Abstract
Metal ions and ligand binding are crucial in various biological processes, and their rational design can be used to develop novel therapeutic drugs and diagnostic tools. Metal atoms are soluble in biological fluids due to their ability to easily lose electrons and form positively charged ions. Because of their electron deficiency, they can interact with electron-rich biomolecules like proteins and DNA, and potentially participate in catalytic mechanisms or stabilize their tertiary or quaternary structures. Antibacterial resistance has become a major global concern and requires novel strategies to combat resistance mechanisms in infectious microbes.
1. Introduction
Microorganisms plays an important role in the spoilage and decomposition of organic substances. To prevent the transmission of infections and diseases, regularization of microbial populations is needed [1]. Due to increasing microbial resistance, old antibiotics are becoming less effective, causing numerous deaths [2]. Metal ions play a fundamental role in biology, because they function as both pharmaceuticals and diagnostic agents [3]. Variable coordination modes, redox activity, and reactivity towards organic substances are the unique characteristics of metals that help in the regulation of their reactivity under normal conditions. Advancements in coordination chemistry have established metal complexes with optimistic pharmacological potential as either drugs or pro-drugs. Metal complexes have emerged as highly attractive options in pharmaceutical chemistry due to their potential to enhance the therapeutic efficacy [4]. Studies have established transition metal complexes as therapeutic agents for the treatment of human diseases [5]. The transition metals Fe, Mn, and Cu, involved in numerous biological functions including electron transfer and catalysis as well as structural roles, are found in the active sites of enzymes and proteins. Their complexes exhibit antidiabetic, anti-infective, and anti-inflammatory activities [6]. The synthesis of metal-based drugs with antimicrobial properties, a growing research field in inorganic, pharmaceutical, and medicinal chemistry, is thus essential for their use in pharmaceutical and drug delivery systems.
2. Schiff Bases
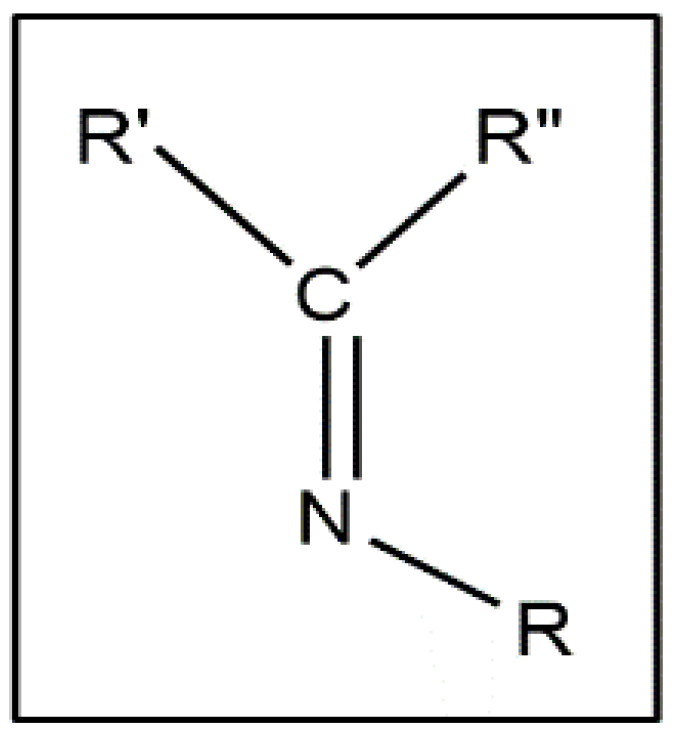
Schiff bases are chemical compounds formed by the condensation of an aldehyde or ketone with primary amines. It is an analogue of aldehyde and ketone, having an azomethine or imine in place of a C=O group (Figure 1).
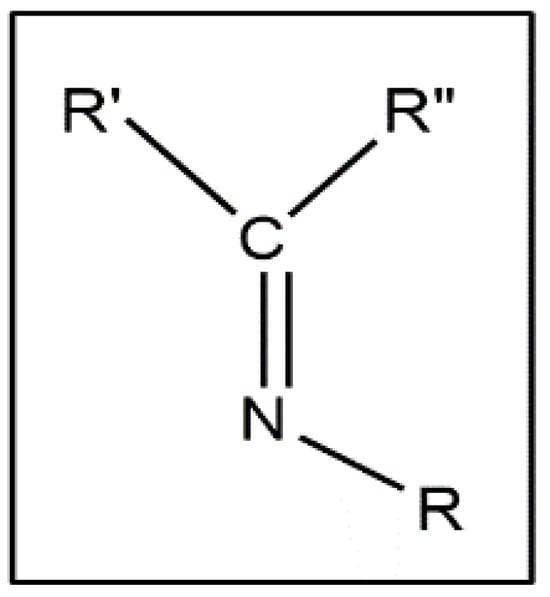
Figure 1.
General structure of Schiff base.
They coordinate with metals to form stable metal complexes [7]. Schiff base ligands have been widely explored in coordination chemistry due to their ease of synthesis, accessibility, and favourable electronic characteristics. Schiff base coordination chemistry has garnered substantial attention because of its crucial applications in analytical chemistry, organic synthesis, metal refining, electroplating, metallurgy, and photography [8]. The advancement of bioinorganic chemistry and modern coordination chemistry is greatly influenced by Schiff bases. The formation of Schiff bases occurs more readily with aldehydes than with ketones because of differences in carbonyl reactivity. These ligands are readily prepared and demonstrate good chelating characteristics. Schiff bases can regulate the performance of metal ions in different catalytic reactions by stabilizing them in various oxidation states [9]. They play a vital role in medicine and drug discovery due to their diverse pharmacological properties, including antioxidant, anticancer, antitubercular, antibacterial, analgesic, inflammatory, and cardiovascular effects. Apart from these biological properties, Schiff bases are extensively used as catalysts, corrosion inhibitors, dyes, and polymer stabilizers [10]. Bi- or tridentate Schiff base ligands form stable complexes with transition metals, which are used in drug discovery. Transition metal complexes are used in treating microbial infections due to their higher biological activity as compared to ligands. Ommenya et al. synthesized complexes of Mn(II), Ni(II), Co(II), Cu(II), and Zn(II) using the Schiff base 4-chloro-2-{(E)-[(4-fluorophenyl)imino]methyl}phenol, which was prepared by the condensation of 4-fluoroaniline and 5-chlorosalicylaldehyde. These complexes were investigated for their antibacterial activity against B. subtilis, S. aureus, P. aeruginosa, and E. coli [11]. Similarly, Anacona et al. reported Mn(II), Co(II), Ni(II), Cu(II), and Zn(II) complexes of a ceftriaxone-based Schiff base ligand, and found that the Zn(II) complex exhibited significant antibacterial activity against S. aureus (MIC = 0.0048 μmol/mL) and E. coli (MIC = 0.0024 μmol/mL) compared to the free ligand [12]. Other than antibacterial activity, Saritha and Metilda synthesized Mn(II), Co(II), Ni(II), Cu(II), and Zn(II) complexes of 2-[5-hydroxy-1,7-bis (4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-hepta-1,4,6-triene-3-ylidene] hydrazine carboxamide [HMHC] ligand and these complexes exhibited anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, and antifungal activities. The anti-inflammatory findings demonstrated that the Zn(II) complex showed higher inhibition (92.2%) than the ligand. The enhanced activity of the Zn(II) complex may be due to its ability to be easily reduced and oxidized. The antimicrobial assay demonstrated that all the complexes exhibited moderate activity against the tested strain. The Zn(II) complex exhibited superior antifungal and antibacterial activity due to its higher lipid solubility, making it a promising candidate for in vivo drug development [13]. In contrast, Anita et al. synthesized complexes of Mn(II) and Co(II) of (Z)-2-(2-methyl-1-phenylpropylidene)hydrazine-1-carbothioamide ligand and reported antibacterial activity against S. aureus as well as antifungal activity towards C. albicans and A. fumigatus. The results showed that the complexes had increased activity compared to the ligand [14]. In addition, Gavali et al. also reported mixed ligand metal complexes (Ni(II), Co(II), Cu(II), Zn(II), and Cd(II)) of terephthalaldehyde bis(thiosemicarbazone) (TPTSC) as primary ligand and alanine as co-ligand. These complexes displayed antibacterial activity against S. aureus, K. pneumoniae, S. typhi, E. Faecalis, and E. coli and antifungal activity against A. niger and A. flavus [15]. Other than antibacterial activity, Deswal et al. reported Co(II), Ni(II), Cu(II), and Zn(II) complexes with Schiff base ligands and evaluated their antidiabetic potential using in vitro tests on α-amylase and α-glucosidase enzymes. The complexes exhibited strong activity, with IC50 values 1.28 ± 0.05 and 0.58 ± 0.06 μmol/mL [16]. In addition, Xiao et al. reported that Co(II) complexes derived from two Schiff base ligands (ON donors), formed by the condensation of p-nitrophenylamine with 3,5-dichlorosalicylaldehyde or 3,5-bromosalicylaldehyde, exhibited better antitumor activity against human cancer cell lines (SK-MEL-30, HT-144, and A-431) as compared to the free ligands [17]. Manimalathi et al. also reported Mn(II), Fe(II), Co(II), Ni(II), Cu(II), and Zn(II) complexes of a hydroxybenzylideneaminocyclohexyliminomethyl-4,6-dibromophenol Schiff base ligand, and these complexes were tested for their antimicrobial activity against S. aureus and E. coli and antifungal activity against A. niger and C. albicans. The anticancer potential of the Zn(II) complex was also evaluated on MCF-7 breast cancer cell line (IC50 = 86.68 ± 0.72 μg/mL) [18]. Furthermore, Yadav et al. reported Co(II), Cu(II), and Zn(II) complexes with tetraaza macrocyclic Schiff base ligand. These complexes were tested for their anticancer activity against a human liver cancer cell line (Hep-G2 cells) as well as antibacterial efficacy against tested bacterial strains [19]. Similarly, Raju et al. synthesized Ni (II), Cu(II), Co(II), and Zn(II) complexes of [4-(2-oxo-1,2-diphenylethylidene) amino] benzenesulphonamide and the complexes exhibited anticancer activity against a breast cancer cell line [20].
