of the best species for specific types of water and regional conditions.
The importance of clearly analyzing the ornamental species used in CWs, their removal efficiencies, and their usefulness cannot be overstated. Therefore, this study aims to (1) highlight recent efforts concerning the importance, functionality, and applications of CWs, and (2) investigate the most used ornamental vegetation in full-scale CWs and their essential role in wastewater treatment. This information will be highly beneficial for the design and implementation of new CWs.
2. Materials and Methods
This review involves an investigation of full-scale CWs. Specifically, experiments conducted on-site, where wastewater is generated and at least part of the influent wastewater is treated on-site, were considered full-scale systems. The surface area of these systems can range from 50 m2 to unlimited sizes. In contrast to pilot systems, which generally retain an experimental objective and are typically smaller in size (<50 m2).
This systematic review was conducted in accordance with the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines (Figure 1) in the URL: https://estech.shinyapps.io/prisma_flowdiagram/, accessed on 6 September 2025. The inclusion criteria were established based on the relevance of articles concerning constructed wetlands with ornamental plants, published between 1996 and 2025, to ensure comprehensive coverage of the literature from the inception of research to the present date.
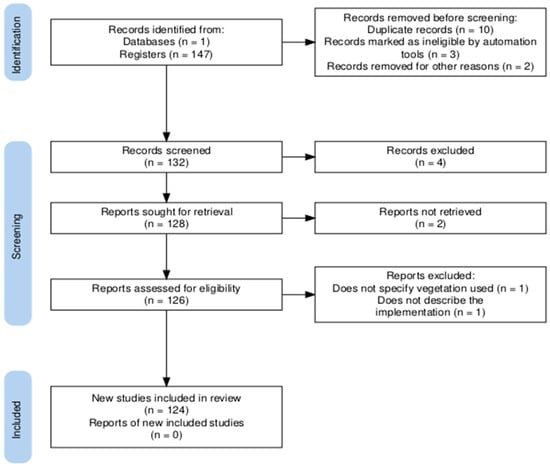
Figure 1.
PRISMA flow diagram illustrating the identification process for the sample of 147 publications on constructed wetlands (CWs) featuring ornamental plants. Note: PRISMA = Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses.
The search was conducted using Dimensions (www.dimensions.ai, accessed on 6 September 2025), a metasearch engine that serves as a new scholarly database designed to address the diverse set of use cases faced by academics today. Unlike other databases, Dimensions offers a free version that includes a searchable index of publications and links to various related entities [17]. To find articles related to constructed wetlands with ornamental vegetation in the processes of wastewater treatment, the search terms “constructed wetland AND ornamental plants” were utilized in English, focusing only on the title and abstract sections (based on the predefined inclusion criteria). A total of 147 texts were identified and reviewed, specifically examining cases that involved full-scale treatment wetlands; co-occurrence with countries was performed on the full search results.
The exclusion criteria intricate studies outside the demarcated timeframe, languages other than English, and articles not directly related to CWs with OPs. The document types considered for this systematic review encompassed Articles, Books, and Book chapters, excluding reviews and conference proceedings. The search was restricted to the Dimensions database. Two reviewers independently screened each record and report retrieved. They worked independently to ensure reliability. Some screens were applied and are described in Figure 1.
The data were exported as a .csv file and analyzed using the VOSviewer program (version 1.6.20) to create a map highlighting the countries with the research on CWs with OPs, through a citation analysis with countries as the unit of analysis. Prior to mapping, bibliographic entries were inspected to eliminate duplicates and inaccurate items. Manual inspection and correction were also conducted to standardize the terms used in the analysis. The counting method applied was full counting.
After identifying the country with the highest number of studies on CWs with OP, further analysis was conducted on the vegetation used in the studies analyzed, the installed treatment areas, the contaminants removed (percentage; %), and the cultural or artisanal uses of the plants involved in such studies. Such topics were discussed and compared with other studies.
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Description of Treatment Wetlands and Their Importance in Wastewater Purification
CWs are eco-engineered systems designed to remove contaminants from wastewater using physical, chemical, and biological processes, mimicking the natural decomposition processes that occur in wetlands [18,19,20]. CWs can be categorized into two types: surface flow wetlands (SCWs) and subsurface flow wetlands (SSCWs) (Figure 2).
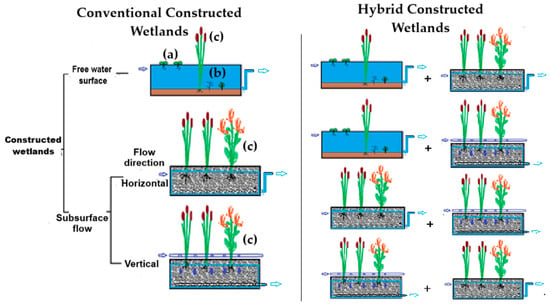
Figure 2.
Types of constructed wetlands: (a) floating plants, (b), submerged plants (c) emergent plants.
SCWs consist of cells with floating, emergent, or submerged plants, where wastewater is in direct contact with the atmosphere. On the other hand, SSCWs are more commonly used, particularly for wastewater treatment, odor reduction and absence of mosquitoes; these systems are composed of cells filled with porous granular material that supports the growth of microbial films, which are the primary agents responsible for pollutant removal. The substrate used in these wetlands can include materials like tezontle, river rock, tepezil, rough or folded plastics, cobbles and gravel (medium and fine gravel), and zeolite in different porosities (20–50%) [19,20,21]. This substrate not only anchors the vegetation but also acts as a filter to adsorb contaminants. Water flow in SSCWs can be either horizontal (HSSCWs) or vertical (VSSCWs). VSSCWs are less commonly used, particularly due to the energy requirements to distribute the water pulses from top to bottom.
When SCWs are combined with SSCWs, or when SSCWs with differing flow rates are used together to improve pollutant removal, they are referred to as hybrid wetlands [18,19,20]. VSSCWs systems have a much greater oxygen transport capacity and, therefore, provide much better conditions for nitrification (ammonia removal, converting ammonia to nitrate), while HSSCWs beds are better suited for denitrification processes (nitrate converted to nitrogen gas) in anoxic-anaerobic conditions and also remove organic matter and other parameters.
Among the primary advantages of CWs are their requirement for no electricity or specialized labor for operation and the absence of chemicals in the treatment process.
3.2. Ornamental Plants and Their Role in Constructed Wetlands
The use of terrestrial ornamental species in CWs has been utilized to assess their adaptability and pollutant removal capabilities. In addition to enhancing visual landscapes, the cultivation of ornamental flowers can exploit their floristic potential for producing commercial products or handicrafts derived from plant tissue [22,23].
Vegetation plays several crucial roles in the pollutant removal process (see Figure 3). One of the key functions of plants occurs through their roots, where oxygen enters from the atmosphere and is subsequently released into the rhizosphere (ROL; radial oxygen loss) (Figure 3(a)). The rhizosphere refers to the area adjacent to the root and the soil or substrate (Figure 3(b)). The ROL promotes the growth of aerobic bacteria, which rely on oxygen for survival [24].
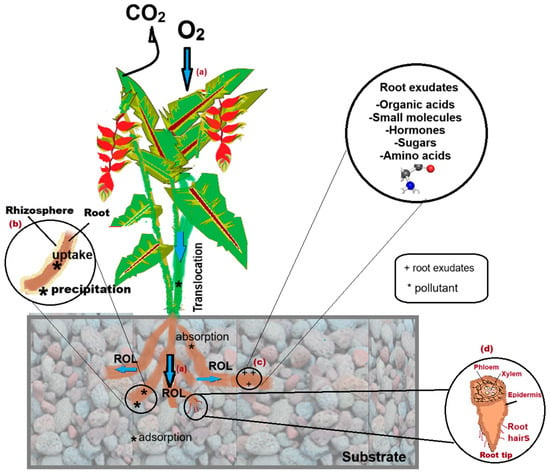
Figure 3.
