Detection of Proteus spp. in Artificial Surface Samples and Estimation of the LOD of the Qualitative Microbiological Method †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Artificial Contamination of Surfaces
2.2. Surface Sampling, Isolation and Identification of Proteus spp.
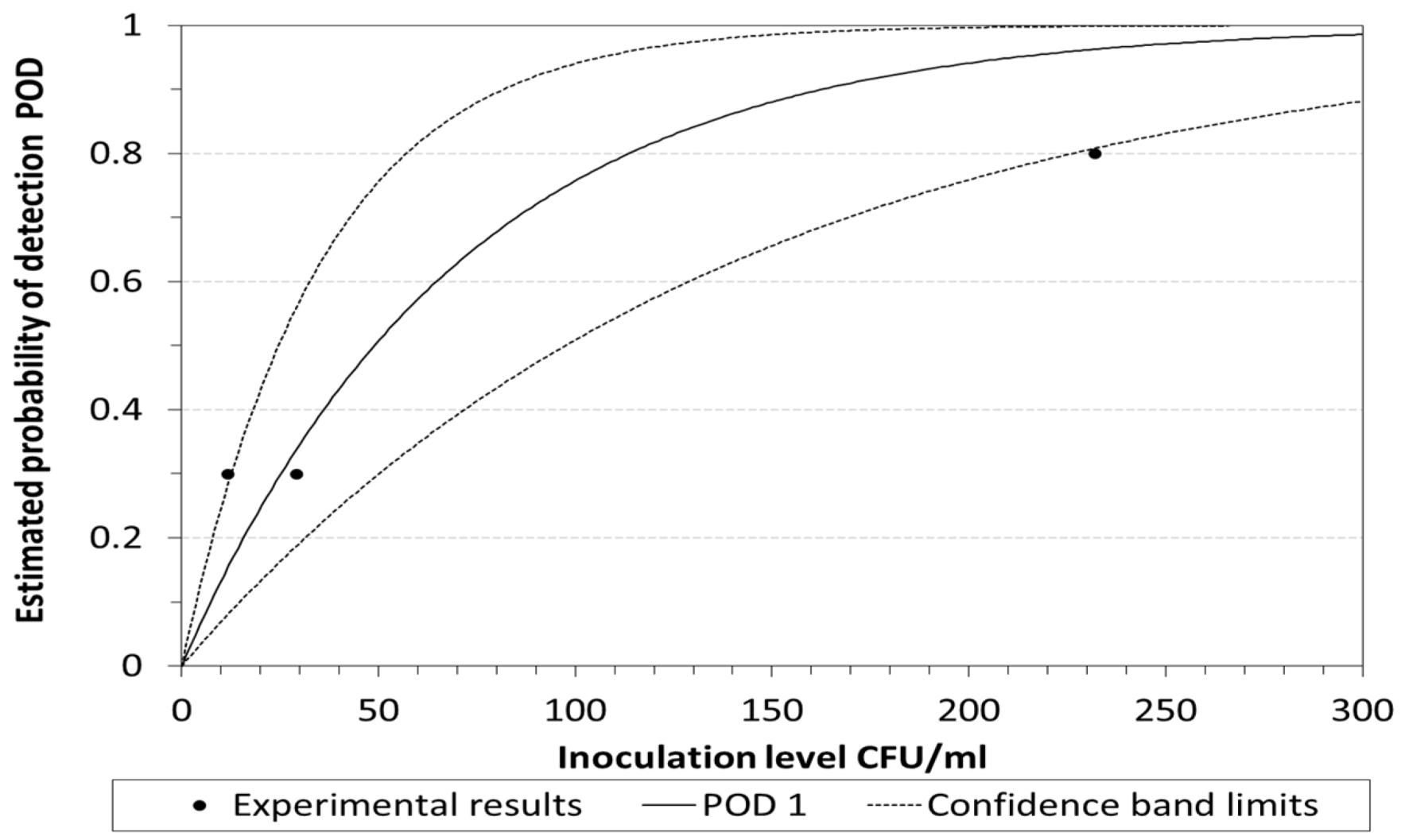
2.3. POD and LOD Calculation
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Drzewiecka, D. Significance and Roles of Proteus spp. Bacteria in Natural Environments. Microbial Ecol. 2016, 72, 741–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Y.; Wang, Y.; Kang, X.; Cai, X. Genomic insights of the emerging human pathogen Proteus appendicitidis sp. nov. Heliyon 2024, 10, e37114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozlovska, G. Bioecology and pathogenicity of Proteus bacteria: A literature review. Ukr. J. Vet. Sci. 2023, 14, 91–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prywer, J.; Olszynski, M. Bacterially induced formation of infectious urinary stones: Recent developments and future challenges. Curr. Med. Chem. 2017, 24, 292–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Kubaisi, M.S.; Al-Deri, A.H. Isolation of Proteus spp. bacterial pathogens from raw minced meat in Alkarkh area, Baghdad provelance. Int. J. Health Sci. 2022, 6, 4196–4204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Joossens, M.; Van den Abeele, A.-M.; Kerkhof, P.-J.; Houf, K. Isolation, characterization and antibiotic resistance of Proteus mirabilis from Belgian broiler carcasses at retail and human stool. Food Microbiol. 2021, 96, 103724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Yu, J.; Zhang, H.; Yuan, Z.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, Y.; Song, H. An outbreak of Proteus mirabilis food poisoning associated with eating stewed pork balls in brown sauce, Beijing. Food Control 2010, 21, 302–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.Q.; Han, Y.Y.; Zhou, L.; Peng, W.Q.; Mao, L.Y.; Yang, X.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, T.J.; Wang, H.N.; Lei, C.W. Contamination of Proteus mirabilis harbouring various clinically important antimicrobial resistance genes in retail meat and aquatic products from food markets in China. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 16, 1086800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanches, M.S.; Baptista, A.A.S.; de Souza, M.; Menck-Costa, M.F.; Koga, V.L.; Kobayashi, R.K.T.; Rocha, S.P.D. Genotypic and phenotypic profiles of virulence factors and antimicrobial resistance of Proteus mirabilis isolated from chicken carcasses: Potential zoonotic risk. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2019, 50, 685–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Pan, X. Bacteria: Proteus. In Encyclopedia of Food Safety; Motarjemi, Y., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2014; pp. 486–489. [Google Scholar]
