Abstract
Beaches are major sites of microbiological pollution. Assessment of the abundance of resistant forms of enteric protozoa on these recreational waters is important for the prevention and management of health risks. Based on sedimentation and flotation methods, this study found that Kribi beach waters concentrate considerable amounts of enteric protozoa, which are potentially pathogenic. They include Coccidia (Cryptosporidium sp. and Cyclospora cayetanensis), Amoebae (Endolimax nana, Entamoeba histolytica and Entamoeba coli) and Flagellates (Giardia intestinalis). In general, seasonal changes and tidal cycles have significantly impacted the spread of these parasites along Kribi beaches. Thus, at all sites surveyed (Mpalla, Ngoyè and Mboamanga), maximum protozoan abundances were recorded at low tide and during the rainy seasons. It should also be noted that at each sampling site, significant correlations were recorded between certain protozoa and certain physico-chemical variables (p < 0.05). At Mboamanga, for example, Cryptosporidium sp. and Endolimax nana were positively correlated during the Short Rainy Season with temperature (r = 0.601, p = 0.044 and r = 0.632, p = 0.042). At Mpalla, a positive and significant correlation was observed during the Short Rainy Season between Entamoeba coli and pH (r = 0.605, p = 0.033). The high concentration of resistant forms of these enteric protozoa at Kribi beaches is a real public health threat for bathers. Therefore, in this tourist town, it is urgent to put in place an effective plan for the collection and sustainable treatment of solid and liquid waste, which are the main sources of contamination.
1. Introduction
Coastal territories are places of exchange between the continent and the ocean; they are very rich environments from an ecological point of view. They represent a home to a great deal of biodiversity and to a variety of natural areas: foreshores, rocky coasts and cliffs, maritime marshes and estuaries [1,2]. Attractive ecosystems, coastal environments are subject to many uses, particularly related to tourism [3,4]. Because of their importance, both ecological and economic, coasts should be subject to many protections and management measures, and their preservation appears to be a major issue [5]. Indeed, microbiological contamination of coastal ecosystems, due to the significant contribution of fecal germs in the environment, can cause a health risk for bathers [6,7,8]. Among the potentially pathogenic germs, enteric protozoa are distinguished as a diverse group of microorganisms. Some enteric protozoa are pathogenic and have been associated with bathing-water-borne disease outbreaks [9,10]. These parasites can be found in water as a result of direct or indirect contamination by human or animal feces [11].
Because of their strategic location for economic development, coastal ecosystems are under strong anthropic pressure, accentuated by the arrival of tourists who seek these places for their vacations [12,13]. This massive arrival can constitute a direct source of fecal contamination [14]. Bathing activities are considered a direct source of fecal bacteria [13]. Indeed, 100 g of feces allows the dissemination of 1014 cells of pathogens in the water column, and on average, a bather can bring 0.14 g of fecal waste during a 15 min swim [11,13]. Recreational activities, such as unsewered campsites and boaters discharging untreated sewage directly on or off beaches, may contribute to the input of fecal microorganisms into these environments. Several studies have also shown a strong correlation between the presence of animals and contamination events in these ecosystems [15,16].
The deterioration of coastal and marine ecosystems due to microbial and physico-chemical pollution inevitably leads to a public health risk in the context of bathing activities following an alteration in water quality [17]. In fact, numerous epidemiological studies have confirmed that contact with recreational waters contaminated by fecal waste presents health risks for users [14]. The vulnerability of aquatic ecosystems in Sub-Saharan Africa is important on urbanized coastlines and is accentuated by local development, population growth and tourism. This phenomenon is also intensified by the health context of the last three years with the COVID-19 pandemic, which has prompted populations from large cities to migrate to rural and coastal areas in search of spaces considered of better “quality” because they are less populated and, therefore, less dense. In Cameroon, the degradation of coastal environments by fecal contamination