Much literature is available on the later elements of the first transition series, and complexes of vanadium have been, as of yet, not explored very much. Vanadium, an important transition element, with its unique properties, has drawn considerable interest from biologists, chemists, toxicologists, biochemists, and pharmacologists. In the III, IV, and V oxidation states, they readily bind with S, N, and O [21]. Previous studies have demonstrated that vanadium complexes possess a broad spectrum of possible diagnostic and medicinal uses due to their low toxicity. One of the most important impetuses for medical applications of vanadium complexes has been the ability to boost insulin activity in the pathophysiological condition of diabetes mellitus in humans [22]. In 1992, the discovery of the insulin-enhancing properties of oxovanadium(IV) [23] and oxovanadate(V) (2001) [24] complexes in vivo, along with the ‘benchmark’ complex bis(maltolato)oxovanadium(IV) (BMOV), drove the exploration of vanadium-based complexes as potential treatments for type II diabetes. Studies have reported vanadium complexes with a wide range of medicinal and diagnostic application with low toxicity and as an insulin-enhancing agent essential for humans. In addition to their antidiabetic properties, vanadium complexes have been found to exhibit various medicinal properties like antibacterial, anticancer, tissue regeneration, and anti-inflammatory effects, etc., [25,26,27,28]. This review focuses on the biological applications of vanadium complexes as antibacterial agents.
3. Vanadium as an Enzyme Switch
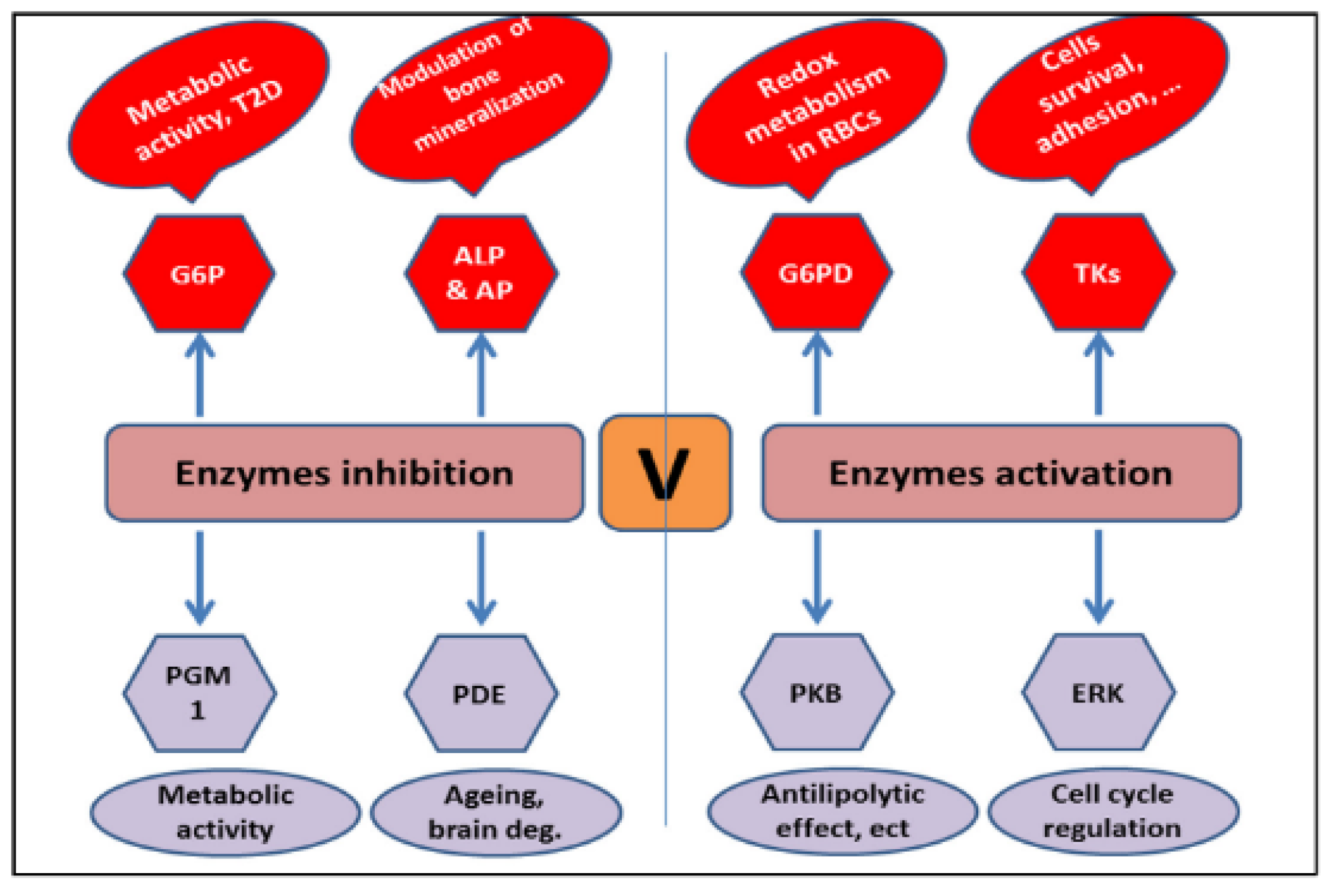
The ability of vanadium to activate enzymes is enhanced due to its complexation with the ligand. The anionic form of vanadium (VO4)−3 has been reported to stimulate glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase in mammalian cells [29]. Vanadate compounds are also known to energize the tyrosine kinases p59fyn and p56Ick [30,31]. The activation of protein kinase B (PKB/AKT) and extracellular-signal-regulated kinases (ERKs), crucial for regulating antilipolytic processes and the cell cycle, have been reported for vanadium complexes (Figure 2). Vanadium has shown the ability to inhibit the enzymes acid phosphatase (AP) and alkaline phosphatase (ALP), involved in the mineralization of bone [32,33], and glucose-6-phosphatase (G6P) [34,35]. The literature has established the regulatory role of vanadium complexes in a variety of biological processes [36].
