Effect of Soil Texture, Nanoparticle Size, and Incubation Period on the Dissolution of ZnO Nanoparticles
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Evaluate the effect of different textures (high clay and low clay) on the pore water solubility of ZnO NPs.
- Evaluate the role of the size of NPs on the soluble fraction of Zn.
- Evaluate the effect of the incubation period on the leached amount of Zn.
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Synthesis of ZnO NPs and Characterization
2.2.1. Small-Sized NPs
2.2.2. Large-Sized NPs
2.2.3. Crystal Size Calculation of NPs
2.3. Sampling and Characterization of Soil
2.4. Spiking of Soil with ZnO NPs
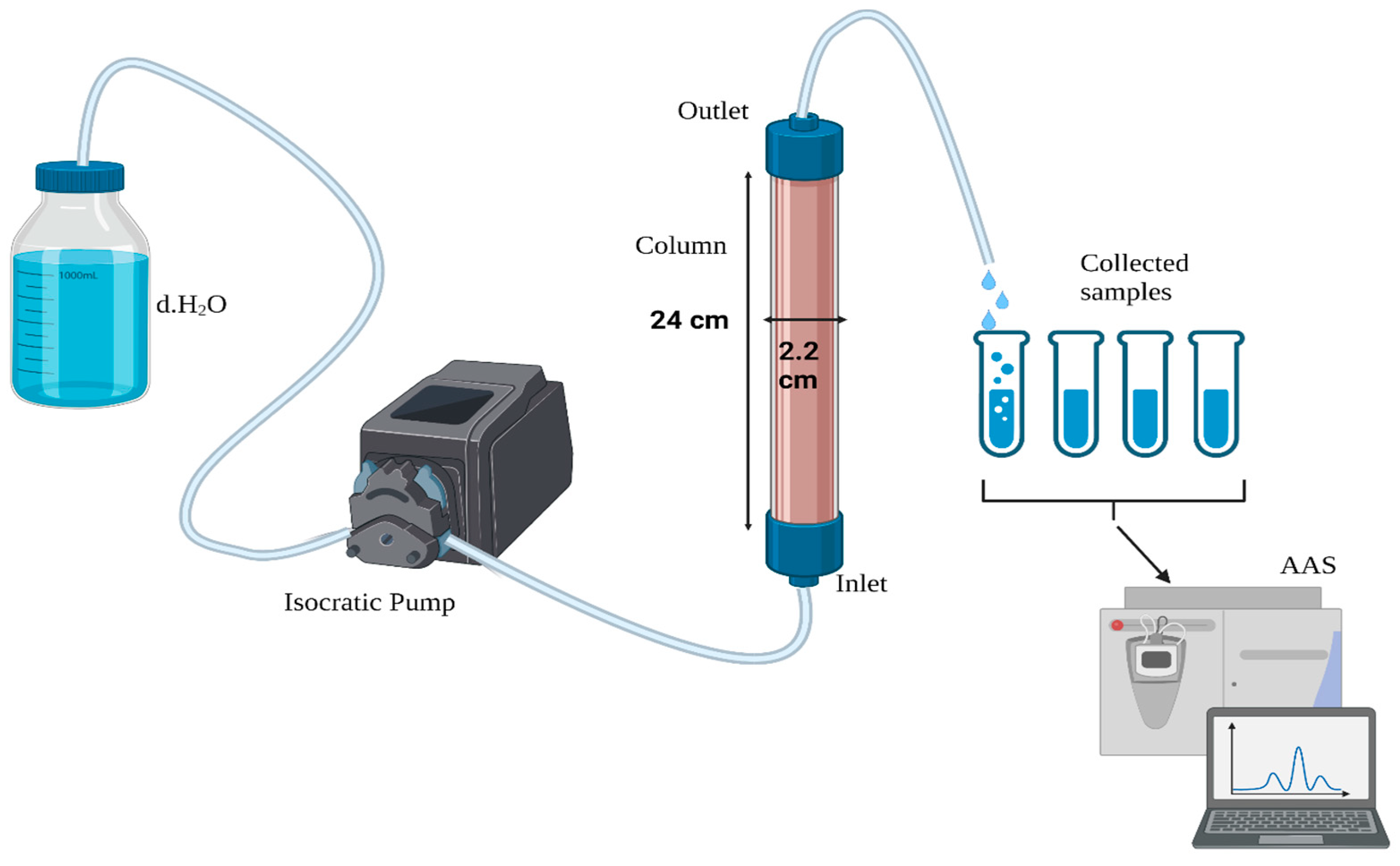
2.5. Leaching of Spiked Soil
2.6. Extraction of Zn Retained in Soil Matrix
2.7. Analysis of Leachate
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
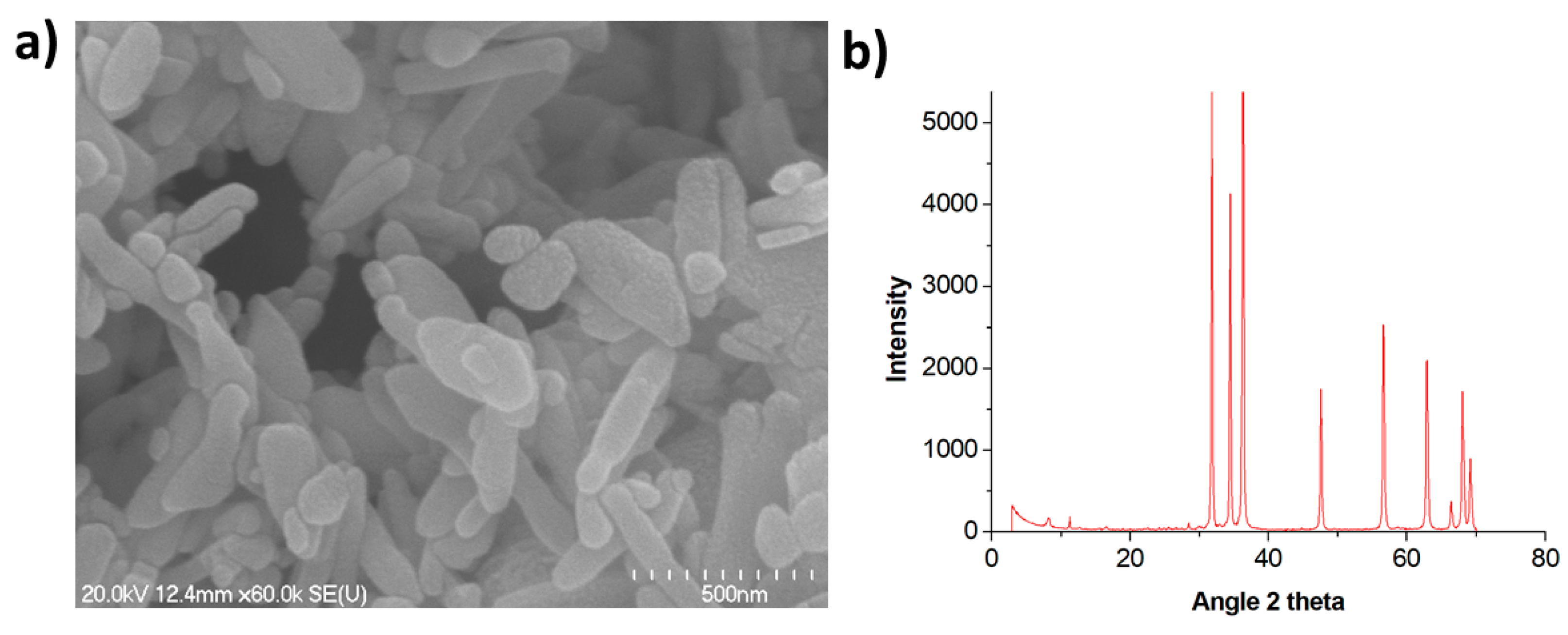
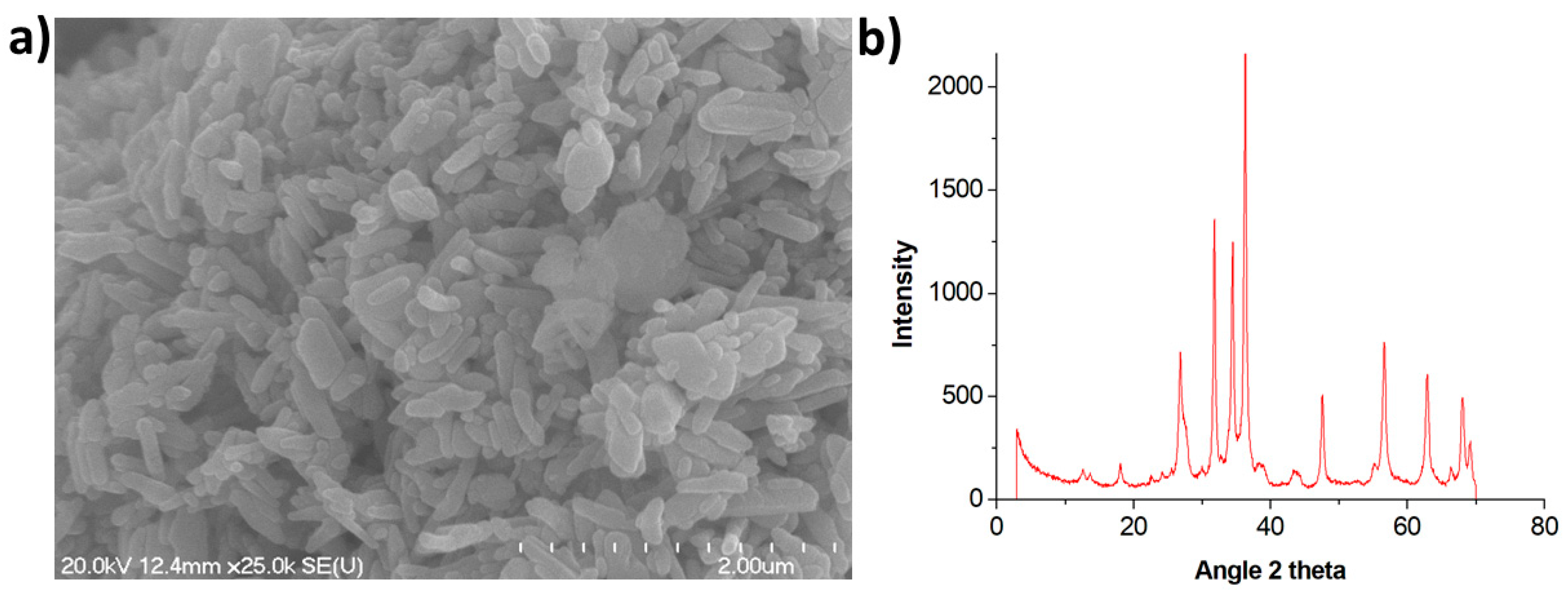
3.1. Characterization of ZnO NPs
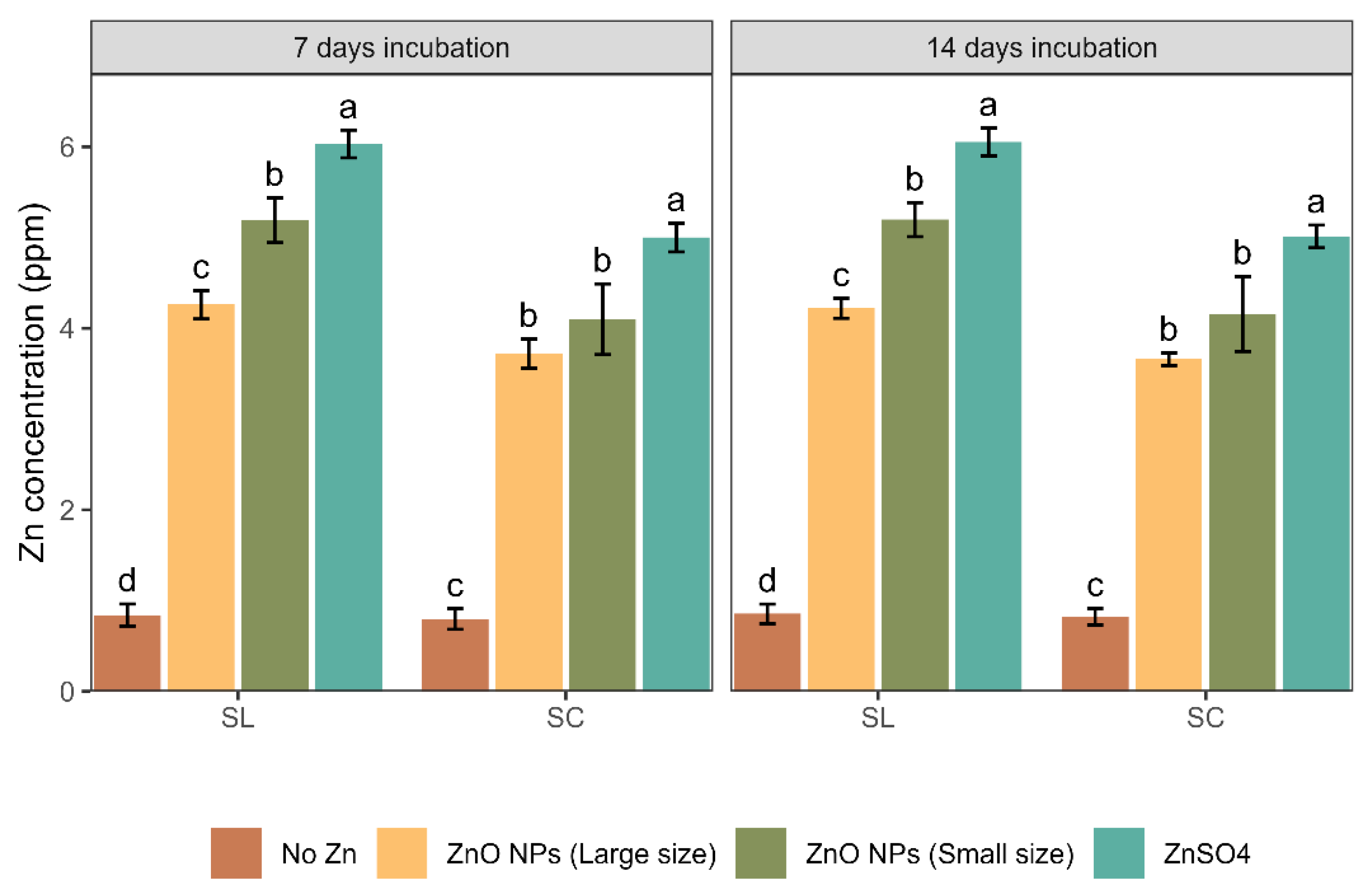
