Changes in Regional Practices and Their Effects on the Water Quality of Portuguese Reservoirs
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
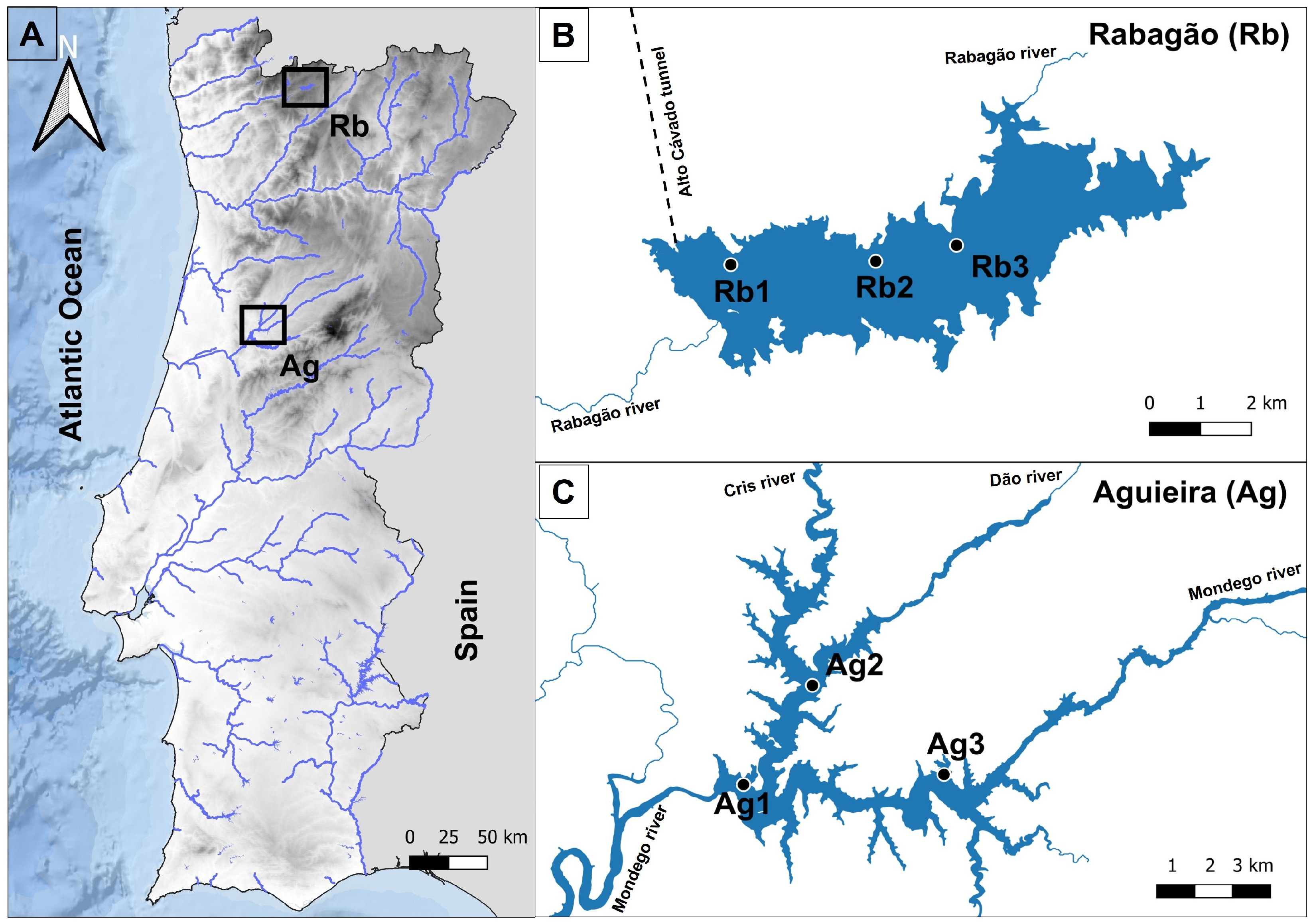
2.1. Studies Areas
2.2. Surrounding Landscape
2.3. Surrounding Land Pressures
2.4. Monitoring Water Quality over Time
2.5. Water Quality Assessment
2.5.1. Sampling Methodologies
2.5.2. Laboratorial Methodologies
2.5.3. Data Analysis
3. Results
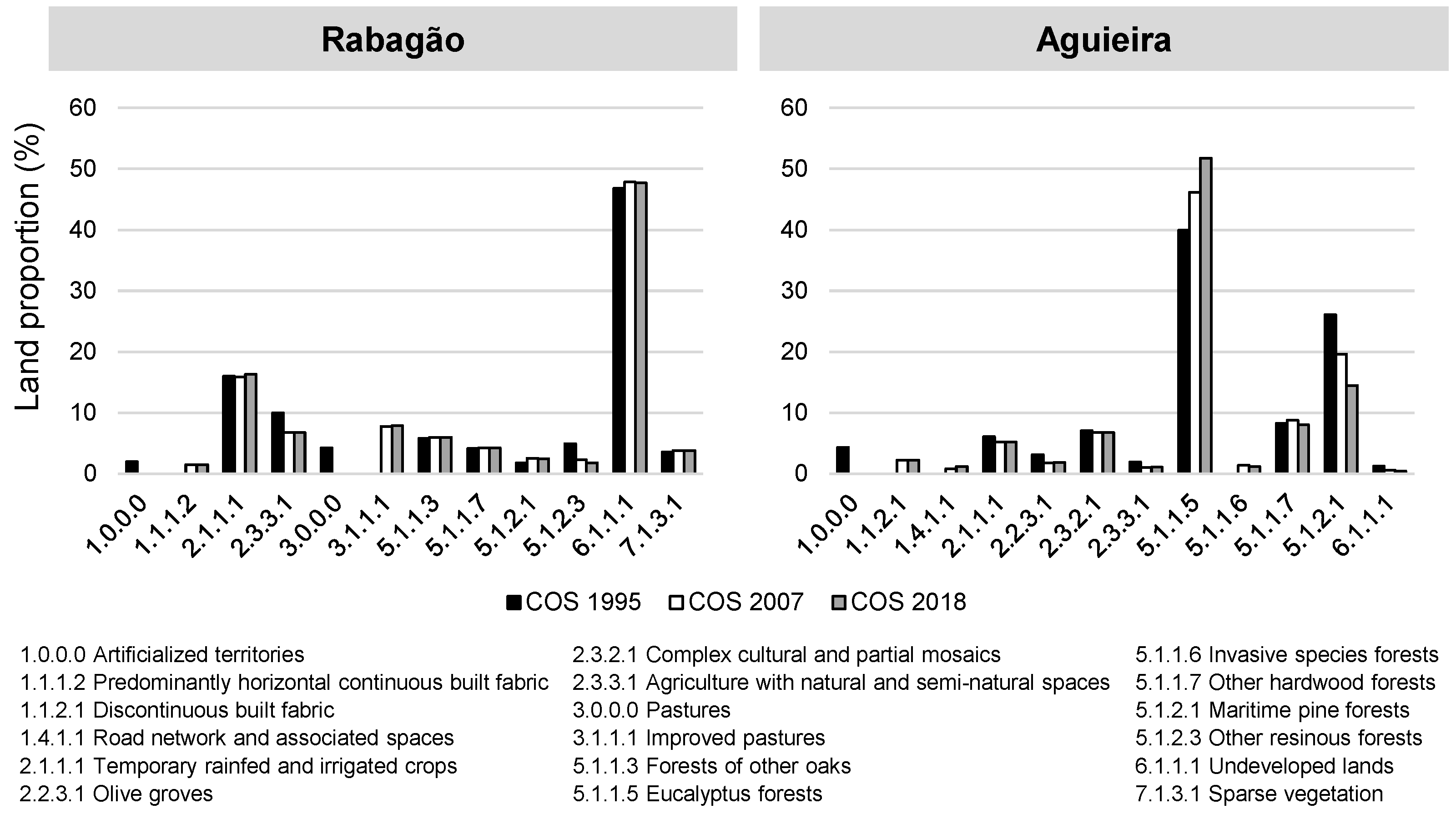
3.1. Surrounding Landscape
3.2. Surrounding Land Pressures
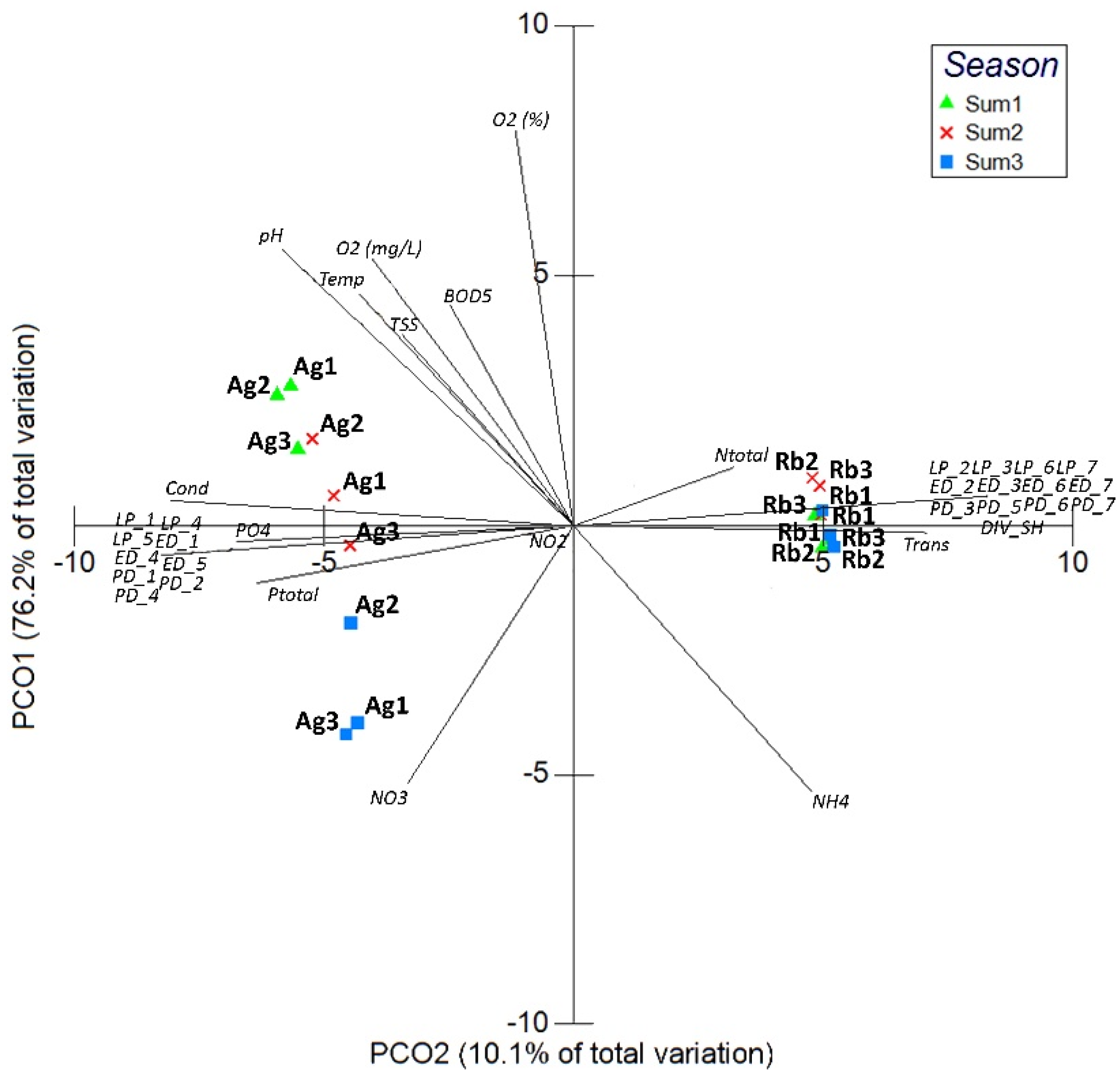
3.3. Monitoring Water Quality
4. Discussion
4.1. Regional Relationships Between Land Use Patterns and Water Quality
4.2. Spatial and Seasons Scales Effects on Water Quality
5. Management Implication
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Qiu, M.; Wei, X.; Hou, Y.; Spencer, S.A.; Hui, J. Forest Cover, Landscape Patterns, and Water Quality: A Meta-Analysis. Landsc. Ecol. 2023, 38, 877–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, I.; Rodrigues, S.; Antunes, S.C. Assessment of the Benthic Macroinvertebrate Communities in the Evaluation of the