Effects of Ammonia on Juvenile Sunray Surf Clam (Mactra chinensis Philippi) in Laboratory Tests
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Test Organisms
2.2. Test Water and Water Chemistry
2.3. Acute Exposure (96 h)
2.4. Sub-Chronic Exposure (20 d)
2.5. Histological Procedures and Assessment
2.6. Antioxidant Enzyme Activities
2.7. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Acute Toxicity Test
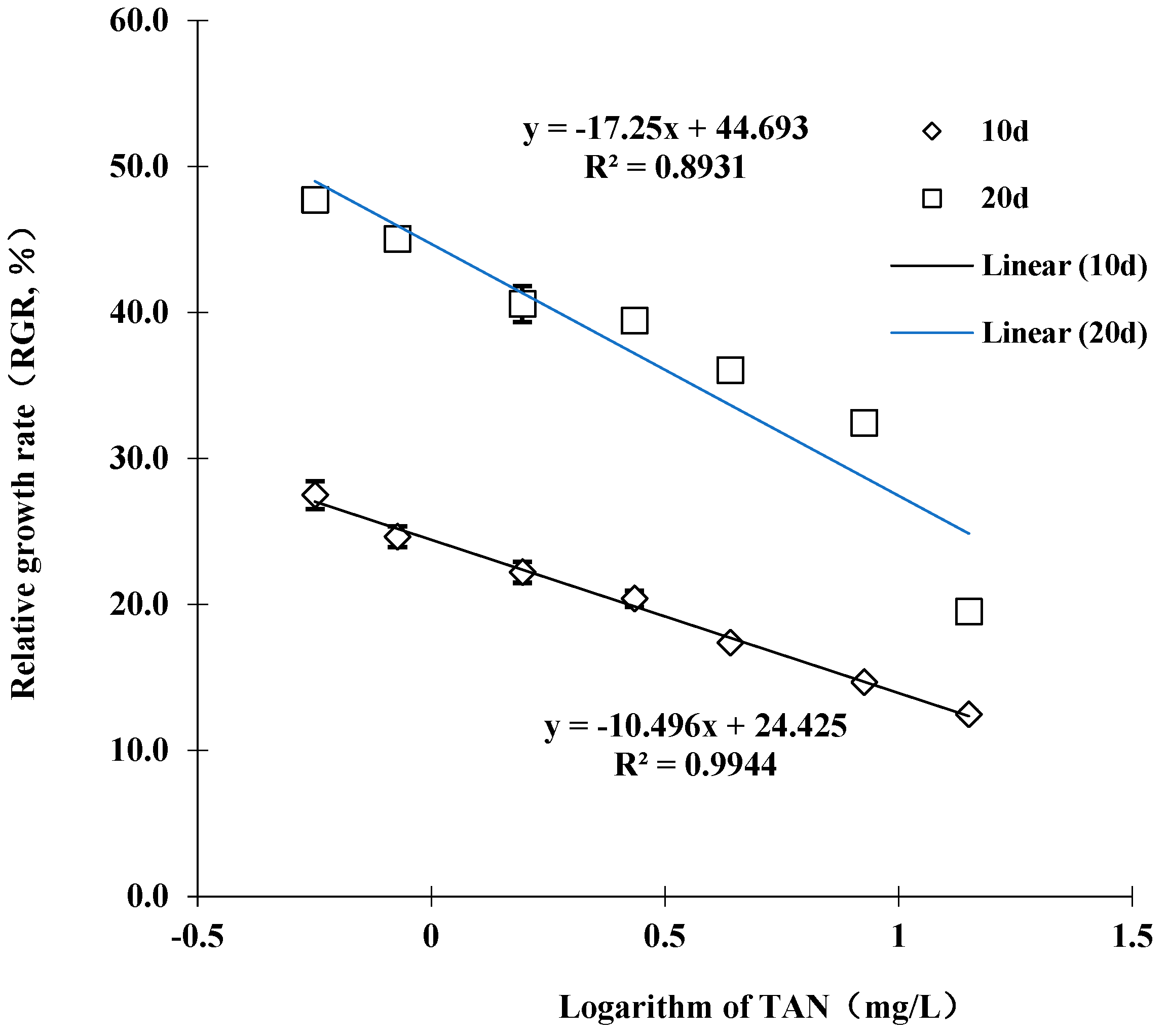
3.2. Sub-Chronic Toxicity Test
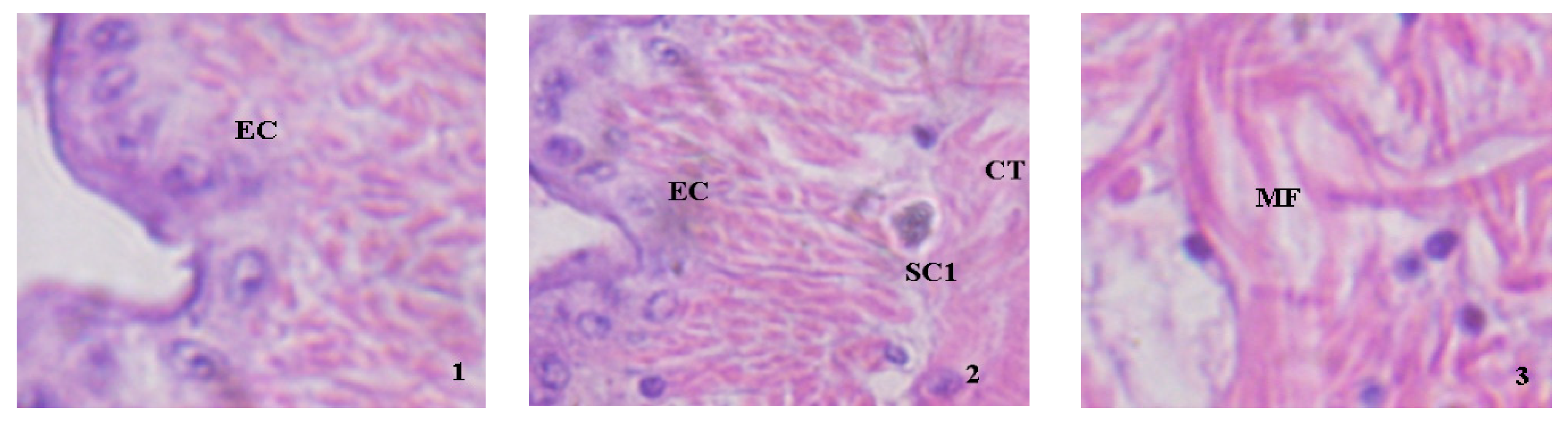
3.3. Histological Observations
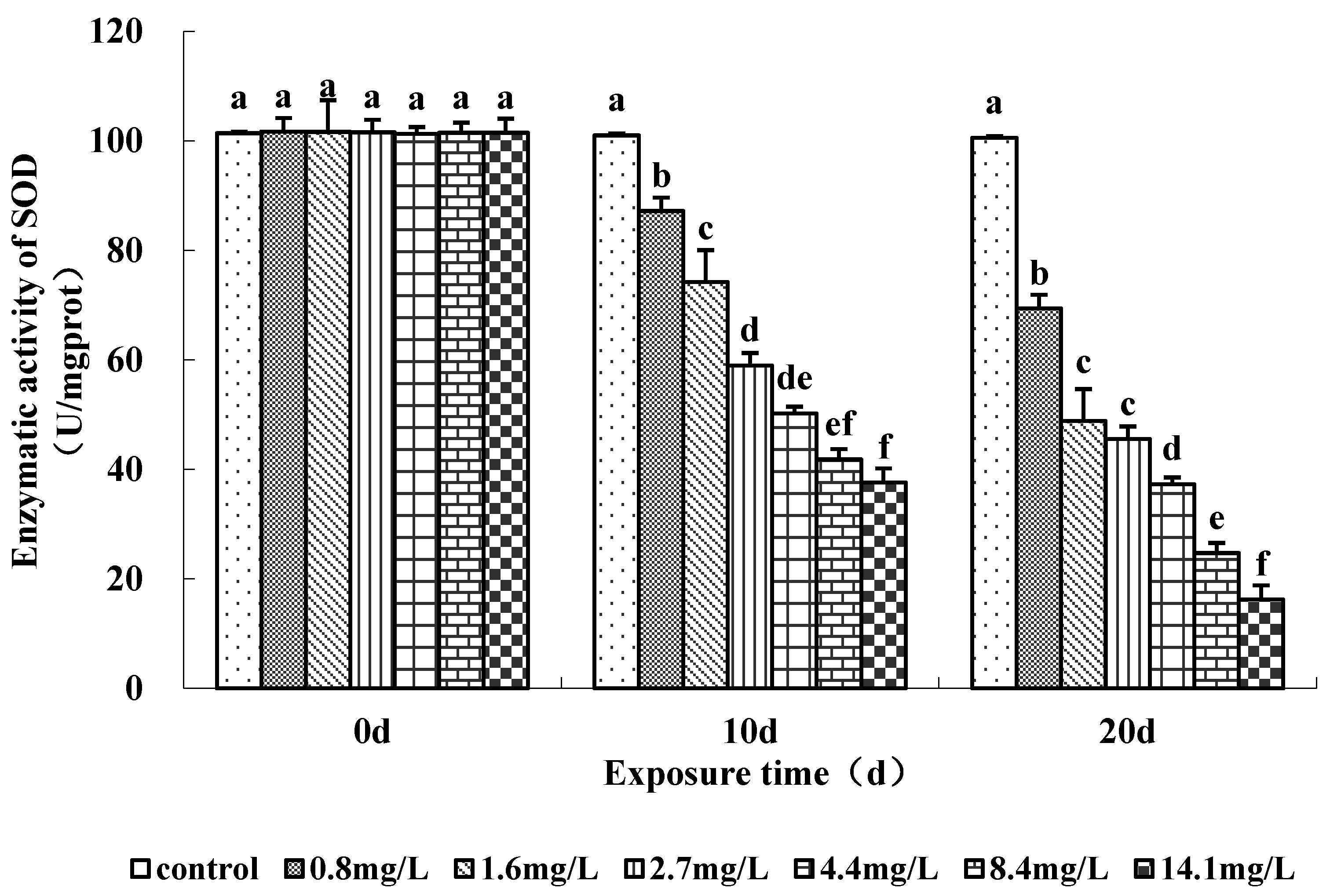
3.4. Enzyme Activities under Sub-Chronic Ammonia Stress
4. Discussions and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- FAO. The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture 2022. Towards Blue Transformation; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2022; Available online: https://www.fao.org/documents/card/en/c/cc0461en (accessed on 16 January 2023).
- Kim, S.H.; Chung, E.; Lee, K. Oocyte Degeneration Associated with Follicle Cells in Female Mactra chinensis (Bivalvia: Mactridae). Dev. Reprod. 2014, 18, 321–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Res, M.; Reunov, A.; Lutaenko, K.; Vekhova, E.; Zhang, J.; Zakharov, E.; Sharina, S.; Alexandrova, Y.; Reunova, Y.; Akhmadieva, A.; et al. In the Asia-Pacific region, the COI DNA test revealed the divergence of the bivalve mollusc Mactra chinensis into three species; can these species be distinguished using shell coloration and sperm structure ? Helgol. Mar. Res. 2021, 75, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, Z.; Huo, Z.; Yan, X.; Yang, F.; Liu, H.; Zhang, X. Effect of substrate component on the growth and survival of juvenile sunray surf clam (Mactra chinensis Philippi). J. Ocean Univ. China 2016, 15, 676–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, M.; Li, Y.; Xu, H.; Lv, J.; Wu, H.; Zhao, Y. Ammonia nitrogen exposure caused structural damages to gill mitochondria of clam Ruditapes philippinarum. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 222, 112528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camargo, J.A.; Alonso, Á. Ecological and toxicological effects of inorganic nitrogen pollution in aquatic ecosystems: A global assessment. Environ. Int. 2006, 32, 831–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Yao, T.; Shi, S.; Ye, L. Effects of acute ammonia nitrogen exposure on metabolic and immunological responses in the Hong Kong oyster Crassostrea hongkongensis. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 237, 113518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boardman, G.D.; Starbuck, S.M.; Hudgins, D.B.; Li, X.; Kuhn, D.D. Toxicity of ammonia to three marine fish and three marine invertebrates. Environ. Toxicol. 2004, 19, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Li, Y.; Wang, H.; Wang, H.; Qiao, R.; Jeppesen, E. Ecosystem complexity explains the scale-dependence of ammonia toxicity on macroinvertebrates. Water Res. 2022, 226, 119266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, M.; Li, Y.; Xu, H.; Lv, J.; Wu, H.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, N.; Ingersoll, C.G.; Hardesty, D.K.; Ivey, C.D.; et al. Effects of acute ammonia exposure on antioxidant and detoxification metabolism in clam Cyclina sinensis. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2021, 26, 2569–2575. [Google Scholar]
- Kallqvist, T.; Svenson, A. Assessment of ammonia toxicity in tests with the microalga, Nephroselmis pyriformis, Chlorophyta. Water Res. 2003, 37, 477–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Lei, S.-C. Toxicity of Ammonia and Nitrite to Penueus monodon Juveniles. J. World Aquac. Soc. 1990, 21, 300–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.; Luo, H.; Wu, J.; Hung, T.C.; Cao, B.; Liu, X.; Yang, J.; Yang, P. A Review of the Emerging Risks of Acute Ammonia Nitrogen Toxicity to Aquatic Decapod Crustaceans. Water 2023, 15, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, L.; Ren, J.; Zhang, H.; Sun, C.; Dong, Y.; Lin, Z. Transcriptomic Analysis of Gill and Hepatopancreas in Razor Clam (Sinonovacula constricta) Exposed to Acute Ammonia. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 832494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferretti, J.A.; Calesso, D.F. Toxicity of ammonia to surf clam (Spisula solidissima) larvae in saltwater and sediment elutriates. Mar. Environ. Res. 2011, 71, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, M.; Wu, H.; Yang, H.; Zhao, J.; Lv, J. Gill damage and neurotoxicity of ammonia nitrogen on the clam Ruditapes philippinarum. Ecotoxicology 2017, 26, 459–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USEPA. Aquatic Life Ambient Water Quality Criteria for Ammonia—Freshwater 2013; USEPA: Washington, DC, USA, 2013; Volume EPA-822-R-18-002. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sites/default/files/2015-08/documents/aquatic-life-ambient-water-quality-criteria-for-ammonia-freshwater-2013.pdf (accessed on 16 January 2023).
- Liu, L.; Zheng, H.; Luan, L.; Luo, X.; Wang, X.; Lu, H.; Li, Y.; Wen, L.; Li, F.; Zhao, J. Functionalized polystyrene nanoplastic-induced energy homeostasis imbalance and the immunomodulation dysfunction of marine clams (Meretrix meretrix) at environmentally relevant concentrations. Environ. Sci. Nano 2021, 8, 2030–2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Ma, C.; Dai, Y.; Wang, X.; Bai, D.; Shang, X.; Jia, L. Effect of dietary nano-Se on oxidation resistance of juvenile tongue sole (Cynogiossus semilaevis). Feed Res. 2019, 1, 25–30. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maoxiao, P.; Xiaojun, L.; Donghong, N.; Bo, Y.; Tianyi, L.; Zhiguo, D. Survival, growth and physiology of marine bivalve (Sinonovacula constricta) in long-term low-salt culture. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 2819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabatini, S.E.; Brena, B.M.; Luquet, C.M.; San Julián, M.; Pirez, M.; de Molina, M.d.C.R. Microcystin accumulation and antioxidant responses in the freshwater clam Diplodon chilensis patagonicus upon subchronic exposure to toxic Microcystis aeruginosa. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2011, 74, 1188–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charles, S.; Veber, P.; Delignette-Muller, M.L. MOSAIC: A web-interface for statistical analyses in ecotoxicology. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 11295–11302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y. Aquaculture Water Environmental Chemistry; China Agricultural Press: Beijing, China, 2004; ISBN 7109085813. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Xu, E.G.; Li, Y.; Liu, H.; Vidal-Dorsch, D.E.; Giesy, J.P. Ecological risks posed by ammonia nitrogen (AN) and un-ionized ammonia (NH3) in seven major river systems of China. Chemosphere 2018, 202, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mummert, A.K.; Neves, R.J.; Newcomb, T.J.; Cherry, D.S. Sensitivity of juvenile freshwater mussels (Lampsilis fasciola, Villosa iris) to total and un-ionized ammonia. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2003, 22, 2545–2553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, H.; Liu, J.; Ni, Q.; Wang, F.; Dong, Z. Effects of acute ammonia exposure and post-exposure recovery on nonspecific immunity in Clam Cyclina sinensis. Isr. J. Aquac. 2022, 74, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batley, G.E.; Simpson, S.L. Development of guidelines for ammonia in estuarine and marine water systems. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2009, 58, 1472–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, M.; Zuo, Q.; Zhang, W.; Feng, Y.; Wang, L.; Yu, L.; Zhang, X.; Li, J.; Huang, Z. Toxicological Assessment of Ammonia Exposure on Carassius auratus red var. Living in Landscape Waters. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2019, 103, 814–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grice, A.M.; Bell, J.D. Application of ammonium to enhance the growth of giant clams (Tridacna maxima) in the land-based nursery: Effects of size class, stocking density and nutrient concentration. Aquaculture 1999, 170, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.; Yang, C.; Yang, F.; Yan, X. Impact of total ammonia nitrogen on survival and growth of larval and juvenile bay scallop Argopecten irradians. J. Dalian Ocean Univ. 2017, 32, 268–274. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Jin, Y.; Jahan, K.; Jami, M.E.H.; Xu, Q.; Huo, Z.; Yang, F.; Yan, X. Effects of ammonia nitrogen on early growth and survival of the ‘Zebra 2’ strain of the manila clam (Ruditapes philippinarum). Aquac. Res. 2021, 52, 4767–4775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soon, T.K.; Ransangan, J. Extrinsic Factors and Marine Bivalve Mass