Abstract
Anthropoid activities are severely altering natural land cover and growing the transport of soil, organic and inorganic compounds, nutrients, toxic chemicals, and other pollutants to the water ecosystem. The eutrophication of the coastal water environment is one of the furthermost bitter consequences of human activities. In this research, we have used three different satellite images for efficient land-use land-cover (LULC) classification, comparison, and further coastal water quality assessment over the coastal zone of the Boseong County of South Korea. The results of LULC classification showed that Landsat-8, Sentinel-2, and WorldView-3 gave an overall accuracy of about 74%, 82%, and 96% with Kappa coefficient of 0.71, 0.78, and 0.91, respectively. By comparing, LULC accuracies and kappa coefficient, the very high-resolution Worldview-3 satellite imagery is considered one of the best-suited satellite imageries for water quality assessment. The study used recently developed algorithms for the calculation of the transparency of Secchi depth, concentration of Chlorophyll-a, Total Phosphorus, and Total Nitrogen; whereas the eutrophication status of the coastal water has been identified using the Carlson Trophic State Index (CTSI) method. The result show that the medium state of eutrophication occurred nearby agricultural regions and urban settlements. Overall, trophic status of the coastal water is ranged from 61.56 to 74.37 with a mean value of 65.63 (CTSI) and placed under the medium eutrophic state. The study analysed that the nutrient entrance from the surrounding land cover is high and needs proper water treatment before releasing into a coastal ecosystem. Hence, these investigations will assist the various local and international agencies in improving the reliability of the monitoring of eutrophication state, dynamics, and potential impacts.
1. Introduction
Littoral and the pelagic coastal environment are key to socio-economic development, and ecological and biodiversity balance in many countries. Anthropogenic activities, such as agriculture (fertilizers), aquaculture (fish feeds), industrialization (salts), social-cultural norms (organic wastes), and atmospheric inputs (nutrients), export as residual waste to the coastal waters [1,2,3,4,5]. Residual wastes contribute to the elevated concentration of nutrients in the water body. Excessive concentrations of Chlorophyll-a (Chl-a), Total Phosphorous (TP), and Total Nitrogen (TN) indicate an oversupply of nutrients (nitrogen, phosphorus, etc.), while under concentrations indicates shorting of the nutrient sources from anthropogenic activities. High concentrations of Chl-a, TP, and TN cause eutrophication, resulting in the development of harmful algal bloom and oxygen depletion conditions, compromising the carrying capacity of the water body [6,7,8,9,10].
The Trophic State Index (TSI) is the valuable method to investigate the state of aquatic systems and classifying the eutrophic stage. Numerous approaches have been employed for the ranking the quality of the water bodies and to specify their trophic status. The most applied index-based eutrophic classification of aquatic bodies is the Carlson Trophic State Index (CTSI) [11]. CTSI is based on the combination of three or many parameters of water quality, such as Chl-a, depth of Secchi-disc transparency (SDT) and total phosphorus (TP) [9,10,11]. However, the application CTSI can be influenced by errors associated with specific imagery technology, terrestrial locations, ecological issues, anthropogenic activities, or inference algorithm [9,10]. In this study, Chl-a, SDT, and TP were employed to analyse the eutrophication status of the Korean coastline water environment.
The literature review revealed that Water quality is often investigated by labour-intensive water sampling and laboratory analysis based on ground-based observations [12,13,14,15]. This method is improper for displaying the spatiotemporal fluctuation of larger aquatic ecosystems in real-time, and is also detrimental in terms of economics, employment, etc. Due to this considerable spatial heterogeneity, monitoring water quality by ship or boat survey becomes challenging. Oceanographic investigations that are insufficient do not fully explain the state of eutrophication along the shoreline. Therefore, this is one of the major motivations of this study to use very first time of high-resolution satellite data to assess the Eutrophic status in the coastline of Korea [14,15,16,17]. In order to understand eutrophication status and production of HABs, researchers are studying remote sensing data, by which they are able to estimate trophic states in the coastline environment and open seas [17,18]. A number of water body colour based trophic studies has been progressed since the late 21st century from reality to simply distinguish their biophysical activities to detect trophic state index using remotely sensed data [14,16,17,18]. Furthermore, the efficient classification, comparison, and subsequent assessment of coastal water quality using high resolution data from three separate satellite pictures (Landsat-8, Sentinel-2, and WorldView-3) have not yet been conducted. In order to bridge this significant scientific gap, this research was conducted.
The remote sensing techniques are capable of sorting out these challenges and are capable of monitoring and evaluating the water quality status jointly at geographical and temporal scales without the need for any arduous ground observation [18,19,20]. Due to the rapid development of photosensitive and thermal sensors, high spatial, spectral, and temporal resolutions were possible for water quality parameter measurements via remote sensing [17,18,19,20,21]. The airborne and satellite remote sensing techniques are very fast and, comparatively, have a lower operative cost procedure than the traditional system and can be employed as an instrument to extract spatiotemporal variability in the water quality of the water bodies [16,17,18].
This research aims to address the typical single imagery bias phenomenon by comparing three advanced moderate to very high-resolution satellite images—Landsat-8, Sentinel-2, and Worldview-3—on the coastal waters of the Korean peninsula. On the bases of the accuracy of land-use classification, the study used the most suitable satellite imagery for extractions of SDT, Chl-a, TP, and TN concentration. The study used CTSI for classification of the selected study region of the coastal environment. Furthermore, the study also investigated the spatial influence of land-cover on the coastal water quality of the selected study region.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site
The chosen study zone is a section of the coastline terrain of Beolgyo in the Boseong County of South Korea. The study range is situated inside the south of Jeollanam-do wetland (latitude 34°49′–34°52′ N, longitude 127°21′–127°25′ E), a complicated natural and anthropoid region. The study zone is located in the southern part of Beolgyo, Boseong County, South Korea (Figure 1). The Korean peninsula situated in north-eastern Asia. Nearly 75% of the land area in South Korea (roughly 38,224 square miles) is made up of highlands and mountains. The coastal zone of South Korea has huge industrial developments, urban settlements, and concentrated aquaculture. The Korean coastal zone has undergone various developments with the major aim of land reclamation since the last decade of the 20th century [22,23,24].
