End-Point Predictors of Water Quality in Tropical Rivers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Data Analysis
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Predictability of the MMIs as End-Point Indicators
4.2. Insect Relationships to Physiochemical Parameters
4.3. Use in Predicting Land-Use Impacts in Tropical River Systems
5. Conclusions: Monitoring Water Quality in Tropical Environments
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Karr, J. Seven Foundations of Biological Monitoring and Assessment. Biol. Ambient. 2006, 20, 7–18. [Google Scholar]
- Keiser, D.; Shapiro, J. Consequences of the Clean Water Act and the demand for water quality. Q. J. Econ. 2019, 134, 349–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karr, J. Assessment of biotic integrity using fish communities. Fisheries 1981, 6, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feio, M.; Hughes, R.; Callisto, M.; Nichols, S.; Odume, O.; Quintella, B.; Kuemmerlen, M.; Aguiar, F.; Almeida, S.; Alonso-EguiaLis, P.; et al. The biological assessment and rehabilitation of the world’s rivers: An overview. Water 2021, 3, 371. [Google Scholar]
- Harmsworth, G.; Young, R.; Walker, D.; Clapcott, J.; James, T. Linkages between cultural and scientific indicators of river and stream health. N. Z. J. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2011, 45, 423–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannan, N.; Anandhi, A.; Jeong, J. Estimation of stream health using flow-based indices. Hydrology 2018, 5, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noori, R.; Berndtsson, R.; Hosseinzadeh, M.; Adamowski, J.; Abyaneh, M. A critical review on the application of the national sanitation foundation water quality index. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 244, 575–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karr, J.; Chu, E. Restoring Life in Running Waters: Better Biological Monitoring; Island Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Sutadian, A.; Muttil, D.; Yilmaz, N.; Perera, B. Development of river water quality index a review. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2016, 188, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoolmaster, D.; Grace, J.; Schweiger, E. A general theory of multimetric indices and their properties. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2012, 3, 773–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, K.; Mitchell, B.; McGill, B. Constructing multimetric indices and testing ability of landscape metrics to assess condition of freshwater wetlands in the Northeastern US. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 66, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannan, N. Stream Health Estimation for the Plum Creek Watershed. Hydrology 2021, 8, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosgen, D. Applied River Morphology; Printed Media Companies: Minneapolis, MN, USA, 1996; 352p. [Google Scholar]
- Rosgen, D. A Practical Method of Computing Streambank Erosion Rate. In Proceedings of the 7th Federal Interagency Sedimentation Conference, Reno, NV, USA, 25–29 March 2001; Volume 2, pp. 9–15. [Google Scholar]
- Kitchell, A.; Schueler, T. Manual 10: Unified Stream Assessment: A User’s Manual; Urban Subwatershed Restoration Manual Series; Center for Watershed Protection: Ellicott City, MD, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, R.; McClellan, N.; Deininger, R.; Tozer, G. A water quality index-do we dare? Water Sew. Work. 1970, 117, 339–343. [Google Scholar]
- Bharti, N.; Katyal, D. Water quality indices used for surface water vulnerability assessment. Int. J. Environ. Sci. 2011, 2, 154e173. [Google Scholar]
- Herman, M.; Nejadhashemi, A. A review of macroinvertebrate and fish-based stream health indices. Ecohydrol. Hydrobiol. 2015, 15, 53–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, T.; Abbasi, S. Water quality indices based on bioassessment: The biotic indices. J. Water Health 2011, 9, 330–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buss, D.; Carlisle, D.; Chon, T.; Culp, J.; Harding, J.; Keizer-Vlek, H.; Robinson, W.; Strachan, S.; Thirion, C.; Hughes, R. Stream biomonitoring using macroinvertebrates around the globe: A comparison of large-scale programs. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 187, 4132. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- León, L. Índice de Calidad del Agua, Ica, Inf. # Sh-9101/01; Instituto Mexicano de Tecnología del Agua: Progreso, Mexico, 1991; 36p. [Google Scholar]
- Montoya, H.; Contreras, C.; García, Y. Estudio Integral De La Calidad Del Agua En El Estado De Jalisco; Comision Nacional del Agua, Gerencia Regional: Guadalajara, Mexico, 1997; 106p. [Google Scholar]
- Rubio, H.; Delgado, R.; Martínez, R.; Terán, R.; Rivero, J.; Burciaga, N. Indice de calidad de agua (ICA) en la presa la boquilla en Chihuahua, Mexico. J. Basic Sci. 2014, 1, 139–150. [Google Scholar]
