Experimental Investigation on the Mechanical Properties of Woven Glass–Polyester–Polypropylene Fiber-Reinforced Epoxy Hybrid Composites †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Fabrication of Hybrid Composite Specimen A
2.3. Fabrication of Hybrid Composite Specimen B
2.4. Fabrication of Hybrid Composite Specimen C
3. Experiment
3.1. Tensile Testing Method
3.2. Failure Mode of Tensile Tests
3.3. Shear Testing Method
3.4. Failure Mode of Shear Tests
3.5. Flexural Testing Method
4. Results
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- The discrepancies seen in the mechanical properties of the samples can be ascribed to variances in the fiber composition, orientation, matrix material, fabrication technique, and interfacial bonding between the materials.
- (2)
- Sample C is a potentially good option for structural applications that require a mix of these qualities because it typically demonstrates a balance between tensile strength, flexural strength, and stiffness.
- (3)
- Additional research on the fracture surfaces and microstructural characterization would shed light on the underlying mechanisms controlling the mechanical behavior of the hybrid composites.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Triki, E.; Zouari, B.; Dammak, F. Dependence of the interlaminar fracture toughness of E-Glass/Polyester woven fabric composites laminates on ply orientation. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2016, 159, 63–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodduru, K.; Kumar, S.; Kandpal, B.C.; Johri, N.; Arunprasath, K.; Singh, L.K. Effect of MXene reinforcement on bending behavior of glass fiber-epoxy based laminated composites. Mater. Today Proc. 2023, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demircan, G.; Kisa, M.; Ozen, M.; Acikgoz, A.; Işıker, Y.; Aytar, E. Nano-gelcoat application of glass fiber reinforced polymer composites for marine application: Structural, mechanical, and thermal analysis. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 194, 115412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramraji, K.; Rajkumar, K.; Subbiah, M.; Balachandar, K.; Kumar, P.S. Stacking layer effect on mechanical and vibration behaviour of woven glass intertwined with kenaf fiber polymeric composites. