Unravelling the Concentrations of Five Rare Earth Elements in Two Vineyard Red Soils
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site and Soil Sampling
2.2. Analytical Procedures
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. General Parameters Data
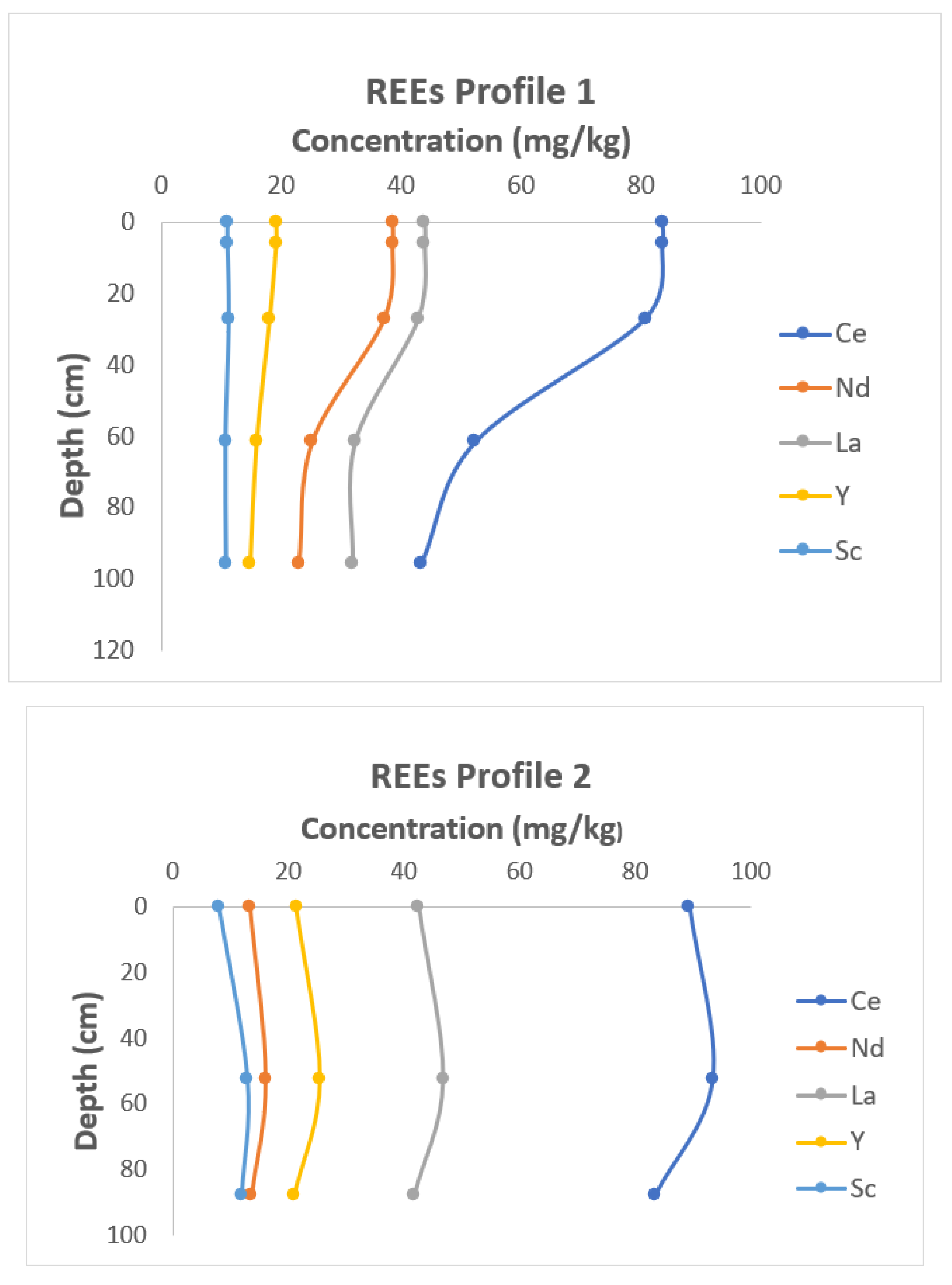
3.2. Contents and Distribution of the Five REEs Analysed in Depth in the Two Soil Profiles
3.3. Environmental Evaluation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rodríguez-Eugenio, N.; McLaughlin, M.; Pennock, D. Soil Pollution: A hidden reality; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2018; p. 142. [Google Scholar]
- Yaalon, D.H.; Yaron, B. Framework for man-made soil changes-an outline of metapedogenesis. Soil Sci. 1966, 102, 272–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brookins, D.G.; Lipin, B.R.; Mckay, G.A. Geochemistry and mineralogy of rare earth elements. Rev. Mineral. 1989, 21, 201–225. [Google Scholar]
- Laveuf, C.; Cornu, S.; Juillot, F. Rare earth elements as tracers of pedogenetic processes. Compt. Rendus Geosci. 2008, 340, 523–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aide, M.T.; Aide, C. Rare earth elements: Their importance in understanding soil genesis. ISRN Soil Sci. 2012, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyler, G. Rare earth elements in soil and plant systems—A review. Plant Soil 2004, 267, 191–206. [Google Scholar]
- Bundschuh, J.; Litter, M.I.; Parvez, F.; Román-Ross, G.; Nicolli, H.B.; Jean, J.-S.; Liu, C.-W.; López, D.; Armienta, M.A.; Guilherme, L.R.G.; et al. One century of arsenic exposure in Latin America: A review of history and occurrence from 14 countries. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 429, 2–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Environment Agency (EEA). Progress in Management of Contaminated Sites. 2014. Available online: https://www.eea.europa.eu/data-and-maps/indicators/progress-in-management-of-contaminated-sites/progress-in-management-ofcontaminated-1 (accessed on 12 November 2022).