- Resh, V.; Brown, A.; Covich, A.; Gurtz, M.; Li, H.; Minshall, G.; Reice, S.; Sheldon, A.; Wallace, J.; Wissmar, R. The role of disturbance in stream ecology. J. N. Am. Benthol. Soc. 1988, 7, 433–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez, A.; Pringle, C.; Douglas, M. Temporal and spatial patterns in stream physicochemistry and insect assemblages in tropical lowland streams. J. N. Am. Benthol. Soc. 2006, 25, 108–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weliange, W.; Amarasinghe, U.; Vijverberg, J.; Leichtfried, M.; Fureder, L. A Comparative Analysis on the Effects of River Discharge on Trophic Interactions in Two Tropical Streams. Int. Rev. Hydrobiol. 2017, 102, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruaro, R.; Gubiani, É. A scientometric assessment of 30 years of the Index of Biotic Integrity in aquatic ecosystems: Applications and main flaws. Ecol. Indic. 2013, 29, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Oosterhout, M.; van der Velde, G. An advanced index of biotic integrity for use in shallow lowland streams in Costa Rica: Fish assemblages as indicators of stream ecosystem health. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 48, 687–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, I.; Macedo, D.; Hughes, R.; Callisto, M. Are multiple multimetric indices effective for assessing ecological condition in tropical basins? Ecol. Indic. 2020, 110, 105953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo, E.; Martínez, E.; Ruepert, C.; Savage, C.; Gilek, M.; Pinnock, M.; Solís, E. Water Quality and Macroinvertebrate Community Response Following Pesticide Applications in a Banana Plantation, Limón, Costa Rica. Sci. Total Environ. 2006, 367, 418–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stan, K.; Sanchez-Azofeifa, A.; Calvo-Rodriguez, S.; Castro-Magnani, M.; Chen, J.; Ludwig, R.; Zou, L. Climate change scenarios and projected impacts for forest productivity in Guanacaste Province (Costa Rica): Lessons for tropical forest regions. Reg. Environ. Chang. 2020, 20, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MINAE. Regulation for the Evaluation and Classification of the Quality of Surface Water Bodies; Executive Decree No. 33903; MINAE: San José, Costa Rica, 2007.
- Jovanelly, T.; Rodríguez-Montero, L.; Sánchez-Gutiérrez, R.; Mena-Rivera, L.; Thomas, D. Evaluating watershed health in Costa Rican national parks and protected areas. Sustain. Water Resour. Manag. 2020, 6, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahady, T.; Boniface, H. Water quality management thorough community engagement in Costa Rica. J. Environ. Sci. Stud. 2018, 8, 488–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capdevila, A.; Kokimova, A.; Ray, S.; Avellán, T.; Kim, J.; Kirschke, S. Success factors for citizen science projects in water quality monitoring. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 728, 137843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirschke, S.; Newig, J.; Völker, J.; Borchardt, D. Does problem complexity matter for environmental policy delivery? How public authorities address problems of water governance. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 196, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conrad, C.; Hilchey, K. A review of citizen science and community-based environmental monitoring: Issues and opportunities. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2011, 176, 273–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storey, R.; Wright-Stow, A.; Kin, E.; Davies-Colley, R.; Stott, R. Volunteer stream monitoring: Do the data quality and monitoring experience support increased community involvement in freshwater decision making? Ecol. Soc. 2016, 21, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbour, M.; Gerritsen, J.; Snyder, B.; Stribling, J. Rapid Bioassessment for Use in Streams and Wadeable Rivers: Periphyton, Benthic Macroinvertebrates and Fish, 2nd ed.; EPA 841-B-99-002; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Office of Water: Washington, DC, USA, 1999.
- Springer, M.; Ramírez, A.; Hanson, P. Macroinvertebrados de agua dulce de Costa Rica I: Introducción a los grupos de macroinvertebrados, métodos, biomonitoreo, Ephemeroptera, Odonata, Plecoptera, Trichoptera. Rev. Biol. Trop. 2010, 58 (Suppl. 4), 1–200. [Google Scholar]
- Fernández, H.; Domínguez, E. Guia para la Determinacion de los Artropodos Bentonicos Sudamericanos; Universidad Nacional De Tucuman, Facultad De Ciencias Naturales e Instituto Miguel Lillo: Tucumán, Argentina, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Baird, R.; Bridgewater, L. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 23rd ed.; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- EPA. Standard Operating Procedure Calibration of Field Instruments; Quality Assurance Unit, U.S. Environmental Protection Agengy: North Chelmsford, MA, USA, 2017.
- Novak, M.; Bode, R. Percent model affinity: A new measure of macroinvertebrate community composition. J. N. Am. Benthol. Soc. 1992, 11, 80–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plafkin, J.; Barbour, T.; Porter, K.; Gross, S.; Hughes, R. Rapid Bioassessment Protocols for Use in Streams and Rivers: Benthic Macroinvertebrates and Fish; 444/4-89-001; United States Environmental Protection Agency EPA: Washington, DC, USA, 1989.