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 62, 1356–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmud, S.H.; Akram, M.W.; Ferdous, S.M.; Islam, D.; Fatema, K.; Chowdhury, M.S.; Das, A.; Ovi, S.M. Fabrication and mechanical performance investigation of jute/glass fiber hybridized polymer composites: Effect of stacking sequences. Next Mater. 2024, 5, 100236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suriani, M.J.; Radzi, F.S.; Ilyas, R.A.; Petrů, M.; Sapuan, S.M.; Ruzaidi, C.M. Flammability, tensile, and morphological properties of oil palm empty fruit bunches fiber/pet yarn-reinforced epoxy fire retardant hybrid polymer composites. Polymers 2021, 13, 1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radzi, A.M.; Zaki, S.A.; Hassan, M.Z.; Ilyas, R.A.; Jamaludin, K.R.; Daud, M.Y.; Aziz, S.A. Bamboo-fiber-reinforced thermoset and thermoplastic polymer composites: A review of properties, fabrication, and potential applications. Polymers 2022, 14, 1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muniandy, S.K.; Sapuan, S.M.; Ilyas, R.A.; Azmi, A. Sugar palm lignocellulosic fiber reinforced polymer composite: A review. J. Fibers Polym. Compos. 2022, 1, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suriani, M.J.; Sapuan, S.M.; Ruzaidi, C.M.; Nair, D.S.; Ilyas, R.A. Flammability, morphological and mechanical properties of sugar palm fiber/polyester yarn-reinforced epoxy hybrid biocomposites with magnesium hydroxide flame retardant filler. Text. Res. J. 2021, 91, 2600–2611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suriani, M.J.; Ilyas, R.A.; Zuhri, M.Y.; Khalina, A.; Sultan, M.T.; Sapuan, S.M.; Ruzaidi, C.M.; Wan, F.N.; Zulkifli, F.; Harussani, M.M.; et al. Critical review of natural fiber reinforced hybrid composites: Processing, properties, applications and cost. Polymers 2021, 13, 3514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haris, N.I.; Ilyas, R.A.; Hassan, M.Z.; Sapuan, S.M.; Afdzaluddin, A.; Jamaludin, K.R.; Zaki, S.A.; Ramlie, F. Dynamic mechanical properties and