- SSR. Soil Contamination in West Africa|Environmental Remediation|Pollution. 2010. Available online: https://www.scribd.com/doc/71599035/SoilContamination-in-West-Africa (accessed on 12 November 2022).
- Wu, T.; Bi, X.; Li, Z.; Sun, G.; Feng, X.; Shang, L.; Zhang, H.; He, T.; Chen, J. Contaminations, sources, and health risks of trace metal (Loid)s in street dust of a small city impacted by artisanal Zn smelting activities. Int. J. Environ. Public Health 2017, 14, 961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Yamasaki, S.; Kimura, K. Rare earth element content in various waste ashes and the potential risk to Japanese soils. Environ. Int. 2001, 27, 393–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arunrat, N.; Sereenonchai, S.; Chaowiwat, W.; Wang, C.; Hatan, R. Carbon, Nitrogen and Water Footprints of Organic Rice and Conventional Rice Production over 4 Years of Cultivation: A Case Study in the Lower North of Thailand. Agronomy 2022, 12, 380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omeje, K.O.; Ezema, B.O.; Okonkwo, F.; Onyishi, N.C.; Ozioko, J.; Rasaq, W.A.; Sardo, G.; Okpala, C.O.R. Quantification of Heavy Metals and Pesticide Residues in Widely Consumed Nigerian Food Crops Using Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy (AAS) and Gas Chromatography (GC). Toxins 2021, 13, 870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amorós, J.A.; Bravo, S.; García-Navarro, F.J.; Pérez-de-los-Reyes, C.; Chacón, J.L.; Martínez, J.; Jiménez-Ballesta, R. Atlas de Suelos de Castilla-La Mancha, 1st ed.; Globalcaja and Universidad de Castilla-La Mancha: Ciudad Real, Spain, 2015; p. 318. [Google Scholar]
- IUSS Working Group WRB. World Reference Base for Soil Resources 2015. In International Soil Classification System for Naming Soils and Creating Legends for Soil Maps; World Soil Resources Reports No. 106; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2015; Available online: http://www.fao.org/3/i3794en/I3794en.pdf (accessed on 12 November 2022).