is frequent and recurrent in different types of aquatic ecosystems with diverse geographical contexts. Thus, Cameroon’s coastal ecosystems are increasingly weakened by intense and growing anthropic pressure, resulting in increased risks to public health. Among these risks, those caused by fecal contamination of bathing water can have negative consequences for human health, including the appearance of certain diseases, such as ear infections, gastroenteritis or skin irritations. Preserving the health status of Cameroonian coastal environments, but also ensuring the health security of the populations in these regions, is of primary importance. The main objective of this study was to assess the health risks associated with enteric protozoan pollution along Kribi beaches in the Southern Region of Cameroon. Specifically, it was to identify and quantify the resistance patterns of enteric protozoa in the waters of three highly frequented beaches of the city of Kribi (Mpalla, Ngoyè and Mboamanga), according to seasons and tidal cycles.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Sampling Stations
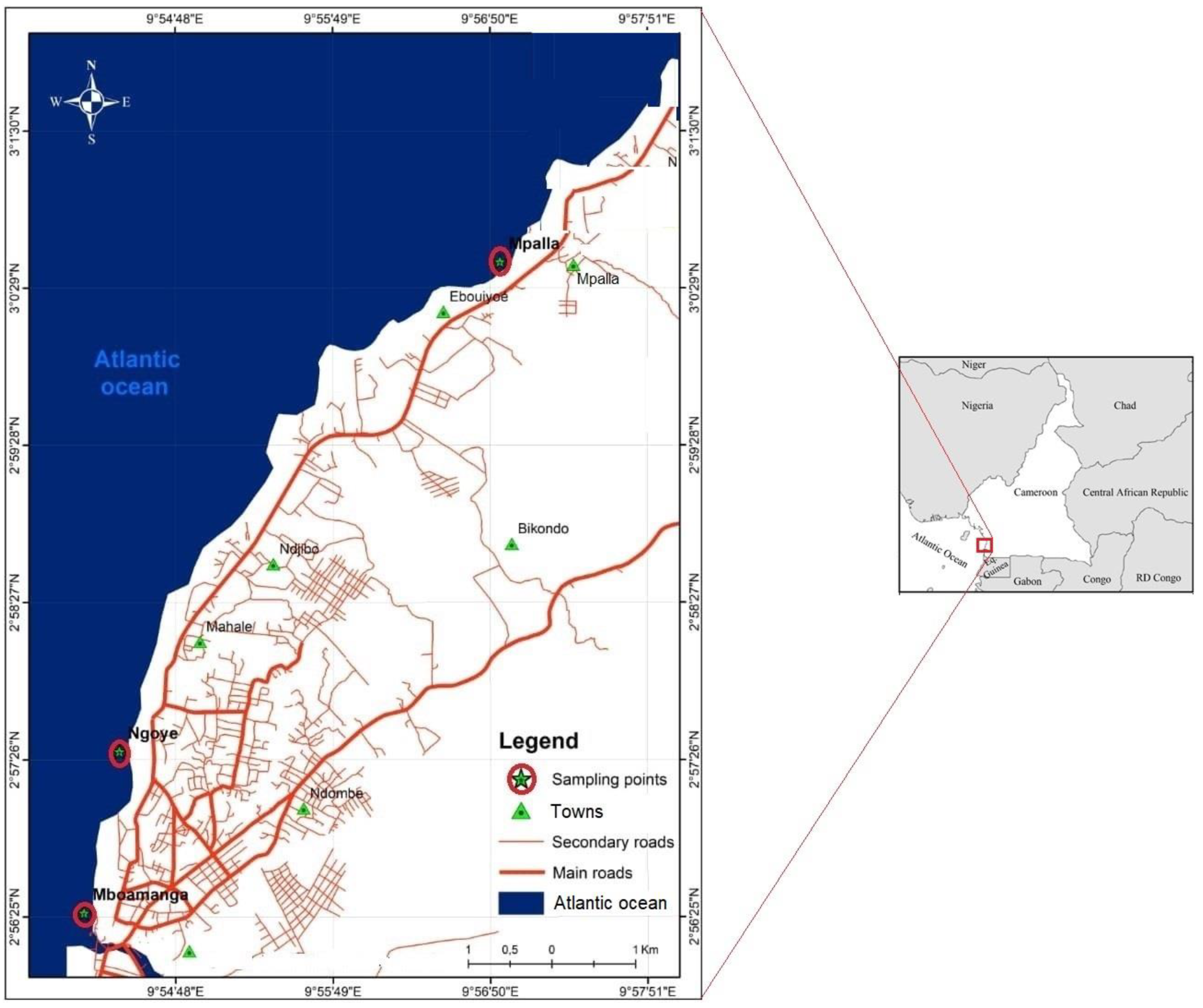
The study was conducted in 2021 on the three most frequented beaches of the city of Kribi, in the Ocean Division, Cameroon southern Atlantic coast (Figure 1). This area is subject to a Guinean-type equatorial climate, characterized by four seasons: Long Dry Season (LDS) from December to February, Short Rainy Season (SRS) from March to May, Short Dry Season (SDS) from June to July and Long Rainy Season (LRS) from August to November [18,19,20]. Four sampling campaigns were conducted: January (LDS), April (SRS), July (SDS) and October (LRS). Overall, the water depth on the Kribi beaches varies from 0.30 to 0.48 m at low tide and from 1.33 to 2.07 m [6]. At the level of each beach, one sampling station was surveyed based on it accessibility and frequentation. Station 1 was located at Mpalla beach (3°00′29″ N–9°56′54.5″ E) and characterized by a gray sandy substrate. Station 2 was situated at Ngoyè (2°57′26.6″ N–9°54′36.9″ E), 4 km from Mpalla, and characterized by a black sandy substrate. Located 9 km from Ngoyè, station 3 on Mboamanga beach (2°56′22.4″ N–9°54′12.3″ E) is characterized by a sandy, clay, gray substrate.
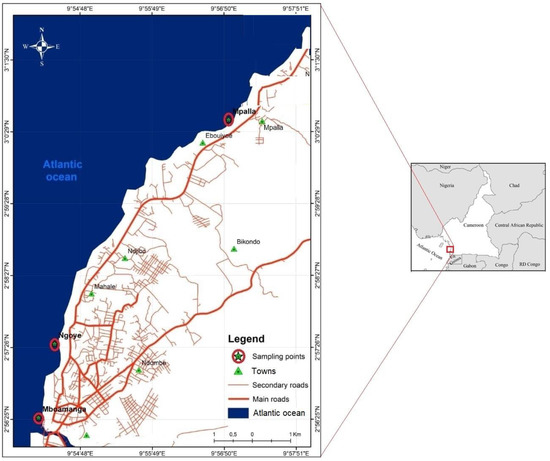
Figure 1.
Portion of the coastal strip indicating the sampling points along the Kribi beaches.
2.2. Measurement of Environmental Variables
To determine the water properties at each sampling station and each season, eight environmental variables were measured in situ, in triplicate, during each tide period (low and high tide), using a handheld HANNA HI 9829 multimeter, following Rodier et al. [21] and APHA [22] standard methods. These environmental parameters include Temperature (°C), Dissolved Oxygen [DO] (mg·L−1), pH, Salinity (PSU), Electrical Conductivity [EC] (mS·cm−1), Turbidity (NTU), Total Dissolved Solids [TDS] (mg·L−1) and Suspended Solids [SS] (mg·L−1). Additionally, the water depth was also measured during low and high tides.
2.3. Enteric Protozoa Analysis
The identification and enumeration of enteric protozoa was completed in the laboratory. The samples were first left for 24 h at room temperature in the sedimentation flasks. After sedimentation, the supernatant was poured, and the muddy deposit obtained was then measured, homogenized and distributed in test tubes. The Merthiolate-Iodine-Formol (MIF) and Ziehl–Neelsen concentration techniques enabled us to concentrate the parasitic elements in order to guarantee a better enumeration. Therefore, in each test tube, 1 mL of 10% formalin, 5 mL of distilled water, and 2–3 drops of Lugol were added, and the tubes were centrifuged at 500 rpm for 5 min using a centrifuge (Medifriger). Each time, the pellet was recovered and placed on slides for direct observation and enumeration of cysts or oocysts under an optical microscope (Olympus model CK2). The forms of resistance of protozoa were identified using the WHO manual [23] and the Thivierge workbook [24]. The number of eggs or larvae contained in 1 L of sample was obtained by the following formula, proposed by Ajeagah et al. [25]:
X = y·Vx/Vy
X = number of parasites, Vx = volume of the pellets of 1 L of sample, Vy = volume of the pellets used for observation, y = number of parasites observed in Vy.
2.4. Statistical Analysis
The Kruskal–Wallis test followed by the Mann–Whitney pairwise test were performed to verify significant differences in the spatial and seasonal variations of environmental parameters and parasite abundances recorded during the study period.
