Abstract
Temperature-dependent chemical toxicity has become a crucial issue taking into consideration that lakes, especially shallow waterbodies, are impacted by climate change worldwide. In this study, we are looking for an answer to what extent standard ecotoxicity assays being performed under constant and relatively low temperatures are capable of predicting the chemical risk posed by pesticides. Lemna minor test plants were exposed to glyphosate in concentrations in the range of 25, 50, 100, 200, and 400 μg/L at temperatures 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, and 35 °C. Two peaks appeared when growth inhibition was assessed; lower concentrations elucidated higher inhibition, at 20 °C, while higher concentrations were found at a higher temperature of 30 °C. The toxic effect experienced at 20 °C indicates that reported PNEC values cannot be sufficient to protect non-target aquatic species in certain environmental scenarios. In addition to growth inhibition, phytotoxicity was also assessed based on peroxidase (POD) concentrations. In general, POD showed greater sensitivity, already showing a response at the lowest temperature tested, 10 °C. Decreased POD activity was detected in the temperature range of 10–30 °C, most probably indicating damage to cell and plasma membranes.
1. Introduction
Lakes worldwide are impacted by climate change, shallow lakes being the most vulnerable [1]. In recent decades, the increase in annual water temperature was estimated to be about 0.15–0.3 °C per decade in 24 European lakes [2].
Climate change is expected to alter the environmental fate and behaviour of pesticides. Increased temperature will most likely increase volatilization and speed up degradation; on the other hand, in warmer scenarios, pesticide application might grow [3].
As standard ecotoxicological tests use pre-set and relatively low temperatures, the following question arises: to what extent can these tests predict toxicological response to a certain chemical in waters with elevated temperatures? In the literature, contradictory data are available; some authors report an increase and others a decrease in toxicity at higher temperatures [4]. Several studies have already dealt with the temperature dependence of the effect of chemicals on aquatic organisms, which is often explained using the concept of Q10 (the doubling of the metabolic rate as a result of a 10 °C increase in temperature). The point of this is that as the temperature rises, the rate of metabolism increases, thus increasing the uptake and distribution of toxins [5,6,7]. Moreover, as the temperature rises, the solubility of oxygen in water decreases, which indirectly affects the response of organisms to toxic substances [8]. On the other hand, higher temperatures also enhance biochemical detoxification and the removal of chemicals [9].
The glyphosate-based formulation [N-(phosphonomethyl)glycine, CAS No. 1071-83-6] (in the following: glyphosate) that we used is a systemic, broad-spectrum herbicide, which has become the most frequently used herbicide globally [10]. The mode of glyphosate’s action is blocking the shikimic acid pathway by inhibiting enolpyruvyl shikimic phosphate (EPSP) synthase, resulting in stunted growth, leaf malformation, loss of green coloration, tissue damage, and finally, death [11]. Considering that glyphosate is a non-selective herbicide, it affects both weeds and crops [12]. Based on the research of Radwan and Fayez, the application of glyphosate, even at low doses, caused chlorosis and curling of the leaf edges on peanut plants, and significantly increased POD and CAT activity, which indicates oxidative stress [13]. However, its use is considered safe, as microorganisms decomposed it into phosphate and carbon dioxide within a short time when it entered into the soil [12].
During a large-scale monitoring program between 1990 and 2015, traces of pesticides found in surface waters were examined in Hungary. The results brought a startling realization, according to which pesticide residues were found in detectable quantities even in the majority of nature conservation or recreation areas [14]. Extremely high concentrations of pesticides found in the environment of industrial plants (in water paths flowing from artificial ponds and basins) are a particular concern [15].
In our study, the phytotoxicity of glyphosate (GLP) was assessed at different temperatures following the protocol of the standard Lemna sp. growth inhibition test [16]. Lemna sp. have been widely applied as representatives of non-target species (e.g., [17]) as GLP is well-known to affect non-target aquatic organisms [18]. GLP’s effects have been well documented for this test organism [19]. Lewis and Thursby (2018) found duckweed to be amongst the species most sensitive to glyphosate [20]. Duckweeds are also representative test species, as they float on the surface. Lake surface water temperatures in many lakes worldwide show clear warming trends [21]. As GLP is highly water-soluble, water contamination by leaching into nearby waterbodies is a growing problem [22].
In addition to the growth rate and its inhibition, and the end-points originally described by OECD guidelines, peroxidase levels were also measured. Camp and Buchwalter (2016) highlight the importance of assessment of sublethal endpoints in acute toxicity assays when temperature-dependent toxicity is to be evaluated [23]. In the study by Passardi et al. (2005), peroxidases showed the strongest response in comparison to other biomarkers such as superoxide dismutase or glutathione reductase levels [24]. POD was found to be the most sensitive end-point in heavy-metal (CuO)-stressed Lemna minor (Linnaeus, 1753) [25]. In the comparative study by Radwan and Fayez (2016), POD showed the strongest response to GLP treatment of antioxidant enzymes [13]. POD activity measured in white mustard (Sinapis alba) seedlings treated with PAH extract showed a correlation with the amount of PAH accumulated by the plant [13].
The protocols used to assess the ecotoxic effect accurately describe the incubation temperature, which is advantageous from the point of view of comparability, but it is based on an average temperature that varies due to global climate change. The aim of our study is to learn about the effect of glyphosate on a wide temperature spectrum on the commonly used Lemna minor test subject, whereby in addition to growth inhibition, we also observe the POD enzyme activity.
2. Materials and Methods
A local clone of L. minor was isolated from plants collected in Tapolca stream, Hungary (46°51′01.6″ N 17°25′17.4″ E), and maintained as stock culture in Steinberg medium (OECD 2006). The collected plant material was identified by Dr Katalin Hubai, and voucher specimens were deposited at the Herbarium of the Department of Limnology, University of Pannonia, Veszprém. Prior the experiments, plants were acclimated for one month according to guidelines, at room temperature, in the prescribed growth medium and illuminated with ~8500 lux in a 16/8 light cycle.
Taifun® Forte (360 g/L glyphosate [isopropylamine salt], Adama Hungary Ltd., Budapest, Hungary) was used. It is recommended for arable lands as well as in horticulture and viticulture, for both mono- and dicotyledonous plant control. The different test concentrations were prepared from a stock solution by dissolving the commercial product in deionized water.