- Soil Survey Staff. Key to Soil Taxonomy, 12th ed.; USDA-Natural Resources, Conservation Service: Washington, DC, USA, 2014; p. 379. [Google Scholar]
- Tepanosyan, G.; Norik, H.; Lilit, S. Revealing XRF data quality level, comparability with ICP-ES/ICP-MS soil PTE contents and similarities in PTE induced health risk. Environ. Geochem. Health 2022, 44, 1739–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravansari, R.; Wilson, S.C.; Tighe, M. Portable X-ray fluorescence for environmental assessment of soils: Not just a point and shoot method. Environ. Int. 2020, 134, 105250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peech, M.; Alexander, L.T.; Dean, L.A.; Reed, J.F. Methods of Soil Analysis for Soil Fertility Investigations, 1st ed.; United States Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 1947; p. 25. [Google Scholar]
- Gee, G.W.; Bauder, J.W. Methods of Soil Analysis. Part 1. Physical and Mineralogical Methods, 2nd ed.; ASA-SSSA: Madison, WI, USA, 1986; pp. 383–411. [Google Scholar]
- Nelson, D.W.; Sommers, L.E. Total Carbon, Organic Carbon and Organic Matter; ASA-SSSA: Madison, WI, USA, 1982; pp. 539–579. [Google Scholar]
- Loeppert, R.H.; Suarez, D.L. Carbonate. In Methods of Soil Analysis. Part 3. Chemical Methods; Sparks, D.L., Ed.; ASA and SSSA: Madison, WI, USA, 1996; pp. 437–474. [Google Scholar]
- Laveuf, C.; Cornu, S. A Review on the Potentiality of Rare Earth Elements to Trace pedogenetic processes. Geoderma 2009, 154, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Ohlander, B.; Land, M.; Ingri, J.; Widerlund, A. Mobility of rare earth elements during weathering of till in northern Sweden. Appl. Geochem. 1996, 11, 93–99. [Google Scholar]
- Alexander, J.D.; Beavers, A.H.; Johnson, P.R. Zirconium content of coarse silt in loess and till of Wisconsin age in northern Illinois. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. Proc. 1962, 26, 189–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, S.C.; Horn, M.E. Parent material uniformity and origin of silty soils in northwest Arkansas based on zirconium-titanium contents. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. Proc. 1968, 32, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García Navarro, F.J.; Amorós Ortiz-Villajos, J.A.; Sánchez Jiménez, C.; Jiménez Ballesta, R. Red Soil Geochemistry in a semmiarid mediterranen environment and its suitability for vineyards. Environ. Geochem. Health 2011, 33, 279–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alloway, B.J. Heavy Metals in Soils; Blackie Academic & Professional: Glasgow, UK, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Pang, X.; Li, D.; Peng, A. Application of rare-earth elements in the agriculture of China and its environmental behavior in soil. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Int. Res. 2002, 9, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, D.L. Trivalent metal (Cr, Y, Rh, La, Pr, Gd) sorption in two acid soils and its consequences for bioremediation. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 1997, 48, 697–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piasecki, W.; Sverjensky, D.A. Speciation of adsorbed yttrium and rare earth elements on oxide surfaces. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2008, 72, 3964–3979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caspari, T.; Bäumler, R.; Norbu, C.; Tshering, K.; Baillie, I. Geochemical investigation of soils developed in different lithologies in Bhutan, Eastern Himalayas. Geoderma 2006, 136, 436–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aide, M.T.; Smith, C.C. Soil genesis on peralkaline felsics in Big Bend National Park, Texas. Soil Sci. 2001, 166, 209–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volokh, A.A.; Gorbunov, A.V.; Gundorina, S.F.; Revich, B.A.; Frontasyeva, M.V.; Pal, C.S. Phosphorus-fertilizer production as a source of rare-earth elements pollution of the environment. Sci. Total Environ. 1990, 95, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hu, Z.; Haneklaus, S.; Sparovek, G.; Schnug, E. Rare earth elements in soils. Commun Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2006, 37, 1381–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, P.J.; Carpenter, D.; Boutin, C.; Allison, J.E. Rare earth elements (REEs): Effects on germination and growth of selected crop and native plant species. Chemosphere 2014, 96, 57–66. [Google Scholar]
- Turra, C.; Fernandes, E.A.N.; Bacchi, M.A. Evaluation on rare earth elements of Brazilian agricultural supplies. J. Environ. Chem. Ecotoxicol. 2011, 3, 86–92. [Google Scholar]
- Ramos, S.J.; Dinali, G.S.; Oliveira, C.; Martins, G.C.; Moreira, C.G.; Siqueira, J.O.; Guilherme, L.R. Rare Earth Elements in the Soil Environment. Curr. Pollut. Rep. 2016, 2, 28–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, J.R.; Velbel, M.A. Chemical weathering indices applied to weathering profiles developed on heterogeneous felsic metamorphic parent rocks. Chem. Geol. 2003, 202, 397–416. [Google Scholar]
- Müller, G. Index of geo-accumulation in sediments of the Rhine River. GeoJournal 1969, 2, 108–118. [Google Scholar]
- Jiménez-Ballesta, R.; Conde-Bueno, P.; Martín-Rubí, J.A.; García-Giménez, R. Pedo-geochemical baseline content levels and soil quality reference values of trace elements in soils from the Mediterranean (Castilla la Mancha, Spain). Cent. Eur. J. Geosci. 2010, 2, 441–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, F.B.V.; Nascimento, C.W.A.; Alvarez, A.M.; Araújo, P.R.M. Inputs of rare earth elements in Brazilian agricultural soils via P-containing fertilizers and soil correctives. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 232, 90–96. [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira, M.D.S.; Fontes, M.P.F.; Bellato, C.R.; Marques Neto, J.D.O.; Lima, H.N.; Fendorf, S. Geochemical signatures and natural background values of rare earth elements in soils of Brazilian Amazon. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 277, 116743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