The two-way ANOVA test was carried out on normalized datasets (square root transformation) to assess the significance of the influences of tides, seasons and their interaction on the variation of enteric protozoa abundances. The safety threshold was 5% (p < 0.05).
3. Results
3.1. Physico-Chemical Variables
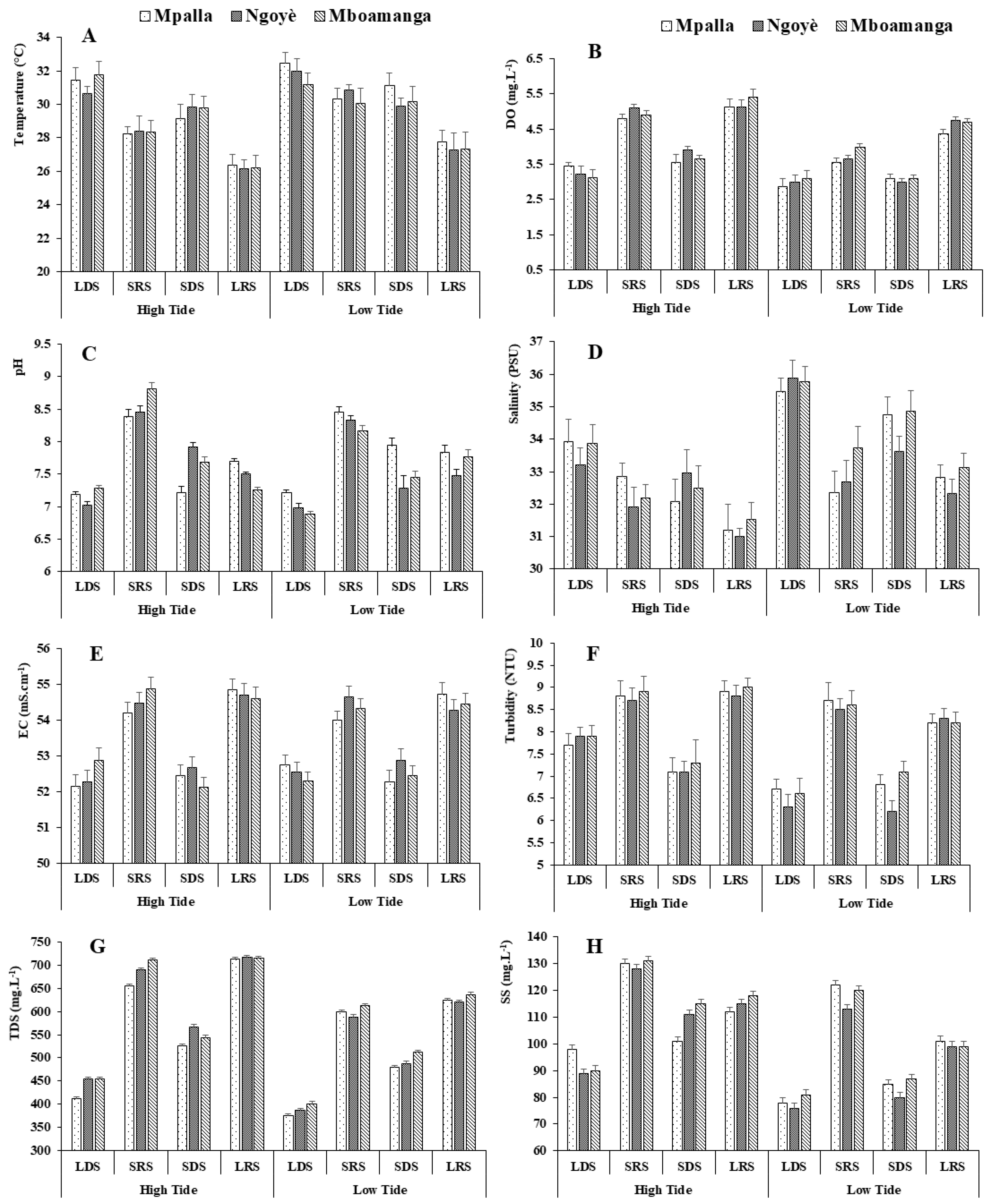
Temperature is a parameter that drives various biological and chemical activities in the water and plays a major role in the distribution and development of fauna and flora. Along Kribi beaches, temperatures recorded during the study period ranged from 26.16 °C to 32.44 °C (Figure 2A). In contrast to the minimum temperatures, it was clearly observed that the maximum temperatures were recorded during low tides and dry seasons (LDS, SDS). Dissolved oxygen, considered one of the main vital factors that dictate biological processes in aquatic ecosystems, was more concentrated during high tide and rainy seasons (Figure 2B). Overall, the waters of Mpalla were less oxygenated compared to the other sampled sites.
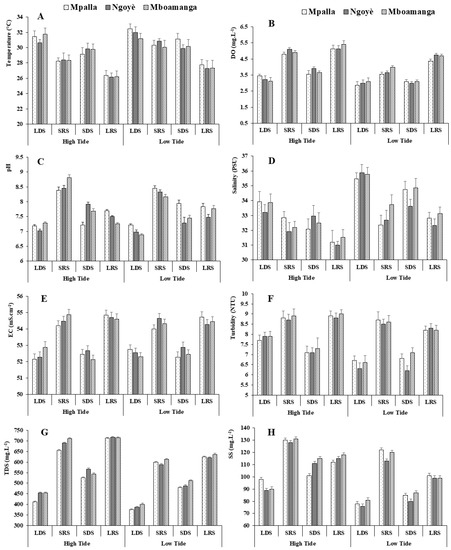
Figure 2.
Abiotic variables according to tidal cycles and seasons. (A) Temperature; (B) Dissolved Oxygen—DO; (C) pH; (D) Salinity; (E) Electrical Conductivity—EC; (F) Turbidity; (G) Total Dissolved Solids—TDS; (H) Suspended Solids—SS.
The pH indicates the degree of acidity or alkalinity of water. Data recorded at various sites ranged from slightly acidic (6.89 at low tide, during the short dry season at Mboamanga) to moderately basic (8.81 at high tide, during the short rainy season, also at Mboamanga) (Figure 2C). Salinity is an important parameter that controls the density of seawater and allows us to understand the circulation of water masses and to differentiate them. This parameter is considered a limiting factor for the growth of microorganisms in various environments. At all the sites surveyed, the highest values of salinity were obtained at low tides, mainly in dry seasons (Figure 2D).