A range of nominal concentrations within 25–400 μg/L were selected (25, 50, 100, 200 and 400 μg/L), based on the study of Silva et al. [26]. This range covers the 112 μg/L PNEC value suggested for Italy [27]. Clean Steinberg medium was used as the negative control. A static test was performed with no renewal of the test medium, as herbicide application is normally a single event [28].
Some 15 healthy colonies consisting of 2 fronds each were placed in 150 mL Erlenmeyer flasks. Controls and test vessels were places randomly in an incubator (Velp Refrigerated Incubator FOC 225I), where they were repositioned every day to minimise the influence of spatial differences in light intensity or temperature. Tests were performed in accordance with the protocol defined by OECD (2006). The only significant diversion from the protocol was the temperature regime; the OECD protocol defines the standard temperature 24 ± 2 °C, while in our study, incubation temperatures were as follows: 10 °C, 15 °C, 20 °C, 25 °C, 30 °C, and 35 °C. The tests at different temperatures were performed in the same incubator one after the other, always at only one temperature at a time. Frond and colony numbers and the appearance of the colonies were recorded at the end of the exposure, after 7 days. Specific growth rates were calculated following the formula given by OECD guidelines:
where µ is the growth rate, Ft is the number of fronds after 7 days, F0 is the initial number of fronds, and t is the exposition time (7 days).
where Ir% is the growth inhibition, µk is the growth rate of the control, and µt is the growth rate of the sample.
For measuring peroxidase activity and total protein content, frozen leaves were homogenised in ice cold mortar with phosphate buffer (50 mmol/L, pH 7), 1 mmol/L EDTA and 0.5 mmol/L PMSF. After 20 min centrifugation at 15,000× g at 4 °C, the supernatant was collected and TMB peroxidase activity (A 654) was measured according to the method of Imberty et al. (1984), with minor modifications [29]. The oxidation rate was estimated by measuring the absorbance change in A 654 nm, and enzyme activity in the U/mL extract was measured.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Growth Inhibition
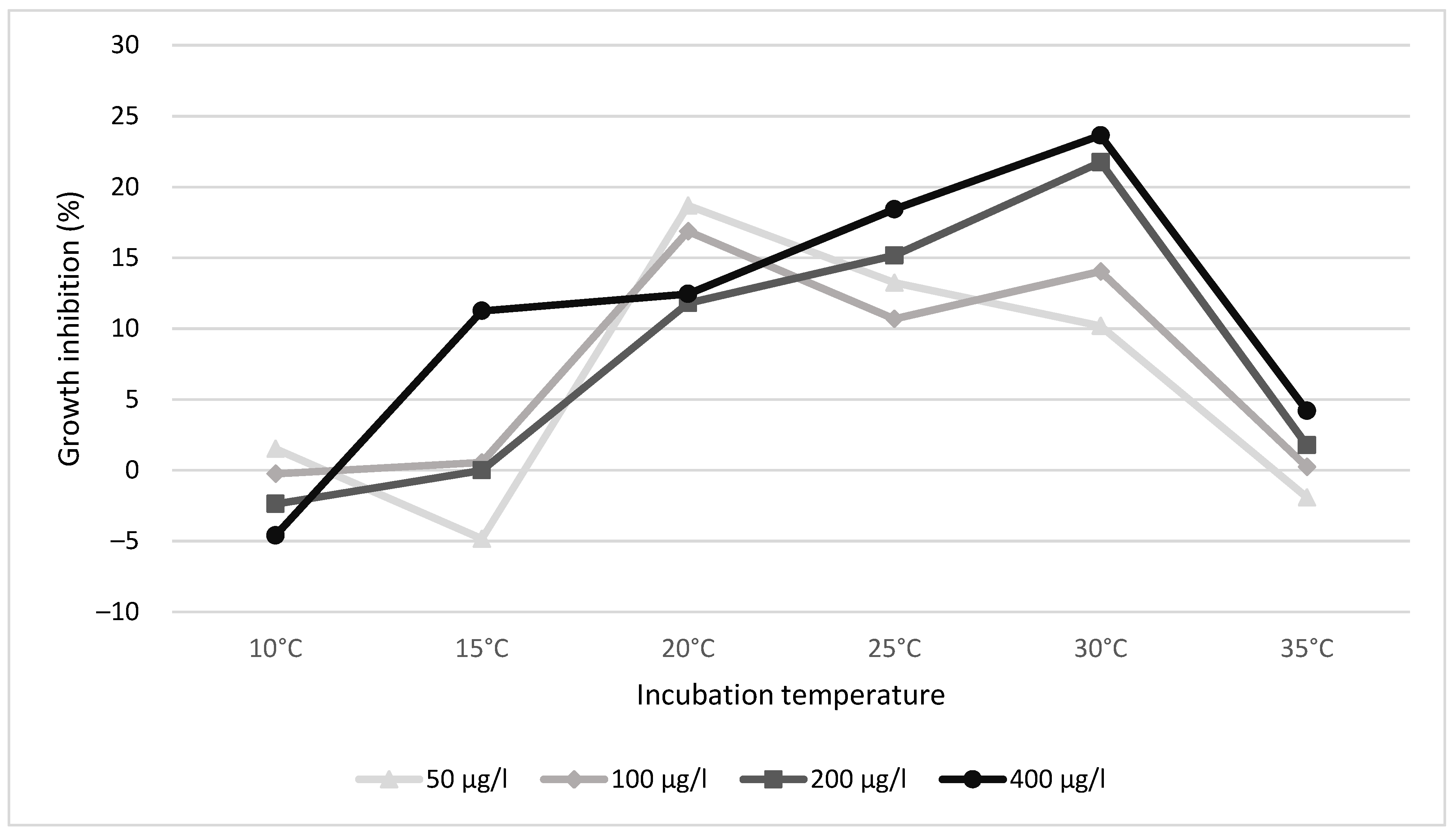
The growth rate of the control was highest at 30 °C and lowest at 15 °C, starting at 10 °C, respectively: 3.026, 2.948, 3.456, 3.521, 3.704, and 3.026. Figure 1 and Table 1 show the growth inhibition recorded at different temperatures. The highest inhibition in the case of the higher concentrations applied (400 and 200 μg/L) was experienced at 30 °C. On the contrary, the two lower concentrations applied (100 and 50 μg/L) triggered the highest inhibition at 20 °C. No inhibition was experienced at lower or higher temperatures. At the lowest temperature tested (10 °C), no growth was experienced.

Figure 1.
Growth inhibition expressed as a % of control at different temperatures.

Table 1.
The growth inhibition induced by each glyphosate concentration at the given temperatures.