Diagram illustrating the role of plants in constructed wetlands during wastewater treatment. (a) oxygen processes for radial oxygen loss, (b) Rhizosphere zone, (c) Root exudates mechanisms, (d) Radial oxygen loss processes.
Certain wetland plants have been evaluated for their ROL. For instance, Sorrell [25] reported a ROL of 386.4 µmol O2 d−1 g−1 of dry root mass for Juncus effusus. Similarly, Sanches-Olivares et al. [24] found an ROL of 53–65 µmol O2 d−1 g−1 for Pontederia sagittata. Both cases highlight the oxygen-pumping function of plants, which is essential for their survival and for the removal of contaminants in anoxic environments [26].
Another important process that occurs in plant roots is the release of root exudates (Figure 3(c)). Root exudates are defined as the passive release of low-molecular-weight compounds from the roots into the surrounding rhizospheric zone [27]. These compounds include sugars, amino acids, flavonoids, organic acids, and even vitamins that are utilized by the microbes living in the rhizosphere [28]. These bacteria can metabolize contaminants, contributing to their reduction in wastewater.
Haviland and Noyce [29] investigated the carbon release from root exudates of four different plant species: Spartina patens, Phragmites australis, Schoenoplectus americanus, and Spartina alterniflora. They reported the total carbon release (in micrograms per gram of root dry mass per hour) in ascending order: S. alterniflora (~300 µg), S. americanus (~500 µg), P. australis (~1000 µg), and S. patens (~2600 µg). These findings indicate that carbon input to the rhizosphere can vary significantly among wetland plant species, with potentially major implications for biogeochemical cycling. This highlights the need for further understanding of how plant rhizosphere processes influence soil biogeochemistry at the community level.
Nutrient uptake is a crucial function of plants, particularly in the process known as phytoremediation. Nutrients and water are absorbed by the roots through structures such as root hairs, root tips, and the root epidermis and cortex (Figure 3d) [30,31,32]. This absorption or movement of ions in plant cells can occur in two ways: passive diffusion, which happens due to concentration differences between the substrate in the CWs and the root, or active transport mechanisms, such as proton pumps and ion channels [33,34].
Additionally, the translocation of contaminants occurs in the presence of vegetation and involves the movement of pollutants from the roots or leaves to other parts of the plant [34]. This process takes place primarily through two transport systems: the xylem and the phloem. The xylem transports water and dissolved nutrients from the roots to the stems and leaves, while the phloem carries sugars, amino acids, and other nutrients from the leaves to different parts of the plant [34,35].
The uptake and translocation of organic pollutants by plants are influenced by several factors, including the physical and chemical properties of the pollutants (such as molecular mass, volatility, and concentration), the biological characteristics of the plants (including hydrophobicity and lipid or carbohydrate content), and the environmental conditions (like pH, type of background electrolyte, organic carbon content, and temperature) [35,36,37].
In a study conducted in CWs with ornamental plants—specifically Iris sibrica and Zantedeschia aethiopica—the uptake of carbamazepine (CBZ) was evaluated. The findings revealed that the uptake by I. sibrica was 10% higher than that of Z. aethiopica, confirming I. sibrica’s ability to translocate and accumulate CBZ, primarily in its leaves [38].
Plants in CWs have special adaptations that enable them to transport oxygen from the atmosphere to their roots, as well as to transfer gases from the soil or substrate to the atmosphere (ventilation) [19,39]. These adaptations help the plants survive in waterlogged conditions through a passive molecular diffusion mechanism, on pressurized gas flow, or Venturi-induced convection [40,41]. One key feature is the system of air channels and intercellular spaces known as aerenchyma. This structure develops in various parts of the plant, including the roots, stems, and leaves [41]. In aquatic species, these intercellular spaces can vary significantly among different species and may account for up to 60% of the leaf volume. In contrast, mesophytes typically have intercellular volumes ranging from 2% to 7%. Consequently, for species that are not flood-tolerant, flooding can lead to the plant’s demise [42,43].
In Figure 4a, a cross-section of a leaf of Typha angustifolia is presented is presented. Figure 4b reveals large air spaces that are interconnected throughout the plant. Figure 4b displays a transection of the stem, which contains lacunae filled with thin-walled aerenchymal tissue. Meanwhile, Figure 4c exemplify the flower of the specie T. angustifolia. Figure 4d,e illustrates the porous tissue of the stem of Zantedeschia aethiopica (depicted in Figure 4f). Understanding these characteristics in the plants used in CWs can guide design considerations for ecological wastewater treatment systems.
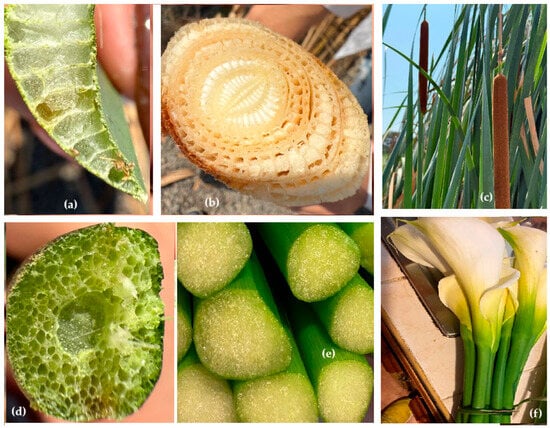

Figure 4.
Fiber bundles, air channels, vascular bundles, and aerenchyma of typical macrophytes found in wetlands. Example: Typha angustifolia (above), Zantedeschia aethiopica (below). (a) cross-section of a leaf of Typha angustifolia; (b) transection of the stem of T. angustifolia; (c) flower of the specie T. angustifolia; (d,e) porous tissue of the stem of Zantedeschia aethiopica; (f) Zantedeschia aethiopica flowers.
Using microcomputed tomography and scanning electron microscopy, Liu et al. [44] reported that the leaves of Typha angustifolia have a total porosity close to 96%, demonstrating high strength combined with low density. This detailed information highlights the physiological properties of hydrophytes, although data is limited regarding the vast diversity of existing species.
Several authors have reported on the most used ornamental plants in CWs [10,45,46]. 7-These include calla lilies (Zantedeschia aethiopica) [5,47,48,49], irises (Iris spp.) [50,51], cannas (Canna hybrids) [52,53,54], papatla (Canna indica) [55], and various species of heliconias (Heliconia spp.) [56,57] (see Figure 5).
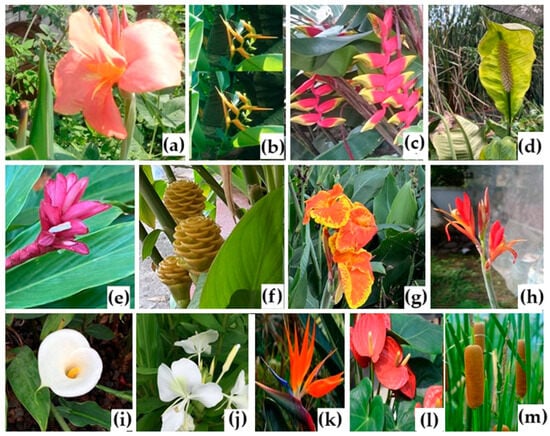
Figure 5.
Typical Ornamental Plants Used in Treatment Wetlands: (a) Canna hybrids, (b) Heliconia latispatha, (c) Heliconia rostrata, (d) Spathiphyllum blandum, (e) Alpinia purpurata, (f) Zingiber spectabile, (g) Canna generalis, (h) Canna indica, (i) Zantedeschia aethiopica, (j) Hedychium coronarium, (k) Strelitzia reginae, (l) Anthurium sp., (m) Typha dominguensis.
Additionally, there are other species that are less commonly used but have been tested for their bioremediation effects. These include Moses cradle (Spathiphyllum wallisii) [58,59], maracas (Zingiber spectabile) [60], red ginger (Alpinia purpurata) [53,61], white ginger (Hedychium coronarium) [14], and anthurium (Anthurium spp.) [62]. Tules or cattails (Typha spp.), while typically found in natural wetlands, can also be considered aquatic ornamental species because their flowers are utilized in floral arrangements.
