Monitoring and Future Prediction of Land Use Land Cover Dynamics in Northern Bangladesh Using Remote Sensing and CA-ANN Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
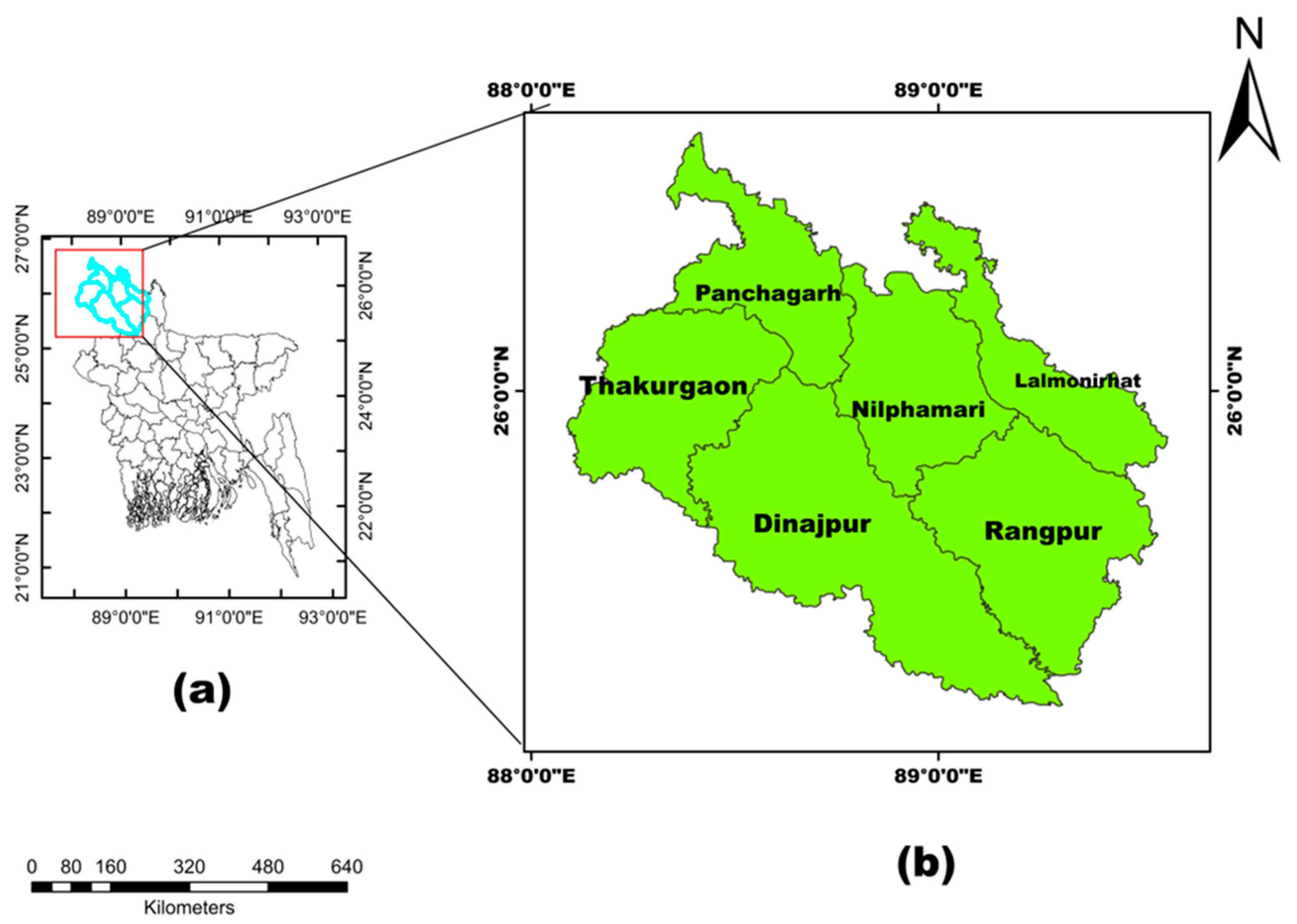
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Satellite Data Acquisition
2.3. Data Pre-Processing
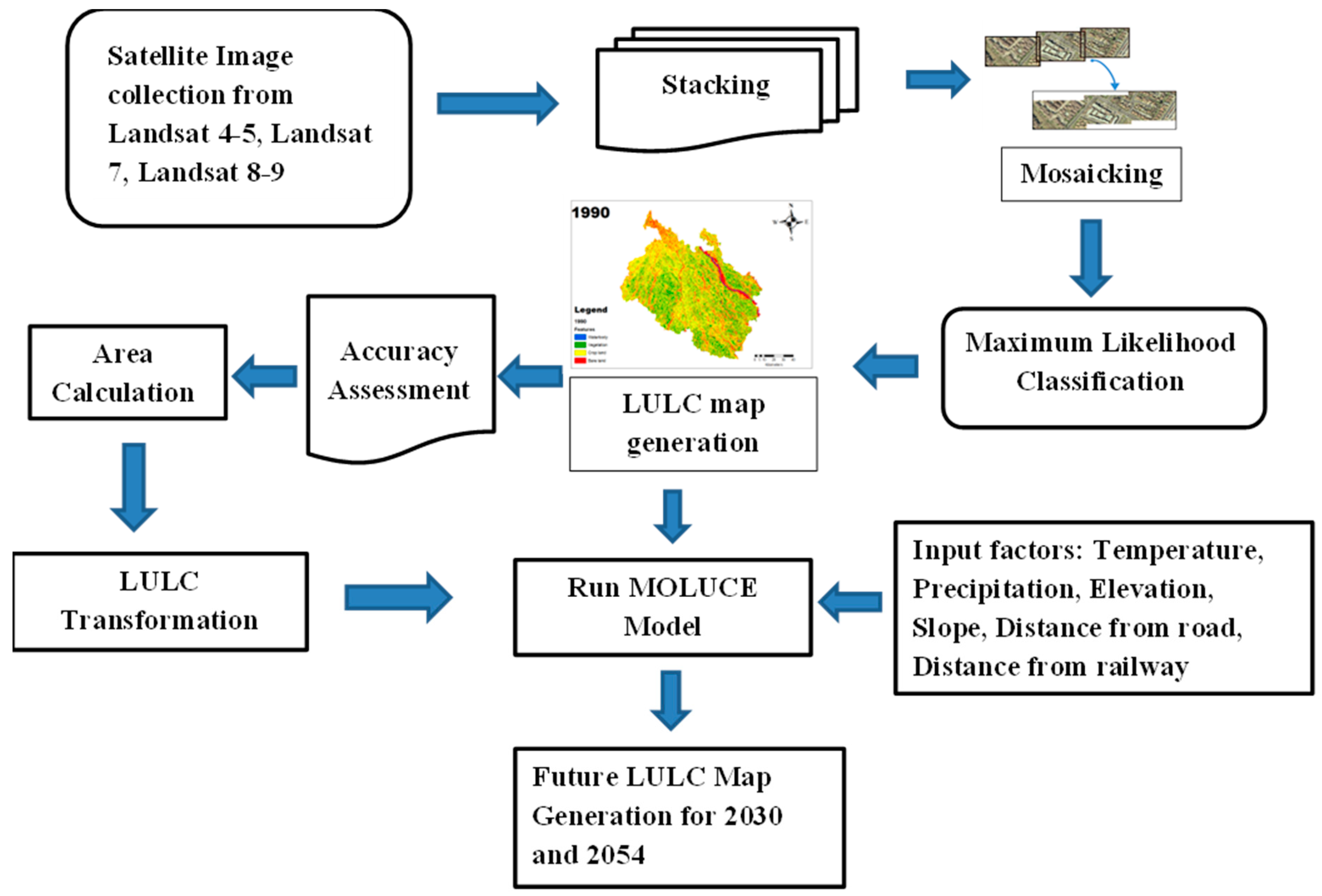
2.4. Data Processing
2.5. LULC Classification
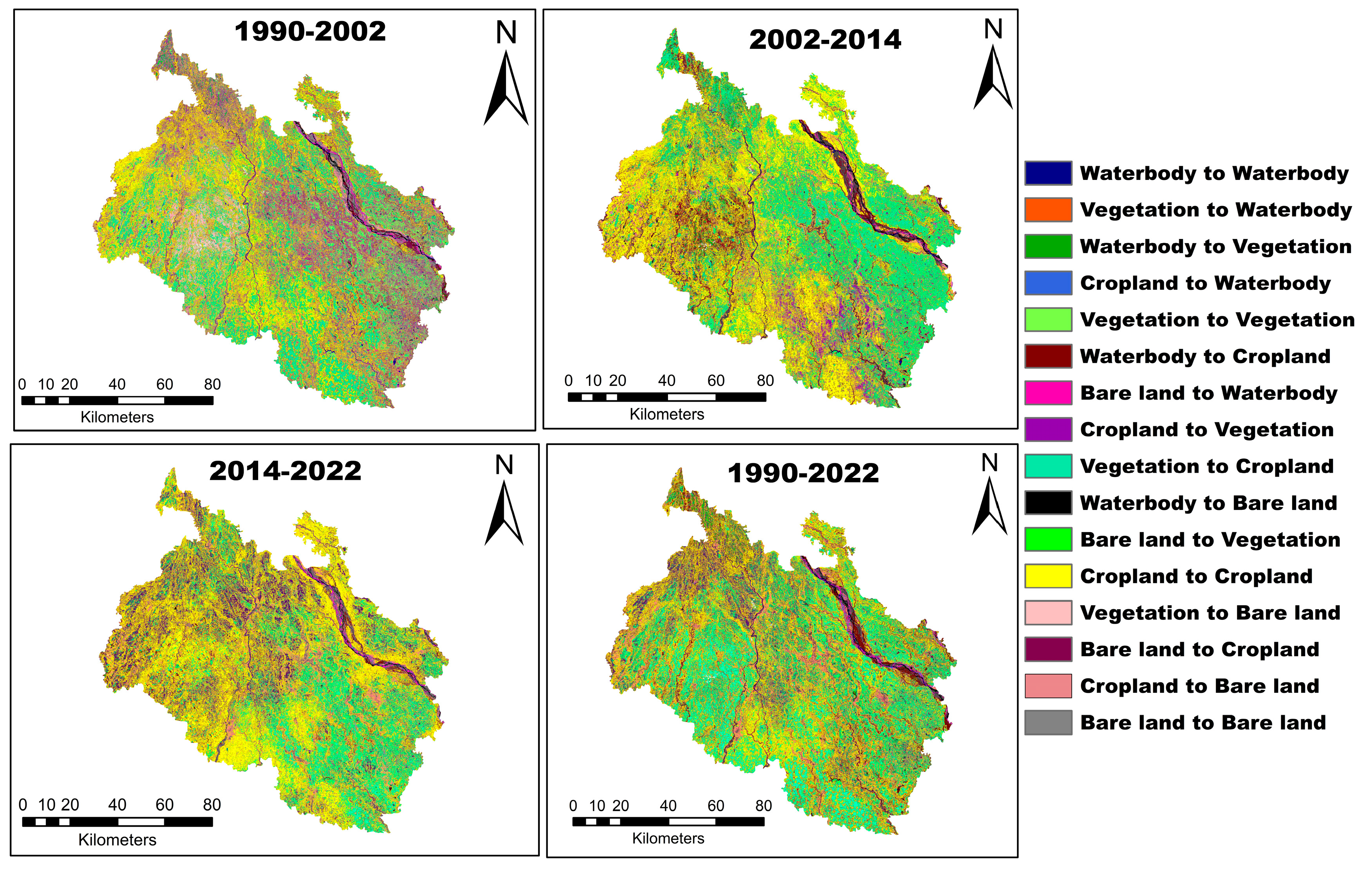
2.6. Detecting LULC Changes Using QGIS
2.7. Computation Method for Transition Matrices and Dynamic Degrees
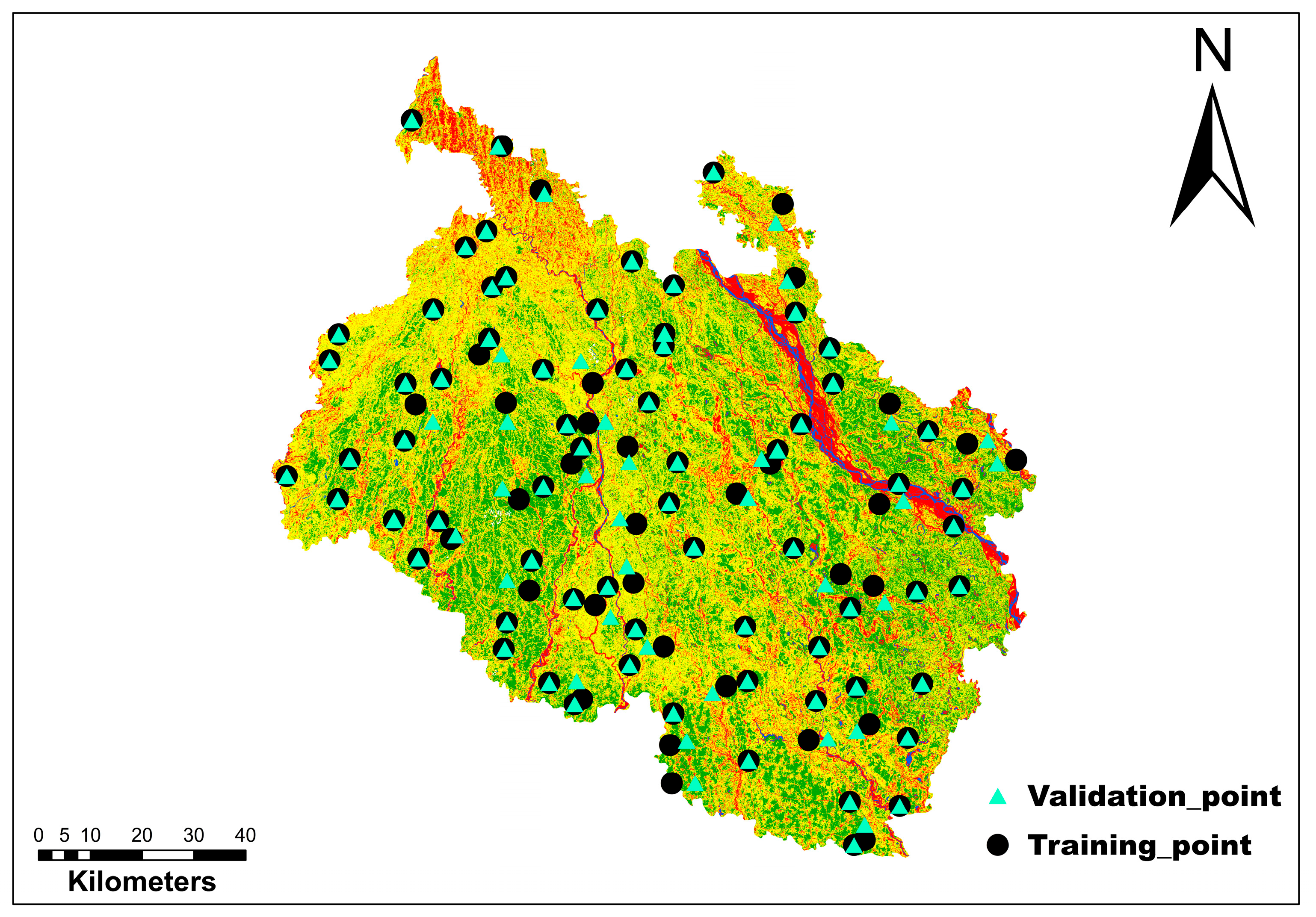
2.8. Methods of Accuracy Assessment
2.9. Modeling Future LULC Changes
2.9.1. Change Evaluation and Modeling Transition Potential
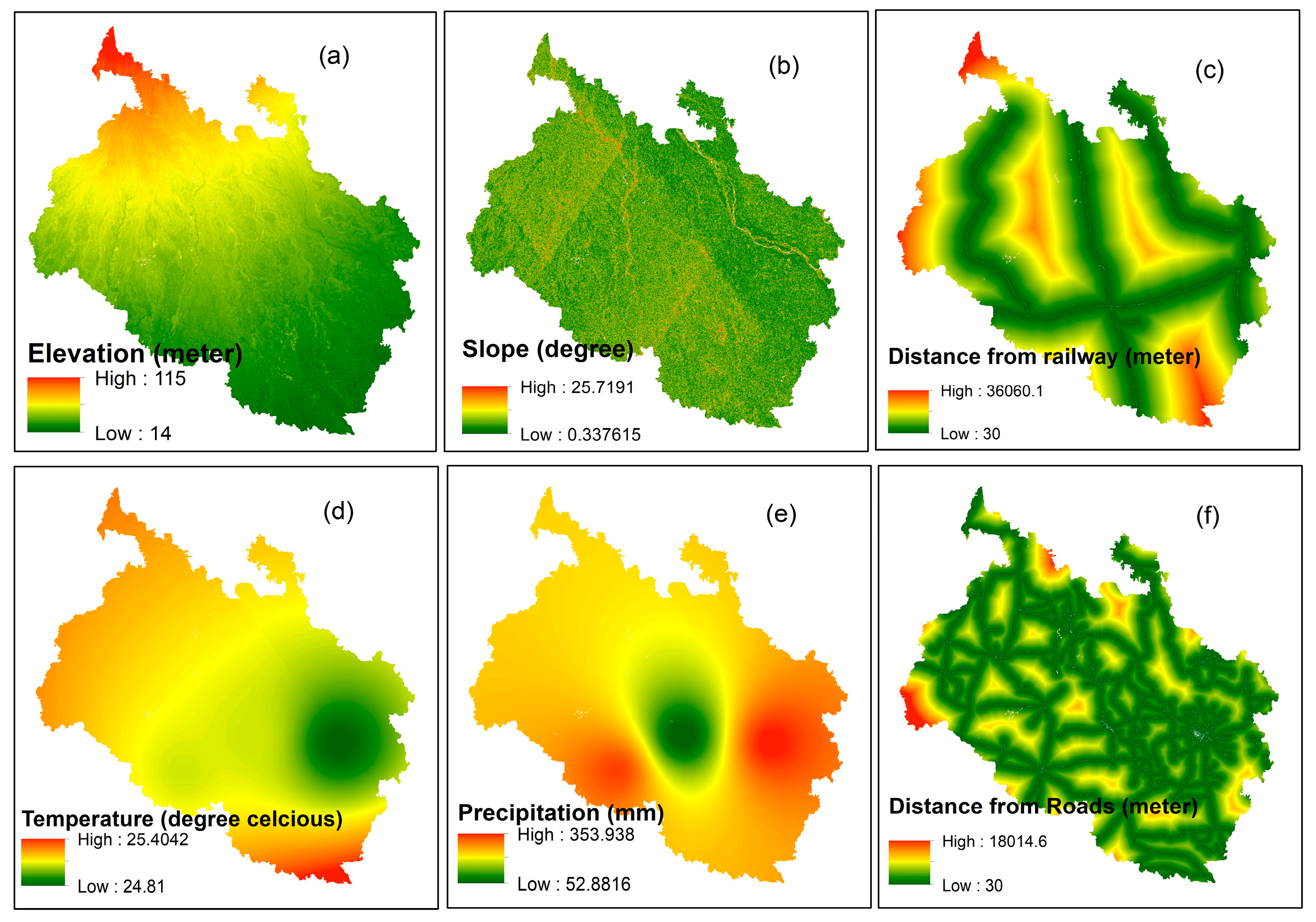
2.9.2. Spatial Variables for Future LULC Prediction
2.9.3. Modeling Future LULC Transitions Using Binary Logistic Regression
3. Results
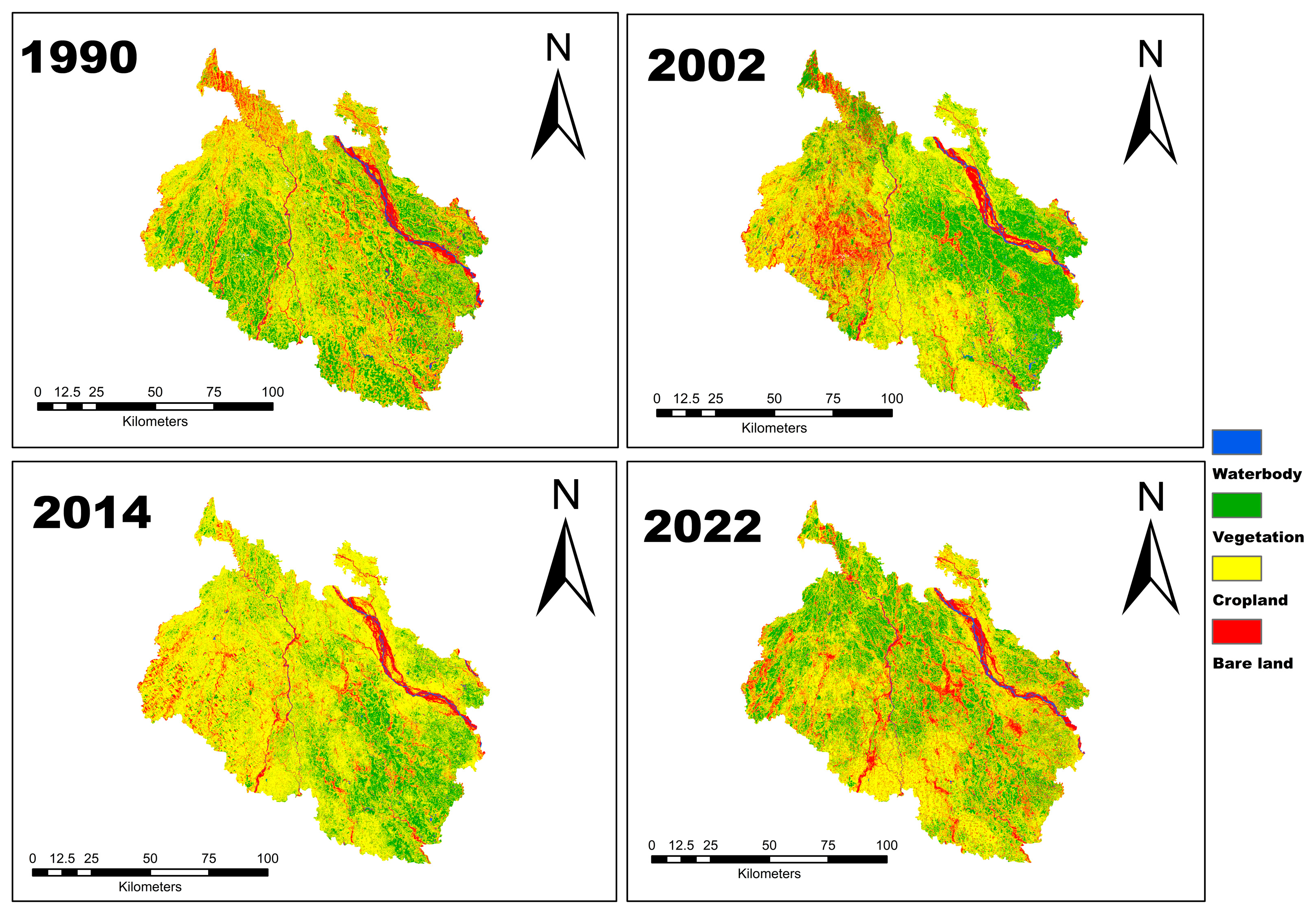
3.1. Land Use/Land Cover Dynamics in Northern Bangladesh During Different Time Periods
3.1.1. Waterbody
3.1.2. Vegetation
3.1.3. Cropland
3.1.4. Bare Land
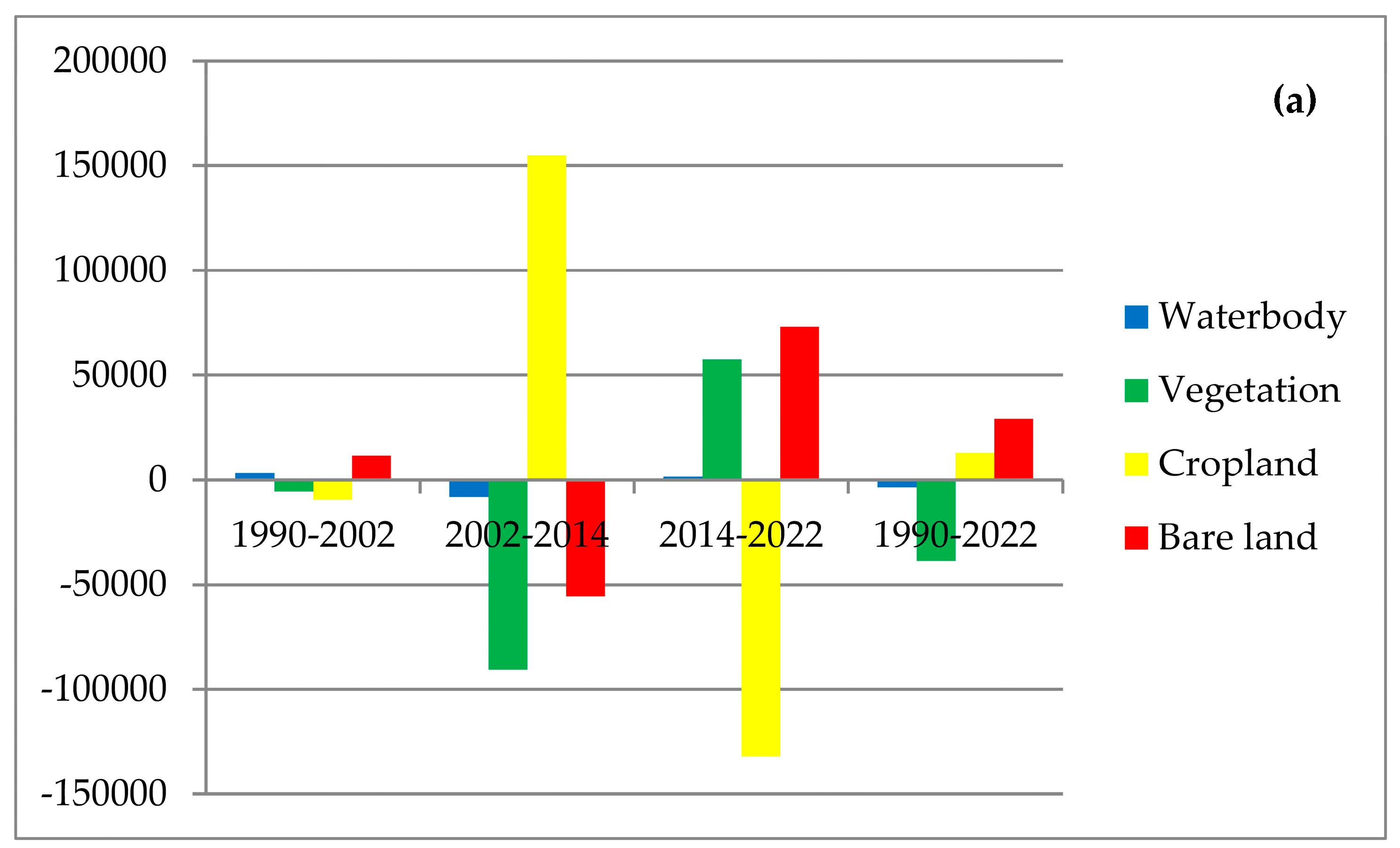
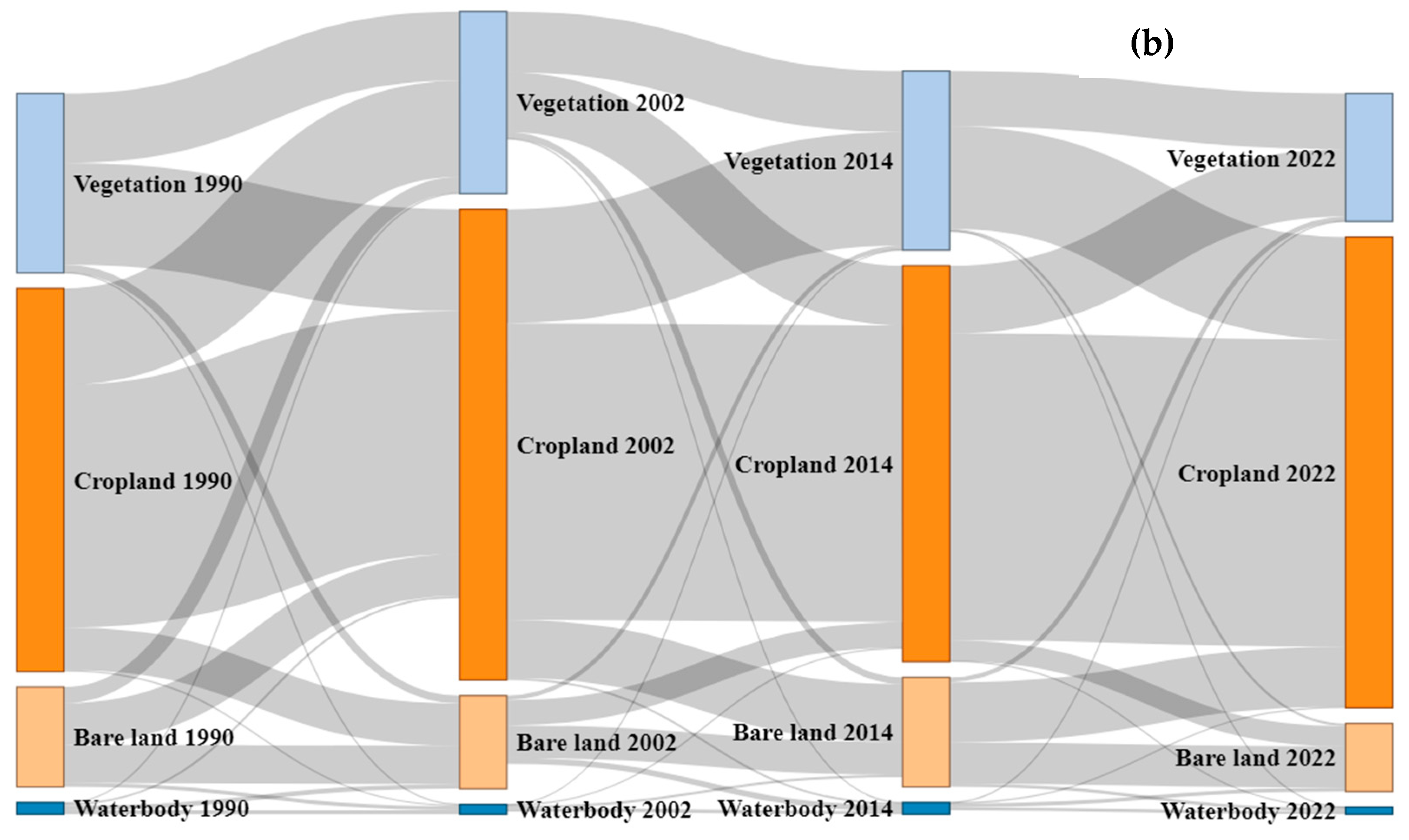
3.2. LULC Change from 1990 to 2022 in Northern Bangladesh
3.3. Dynamic Degrees of LULC Change
3.4. LULC Classification Accuracy
3.5. Future Prediction of LULC in Northern Bangladesh
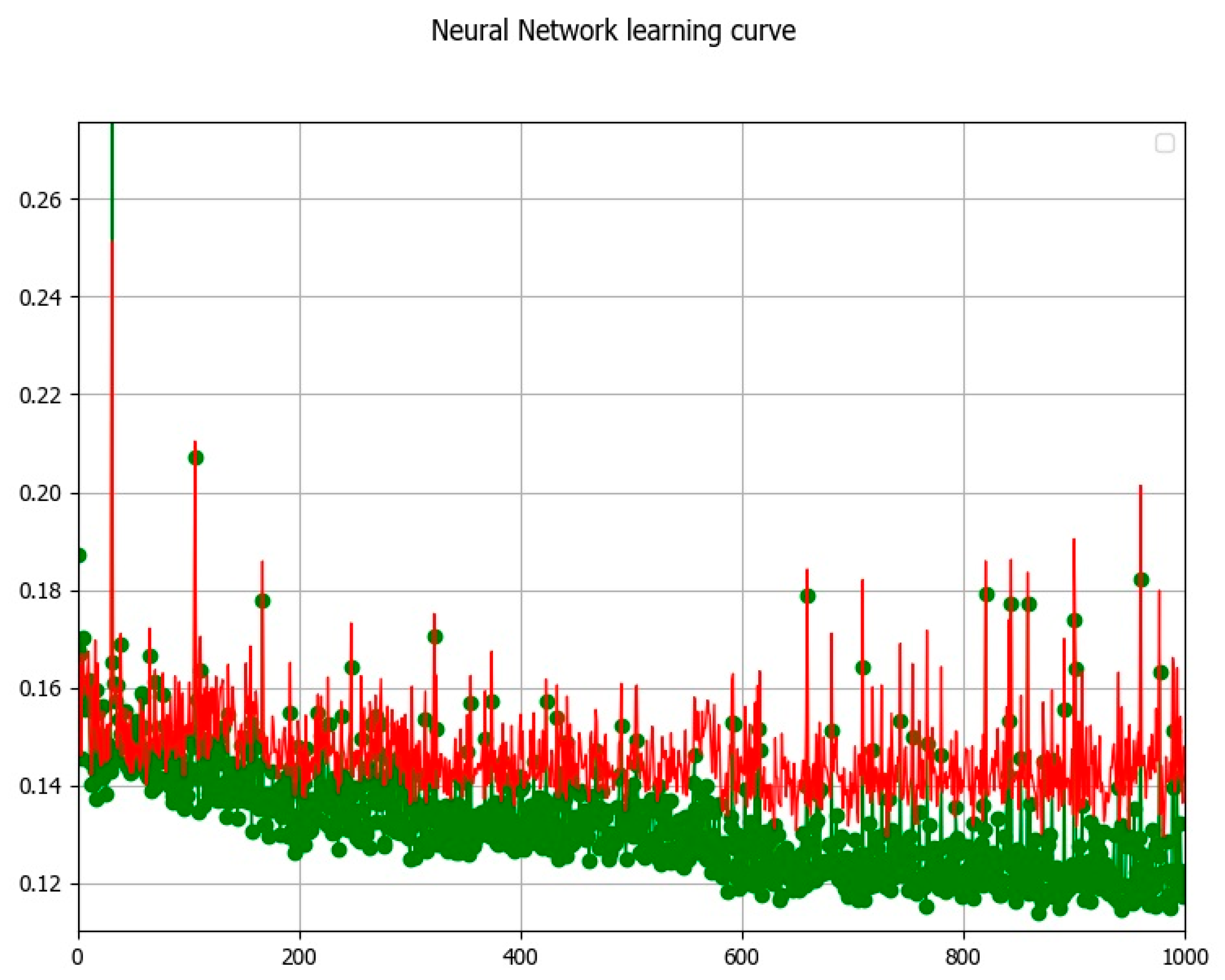
3.5.1. LULC Change Simulation and Prediction Using the CA-ANN Model
3.5.2. LULC Prediction
3.5.3. Projected LULC Transitions and Associated Driving Forces
4. Discussion
4.1. Historical Changes in LULC
4.2. Future Projection of LULC
4.3. Ecological Implications and Drivers of Projected LULC Transitions (2022–2054)
4.4. Model Performance and Future Perspectives
4.5. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Seto, K.C.; Güneralp, B.; Hutyra, L.R. Global Forecasts of Urban Expansion to 2030 and Direct Impacts on Biodiversity and Carbon Pools. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 16083–16088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halmy, M.W.A.; Gessler, P.E.; Hicke, J.A.; Salem, B.B. Land Use/Land Cover Change Detection and Prediction in the North-Western Coastal Desert of Egypt Using Markov-CA. Appl. Geogr. 2015, 63, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.W.; Shen, G.Q.; Wang, H.; Hong, J. Simulating Land Use Change in Urban Renewal Areas: A Case Study in Hong Kong. Habitat Int. 2015, 46, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, D.J.; Li, H.F.; Inohae, T.; Su, W.; Nagaie, T.; Hokao, K. Modeling Urban Land Use Change by the Integration of Cellular Automaton and Markov Model. Ecol. Modell. 2011, 222, 3761–3772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kindu, M.; Schneider, T.; Teketay, D.; Knoke, T. Drivers of Land Use/Land Cover Changes in Munessa-Shashemene Landscape of the South-Central Highlands of Ethiopia. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 187, 452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garedew, E.; Sandewall, M.; Söderberg, U.; Campbell, B.M. Land-Use and Land-Cover Dynamics in the Central Rift Valley of Ethiopia. Environ. Manag. 2009, 44, 683–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewan, A.M.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Rahman, M.Z. Dynamics of Land Use/Cover Changes and the Analysis of Landscape Fragmentation in Dhaka Metropolitan, Bangladesh. GeoJournal 2012, 77, 315–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Z.; Estes, L.; Ziegler, A.D.; Chen, A.; Searchinger, T.; Hua, F.; Guan, K.; Jintrawet, A.; Wood, E.F. Highland Cropland Expansion and Forest Loss in Southeast Asia in the Twenty-First Century. Nat. Geosci. 2018, 11, 556–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Z.; Gower, D.B.; Wood, E.F. Accelerating Forest Loss in Southeast Asian Massif in the 21st Century: A Case Study in Nan Province, Thailand. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2018, 24, 4682–4695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambin, E.F. Modelling and Monitoring Land-Cover Change Processes in Tropical Regions. Prog. Phys. Geogr. 1997, 21, 375–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, M.M.; Nazem, M.N.I. Examination of Land Use/Land Cover Changes, Urban Growth Dynamics, and Environmental Sustainability in Chittagong City, Bangladesh. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2016, 18, 697–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.H.; Manprasert, S. Landlessness and Its Impact on Economic Development: A Case Study on Bangladesh. J. Soc. Sci. 2006, 2, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hussain, K.; Mehmood, K.; Yujun, S.; Badshah, T.; Anees, S.A.; Shahzad, F.; Nooruddin; Ali, J.; Bilal, M. Analysing LULC Transformations Using Remote Sensing Data: Insights from a Multilayer Perceptron Neural Network Approach. Ann. GIS 2024, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panigrahi, S.; Verma, K.; Tripathi, P. Data Mining Algorithms for Land Cover Change Detection: A Review. Sadhana–Acad. Proc. Eng. Sci. 2017, 42, 2081–2097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaidi, S.M.; Akbari, A.; Samah, A.A.; Kong, N.S.; Gisen, J.I.A. Landsat-5 Time Series Analysis for Land Use/Land Cover Change Detection Using NDVI and Semi-Supervised Classification Techniques. Polish J. Environ. Stud. 2017, 26, 2833–2840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Li, B.; Yuan, Y.; Gao, X.; Zhang, T.; Sun, Q. Detecting Different Types of Directional Land Cover Changes Using MODIS NDVI Time Series Dataset. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahana, M.; Ahmed, R.; Sajjad, H. Analyzing Land Surface Temperature Distribution in Response to Land Use/Land Cover Change Using Split Window Algorithm and Spectral Radiance Model in Sundarban Biosphere Reserve, India. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2016, 2, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, B.F.; Ghazi, S.; Ahmad, S.R.; Ahmad, I.; Mansor, R.; Khan, A.; Raoof, A.; Khan, S.; Akmal, F.; Luqman, M.; et al. Spectral Characteristics and Mapping of Rice Fields Using Multi- Temporal Landsat and MODIS Data: A Case of District Narowal. Glob. J. Hum.-Soc. Sci. 2014, 14, 35–60. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, M.; Cao, C.; Zhang, H.; Guo, J.; Nakane, K.; He, Q.; Guo, J.; Chang, C.; Bao, Y.; Gao, M.; et al. Change Detection of an Earthquake-Induced Barrier Lake Based on Remote Sensing Image Classification. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2010, 31, 3521–3534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forkel, M.; Carvalhais, N.; Verbesselt, J.; Mahecha, M.D.; Neigh, C.S.R.; Reichstein, M. Trend Change Detection in NDVI Time Series: Effects of Inter-Annual Variability and Methodology. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 2113–2144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Liu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Wu, J.; Han, Y. Trend Analysis of Vegetation Dynamics in Qinghai-Tibet Plateau Using Hurst Exponent. Ecol. Indic. 2012, 14, 28–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Liu, Y.; Shen, H.; Han, Y.; Pan, Y. Vegetation Coverage Change and Associated Driving Forces in Mountain Areas of Northwestern Yunnan, China Using RS and GIS. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2012, 184, 4787–4798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rimal, B.; Rijal, S.; Kunwar, R. Comparing Support Vector Machines and Maximum Likelihood Classifiers for Mapping of Urbanization. J. Indian Soc. Remote Sens. 2020, 48, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Abd-Elrahman, A. An Object-Based Image Analysis Method for Enhancing Classification of Land Covers Using Fully Convolutional Networks and Multi-View Images of Small Unmanned Aerial System. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.K.; Singh, P.; Drews, M.; Kumar, P.; Singh, H.; Gupta, A.K.; Govil, H.; Kaur, A.; Kumar, M. A Machine Learning-Based Classification of LANDSAT Images to Map Land Use and Land Cover of India. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2021, 24, 100624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imran, H.M.; Hossain, A.; Islam, A.K.M.S.; Rahman, A.; Bhuiyan, M.A.E.; Paul, S.; Alam, A. Impact of Land Cover Changes on Land Surface Temperature and Human Thermal Comfort in Dhaka City of Bangladesh. Earth Syst. Environ. 2021, 5, 667–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.K.; Mojumder, P.; Chowdhury, M.A.A.; Hasan, M.M. Evaluating Mangrove Forest Dynamics and Fragmentation in Sundarbans, Bangladesh Using High-Resolution Sentinel-2 Satellite Images. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2025, 58, e03493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, S.; Qiao, X.; Abbas, M. Addressing the Impact of Land Use Land Cover Changes on Land Surface Temperature Using Machine Learning Algorithms. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 18746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Raza, A.; Syed, N.R.; Acharki, S.; Ray, R.L.; Hussain, S.; Dehghanisanij, H.; Zubair, M.; Elbeltagi, A. Land Use/Land Cover Change Detection and NDVI Estimation in Pakistan’s Southern Punjab Province. Sustainability 2023, 15, 3572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Shrestha, S.; Gilani, H.; Gumma, M.K.; Siddiqui, B.N.; Jain, A.K. Dynamics and Drivers of Land Use and Land Cover Changes in Bangladesh. Reg. Environ. Chang. 2020, 20, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barakat, A.; Ouargaf, Z.; Khellouk, R.; El Jazouli, A.; Touhami, F. Land Use/Land Cover Change and Environmental Impact Assessment in Béni-Mellal District (Morocco) Using Remote Sensing and GIS. Earth Syst. Environ. 2019, 3, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdavi, S.; Salehi, B.; Granger, J.; Amani, M.; Brisco, B.; Huang, W. Remote Sensing for Wetland Classification: A Comprehensive Review. GIScience Remote Sens. 2018, 55, 623–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Li, J.; Sheng, C.; Xu, J.; Wu, L. A Review of Wetland Remote Sensing. Sensors 2017, 17, 777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alqurashi, A.F.; Kumar, L. Investigating the Use of Remote Sensing and GIS Techniques to Detect Land Use and Land Cover Change: A Review. Adv. Remote Sens. 2013, 2, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, S.; Mubeen, M.; Akram, W.; Ahmad, A.; Habib-ur-Rahman, M.; Ghaffar, A.; Amin, A.; Awais, M.; Farid, H.U.; Farooq, A.; et al. Study of Land Cover/Land Use Changes Using RS and GIS: A Case Study of Multan District, Pakistan. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, X.; Zhai, Z.; Fan, C.; Ding, Y.; Ye, L.; Li, J. Modelling Future Land Use Land Cover Changes and Their Impacts on Urban Heat Island Intensity in Guangzhou, China. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 366, 121787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taiwo, B.E.; Kafy, A.-A.; Samuel, A.A.; Rahaman, Z.A.; Ayowole, O.E.; Shahrier, M.; Duti, B.M.; Rahman, M.T.; Peter, O.T.; Abosede, O.O. Monitoring and Predicting the Influences of Land Use/Land Cover Change on Cropland Characteristics and Drought Severity Using Remote Sensing Techniques. Environ. Sustain. Indic. 2023, 18, 100248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elagouz, M.H.; Abou-Shleel, S.M.; Belal, A.A.; El-Mohandes, M.A.O. Detection of Land Use/Cover Change in Egyptian Nile Delta Using Remote Sensing. Egypt. J. Remote Sens. Sp. Sci. 2020, 23, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, M.M. Monitoring Land Use/Land Cover Change, Urban Growth Dynamics and Landscape Pattern Analysis in Five Fastest Urbanized Cities in Bangladesh. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2017, 7, 69–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sewnet, A. Land Use/Cover Change at Infraz Watershed by Using GIS and Remote Sensing Techniques, Northwestern Ethiopia. Int. J. River Basin Manag. 