thermal properties of longitudinal basalt/woven glass fiber reinforced unsaturated polyester hybrid composites. Polymers 2021, 13, 3343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devendrappa, S.K.; Puttegowda, M.; Nagaraju, S.B. Enhancing wear resistance, mechanical properties of composite materials through sisal and glass fiber reinforcement with epoxy resin and graphite filler. J. Indian Chem. Soc. 2024, 101, 101349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dash, S.; Routara, B.C.; Satpathy, M.P. Fibre stacking sequence and mechanical characterization of polymer hybrid composites: An experimental study. Mater. Today Proc. 2023, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saba, N.; Jawaid, M.; Sultan, M.T. An overview of mechanical and physical testing of composite materials. In Mechanical and Physical Testing of Biocomposites, Fibre-Reinforced Composites and Hybrid Composites; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2019; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar]
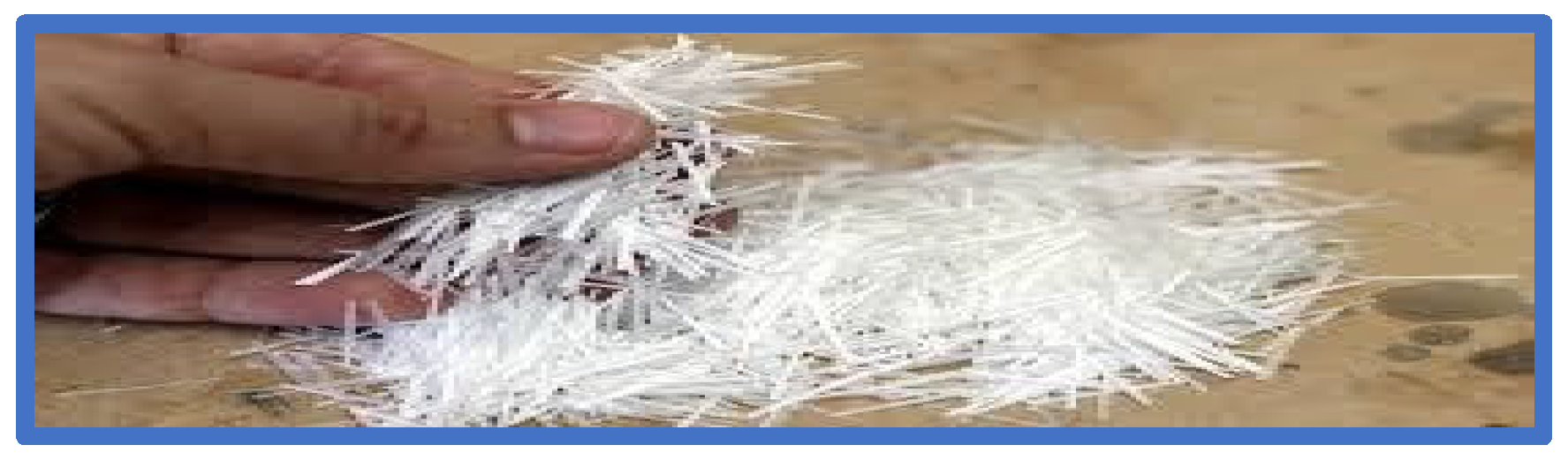