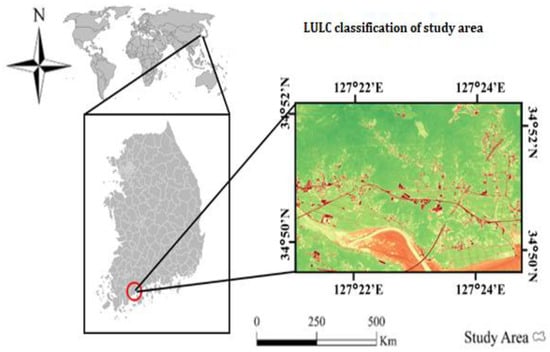
Figure 1.
The location of the study area inside the southern part of Beolgyo, Boseong County, South Korea.
The Boseong region is located in the southern coastal zone of the Korean peninsula. It is comprised of an area of about 660 km2 and with a population of around half million in 2014. The region has productive soil and surrounded by highlands and mountains. The climate of the county is mostly warm and rainy, with a yearly mean temperature of 12.5 °C (0–1 °C in December-February and 20–25 °C in September–October), and a yearly mean precipitation of 1600 mm [25], whereas Beolgyo is a village which located in the municipality of the Boseong County, the province of Jeollanam-do, in the southern part of the country, 300 km south of the country capital Seoul. The Beolgyo village is famous for sea foods, the Korean name Kuma, and green tea. According to an updated Koppen-Geiger climate classification map, the Beolgyo climate is humid and subtropical. An average temperature in the region is 13 °C. The warmest temperature occurs in August at 24 °C, and the coldest in January at 1 °C. The average rainfall is 1999 mm per year [26].
2.2. Remote Sensing Data
An airborne and satellite remote sensing is the valuable tools with the low operational cost in monitoring and investigating the eutrophication status both at spatial and temporal scales without any painstaking ground observations [27,28,29,30]. In our study, we have used three different satellite images, the Worldview-3, Sentimental-2, and Landsat-8 satellites to a more inclusive identification, the satellite superiority was evaluated through a comparison of performance evaluation, in respect to the LULC classification. The most appropriate satellite image with the high accuracy percentage and Kappa coefficient was used for the identification of Chl-a, SDT, TP, and TN concentrations.
2.2.1. WordView-3
Worldview-3 is a very high-resolution commercial satellite and owned by the digital globe. It was launched in 2014 to acquire observations of the ground surface from the orbit. It is the sixth satellite of digital globe earth observation mission satellite series, similar to the spy satellite, but not intending military purposes. It has equipped with 29 spectral bands, more than other sister satellites of the digital globe, QuickBird, WorldView-2, Ikonos, GeoEye-1, and Worldview-1. The Worldview series is quite alike in terms of the electromagnetic spectrum of the Visible (VIS) and Near Infrared (NIR) bands. In the near-infrared (NIR) and visible electromagnetic spectra. Worldview-3 also provide very high-resolution panchromatic spectra with a spatial resolution of about 31 cm. It also provides eight multispectral bands with 1.24 m spatial resolution, Shortwave infrared (SWI) with a resolution of 3.7 m, and CAVIS electromagnetic spectra at 30 m resolution. With the addition of the four additional bands, and the conventional blue, green, and near-infrared-1 wavelengths, WorldView-2 delivers a total of six bands, whereas four new VNIR Colors have been introduced to the VNIR Color palette: coastal (red edge), yellow (yellow edge), and Near-IR (near-IR). Around 617 kilometres above the Earth’s surface, the Worldview-3 has a revisit time of less than a day [31,32,33]. With no cloud cover above our study location, a Worldview-3 image taken on 16 July 2016, was utilized to identify Chl-a, SDT, TP, and TN concentrations.
2.2.2. Sentinel-2
European Space Agency launched the Sentinel-2A spacecraft, which is equipped to deliver high spatial resolution optical images of the world’s land surfaces, as part of the Copernicus European programme on 23 June 2015 [34]. After three decades of SPOT and Landsat, the EU’s Sentinel-2A satellite is able to take full benefit of these decades of experience with technology and skills. The 290 km SWAT width, better resolution, and multi-spectral imager of the Sentinel-2 satellite are all aboard the spacecraft (MSI). It possesses thirteen different electromagnetic spectra, including the visible (VIS), near-infrared (NIR), and short-wave infrared (433–2190 nm) wavelength ranges [35]. Using this study’s 60 and 10 m spatial resolution bands, the 60 m spatial resolution band must be resampled to 10 m by the nearest neighbouring method. According to the results, the best association could be found between reflectance values and ground measurements using Sentinel-2 imagery’s red/blue/green/coast band.