Zitácuaro et al. [23] classified the different uses of ornamental plants growing in CWs. The social potential was classified as ornamental, artisan, medicinal, and food. Therefore, plant species can be used as raw material in the elaboration of handicrafts, flower arrangements, and the cultivation of seedlings in pots. Economic potential refers to the commercialization of cut flowers, foliage, stems, and plants in pots. The environmental potential is related to the ability to remove pollutants from the plants. At the same time, a culture promoting the efficient use of natural resources would develop in localities where CW is planted with ornamental plants. The selection of the plants is related to the physical characteristics described previously, considering the adaptation feasibility in wetland conditions.
Systems with flowers are constructed, such as the Pinoltepec project in the municipality of Emiliano Zapata, Veracruz, Mexico [47]. To take advantage of the social potential that ornamental plants have, it is important to describe their uses considering the benefits they provide to society, i.e., artisanal, ornamental, cultural, and medicinal benefits (Figure 4).
Figure 5 showcases various ornamental plant species commonly used in treatment wetlands.
3.3. Bibliometric Analysis of the Use of Wastewater Treatment with Ornamental Plants and Case Studies
This bibliometric analysis aimed to assess the productivity of publications by country regarding the use of ornamental plants for wastewater treatment (Figure 6). The findings reveal that Mexico leads this field of research with a total of 982 citations. It is followed by India with 622 citations, China with 434, and the United States with 173. This observation aligns with the report from García-Ávila et al. [46] in 2023, which underscores Mexico’s significance in this area of study. The extensive biodiversity of its flora, attributed to its geographic location, and the pressing need to address global challenges such as water pollution contribute to this prominence.
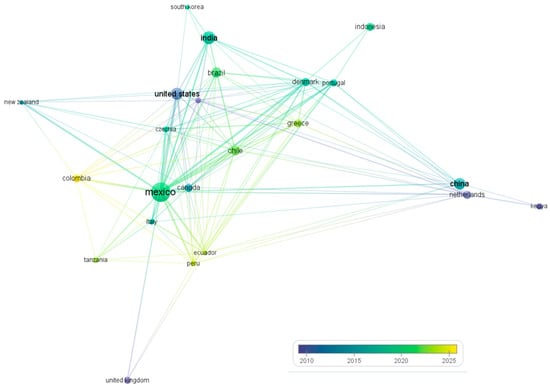
Figure 6.
A network visualization of the main countries involved in the research on wastewater treatment using CWs and ornamental plants.
The analysis also indicates that most publications on this topic in Mexico have emerged since 2018, demonstrating the country’s increasing engagement in exploring solutions for wastewater treatment using ornamental plants over less than a decade. The map highlights that Latin American countries are increasingly adopting nature-based solutions. It also shows a strong collaboration in research between Latin American and Asian countries, which should be further strengthened to foster innovation in ecotechnology and its processes.
After determining that Mexico has extensive research on watershed management issues, studies involving the full-scale implementation of CWs were identified. Reports from the National Water Commission (CONAGUA), the country’s water management agency, indicate that the utility of CWs is increasing, albeit gradually. Table 1 lists several studies that have evaluated the use of ornamental flowering plants in CWs. These plants include commercially valuable species such as the calla lily, anthurium, plantain, and Moses’ cradle.
The studies summarized in Table 1 present the results of wastewater pollutant removal assessments in CWs, achieving removal rates of up to 91% for chemical oxygen demand (COD), 89% for biochemical oxygen demand over five days (BOD5), 93% for coliforms, and 90% for dissolved solids, among other pollutants. These findings highlight the effectiveness of CWs in treating wastewater. Such removals are similar to those observed in conventional systems (activated sludge, anaerobic reactors), but require greater processes, electricity costs and specialized labor [2,47,49].
The CW system design must be according to the local regulations. For example, for Mexico, regulations are defined in the NOM-001-SEMARNAT-2021, which establishes the maximum allowable pollutant limits for wastewater discharges into national receiving bodies. To protect rivers, established limits by this Mexican standard are COD, 150 mg/L; TSS, 60 mg/L; TN, 25 mg/L; and TP, 15 mg/L.
The processes responsible for pollutant removal in CWs include adsorption, absorption, filtration, sedimentation, flocculation, precipitation, coprecipitation, mineralization, and nitrification/denitrification. Additionally, phytoremediation plays a significant role. This environmentally friendly technique involves using vegetation to extract or degrade various pollutants [19,63].

Table 1.
Full-Scale Constructed Wetlands with Ornamental Plants in Mexico.
Table 1.
Full-Scale Constructed Wetlands with Ornamental Plants in Mexico.
| Study Site | Wastewater Treated | Plants Used | CW Area (m2) | Removal (%) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Palmas de Abajo, Actopan, Veracruz | Community | Sansevieria zeylanica, Typha angustifolia, Cyperus (alternifolius, papyrus), Canna hybrid, Heliconia psittacorum. | 300 | TN: 56 TP: 72 COD: 90 | Marín-Muñiz et al. [64] |
| Nautla, Veracruz | Municipal wastewater | Sansevieria trifasciata, Canna (indica, hybrids), Colocasia esculenta, Pontederia cordata, Heliconia psittacorum, Ruellia sp., Sagittaria graminea, Cyperus papyrus, Berberis thunbergii. | 430 | COD: 93 N-NO3: 92 N-NH4: 93 TN: 91 | Sangabriel et al. [65] |
| Veracruz | Swine | Typha angustifolia, Canna hybrids | 100 | COD: 84, TSS: 82, TN: 94, TP: 82 | Sandoval-Herazo et al. [66] |
| Salvador Diaz Miron, Misantla, Veracruz | Community | Alocasia odora, Hedychium coronarium, Heliconia psittacorum, Zantedeschia aethiopica, Canna indica | not specified | TN: 40 TP: 68 COD: 93 | Monzón-Reyes et al. [67] |
| Pastorías, Actopan, Veracruz | Community | Typha sp., Canna hybrids, Anturium sp., Sphathiphylum blandum | 70 | COD: 84 TS: 90 | Sandoval et al. [68] |
| Pinoltepec, Emiliano Zapata, Veracruz | Community | Typha sp., Zantedeschia aethiopica., Hedychium coronarium. Thalia sp. | 60 | TN: 47 TP: 33 COD: 67 | Hernández [47] |
| Chapala, Jalisco, México | Community | Canna hybrids and Strelitzia reginae | 70 | COD: 86 TN: 30–33 TP: 24–44 | Merino-Solís et al. [54] |
| San Juan de Aragón, Gustavo A. Madero. México | Eutrophic lake | Phragmites australis., Equisetum hyemale y Cyperus papyrus | 1613 | BOD: 88 TN: 72 TP: 50 | Luna-Pabello y Aburto-Castañeda, [69] |
| Santa Fe de la Laguna, Quiroga, Michoacán | Municipal | Phragmites australis, Typha latifolia | 8800 | BOD: 94–98 COD: 91–93 TS: 91–97 TN: 56–88 | Rivas et al. [70] |
| University UAM Xochimilco, México. | Municipal | Arundo donax, Medicago sativa y Zandechia aethiopica | 55 | COD: 92 N-NH4: 85% P-PO4: 80% | Ramírez-Carrillo et al. [71] |
| UAM-Azcapotzalco. Mexico City | Municipal | Phragmites australis, Typha latifolia | 200 | BOD: 80 | Barceló et al. [72] |
| Cucuchucho, Tzintzuntzan, Michoacán | Community | Phragmites australis, Typha latifolia y Zantedeschia aethiopica | 3265 Sumado a otros 7 sistemas | BOD: 89 TN: 80 TP: 74 | González and Rivas [73] |
| Area “Instituto Tecnológico de Boca del Río, Veracruz” | University | Alpinia purpurata., Ruellia brottoniana., Canna hybrids., Cyperus papyrus., Heliconia pisittacorum., Pennisetum setaceumy and others ND. | 157 | TN: >70 TP: >70 COD: 15 | Lango et al. [74] |
| Felipe carrillo Puerto, Tapachula, Chiapas | Domestic | Heliconia psittacorum., Alpinia purpurata, Typha domingensis | 110 | COD: 64 BOD: 50 TN: 30–39 TP: 44 | Méndez-Mendoza et al. [15] |
| Argovia, Tapachula, Chiapas. | Wet coffee processing | Saccharum spp., Panicum máximum., Heliconia psittacorum., Vetiveria zizanoides y Clorophytum conmutatum | 300 | COD: 91 Coliforms: 93 | Orozco et al. [75] |
| Erongarícuaro, Michoacán | Municipal | Phragmites communis, Typha latifolia | 11,600 | BOD: 70–9 COD: 70–90 | Sánchez-Chávez et al. [76] |
The reported removals pertain to the treatment of community and municipal wastewater, as well as wastewater from the industrial sector. This highlights the significance of CWs in wastewater treatment, as these systems have proven to be more sustainable than conventional alternatives like membrane bioreactors, trickling filters, sequencing batch reactors, pond systems, and extended aeration methods [9]. Thus, CWs serve as an effective solution for water health.