Basiglini et al. (2018) assessed the phytotoxic effects of treated wastewater samples, on duckweed both under winter and summer conditions. Under winter conditions, no growth was reported either in the control or in the sample [30]. Seasonal variation in the growth rates of duckweed is a normal phenomenon [31]. Van Der Heide et al. (2006) measured the growth rate of L. minor at temperatures between 15 and 33 °C. The highest growth rate was experienced at 24 °C. Significantly lower rates were found at the two lowest temperatures, and modestly reduced growth rates at the two highest [32].
In the study of Rosenkrantz et al. (2013), herbicide flupyrsulfuron-methyl toxicity decreased by a factor of 2 at a lower temperature of 15 °C in comparison to 24 °C. The explanation given was that the growth rate of the plants was reduced at the lower temperature [33].
Photosynthetic activity is a temperature-dependent process, although some controversy surrounding this exists in the literature. Some authors report decreases but others increases in photosynthetic rates as a result of warming, most likely depending on species [34]. Inhibition of photosynthetic processes is generally responsible for phytotoxic effects, which in turn determine biomass [35]. Mateos-Naranjo and Perez-Martin (2013) exposed Bolboschoenus maritimus to sub-lethal doses of glyphosate herbicides, and found a significant decrease in biomass at higher concentrations, most likely due to a decrease in the net photosynthetic rate. Overall, GLP had negative impact on photochemical (PSII) apparatus [36]. Gomes et al. (2017) reported that glyphosate acid and its formulation roundup negatively affected the activities of enzymes associated with the mitochondrial electron transport chain in Dimorphandra wilsonii [37]. Da Silva Santos (2020) found that glyphosate decreased chlorophyll a and b contents and the photosystem II (PSII) photochemical activity, and also promoted oxidative stress [38]. Concentration-dependent induction of antioxidant enzymes such as peroxidase, catalase, ascorbate peroxidase, and superoxide dismutase was reported by Radwan and Fayez [13].
At higher temperatures, biochemical detoxification and elimination mechanisms will most likely increase, thereby lowering the toxic risk of pesticides [26]. This might explain why growth inhibition reduces at temperatures above 20 °C in cases of lower concentrations, i.e., 50 and 100 μg/L. However, it seems that the toxic effect(s) caused by higher concentrations (200 and 400 μg/L) cannot be counteracted.
It should be noted that the lower concentrations tested, 50 and 100 μg/L, trigger the highest growth inhibition at 20 °C. On one hand, this suggests that the aforementioned 112 μg/L PNEC value defined for Italy cannot be protective enough for non-target plants. A temperature of 20 °C was found to be optimal for growth in the study by Paolacci et al. [39]. Additionally, 20 °C is a relevant environmental scenario in temperate lakes; for example, the average temperature in Lake Balaton (Hungary) during summer is 22.5 °C (and on the hottest days, 26–28 °C) [40].
Environmental risk seems to appear at a high water temperature (30 °C) and high GLP concentration (in the range of 200–400 μg/L), and may be environmentally relevant, for example, to South America, where extremely high GLP concentrations were reported (such as 2777 μg/L in Colombia or 10,500 μg/L in Argentina) [41].
3.2. Peroxidase Activity
In general, chemical stress might trigger the overproduction of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in plants [42]. POD, an antioxidant defense enzyme, plays a major role in overcoming oxidative stress [43].
Figure 2, Figure 3, Figure 4, Figure 5 and Figure 6 show the concentration–effect relationships of GLP concentrations and POD activity levels at different temperatures between 10 and 35 °C. Peroxidase activity is expected to show concentration-dependent increase, as reported by most studies, while no response has also been observed in cases of low levels of contamination [44]. On the contrary, high levels of treatment might trigger a significant decrease [42,45,46]. It may be assumed that cell and plasma membranes are damaged, and the plants’ ability to counteract toxic stress is reduced. The sensitivity of plants, however, might be species-specific; in the study by Wang et al. (2015), atrazine triggered a decrease in the POD activity of Scirpus tabernaemontani in a concentration-dependent manner, but applying the same concentrations resulted in an increase in the enzyme activity in Acorus calamus [47].

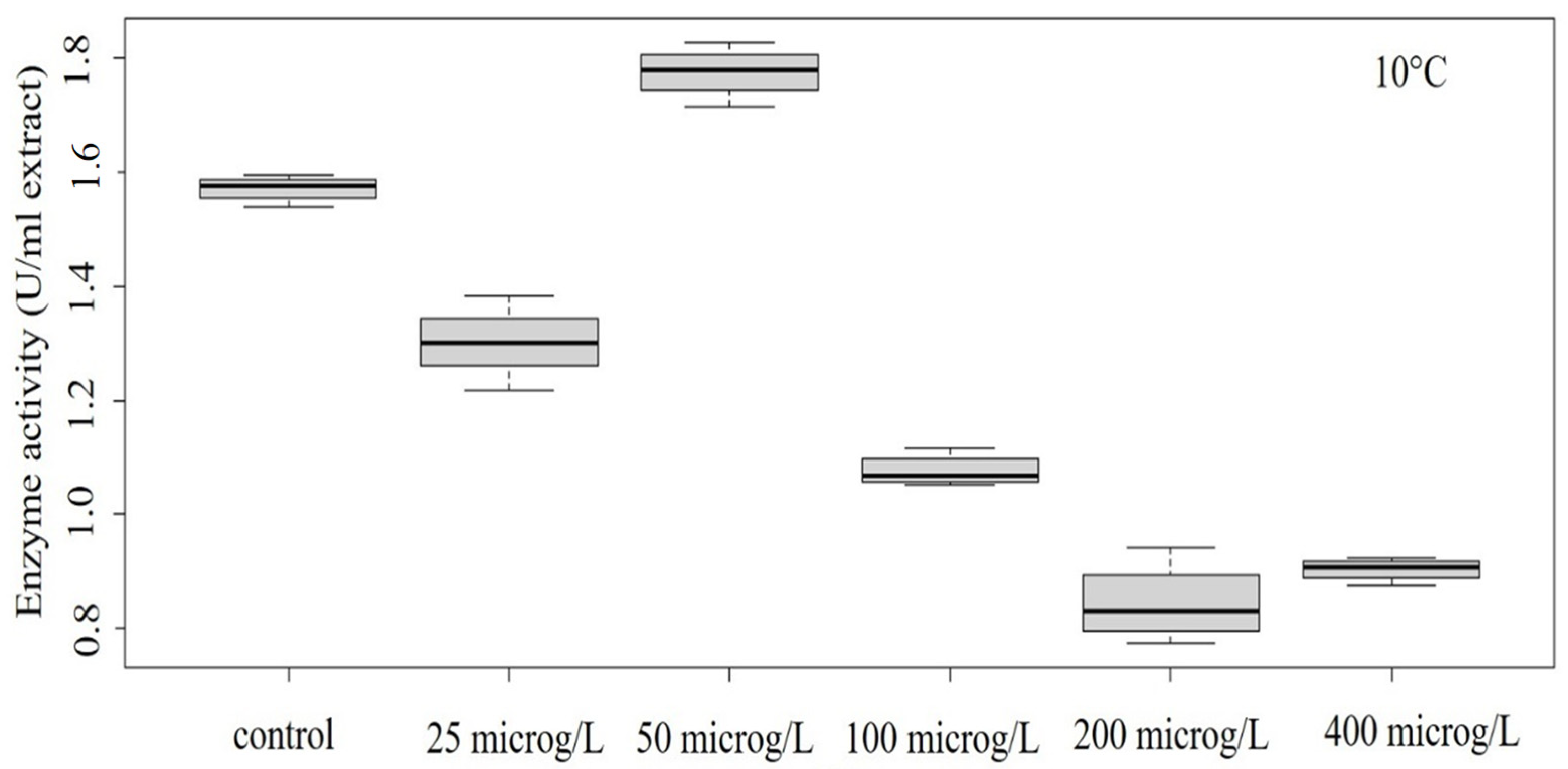
Figure 2.