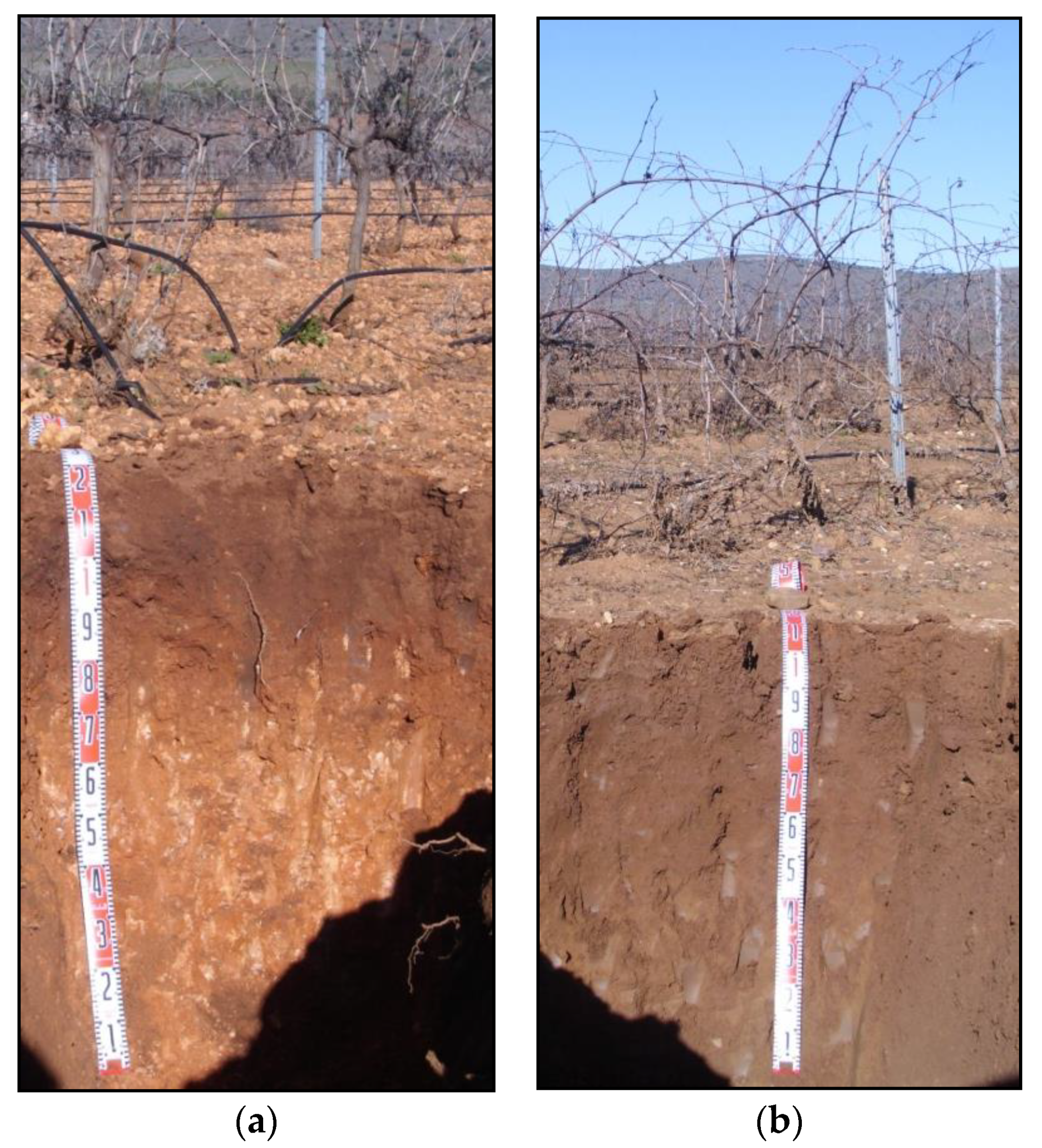


| Profile | Location (Coordinates) | Parent Material | Slope | Drainage | Morphology | Soil Type (FAO/Soil Taxonomy) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Moral de Calatrava 38°43′47.6″ (N) 03°35′06.4″ (W) | Quarcitic and calcareous sediments | Slightly inclined 4% | Moderately well-drained | Ap-Bt-Bt/Ck-Ck | Calcic Luvisol (Profondic, Rhodic)/ Calcic Rhodoxeralf |
| 2 | Moral de Calatrava 38°43′23.7″ (N) 03°34′50.3″ (W) | Fluvial sediments | Flat 1% | Imperfectly drained | Ap-Bt-C | Haplic Luvisol (Profondic, Novic)/ Typic Haploxeralf |
| Profile | Horizon | Depth (cm) | pH H2O (1:2.5) | pH KCl (1:2.5) | CaCO3 (%) | E.C. (dS/m) | O.M. (%) | Clay (%) | Ti/Zr |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Ap | 0–12 | 8.2 | 7.5 | 8.0 | 0.12 | 2.9 | 12.2 | 11.9 |
| Bt | 12–42 | 8.3 | 7.5 | 5.5 | 0.09 | 1.3 | 38.2 | 12.4 | |
| Bt/Ck | 42–81 | 8.6 | 7.9 | 30.7 | 0.15 | 0.2 | 31.4 | 13.2 | |
| Ck | >81 | 8.7 | 7.8 | 40.7 | 0.14 | 0.0 | 36.2 | 16.2 | |
| 2 | Ap | 0–31 | 8.3 | 7.7 | 0.8 | 0.08 | 1.9 | 14.2 | 14.5 |
| Bt | 31–4 | 8.2 | 7.4 | 3.6 | 0.06 | 1.3 | 32.2 | 12.7 | |
| C | >74 | 8.2 | 7.4 | 10.2 | 0.17 | 0.2 | 32.2 | 15.1 |
| Profile | Hor. | Ce | Nd | La | Y | Sc |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Ap | −0.10 | 0.16 | 0.22 | −0.56 | −1.63 |
| Bt | −0.15 | 0.10 | 0.19 | −0.65 | −1.61 | |
| Bt/Ck | −0.78 | −0.45 | −0.21 | −0.84 | −1.67 | |
| Ck | −1.05 | −0.58 | −1.34 | −0.94 | −1.66 | |
| 2 | Ap | −0.01 | −1.37 | 0.18 | −0.41 | −2.10 |
| Bt | 0.05 | −1.09 | 0.31 | −0.16 | −1.40 | |
| C | −0.11 | −1.34 | 0.15 | −0.43 | −1.52 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiménez-Ballesta, R.; García-Navarro, F.J.; Amorós, J.A.; Pérez-de-los-Reyes, C.; Bravo, S. Unravelling the Concentrations of Five Rare Earth Elements in Two Vineyard Red Soils. Pollutants 2023, 3, 114-122. https://doi.org/10.3390/pollutants3010010
Jiménez-Ballesta R, García-Navarro FJ, Amorós JA, Pérez-de-los-Reyes C, Bravo S. Unravelling the Concentrations of Five Rare Earth Elements in Two Vineyard Red Soils. Pollutants. 2023; 3(1):114-122. https://doi.org/10.3390/pollutants3010010
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiménez-Ballesta, Raimundo, Francisco J. García-Navarro, José A. Amorós, Caridad Pérez-de-los-Reyes, and Sandra Bravo. 2023. "Unravelling the Concentrations of Five Rare Earth Elements in Two Vineyard Red Soils" Pollutants 3, no. 1: 114-122. https://doi.org/10.3390/pollutants3010010
APA StyleJiménez-Ballesta, R., García-Navarro, F. J., Amorós, J. A., Pérez-de-los-Reyes, C., & Bravo, S. (2023). Unravelling the Concentrations of Five Rare Earth Elements in Two Vineyard Red Soils. Pollutants, 3(1), 114-122. https://doi.org/10.3390/pollutants3010010