- Hilsenhoff, W. Use of Arthropods to Evaluate Water Quality of Streams; Technical Bulletin Number 100, Department of Natural Resources: Madison, WI, USA, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Addinsoft. XLSTAT Statistical and Data Analysis Solution; Addinsoft: Long Island, NY, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Mahalanobis, P. On the generalized distance in statistics. Proc. Natl. Inst. Sci. India 1936, 2, 49–55. [Google Scholar]
- Sawyer, J.; Stewart, P.; Mullen, M.; Simon, T.; Bennett, H. Influence of habitat, water quality, and land use on macro-invertebrate and fish assemblages of a southeastern coastal plain watershed, USA. Aquat. Ecosyst. Health Manag. 2004, 7, 85–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Praus, P. Evaluation of biological wastewater treatment process using Mahalanobis distances in original and principal component space: A case study. Appl. Water Sci. 2018, 8, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farber, O.; Kadmon, R. Assessment of alternative approaches for bioclimatic modeling with special emphasis on the Mahalanobis distance. Ecol. Model. 2003, 160, 115–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Chen, H.; Li, F. Identifying spatial heterogeneity of groundwater and its response to anthropogenic activities. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 29435–29448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farres, M.; Platikanov, S.; Tsakovski, S.; Tauler, R. Comparison of the variable importance in projection (VIP) and of the selectivity ratio (SR) methods for variable selection and interpretation. J. Chemom. 2015, 29, 528–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabachnick, B.; Fidell, L. Using Multivariate Statistics, 5th ed.; Allyn & Bacon: Boston, MA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Brooks, S.; Palmer, M.; Cardinal, B.; Swan, C.; Ribblett, S. Assessing stream ecosystem rehabilitation: Limitations of community structure data. Restor. Ecol. 2002, 10, 156–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghani, W.; Kutty, A.; Mahazar, M.; Al-Shami, S.; Hamid, S. Performance of Biotic Indices in Comparison to Chemical-Based Water Quality Index (WQI) in Evaluating the Water Quality of Urban River. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2018, 190, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herlihy, A.; Sifneos, J.; Hughes, R.; Peck, D.; Mitchell, R. The Relation of Lotic Fish and Benthic Macroinvertebrate Condition Indices to Environmental Factors Across the Conterminous USA. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 112, 105958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, J. The influence of land use on stream ecosystems. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2004, 35, 257–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolman, M. A cycle of sedimentation and erosion in urban river channels. Geogr. Ann. 1967, 49, 385–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, A. Urban transformation of river landscapes in a global context. Geomorphology 2006, 79, 460–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maklin, M.; Lewin, J. River stresses in anthropogenic times: Large-scale global patterns and extended environmental timelines. Prog. Phys. Geogr. 2019, 43, 3–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornejo, A.; Tonin, A.; Checa, B.; Tuñon, A.; Pérez, D.; Coronado, E.; González, S.; Ríos, T.; Macchi, P.; Correa-Araneda, F.; et al. Effects of multiple stressors associated with agriculture on stream macroinvertebrate communities in a tropical catchment. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0220528. [Google Scholar]
- Gutiérrez-Fonseca, P.; Ramírez, A. Mayfly Emergence Production and Body Length Response to Hydrology in a Tropical Lowland Stream. PeerJ 2020, 8, e9883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mena-Rivera, L.; Vásquez-Bolaños, O.; Gomez-Castro, C.; Rodríguez-Rodríguez, A.; Sánchez-Gutiérrez, R. Ecosystemic assessment of surface water quality in the Virilla River: Towards sanitation processes in Costa Rica. Water 2018, 10, 845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohlmann, B.; Arroyo, A.; Springer, M.; Vásquez, D. Chapter: 13. Agrorural effects on the macroinvertebrate assemblage in a tropical river. In Biodiversity in Ecosystems—Linking Structure and Function; Blanco, J.A., Ed.; InTech: London, UK, 2015; pp. 317–351. [Google Scholar]
- Ramírez, A.; Pringle, C. Structure and Production of a Benthic Insect Assemblage in a Neotropical Stream. J. N. Am. Benthol. Soc. 1998, 17, 443–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mena-Rivera, L.; Salgado-Silva, V.; Benavides-Benavides, C.; Coto-Campos, J.; Swinscoe, T. Spatial and season surface water quality assessment in a tropical urban catchment: Burio River. Costa Rica Water 2017, 9, 558–568. [Google Scholar]