Concentration–effect relationship of enzyme activity at 10 °C.

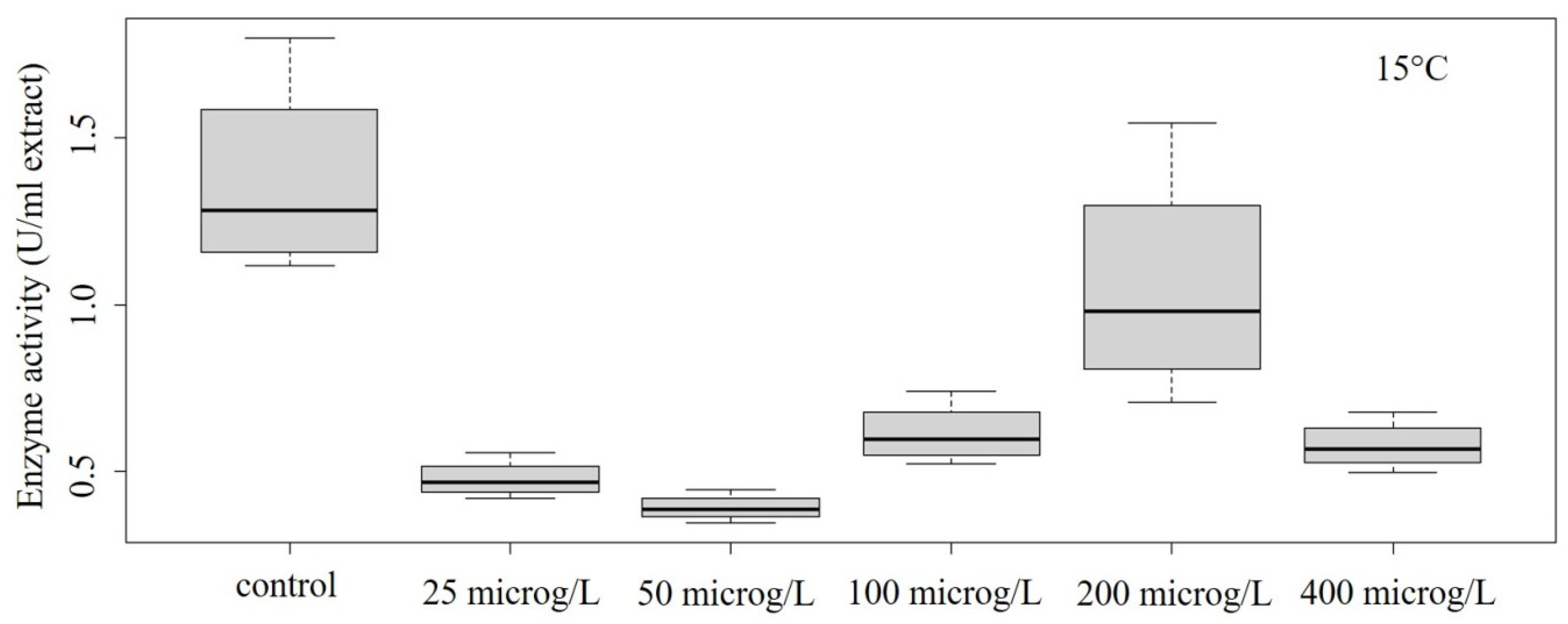
Figure 3.
Concentration–effect relationship of enzyme activity at 15 °C.