2.2.3. Landsat-8
The Landsat package has been offering images which have been functional in the earth surface assessment since 1972 [36]. Landsat it is the longest functional continuous earth and atmosphere observation package. The latest satellite of the Landsat programme is the Landsat-8 satellite which eighth satellite of Landsat program. The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) completed construction, engineering work, and procurement of the launching vehicle, whereas the United States Geological Survey (USGS), offered for advancement of the ground control unit [37]. Landsat-8 comprises of two sensors, OLI (Operational Land Imager) and TRIS (Thermal Infrared Sensor). The OLI is an improved sensor than prior Landsat satellite series. Landsat-8 provides high resolution imagery with a spatial resolution of 15 m to 100 m. It captures around 700 ground scenes per day and stored them in the United State Landsat programme archive [38]. The Landsat-8 provides the finer resolution wavelength spectra than the Landsat prior series plus additional new aerosol/coastal band (440 nm) for detecting coastal shorelines, Chl-a, blue green algae, and aerosol particles [39]. The Landsat image used in the following study were freely attained from the USGS Landsat data archives (https://glovis.usgs.gov accessed on 31 December 2021). The cloudless Landsat-8 OLI scene was utilized in the work. The study utilized corresponding spectral bands such with other satellites for land-use land-cover classifications.
2.3. Processing of Satellite Data
In the reference study, the Siwei Worldview Technology (Beijing, China) Company provided the WorldView-3 image level 2A. The level 2A imagery already has an atmospheric correction and radiometric calibration and was pre-georeferenced to the UTM projection by means of WGS-84. Sentinal-2 and Landsat-8 are freely available and obtained from the USGS Landsat programme data archives (https://glovis.usgs.gov (accessed on 31 December 2021)). For processing of the satellite image, the pixel digital numbers (DN) were obtained from the satellite images for the latitude-longitude coordinate with respect to observation data, whereas for radiometric calibration, DN of the original image value was transformed into radiance values [39]. We used the following formula:
The αCF is the absolute calculation factor, (m) is the effective band width, and R (W m−2 sr−1 mm−1) is the radiance. ACF and are included in the satellite data’s meta information. Atmospheric attenuation reduced the amount of radiation reaching the sensor. An atmospheric correction is required to remove the effect of the atmosphere from the image. To compensate for atmospheric conditions, ENVI (Environment for Visualizing Images) software version 5.2 was employed in this study. The spatially varying resolution should be resampled using the nearest adjacent method for subsequent applications, so that all satellite images have similar spatial resolution for better interpretation, according to this approach.
2.4. Land-Use Land-Cover Classification
Worldview-3 acquired on 16 July 2016, Sentinel-2 and Landsat-8 cloud free images, both having nearby possible image (concurrent) date acquisition, were used as remote sensing images in this research. The same bands of those three datasets were used in the land-use land-cover (LULC) classification. The spatial resolution and spectral bands of all three satellites are shown in Table 1. The landscape features comprised four major classes were extracted using a supervised and unsupervised set of classification schemes. A set of training samples were formed by means of polygons for the land-cover classes: mountainous forest, agricultural land, urban settlements, and water bodies. The land-cover features were extracted using the spectral response of each satellite scenes. The LULC classification schemes are generally categorized as supervised and unsupervised. The main difference between these classification schemes, training by user, and maximum likelihood detection by computers. In supervised classification training of imagery is involved, whereas in unsupervised classification no training is required and the interpreter assign different classes [40,41,42]. Data training is the procedure of choosing random sample data from the imagery and via it to create thresholds signatures to demarcate the specific land-cover on the earth surface landscape. For the LULC classification, spectral signature of around 100 samples were created from each image and employed supervised classification in ArcGIS.

Table 1.
Spectral bands and spatial resolutions of the remote sensing datasets.
2.5. Water Quality Parameters Assessment
Based on the accuracy of the satellite scenes for LULC mapping, imagery having the highest accuracy and the finest spatial resolution (WorldView-3) were selected for assessments of water quality parameters. The study used recently developed algorithms for extraction of water quality information’s including the transparency depth of Disk [43], that is:
For the calculation of chlorophyll-a, algorithm developed for complex coastal water quality was used [44]:
For the estimation of TP, the band ratio model was used in this study [45]:
Algorithm for TN calculation [46]:
where B5, B3, and B2 are the red, green, and blue band value of the Worldview-3 multispectral bands. All of the above calculation is performed using above algorithm in ENVI 5.2 (“Environment for Visualizing Images” 5.2) software.
2.6. Evaluation and Accuracy Assessment
2.6.1. Accuracy Assessment of Land-Cover Classification
The objective of accuracy assessment is to evaluate quantitatively performance of different satellite scenes in respect to land-cover extraction. Furthermore, the main focus of accuracy assessment was on the classes that could be obviously recognized on both satellite images, Google earth. The maximum likelihood classification results were assessed via ground observation and for land-cover validation.
2.6.2. Accuracy Assessment of Water Quality Parameters
Due to the geopolitical sensitivity of the Korean Peninsula, it is extremely difficult to obtain a very high resolution prefixed the date image of WorldView-3 of the specific predefined location. Therefore, owing to the lack of ground observation data (unavailability of prefixed date image), the study used the recently developed algorithm and validated it with the previously published different algorithms [43,44,45,46]. The statistical analysis was performed to assess the reliability of the used algorithm in the reference study with some of the other previous study algorithm. The Root Mean Square Error (RMSE), bias, and Pearson correlation coefficient (R) were used to study accuracy assessment [47]. The Bias is the measure of the difference between two values [47]:
RMSE value is used to indicate the suitability of used algorithm [47]:
Pearson correlation coefficient (R) was calculated by the following equation:
where yi(rda) is pixel values obtained from the study results, while yi(osa) is the other study available algorithm, and n is the total number of pixels in the study area.