Water Quality of Portuguese Reservoirs: An Experimental Approach. Water 2021, 13, 3391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sliva, L.; Dudley Williams, D. Buffer Zone versus Whole Catchment Approaches to Studying Land Use Impact on River Water Quality. Water Res. 2001, 35, 3462–3472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uuemaa, E.; Roosaare, J.; Mander, Ü. Landscape Metrics as Indicators of River Water Quality at Catchment Scale. Hydrol. Res. 2007, 38, 125–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Xu, G.; Li, Z.; Dang, Y.; Li, Q.; Min, Z.; Gu, F.; Wang, B.; Liu, S.; Zhang, Y. Effects of Comprehensive Landscape Patterns on Water Quality and Identification of Key Metrics Thresholds Causing Its Abrupt Changes. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 333, 122097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, G.D.; Myers, W.L.; Patil, G.P. Predictability of Surface Water Pollution Loading in Pennsylvania Using Watershed-Based Landscape Measurements. JAWRA J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2001, 37, 821–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Learning Landscape Ecology; Gergel, S.E., Turner, M.G., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2017; ISBN 978-1-4939-6372-0. [Google Scholar]
- Portela, A.P.; Gonçalves, J.; Cardoso, A.S.; Vaz, A.S.; de Lima, L.T.; Pinto, I.; Rodrigues, S.; Antunes, S.C.; Honrado, J. Landscape Functioning in Reservoir Water Quality Prediction: Current Use and Predictive Capacity. Ecohydrology 2024, 17, e2702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-W.; Hwang, S.-J.; Lee, S.-B.; Hwang, H.-S.; Sung, H.-C. Landscape Ecological Approach to the Relationships of Land Use Patterns in Watersheds to Water Quality Characteristics. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2009, 92, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, S.T.Y.; Chen, W. Modeling the Relationship between Land Use and Surface Water Quality. J. Environ. Manag. 2002, 66, 377–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberti, M.; Booth, D.; Hill, K.; Coburn, B.; Avolio, C.; Coe, S.; Spirandelli, D. The Impact of Urban Patterns on Aquatic Ecosystems: An Empirical Analysis in Puget Lowland Sub-Basins. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2007, 80, 345–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burić, D.; Mijanović, I.; Doderović, M.; Mihajlović, J.; Trbić, G. Assessment of the Environmental Quality of Lake Skadar and Its Ur-Ban Surroundings in Montenegro. Eur. J. Geogr. 2023, 14, 76–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UN Wastewater: The Untapped Resource; The United Nations World Water Development Report 2017; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2017.
- IPCC Summary for Policymakers. In Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Masson-Delmotte, V., Zhai, P., Pirani, A., Connors, S.L., Péan, C., Berger, S., Caud, N., Chen, Y., Goldfarb, L., Gomis, M.I., et al., Eds.; Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) Publisher: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021; ISBN 978-92-9169-163-0. [Google Scholar]
- Agência Portuguesa do Ambiente Critérios Para a Classificação Das Massas de Água; Lisboa, 2023. Available online: https://apambiente.pt/sites/default/files/_Agua/DRH/ParticipacaoPublica/PGRH/2022-2027/3_Fase/PGRH_3_SistemasClassificacao.pdf (accessed on 13 August 2024).