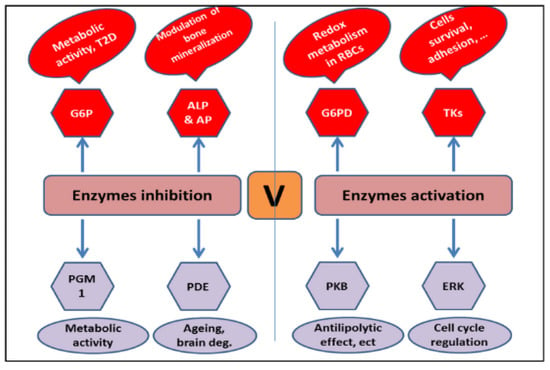
Figure 2.
Various enzyme targets of vanadium complexes [26].
4. Antibacterial Activity of Vanadium Complexes
Pawar et al. reported the synthesis of oxovanadium (IV) complexes with macrocyclic Schiff base ligands. These complexes have been found to inhibit the bacterial strains B. licheniformis, S. aureus, M. luteus, and E. coli [37]. Rosu et al. synthesized a VO(II) complex using a 3-formyl-6-methyl-chromone and 4-amino-2,3-dimethyl-1-phenyl-3-pyrazolin-5-one functionalized Schiff base ligand. These complexes have been reported to exhibit antibacterial activity against S. aureus, E. coli, K. pneumoniae, and P. aeruginosa [38].
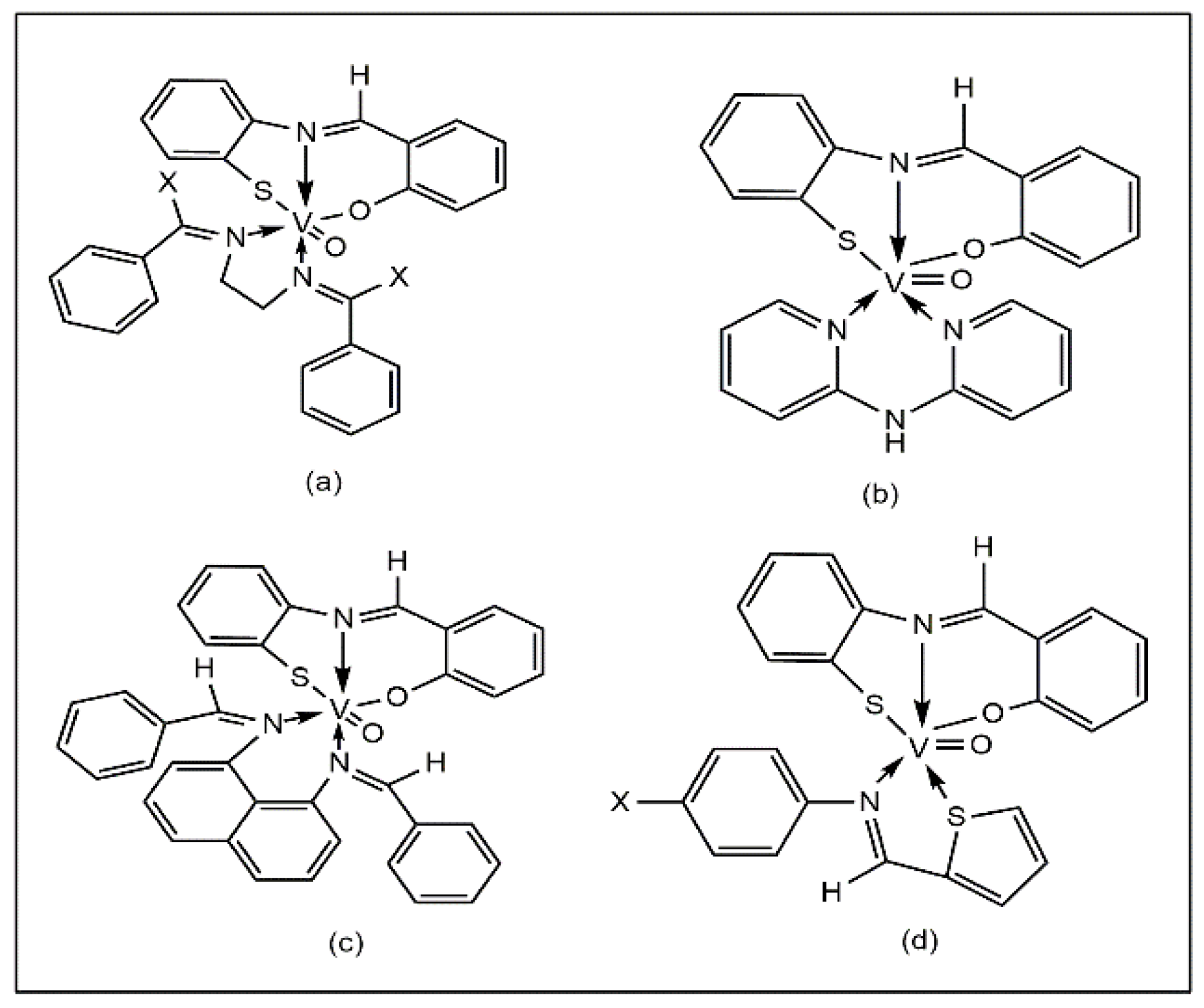
A series of oxovanadium (IV)-salicylidene-o-aminothiophenol complexes containing heteroligands have been reported to exhibit good antibacterial activity against E. coli, S. typhi, and S. marcescens using the disc diffusion method (Figure 3a–d). The results of this study show that the complexes exhibit higher activity (40–60% inhibition) compared to the corresponding uncoordinated ligands (10–25%) [39].
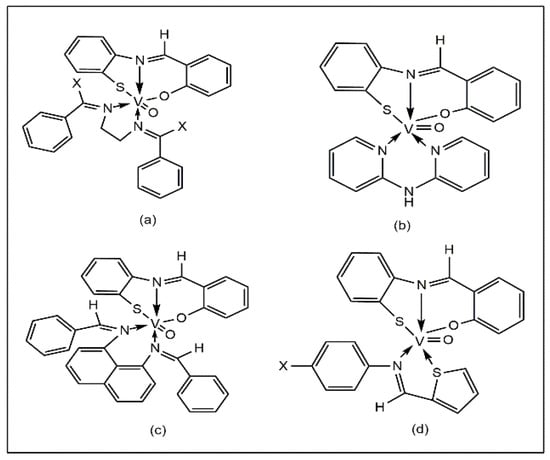
Figure 3.
Oxovanadium heteroligand complexes containing common ligand salicylidene-o-aminothiophenol [VO(L)(A1–6)], (a) A1 =bis(benzylidene)ethylenediamine, A2 = bis(acetophenone)ethylenediamine, (b) A3 = 2,2’-bipyridylamine, (c) A4 =bis(benzylidene)-1,8-diaminonaphthalene, (d) A5 = thiophene-o-carboxaldeneaniline and A6 = thiophene-o-carboxaldene-p-anisidine.
Good antibacterial activities against B. subtilis, S. aureus, S. flexneri, E. coli, S. typhi, and P. aeruginosa have also been reported by Chohan et al. for oxovanadium (IV) complexes derived from a 1,2,4-triazole Schiff base. The presence of the NO2 group in the ligand has been suggested to be responsible for its antibacterial activity (Figure 4a). This study reported a minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) of 8.523 × 10−4 M, establishing the higher activity of the complexes compared to their uncoordinated ligand [40]. Chohan and Sumrra synthesized an oxovanadium (IV) complex using a thienyl-derived triazole Schiff base ligand and the complex was found to be more efficient than the ligands in inhibiting bacterial growth (Figure 4b), with the lowest MIC value of 3.891 × 10−8 M against B. subtilis [41].
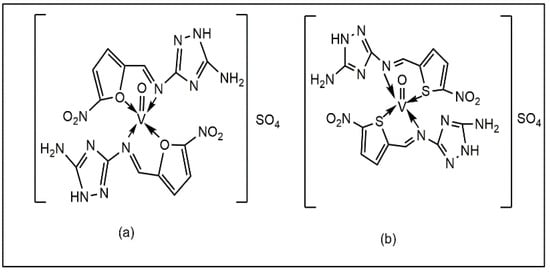
Figure 4.