3.2. Zn Concentration in ZnO NP Spiked Soil Leachates
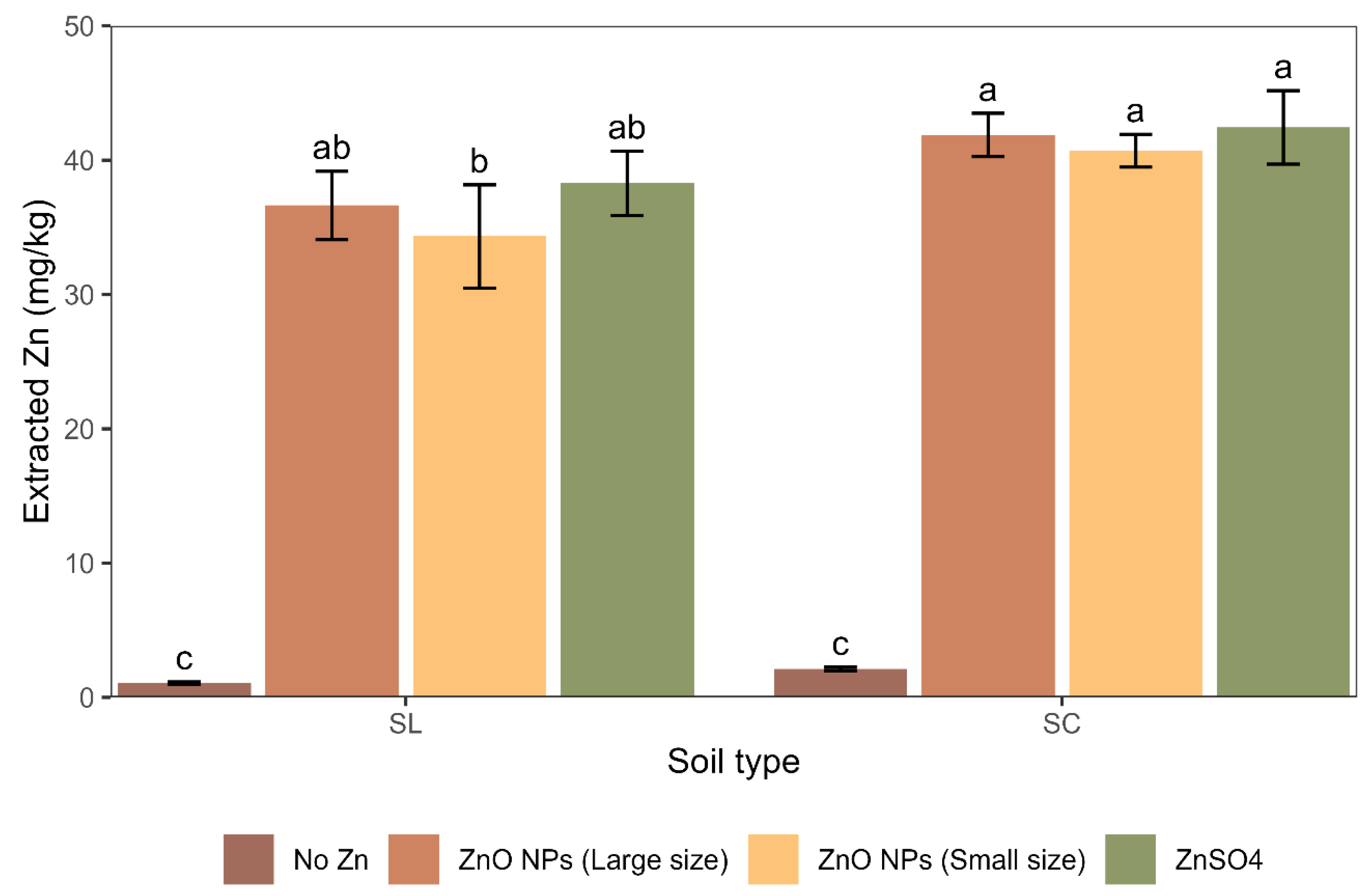
3.3. The Potential Availability of Zn Retained in the Soil Matrix
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Seleiman, M.F.; Almutairi, K.F.; Alotaibi, M.; Shami, A.; Alhammad, B.A.; Battaglia, M.L. Nano-fertilization as an emerging fertilization technique: Why can modern agriculture benefit from its use? Plants 2021, 10, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shemawar; Mahmood, A.; Hussain, S.; Mahmood, F.; Iqbal, M.; Shahid, M.; Ibrahim, M.; Ali, M.A.; Shahzad, T. Toxicity of biogenic zinc oxide nanoparticles to soil organic matter cycling and their interaction with rice-straw derived biochar. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 8429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheteiwy, M.S.; Shaghaleh, H.; Hamoud, Y.A.; Holford, P.; Shao, H.; Qi, W.; Hashmi, M.Z.; Wu, T. Zinc oxide nanoparticles: Potential effects on soil properties, crop production, food processing, and food quality. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 36942–36966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gruère, G.; Narrod, C.; Abbott, L. Agricultural, Food, and Water Nanotechnologies for the Poor Opportunities, Constraints, and Role of the Consultative Group on International Agricultural Research. Communications February 2011. [Online]. Available online: http://www.ifpri.org/sites/default/files/publications/ifpridp01064.pdf (accessed on 12 December 2022).