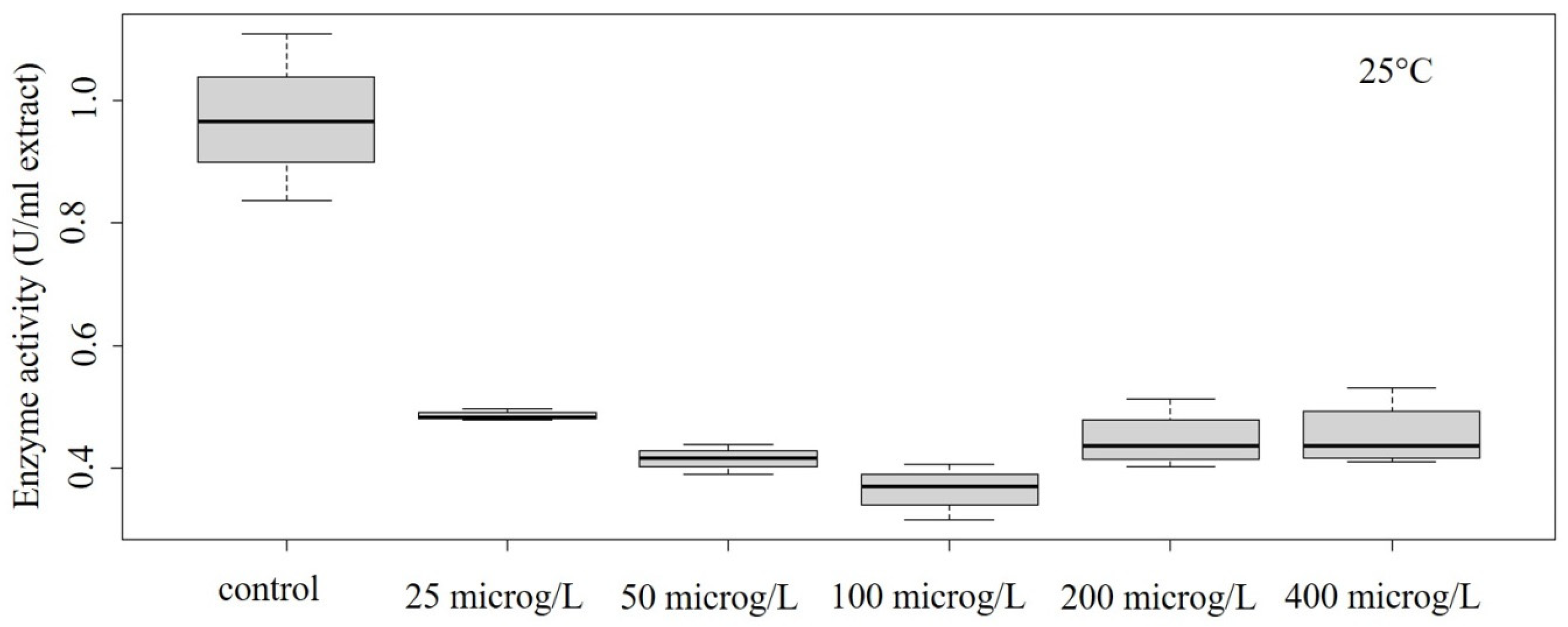
Figure 4.
Concentration–effect relationship of enzyme activity at 25 °C.

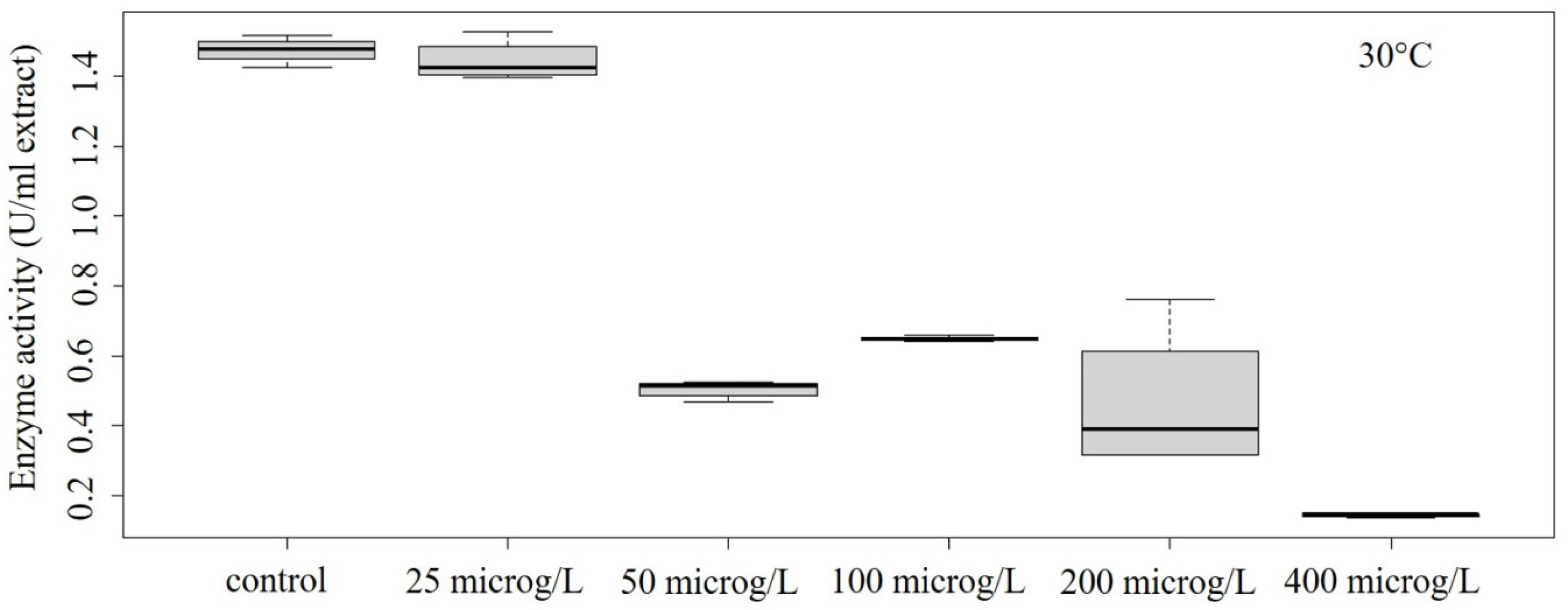
Figure 5.
Concentration–effect relationship of enzyme activity at 30 °C.