Vanadium complexes with (a) 1,2,4-triazole derived Schiff base, (b) thienyl derived triazole Schiff base.
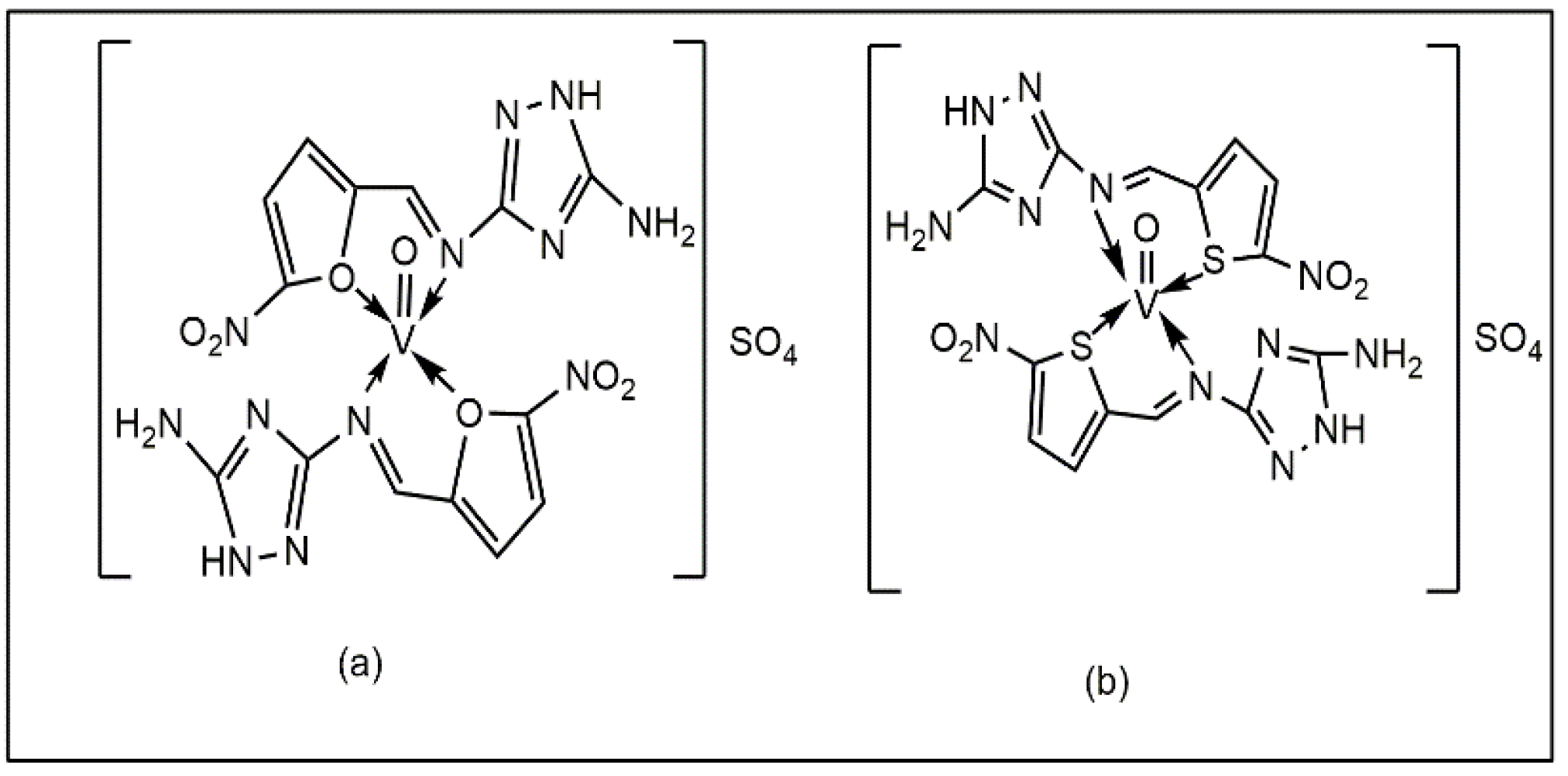
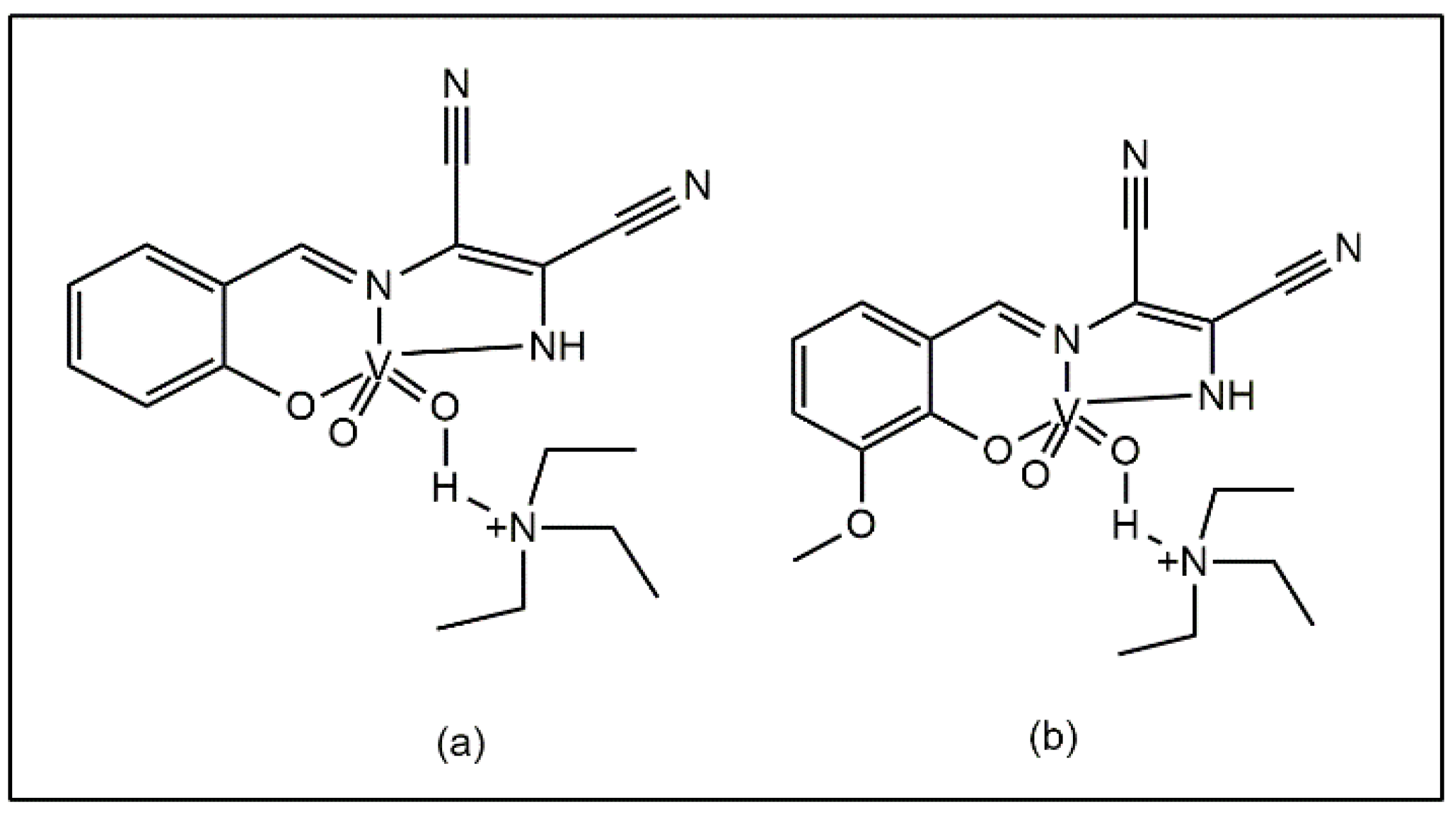
Sheikhshoaie et al. reported that vanadium (V) complexes containing a dimalonitrile-based Schiff base (Figure 5a,b) exhibited antibacterial activity against P. aeruginosa, E. coli, and K. pneumoniae. The experimental data showed that the complexes exhibited superior efficacy compared to vanadium sulphate and ciprofloxacin against L. monocytogenes, E. faecalis, and C. albicans, with MIC values of 0.62, 1.25, and 2.5 mg/mL [42].