Additionally, it was observed that ornamental plants are predominantly utilized as polycultures within CWs. This approach results in a greater diversity of species and a variety of flowering colors, which in turn attract insects and pollinating birds.
According to Table 1, nitrogen and phosphorus compounds are removed within a range of 30 to 90 mg/L. This variation, which is lower than that observed for BOD or COD, has been documented in several studies. These investigations indicate that low water temperatures negatively affect the effectiveness of nitrogen and phosphorus removal [77,78]. Xu Et Al. [79] reported that increasing the hydraulic retention time in constructed wetlands allows microorganisms to remain longer in the system, thereby facilitating the completion of the nitrogen removal process. Additionally, a portion of both nutrients is absorbed by plants, depending on the specific requirements of each species [74,76].
Complete nitrogen removal requires aerobic processes that promote nitrification, followed by anaerobic processes that enable denitrification. However, in subsurface constructed wetlands (SSCW), aerobic conditions are limited, which restricts the total removal of pollutants [19,20]. Additionally, the filter medium plays a crucial role in mitigating nitrogen compounds in constructed wetlands through adsorption mechanisms. The microstructure of the filter material determines the physical and chemical properties of the substrate and provides surface area for nutrient adsorption [80].
Another important characteristic of plants in constructed wetlands is their contribution to water loss through evapotranspiration. Many wetland plant species are unable to retain water, resulting in significant transfer of water to the atmosphere. This effect is particularly pronounced under warm or windy conditions, where evapotranspiration rates can be seven to eight times higher than evaporation from systems without plants [80,81]. Reported evapotranspiration rates for constructed wetland plants range from 7 to 17 mm per day, with values varying according to growth stages and showing strong correlations with phenological parameters [82]. This relationship warrants further investigation, as current information is limited. Beebe Et Al. [83] noted that evapotranspiration is expected to influence the concentration of conservative constituents.
Table 1 presents data on the use of constructed wetlands in Mexico. However, it is important to consider whether this usage is comparable to the adoption of the technology in other countries. According to Chen Et Al. [84], the use of constructed wetlands is more prevalent in Europe (158 studies) and Asia (130 studies) than in America (55 studies), Oceania (10 studies), and Africa (6 studies). These differences are attributed to variations in wastewater policies, engineering practices, economic development, environmental priorities, regulatory frameworks, cultural factors, and collaborative governance. Despite the complex dynamics between technology and governance in Latin America, constructed wetlands provide valuable insights for addressing wastewater challenges, which should be further examined by policymakers [85].
3.4. Utilization of Ornamental Plants in Constructed Wetlands
The use of ornamental plants in CWs not only facilitates the removal of pollutants but also enhances the aesthetic appeal of landscapes. Additionally, these plants can be repurposed for artistic, cultural, or artisanal projects. For example, the Typha angustifolia plant can be used to craft woven chairs (Figure 7a), hampers (Figure 7b), baskets (Figure 7c), and mats (Figure 7d). Furthermore, the ornamental vegetation produced in these systems can be utilized to create floral arrangements (Figure 7e). These products, derived from Phytoremediating wetland vegetation, exemplify the benefits of wetlands and contribute to the economic sustainability of the operators or groups managing the systems. Careful selection of plants, understanding pollutant concentrations, and using appropriate disposal methods for the harvested plant biomass are crucial steps to mitigate risks of health concerns by accumulations of heavy metals in the plant tissues, especially when creating products for public use. Further research is required in this regard, since only the effect of plant phytoremediation on heavy metals in soil and water is commonly analyzed [86,87].
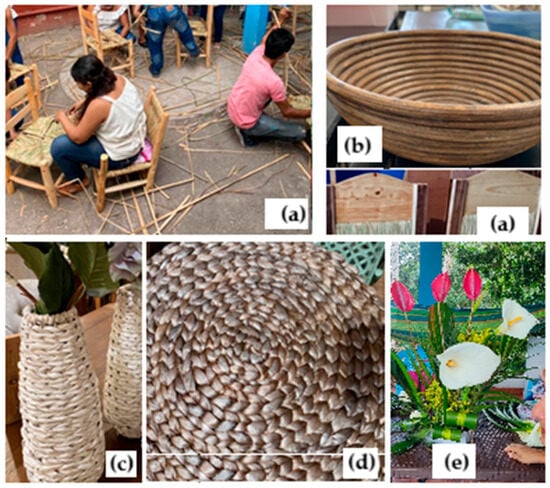

Figure 7.
Handcrafted products made from the Typha angustifolia plant. (a) woven chairs, (b) hampers, (c) baskets, (d) mats, (e) floral arrangements with flowers produced in the CW.
This study showcases the installation of CWs to treat community wastewater. However, these systems are often initially operated by researchers or thesis project coordinators, which raises concerns about their long-term sustainability. Therefore, it is crucial to involve the community and provide ongoing support to promote the acceptance and ownership of CWs.
Some studies have engaged residents in the construction, management, and operation of the wetlands. This involvement is essential for fostering the adoption of ecotechnologies [66,88]. Additionally, once the system is established, community groups may utilize the vegetation as raw material for handicrafts or floral arrangements, which can include recreational workshops and continued support [47,89]. Both approaches contribute to ensuring the long-term functionality of the system.
Stable relationships based on trust, reciprocity, and cooperation contribute in three key ways: they lower transaction costs, generate public goods, and promote the formation of effective grassroots management organizations, social actors, and healthy civil societies [85]. Social capital encompasses elements such as the degree of trust among individuals, civic behavior norms, and the level of associativity. These factors enhance the quality and strength of internal relationships within groups and reinforce the social fabric [90].
Local communities are seen as essential units of social organization and serve as a focal point for development initiatives [91,92,93]. According to Zitácuaro et al. [23], the combination of social capital and community wealth positively contributes to sustainable development by providing environmental, economic, and social benefits. This was illustrated through four years of collaborative work on CW management and artisanal production with a group of organized women in Veracruz, Mexico, who utilize local vegetation for their crafts [89].
In general, the use of constructed wetlands offers opportunities to address wastewater challenges, supply materials for alternative uses, and serve as sites for educational activities similar to natural laboratories. Some reviews on innovations in constructed wetlands discuss their application at household, industrial, and educational levels, as well as research on design parameters and maintenance processes [94,95]. These systems can function as water treatment plants, habitat creation sites, urban wildlife refuges, recreational or educational facilities, landscape engineering projects, and ecological areas [96].