- Feeley, H.; Davis, S.; Bruen, M.; Blacklocke, S.; Kelly-Quinn, M. The impact of a catastrophic storm event on benthic macroinvertebrate communities in upland headwater streams and potential implications for ecological diversity and assessment of ecological status. J. Limnol. 2012, 71, 299–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamora-Munõz, C.; Sainz-Cantero, C.; Sanchez-Ortega, A.; Alba-Tercedor, J. Are biological indices BMPW and ASPT and their significance regarding water quality seasonally dependent? Factors explaining their variations. Water Res. 1995, 29, 285–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, R.; Boyer, R.; Smith, R.; Schwarz, G.; Moore, R. The role of headwater streams in downstream water quality. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2007, 43, 41–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czerniawska-Kusza, I. Comparing modified biological monitoring working party score system and several biological indices based on macroinvertebrates for water-quality assessment. Limnologica 2005, 35, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deborde, D.; Hernandez, M.; Magbanua, F. Benthic Macroinvertebrate Community as an Indicator of Stream Health: The Effects of Land Use on Stream Benthic Macroinvertebrates. Sci. Diliman 2016, 28, 5–26. [Google Scholar]
- Dominguez-Granda, L.; Lock, K.; Goethals, P. Using multi-target clustering trees as a tool to predict biological water quality indices based on benthic macroinvertebrates and environmental parameters in the Chaguana watershed (Ecuador). Ecol. Infoma. 2011, 6, 303–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratia, H.; Vuori, K.; Oikari, A. Caddis larvae (Trichoptera, Hydropsychidae) indicate delaying recovery of a watercourse polluted by pulp and paper industry. Ecol. Indic. 2012, 15, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Wang, Z.; Duan, X.; Pan, B. Effects of pollution on macroinvertebrates and water quality bio-assessment. Hydrobiologia 2014, 729, 247–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohlmann, B.; Arroyo, A. Chapter 6. In Integrated Analytical Approaches for Pesticide Management; Maestroni, B., Cannavan, A., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018; pp. 83–106. [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez-Arguello, R.; Cornejo, A.; Pearson, R.; Boyero, L. Spatial and temporal variation of stream communities in a human-affected tropical watershed. Int. J. Limnol. 