2016, 14, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahaman, S. Impacts of Future Land Use/Land Cover (LULC) and Climate Change on Runoff of the Teesta Basin. Master’s Thesis, Bangladesh University of Engineering and Technology (BUET), Dhaka, Bangladesh, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Blissag, B.; Yebdri, D.; Kessar, C. Spatiotemporal Change Analysis of LULC Using Remote Sensing and CA-ANN Approach in the Hodna Basin, NE of Algeria. Phys. Chem. Earth 2024, 133, 103535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kafy, A.A.; Naim, M.N.H.; Subramanyam, G.; Al Faisal, A.; Ahmed, N.U.; Rakib, A.A.; Kona, M.A.; Sattar, G.S. Cellular Automata Approach in Dynamic Modelling of Land Cover Changes Using RapidEye Images in Dhaka, Bangladesh. Environ. Challenges 2021, 4, 100084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Li, W. Multiple Land Use Change Simulation with Monte Carlo Approach and CA-ANN Model, a Case Study in Shenzhen, China. Environ. Syst. Res. 2015, 4, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, R.; Zhang, W.; Abbas, Z.; Guo, F.; Gwiazdzinski, L. Spatiotemporal Change Analysis and Prediction of Future Land Use and Land Cover Changes Using QGIS MOLUSCE Plugin and Remote Sensing Big Data: A Case Study of Linyi, China. Land 2022, 11, 419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alipbeki, O.; Alipbekova, C.; Mussaif, G.; Grossul, P.; Zhenshan, D.; Muzyka, O.; Turekeldiyeva, R.; Yelubayev, D.; Rakhimov, D.; Kupidura, P.; et al. Analysis and Prediction of Land Use/Land Cover Changes in Korgalzhyn District, Kazakhstan. Agronomy 2024, 14, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziaul Hoque, M.; Islam, I.; Ahmed, M.; Shamim Hasan, S.; Ahmed Prodhan, F. Spatio-Temporal Changes of Land Use Land Cover and Ecosystem Service Values in Coastal Bangladesh. Egypt. J. Remote Sens. Space Sci. 2022, 25, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, K.F.; Ahamed, T. Assessment of Land Use Land Cover Changes for Predicting Vulnerable Agricultural Lands in River Basins of Bangladesh Using Remote Sensing and a Fuzzy Expert System. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharjee, S.; Islam, M.T.; Kabir, M.E.; Kabir, M.M. Land-Use and Land-Cover Change Detection in a North-Eastern Wetland Ecosystem of Bangladesh Using Remote Sensing and GIS Techniques. Earth Syst. Environ. 2021, 5, 319–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, A.Y.M.; Masrur, A.; Gani Adnan, M.S.; Al Baky, M.A.; Hassan, Q.K.; Dewan, A. Spatio-Temporal Patterns of Land Use/Land Cover Change in the Heterogeneous Coastal Region of Bangladesh between 1990 and 2017. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.T.U.; Tabassum, F.; Rasheduzzaman, M.; Saba, H.; Sarkar, L.; Ferdous, J.; Uddin, S.Z.; Zahedul Islam, A.Z.M. Temporal Dynamics of Land Use/Land Cover Change and Its Prediction Using CA-ANN Model for Southwestern Coastal Bangladesh. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2017, 189, 565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewan, A.M.; Yamaguchi, Y. Using Remote Sensing and GIS to Detect and Monitor Land Use and Land Cover Change in Dhaka Metropolitan of Bangladesh during 1960-2005. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2009, 150, 237–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, S.S.; Deng, X.; Li, Z.; Chen, D. Projections of Future Land Use in Bangladesh under the Background of Baseline, Ecological Protection and Economic Development. Sustainability 2017, 9, 505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, A.; Bhat, M.S.; Maheen, M. Using Landsat Satellite Data for Assessing the Land Use and Land Cover Change in Kashmir Valley. GeoJournal 2020, 85, 1529–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoque, M.Z.; Ahmed, M.; Islam, I.; Cui, S.; Xu, L.; Prodhan, F.A.; Ahmed, S.; Rahman, M.A.; Hasan, J. Monitoring Changes in Land Use