On the other hand, some limitations on the long-term functioning of constructed wetlands include, scale limitations, making them difficult to implement in areas where space is scarce and costly: mainly in rural areas, where constant advice must be provided for the adoption and appropriation of the system, in addition to access to economic resources to avoid aversion to ecotechnology as has been shown in other studies [97]. In addition, the climate conditions are also a limitation; low temperatures reduce performance, while high temperatures and arid conditions can increase water loss through evaporation and risk odor and mosquito issues [98,99]. Long-term stability is challenged by potential clogging from sediments and biofilms, requiring consistent operation and maintenance to prevent functional decline. The use of proper particle size, multilayer substrates and backwashing helps to slow CW clogging [100].
It is important to highlight that CWs significantly contribute to achieving the UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) by offering NbS for wastewater treatment, resource management, and ecosystem restoration. They primarily support SDG 6, “ensure availability and sustainable management of water and sanitation for all”, through effective, low-cost wastewater treatment and safe water reuse. CWs also advance SDG 15 (Life and Land) by enhancing biodiversity, and can help in SDG 11 (Sustainable cities and communities) through decentralized water management and green infrastructure. Additionally, they play a role in SDG 13 (Climate action) by managing water resources and contributing to the stability of ecosystems, and contribute to SDG 12 (Responsible consumption and production) by promoting water conservation and resource efficiency [101,102]. Similarly, this study also accentuates the importance of considering cooperation for integrated environmental governance and enhancing policy consistency in sustainable development management. Additionally, different investigations have reported that CWs contribute to the circular economy through water reutilization, commercial value of the vegetation growing in the systems, nutrient recovery, energy generation during the removal of pollutants, utilizing the ecotechnology as living laboratories, and providing well-being through environmental services [96,103,104].
4. Conclusions
Addressing water pollution requires the use of ecological alternatives, such as CWs, where vegetation plays a crucial role in the purification of pollutants. The incorporation of ornamental plants into CWs not only enhances the aesthetic appeal of ecotechnology but also generates commercially valuable products, making it a more attractive option for acceptance within communities.
Mexico stands out as a leader in the implementation of CWs with ornamental plants. Research has shown that engaging communities with polycultures of ornamental plants, particularly those of commercial value, can significantly improve treatment efficiency and intensify plant biodiversity by creating attractive ecosystems for other insects such as butterflies, hummingbirds, and dragonflies. This is primarily achieved through the processes occurring in the roots and tissues of the plants, which demonstrate effective removal of both organic and inorganic contaminants. Furthermore, the use of vegetation contributes to the creation of handicrafts, adding an additional layer of value.
It is recommended that community participation be integrated into the construction, operation, and management of these technologies. Building relationships of trust through social capital can promote the long-term sustainability of ecotechnologies like CWs. The findings from this study can be utilized to plan intervention projects in areas facing water pollution issues and projects that promote biodiversity and improve the human–nature relationship. These projects should carefully consider the most suitable ornamental plants based on this research and emphasize the importance of involving the civil society sector to effectively operate and manage the ecotechnology alongside community social capital initiatives. Additionally, these systems have the potential to promote socio-environmental well-being.
This study provides a comprehensive analysis of the processes underlying contaminant removal in constructed wetlands employing ornamental plants, identifies suitable ornamental species for future implementation, and delineates the principal mechanisms supporting the long-term functionality of these systems. The review’s significance is underscored by its potential to inform the optimization of wastewater treatment, augment ecological benefits, and enhance the aesthetic quality of constructed wetlands through the integration of ornamental flowering plants. An in-depth understanding of the specific attributes and performance metrics of diverse ornamental species facilitates improved design and management strategies, thereby maximizing pollutant removal efficacy and the provision of valuable ecosystem services. Future research should address the comparative analysis of construction and utilization costs within the context of a circular economy to further inform sustainable practice. Furthermore, further research must be conducted to evaluate the adoption and appropriation of eco-technology in society.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.L.M.-M. and S.A.Z.-C.; methodology, J.C.M.-S., and M.G.H.y.O., J.L.M.-M.; software and bibliometric analysis, G.A.M.E. and J.S.L.; validation, I.Z.-C., and J.L.M.-M.; formal analysis, S.A.Z.-C. and M.G.H.y.O.; investigation, J.L.M.-M. and I.Z.-C.; resources and data curation; G.A.M.E., J.C.M.-S.; writing—original draft preparation, J.S.L. and I.Z.-C.; writing—review and editing, M.G.H.y.O. and J.L.M.-M.; visualization, S.A.Z.-C. and G.A.M.E.; supervision, J.L.M.-M.; project administration, S.A.Z.-C. and M.G.H.y.O.; funding acquisition, J.C.M.-S. and J.S.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The author thanks the ITSM (Higher Technological Institute of Misantla) for providing the space for the research.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change. Paris Agreement. 2015. Available online: https://unfccc.int/sites/default/files/english_paris_agreement.pdf (accessed on 7 May 2025).
- Bose, D.; Bhattacharya, R.; Kaur, T.; Banerjee, R.; Bhatia, T.; Ray, A.; Mondal, A.; Ghosh, P.; Monda, S. Overcoming water, sanitation, and hygiene challenges in critical regions of the global community. Water-Energy Nexus 2024, 7, 7277–7296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abney, S.E.; Bright, K.R.; McKinney, J.; Khalid, M.; Gerba, C.P. Toiled hygiene-review and research needs. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2021, 131, 2705–2714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mojiri, A. Treatment of Water and Wastewater: Challenges and Solutions. Separations 2023, 10, 385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, H.; South, N.; Walters, R. The commodification and exploitation of fresh water: Property, human rights and green criminology. Int. J. Law. Crime. Justice 2016, 44, 146–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UN Habitat; WHO. Progress on Wastewater Treatment—Global Status and Acceleration Needs for SDG Indicator 6.3.1; United Nations Human Settlements Programme (UN-Habitat): Geneva, Switzerland; World Health Organization (WHO): Geneva, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, J.A. Wastewater Treatment and Reuse for Sustainable Water Resources Management: A Systematic Literature Review. Sustainability 2023, 15, 10940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kama, R.; Song, J.; Liu, Y.; Hamani, A.K.M.; Zhao, S.; Li, Z. Water Availability and Status of Wastewater Treatment and Agriculture Reuse in China: A Review. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molinos-Senante, M.; Gómez, T.; Garrido-Baserba, M.; Caballero, R.; Sala-Garrido, R. Assessing the sustainability of small wastewater treatment systems: A composite indicator approach. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 497–498, 607–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parde, D.; Patwa, A.; Shukla, A.; Vijay, R.; Killedar, D.; Kumar, R. A review of constructed wetland on type, treatment and technology of wastewater. Envion Technol. Innov. 2021, 21, 101261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vymazal, J. Plants used in constructed wetlands with horizontal subsurface flow: A review. Hydrobiologia 2011, 674, 133–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vymazal, J. Emergent plant used in free water surface constructed wetlands: A review. Ecol. Eng. 2013, 61, 582–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zheng, B.; Chen, X.; Li, Z.; Xia, Q.; Wang, H.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, H. The Use of Constructed Wetland for Mitigating Nitrogen and Phosphorus from Agricultural Runoff: A Review. Water 2021, 13, 476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández, M.E.; Marín-Muñiz, J.L. Greenhouse gas emissions and treatment performance in constructed wetlands with ornamental plants: Case Studies in Veracruz, Mexico. In Artificial or Constructed Wetlands a Suitable Technology for Sustainable Water Management; Durán-Domínguez, M., Navarro-Frómeta, A., Bayona, J., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA; Taylor & Francis Group: Abingdon, UK, 2018; pp. 163–177. [Google Scholar]