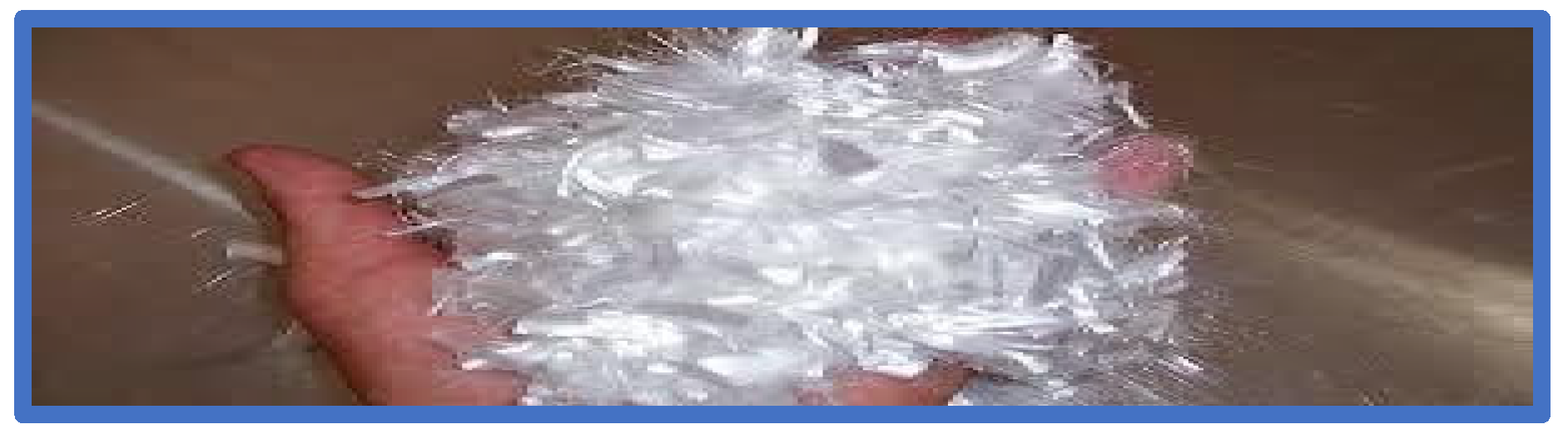
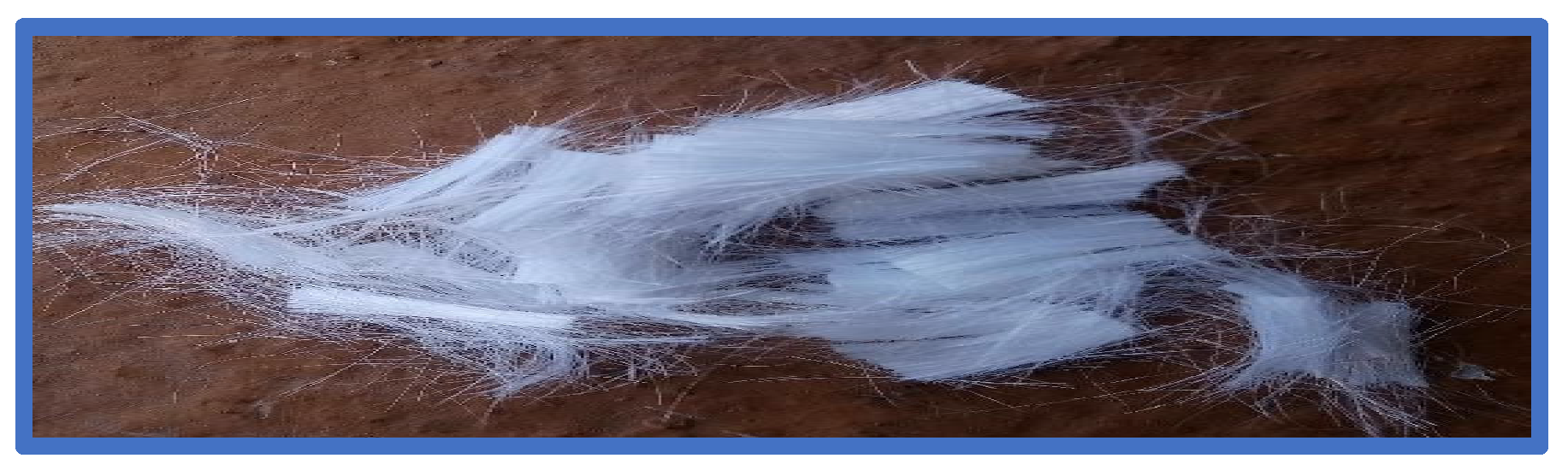
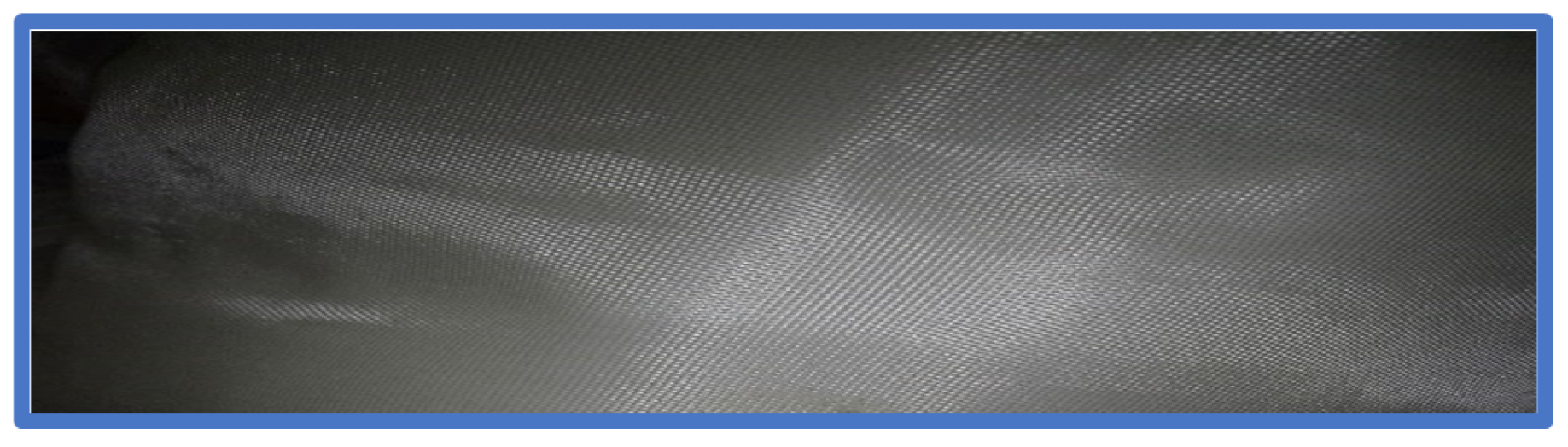
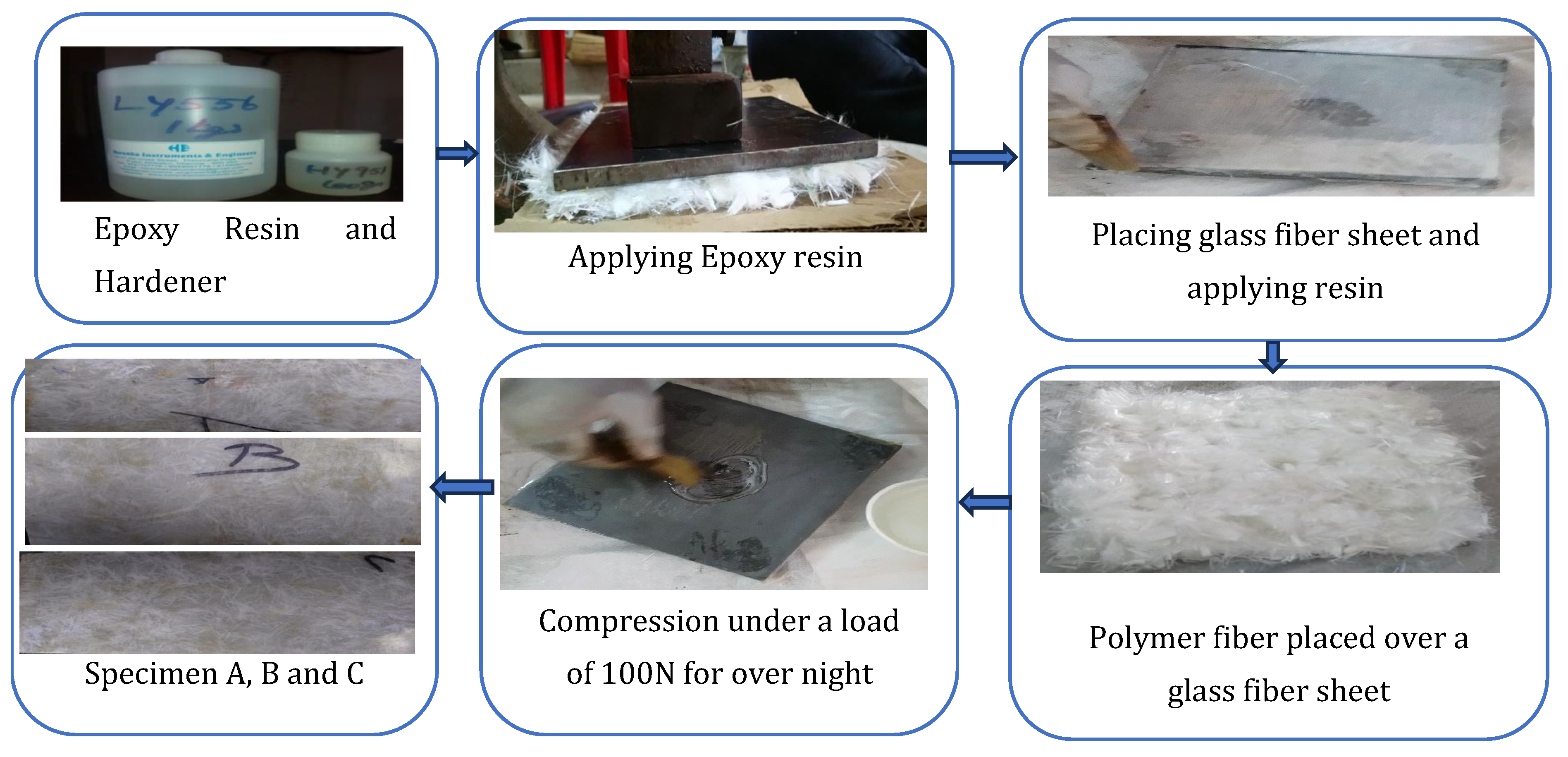















| Samples | Epoxy Matrix (wt.%) | Woven Glass Fiber (wt.%) | Mono and bi Filament Polypropylene Short Fiber (wt.%) | Polyester Fiber (wt.%) | Woven Polypropylene Fiber (wt.%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Epoxy | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| A | 62.6 | 18 | 12.12 | 6.6 | 0 |
| B | 62.6 | 12 | 12.12 | 6.6 | 6 |
| C | 68.56 | 12 | 12.12 | 6.6 | 0 |
| PROPERTIES | SAMPLE A | SAMPLE B | SAMPLE C |
|---|---|---|---|
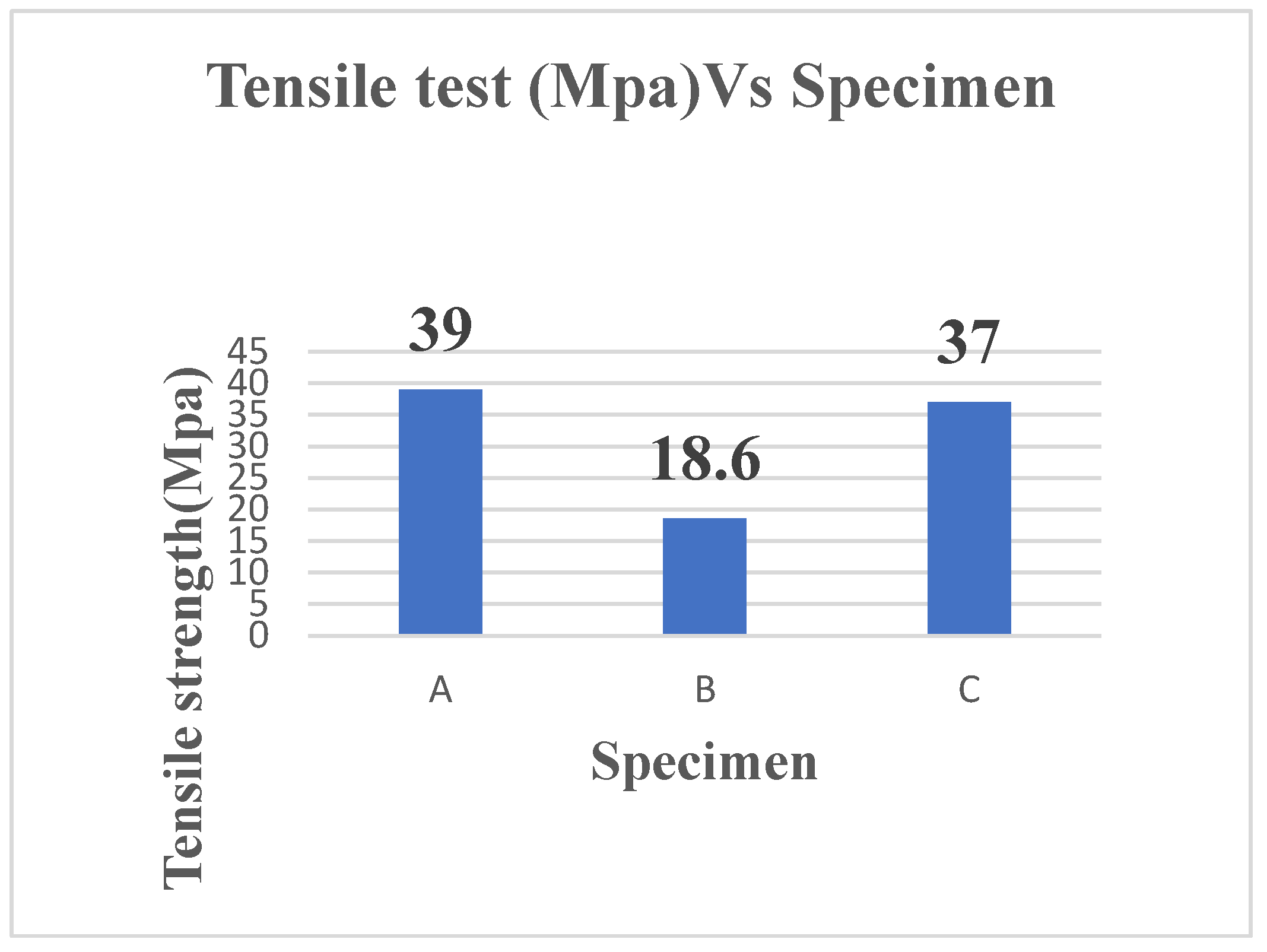
| Ultimate tensile strength (Mpa) | 39 | 18.6 | 37 |
| Youngs modulus (Mpa) | 629.33 | 789 | 291.14 |
| Bulk modulus (Mpa) | 320.76 | 347.88 | 122.843 |
| Flexural strength (Mpa) | 41 | 36 | 47 |
| Flexural strain | 0.0524 | 0.0867 | 0.0877 |
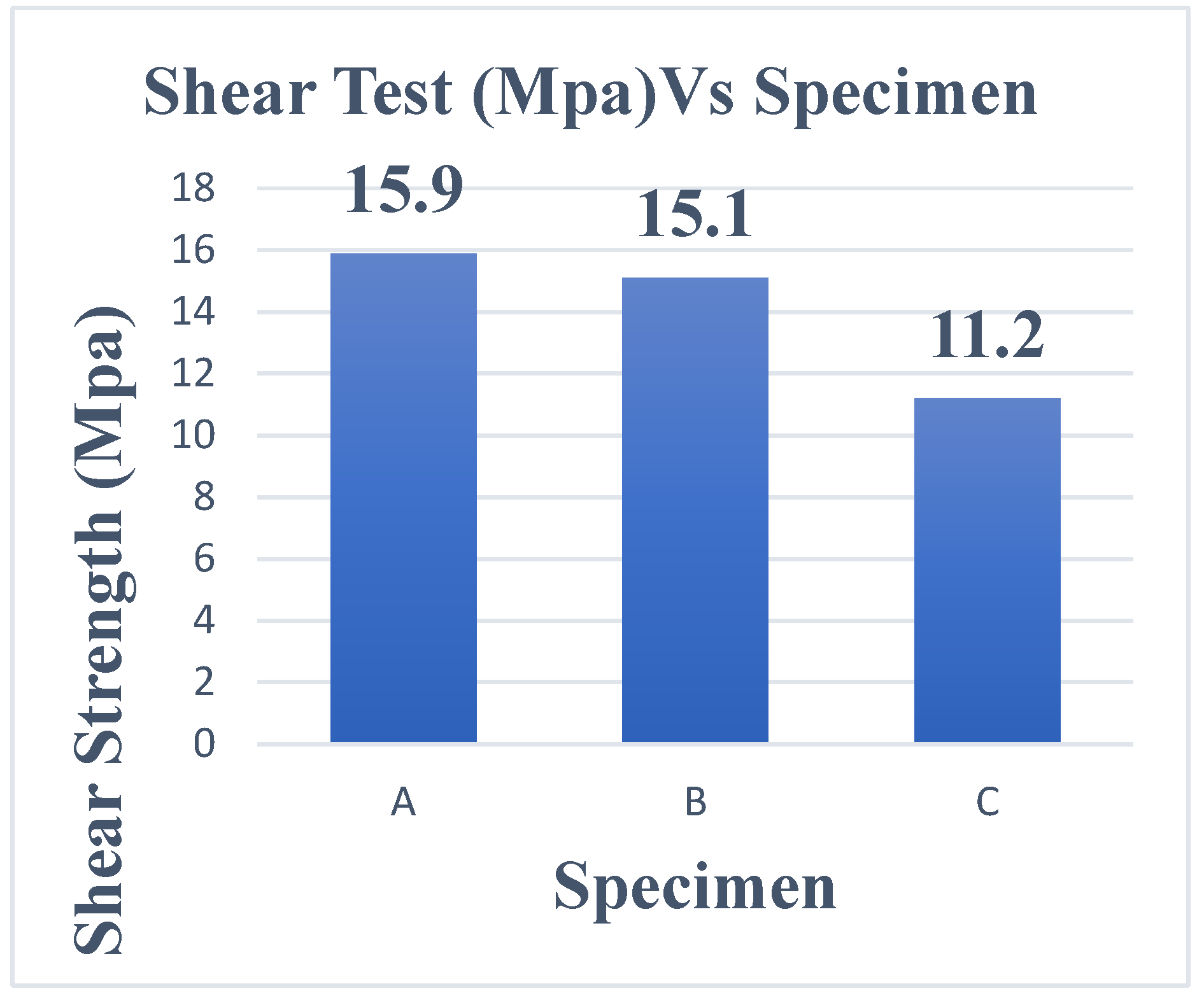
| Shear strength (Mpa) | 15.9 | 15.1 | 11.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Murugesan, S.; Kayaroganam, P. Experimental Investigation on the Mechanical Properties of Woven Glass–Polyester–Polypropylene Fiber-Reinforced Epoxy Hybrid Composites. Eng. Proc. 2025, 93, 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2025093007
Murugesan S, Kayaroganam P. Experimental Investigation on the Mechanical Properties of Woven Glass–Polyester–Polypropylene Fiber-Reinforced Epoxy Hybrid Composites. Engineering Proceedings. 2025; 93(1):7. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2025093007
Chicago/Turabian StyleMurugesan, Sundarapandiyan, and Palanikumar Kayaroganam. 2025. "Experimental Investigation on the Mechanical Properties of Woven Glass–Polyester–Polypropylene Fiber-Reinforced Epoxy Hybrid Composites" Engineering Proceedings 93, no. 1: 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2025093007
APA StyleMurugesan, S., & Kayaroganam, P. (2025). Experimental Investigation on the Mechanical Properties of Woven Glass–Polyester–Polypropylene Fiber-Reinforced Epoxy Hybrid Composites. Engineering Proceedings, 93(1), 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2025093007