Carlson’s Trophic State Index (CTSI):
2.7. Adding Another Trophic Index
As Carlson [11] described that TSI is not only limited to three parameters. Thus, another index has been developed to be employed with the basic three. Since another nutrient, such as nitrogen, also performs a significant role in eutrophication development. Thus, the influence of TN can be assessed by having a sister index to the TP. The TSI for TP was developed by the Kratzer [48] by using CTSI type index for TN. The TSI index for TN can be estimated using the following equation:
3. Results
3.1. Analysis and Assessment of the Land-Cover Classification
Accuracy assessment report of Landsat-8, Sentinel-2, and WorldView-3 scenes are shown in Table 2. Due to the spatial landscape of the chosen study region, the general classes named urban settlement, mountainous forest, water, and agricultural farms were considered as LULC feature classes. About 60% of the study region is covered by the mountainous forest. Figure 2a shows that the eastern side of the coastal water is connected with the agricultural land and urban settlement. After extracting the LULC classified image, accuracy assessment for all three images was performed using 100 random sampling points. By means of the randomly selected sample assessment, the Worldview-3 classified image presented the higher value of Kappa coefficient and higher overall accuracy, about 96%, than Sentinel-2 and Landsat-8 classified images (Table 2). The Land-use land-cover classes having the highest accuracy derived from the WorldView-3 satellite image is shown in Table 2 and Figure 2a. The exact area of water body was classified by using the technique of land-use land-cover classification system. From these accuracy assessments, it can be deduced that high-resolution image can be best suited for water body detection and the further assessment of the water body.

Table 2.
The accuracy assessment approach between observed and land cover dataset.
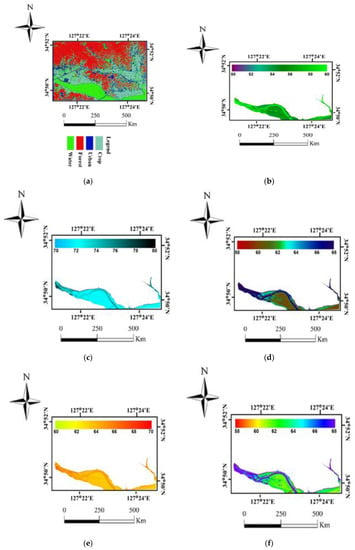
Figure 2.
(a) Land-use Land-cover classification map, (b) TSI of Chl-a, (c) TSI of SDT, (d) TSI of TP, (e) TSI of TN, and (f) Overall CTSI.
3.2. Accuracy Assessment of the Employed Models
The statistical analysis assessment (Table 3) shows that models used in this study are reliable to investigate the trophic state of the coastal water by using a very high-resolution WorldView-3 imagery. The statistical analysis show that the result is well agreed with other regional/world-wide algorithms. The values show that the result has a high value of correlation coefficient, low bias, and the low RMSE value for Chl-a, SDT, and TP. Hence, this study can be reliable in monitoring and classifying the water quality status of the selected coastal zone.
3.3. Analysis of the Trophic Status
The Carlson Trophic State Index (CTSI) of the Korean coastline environment was determined using very high-resolution WorldView-3 imagery are shown in Figure 2b–f. The CTSI values calculated by averaging TSI of SDT, Chl-a, and TP of the water body presented in the image is shown in Figure 2f. The result clearly indicates that the region nearby the cropping area, urban land, and the deep drain coming from agricultural zone have higher TSI index as compared to the extent in other regions and is shown in Figure 2b. This means that Chl-a nutrients loading arrived from the surrounding environment, especially the agricultural region, which will contribute the algal growth in the Korean coastal waters [49]. TSI for Chl-a is ranged from 51.81 to 59.67, with the mean value of 55.83, which is classified as the light eutrophic stage [9,10,11]. Table 3 shows that the mean value of TSI for water clarity (the transparency of Secchi depth) is about 69.78, placed in medium trophic status classification (Table 4), which has been linked with poor water status due to turbidity of organic material or presence of suspended solid [50].
The TSI status of the major agrochemical nutrients, TP and TN are higher nearby the cropping area and urban settlements. Which means, the major plant nutrients release from agricultural land and other human activities. Another aspect which has been emphasized in this research is the trophic status of SDT. It is shown in Figure 3 that the TSI value based on SDT is the higher than other TSI of Chl-a, TP and TN. The reason for this low water clarity is may be due to the presence of large numbers of suspended solids [49]. The monsoon’s season along with anthropogenic activity also play a significant role in nutrient development nearby the surrounding regions of coastal waters. The cause for this is due to the rainy season in the prior months (June to September) in the county. Throughout the rainy season, the water flow in the drain and cropping extent is high due to an enhancement in surface runoff, which carries with it an augmented quantity of pollutants along with toxic substances from the agronomic and urban settlement, thus contaminating the coastal waters [49,51].
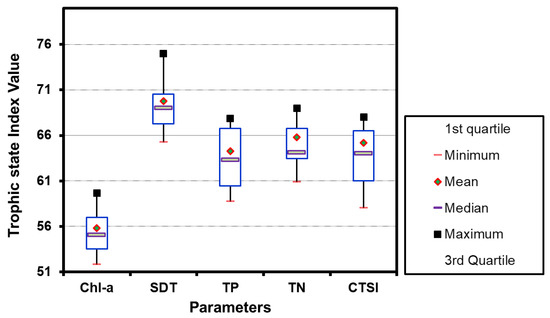
Figure 3.
Graphical representation the trophic status of water quality parameters with box and whisker plots.
The spatial variation analysis of water quality parameters provided a very good insight for viewing and connecting with lands use and another factor for aid in decision making and management practices [52]. As evident from LULC, the spatial view of CTSI shows that the water body to high anthropoid activities such a cropping zone and the land settlement has the high disposal of nutrients. Thus, the debris of numerous agrochemicals and household discharge particles cause water bodies to become deteriorated [49,50]. Overall, CTSI of coastal water to be found in the state of medium eutrophic (Figure 3 and Table 4), with values ranging from minimum 58.13 to maximum 67.71, with a mean value of about 65.19. According to the trophic classification of the study region, it is evident that based on CTSI values, the Korean coastal water zone under study falls under the categories of medium trophic state (Table 4) [8,9,10,11,48,49,50,51]. If the present status of contaminating the coastal water is sustained, it is forecast that the Korean coastal water may become further deteriorated in the future.