- Méndez-Mendoza, A.S.; Bello-Mendoza, R.; Herrera-López, D.; Mejía-González, G.; Calixto-Romo, A. Performance of constructed wetlands with ornamental plants in the treatment of domestic wastewater under the tropical climate of South Mexico. Water Pract. Technol. 2015, 10, 110–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vera-Puerto, I.; Marca, N.; Contreras, C.; Zuñiga, F.; López, J.; Sanguesa, C.; Correo, C.; Arias, C.; Valenzuela, M. Performance of vertical and horizontal treatment wetlands planted with ornamental plants in Central Chile: Comparative analysis of initial operations stage for effluent reuse in agriculture. Env. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 50398–50410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hook, D.; Porter, S.; Herzong, C. Dimensions: Building context for search and evaluation. Front. Res. Metr. Anal. 2018, 3, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marín-Muñiz, J.L.; Sandoval, L.C.; López-Méndez, M.C.; Sandoval-Herazo, M.; Meléndez-Armenta, R.Á.; González-Moreno, H.R.; Zamora, S. Treatment wetlands in Mexico for control of wastewater contaminants: A review of experiences during the last twenty-two years. Processes 2023, 11, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsch, W.J.; Gosselink, J.; Anderson, C.; Fennessy, S. Wetland, 6th ed.; John Wiley and Sons Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Masi, F.; Martinuzzi, N. Constructed wetlands for the Mediterranean countries: Hybrid systems for water reuse and sustainable sanitation. Desalination 2007, 215, 44–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandoval, L.; Alvarado-Lassman, A.; Marín-Muniz, J.L.; Rodríguez-Miranda, J.P.; Fernández-Lambert, G. A critical review of mineral substrates used as filter media in subsurface constructed wetlands: Costs as a selection criterion. Environ. Technol. Rev. 2023, 12, 251–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campaña, L.M.V.; Molina, C.R.; Romero, F.C.A. Las potencialidades artesanales. Un análisis desde la perspectiva de desarrollo sostenible para su revalorización y empresarialidad turística. Retos Turísticos 2015, 14, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zitácuaro-Contreras, I.; Vidal-Álvarez, M.; Hernández y Orduna, M.; Zamora-Castro, S.; Betanzo-Torres, E.; Marín-Muniz, J.; Sandoval-Herazo, L. Environmental, economic, and social potentialities of ornamental vegetation cultivated in constructed wetlands of Mexico. Sustainability 2021, 13, 6267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Olivares, E.; Marín-Muniz, J.L.; Hernández-Alarcón, M.E. Liberación de oxígeno radial por las raíces de las plantas nativas de humedales tropicales costeros de Veracruz en respuesta a diferentes condiciones de inundación. Bot. Sci. 2019, 97, 202–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorrell, B.K. Effect of external oxygen demand on radial oxygen loss by Juncus roots in titanium citrate solutions. Plant Cell Environ. 1999, 22, 1587–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, W.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Z. Radial oxygen loss, photosynthesis, and nutient removal of 35 wetland plants. Ecol. Eng. 2012, 39, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveros-Bastidas, J.; Macías, F.; Carrera, C.; Marín, D.; Molinillo, J. Exudados de la raíz y su relevancia actual en las interacciones alelopáticas. Quim. Nova 2009, 32, 198–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Du, Y.; Peng, W.; Zhang, S.; Liu, X.; Wang, S.; Yuan, S.; Kolditz, O. Modelling the impacts of plants and internal organic carbon on remediation performance in the integrated vertica flow constructed wetlands. Water Res. 2021, 204, 117635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haviland, K.; Noyce, G. Assessing root-soil interactions in wetland plants: Root exudation and radial oxygen loss. Biogeosciences 2024, 21, 5185–5198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marin, M.; Feeney, D.S.; Brown, L.K.; Naveed, M.; Ruiz, S.; Koebernick, N.; Bengough, A.G.; Hallett, P.D.; Roose, T.; Puértolas, J.; et al. Significance of root hairs for plant performance under contrasting field conditions and water deficit. Ann. Bot. 2021, 128, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Jang, J.; Seomun, S.; Yoon, Y.; Jang, G. Division of cortical cells is regulated by auxin in Arabidopsis roots. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 953225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyainleta, G.; Pesik, A.; Hiariej, A. Epidermal structure and leaf stomata of several accessions of banana plants (Musa spp.). J. Penelit. Pendidik. IPA 2022, 8, 2974–2979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiri, I. Mechanisms of Nutrient Uptake and Assimilation Processes in Some Plants: A Review. Dutse. J. Pure Appl. Sci. 2023, 9, 223–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, S.; Qin, A.; Zain, M.; Mushtaq, Z.; Mehmood, F.; Riaz, L.; Naveed, S.; Ansari, M.; Saeed, M.; Ahmad, I.; et al. Pb uptake, accumulation, and translocation in plants: Plants physiological, biochemical, and molecular response: A review. Helyon 2024, 10, e27724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, A.; Bhardwaj, S.; Ishtiaq, H.; Devi, Y.; Kapoor, D. Lead uptake, toxicity and mitigation strategies in plants. Plant Arch. 2021, 21, 293–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Feng, Y.; Liu, Y.; Chang, H.; Li, Z.; Xue, J. Uptake and translocation of organic pollutants in plants: A review. J. Integr. Agric. 2017, 16, 1659–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dettenmaier, E.; Doucette, W.; Bugbee, B. Chemical hydrophobicity and uptake by plant roots. Environ. Sci. Tecnol. 2009, 43, 324–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tejeda, A.; Torres-Bojorges, Á.X.; Zurita, F. Carbamazepine removal in three pilot-scale hybrid wetlands planted with ornamental species. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 98, 410–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colmer, T.D. Long-Distance Transport of Gases in Plants: A Perspective on Internal Aeration and Radial Oxygen Loss from Roots. Plant Cell Environ. 2003, 26, 17–36. [Google Scholar]
- Jackson, M.B.; Armstrong, W. Formation of Aerenchyma and the Processes of Plant Ventilation in Relation to Soil Flooding and Submergence. Plant Biol. 1999, 1, 274–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Björn, L.O.; Middleton, B.A.; Germ, M.; Gaberščik, A. Ventilation Systems in Wetland Plant Species. Diversity 2022, 14, 517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laan, P.; Berrevoets, M.J.; Lythe, S.; Armstrong, W.; Blom, C.W.P.M. Root Morphology and Aerenchyma Formation as Indicators of the Flood-Tolerance of Rumex Species. J. Ecol. 1989, 77, 693–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larcher, W. Physiological Plant Ecology: Ecophysiology and Stress Physiology of Functional Groups, 4th ed.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Yu, Z.; Liang, Y.; Li, X.; Ren, L. The structure and flexural properties of Typha leaves. Appl. Bionics Biomech. 2017, 2017, 1249870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanatou, A.; Schiza, S.; Petousi, I.; Rizzo, A.; Masi, F.; Stasinakis, A.; Fyllas, N.; Fountoulakis, M. Use of climbing and ornamental plants in vertical flow constructed wetlands treating greywater. J. Water Proc. Eng. 2023, 53, 103832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Avila, F.; Aviles-Anazco, A.; Cabello-Torres, R.; Guanuchi-Quito, A.; Cadme-Galabay, M.; Gutierrez-Ortega, H.; Alvarez-Ochoa, R.; Zhindon-Arevalo, C. Application of ornamental plants in constructed wetlands for wastewater treatment: A scientometric analysis. Case Stud. Chem. Environ. Eng. 2023, 7, 100307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández, M.E. Humedales ornamentales con participación comunitaria para el saneamiento de aguas municipales en México. Rinderesu 2016, 1, 1–12. (accessed on 5 June 2025). (In Spanish). [Google Scholar]
- Zurita, F.; de Anda, J.; Belmont, M.A. Performance of laboratory-scale wetlands planted with tropical ornamental plants to treat domestic wastewater. Water Qual. Res. J. Can. 2006, 41, 410–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zurita, F.; De Anda, J.; Belmont, M.A. Treatment of domestic wastewater and production of commercial flowers in vertical and horizontal subsurface-flow constructed wetlands. Ecol. Eng. 2009, 35, 861–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Echeverría, E.; Sandoval-Herazo, L.C.; Zurita, F.; Betanzo-Torres, E.; Sandoval-Herazo, M. Development of Heliconia latispatha in constructed wetlands, for the treatment of swine/domestic wastewater in tropical climates, with PET as a substitute for the filter medium. Rev. Mex. Ing. Quím 2022, 21, IA2811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.; Chen, D.; Wu, F.; He, S.; Huang, J. Recycled utilization of Iris pseudacorus in constructed wetlands: Litters self-consumption and nitrogen removal improvement. Chemosphere 2021, 262, 127863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polomski, R.; Bielemberg, D.; Whitwell, T.; Taylor, M.; Bridges, W.; Klaine, S. Nutrient recovery by seven aquatic garden plants in a laboratory-scale subsurface-constructed wetland. Hort. Sci. 2007, 42, 1674–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marín-Muñiz, J.L.; Hernández, M.E.; Gallegos-Pérez, M.P.; Amaya-Tejeda, S.I. Plant growth and pollutant removal from wastewater in domiciliary constructed wetland microcosms with monoculture and polyculture of tropical ornamental plants. Ecol. Eng. 2020, 147, 105658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merino-Solís, M.; Villegas, E.; Anda, J.; López-López, A. The Effect of the hydraulic retention time on the performance of an ecological wastewater treatment system: An anaerobic filter with a constructed wetland. Water 2015, 7, 1149–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, S.V.; Argyilan, E.P.; Krekeler, M.P.S. An environmental investigation of the mineralogical, geotechnical, hydrogeologic and botanical properties of subsurface flow constructed wetlands in Akumal Mexico. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 73, 2299–2317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida-Naranjo, C.; Guachamín, G.; Guerrero, V.; Villamar, C.-A. Heliconia stricta behavior on hybrid constructed wetlands fed with synthetic domestic wastewater. Water 2020, 12, 1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivas, R. Elaboración del Diagnóstico del Humedal de Acamixtla, Recomendaciones y Propuesta de Acciones para su Rehabilitación, en la Localidad de Acamixtla Municipio de Taxco de Alarcón, en el Estado de Guerrero. Informe Final. IMTA. 2016. Available online: http://repositorio.imta.mx/handle/20.500.12013/1743 (accessed on 18 May 2025). (In Spanish).