2010, 46, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pineda-Pinead, J.; Rosas-Acevedo, J.; Sigarreta-Almira, J.; Hernandez-Gomez, J.; Reyes-Umana, M. Biotic indices to evaluate water quality: BMWP. Int. J. Environ. Ecol. Fam. Urban Stud. 2018, 8, 23–36. [Google Scholar]
- Connolly, N.; Pearson, R. The effect of fine sedimentation on tropical stream macroinvertebrate assemblages: A comparison using flow-through artificial stream channels and recirculating mesocosms. Hydrobiologia 2007, 592, 423–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorion, C.; Kennedy, B. Relationship between Deforestation, Riparian Forest Buffers and Benthic Macroinvertebrates in Neotropical Headwater Streams. Freshw. Biol. 2009, 54, 165–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Callaghan, P.; Kelly-Quinn, M. Performance of Selected Macroinvertebrate-Based Biotic Indices for Rivers Draining the Merendón Mountains Region of Honduras. Cuad. Investig. UNED 2013, 5, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- TCRN Staff. Water Law in Costa Rica, Crime or Sin of Omission. Costa Rica Times. 4 December 2020. Available online: https://thecostaricanews.com/water-law-in-costa-rica-crime-or-sin-of-omission/ (accessed on 20 April 2022).
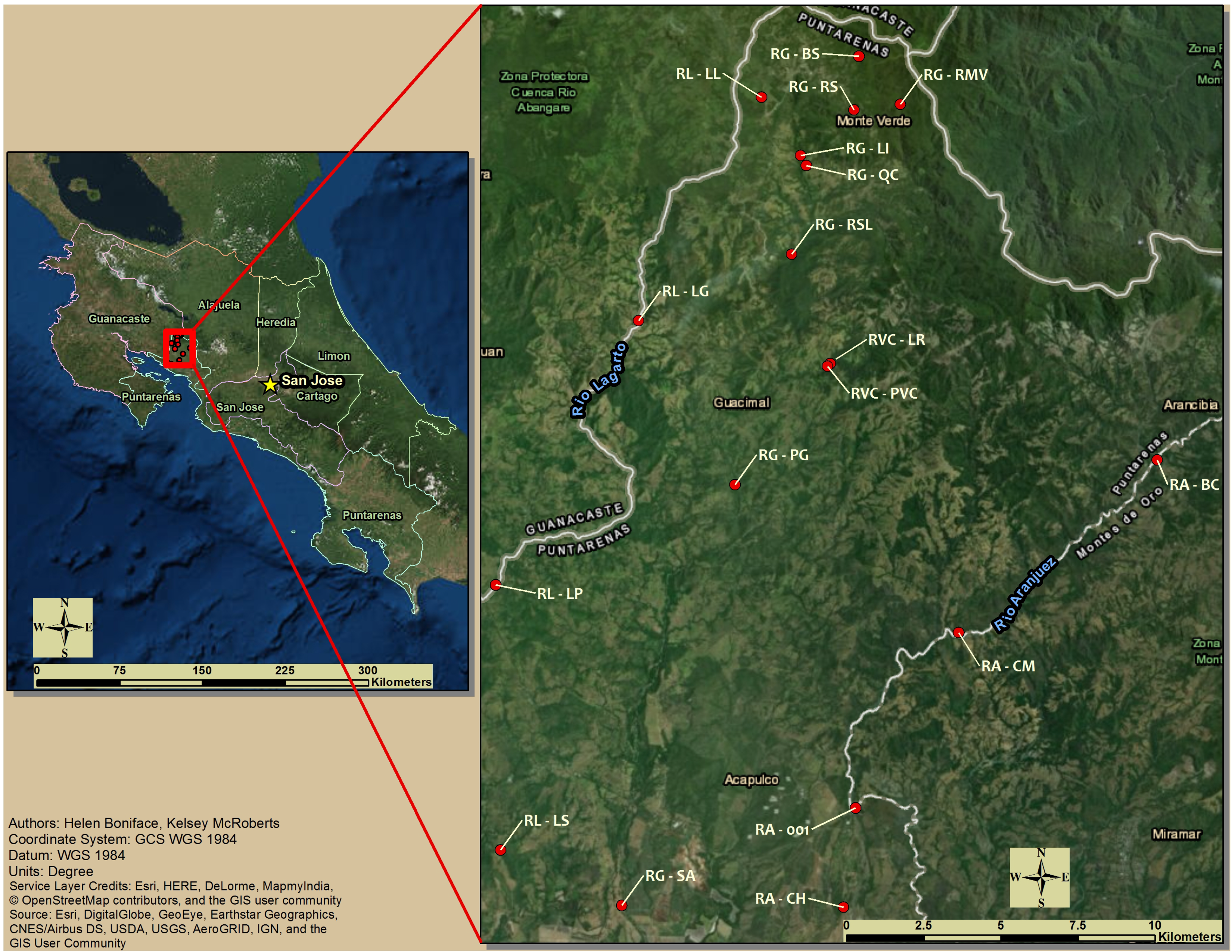

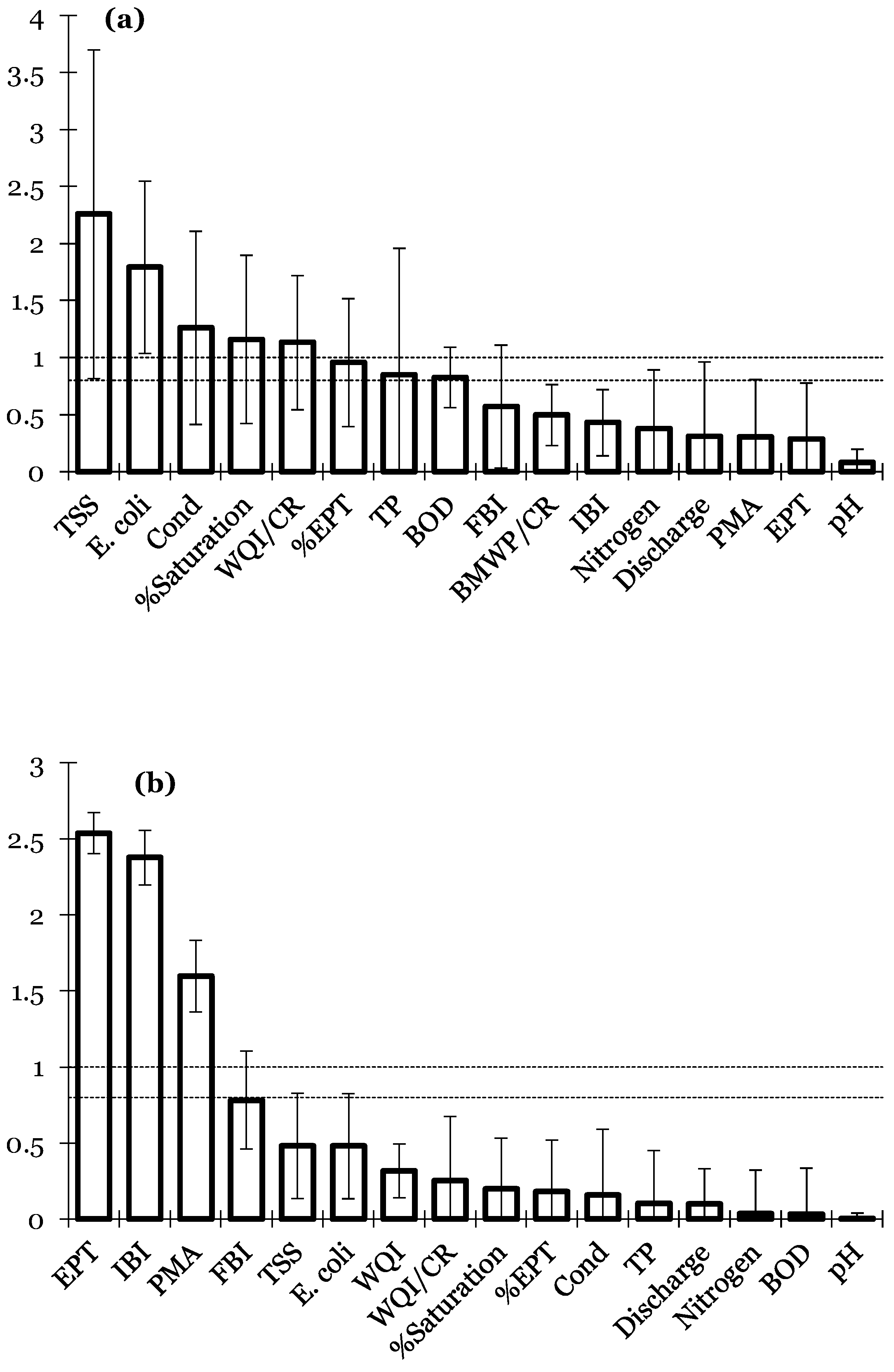
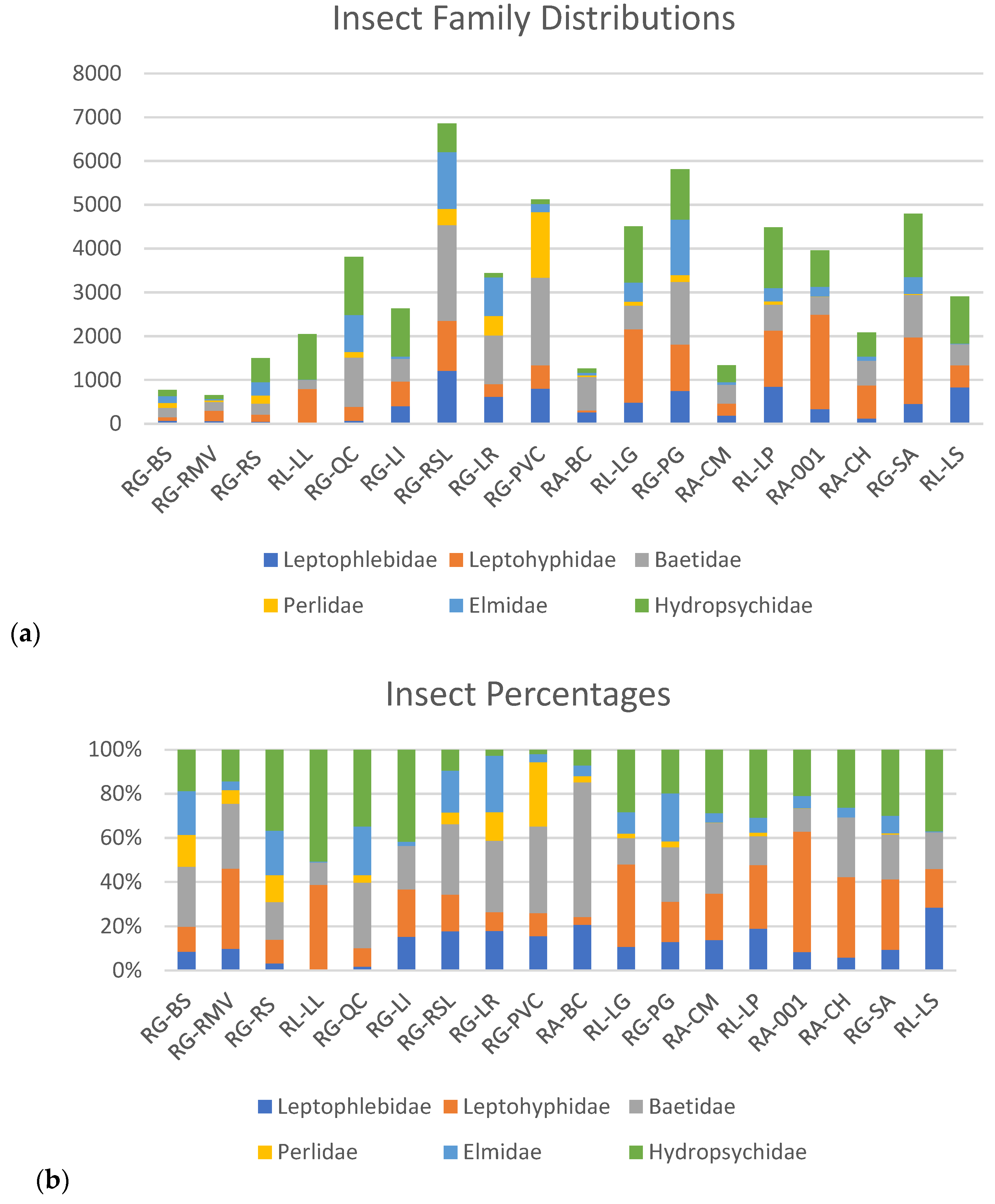
| Site | Elevation (M) | EPT | BMWP/CR | PMA | WQI | WQI/CR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RG-BS | 1555 | 5.2 ± 0.4 | 81.7 ± 4.6 | 46.0 ± 5.2 | 81.6 ± 1.7 | 5.2 ± 0.4 |
| RG-RMV | 1450 | 5.5 ± 0.4 | 73.7 ± 5.3 | 51.1 ± 2.1 | 83.3 ± 1.6 | 6.0 ± 0.4 |
| RG-RS | 1372 | 4.5 ± 0.5 | 68.1 ± 6.1 | 37.2 ± 3.6 | 84.7 ± 1.7 | 5.7 ± 0.4 |
| RL-LL | 1220 | 3.1 ± 0.2 | 49.1 ± 3.5 | 44.1 ± 2.1 | 79.8 ± 2.0 | 6.2 ± 0.4 |
| RG-QC | 903 | 5.6 ± 0.4 | 78.2 ± 4.6 | 56.5 ± 2.9 | 75.8 ± 1.7 | 6.4 ± 0.4 |
| RG-LI | 872 | 6.3 ± 0.5 | 87.8 ± 6.3 | 60.4 ± 3.1 | 77.9 ± 1.3 | 6.1 ± 0.4 |
| RG-RSL | 661 | 6.8 ± 0.4 | 93.2 ± 5.1 | 61.3 ± 3.3 | 77.9 ± 1.1 | 6.5 ± 0.4 |
| RG-LR | 653 | 6.8 ± 0.5 | 95.4 ± 6.7 | 67.6 ± 2.8 | 74.8 ± 4.1 | 6.1 ± 0.4 |
| RG-PVC | 644 | 7.1 ± 0.3 | 100.6 ± 4.8 | 67.2 ± 3.5 | 80.6 ± 1.6 | 5.8 ± 0.4 |