Land Cover and Ecosystem Service Values of Dynamic Saltwater and Freshwater Systems in Coastal Bangladesh by Geospatial Techniques. Water 2022, 14, 2293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakma, M.; Hayat, U.; Meng, J.; Hassan, M.A. An Assessment of Landscape and Land Use/Cover Change and Its Implications for Sustainable Landscape Management in the Chittagong Hill Tracts, Bangladesh. Land 2023, 12, 1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasnahena; Sarker, S.C.; Islam, M.S.; Rahman, M.Z. The Rate and Pattern of the Spatio-Temporal Expansion of Rangpur City Corporation, Rangpur, Bangladesh. Curr. J. Appl. Sci. Technol. 2021, 40, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, B.; Bari, E.; Nipa, N.J.; Ani, S.A. Comparison of Temporal Changes in Urban Settlements and Land Surface Temperature in Rangpur and Gazipur Sadar, Bangladesh after the Establishment of City Corporation. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2021, 23, 100587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Kafy, A.; Rahman, M.S.; Faisal, A.A.; Hasan, M.M.; Islam, M. Modelling Future Land Use Land Cover Changes and Their Impacts on Land Surface Temperatures in Rajshahi, Bangladesh. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2020, 18, 100314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.N.; Saleheen, M.M.; Islam, A.R.M.T.; Sohel, M.S.; Islam, M.S. Assessing and Predicting the Dynamics of Land Use/Land Cover in Northern Bangladesh Using Cellular Automata-Markov Chain Model. Geol. Ecol. Landsc. 2024, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherif, K.; Yahia, N.; Bilal, B.; Bilal, B. Erosion Potential Model-Based ANN-MLP for the Spatiotemporal Modeling of Soil Erosion in Wadi Saida Watershed. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2023, 9, 3095–3117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razavi, B.S. Predicting the Trend of Land Use Changes Using Artificial Neural Network and Markov Chain Model (Case Study: Kermanshah City). Res. J. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 6, 215–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, X.; Kuang, W.; Zhou, W.; Zhang, S.; Li, R.; Yan, C.; Yu, D.; Wu, S.; et al. Spatial Patterns and Driving Forces of Land Use Change in China during the Early 21st Century. J. Geogr. Sci. 2010, 20, 483–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nath, B.; Wang, Z.; Ge, Y.; Islam, K.; Singh, R.P.; Niu, Z. Land Use and Land Cover Change Modeling and Future Potential Landscape Risk Assessment Using Markov-CA Model and Analytical Hierarchy Process. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2020, 9, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giri, C. Observation and Monitoring of Mangrove Forests Using Remote Sensing: Opportunities and Challenges. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, N.T.; Chen, C.F.; Chang, N.B.; Chen, C.R.; Chang, L.Y.; Thanh, B.X. Mangrove Mapping and Change Detection in ca Mau Peninsula, Vietnam, Using Landsat Data and Object-Based Image Analysis. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2015, 8, 503–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Liu, M.; Zhuang, D.; Zhang, Z.; Deng, X. Study on Spatial Pattern of Land-Use Change in China during 1995–2000. Sci. China, Ser. D Earth Sci. 2003, 46, 373–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nath, B.; Niu, Z.; Singh, R.P. Land Use and Land Cover Changes, and Environment and Risk Evaluation of Dujiangyan City (SW China) Using Remote Sensing and GIS Techniques. Sustainability 2018, 10, 4631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waghela, H.; Patel, S.; Sudesan, P.; Raorane, S.; Borgalli, R. Land Use Land Cover Classification Using Machine Learning. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Conference on Automation, Computing and Renewable Systems (ICACRS), Pudukkottai, India, 13–15 December 2022; pp. 708–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunathilaka, M.D.K.L.; Fernando, S.L.J. Accuracy Assessment of Unsupervised Land Use and Land Cover Classification Using Remote Sensing and Geographical Information Systems. Int. J. Environ. Eng. Educ. 2022, 4, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saini, R.; Rawat, S. Land Use Land Cover Classification in Remote Sensing Using Machine Learning Techniques. In Proceedings of the 2023 1st International Conference on Innovations in High Speed Communication and Signal Processing (IHCSP), Bhopal, India, 4–5 March 2023; pp. 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jogun, T.; Lukić, A.; Gašparović, M. Simulation Model of Land Cover Changes in a Post-Socialist Peripheral Rural Area: Požega-Slavonia County, Croatia. Hrvat. Geogr. Glas. 2019, 81, 31–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Cheng, D.; Iqbal, J.; Yao, S. Spatiotemporal Change Analysis and Prediction of the Great Yellow River Region (GYRR) Land Cover and the Relationship Analysis with Mountain Hazardss. Land 2023, 12, 340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mogonong, B.P.; Twine, W.; Feig, G.T.; Van der Merwe, H.; Fisher, J.T. Influences of Climate Variability on Land Use and Land Cover Change in Rural South Africa. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukas, P.; Melesse, A.M.; Kenea, T.T. Prediction of Future Land Use/Land Cover Changes Using a Coupled CA-ANN Model in the Upper Omo–Gibe River Basin, Ethiopia. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saputra, M.H.; Lee, H.S. Prediction of Land Use and Land Cover Changes for North Sumatra, Indonesia, Using an Artificial-Neural-Network-Based Cellular Automaton. Sustainability 2019, 11, 3024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saini, R.; Ghosh, S.K. Crop Classification on Single Date Sentinel-2 Imagery Using Random Forest and Suppor Vector Machine. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2018, XLII–5, 683–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiye, F.S.; Korecha, D.; Gutema, T.M.; Gemeda, D.O. Modeling Land Use and Land Cover Dynamics of Bale Mountains National Park Using Google Earth Engine and Cellular Automata–Artificial Neural Network (CA-ANN) Model. PLoS ONE 2025, 20, e0320428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carson, A.; Parmer, C.; Hocking, T.; Chamberlain, S.; Ram, K. Create Interactive Web Graphics via “Plotly.Js”. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/plotly/plotly.pdf (accessed on 30 March 2025).
- Mangortey, E.; Puranik, T.G.; Pinon, O.J.; Mavris, D.N. Classification, Analysis, and Prediction of the Daily Operations of Airports Using Machine Learning. In Proceedings of the AIAA Scitech 2020 Forum, Orlando, FL, USA, 6–10 January 2020; pp. 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.R.; Miah, M.G.; Inoue, Y. Analysis of Land Use and Land Cover Changes in the Coastal Area of Bangladesh Using Landsat Imagery. Land Degrad. Dev. 2016, 27, 899–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.M.; Mondol Nilay, M.S.; Jibon, N.H.; Rahman, R.M. LULC Changes to Riverine Flooding: A Case Study on the Jamuna River, Bangladesh Using the Multilayer Perceptron Model. Results Eng. 2023, 18, 101079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, I.; Tonny, K.F.; Hoque, M.Z.; Abdullah, H.M.; Khan, B.M.; Islam, K.H.S.; Prodhan, F.A.; Ahmed, M.; Mohana, N.T.; Ferdush, J. Monitoring and Prediction of Land Use Land Cover Change of Chittagong Metropolitan City by CA-ANN Model. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 21, 6275–6286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Sensor Name | Time Period and Date | Row and Path | Resolution | Source | Projection UTM/WGS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Landsat 4–5 TM | 29/10/1990 | 042/138 | 30 Meter | USGS | UTM/WGS 84 |
| 20/10/1990 | 042/139 | ||||
| Landsat 7 ETM+ | 06/10/2002 | 042/138 | 30 Meter | USGS | UTM/WGS 84 |
| 29/10/2002 | 042/139 | ||||