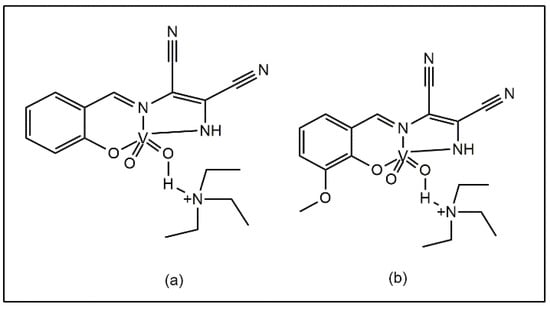
Figure 5.
Vanadium complexes with dimalonitrile-based Schiff base: (a) triethylammonium 1,2-dicyano-2-(2-oxidobenzylidene)amino)vinyl)amide di-oxido vanadate, (b) triethylammonium 1,2-dicyano-2-(3-methoxy-2-oxidobenzylidene)amino) vinyl)amide di-oxido vanadate.
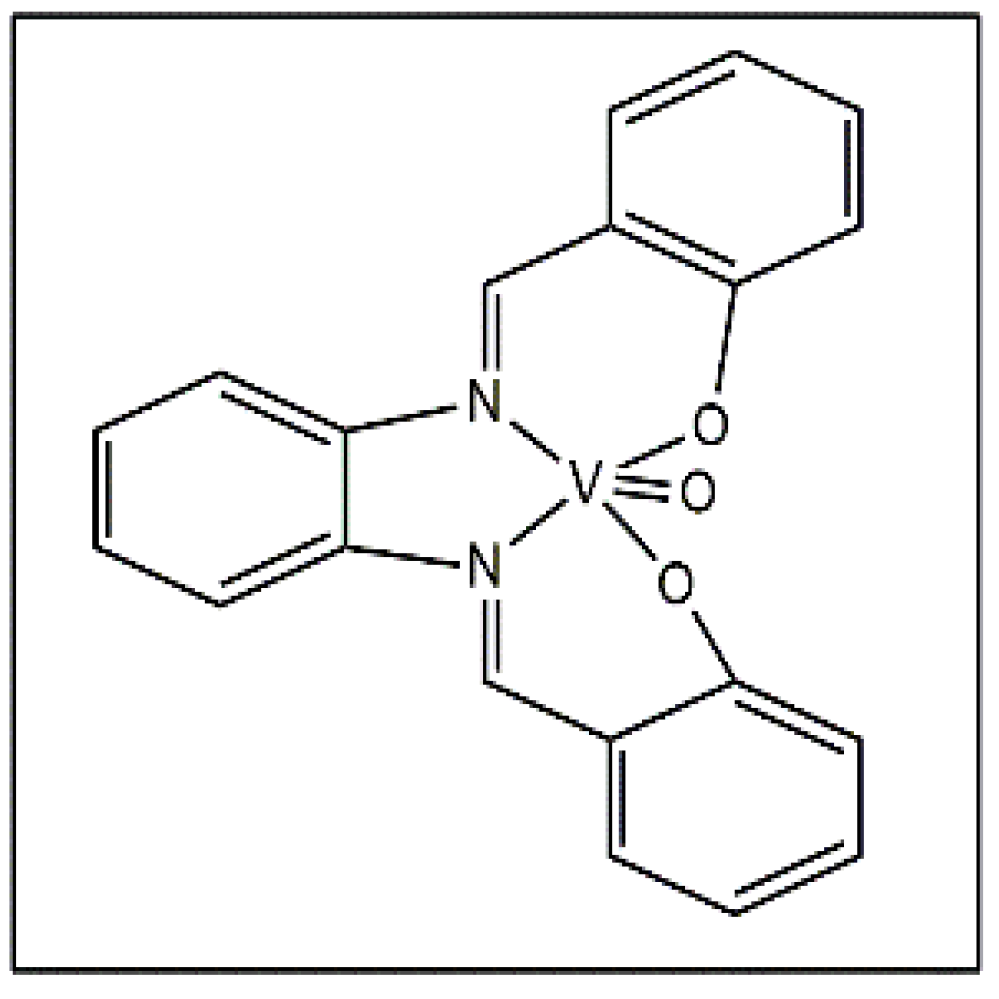
Machado et al. reported a vanadium stilbene complex (Figure 6) and the complex was tested against T. cruzi and Leishmania sp., which causes leishmaniasis, with an IC50 value of 3.51 µM against L. amazonensis [43].
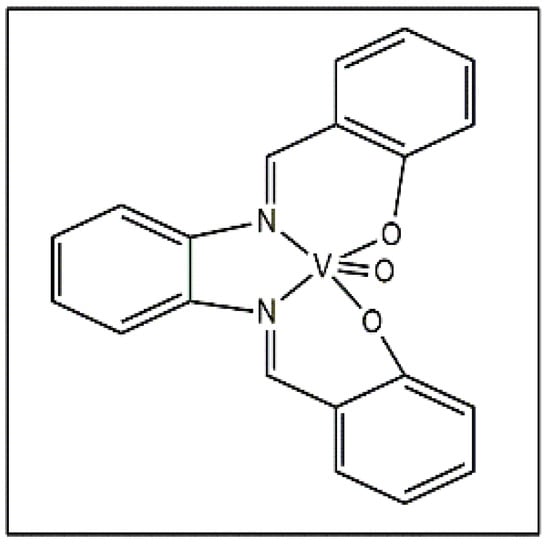
Figure 6.
Vanadium stilbene complex.
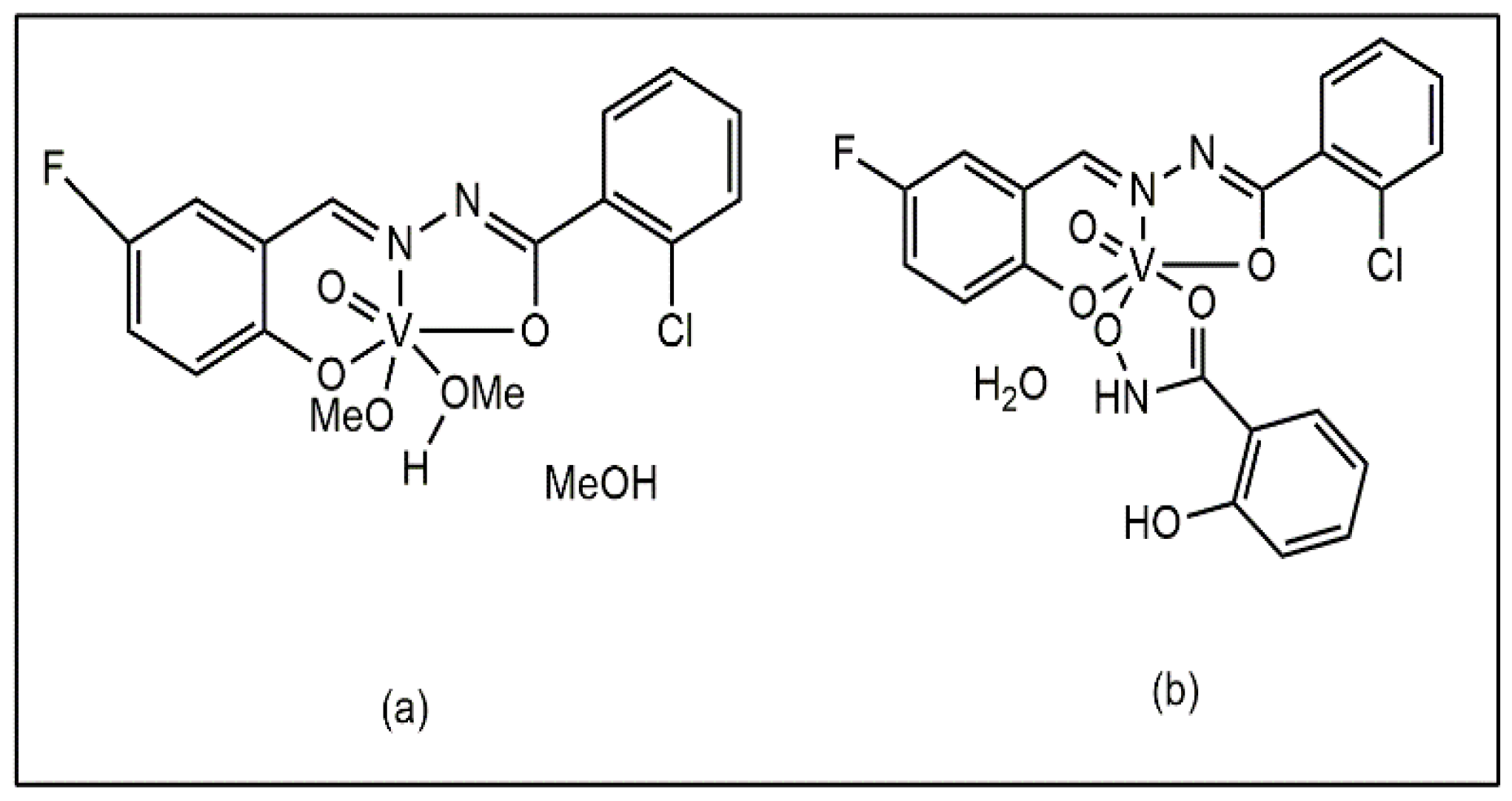
Liu et al. also reported that mixed ligand vanadium complexes containing methanol and methoxy ligands, [VOL(OMe)(MeOH)] MeOH and salicylhydroxamic acid ([VOL(SHA)]·H2O) (Figure 7a,b), showed antibacterial activity against S. aureus, B. subtilis, K. pneumoniae, P. aeruginosa, and E. coli [44].