The electrical conductivity is an indicator of the total concentration of dissolved salts. Independent of tidal cycles, electrical conductivity values were influenced by the seasons. Indeed, the waters of Kribi beaches were more concentrated in dissolved salts during the rainy seasons than during the dry seasons (Figure 2E). Turbidity measures and quantifies the state of water disturbed by suspended particles; thus, it reflects the state of a liquid due to the presence of fine, but visible, suspended particles that impede the passage of light. At the sampled sites, the minimum values were recorded during the dry seasons (Figure 2F).
TDS is a measure of anything that has dissolved in the water column. This includes minerals, such as calcium and sodium, that have separated from the chemicals, as well as dissolved dust, pollen and pollution. In the waters of Kribi beaches, this parameter was more concentrated during the rainy seasons, regardless of the tidal cycles. The minimum value (375 mg·L−1) was obtained at Mpalla during low tide and during the LDS (Figure 2G). Suspended solids are all the solid mineral and/or organic particles present in a water column, and their amount indicates the presence of larger particles in the water column. On Kribi beaches, the concentrations of suspended solids varied between 76 and 131 mg·L−1. Seasonally, the maximum values were collected during the short rainy seasons (Figure 2H).
3.2. Diversity and Abundance of Parasites
3.2.1. Cryptosporidium sp.
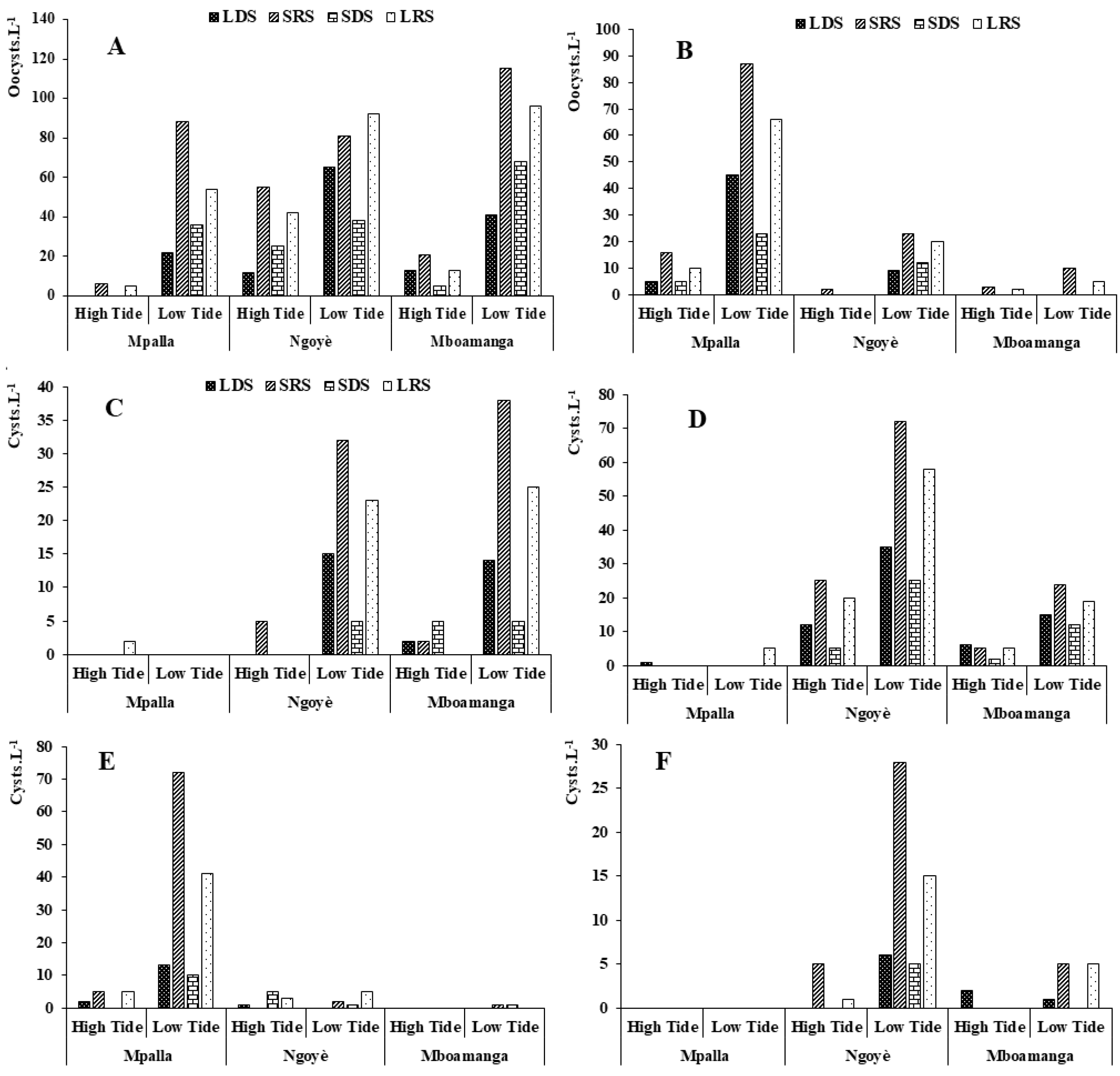
Cryptosporidium sp. is a protozoan parasite that causes cryptosporidiosis. Symptoms appear abruptly about 7 days after infection and consist mainly of abdominal cramps and profuse, watery diarrhea. Nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, fever and weakness may also occur. Symptoms usually last 1 to 2 weeks and then disappear. People may continue to pass eggs in their feces for several weeks after symptoms have resolved. Oocyst concentrations ranged from 0 in the dry seasons at Mpalla to 115 oocysts·L−1 at low tide during the SRS at Mboamanga (Figure 3A).
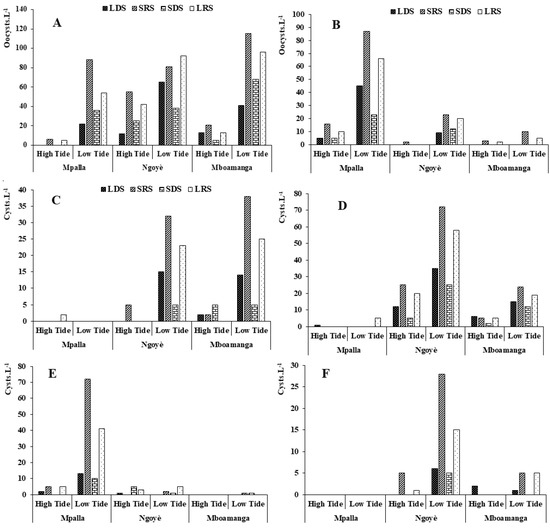
Figure 3.