| Landsat 8–9 OLI/TIRS | 31/10/2014 | 042/138 | 30 Meter | USGS | UTM/WGS 84 |
| 11/11/2014 | 042/139 | ||||
| Landsat 8–9 OLI/TIRS | 21/10/2022 | 042/138 | 30 Meter | USGS | UTM/WGS 84 |
| 20/10/2022 | 042/139 |
| LULC Classes | Description of Classes |
|---|---|
| Waterbody | Waterbody includes rivers, narrow rivers, ponds, canals, reservoirs that are created by dams, lakes, etc. |
| Vegetation | Vegetation includes trees nearby homestead, roads, social forest and dense vegetation, woodlot |
| Cropland | Cultivated and uncultivated land, broadleaved cropland (maize), tea garden |
| Bare land | Bare land represents the barren soil, sandy river bed, built-in area, and other settlements |
| SL | Class | 1990 | 2002 | 2014 | 2022 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Waterbody | 17,433.99 (1.46%) | 20,692.08 (1.74%) | 12,443.12 (1.05%) | 13,844.97 (1.17%) |
| 2 | Vegetation | 321,421.05 (27.06%) | 315,934.2 (26.6%) | 225,263.77 (18.97%) | 282,783.42 (23.81%) |
| 3 | Cropland | 684,749.88 (57.65%) | 675,246.78 (56.85%) | 829,986.63 (69.88%) | 697,798.44 (58.75%) |
| 4 | Bare land | 164,103.84 (13.81%) | 175,835.7 (14.8%) | 120,015.24 (10.1%) | 193,281.93 (16.27%) |
| Total | 1,187,708.76 | 1,187,708.76 | 1,187,708.76 | 1,187,708.76 |
| Land Cover Change (1990–2002) | |||
| LULC classes | Magnitude Area (ha) | % Change | Annual Rate of Change (ha/year) |
| Waterbody | +3258.09 | +18.83 | +271.51 |
| Vegetation | −5486.85 | −1.70 | −457.24 |
| Cropland | −9503.1 | −1.38 | −791.93 |
| Bare land | +11,731.86 | +7.15 | +977.65 |
| Land Cover Change (2002–2014) | |||
| LULC classes | Magnitude Area (ha) | % Change | Annual Rate of Change (ha/year) |
| Waterbody | −8248.96 | −39.86 | −687.41 |
| Vegetation | −90,670.43 | −28.69 | −7555.87 |
| Cropland | +154,739.85 | +22.91 | +12,894.99 |
| Bare land | −55,820.46 | −31.75 | −4651.71 |
| Land Cover Change (2014–2022) | |||
| LULC classes | Magnitude Area (ha) | % Change | Annual Rate of Change (ha/year) |
| Waterbody | +1401.85 | +11.17 | +175.23 |
| Vegetation | +57,519.65 | +25.51 | +7189.96 |
| Cropland | −132,188.19 | −15.92 | −16,523.52 |
| Bare land | +73,266.69 | +61.01 | +9158.33 |
| Land Cover Change (1990–2022) | |||
| LULC classes | Magnitude Area (ha) | % Change | Annual Rate of Change (ha/year) |
| Waterbody | −3589.02 | −20.75 | −112.16 |
| Vegetation | −38,637.63 | −12.02 | −1207.43 |
| Cropland | +13,048.56 | +1.90 | +407.77 |
| Bare land | +29,178.09 | +17.78 | +911.82 |
| LULC Classes | DD% Variations in Time | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1990–2002 | 2002–2014 | 2014–2022 | 1990–2022 | |
| Waterbody | 1.64 | −3.28 | 1.29 | −0.62 |
| Vegetation | −0.14 | −2.39 | 3.19 | −0.37 |
| Cropland | −0.12 | 1.91 | −1.99 | 0.07 |
| Bare land | 0.60 | −2.64 | 7.63 | 0.56 |
| Year | Producer’s Accuracy (%) | User’s Accuracy (%) | Overall Accuracy (%) | Kappa Coefficient |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1990 | 82.43 | 85.67 | 84.54 | 0.74 |
| 2002 | 86.60 | 78.76 | 82.34 | 0.81 |
| 2014 | 88.73 | 85.01 | 86.23 | 0.78 |
| 2022 | 73.00 | 81.78 | 80.75 | 0.75 |
| LULC Class | Actual LULC in 2014 (ha) | Simulated LULC in 2014 (ha) |
|---|---|---|
| Waterbody | 12,540.6 | 12,355.29 |
| Vegetation | 225,309.4 | 246,697.5 |
| Cropland | 829,768.8 | 833,937.8 |
| Bare land | 120,042.8 | 94,671.09 |
| Total | 1,187,662 | 1,187,662 |
| LULC Classes | Producer Accuracy (%) | User Accuracy(%) | Kappa Hat |
|---|---|---|---|
| Waterbody | 11.34 | 11.51 | 0.11 |
| Vegetation | 74.12 | 67.70 | 0.60 |
| Cropland | 87.84 | 87.40 | 0.58 |
| Bare land | 43.74 | 55.46 | 0.50 |
| Kappa hat classification = 0.566 | |||
| Overall accuracy [%] = 79.98 | |||
| Class | 2022 | 2030 | 2054 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total Area | % of Total Area | Total Area | % of Total Area | Total Area | % of Total Area | |
| Waterbody | 13,844.97 | 1.17 | 12,982.14 | 1.09 | 9082.26 | 0.76 |
| Vegetation | 282,783.42 | 23.81 | 283,076.64 | 23.83 | 295,901.10 | 24.91 |