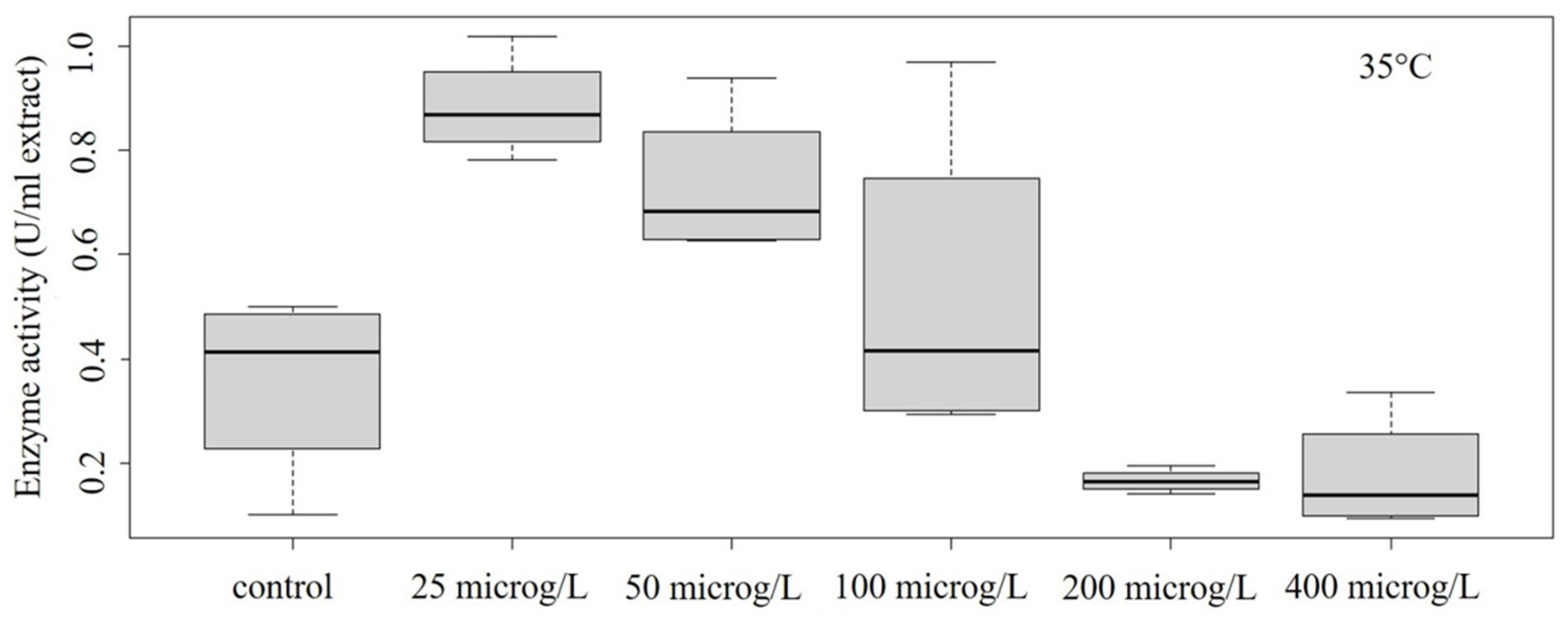
Figure 6.
Concentration–effect relationship of enzyme activity at 35 °C.
In our study, decreased POD activity was detected in the temperature range of 10–30 °C (Figure 2, Figure 3, Figure 4 and Figure 5). At 10 °C, the effect on enzyme activity caused by GLP was significant (ANOVA: Df = 5; F = 364.7; p = 1.13 × 10–12) (Figure 2). Significant effects could be also determined in the case of treatment performed at 15 °C (ANOVA: Df = 5; F = 5.776; p = 0.00608) (Figure 3) and at 25 °C (ANOVA: Df = 5; F = 28.52; p = 0.00000289) (Figure 4).
At 30 °C, the enzyme activity showed significant differences at different concentrations (ANOVA: Df = 4; F = 4.804; p = 0.0121) (Figure 5). At 35 °C, significant differences in enzyme activity were still obtained (ANOVA: Df = 5; F = 5.096; p = 0.00977) (Figure 6); however, a biphasic response was experienced (an increase in the protective enzyme concentration at lower concentrations, but a decrease at higher concentrations, indicating serious damage).
A biphasic response of G-POD was observed in the study of Teisseire and Vernet [48]. Lemna minor test plants were treated with the phenylurea herbicide diuron. An increase in enzyme activity was experienced during the first part of the exposure, but later, a significant decrease was observed. Hu et al. (2018) found a significant increase in POD enzyme activity in L. minor after 10 µM Cu treatment, while a concentration of 20 µM decreased POD activity (p < 0.05) [49]. A similar biphasic response was reported in the study of Pouresmaeil et al. (2022), when the potential herbicidal effect of Moldavian dragonhead (Dracocephalum moldavica L.) essential oil was investigated [50]. Lower levels of potential damage can be attributed to faster metabolic processes, similar to growth inhibition [26].
GLP has been widely reported to increase ROS production, leading to oxidative damage [51]. Our results support that POD activity reflects oxidative stress even at very low concentrations. Smedbol et al. (2018), however, reported that only the highest glyphosate (500 and 1000 mg/L) concentrations triggered changes (increase) in peroxidase activity when a commercial GBH formulation, Factor540®, was tested on freshwater phytoplankton species. Comparison might suggest the increased sensitivity of L. minor either as test species or as a dominant member of freshwater associations [52].
Enzyme activity was found to be a more sensitive endpoint in comparison to biomass reduction when the phytotoxic effects caused by the herbicide trichloroacetate were evaluated. Geoffroy et al. (2004) also found antioxidant enzyme activity a more sensitive end-point than biomass when L. minor test plants were exposed to the herbicide flumioxazin [53].
It should be noted that predicted temperature increases will have a general effect on the toxicity of different chemicals used in aquatic environments. Moraies et al. (2023) demonstrated the synergistic effect of increased temperature and endocrine disrupters in coastal habitats [54]. Predictions suggest that the combined effects of pesticides and elevated temperatures will be present on different trophic levels, affecting whole communities, and will be most severe in cases of heatwaves [55]. Higher temperature regimes will most likely result in a higher prevalence of agricultural pests, which in turn require higher dosages of pesticides [56].
4. Conclusions
The phytotoxicity of glyphosate (GLP) was assessed using the Lemna sp. growth inhibition test in different temperature scenarios. In addition to growth inhibition, peroxidase activity was also measured. Growth inhibition showed a clear concentration- and temperature-dependent pattern. The lower concentrations tested, 50 and 100 μg/L, triggered the highest growth inhibition at 20 °C, while in cases of higher concentrations being applied (400 and 200 μg/L), the highest inhibition was experienced at 30 °C. No inhibition was experienced at lower or higher temperatures. In general, the growth rate of the plants is reduced at lower temperatures, while at higher temperatures, biochemical detoxification and elimination mechanisms will most likely increase. On the other hand, POD activity already produced aresponse at the lowest temperature tested, 10 °C. Decreased POD activity was detected in the temperature range of 10–30 °C, most likely indicating damage to cell and plasma membranes. In general, POD seems to be a more sensitive end-point in detecting the phytotoxic effects of GLP in different temperature scenarios.