Mortalities: An Overview. J. Shellfish Res. 2019, 38, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasee, B.A. Histological and Ultrastructural Studies of Larval and Juvenile Lampsilis (Bivalvia) from the Upper Mississippi River; Iowa State University: Ames, IA, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Carella, F.; Feist, S.W.; Bignell, J.P.; De Vico, G. Comparative pathology in bivalves: Aetiological agents and disease processes. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2015, 131, 107–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlahogianni, T.; Dassenakis, M.; Scoullos, M.J.; Valavanidis, A. Integrated use of biomarkers (superoxide dismutase, catalase and lipid peroxidation) in mussels Mytilus galloprovincialis for assessing heavy metals’ pollution in coastal areas from the Saronikos Gulf of Greece. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2007, 54, 1361–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.H.; Chen, J.C. Effect of ammonia on the immune response of white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei and its susceptibility to Vibrio alginolyticus. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2004, 16, 321–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Yan, Z.; Zheng, X.; Wang, S.; Fan, J.; Liu, Z. Effects of acute ammonia toxicity on oxidative stress, DNA damage and apoptosis in digestive gland and gill of Asian clam (Corbicula fluminea). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2020, 99, 514–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Feng, K.; Zhang, L.; Bai, Y.; Yao, W. Effects of acute ammonia stress on antioxidant responses, histopathology and ammonia detoxification metabolism in triangle sail mussels (Hyriopsis cumingii). Water 2021, 13, 425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Australian and New Zealand Environment and Conservation Council. Australian and New Zealand Guidelines for Fresh and Marine Water Quality Volume 1; Australian and New Zealand Environment and Conservation Council: Canberra, Australia, 2000. Available online: https://www.waterquality.gov.au/sites/default/files/documents/anzecc-armcanz-2000-guidelines-vol1.pdf (accessed on 29 December 2022).