Oocysts and cysts abundances according to tidal cycles and seasons. (A) Cryptosporidium sp.; (B) Cyclospora cayetanensis; (C) Endolimax nana; (D) Entamoeba histolytica; (E) Entamoeba coli; (F) Giardia intestinalis.
3.2.2. Cyclospora cayetanensis
Cyclosporiasis is an infection of the small intestine caused by the parasite Cyclospora cayetanensis. The main symptoms of cyclosporiasis are sudden watery, non-bloody diarrhea and nausea. Other symptoms include fever, abdominal cramps, vomiting and weight loss. The maximum abundance (87 oocysts·L−1) was recorded at low tide and during SRS at Mpalla. Unlike Mpalla, Mboamanga beach was less polluted by this parasite (Figure 3B).
3.2.3. Endolimax nana
Endolimax nana is an intestinal amoeba that exclusively parasitizes the intestine of humans; however, it is a commensal parasite, which means that it does not cause considerable harm to humans. The distribution of this amoeba is cosmopolitan, but it is more likely to be found in warm and humid environments. Although it does not cause disease like other amoebae, cases of chronic diarrhea, hives, constipation, rectal pain, vomiting and others symptoms have been reported in some immunocompromised patients. Practically absent in Mpalla, this parasite is poorly represented along Kribi beaches. The maximum concentration (38 cysts·L−1) was recorded at low tide during the SRS at Mboamanga (Figure 3C).
3.2.4. Entamoeba histolytica
Amoebiasis is caused by the amoeba Entamoeba histolytica, a parasite specific to humans. It is a protozoan that can surround itself with a thin shell to form a cyst a few microns in diameter. Amoebae implant themselves in the mucous membrane of the intestine. As they pass through it, they cause amoebiasis, the symptoms of which can range from mild diarrhea to dysentery, with blood and mucus in the feces. The destruction of the intestinal wall can subsequently lead to the formation of ulcers. When the parasite reaches the bloodstream, it can infect the liver, resulting in abscesses which, if left untreated, can lead to a fatal outcome. Along Kribi beaches, the abundance of cysts of this amoeba varied from one season to another according to the tidal cycles (Figure 3D). Ngoyè was the beach most contaminated by this amoeba, with mean abundances of 62 cysts·L−1 and 190 cysts·L−1 at high and low tide, respectively.
3.2.5. Entamoeba coli
Morphologically similar to Entamoeba histolytica, Entamoeba coli is a non-pathogenic amoeba, commensal of the human digestive tract. This amoeba was particularly recorded at low tide at Mpalla, with values of 13, 72, 10 and 41 cysts·L−1 in LDS, SRS, SDS and LRS, respectively (Figure 3E).
3.2.6. Giardia intestinalis
Giardiasis is an intestinal infection caused by the parasite Giardia intestinalis, which mainly infects the upper intestine (duodenum and jejunum). The parasite exists in two forms: the cyst and the trophozoite. The cyst is the infective form of the parasite; it can survive for several months in the environment. In the duodenum, cysts release trophozoites, which subsequently multiply and may remain in the lumen of the small intestine or attach to its wall. In the ileum and colon, trophozoites develop into cysts, which are passed in the feces. Totally absent in Mpalla, this parasite was mainly identified in Ngoyè during low tide, with maximum abundances obtained during SRS (28 cysts·L−1) and LRS (15 cysts·L−1) (Figure 3F).
3.3. Relationship between Physico-Chemical Parameters and Abundance of Parasites
On the basis of the statistical tests carried out, the interdependence links were proven and highlighted between some environmental parameters and some protozoan parasites along the beaches of Kribi. The tidal cycles and the seasons have strongly conditioned these existing affinities between these biotic and abiotic variables. Note that no significant correlation was found during high tides and during the two dry seasons. Thus, at Mboamanga, Cryptosporidium sp. and Endolimax nana were positively related to temperature (r = 0.601, p = 0.044 and r = 0.632, p = 0.042). At the Ngoyè site, Entamoeba histolytica and EC were interrelated (r = 0.521, p = 0.039). Finally, at the Mpalla site, a very strong relationship was observed between Entamoeba coli and pH (r = 0.605, p = 0.033). All of these dependency relationships were observed only during SRS. Rainfall is one of the main environmental factors causing the increase in concentration of resistant forms of enteric protozoa in the waters of Kribi beaches.
The Mann–Whitney U test revealed a statistically significant dissimilarity in Mboamanga between the mean concentrations of Cryptosporidium sp. during the two main seasons of the year (p = 0.034). Further, in Ngoyè, a dissimilarity was observed when comparing the mean concentrations of Entamoeba histolytica during the two main seasons (p = 0.042). On the other hand, at the three sampling sites, during high tides, these comparison tests revealed no dissimilarity. Overall, hydrodynamic variables, seasons and physico-chemical parameters seem to impact the structure and abundance of enteric protozoa in the Cameroonian coastal zone.
4. Discussion
The study showed variable concentrations of resistant forms of enteric protozoa (Cryptosporidium sp., Cyclospora cayetanensis, Endolimax nana, Entamoeba histolytica, Entamoeba coli and Giardia intestinalis) along the Kribi beaches. For the majority, these parasites constitute a public health problem for tourists and populations bathing in these waters [26,27]. The concentrations of enteric protozoa in a watershed are influenced by multiple environmental conditions and processes, which vary between watersheds and whose characteristics are often poorly known [27]. However, some appear to be applicable to various water sources. Assako et al. [15] provide a good discussion of environmental changes—including land use patterns and climate, social and demographic determinants—that may, at the local scale, affect parasite transmission.