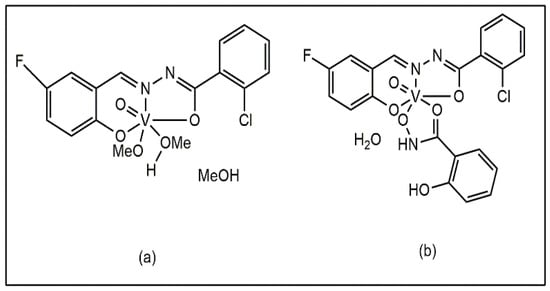
Figure 7.
Vanadium Complexes of Fluoro- and Chloro-Substituted Benzohydrazone Ligands: (a) with methanol and methoxy ligands [VOL(OMe)(MeOH)] MeOH, (b) with salicylhydroxamic acid [VOL(SHA)]⋅H2O.
Another series of transition metal complexes of VO(IV), CO(III), Ni(II), and Cu(II) of a 2-ethoxy-6-(E)-[(prop-2-em-1-yl)imino]methylphenol Schiff base ligand was reported and the synthesized complexes displayed considerable anticancer and antioxidant activities [45]. Additionally, Askarian et al. reported vanadium complexes of N,N′-dipyridoxyl(1,2-propanediamine) Schiff bases and the complexes exhibited significant cytotoxicity against a human prostate cancer (PC-3) cell line [46]. Lewis et al. also reported mixed ligand vanadium complexes with a Schiff base and thiosemicarbazone ligands and the complexes exhibited antitumor effects against non-malignant colon myofibroblasts (CCD18-Co) and various colon cancer cell lines, including Caco-2, HTC-116, and HT-29 [47]. On the other hand, vanadium-based coordination compounds are widely studied due to their essential biological functions and their ability to mimic insulin [48]. Studies have shown that vanadium complexes are more effective than vanadium salts in reducing blood glucose levels, suggesting their strong potential as insulin-mimicking agents [49]. Patel et al. synthesized vanadium complexes with a Schiff base and imidazole as a co-ligand, including [VO(L1)(H2O)]NO3, [VO(L2)(H2O)]NO3, and [VO(L2)(ImH)2]SO4·H2O (L1 = Acetic acid (2-hydroxy-3-methoxy-benzylidene)-hydrazide, and L2 = 5-bromo-2-[(E)-(pyridine-2-ylhydrazono)methyl]phenol) and reported antidiabetic activity [50].
Vanadium complexes, along with their ligands, exhibit improved antibacterial activity. The increased activity of the complex over the ligand can be attributed to the chelation theory. Chelation leads to enhanced bactericidal properties in contrast to the ligand itself. The biological activity of metal-based drugs is regulated by the formation of metal ion complexes, which depend on the ligand type and the metal’s oxidation state [51]. Various target sites within an organism are influenced by metal chelates, including the following:
- Tweedy’s chelation theory suggests that when metal ions bind to ligands, the polarity of the metal atom is reduced as its positive charge is partially shared with donor groups, and the electrons become delocalized across the entire chelate structure. This enhances the chelates’ lipophilicity, improving their ability to penetrate the lipid membranes of bacterial cells [52].
- Metal complexes disrupt cell wall formation, which alters the cell’s permeability, causing the lipid–protein structure to become disorganized and ultimately leading to the death of the cell.
- The regular cellular functions are disrupted by metal complexes, causing the denaturation of one or more enzymes [53].
Mechanisms of the Antibacterial Activity of Vanadium
The antibacterial activity of vanadium complexes has not been established yet. A review of the literature suggests potential mechanisms involving the following:
- Disruption of Na+/K+-ATPase activity [54,55,56,57].
- ROS formation [58].
- The uptake of substrates through the bacterial cell membrane, along with the activation of K+ efflux from the cell [59].
- The interaction with topoisomerase type-II (gyrase), which is essential for genome function and bacterial growth, using the ATP-binding site as a target for antibacterial drugs [60,61].
- Interaction with DNA through intercalation [62].
- The disruption of cytoskeleton interactions, leading to changes in bacterial cell morphology and inhibiting proper cell division [56].
- Other non-specific mechanisms, emphasizing the improved bioavailability of vanadium complexes, facilitated by a specific ligand that enables the complex to pass through the hydrophobic, lipid-rich bacterial wall [63].