- Ramião, J.P.; Pascoal, C.; Pinto, R.; Carvalho-Santos, C. Mitigating Water Pollution in a Portuguese River Basin under Climate Change through Agricultural Sustainable Practices. Mitig. Adapt. Strateg. Glob. Change 2024, 29, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramião, J.P.; Pascoal, C.; Carvalho-Santos, C. Climate Change Adaptation for Drinking Water and Ecological Flows through Sustainable Agricultural Practices. Int. J. Water Resour. Dev. 2024, 40, 832–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Instituto da Água. Modelação Matemática Da Qualidade Da Água Em Albufeiras Com Planos de Ordenamento. In VI—Albufeira Do Alto Rabagão; Instituto da Água: Lisboa, Portugal, 2011. Available online: https://apambiente.pt/sites/default/files/_SNIAMB_Agua/DRH/MonitorizacaoAvaliacao/EstadoMassasAgua/ModelacaoQualidadeAgua_AAP/VI_RelatorioModelacao_AltoRabagao.pdf (accessed on 13 August 2024).
- Pinto, I.; Azevedo, L.; Antunes, S.C. The Role of Crustacean Zooplankton in Water Quality Monitoring: Findings from Two Portuguese Reservoirs. Ecohydrol. Hydrobiol. 2025, 100646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, R.; Sousa Pinto, I.; Antunes, S.C. Contribution of Zooplankton as a Biological Element in the Assessment of Reservoir Water Quality. Limnetica 2020, 39, 245–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agência Portuguesa do Ambiente Plano de Ordenamento Da Albufeira Do Alto Rabagão; Relatório Síntese. Agência Portuguesa do Ambiente: Lisboa, Portugal, 2009; Volume II. Available online: https://www.cm-montalegre.pt/cmmontalegre/uploads/writer_file/document/610/poaar-rela1258041017.pdf (accessed on 13 August 2024).
- Agência Portuguesa do Ambiente Plano de Ordenamento Da Albufeira Da Aguieira; Agência Portuguesa do Ambiente: Lisboa, Portugal, 2005. Available online: https://www.apambiente.pt/_zdata/Ordenamento/POA/Aguieira/Relatorio.pdf (accessed on 13 August 2024).
- Pinto, I.; Rodrigues, S.; Lage, O.M.; Antunes, S.C. Assessment of Water Quality in Aguieira Reservoir: Ecotoxicological Tools in Addition to the Water Framework Directive. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 208, 111583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, S.; Pinto, I.; Martins, F.; Formigo, N.; Antunes, S.C. Can Biochemical Endpoints Improve the Sensitivity of the Biomonitoring Strategy Using Bioassays with Standard Species, for Water Quality Evaluation? Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 215, 112151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medeiros, A.; Fernandes, C.; Gonçalves, J.F.; Farinha-Marques, P. A Diagnostic Framework for Assessing Land-Use Change Impacts on Landscape Pattern and Character—A Case-Study from the Douro Region, Portugal. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2022, 228, 104580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agência Portuguesa do Ambiente Plano de Gestão de Ragião Hidrográfica 3o Ciclo—Cávado, Ave E Leça (RH2)—Fichas de Massa de Água; Agência Portuguesa do Ambiente: Lisboa, Portugal, 2022.
- Agência Portuguesa do Ambiente Plano de Gestão de Região Hidrográfica 3o Ciclo—Vouga, Mondego e Lis (RH4A)—Fichas de Massa de Água; Agência Portuguesa do Ambiente: Lisboa, Portugal, 2022.
- Lenore, S.; Clesceri, A.E.; Greenberg, A.D.E. APHA Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 17th ed.; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 1989; ISBN 978-0875532356. [Google Scholar]
- Baker, A.L. Phycokey—An Image Based Key to Algae (PS Protista), Cyanobacteria, and Other Aquatic Objects. Available online: http://cfb.unh.edu/phycokey/phycokey.htm (accessed on 13 August 2019).