| Cropland | 697,798.44 | 58.75 | 702,030.69 | 59.11 | 689,341.41 | 58.04 |
| Bare land | 193,281.93 | 16.27 | 189,619.29 | 15.97 | 193,383.99 | 16.28 |
| Class | 2022–2030 | 2022–2054 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Change (ha) | Rate of Change (%) | Change (ha) | Rate of Change (%) | |
| Waterbody | −862.83 | −6.23 | −4762.71 | −34.40 |
| Vegetation | +293.22 | +0.10 | +13,117.68 | +4.64 |
| Cropland | +4232.25 | +0.61 | −8457.03 | −1.21 |
| Bare land | −3662.64 | −1.89 | +102.06 | +0.05 |
| Transition | Area (ha) | % of Total Landscape Area | % of Source Class Transitioned | Ecological Interpretation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cropland (3) → Vegetation (2) | 8436.87 | 0.71% | 1.21% | Fallow land regeneration, afforestation, mixed agroforestry, tea plantation |
| Waterbody (1) → Vegetation (2) | 4760.73 | 0.40% | 34.39% | Drying wetlands, vegetative encroachment |
| Predictor | Logistic Coef. (Direction) | p-Value | Interpretation (Crop → Vegetation) | Logistic Coef. (Direction) | p-Value | Interpretation (Water → Vegetation) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Elevation | +0.005 (↑ transition) | *** | Higher elevation slightly favors transition from cropland to vegetation. | +0.002 (↑ transition) | *** | Higher elevation moderately increases likelihood of water areas becoming vegetated. |
| Slope | −0.014 (↓ transition) | *** | Steeper slopes reduce the likelihood of cropland reverting to vegetation. | +0.305 (↑ transition) | *** | Water-to-vegetation transition is more likely on steeper slopes, possibly due to sediment deposition or wetland edge growth. |
| Distance to road | +2.5948 × 10−5 (↑ transition) | ** | Areas farther from roads are more likely to transition from cropland to vegetation, possibly due to abandonment. | +1.837 × 10−4 (↑ transition) | *** | Greater distance from roads promotes transition from water to vegetation, likely due to reduced disturbance. |
| Distance to highway | +6.185 × 10−5 (↑ transition) | *** | Greater distance from highways slightly increases transition probability, likely reflecting reduced land use pressure. | −2.707 × 10−5 (↓ transition) | *** | Areas closer to highways are more likely to transition from water to vegetation, possibly reflecting encroachment or wetland fill. |
| Rainfall | −0.005 (↓ transition) | *** | Lower rainfall areas are more likely to see cropland converting to vegetation, possibly due to marginal crop productivity. | +0.001 (↑ transition) | *** | Increased rainfall favors vegetation colonizing water areas (e.g., emergent wetland vegetation). |
| Temperature | +1.384 (↑ transition) | *** | Warmer areas promote vegetation regrowth over former cropland. | −5.101 (↓ transition) | *** | High temperatures inhibit vegetation establishment in waterbody areas, possibly due to stress or drying. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Das, D.; Prodhan, F.A.; Hoque, M.Z.; Haque, M.E.; Kabir, M.H. Monitoring and Future Prediction of Land Use Land Cover Dynamics in Northern Bangladesh Using Remote Sensing and CA-ANN Model. Earth 2025, 6, 73. https://doi.org/10.3390/earth6030073
Das D, Prodhan FA, Hoque MZ, Haque ME, Kabir MH. Monitoring and Future Prediction of Land Use Land Cover Dynamics in Northern Bangladesh Using Remote Sensing and CA-ANN Model. Earth. 2025; 6(3):73. https://doi.org/10.3390/earth6030073
Chicago/Turabian StyleDas, Dipannita, Foyez Ahmed Prodhan, Muhammad Ziaul Hoque, Md. Enamul Haque, and Md. Humayun Kabir. 2025. "Monitoring and Future Prediction of Land Use Land Cover Dynamics in Northern Bangladesh Using Remote Sensing and CA-ANN Model" Earth 6, no. 3: 73. https://doi.org/10.3390/earth6030073
APA StyleDas, D., Prodhan, F. A., Hoque, M. Z., Haque, M. E., & Kabir, M. H. (2025). Monitoring and Future Prediction of Land Use Land Cover Dynamics in Northern Bangladesh Using Remote Sensing and CA-ANN Model. Earth, 6(3), 73. https://doi.org/10.3390/earth6030073