On Kribi beaches, tidal cycles (high and low) and seasons (LDS, SRS, SDS and LRS) have shown an impact on the quality and density of identified protozoa. Indeed, contamination is favored at low tides by low flows due to less dilution of the water [28]. At the shoreline level, periods of spring tides, due to high tidal coefficients, are the most favorable for the dilution of pollution [29]. Studies have concluded that precipitation has a significant impact on the microbiological quality of beach waters, although the exact conditions that lead to increased pathogen loading vary [11,13]. These conditions favor high concentrations of parasites in the waters during low tide and rainy seasons (SRS and LRS). In Mboamanga, the highest concentrations of Cryptosporidium sp. oocysts and Endolimax nana cysts are related to their ability to adapt to environmental changing conditions [30,31]. On the other hand, the low density of Entamoeba coli and Giardia intestinalis cysts in all sampled sites is related to the high salinity of the waters. It should be noted that infection by enteric protozoa in beach waters is widespread worldwide, especially in tropical regions with poor hygiene [27,32]. Giardia cysts and Cryptosporidium oocysts can survive in the environment for a long time, depending on water characteristics. They are able to withstand a variety of environmental stresses, including freezing and exposure to seawater [32,33].
It Is possible to identify several causes of contamination, which explain the arrival of these enteric parasites on Kribi beaches in varying quantities.
First of all, it is important to note that fecal contamination came from human or animal feces. These feces are very rich in protozoa, bacteria and enteric viruses, the main components of the intestinal microbiota [11]. These microorganisms are found in aquatic ecosystems through different sources located near these environments. Thus, these microorganisms can be classified according to their human or animal origins and according to their diffusion or point sources in aquatic environments [11,13].
On Kribi beaches, human activities are the main source of fecal contamination [15]. The significant urbanization and industrial development in the Kribi coastal zone can, as a result of the nonexistence of sewage systems and wastewater treatment facilities, influence the input of fecal contaminants into bathing areas [34,35]. Due to its strategic location for economic development, the coastal ecosystems of the city of Kribi are subject to strong anthropic pressure accentuated by tourism, which can be a direct source of fecal contamination. Bathing activities are considered a direct source of fecal bacteria. Indeed, 100 g of feces allows the dissemination of 1014 cells of pathogens in the water column [36,37].
The Kribi agglomeration has experienced strong demographic growth in recent decades. It has a flat terrain with some geomorphic depressions, and only 15% of households have modern latrines. For the most part, household waste and wastewater are washed directly to the river banks after rainy episodes [15]. Regarding the hotels built a few meters from the beaches, the majority entrust the emptying of their septic tanks to private emptying companies from Douala. This waste is taken to the Wouri estuary wastewater dump in Douala, although it is not impossible that some of these trucks are emptied into the rivers (Nyong, Kienké and Lokoundje) that cross the Kribi–Douala road [38]. Other hotels channel their sewage directly to the shoreline with impunity.
Contamination from animals mainly comes from agro-pastoral activities in the city of Kribi and its surroundings, such as the leaching of grazed surfaces and the movement of livestock, which, during rainy periods, drain the contamination present in the soil to the waterways that flow into the sea (Nyong, Kienké and Lokoundje). Rainfall is one of the main environmental factors that favors the distribution and the increase in the concentration of protozoan parasites in the waters of Kribi beaches [16,39]. Indeed, it can impact the contribution of fecal contaminants in two main ways. Storm water runoff leaches mineral and organic matter from soils into the watershed [40,41]. Statistically significant differences were observed when comparing parasite abundances according to the main seasons of the year. An increase in the concentration of enteric protozoa was systematically observed at all sites surveyed (Mpalla, Ngoyè and Mboamanga) during the rainy seasons. Then, during heavy rainfall events, some households in the city of Kribi empty their septic tanks, which run directly to the beaches. As in other countries around the world, ballast water is also a potential source of enteric protozoa in Cameroonian coastal waters [29,42,43].
Finally, abiotic factors considerably influence the abundance of fecal contaminants in the waters of Kribi beaches. Indeed, depending on the nature (protozoa, bacteria, viruses or chemical molecules), origin (human or non-human) and sources of fecal contaminants, several environmental factors can influence their dynamics by favoring, or not, their development and accumulation in the environment. Temperature, for example, allows us to define the water masses that influence the variability of seasonal cycles. The growth and seasonal dynamics of microorganisms are also controlled by temperature fluctuations. Rainfall is one of the main environmental factors favoring the increase of enteric protozoa in the waters of Kribi beaches. It can impact the input of fecal contaminants through storm water runoff and leaching from soils in the watershed.
Swimming in beach waters can lead to more or less intense contact with pathogenic germs that may be present in the water in greater or lesser quantities, depending on the vulnerability of the sites [8,44]. The pathologies associated with these germs concern the ENT sphere, the digestive system, the eyes and the skin. The risk incurred by the bather depends on several factors: the level of contamination of the water, the health status of the bather, the modalities of swimming [17,45]. Numerous epidemiological studies have focused on estimating the risks of contracting different pathologies due to bathing in general or by characterizing exposure more precisely by taking into account water quality. The World Health Organization has initiated work to establish recommendations for microbiological criteria and reference levels for assessing recreational water quality [26]. These data obtained in a temperate context are not always applicable in tropical regions where hygiene and sanitation conditions are insufficient.
5. Conclusions
The major objective of this study was the identification and quantification of resistant forms of enteric protozoa contained in the waters of Kribi beaches in order to assess the associated health risks. Oocysts and cysts of Coccidia (Cryptosporidium sp. and Cyclospora cayetanensis), Amoebae (Endolimax nana, Entamoeba histolytica and Entamoeba coli) and Flagellates (Giardia intestinalis) were identified at varying concentrations, depending on the sampling sites and seasons. It is important to note that water represents an important element in the sociocultural and economic life of coastal peoples. In Kribi, the beaches are used a great deal by the Batanga, Ngoumba and Mabéa communities for bathing, washing dishes, laundry, fishing, and even traditional ceremonies. The coastal and marine ecosystems’ pollution by micro-organisms (viruses, bacteria and parasites) contained in feces presents a constant concern in Cameroon’s coastal areas in general and on Kribi beaches in particular. In the absence of a real and effective waste collection and treatment plan, particularly for wastewater in the city of Kribi, this study clearly demonstrates that the Kribi beaches are permanently polluted by feces. This pollution is more important during low tides and the rainy season. Thus, the poor management of these aquatic ecosystems can make the water resource dangerous, exposing the population to health risks. The municipality of the city of Kribi should now take adequate measures to limit this pollution, which could have health and economic consequences. To better understand the public health problem related to this microbial pollution on Kribi beaches, we plan to conduct an epidemiological study in the city of Kribi in our future work. The data obtained would lead us to the establishment of a microbial quality (Enteric protozoa) grid of beach waters in the Cameroonian context in particular and in Sub-Saharan Africa in general.