- Zamora-Castro, S.; Marín-Muñiz, J.L.; Sandoval, L.; Vidal-Álvarez, M.; Carrión-Delgado, J. Effect of ornamental plants, seasonality, and filter media material in fill-and-drain constructed wetlands treating rural community wastewater. Sustainability 2019, 11, 2350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cárdenas, D.; Barbosa, G. Uso de humedales artificiales de flujo subsuperficial para postramiento de aguas residuales de la industria textil. Jovenes Cienc. 2015, 1, 1427–1431. Available online: https://www.jovenesenlaciencia.ugto.mx/index.php/jovenesenlaciencia/article/view/98 (accessed on 9 July 2025). (In Spanish).
- Manzano, E.; Hernández-Vásquez, L.A.; Alvarado-Lassman, A.; Sánchez-Valera, O.; Hernández-Salina, G. Zingiber spectabile en humedales artificiales para el tratamiento de aguas residuales y su uso en la agricultura. Cienc. Tecn. Agrop. Mex. 2022, 10, 84–92. Available online: http://www.somecta.org.mx/wp-content/uploads/2022/12/11-Spectabili-tratamiento-agua.pdf (accessed on 9 July 2025). (In Spanish).
- Nani, G.; Sandoval-Herazo, M.; Martínez-Reséndiz, G.; Marín-Pena, O.; Zurita, F.; Sandoval Herazo, L.C. Influence of Bed Depth on the Development of Tropical Ornamental Plants in Subsurface Flow Treatment Wetlands for Municipal Wastewater Treatment: A Pilot-Scale Case. Plants 2024, 13, 1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tejeda, A.; Zurita, F. Capacity of two ornamental species (Iris sibrica and Zantedeschia aethiopica) to take up, translocate, and accumulate carbamazepine under hydroponic conditions. Water 2020, 12, 1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartucca, M.L.; Cerri, M.; Forni, C. Phytoremediation of Pollutants: Applicability and Future Perspective. Plants 2023, 12, 2462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marín-Muñiz, J.L. Humedales Construidos: Un Caso de Éxito en Palmas de Abajo, Actopan, Veracruz, [Virtual Conference]; Secretaría de Finanzas y Planeación del Estado de Veracruz y secretaría de Medio Ambiente: “Conferencias sobre Medio Ambiente” Heroica Veracruz, Mexico, 2025. (In Spanish)
- Lomeli, J.S.; Zamora-Castro, S.A.; Zamora-Lobato, T.; Sandoval-Herazo, E.J.; Adame-Garcia, J.; Zurita, F.; Monroy-Pineda, M.C.; Aguilar-Cortes, G.; Rivera, S.; Sandoval-Herazo, M. Performance of Large-Scale Ornamental Wetlands for Municipal Wastewater Treatment: A Case Study in a Polluted Estuary in the Gulf of Mexico. Sustainability 2025, 17, 2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandoval-Herazo, M.; Martínez-Reséndiz, G.; Fernández Echeverria, E.; Fernández-Lambert, G.; Sandoval Herazo, L.C. Plant Biomass Production in Constructed Wetlands Treating Swine Wastewater in Tropical Climates. Fermentation 2021, 7, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monzon-Reyes, B.L.; Gonzalez-Moreno, H.R.; Month, A.E.A.; Peralta Vega, A.J.; Ballut-Dajud, G.; Sandoval Herazo, L.C. Wastewater Management Strategies in Rural Communities Using Constructed Wetlands: The Role of Community Participation. Earth 2025, 6, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandoval, L.C.; Marín-Muniz, L.C.; Alvarado-Lassman, A.; Zurita, F.; Marín-Peña, O.; Sandoval-Herazo, M. Full-scale constructed wetlands planted with ornamental species and pet as a substitute for filter media for municipal wastewater treatment: An experience in a Mexican community. Water 2023, 15, 2280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luna-Pabello, V.M.; Aburto-Castañeda, S. Sistema de humedales artificiales para el control de la eutroficación del lago del Bosque de San Juan de Aragón. TIP Rev. Esp. Cienc. Quím-Biol. 2014, 17, 32–55. Available online: https://www.scielo.org.mx/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S1405-888X2014000100003 (accessed on 2 May 2025). (In Spanish). [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Rivas, A.; Barceló-Quintal, I.; Moeller, G.E. Pollutant removal in a multi-stage municipal wastewater treatment system comprised of constructed wetlands and a maturation pond, in a temperate climate. Water Sci. Technol. 2011, 64, 980–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramírez-Carrillo, H.F.; Luna-Pabello, V.M.; Arredondo-Figueroa, J.L. Evaluación de un humedal artificial de flujo vertical intermitente, para obtener agua de buena calidad para la acuicultura. Rev. Mex. Ing. Quím 2009, 8, 93–99. Available online: https://www.scielo.org.mx/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S1665-27382009000100009 (accessed on 1 May 2025). (In Spanish).
- Barceló, I.D.; Rivas, A.; Solís, H.E.; García, J.; Salazar, M.; Giacomán, G.; Zetina, C. Comportamiento de un sistema humedal-laguna de maduración-humedal de pulimento a nivel piloto para el tratamiento de aguas municipales en la Universidad Autónoma Metropolitana de la unidad Azcapotzalco en la Cd. de México, México. In Book of Abstracts II Panamerican Conference of Wetland Systems for Treatment and Improvement of Water Quality; Hupanam: Morelia, México, 2014; pp. 55–58. Available online: https://hupanam.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/04/Memorias-II-Conferencia-Mexico.pdf (accessed on 1 June 2024). (In Spanish)
- González, C.E.; Rivas, A. Humedales artificiales para el tratamiento de las aguas residuales generadas en áreas rurales ribereñas al lago de Pátzcuaro. Tláloc 2008, 41, 8–13. Available online: https://amh.org.mx/wp-content/uploads/2024/10/TLALOC_41.pdf (accessed on 5 June 2022). (In Spanish).