Author Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Conceptualization was performed by B.E.-V. and N.K.; data collection and analyses were performed by B.E.-V., K.H. and T.-A.S. The first draft of the manuscript was written by N.K. and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The research presented in this article was carried out with the support of the NKFIH-872-2/2020 project, the ‘Establishment of a National Multidisciplinary Laboratory for Climate Change’.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets generated during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Öğlü, B.; Möls, T.; Kaart, T.; Cremona, F.; Kangur, K. Parameterization of surface water temperature and long-term trends in Europe’s fourth largest lake shows recent and rapid warming in winter. Limnologica 2020, 82, 125777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeppesen, E.; Mehner, T.; Winfield, I.J.; Kangur, K.; Sarvala, J.; Gerdeaux, D.; Rask, M.; Malmquist, H.J.; Holmgren, K.; Volta, P.; et al. Impacts of climate warming on the long-term dynamics of key fish species in 24 European lakes. Hydrobiologia 2012, 694, 1–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noyes, P.D.; McElwee, M.K.; Miller, H.D.; Clark, B.W.; Van Tiem, L.A.; Walcott, K.C.; Erwin, K.N.; Levin, E.D. The toxicology of climate change: Environmental contaminants in a warming world. Environ. Int. 2009, 35, 971–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daam, M.A.; Van den Brink, P.J. Implications of differences between temperate and tropical freshwater ecosystems for the ecological risk assessment of pesticides. Ecotoxicology 2010, 19, 24–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howe, G.E.; Marking, L.L.; Bills, T.D.; Rach, J.J.; Mayer, F.L., Jr. Effects of water temperature and pH on toxicity of terbufos, trichlorfon, 4-nitrophenol and 2, 4-dinitrophenol to the amphipod Gammarus pseudolimnaeus and rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 1994, 13, 51–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyer, S.D.; Belanger, S.E.; Carr, G.J. An initial evaluation of the use of Euro/North American fish species for tropical effects assessments. Chemosphere 1997, 35, 2767–2781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heugens, E.H.W.; Tokkie, L.T.B.; Kraak, M.H.S.; Hendriks, A.J.; Van Straalen, N.M.; Admiraal, W. Population growth of Daphnia magna under multiple stress conditions: Joint effects of temperature, food, and cadmium. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2006, 25, 1399–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viswanathan, P.N.; Krishna Murti, C.R. Effects of temperature and humidity on ecotoxicology of chemicals. In Ecotoxicology and Climate: With Special Reference to Hot and Cold Climates; Bourdeau, P., Haines, J.A., Klein, W., Krishna Murti, C.R., Eds.; Wiley: Chichester, UK, 1989; pp. 139–154. [Google Scholar]
- Bérard, A.; Leboulanger, C.; Pelte, T. Tolerance of Oscillatoria limnetica Lemmermann to atrazine in natural phytoplankton populations and in pure culture: Influence of season and temperature. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 1999, 37, 472–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benbrook, C.M. Trends in glyphosate herbicide use in the United States and globally. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2016, 28, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meftaul, I.M.; Venkateswarlu, K.; Dharmarajan, R.; Annamalai, P.; Asaduzzaman, M.; Parven, A.; Megharaj, M. Controversies over human health and ecological impacts of glyphosate: Is it to be banned in modern agriculture? Environ. Pollut. 2020, 263, 114372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torstensson, L. Behaviour of glyphosate in soils and its degradation. In The Herbicide Glyphosate; Grossbard, E., Atkinson, D., Eds.; Butterworths: London, UK, 1985; pp. 137–150. [Google Scholar]
- Radwan, D.E.M.; Fayez, K.A. Photosynthesis, antioxidant status and gas-exchange are altered by glyphosate application in peanut leaves. Photosynthetica 2016, 54, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Székács, A.; Mörtl, M.; Darvas, B. Monitoring Pesticide Residues in Surface and Ground Water in Hungary: Surveys in 1990–2015. J. Chem. 2015, 2015, 717948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maloschik, E.; Ernst, A.; Hegedűs, G.; Darvas, B.; Székács, A. Monitoring water-polluting pesticides in Hungary. Microchem. J. 2007, 85, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD. Test No. 221: Lemna sp. Growth Inhibition Test. In OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals, Section 2; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostopoulou, S.; Ntatsi, G.; Arapis, G.; Aliferis, K.A. Assessment of the effects of metribuzin, glyphosate, and their mixtures on the metabolism of the model plant Lemna minor L. applying metabolomics. Chemosphere 2020, 239, 124582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vera, M.S.; Lagomarsino, L.; Sylvester, M.; Pérez, G.L.; Rodríguez, P.; Mugni, H.; Sinistro, R.; Ferraro, M.; Bonetto, C.; Zagarese, H.; et al. New evidences of Roundup (glyphosate formulation) impact on the periphyton community and the water quality of freshwater ecosystems. Ecotoxicology 2010, 19, 710–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sikorski, Ł.; Baciak, M.; Bęś, A.; Adomas, B. The effects of glyphosate-based herbicide formulations on Lemna minor, a non-target species. Aquat. Toxicol. 2019, 209, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, M.; Thursby, G. Aquatic plants: Test species sensitivity and minimum data requirement evaluations for chemical risk assessments and aquatic life criteria development for the USA. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 238, 270–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccolroaz, S.; Zhu, S.; Ptak, M.; Sojka, M.; Du, X. Warming of lowland Polish lakes under future climate change scenarios and consequences for ice cover and mixing dynamics. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2021, 34, 100780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanchoud, H.; Moreau-Guigno, E.; Farrugia, F.; Chevreuil, M.; Mouchel, J.M. Contribution by urban and agricultural pesticide uses to water contamination at the scale of the Marne watershed. Sci. Total Environ. 2007, 375, 168–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camp, A.A.; Buchwalter, D.B. Can’t take the heat: Temperature-enhanced toxicity in the mayfly Isonychia bicolor exposed to the neonicotinoid insecticide imidacloprid. Aquat. Toxicol. 2016, 178, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passardi, F.; Cosio, C.; Penel, C.; Dunand, C. Peroxidases have more functions than a Swiss army knife. Plant Cell Rep. 2005, 24, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koce, J.D. Effects of exposure to nano and bulk sized TiO2 and CuO in Lemna minor. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 119, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, L.C.M.; Daam, M.A.; Gusmao, F. Acclimation alters glyphosate temperature-dependent toxicity: Implications for risk assessment under climate change. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 385, 121512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Guardo, A.; Finizio, A. A new methodology to identify surface water bodies at risk by using pesticide monitoring data: The glyphosate case study in Lombardy Region (Italy). Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 610–611, 421–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sobrero, M.C.; Rimoldi, F.; Ronco, A.E. Effects of the Glyphosate Active Ingredient and a Formulation on Lemna gibba L. at Different Exposure Levels and Assessment End-Points. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2007, 79, 537–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imberty, A.; Goldberg, R.; Catesson, A.M. Tetramethylbenzidine and p-phenylenediamine-pyrocatechol for peroxidase histochemistry and biochemistry: Two new, non-carcinogenic chromogens for investigating lignification process. Plant Sci. Lett. 1984, 35, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basiglini, E.; Pintore, M.; Forni, C. Effects of treated industrial wastewaters and temperatures on growth and enzymatic activities of duckweed (Lemna minor L.). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 153, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherr, C.; Simon, M.; Spranger, J.; Baumgartner, S. Test system stability and natural variability of a Lemna gibba L. bioassay. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e3133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Heide, T.; Roijackers, R.M.M.; Peeters, E.T.H.M.; Van Nes, E.H. Experiments with duckweed–moth systems suggest that global warming may reduce rather than promote herbivory. Freshw. Biol. 2006, 51, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenkrantz, R.T.; Cedergreen, N.; Baun, A.; Kusk, K.O. Influence of pH, light cycle, and temperature on ecotoxicity of four sulfonylurea herbicides towards Lemna gibba. Ecotoxicology 2013, 22, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, S.; Li, Z.; Xia, J.; Han, Y.; Wu, M.; Wan, S. Climatic warming changes plant photosynthesis and its temperature dependence in a temperate steppe of northern China. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2008, 63, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zezulka, S.; Kummerová, M.; Babula, P.; Vánová, L. Lemna minor exposed to fluoranthene: Growth, biochemical, physiological and histochemical changes. Aquat. Toxicol. 2013, 140–141, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mateos-Naranjo, E.; Perez-Martin, A. Effects of sub-lethal glyphosate concentrations on growth and photosynthetic performance of non-target species Bolboschoenus maritimus. Chemosphere 2013, 93, 2631–2638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes, M.P.; da Silva Cruz, F.V.; Bicalho, E.M.; Borges, F.V.; Fonseca, M.B. Effects of glyphosate acid and the glyphosate-commercial formulation (Roundup) on Dimorphandra wilsonii seed germination: Interference of seed respiratory metabolism. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 220, 452–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Silva Santos, J.; da Silva Pontes, M.; Grillo, R.; Fiorucci, A.R.; de Arruda, G.J.; Santiago, E.F. Physiological mechanisms and phytoremediation potential of the macrophyte Salvinia biloba towards a commercial formulation and an analytical standard of glyphosate. Chemosphere 2020, 259, 127417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paolacci, S.; Harrison, S.; Jansen, M.A.K. Are alien species necessarily stress sensitive? A case study on Lemna minuta and Lemna minor. Flora 2018, 249, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sváb, E. Sekélyvizű Tavak Vízminıség-Vizsgálata, Állapotfelmérése Műholdas Távérzékelés Segítségével. Ph.D. Thesis, Eötvös Loránd University, Budapest, Hungary, 2008. (In Hungarian). [Google Scholar]
- Brovini, E.M.; de Deus, B.C.T.; Vilas-Boas, J.A.; Quadra, G.R.; Carvalho, L.; Mendonça, R.F.; Pereira, R.d.O.; Cardoso, S.J. Three-bestseller pesticides in Brazil: Freshwater concentrations and potential environmental risks. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 771, 144754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubai, K.; Kováts, N.; Sainnokhoi, T.A.; Eck-Varanka BHoffer, A.; Tóth, Á.; Teke, G. Phytotoxicity of particulate matter from controlled burning of different plastic waste types. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2022, 109, 852–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alla, M.M.N.; Hassan, N.M. Changes of antioxidants levels in two maize lines following atrazine treatments. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2006, 44, 202–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitrovic, S.M.; Pflugmacher, S.; James, K.J.; Furey, A. Anatoxin-a elicits an increase in peroxidase and glutathione S-transferase activity in aquatic plants. Aquat. Toxicol. 2004, 68, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Lu, Y.; Gao, X.; Du, G.; Ma, X.; Liu, M.; Guo, J.; Chen, Y. Ammonium-induced oxidative stress on plant growth and antioxidative response of duckweed (Lemna minor L.). Ecol. Eng. 2013, 58, 355–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Weisman, D.; Ye, Y.-B.; Cui, B.; Huang, Y.-H.; Colón-Carmona, A.; Wang, Z.-H. An oxidative stress response to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon exposure is rapid and complex in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Sci. 2009, 176, 375–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Que, X.; Zheng, R.; Pang, Z.; Li, C.; Xiao, B. Phytotoxicity assessment of atrazine on growth and physiology of three emergent plants. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 9646–9657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teisseire, H.; Vernet, G. Is the “Diuron Effect” Due to a Herbicide Strengthening of Antioxidative Defenses of Lemna minor? Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2000, 66, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Liu, L.; Li, X.; Xu, Y.; Ge, Z.; Zhao, Y. Effect of graphene oxide on copper stress in Lemna minor L.: Evaluating growth, biochemical responses, and nutrient uptake. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 341, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pouresmaeil, M.; Sabzi-Nojadeh, M.; Movafeghi, A.; Aghbash, B.N.; Kosari-Nasab, M.; Zengin, G.; Maggi, F. Phytotoxic activity of Moldavian dragonhead (Dracocephalum moldavica L.) essential oil and its possible use as bio-herbicide. Process. Biochem. 2022, 114, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, M.P.; Juneau, P. Temperature and light modulation of herbicide toxicity on algal and cyanobacterial physiology. Front. Environ. Sci. 2017, 5, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smedbol, E.; Gomes, M.P.; Paquet, S.; Labrecque, M.; Lepage, L.; Lucotte, M.; Juneau, P. Effects of low concentrations of glyphosate-based herbicide factor 540® on an agricultural stream freshwater phytoplankton community. Chemosphere 2018, 192, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geoffroy, L.; Frankart, C.; Eullaffroy, P. Comparison of different physiological parameter responses in Lemna minor and Scenedesmus obliquus exposed to herbicide flumioxazin. Environ. Pollut. 2004, 131, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morais, H.; Arenas, F.; Cruzeiro, C.; Galante-Oliveira, S.; Cardoso, P.G. Combined effects of climate change and environmentally relevant mixtures of endocrine disrupting compounds on the fitness and gonads’ maturation dynamics of Nucella lapillus (Gastropoda). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 190, 114841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermann, M.; Peeters, E.T.H.M.; Van den Brink, P.J. Heatwaves, elevated temperatures, and a pesticide cause interactive effects on multi-trophic levels of a freshwater ecosystem. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 327, 121498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Megías, C.; Mentzel, S.; Fuentes-Edfuf, Y.; Moe, S.J.; Rico, A. Influence of climate change and pesticide use practices on the ecological risks of pesticides in a protected Mediterranean wetland: A Bayesian network approach. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 878, 163018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).