- Han, T.; Yang, F.; Jia, J.; Li, X.; Yan, X. Effects of total ammonia nitrogen content on early growth and development of Manila clam Ruditapes philippinarum. J. Dalian Ocean Univ. 2018, 33, 210–216. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canadian Council of Ministers of the Environment. Canadian Water Quality Guidelines for the Protection of Aquatic Life: Ammonia; Canadian Council of Ministers of the Environment: Winnipeg, Canada, 2010; Available online: https://ccme.ca/en/res/ammonia-en-canadian-water-quality-guidelines-for-the-protection-of-aquatic-life.pdf (accessed on 3 December 2022).
- GB11607-89; Water Quality Standard for Fisheries. Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 1990. Available online: https://www.chinesestandard.net/PDF/English.aspx/GB11607-1989 (accessed on 30 November 2022).


| Time (h) | LC50-TAN (mg/L) | LC50-NH3 (mg/L) |
|---|---|---|
| 24 | 90.4 (78.0; 106.0) | 4.14 (3.57; 4.85) |
| 48 | 16.5 (15.1; 18.3) | 0.79 (0.72; 0.88) |
| 96 | 11.1 (10.0; 12.0) | 0.56 (0.50; 0.60) |
| Species | Stage | Effect | Response | Duration (h) | pH | T (°C) | Salinity | Toxicological Values (TAN/NH3, mg/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spisula Solidissima [15] | Larvae | Mortality | LC50 | 48 | 8.14 ± 0.06 | 19.7 ± 0.4 | 31 ± 0.5‰ | 10.6/0.53 |
| Growth | EC50 | 2.35/0.12 | ||||||
| Cyclina Sinensis [26] | 3.38 ± 0.21 g | Mortality | LC50 | 72 | 8.0 ± 0.3 | 24 | 21 ppt | 105.0/5.22 |
| 96 | 80.7/4.01 | |||||||
| Ruditapes philippinarum [29] | Larvae | Growth | MATC | 96 | 8.1 | 23.05 | 27 | 2.98–5.85/0.09–0.18 |
| Juvenile | 8.18 | 27.65 | 27.5 | 58.05–95.69/3.01–4.97 | ||||
| Argopecten Irradians [30] | Larvae | Growth | EC50 | 144 | 7.95–8.10 | 23–25 | 27–28 | 2.023/0.089 |
| Embryo | Hatching | MATC | 24 | 8.20–8.30 | 21.5–22.5 | 0.86–1.80/0.054–0.113 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dai, Y.; Dong, Y.; Yang, F.; Chen, Z.; Jia, J. Effects of Ammonia on Juvenile Sunray Surf Clam (Mactra chinensis Philippi) in Laboratory Tests. Pollutants 2023, 3, 232-242. https://doi.org/10.3390/pollutants3020017
Dai Y, Dong Y, Yang F, Chen Z, Jia J. Effects of Ammonia on Juvenile Sunray Surf Clam (Mactra chinensis Philippi) in Laboratory Tests. Pollutants. 2023; 3(2):232-242. https://doi.org/10.3390/pollutants3020017
Chicago/Turabian StyleDai, Yuanyuan, Yubo Dong, Feng Yang, Zhongzhi Chen, and Jia Jia. 2023. "Effects of Ammonia on Juvenile Sunray Surf Clam (Mactra chinensis Philippi) in Laboratory Tests" Pollutants 3, no. 2: 232-242. https://doi.org/10.3390/pollutants3020017
APA StyleDai, Y., Dong, Y., Yang, F., Chen, Z., & Jia, J. (2023). Effects of Ammonia on Juvenile Sunray Surf Clam (Mactra chinensis Philippi) in Laboratory Tests. Pollutants, 3(2), 232-242. https://doi.org/10.3390/pollutants3020017