Author Contributions
P.A.N., M.P.M., S.T., K.M. and R.S.M.P. conceptualized the manuscript and contributed to data acquisition and analysis. M.N. and T.S.-N. contributed critically to the drafts of the manuscript and gave the final approval for publication. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
We sincerely thank Djaïli Amadou Amal for the library graciously offered to the youth of the municipality of Douala 3rd. This library is a comfortable and friendly work space in the city of Douala.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
References
- Elliott, M.; Day, J.W.; Ramachandran, R.; Wolanski, E. A Synthesis: What Is the Future for Coasts, Estuaries, Deltas and Other Transitional Habitats in 2050 and Beyond? In Coasts and Estuaries; Wolanski, E., Day, J.W., Elliott, M., Ramachandran, R., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 1–28. [Google Scholar]
- Lemos, V.M.; Lanari, M.; Copertino, M.; Secchi, E.R.; de Abreu, P.C.O.V.; Muelbert, J.H.; Garcia, A.M.; Dumont, F.C.; Muxagata, E.; Vieira, J.P.; et al. Patos Lagoon estuary and adjacent marine coastal biodiversity long-term data. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2022, 14, 1015–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed Marafa, L. Integrating Sustainable Tourism Development in Coastal and Marine Zone Environment. Étudescaribéennes 2008, 9–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Wang, M.; Su, S.; Kang, M. Explicit quantification of coastal cultural ecosystem services: A novel approach based on the content and sentimental analysis of social media. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 137, 108756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phelan, A.; Ruhanen, L.; Mair, J. Ecosystem services approach for community-based ecotourism: Towards an equitable and sustainable blue economy. J. Sustain. Tour. 2020, 28, 1665–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nana, P.A.; Ebonji Seth, R.; Ndjuissi Tamko, N.A.; Onambélé Ossomba, V.R.; Bricheux, G.; Metsopkeng, C.S.; Nola, M. Sime-Ngando, T. Tidal effect on the dispersion of fecal pollution indicator bacteria and associated health risks along the Kribi beaches (Southern Atlantic coast, Cameroon). Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2023, 60, 102831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sala-Comorera, L.; Reynolds, L.J.; Martin, N.A.; Pascual-Benito, M.; Stephens, J.H.; Nolan, T.M.; Gitto, A.; O’Hare, G.M.P.; O’Sullivan, J.J.; García-Aljaro, C.; et al. crAssphage as a human molecular marker to evaluate temporal and spatial variability in faecal contamination of urban marine bathing waters. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 789, 147828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wade, T.J.; Arnold, B.F.; Schiff, K.; Colford, J.M., Jr.; Weisberg, S.B.; Griffith, J.F.; Dufour, A.P. Health risks to children from exposure to fecally contaminated recreational water. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0266749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavridou, A.; Pappa, O.; Papatzitze, O.; Dioli, C.; Kefala, A.M.; Drossos, P.; Beloukas, A. Exotic Tourist Destinations and Transmission of Infections by Swimming Pools and Hot Springs-A Literature Review. Int. J. Env. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 2730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magana-Arachchi, D.N.; Wanigatunge, R.P. Ubiquitous waterborne pathogens. Waterborne Pathog. 2020, 15–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, J.; Gallampois, C.M.J.; Haglund, P.; Timonen, S.; Rowe, O. Bacterial communities as indicators of environmental pollution by POPs in marine sediments. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 268, 115690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, H.; Lovell, C.R. Microbial surface colonization and biofilm development in marine environments. Microbiol. Mol. Bio. Rev. 2016, 80, 91–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basili, M.; Campanelli, A.; Frapiccini, E.; Marco Lunaa, G.; Queroa, G.M. Occurrence and distribution of microbial pollutants in coastal areas of the Adriatic Sea influenced by river discharge. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 285, 117672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nimnoi, P.; Pongsilp, N. Marine bacterial communities in the upper gulf of Thailand assessed by Illumina next-generation sequencing platform. BMC Microbiol. 2020, 20, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assako Assako, R.J.; Tonmeu Djilo, C.A.; Bley, D. Risques sanitaires et gestion des eaux usées et des déchets à Kribi (Cameroun). In Sociétés, Environnements, Santé; Vernazza-Licht, N., Gruénais, M., Bley, D., Eds.; IRD Éditions: Marseille, France, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manini, E.; Baldrighi, E.; Ricci, F.; Grilli, F.; Giovannelli, D.; Intoccia, M.; Casabianca, S.; Capellacci, S.; Marinchel, N.; Penna, P.; et al. Assessment of Spatio-Temporal Variability of Faecal Pollution along Coastal Waters during and after Rainfall Events. Water 2022, 14, 502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, B.F.; Wade, T.J.; Benjamin-Chung, J.; Schiff, K.C.; Griffith, J.F.; Dufour, A.P.; Weisberg, S.B.; Colford, J.M., Jr. Acute Gastroenteritis and Recreational Water: Highest Burden Among Young US Children. Am. J. Public Health 2016, 106, 1690–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olivry, J.C. Fleuves et Rivières du Cameroun; Coll. Monog. Hydro.9 ORSTOM: Paris, France, 1986; 733p. [Google Scholar]
- Dzana, J.G.; Ndam, J.R.N.; Tchawa, P. The Sanaga discharge atthe Edea Catchment outlet (Cameroon): An example of hydrologic responses of a tropical rain-fed river system to changes inprecipitation and groundwater inputs and to flow regulation. River Res. Appl. 2011, 27, 754–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mama, A.C.; Ghepdeu, G.F.Y.; Ndam, J.R.E.N.; Bonga, M.D.; Onana, F.M.; Onguene, R. Assessment of Water Quality in the Lower Nyong Estuary (Cameroon, Atlantic Coast) from Environmental Variables and Phytoplankton Communities Composition. Afr. J. Environ. Sci. Techn. 2018, 12, 198–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodier, J.; Legube, B.; Merlet, N. The Water Analysis, 9th ed.; Dunod: Paris, France, 2009; 1579p. [Google Scholar]
- APHA (American Public Health Association). Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 22nd ed.; APHA (American Public Health Association): Washington, DC, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- WHO (World Health Organisation). Plates for the Diagnosis of Intestinal Parasites; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 1994; 29p.