Table 3.
Statistical comparisons of used algorithm in this study with other regional/world-wide algorithms.
Table 3.
Statistical comparisons of used algorithm in this study with other regional/world-wide algorithms.
| Algorithms | R | Bias | RMSE |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chl-a [53] | 0.97 | 0.13 | 0.23 |
| SDT [54] | 0.79 | 0.07 | 0.02 |
| TP [55] | 0.91 | 0.15 | 0.17 |
| TN [55] | 0.89 | 0.21 | 0.22 |

Table 4.
Carlson Trophic Index classification [11].
Table 4.
Carlson Trophic Index classification [11].
| Index Value | Trophic Status | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| <30 | Ultraoligotrophic | The nutrients quantity is negligible. The water is almost pure, has plenty of dissolve oxygen concentration. |
| 30–40 | Oligotrophic | The nutrients quantity in water body is low. The water is good for aquatic life |
| 40–50 | Mesotrophic | The nutrients concentration is moderate. The clarity of the water is in medium state. |
| 50–60 | Light Eutrophic | The nutrients concentration is high. Declining in water purity. Only fish can live in warm water. Water body need proper treatment. |
| 60–70 | Medium Eutrophic | The nutrients concentration is high. Algal blooms development is started. Problematic for aquatic environment. |
| 70–80 | Heavy Eutrophic | The nutrients concentration is high. Harmful algal blooms occurred |
| >80 | Hyper Eutrophic | The nutrients concentration is very high. Algal clamping is developed. Most of the aquatic life including fish cannot survive |
4. Discussion
Along with an increasing eutrophication status, variations in the biological and physical parameters of the water environment may expressively provide chance of harmful algal bloom development [2,3,4,5]. The nutrient rich coastal water ecosystem has plenty can provide colonies to the microorganism and their emergence revolute with worsening oxygen conditions and the declining transparency of water, which go together with the development of eutrophication [56]. Generally, urban development activities had a greater impact on water quality by changing hydrological processes like runoff and erosion, whereas agricultural and forest-related activities had a greater impact on water quality through their significant positive correlation with physical and chemical indicators of water quality. Moreover, surface water quality is negatively impacted by land use for agriculture and construction, although it is slightly improved by woodland use. In pertinent research, correlation analysis, regression analysis, redundancy analysis, etc., are the key statistical techniques used. Different approaches each have their own benefits and drawbacks. Remote sensing monitoring technology has advanced quickly in recent years and is now a useful instrument for managing and accessing water quality in its entirety. However, the rise in data volume that came along with the increase in spatial resolution of remote sensing data has complicated information interpretation and other issues. Previous studies have investigated different water ecosystems, the numbers and biomass of different nutrients have been increasing together with the development of eutrophication [57]. Although early studies of eutrophication were based on lakes, pond data, the status of this process in the ecological study is widely familiar. According to the study of Dodds [58], trophic status is an important property of the ecosystem constructions linked to the anthropogenic influences and water quality of streams.
The use of numerous procedures is largely resolute by the scope of the study and the purposes of such investigations. The current work engaged the CTSI trophic assessment with the consideration that it is a well-established and globally applied vigorous evaluating technique and replicable procedure in view of biophysical parameters [8,9,10,11,58]. Table 4 shows that an index value between 50 to 60 is usually associated with light trophic status named as light eutrophication (high nutrients); indexes larger than 70 are accompanying with heavy eutrophic (high nutrient), and index numbers less than 30 are allied with ultraoligotrophic condition (very low nutrients) of the aquatic environment [59]. If the eutrophication status is identified using the Carlson Trophic State Index method, measuring TSI (SDT), TSI (Chl-a), and TSI (TP) values, the current work discloses that the Korean coastal environment has an Index value under range from 60–70, and is thus considered to be medium eutrophic coastal water.
Eutrophication usually occur due to the excessive amount of organic and inorganic pollutants such as Chl-a TN and TP is a worldwide aquatic and marine water bodies ecological issue [50]. The coastal water eutrophication can consequence in harmful algal bloom development and deterioration of ocean water quality, which can influence on the eco health of the marine system. The TSI offers an inclusive evaluation of the trophic state and endorses decision making groups and association to help in managing the sustainable eco healthy water environment. Consequently, over the previous eras, exertions have been dedicated to the classification of the trophic states of different surface and the marine water system [11,60,61]. Furthermost trophic classification schemes have been based on water quality parameters, such as an organic and inorganic pollutants, chlorophyll, and biomass production quantities. However, this study has some limitations due to geo-political sensitivity of the region for acquiring prefixed image date. Hence, this study is lacked with ground truth information’s. Therefore, future research is required to link the in situ data, anthropogenic activities, environmental, and ecological conditions with the coastal waters’ eutrophication status [51].