5. Conclusions
Metal ions are important for cellular processes and biological functions in microorganisms. Vanadium is a well-known transition metal, and its complexes have been extensively studied for their medicinal properties. Schiff bases are considered valuable ligands because they are easy to synthesize and readily form complexes, with a wide range of metal ions exhibiting different denticity. The bioactive azomethine core is responsible for the medicinal importance attributed to various Schiff bases. The diverse therapeutic applications of Schiff bases and their metal complexes have initiated a new era in medicinal science. Metal complexes demonstrate superior antibacterial efficacy as compared to their Schiff base ligands. Research on antimicrobial metallodrugs is crucial for combating antibiotic resistance. Still, the mechanisms of toxicity remain uncertain, and limited in vivo data hinder further development due to the limited number of bacterial targets. Future multidisciplinary research on vanadium complexes as potential antibacterial agents offers opportunities to explore biochemistry and improve solubility, bioavailability, and toxicity and focus on developing novel strategies for targeting toxic metals and nanostructured antimicrobials for better understanding metal complex behaviour in living organisms [64,65]. Further exploration of vanadium complexes for their antibacterial potential will help to develop new lines of drugs for targeting these resistant bacteria and resolve the challenge of drug resistance to some extent.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.J. and K.H.; resources, S.J.; data curation, K.H., T.K. and S.J.; writing—original draft preparation, K.H. and S.J.; writing—review and editing, K.H., S., P.M., E.V., T.K. and S.J.; visualization, K.H., T.K. and S.J.; supervision, S.J. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
No new data was generated during the study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Manawar, R.B.; Gondaliya, M.B.; Mamtora, M.J.; Shah, M. Synthesis and bioactivity study of 2-((E)-(((E)-2,6-dichlorobenzylidene) hydrazono) methyl) phenol have N, O-Bidentate ligand site and it’s metal complex. World Sci. News 2019, 126, 222–247. [Google Scholar]
- Balouiri, M.; Sadiki, M.; Ibnsouda, S.K. Methods for in vitro evaluating antimicrobial activity: A review. J. Pharm. Anal. 2016, 6, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sigel, A. Metal Ions in Biological Systems: Volume 41: Metal Ions and Their Complexes in Medication; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2004; Volume 30, p. 315. [Google Scholar]
- Satya; Hashmi, K.; Gupta, S.; Singh, N.; Khan, T.; Joshi, S. Nanofabrication of metals and their compounds for effective medicinal and environmental applications (a review). Russ. J. Gen. Chem. 2023, 93, 635–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagajothi, A.; Kiruthika, A.; Chitra, S.; Parameswari, K. Fe (III) complexes with Schiff base ligands: Synthesis, characterization, antimicrobial studies. Res. J. Chem. Sci. ISSN 2013, 3, 35–43. [Google Scholar]
- Zoubi, A.W. Biological activities of Schiff bases and their complexes: A review of recent works. Int. J. Org. Chem. 2013, 2013, 73–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, T.; Zehra, S.; Alvi, A.; Fatima, U.; Lawrence, A.J. Medicinal utility of some Schiff bases and their complexes with first transition series metals: A review. Orient. J. Chem. 2021, 37, 1051–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvat, A.; Antonnacci, L.; Fortunato, R.H.; Suarez, E.Y.; Godoy, H.M. Screening of some plants from Northern Argentina for their antimicrobial activity. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2001, 32, 293–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costes, J.P.; Dahan, F.; Fernandez Fernandez, M.B.; Fernandez Garcia, M.I.; Garcia Deibe, A.M.; Sanmartin, J. General Synthesis of “Salicylaldehyde Half-Unit Complexes”: Structural Determination and Use as Synthon for the Synthesis of Dimetallic or Trimetallic Complexes and of “Self-Assembling Ligand Complexes. Inorg. Chim. Acta 1998, 274, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raju, S.K.; Settu, A.; Thiyagarajan, A.; Rama, D.; Sekar, P.; Kumar, S. Biological applications of Schiff bases: An overview. GSC Biol. Pharm. Sci. 2022, 21, 203–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ommenya, F.K.; Nyawade, E.A.; Andala, D.M.; Kinyua, J. Synthesis, Characterization and Antibacterial Activity of Schiff Base, 4-Chloro-2-{(E)-[(4-Fluorophenyl) imino] methyl} phenol Metal (II) Complexes. J. Chem. 2020, 2020, 1745236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anacona, J.R.; Santaella, J.; Al-Shemary, R.K.R.; Amenta, J.; Otero, A.; Ramos, C.; Celis, F. Ceftriaxone-based Schiff base transition metal (II) complexes. Synthesis, characterization, bacterial toxicity, and DFT calculations. Enhanced antibacterial activity of a novel Zn (II) complex against S. aureus and E. coli. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2021, 223, 111519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saritha, T.J.; Metilda, P. Synthesis, spectroscopic characterization and biological applications of some novel Schiff base transition metal (II) complexes derived from curcumin moiety. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 2021, 25, 101245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anita; Ghanghas, P.; Poonia, K. Synthesis, characterization and biological activities of novel Schiff base ligand and its Co (II) and Mn (II) complexes. Results Chem. 2024, 7, 101221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavali, L.V.; Mohammed, A.A.; Al-Ogaili, M.J.; Gaikwad, S.H.; Kulkarni, M.; Das, R.; Ubale, P.A. Novel terephthalaldehyde bis (thiosemicarbazone) Schiff base ligand and its transition metal complexes as antibacterial Agents: Synthesis, characterization and biological investigations. Results Chem. 2024, 7, 101316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deswal, Y.; Asija, S.; Dubey, A.; Deswal, L.; Kumar, D.; Jindal, D.K.; Devi, J. Cobalt(II), nickel(II), copper(II) and zinc(II) complexes of thiadiazole based Schiff base ligands: Synthesis, structural characterization, DFT, antidiabetic and molecular docking studies. J. Mol. Struct. 2022, 1253, 132266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.J.; Diao, Q.C.; Liang, Y.H.; Zeng, K. Two novel Co (II) complexes with two different Schiff bases: Inhibiting growth of human skin cancer cells. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2017, 50, e6390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manimalathi, S.; Priya, J.; Madheswari, D. Exploration on Synthesis, Characterization and Biological Activities of Transition Metal Complexes Comprising Hydroxybenzylideneaminocyclohexylimino-methyl-4, 6-dibromophenol Schiff Base Ligand. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2024, 49, 9691–9711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, M.; Yadav, D.; Kansal, S.; Angrup, A.; Taneja, N.; Singh, D.P.; Kapoor, J.K. Pharmacologically important tetraaza macrocyclic Schiff base complexes of Zn (II), Cu (II) and Co (II): Synthesis, characterization, DFT studies, molecular docking and in vitro anti-bacterial and anti-cancer studies. J. Mol. Struct. 2024, 1317, 139078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raju, S.K.; Sekar, P.; Kumar, S.; Jeyakumar, T.C.; Sankarganesh, M.; Murphy, M.; Govindasamy, C. Synthesis, DFT calculation, molecular docking and in vitro anticancer activities of sulphanilamide incorporated Schiff base metal complexes. J. Mol. Struct. 2025, 1321, 140211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, K.H.; McNeill, J.H.; Orvig, C. Vanadium compounds as insulin mimics. Chem. Rev. 1999, 99, 2561–2572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakurai, H.; Kojima, Y.; Yoshikawa, Y.; Kawabe, K.; Yasui, H. Antidiabetic vanadium (IV) and zinc (II) complexes. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2002, 226, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNeill, J.H.; Yuen, V.G.; Hoveyda, H.R.; Orvig, C. Bis (maltolato) oxovanadium (IV) is a potent insulin mimic. J. Med. Chem. 1992, 35, 1489–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanamori, K.; Nishida, K.; Miyata, N.; Okamoto, K.I.; Miyoshi, Y.; Tamura, A.; Sakurai, H. Syntheses, structures, stability, and insulin-like activities of peroxovanadium (V) complexes with a heteroligand. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2001, 86, 649–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashmi, K.; Gupta, S.; Siddique, A.; Khan, T.; Joshi, S. Medicinal applications of vanadium complexes with Schiff bases. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2023, 79, 127245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satya; Hashmi, K.; Gupta, S.; Siddique, A.; Joshi, S. Vanadium Complexes as Potential Anticancer Agents. Eng. Proc. 2023, 56, 91. [Google Scholar]