- Bellinger, E.G.; Sigee, D.C. A Key to the More Frequently Occurring Freshwater Algae. In Freshwater Algae; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 141–252. ISBN 9780470058145. [Google Scholar]
- Pinto, I.; Nogueira, S.; Rodrigues, S.; Formigo, N.; Antunes, S.C. Can Zooplankton Add Value to Monitoring Water Quality? A Case Study of a Meso/Eutrophic Portuguese Reservoir. Water 2023, 15, 1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shehab, Z.N.; Jamil, N.R.; Aris, A.Z.; Shafie, N.S. Spatial Variation Impact of Landscape Patterns and Land Use on Water Quality across an Urbanized Watershed in Bentong, Malaysia. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 122, 107254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Bai, Y.; You, H.; Wang, X.; Ma, Z.; Zhang, H. Water Quality Assessment and the Influence of Landscape Metrics at Multiple Scales in Poyang Lake Basin. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 141, 109096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heino, M.; Kummu, M.; Makkonen, M.; Mulligan, M.; Verburg, P.H.; Jalava, M.; Räsänen, T.A. Forest Loss in Protected Areas and Intact Forest Landscapes: A Global Analysis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0138918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Mwagona, P.C.; Shabani, I.E.; Hou, W.; Li, X.; Zhao, F.; Chen, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, D.; Li, X.; et al. Phytoplankton Functional Groups Response to Environmental Parameters in Muling River Basin of Northeast China. Ann. Limnol. Int. J. Limnol. 2019, 55, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, N.W.; Baillie, B.R.; Bishop, K.; Ferraz, S.; Högbom, L.; Nettles, J. The Effects of Forest Management on Water Quality. For Ecol. Manage. 2022, 522, 120397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Instituto da Água. Modelação Matemática da Qualidade da Água em Albufeiras com Planos de Ordenamento—Lll—Albufeira da Aguieira; Ministério da Agricultura, Mar, Ambiente e Ordenamento do Território; Instituto da Água, I.P.: Lisboa, Portugal, 2011. Available online: https://www.apambiente.pt/_zdata/Ordenamento/ModQualAgua/III-Relatrio_Modelao_Aguieira.pdf (accessed on 13 August 2024).
- Latterini, F.; Mederski, P.S.; Jaeger, D.; Venanzi, R.; Tavankar, F.; Picchio, R. The Influence of Various Silvicultural Treatments and Forest Operations on Tree Species Biodiversity. Curr. For. Rep. 2023, 9, 59–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, P.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.; Li, P.; Xu, G. Influence of Land Use and Land Cover Patterns on Seasonal Water Quality at Multi-Spatial Scales. Catena 2017, 151, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Lu, J. Spatial Scale Effects of Landscape Metrics on Stream Water Quality and Their Seasonal Changes. Water Res. 2021, 191, 116811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, S.; Jiang, C. Effects of Land Use on Water Quality in a River Basin (Daning) of the Three Gorges Reservoir Area, China: Watershed versus Riparian Zone. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 113, 106226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffith, J.A. Geographic Techniques and Recent Applications of Remote Sensing to Landscape-Water Quality Studies. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2002, 138, 181–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Rabagão | Hydrographic Basin | Aguieira | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2nd Cycle | 3rd Cycle | Water Framework Directive | 2nd Cycle | 3rd Cycle | |
| Punctual Qualitative Pressures | |||||
| Urban | 0 | 0 | Soil—secundary | 7 | 7 |
| 0 | 0 | Soil—primary | 10 | 0 | |
| 0 | 0 | Hydro—more advanced than secondary | 1 | 0 | |
| 0 | 0 | Hydro—secondary | 12 | 24 | |
| 0 | 0 | Hydro—primary | 3 | 2 | |