| RA-BC | 568 | 4.4 ± 0.5 | 58.4 ± 6.4 | 43.0 ± 3.5 | 82.7 ± 1.3 | 5.5 ± 0.4 |
| RL-LG | 336 | 5.9 ± 0.3 | 86.9 ± 7.4 | 54.7 ± 2.5 | 77.7 ± 1.1 | 6.3 ± 0.4 |
| RG-PG | 306 | 6.8 ± 0.4 | 90.2 ± 5.0 | 58.2 ± 2.7 | 77.3 ± 1.1 | 6.9 ± 0.3 |
| RA-CM | 280 | 4.6 ± 0.4 | 54.2 ± 5.1 | 50.1 ± 1.8 | 80.0 ± 1.2 | 5.7 ± 0.3 |
| RL-LP | 113 | 6.2 ± 0.4 | 90.3 ± 7.2 | 51.4 ± 2.1 | 67.4 ± 3.5 | 5.8 ± 0.4 |
| RG-001 | 101 | 5.3 ± 0.4 | 66.3 ± 5.5 | 46.5 ± 2.4 | 77.6 ± 1.6 | 5.8 ± 0.4 |
| RA-CH | 33 | 4.2 ± 0.3 | 42.5 ± 4.4 | 46.6 ± 2.3 | 71.8 ± 2.5 | 6.1 ± 0.4 |
| RG-SA | 23 | 5.6 ± 0.5 | 75.8 ± 6.2 | 51.1 ± 1.5 | 75.4 ± 1.3 | 6.2 ± 0.4 |
| RL-LS | 15 | 5.1 ± 0.4 | 67.4 ± 6.9 | 43.0 ± 2.5 | 70.0 ± 1.7 | 6.8 ± 0.3 |
| Family | WQI | TP | BMWP |
|---|---|---|---|
| Leptohyphidae | 2.09 ± 0.26 | 0.10 ± 0.59 | 1.33 ± 1.56 |
| Perlidae | 0.88 ± 0.50 | 0.35 ± 0.48 | 1.73 ± 1.15 |
| Baetidae | 0.71 ± 0.81 | 1.36 ± 0.86 | 0.02 ± 1.42 |
| Leptophlebiidae | 0.43 ± 0.57 | 0.27 ± 0.70 | 0.17 ± 1.49 |
| Hydropsychidae | 0.34 ± 0.56 | 1.99 ± 0.71 | 1.01 ± 1.79 |
| Elmidae | 0.19 ± 0.43 | 0.01 ± 0.74 | 0.42 ± 1.08 |
| RGBS | RG RMV | RG-RS | RL-LL | RG-QC | RG-LI | RG-RSL | RG-LR | RG-PVC | RA-BC | RL-LG | RG-PG | RA-CM | RL-LP | RG-001 | RA-CH | RG-SA | RL-LS | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RG-BS | 0 | 0.11 | 0.33 | 1.89 | 0.02 | 0.06 | 0.23 | 0.33 | 0.63 | 0.96 | 0.05 | 0.13 | 1.34 | 0.13 | 0.42 | 2.73 | 0.06 | 0.05 |
| RG-RMV | 0.04 | 0 | 0.06 | 1.08 | 0.04 | 0.35 | 0.67 | 0.84 | 1.28 | 0.41 | 0.31 | 0.49 | 0.67 | 0.49 | 0.09 | 1.73 | 0.08 | 0.31 |
| RG-RS | 0.13 | 0.03 | 0 | 0.64 | 0.18 | 0.69 | 1.12 | 1.31 | 1.88 | 0.17 | 0.01 | 0.87 | 0.34 | 0.88 | 0.01 | 1.16 | 0.11 | 0.63 |
| RL-LL | 0.05 | 0.18 | 0.34 | 0 | 1.51 | 2.65 | 3.45 | 3.81 | 4.71 | 0.16 | 2.53 | 3.01 | 0.05 | 3.01 | 0.53 | 0.08 | 1.26 | 2.53 |
| RG-QC | 0.47 | 0.79 | 1.11 | 0.22 | 0 | 0.16 | 0.39 | 0.52 | 0.88 | 0.69 | 021 | 0.25 | 1.02 | 0.26 | 0.25 | 2.25 | 0.01 | 0.13 |
| RG-LI | 0.19 | 0.41 | 0.63 | 0.05 | 0.07 | 0 | 0.05 | 0.11 | 0.25 | 1.59 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 1.99 | 0.01 | 0.82 | 3.63 | 0.26 | 0.74 |
| RG-RSL | 0.19 | 0.41 | 0.64 | 0.05 | 0.06 | 0.00 | 0 | 0.01 | 0.10 | 2.14 | 0.07 | 0.02 | 2.67 | 0.02 | 1.28 | 4.56 | 0.54 | 1.18 |
| RG-LR | 0.63 | 0.99 | 1.34 | 0.33 | 0.01 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0 | 0.05 | 2.53 | 0.13 | 0.05 | 3.02 | 0.05 | 1.51 | 4.97 | 0.69 | 1.39 |