5. Conclusions
In the current study, a eutrophic state assessment was performed for the first time using very high-resolution Worldview-3 satellite imagery over the geo-political sensitive region of the Korean peninsula. The LULC was classified using three different high-resolution satellite images Landsat-8, Sentinel-2, and WorldView-3. On the basis of classification accuracies and kappa coefficient, Worldview-3 imagery is selected for trophic state assessment. The results of LULC classification showed that Landsat-8, Sentinel-2, and WorldView-3 gave an overall accuracy of about 74%, 82%, and 96% with Kappa coefficient of 0.71, 0.78, and 0.91, respectively. The implemented approach for assessing trophic status in the Beolgyo village coastal water uses TSI(Chl-a), TSI(SDT), and TSI(TP), averaging them to come up with an overall CTSI of the Korean coastal water environment. The result show that the medium state of eutrophication occurred nearby agricultural regions and urban settlements. Overall, trophic status of the coastal water is ranged from 61.56 to 74.37, with a mean value of 65.63 (CTSI), and placed under the medium eutrophic state. Overall, CTSI of coastal water to be found in the state of medium eutrophic (Figure 3 and Table 4), with values ranging from minimum 58.13 to maximum 67.71, with a mean value of about 65.19. Through the investigation of the Korean coastal water environment nearby Boseong county recently, we believe that coastal eutrophication is the process in which the anthrophonic debris transport occurs resulting in the deterioration of the water quality due to the enrichment of nutrients. The containment transport is the radical factor of coastal water eutrophication, including the exterior engrossment, such as human activities, organic and inorganic sedimentations, and interior contribution, such as different biophysical and chemical processes.
Based on the results of the Carlson Trophic Status Indexes, it is concluded largely; trophic state near agriculture farms and urban settlement are high, water must be treated before discharge and land-use management strategies should be implemented to protect the coastal water environment. Furthermore, this study also determined that the Korean coastal water neighbouring Boseong County is under medium eutrophic conditions. Thus, the nutrient concentration of coastal water is high and it is dominated by the harmful algal blooms, aquatic plants are under threatening. Our results recommended that wastewater treatment plant in the Beolgyo village must be installed so that the water discharged from the cropping zone and residential land could be treated, and the coastal environment can be preserved. A revolution in land-use management strategies is obviously required in order to protect and preserve one of the most important coastal water ecosystems.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.M.I., T.R. and S.H.; methodology, M.M.I., M.U.N., M.S.W. and S.H.; software, M.M.I., M.A. and S.H.; validation, M.M.I., M.N.A. and S.H.; formal analysis, M.M.I., M.A. and S.H.; investigation, M.M.I. and S.H.; resources, M.M.I., M.A. and S.H.; data curation, M.M.I. and S.H.; writing—original draft preparation, M.M.I. and S.H.; writing—review and editing, M.M.I., T.R., S.H., M.U.N., M.S.W., M.A. and M.N.A.; visualization, M.M.I. and S.H.; supervision, M.M.I., T.R. and S.H.; project administration, M.M.I. and S.H.; funding acquisition, M.M.I. and S.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The authors were supported through a scholarship program (HRDI-UESTP) by the Higher Education Commission (HEC), Pakistan.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Department of Water Resources, Sungkyunkwan University, for support and providing resources.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Meng, W.; Qin, Y.; Zheng, B.; Zhang, L. Heavy metal pollution in Tianjin Bohai Bay, China. J. Environ. Sci. 2008, 20, 814–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soo, B.; Ho, J.; Kim, J.; Ho, S.; Han, M. Intraspecific bloom succession in the harmful dinoflagellate Cochlodinium polykrikoides (Dinophyceae) extended the blooming period in Korean coastal waters in 2009. Harmful Algae 2018, 71, 78–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, N.; Wang, N.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, J. Temporal and spatial characteristics of harmful algal blooms in the Bohai Sea during 1952–2014. Cont. Shelf Res. 2016, 122, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Miller-rushing, A.J. Degradation, urbanization, and restoration: A review of the challenges and future of conservation on the Korean Peninsula. Biol. Conserv. 2014, 176, 262–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleynik, D.; Dale, A.C.; Porter, M.; Davidson, K. A high-resolution hydrodynamic model system suitable for novel harmful algal bloom modelling in areas of complex coastline and topography. Harmful Algae 2016, 53, 102–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Jin, H.; Du, Y.; Young, E. Mixotrophic dinoflagellate red tides in Korean waters: Distribution and ecophysiology. Harmful Algae 2013, 30, S28–S40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.; Park, T.; Park, Y.; Lim, W. Monitoring and trends in harmful algal blooms and red tides in Korean coastal waters, with emphasis on Cochlodinium polykrikoides. Harmful Algae 2013, 30, S3–S14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, K.; Gowen, R.J.; Harrison, P.J.; Fleming, L.E.; Hoagland, P.; Moschonas, G. Anthropogenic nutrients and harmful algae in coastal waters. J. Environ. Manag. 2014, 146, 206–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saputra, A.N.; Danoedoro, P.; Kamal, M. Application of Landsat 8 OLI Image and Empirical Model for Water Trophic Status Identification of Riam Kanan Reservoir, Banjar, South Kalimantan. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2017, 98, 012020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patra, P.P.; Dubey, S.K.; Trivedi, R.K.; Sahu, S.K.; Rout, S.K. Estimation of chlorophyll-a concentration and trophic states in Nalban Lake of East Kolkata Wetland, India from Landsat 8 OLI data. Spat. Inf. Res. 2017, 25, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, R.E. A trophic state index for lakes. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1977, 22, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Guan, J.; Ma, Y.; Yu, S.; Guo, H.; Bao, L. Aquatic environmental quality variation in Lake Dianchi Watershed. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2010, 2, 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anttila, S.; Fleming-lehtinen, V.; Attila, J.; Alasalmi, H.; Hällfors, H.; Kervinen, M.; Koponen, S. A novel earth observation based ecological indicator for cyanobacterial blooms. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2018, 64, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gittings, J.A.; Raitsos, D.E.; Racault, M.; Brewin, R.J.W.; Pradhan, Y.; Sathyendranath, S.; Platt, T. Seasonal phytoplankton blooms in the Gulf of Aden revealed by remote sensing. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 189, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertani, I.; Steger, C.E.; Obenour, D.R.; Fahnenstiel, G.L.; Bridgeman, T.B.; Johengen, T.H.; Sayers, M.J.; Shuchman, R.A.; Scavia, D. Tracking cyanobacteria blooms: Do different monitoring approaches tell the same story? Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 575, 294–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.; Pyo, J.; Sung, Y.; Cha, Y.; Lee, H.; Kang, T.; Hwa, K. Evaluating physico-chemical influences on cyanobacterial blooms using hyperspectral images in inland water, Korea. Water Res. 2017, 126, 319–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ottaviani, M.; Foster, R.; Gilerson, A.; Ibrahim, A.; Carrizo, C.; El-Habashi, A.; Cairns, B.; Chowdhary, J.; Hostetler, C.; Hair, J.; et al. Airborne and shipborne polarimetric measurements over open ocean and coastal waters: Intercomparisons and implications for spaceborne observations. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 206, 375–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.C.; Son, S.; Kim, Y.H.; Khim, J.S.; Nam, J.; Chang, W.K.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, C.H.; Ryu, J. Remote sensing and water quality indicators in the Korean West coast: Spatio-temporal structures of MODIS-derived chlorophyll-a and total suspended solids. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 121, 425–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giardino, C.; Pepe, M.; Brivio, P.A.; Ghezzi, P.; Zilioli, E. Detecting chlorophyll, Secchi disk depth and surface temperature in a sub-alpine lake using Landsat imagery. Sci. Total Environ. 2001, 268, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nas, B.; Ekercin, S.; Karabörk, H.; Berktay, A.; Mulla, D.J. An application of landsat-5TM image data for water quality mapping in Lake Beysehir, Turkey. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2010, 212, 183–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senay, G.; Shafique, N. The selection of narrow wavebands for optimizing water quality monitoring on the Great Miami River, Ohio using hyperspectral remote sensor data. J. Spat. Hydrol. 2001, 1, 1–22. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, S.H.; Yim, U.H.; Shim, W.J.; Li, D.H.; Oh, J.R. Nationwide monitoring of polychlorinated biphenyls and organochlorine pesticides in sediments from coastal environment of Korea. Chemosphere 2006, 64, 1479–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, D.W.; Kim, S.G.; Choi, M.; Lee, I.S.; Kim, S.S.; Choi, H.G. Monitoring of trace metals in coastal sediments around Korean Peninsula. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 102, 230–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Park, J. Mathematical modeling of coastal marine environments using observational data for coastal management. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2015, 116, 396–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, J.; Macpherson, A. The impact of geographical indication on the revitalisation of a regional economy: A case study of ‘Boseong’ green tea. Area 2007, 39, 518–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peel, M.C.; Finlayson, B.L.; Mcmahon, T.A. Updated world map of the Koppen-Geiger climate classification. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2007, 11, 1633–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, M.M.; Hussain, S.; Cheema, M.J.M.; Lyul, J.J.P.J.A.S. Seasonal effect of agricultural pollutants on coastline environment: A case study of the southern estuarine water ecosystem of the boseong county Korea. Pak. J. Agri. Sci. 2022, 59, 117–124. [Google Scholar]
- Zilioli, E.; Brivio, P.A. The satellite derived optical information for the comparative assessment of lacustrine water quality. Sci. Total Environ. 1997, 196, 229–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamun, M.; An, K.G. Major nutrients and chlorophyll dynamics in Korean agricultural reservoirs along with an analysis of trophic state index deviation. J. Asia-Pac. Biodivers. 2017, 10, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korhonen, L.; Packalen, P.; Rautiainen, M. Comparison of Sentinel-2 and Landsat 8 in the estimation of boreal forest canopy cover and leaf area index. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 195, 259–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jawak, S.D.; Luis, A.J.; Panditrao, S.N.; Khopkar, P.S.; Jadhav, P.S. Advancement in Land Cover Classification Using Very High Resolution Remotely Sensed 8-Band Worldview-2 Satellite Data. Int. J. Earth Sci. Eng. 2013, 6, 1742–1749. [Google Scholar]
- Ranaie, M.; Soffianian, A.; Pourmanafi, S.; Mirghaffari, N.; Tarkesh, M. Evaluating the statistical performance of less applied algorithms in classification of worldview-3 imagery data in an urbanized landscape. Adv. Space Res. 2018, 61, 1558–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Tian, S.; Di, B. Extracting mineral alteration information using WorldView-3 data. Geosci. Front. 2017, 8, 1051–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donlon, C.; Berruti, B.; Buongiorno, A.; Ferreira, M.; Féménias, P.; Frerick, J.; Goryl, P.; Klein, U.; Laur, H.; Mavrocordatos, C.; et al. The Global Monitoring for Environment and Security (GMES) Sentinel-3 mission. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 120, 37–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drusch, M.; Del Bello, U.; Carlier, S.; Colin, O.; Fernandez, V.; Gascon, F.; Hoersch, B.; Isola, C.; Laberinti, P.; Martimort, P.; et al. Sentinel-2: ESA’ s Optical High-Resolution Mission for GMES Operational Services. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 120, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, W.; Rondinini, C.; Pettorelli, N.; Mora, B.; Leidner, A.K.; Szantoi, Z.; Buchanan, G.; Dech, S.; Dwyer, J.; Herold, M.; et al. Free and open-access satellite data are key to biodiversity conservation. Biol. Conserv. 2015, 182, 173–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barsi, J.A.; Lee, K.; Kvaran, G.; Markham, B.L.; Pedelty, J.A. The Spectral Response of the Landsat-8 Operational Land Imager. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 10232–10251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodcock, C.E.; Allen, R.; Anderson, M.; Belward, A.; Bindschadler, R.; Cohen, W.; Gao, F.; Goward, S.N.; Helder, D.; Helmer, E.; et al. Free Access to Landsat Imagery. Science 2008, 320, 1011–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadjimitsis, D.G.; Clayton, C.R.I.; Hope, V.S. An assessment of the effectiveness of atmospheric correction algorithms through the remote sensing of some reservoirs. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2004, 25, 3651–3674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rujoiu-Mare, M.-R.; Mihai, B.-A. Mapping Land Cover Using Remote Sensing Data and GIS Techniques: A Case Study of Prahova Subcarpathians. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2016, 32, 244–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, M.I.; Basak, R. Land cover change detection using GIS and remote sensing techniques: A spatio-temporal study on Tanguar Haor, Sunamganj, Bangladesh. Egypt. J. Remote Sens. Space Sci. 2017, 20, 251–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butt, A.; Shabbir, R.; Ahmad, S.S.; Aziz, N. Land use change mapping and analysis using Remote Sensing and GIS: A case study of Simly watershed, Islamabad, Pakistan. Egypt. J. Remote Sens. Space Sci. 2015, 18, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Zheng, Z.; Li, Y.; Lv, G.; Wang, Q.; Lyu, H.; Huang, C.; Liu, G.; Du, C.; Mu, M.; et al. Remote observation of water clarity patterns in Three Gorges Reservoir and Dongting Lake of China and their probable linkage to the Three Gorges Dam based on Landsat 8 imagery. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 625, 1554–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nazeer, M.; Nichol, J.E. Development and application of a remote sensing-based Chlorophyll-a concentration prediction model for complex coastal waters of Hong Kong. J. Hydrol. 2016, 532, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Wu, J.; Qi, J.; Zhang, L.; Huang, H.; Lou, L.; Chen, Y. Empirical estimation of total phosphorus concentration in the mainstream of the Qiantang River in China using Landsat TM data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2010, 31, 2309–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torbick, N.; Hession, S.; Hagen, S.; Wiangwang, N.; Becker, B.; Qi, J. Mapping inland lake water quality across the Lower Peninsula of Michigan using Landsat TM imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2013, 34, 7607–7624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Ocean-Colour Coordinating Group. IOCCG Report Number 05: Reports of the International Ocean-Colour Coordinating Group. In Remote Sensing of Inherent Optical Properties: Fundamentals, Tests of Algorithms, and Applications; International Ocean Colour Coordinating Group (IOCCG): Dartmouth, NS, Canada, 2006; Volume 5, ISBN 9781896246567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kratzer, C.R.; Brezonik, P.L. A Carlson-Type Trophic State Index for Nitrogen in Florida Lakes. JAWRA J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 1981, 17, 713–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, M.M.; Li, L.; Hussain, S.; Lee, J.L.; Mumtaz, F.; Elbeltagi, A.; Waqas, M.S.; Dilawar, A.J.W. Analysis of Seasonal Variations in Surface Water Quality over Wet and Dry Regions. Water 2022, 14, 1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borkman, D.G.; Smayda, T.J. Coincident patterns of waste water suspended solids reduction, water transparency increase and chlorophyll decline in Narragansett Bay. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 107, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, V.H.; Tilman, G.D.; Nekola, J.C. Eutrophication: Impacts of excess nutrient inputs on freshwater, marine, and terrestrial ecosystems. Environ. Pollut. 1998, 100, 179–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Sun, X.; Zhou, Y.; Zhao, C.; Du, Z.; Liu, R.Y. Ecosystem health assessment in coastal waters by considering spatio-temporal variations with intense anthropogenic disturbance. Environ. Model. Softw. 2017, 96, 128–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, F.S.Y.; Alcântara, E.; Rodrigues, T.W.P.; Imai, N.N.; Barbosa, C.C.F.; da Silva Rotta, L.H. Estimation of chlorophyll-a concentration and the trophic state of the barra bonita hydroelectric reservoir using OLI/landsat-8 images. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 10391–10417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kloiber, S.M.; Brezonik, P.L.; Olmanson, L.G.; Bauer, M.E. A procedure for regional lake water clarity assessment using Landsat multispectral data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 82, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, K.; Zhu, G.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, Y. Monitoring spatiotemporal variations in nutrients in a large drinking water reservoir and their relationships with hydrological and meteorological conditions based on Landsat 8 imagery. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 599–600, 1705–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferdous, Z.; Muktadir, A.K.M. A Review: Potentiality of Zooplankton as Bioindicator. Am. J. Appl. Sci. 2009, 6, 1815–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.; Mei, X.; Liu, J. Comparative Studies on Community Structure, Biodiversity of Plankton and Zoobenthos in Four Lakes of Different Trophic States in China. Water 2003, 16, 361–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodds, W.K.; Jones, J.R.; Welch, E.B. Suggested classification of stream trophic state: Distributions of temperate stream types by chlorophyll, total nitrogen, and phosphorus. Water Res. 1998, 32, 1455–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murthy, G.P.; Shivalingaiah; Leelaja, B.; Hosmani, S.P. Trophic State Index in Conservation of Lake Ecosystems. In Proceedings of the Taal 2007 12th World Lake Conference Trophic, Jaipur, India, 28 October–2 November 2007; pp. 840–843. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; Cai, Q.; Han, X.; Shao, M.; Liu, R. Factors regulating trophic status in a large subtropical reservoir, China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2010, 169, 237–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.S.; Kwon, Y.S.; Hwang, S.J.; Park, S. Characterizing effects of landscape and morphometric factors on water quality of reservoirs using a self-organizing map. Environ. Model. Softw. 2014, 55, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).