- Thivierge, K. Identification Morphologique des Parasites Intestinaux; Cahier de Stage; Institut National de Santé: Québec, QC, Canada, 2014; 58p. [Google Scholar]
- Ajeagah, G.A.; Njine, T.; Bilong Bilong, C.F.; Foto, S.M.; Wouafo, N.M.; Nola, M.; Di, G.G.D.; Huw, S. Seasonal distribution of enteric opportunistic cryptosporidium spp. Oocysts and Giardia spp. Cysts in a tropical water basin, Cameroon. Waters 2010, 2, 44–57. [Google Scholar]
- Soller, J.A.; Schoen, M.E.; Bartrand, T.; Ravenscroft, J.E.; Ashbolt, N.J. Estimated human health risks from exposure to recreational waters impacted by human and non-human sources of faecal contamination. Water Res. 2010, 44, 4674–4691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natnael, T. Health-related behaviors and associated factors among swimming pool users in Kombolcha Town, Northeastern Ethiopia. Front. Public Health 2022, 10, 985335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madani, M.; Seth, R.; Leon, L.F.; Valipour, R.; McCrimmon, C. Three dimensional modelling to assess contributions of major tributaries to fecal microbial pollution of Lake St. Clair and Sandpoint Beach. J. Great Lakes Res. 2020, 46, 159–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraus, R.; Baljak, V.; VukićLušić, D.; Kranjčević, L.; Cenov, A.; Glad, M.; Kauzlarić, V.; Lušić, D.; Grbčić, L.; Alvir, M.; et al. Impacts of Atmospheric and Anthropogenic Factors on Microbiological Pollution of the Recreational Coastal Beaches Neighboring Shipping Ports. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 8552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fotseu Kouam, A.L.; Ajeagah, G.A. Dissemination of the resistant forms of intestinal worms in the marshy areas of the city of Yaoundé (Cameroon): Importance of some abiotic factors of the medium. Appl. Wat. Sc. 2019, 9, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manezeu Tonleu, E.O.; Nana, P.A.; Onana, F.M.; Nyamsi Tchatcho, N.L.; Tchakonté, S.; Nola, M.; Sime-Ngando, T.; Ajeagah Aghaindum, G. Evaluation of the health risks linked to two swimming pools regularly frequented from the city of Yaoundé in Cameroon (Central Africa). Environ. Monit. Assess. 2021, 193, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong-Miao, Z.; Peng-Cheng, X.; Wei-Wei, D.; Xiaochang, C.W. Exposure parameters and health risk of Cryptosporidium and Giardia in the recreational water activities for urban residents in China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 1573–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braima, K.; Zahedi, A.; Egan, S.; Austen, J.; Xiao, L.; Feng, Y.; Witham, B.; Pingault, N.; Perera, S.; Oskam, C.; et al. Molecular analysis of cryptosporidiosis cases in Western Australia in 2019 and 2020 supports the occurrence of two swimming pool associated outbreaks and reveals the emergence of a rare C. hominis IbA12G3 subtype. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2021, 92, 104859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammed, R.L.; Echeverry, A.; Stinson, C.M.; Green, M.; Bonilla, T.D.; Hartz, A.; McCorquodale, D.S.; Rogerson, A.; Esiobu, N. Survival trends of Staphylococcus aureus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Clostridium perfringens in a sandy South Florida beach. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2012, 64, 1201–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soto-Varela, Z.E.; Rosado-Porto, D.; Bolívar-Anillo, H.J.; Pichón González, C.; Granados Pantoja, B.; Estrada Alvarado, D.; Anfuso, G. Preliminary Microbiological Coastal Water Quality Determination along the Department of Atlántico (Colombia): Relationships with Beach Characteristics. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiskerger, C.J.; Brandão, J.; Ahmed, W.; Aslan, A.; Avolio, L.; Badgley, B.D.; Boehm, A.B.; Edge, T.A.; Fleisher, J.M.; Heaney, C.D.; et al. Impacts of a changing earth on microbial dynamics and human health risks in the continuum between beach water and sand. Water Res. 2019, 162, 456–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO (World Health Organisation). Guidelines on Recreational Water Quality; Coastal and Fresh Waters: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021; Volume 1, pp. 105–117. [Google Scholar]
- Assako Assako, R.J. Problématique de l’estimation de la qualité de vie dans un front d’urbanisation en Afrique: Le cas du Bois des Singes à Douala (Cameroun). In Cadre de vie et Travail: Les Dimensions d’une Qualité de vie au Quotidien; Bley, D., Ed.; Éditions Edisud: Provence, France, 2005; pp. 65–85. [Google Scholar]
- Di Biase, V.; Hanssen, R.F. Environmental Strain on Beach Environments Retrieved and Monitored by Spaceborne Synthetic Aperture Radar. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yahya, M.; Blanch, A.R.; Meijer, W.G.; Antoniou, K.; Hmaied, F.; Ballesté, E. Comparison of the performance of different microbial source tracking markers among European and North African Regions. J. Environ. Qual. 2017, 46, 760–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edge, T.A.; Boyd, R.J.; Shum, P.; Thomas, J.L. Microbial source tracking to identify fecal sources contaminating the Toronto Harbour and Don River watershed in wet and dry weather. J. Great Lakes Res. 2021, 47, 366–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drake, L.A.; Doblin, M.A.; Dobbs, F.C. Potential microbial bioinvasions via ships’ ballast water, sediment, and biofilm. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2007, 55, 333–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabrini, M.; Cerino, F.; de Olazabal, A.; Di Poi, E.; Fabbro, C.; Fornasaro, D.; Goruppi, A.; Flander-Putrle, V.; Francé, J.; Gollasch, S.; et al. Potential transfer of aquatic organisms via ballast water with a particular focus on harmful and non-indigenous species: A survey from Adriatic ports. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 147, 16–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dufour, A.P.; Behymer, T.D.; Cantú, R.; Magnuson, M.; Wymer, L.J. Ingestion of swimming pool water by recreational swimmers. J. Water Health 2017, 15, 429–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wade, T.J.; Calderon, R.L.; Sams, E.; Beach, M.; Brenner, K.P.; Williams, A.H.; Dufour, A.P. Rapidly measured indicators of recreational water quality are predictive of swimming-associated gastrointestinal illness. Env. Health Perspect. 2006, 114, 24–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).