- Wan, B.; Hu, Z.; Yan, Y.; Liu, F.; Tan, W.; Feng, X. Quantitative investigation of ZnO nanoparticle dissolution in the presence of δ-MnO2. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 14751–14762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zabrieski, Z.; Morrell, E.; Hortin, J.; Dimkpa, C.; McLean, J.; Britt, D.; Anderson, A. Pesticidal activity of metal oxide nanoparticles on plant pathogenic isolates of Pythium. Ecotoxicology 2015, 24, 1305–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umar, W.; Hameed, M.K.; Aziz, T.; Maqsood, M.A.; Bilal, H.M.; Rasheed, N. Synthesis, characterization and application of ZnO nanoparticles for improved growth and Zn biofortification in maize. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2020, 67, 1164–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayub, M.A.; Ahmad, Z.; Umar, W.; Farooqi, Z.u.R.; Waris, A.A.; Fatima, H.; Nadeem, M.; Iftikhar, I. Accumulation, Partitioning, and Bioavailability of Micronutrients in Plants and Their Crosstalk with Phytohormones. In Plant Growth Regulators: Signalling under Stress Conditions; Aftab, T., Hakeem, K.R., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 39–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayub, M.A.; Zia ur Rehman, M.; Umar, W.; Adnan, M.; Farooqi, Z.U.R.; Naveed, M.; Aslam, M.Z.; Ahmad, H.R. Chapter 15—Physiological mechanisms and adaptation strategies of plants under heavy metal micronutrient deficiency/toxicity conditions. In Frontiers in Plant-Soil Interaction; Aftab, T., Hakeem, K.R., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2021; pp. 413–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Recena, R.; García-López, A.M.; Delgado, A. Zinc Uptake by Plants as Affected by Fertilization with Zn Sulfate, Phosphorus Availability, and Soil Properties. Agronomy 2021, 11, 390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemček, L.; Šebesta, M.; Urík, M.; Bujdoš, M.; Dobročka, E.; Vávra, I. Impact of bulk zno, zno nanoparticles and dissolved zn on early growth stages of barley—A pot experiment. Plants 2020, 9, 1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.; Cui, P.; Du, H.; Alves, M.E.; Liu, C.; Zhou, D.; Wang, Y. Dissolution and Transformation of ZnO Nano- and Microparticles in Soil Mineral Suspensions. ACS Earth Space Chem. 2019, 3, 495–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Wang, C.; Hou, J.; Wang, P.; Miao, L.; Lv, B.; Yang, Y.; You, G.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, M.; et al. Aggregation, sedimentation, and dissolution of CuO and ZnO nanoparticles in five waters. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 31240–31249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Hernández, H.; Fernández-Luqueño, F.; Huerta-Lwanga, E.; Mendoza-Vega, J.; Álvarez-Solís José, D. Effect of engineered nanoparticles on soil biota: Do they improve the soil quality and crop production or jeopardize them? Land Degrad. Dev. 2020, 31, 2213–2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sávoly, Z.; Hrács, K.; Pemmer, B.; Streli, C.; Záray, G.; Nagy, P.I. Uptake and toxicity of nano-ZnO in the plant-feeding nematode, Xiphinema vuittenezi: The role of dissolved zinc and nanoparticle-specific effects. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 9669–9678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, G.M.; Amin, M.; Shahid, M.; Ahmad, I.; Khalid, S.; Abbas, G.; Imran, M.; Naeem, M.A.; Shahid, N. Toxicity of ZnO and Fe2O3 nano-agro-chemicals to soil microbial activities, nitrogen utilization, and associated human health risks. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2022, 34, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Menzies, N.W.; Lombi, E.; McKenna, B.A.; Johannessen, B.; Glover, C.J.; Kappen, P.; Kopittke, P.M. Fate of ZnO Nanoparticles in Soils and Cowpea (Vigna unguiculata). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 13822–13830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimkpa, C.O. Soil properties influence the response of terrestrial plants to metallic nanoparticles exposure. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sci. Health 2018, 6, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradl, H.B. Adsorption of heavy metal ions on soils and soils constituents. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2004, 277, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elhaj Baddar, Z.; Matocha, C.J.; Unrine, J.M. Surface coating effects on the sorption and dissolution of ZnO nanoparticles in soil. Environ. Sci. Nano 2019, 6, 2495–2507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domingos, R.F.; Rafiei, Z.; Monteiro, C.E.; Khan, M.A.K.; Wilkinson, K.J. Agglomeration and dissolution of zinc oxide nanoparticles: Role of pH, ionic strength and fulvic acid. Environ. Chem. 2013, 10, 306–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milani, N.; McLaughlin, M.J.; Stacey, S.P.; Kirby, J.K.; Hettiarachchi, G.M.; Beak, D.G.; Cornelis, G. Dissolution kinetics of macronutrient fertilizers coated with manufactured zinc oxide nanoparticles. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 3991–3998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Cao, J.; Fei, X.; Duan, N. High-temperature annealing of ZnO nanoparticles increases the dissolution magnitude and rate in water by altering O vacancy distribution. Environ. Int. 2019, 130, 104930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, N.C.; Farto, M.; Mourinha, C.; Tavares, D.; Duarte, A.C.; Trindade, T.; Pereira, E.; Römkens, P.F.A.M.; Alvarenga, P.; Rodrigues, S.M. Dissolution of ag nanoparticles in agricultural soils and effects on soil exoenzyme activities. Environments 2021, 8, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handy, R.D.; Von Der Kammer, F.; Lead, J.R.; Hassellöv, M.; Owen, R.; Crane, M. The ecotoxicology and chemistry of manufactured nanoparticles. Ecotoxicology 2008, 17, 287–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tso, C.P.; Zhung, C.M.; Shih, Y.H.; Tseng, Y.M.; Wu, S.C.; Doong, R.A. Stability of metal oxide nanoparticles in aqueous solutions. Water Sci. Technol. 2010, 61, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaba, E.Y.; Jacob, J.O.; Tijani, J.O.; Suleiman, M.A.T. A critical review of synthesis parameters affecting the properties of zinc oxide nanoparticle and its application in wastewater treatment. Appl. Water Sci. 2021, 11, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolkova, I.S.; Kazantseva, N.E.; Babayan, V.; Vilcakova, J.; Pizurova, N.; Saha, P. The Role of Diffusion-Controlled Growth in the Formation of Uniform Iron Oxide Nanoparticles with a Link to Magnetic Hyperthermia. Cryst. Growth Des. 2017, 17, 2323–2332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youn, S.-M.; Choi, S.-J. Food Additive Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles: Dissolution, Interaction, Fate, Cytotoxicity, and Oral Toxicity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 6074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudunkotuwa, I.A.; Rupasinghe, T.; Wu, C.M.; Grassian, V.H. Dissolution of ZnO nanoparticles at circumneutral pH: A study of size effects in the presence and absence of citric acid. Langmuir 2012, 28, 396–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, S.W.; Mudunkotuwa, I.A.; Rupasinghe, T.; Grassian, V.H. Aggregation and dissolution of 4 nm ZnO nanoparticles in aqueous environments: Influence of pH, ionic strength, size, and adsorption of humic acid. Langmuir 2011, 27, 6059–6068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, S.; Ribeiro, F.; Wojnarowicz, J.; Lojkowski, W.; Jurkschat, K.; Crossley, A.; Soares, A.M.V.M.; Loureiro, S. Zinc oxide nanoparticles toxicity to Daphnia magna: Size-dependent effects and dissolution. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2014, 33, 190–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hotze, E.M.; Phenrat, T.; Lowry, G.V. Nanoparticle Aggregation: Challenges to Understanding Transport and Reactivity in the Environment. J. Environ. Qual. 2010, 39, 1909–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Qiu, W.; Gao, W. Potential dissolution and photo-dissolution of ZnO thin films. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 178, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legg, B.A.; Zhu, M.; Comolli, L.R.; Gilbert, B.; Banfield, J.F. Impacts of ionic strength on three-dimensional nanoparticle aggregate structure and consequences for environmental transport and deposition. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 13703–13710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, J.; Hansen, T.; Mclean, J.E.; Mcmanus, P.; Das, S.; Britt, D.W.; Anderson, A.J.; Dimkpa, C.O. Salts affect the interaction of ZnO or CuO nanoparticles with wheat. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2015, 34, 2116–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jośko, I.; Oleszczuk, P. Influence of soil type and environmental conditions on ZnO, TiO2 and Ni nanoparticles phytotoxicity. Chemosphere 2013, 92, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettibone, J.M.; Cwiertny, D.M.; Scherer, M.; Grassian, V.H. Adsorption of organic acids on TiO2 nanoparticles: Effects of pH, nanoparticle size, and nanoparticle aggregation. Langmuir 2008, 24, 6659–6667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghaddasi, S.; Fotovat, A.; Khoshgoftarmanesh, A.H.; Karimzadeh, F.; Khazaei, H.R.; Khorassani, R. Bioavailability of coated and uncoated ZnO nanoparticles to cucumber in soil with or without organic matter. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2017, 144, 543–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheoran, V.; Sheoran, A.S.; Poonia, P. Factors Affecting Phytoextraction: A Review. Pedosphere 2016, 26, 148–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Freire, A.; Lofts, S.; Martín Peinado, F.J.; van Gestel, C.A.M. Effects of aging and soil properties on zinc oxide nanoparticle availability and its ecotoxicological effects to the earthworm Eisenia andrei. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2017, 36, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.; Lin, Q.; Wang, Y.; Luo, H.; Huang, Z.; Fu, H.; Chen, H.; Xiao, R. The removal of Cu, Ni, and Zn in industrial soil by washing with EDTA-organic acids. Arab. J. Chem. 2020, 13, 5160–5170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaboudi, K.A.; Ahmed, B.; Brodie, G. Soil washing technology for removing heavy metals from a contaminated soil: A case study. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2020, 29, 1029–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Elements | Units | SL | SC |
|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 7.10 | 8.80 | |
| EC | dS/m | 0.0634 | 0.095 |
| CEC | cmol+/kg | 14.6 | 40.1 |
| Exch. Ca | cmol+/kg | 26.75 | |
| CaCO3 | % | 7.76 | |
| OM | % | 0.61 | 4.90 |
| Sand | % | 65 | 3 |
| Silt | % | 25 | 45.05 |
| Clay | % | 10 | 51.95 |
| Textural class | Sandy loam | Silty Clay | |
| P | mg kg−1 | 170 | 23.75 |
| Zn | mg kg−1 | 1.26 | 2.31 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Umar, W.; Czinkota, I.; Gulyás, M.; Ayub, M.A.; Sebők, A.; Nadeem, M.Y.; Zulfiqar, M.A. Effect of Soil Texture, Nanoparticle Size, and Incubation Period on the Dissolution of ZnO Nanoparticles. Pollutants 2023, 3, 220-231. https://doi.org/10.3390/pollutants3020016
Umar W, Czinkota I, Gulyás M, Ayub MA, Sebők A, Nadeem MY, Zulfiqar MA. Effect of Soil Texture, Nanoparticle Size, and Incubation Period on the Dissolution of ZnO Nanoparticles. Pollutants. 2023; 3(2):220-231. https://doi.org/10.3390/pollutants3020016
Chicago/Turabian StyleUmar, Wajid, Imre Czinkota, Miklós Gulyás, Muhammad Ashar Ayub, András Sebők, Muhammad Yousaf Nadeem, and Muhammad Arslan Zulfiqar. 2023. "Effect of Soil Texture, Nanoparticle Size, and Incubation Period on the Dissolution of ZnO Nanoparticles" Pollutants 3, no. 2: 220-231. https://doi.org/10.3390/pollutants3020016
APA StyleUmar, W., Czinkota, I., Gulyás, M., Ayub, M. A., Sebők, A., Nadeem, M. Y., & Zulfiqar, M. A. (2023). Effect of Soil Texture, Nanoparticle Size, and Incubation Period on the Dissolution of ZnO Nanoparticles. Pollutants, 3(2), 220-231. https://doi.org/10.3390/pollutants3020016