| RG-PVC | 0.01 | 0.10 | 0.23 | 0.01 | 0.33 | 0.10 | 0.11 | 0.46 | 0 | 3.15 | 0.33 | 0.19 | 3.89 | 0.19 | 2.89 | 5.99 | 1.09 | 1.96 |
| RA-BC | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.06 | 0.12 | 0.68 | 0.32 | 0.32 | 0.85 | 0.06 | 0 | 1.43 | 1.79 | 0.03 | 1.80 | 0.11 | 0.45 | 1.22 | 0.14 |
| RL-LG | 0.21 | 0.44 | 0.68 | 0.06 | 0.45 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.11 | 0.12 | 0.35 | 0 | 0.02 | 1.89 | 0.02 | 0.75 | 3.49 | 0.21 | 0.67 |
| RG-PG | 0.26 | 0.50 | 0.76 | 0.08 | 0.03 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.08 | 0.15 | 0.40 | 0.00 | 0 | 2.30 | 0.00 | 1.02 | 4.04 | 0.37 | 0.93 |
| RA-CM | 0.04 | 0.16 | 0.31 | 0.00 | 0.24 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.36 | 0.01 | 0.10 | 1.36 | 0.10 | 0 | 2.31 | 0.26 | 0.24 | 0.82 | 0.31 |
| RL-LP | 2.79 | 3.52 | 1.52 | 2.12 | 0.97 | 1.54 | 1.54 | 0.77 | 2.44 | 3.25 | 1.47 | 1.36 | 2.19 | 0 | 1.02 | 4.05 | 0.37 | 0.93 |
| RG-001 | 0.22 | 0.46 | 0.70 | 0.07 | 0.05 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.10 | 0.13 | 0.36 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.08 | 1.44 | 0 | 1.00 | 0.16 | 0.01 |
| RA-CH | 1.33 | 1.85 | 2.31 | 0.88 | 0.22 | 0.52 | 0.52 | 0.13 | 1.09 | 1.65 | 0.04 | 0.42 | 0.92 | 0.27 | 0.46 | 0 | 1.96 | 1.10 |
| RG-SA | 0.52 | 0.86 | 1.19 | 0.26 | 0.00 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.01 | 0.37 | 6.19 | 0.07 | 0.05 | 2.40 | 0.89 | 0.06 | 0.19 | 0 | 0.125 |
| RL-LS | 1.85 | 2.45 | 2.97 | 1.31 | 0.45 | 0.86 | 0.86 | 0.32 | 1.60 | 2.22 | 0.81 | 0.73 | 1.36 | 0.10 | 0.78 | 0.04 | 0.40 | 0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shahady, T.; Montero-Ramírez, J.J. End-Point Predictors of Water Quality in Tropical Rivers. Pollutants 2023, 3, 461-476. https://doi.org/10.3390/pollutants3040032
Shahady T, Montero-Ramírez JJ. End-Point Predictors of Water Quality in Tropical Rivers. Pollutants. 2023; 3(4):461-476. https://doi.org/10.3390/pollutants3040032
Chicago/Turabian StyleShahady, Thomas, and José Joaquín Montero-Ramírez. 2023. "End-Point Predictors of Water Quality in Tropical Rivers" Pollutants 3, no. 4: 461-476. https://doi.org/10.3390/pollutants3040032
APA StyleShahady, T., & Montero-Ramírez, J. J. (2023). End-Point Predictors of Water Quality in Tropical Rivers. Pollutants, 3(4), 461-476. https://doi.org/10.3390/pollutants3040032