| 0 | 0 | Hydro—unknown | 0 | 1 | |
| Industry | 0 | No data | Waste deposit | 2 | No data |
| 0 | 0 | Food and Wine | 5 | 0 | |
| 0 | 0 | PCIP food and wine | 1 | 0 | |
| 0 | 0 | PCIP transformer | 1 | 0 | |
| 0 | 0 | Extractive | 1 | 0 | |
| 1 | 1 | Aquaculture | 0 | 0 | |
| Others | No data | 0 | Soil rejection | No data | 1 |
| No data | 0 | Hydro rejection | No data | 1 | |
| Punctual Quantitative Pressures | |||||
| Surface Catchments | No data | 1 | Public supply | No data | 3 |
| No data | 4 | Agriculture | No data | 9 | |
| No data | 0 | Green spaces | No data | 2 | |
| No data | 1 | Extractive | No data | 0 | |
| No data | 1 | Hydroelectric | No data | 1 | |
| No data | 0 | Unknown | No data | 2 | |
| Underground Catchments | No data | 13 | Agriculture | No data | 80 |
| No data | 0 | Green spaces | No data | 2 | |
| No data | 0 | Livestock | No data | 1 | |
| No data | 1 | Aquaculture | No data | 0 | |
| No data | 0 | Unknown | No data | 54 | |
| Hydromorphological Pressures | |||||
| 1 | 1 | Large dams | 1 | 1 | |
| No data | 0 | Navigation support | No data | 3 | |
| No data | 0 | Bank bed changes | No data | 1 | |
| Rabagão | Aguieira | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1st Cycle | 2nd Cycle | 3rd Cycle | 1st Cycle | 2nd Cycle | 3rd Cycle | |
| Hydromorphological | Unvalued | Unvalued | Good | Unvalued | Unvalued | Good |
| General physical and chemical | Good or more | Good | Excellent | Moderate | Moderate | Moderate |
| Biological | Good or more | Good | Excellent | Moderate | Poor | Moderate |
| Specific pollutants | Good or more | Good | Good | Good or more | Good | Good |
| Priority substances | Good | Unvalued | Good | Good | Unvalued | Good |
| Global status | Good | Good | Good | Moderate | Poor | Moderate |
| Parameter | Reference Values | Reservoir | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Excellent | Good | Rabagão | Aguieira | ||
| General physical and chemical | Conductivity (μS/cm) | ≤100 | 24.0 | 85.7 | |
| Temperature (°C) | 6.5–25.5 | 22.0 | 24.6 | ||
| Transparency (m) | ≥2.3 | 2.80 | 2.10 | ||
| pH | 6.5–8.5 | 6.0–9.0 | 7.69 | 9.01 | |
| Dissolved oxygen (mg O2/L) | 8.0–12.0 | ≥6.0 | 8.24 | 8.63 | |
| Dissolved oxygen (% O2) | 80–115 | 70–125 | 104.1 | 105.1 | |
| Biological oxygen demand (mg O2/L) | ≤3.0 | ≤4.0 | 0.98 | 1.24 | |
| Total Phosphorus (mg P/L) | ≤0.03 | ≤0.04 | 0.005 | 0.042 | |
| Phosphate (mg PO4/L) | ≤0.08 | ≤0.12 | 0.04 | 0.18 | |
| Total nitrogen (mg N/L) | ≤0.55 | ≤1.0 | 0.49 | 0.24 | |
| Ammonia nitrogen (mg NH4/L) | ≤0.1 | ≤0.2 | 0.03 | 0.02 | |
| Nitrate (mg NO3/L) | ≤2.0 | ≤3.0 | <0.02 | 0.12 | |
| Nitrite (mg NO2/L) | ≤0.01 | ≤0.02 | <0.0115 | <0.0115 | |
| Total suspended solids (mg/L) | ≤12.5 | ≤25.0 | 14.62 | 16.14 | |
| Biological | Phytoplankton | Excellent | [1–0.8] | 0.74 | 0.29 |
| Good | [0.8–0.6] | ||||
| Moderate | [0.6–0.4] | ||||
| Poor | [0.4–0.2] | ||||
| Bad | [0.2–0] | ||||
| Ecological Potential | Good | Poor | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pinto, I.; Azevedo, L.; Antunes, S.C. Changes in Regional Practices and Their Effects on the Water Quality of Portuguese Reservoirs. Earth 2025, 6, 29. https://doi.org/10.3390/earth6020029
Pinto I, Azevedo L, Antunes SC. Changes in Regional Practices and Their Effects on the Water Quality of Portuguese Reservoirs. Earth. 2025; 6(2):29. https://doi.org/10.3390/earth6020029
Chicago/Turabian StylePinto, Ivo, Luísa Azevedo, and Sara C. Antunes. 2025. "Changes in Regional Practices and Their Effects on the Water Quality of Portuguese Reservoirs" Earth 6, no. 2: 29. https://doi.org/10.3390/earth6020029
APA StylePinto, I., Azevedo, L., & Antunes, S. C. (2025). Changes in Regional Practices and Their Effects on the Water Quality of Portuguese Reservoirs. Earth, 6(2), 29. https://doi.org/10.3390/earth6020029