- Hashmi, K.; Rai, S.; Sharma, S.; Satya; Gupta, S.; Mishra, P.; Veg, E.; Khan, T.; Gupta, A.; Joshi, S. Spectroscopic and Quantum chemical studies of some novel mixed-ligand complexes of vanadium and Comparative evaluation of their antimicrobial and antioxidant activities. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2025, 174, 113967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, K.S.; Ramachandrappa, S.U. Potential medicinal applications of vanadium and its coordination compounds in current research prospects: A review. Curr. Bioact. Compd. 2020, 16, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharfalddin, A.A.; Al-Younis, I.M.; Mohammed, H.A.; Dhahri, M.; Mouffouk, F.; Abu Ali, H.; Anwar, M.J.; Qureshi, K.A.; Hussien, M.A.; Alghrably, M.; et al. Therapeutic properties of vanadium complexes. Inorganics 2022, 10, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fantus, I.G.; Kadota, S.; Deragon, G.; Foster, B.; Posner, B.I. Pervanadate [peroxide (s) of vanadate] mimics insulin action in rat adipocytes via activation of the insulin receptor tyrosine kinase. Biochemistry 1989, 28, 8864–8871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schieven, G.L.; Kirihara, J.M.; Myers, D.E.; Ledbetter, J.A.; Uckun, F.M. Reactive oxygen intermediates activate NF-kappa B in a tyrosine kinase-dependent mechanism and in combination with vanadate activate the p56lck and p59fyn tyrosine kinases in human lymphocytes. Blood 1993, 5, 1212–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boruah, J.J.; Kalita, D.; Das, S.P.; Paul, S.; Islam, N.S. Polymer-anchored peroxo compounds of vanadium (V) and molybdenum (VI): Synthesis, stability, and their activities with alkaline phosphatase and catalase. Inorg. Chem. 2011, 50, 8046–8062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parente, J.E.; Naso, L.G.; Jori, K.; Franca, C.A.; da Costa Ferreira, A.M.; Williams, P.A.; Ferrer, E.G. In vitro experiments and infrared spectroscopy analysis of acid and alkaline phosphatase inhibition by vanadium complexes. New J. Chem. 2019, 43, 17603–17619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shehzad, S. The potential effect of vanadium compounds on glucose-6-phosphatase. Biosci. Horiz. Int. J. Stud. Res. 2013, 6, hzt002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Kim, S.M. Synthesis, characterization, antioxidant and anti-diabetic activities of a novel protein–vanadium complex. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2019, 33, e5102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehder, D. Vanadium in biological systems and medicinal applications. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2023, 549, 121387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawar, V.; Joshi, S.; Uma, V. Antibacterial and antioxidant properties of macrocyclic Schiff bases with vanadium (V) complexes. Biokemistri 2011, 23, 1497–1500. [Google Scholar]
- Rosu, T.; Pahontu, E.; Maxim, C.; Georgescu, R.; Stanica, N.; Almajan, G.L.; Gulea, A. Synthesis, characterization and antibacterial activity of some new complexes of Cu (II), Ni (II), VO (II), Mn (II) with Schiff base derived from 4-amino-2, 3-dimethyl-1-phenyl-3-pyrazolin-5-one. Polyhedron 2010, 29, 757–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panchal, P.K.; Parekh, H.M.; Pansuriya, P.B.; Patel, M.N. Bactericidal activity of different oxovanadium (IV) complexes with Schiff bases and application of chelation theory. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2006, 21, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chohan, Z.H.; Sumrra, S.H.; Youssoufi, M.H.; Hadda, T.B. Design and synthesis of triazole Schiff bases and their oxovanadium (IV) complexes as antimicrobial agents. J. Coord. Chem. 2010, 63, 3981–3998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chohan, Z.H.; Sumrra, S.H. Synthesis, characterization and biological properties of thienyl derived triazole Schiff bases and their oxovanadium (IV) complexes. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2012, 27, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikhshoaie, I.; Ebrahimipour, S.Y.; Lotfi, N.; Mague, J.T.; Khaleghi, M. Synthesis, spectral characterization, X-ray crystal structure and antimicrobial activities of two cis dioxido-vanadium (V) complexes incorporating unsymmetrical dimalonitrile-based (NNO) Schiff base ligands. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2016, 442, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Almeida Machado, P.; Mota, V.Z.; de Lima Cavalli, A.C.; de Carvalho, G.S.G.; Da Silva, A.D.; Gameiro, J.; Cuin, A.; Coimbra, E.S. High selective antileishmanial activity of vanadium complex with stilbene derivative. Acta Trop. 2015, 148, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, E.C.; Li, W.; Cheng, X.S. Synthesis, Spectroscopic Characterization, Crystal Structures and Antibacterial Activity of Vanadium (V) Complexes of Fluoro-and Chloro-Substituted Benzohydrazone Ligands. Acta Chim. Slov. 2019, 66, 971–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talebi, A.; Salehi, M.; Khaleghian, A.; Kubicki, M. Evaluation of anticancer activities, apoptosis, molecular docking, and antioxidant studies of new Ni (II), VO (IV), Cu (II) and Co (III) Schiff base complexes. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2023, 546, 121296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Askarian, S.; Beyramabadi, S.A.; Badmasti, F.; Heravi, F.S.; Tabrizi, A.M.A.; Azizi, H.; Mohaghegh, M.A.; Morsali, A.; Bazian, A.; Bozorgmehr, M.R.; et al. Synthesis, characterization and in vitro evaluation of cytotoxicity and antibacterial properties of vanadyl complexes of the pyridoxal Schiff bases. J. Mol. Struct. 2021, 1246, 131189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, N.A.; Liu, F.; Seymour, L.; Magnusen, A.; Erves, T.R.; Arca, J.F.; Beckford, F.A.; Venkatraman, R.; González-Sarrías, A.; Fronczek, F.R.; et al. Synthesis, characterization, and preliminary in vitro studies of vanadium(IV) complexes with a Schiff base and thiosemicarbazones as mixed-ligands. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2012, 2012, 664–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawabe, K.; Yoshikawa, Y.; Adachi, Y.; Sakurai, H. Possible mode of action for insulinomimetic activity of vanadyl (IV) compounds in adipocytes. Life Sci. 2006, 78, 2860–2866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adachi, Y.; Yoshida, J.; Kodera, Y.; Katoh, A.; Takada, J.; Sakurai, H. Bis(Allixinato) Oxovanadium(IV) complex is a potent antidiabetic agent: Studies on structureactivity relationship for a series of hydroxypyrone- vanadium complexes. J. Med. Chem. 2006, 49, 3251–3256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, N.; Prajapati, A.K.; Jadeja, R.N.; Patel, R.N.; Patel, S.K.; Gupta, V.K.; Tripathi, I.P.; Dwivedi, N. Model investigations for vanadium-protein interactions: Synthesis, characterization and antidiabetic properties. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2019, 493, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claudel, M.; Schwarte, J.V.; Fromm, K.M. New antimicrobial strategies based on metal complexes. Chemistry 2020, 2, 849–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paterson, J.R.; Beecroft, M.S.; Mulla, R.S.; Osman, D.; Reeder, N.L.; Caserta, J.A.; Young, T.R.; Pettigrew, C.A.; Davies, G.E.; Williams, J.G.; et al. Insights into the antibacterial mechanism of action of chelating agents by selective deprivation of iron, manganese, and zinc. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2022, 88, e01641-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nworie, F.S. Bis (salicylidene) ethylenediamine (salen) and bis (salicylidene) ethylenediamine-metal complexes: From structure to biological activity. J. Anal. Pharm. Res. 2016, 3, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Pessoa, J.C.; Garribba, E.; Santos, M.F.; Santos-Silva, T. Vanadium and proteins: Uptake, transport, structure, activity and function. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2015, 301, 49–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pessoa, J.C.; Etcheverry, S.; Gambino, D. Vanadium compounds in medicine. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2015, 301, 24–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bijelic, A.; Aureliano, M.; Rompel, A. The antibacterial activity of polyoxometalates: Structures, antibiotic effects and future perspectives. Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 1153–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aureliano, M.; Fraqueza, G.; Ohlin, C.A. Ion pumps as biological targets for decavanadate. Dalton Trans. 2013, 42, 11770–11777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aureliano, M.; De Sousa-Coelho, A.L.; Dolan, C.C.; Roess, D.A.; Crans, D.C. Biological consequences of vanadium effects on formation of reactive oxygen species and lipid peroxidation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 5382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bijelic, A.; Aureliano, M.; Rompel, A. Polyoxometalates as potential next-generation metallodrugs in the combat against cancer. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 2980–2999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietrusiński, M.; Stączek, P. Badania struktury i funkcji prokariotycznych topoizomeraz klasy II szansą dla poszukiwania i syntezy nowych leków przeciwbakteryjnych. Postępy Biochem. 2006, 52, 271–282. [Google Scholar]
- Szafran, M.; Zakrzewska-Czerwińska, J.; Jakimowicz, D. Bacterial type I topoisomerases-biological function and potential use as targets for antibiotic treatments. Postępy Hig. Med. Dośw. 2013, 67, 130–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayaseelan, P.; Akila, E.; Rani, M.U.; Rajavel, R. Synthesis, spectral characterization, electrochemical, anti-microbial, DNA binding and cleavage studies of new binuclear Schiff base metal (II) complexes derived from o-hydroxyacetophenone. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 2016, 20, 625–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pessoa, J.C. Thirty years through vanadium chemistry. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2015, 147, 4–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azad, I.; Khan, T.; Maurya, A.K.; Irfan Azad, M.; Mishra, N.; Alanazi, A.M. Identification of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus-2 inhibitors through in silico structure-based virtual screening and molecular interaction studies. J. Mol. Recognit. 2021, 34, e2918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, T.; Rahman, Q.I.; Raza, S.; Zehra, S.; Ahmad, N.; Husen, A. Nanodimensional Materials: An Approach Toward the Biogenic Synthesis. In Advances in Smart Nanomaterials and Their Applicatios; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023; pp. 523–568. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).