- Lango, F.; Castañeda, M. Humedal Artificial para Tratamiento de Aguas Residuales del Instituto Tecnológico de Boca del Río: Escalamiento. Informe. 2016. Available online: https://www.aguanet.com.mx/foro21/resumenes/ResumenExt2_3_Lango.pdf (accessed on 2 March 2025). (In Spanish).
- Orozco, C.; Cruz, A.; Rodríguez, M.; Pohlan, A. Humedal subsuperficial de flujo vertical como sistema de depuración terciaria en el proceso de beneficiado de café. Hig. Sanid. Ambient. 2006, 6, 190–196. Available online: https://saludpublica.ugr.es/sites/dpto/spublica/public/inline-files/bc51015a2fc8ef6_Hig.Sanid_.Ambient.6.190-196(2006).pdf (accessed on 1 May 2025). (In Spanish).
- Sánchez-Chávez, J.; Bravo-Inclán, L.; Tomasini-Ortiz, C.; González-Villela, R.; Rivas-Hedez, A. Evolución de humedales de tratamiento en comunidades ribereñas del lago de Pátzcuaro (2006–2011). In Book of Abstracts III Panamerican Conference of Wetland Systems for Treatment and Improvement of Water Quality; Hupanam: Santa Fe, Argentina, 2016; Available online: https://hupanam.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/04/Memorias-III-Conferencia-Argentina.pdf (accessed on 20 February 2025). (In Spanish)
- Liu, T.; Li, D.; Tian, Y.; Zhou, J.; Qiu, Y.; Li, D.; Liu, G.; Feng, Y. Enhancing nitrogen removal in constructed wetlands: The role of influent substrate concentrations in integrated vertical-flow systems. Environ. Sci. Ecotech 2024, 21, 100411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Jin, X.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, M.; Wang, H.; Jia, Q.; Yang, Y. Thecnical structure and influencing factors of nitrogen and phosphorus removal in constructed wetlands. Water Sci. Technol. 2024, 89, 271–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; He, S.; Wu, S.; Huang, J.; Zhou, W.; Chen, W. Effects of HRT and water temperature on nitrogen removal in autotrophic gravel filter. Chemosphere 2016, 147, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Liu, M.; Zhou, J.; Chen, L.; Cai, M. Adsorption performance of different wetland substrates for ammonia nitrogen: An experimental study. Water 2024, 16, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borin, M.; Milani, M.; Salvato, M.; Toscano, A. Evaluation of Phragmites australis (Cav.) Trin. evapotranspiration in Northern and Southern Italy. Ecol. Eng. 2011, 37, 721–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milani, M.; Marzo, A.; Toscano, A.; Consoli, S.; Cirelli, G.; Ventura, D.; Barbagallo, S. Evapotranspiration from horizontal subsurface flow constructed wetlands planted with different perennial plant species. Water 2019, 11, 2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beebe, D.; Castle, J.; Molz, F.J.; Rodgers, J. Effects of evapotranspration on treatment performance in constructed wetlands: Experimental studies and modeling. Ecol. Eng. 2014, 71, 394–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Mo, Y.; Gu, X.; Jeppesen, E.; Xie, T.; Ning, Z.; Li, Y.; Chen, C.; Cui, B.; Wu, H. Sustainability of global small-scale constructed wetlands for multiple pollutant control. npj Clean. Water 2024, 7, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores, P.; López, C. Government management of information technlogy in the Latin American context. Salud Cienc. Tecnol. 2024, 3, 682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuel, W.; Richard, B.; Nyantakyi, J.A. Phytoremediation of heavy metals contaminated water and soils from artisanal mining enclave using Heliconia psittacorum. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2022, 8, 591–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrugo-Negrete, J.; Enamorado-Montes, G.; Durango-Hernández, J.; Pinedo-Henrández, J.; Díez, S. Removal of mercury from gold mine effluents using Limnocharis flava in constructed wetlands. Chemosphere 2017, 167, 188–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quevedo, A. Diseño y construcción de humedal artificial para la recuperación de aguas residuales en la población de Alcalá. Rev. Cienc. Tecn. Innov. 2021, 19, 133–148. Available online: https://revistas.usfx.bo/index.php/rcti/article/view/476 (accessed on 2 May 2025). (In Spanish). [CrossRef]
- Zitácuaro, I.; Marín-Muñiz, J.L.; Álvarez-Hernández, L.M. La ciencia, el medio ambiente y la mujer. Colversatorio 2024, 6, 35–40. Available online: https://drive.google.com/file/d/1piFhx_bBFdR3Tal7fvONXp-fW_j9hWaS/view (accessed on 16 March 2025). (In Spanish).
- Flores, M.; Rello, F. Capital Social Rural Experiencias de México y Centroamérica; CEPAL: Santiago, Chile, 2002; Available online: https://www.cepal.org/es/publicaciones/1738-capital-social-rural-experiencias-mexico-centroamerica (accessed on 2 March 2025). (In Spanish)
- Putnam, R.D. The prosperous community. Am. Prospect. 1993, 4, 35–42. Available online: https://prospect.org/infrastructure/prosperous-community-social-capital-public-life/ (accessed on 11 March 2025).
- Bridger, J.C.; Luloff, A.E. Building the Sustainable Community: Is Social Capital the Answer? Sociol. Inq. 2001, 71, 458–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maldonado, G.; Voeks, R. The Paradox of Culturally Useful Invasive Species: Southern Cattail (Typha domingensis) Crafts of Lake Pátzcuaro, Mexico. J. Lat. Am. Geog 2021, 20, 148–174. Available online: https://www.jstor.org/stable/48650405 (accessed on 10 July 2025). [CrossRef]
- Domínguez-Solís, D.; Martínez-Rodríguez, M.C.; Ramírez Escamilla, H.G.; Campos-Villegas, L.E.; Domínguez-Solís, R. Constructed WetlandsasaDecentralizedTreatment OptionforDomesticWastewater: A Systematic Review (2015–2024). Water 2025, 17, 1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorgoglione, A.; Torretta, V. Sustainable management and successful application of constructed wetlands: A critical review. Sustainability 2018, 10, 3910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masoud, A.M.N.; Alfarra, A.; Sorlini, S. Constructed Wetlands as a Solution for Sustainable Sanitation: A Comprehensive Review on Integrating Climate Change Resilience and Circular Economy. Water 2022, 14, 3232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allub, L. Aversión al riesgo y adopción de innovaciones tecnológicas en pequeños productores rurales de zonas áridas: Un enfoque causal. Estud. Sociológicos 2001, 19, 467–493. Available online: https://dialnet.unirioja.es/servlet/articulo?codigo=4469899 (accessed on 7 September 2025). (In Spanish).
- Operacz, A.; Jóźwiakowski, K.; Rodziewicz, J.; Janczukowicz, W.; Bugajski, P. Impact of climate conditions on pollutant concentrations in the effluent from a one-stage constructed wetland: A case study. Sustainability 2023, 15, 13173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knight, R.; Walton, W.; O´Meara, G.; Reisen, W.; Wass, R. Strategies for effective mosquito control in constructed wetlands. Ecol. Eng. 2003, 21, 211–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wangm, H.; Sheng, L.; Xu, J. Clogging mechanisms of constructed wetlands: A critical review. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 295, 126455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waly, M.M.; Mickovski, S.B.; Thomson, C.; Amadi, K. Impact of implementing constructed wetlands on supporting the sustainable development goals. Land 2022, 11, 1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seifollahi-Aghmiuni, S.; Nockrach, M.; Kalantari, Z. The potential of wetlands in achieving the sustainable development goals of the 2030 agenda. Water 2019, 11, 609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez-Crespo, C.; Oliver, N.; Gil-Martinez, E.; Ano, M.; Fernandez-Alba, S.; Benedito, V.; Montoya, T.; Martin, M. Integrating circular economy and biodiversity in upgrading full-scale constructed wetlands (LIFE Renaturwat). Ecol. Eng. 2024, 204, 107263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Campos, S.X.; Soto, M. The Use of Constructed wetlands to treat effluents for water reuse. Environments 2024, 11, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).