- Butucel, E.; Balta, I.; Ahmadi, M.; Dumitrescu, G.; Morariu, F.; Pet, I.; Stef, L.; Corcionivoschi, N. Biocides as Biomedicines against Foodborne Pathogenic Bacteria. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 4833-1; Microbiology of the Food Chain. Horizontal Methods for Enumeration of Microorganisms. Part 1: Colony Count at 30 °C by the Pour Plate Technique. ISO—International Organisation for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2013.
- ISO 18593; Microbiology of the Food Chain. Horizontal Methods for Surface Sampling. ISO—International Organisation for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018.
- POD LOD, Version 12, 2024-03-05, according to Wilrich, C.; Wilrich, P.-T. Estimation of the POD function and LOD of a qualitative microbiological measurement method. J. AOAC Int. 2009, 92, 1763–1772. Available online: https://www.statistics-wilrich.info (accessed on 14 February 2025).
- Wilrich, C.; Wilrich, P.-T. Estimation of the POD function and LOD of a qualitative microbiological measurement method. J. AOAC Int. 2009, 92, 1763–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nissanka, M.C.; Weerasekera, M.; Dilhari, A. Optimization of NaCl Concentration in a General Purpose Medium to Inhibit the Swarming Motility of Proteus mirabilis. In Proceedings of the International Research Symposium of the Faculty of Allied Health Sciences, Galle, Sri Lanka, 10 November 2023; p. 72. [Google Scholar]
- Ostwal, K.; Shah, P.; Rebecca, L.; Shaikh, N.; Inole, K. A tale of two novel Proteus species—Proteus hauseri and Proteus penneri. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. Appl. Sci. 2016, 5, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Różalski, A.; Torzewska, A.; Moryl, M.; Kwil, I.; Maszewska, A.; Ostrowska, K.; Drzewiecka, D.; Zablotni, A.; Palusiak, A.; Siwinska, M.; et al. Proteus sp.—An opportunistic bacterial pathogen—Classification, swarming growth, clinical significance and virulence factors. Acta Univ. Lodz. Folia Biol. Oecolog. 2012, 8, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishore, J. Isolation, identification & characterization of Proteus penneri—A missed rare pathogen. Indian J. Med. Res. 2012, 135, 341–345. [Google Scholar]
- Muñoz-Criado, S.; Muñoz-Bellido, J.L.; Alonso-Manzanares, M.A.; Gutiérrez-Zufiaurre, M.N.; García-Rodríguez, J.A. Psychotropic drugs inhibit swarming in Proteus spp. and related genera. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 1998, 4, 447–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Hara, C.M.; Brenner, F.W.; Steigerwalt, A.G.; Hill, B.C.; Holmes, B.; Grimont, P.A.; Hawkey, P.M.; Penner, J.L.; Miller, J.M.; Brenner, D.J. Classification of Proteus vulgaris biogroup 3 with recognition of Proteus hauseri sp. nov., nom. rev. and unnamed Proteus genomospecies 4, 5 and 6. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2000, 50, 1869–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, H.; Wang, Y.; Fang, Y.; Huang, Z.; Kan, B.; Wang, D. Proteus alimentorum sp. nov., isolated from pork and lobster in Ma’anshan city, China. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2018, 68, 1390–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Zhang, Z.; Qu, H.; Chen, G.; Zhou, J.; Zhou, W.; Peng, Y.; Cai, X. Proteus appendicitidis sp. nov., isolated from the appendiceal pus of an appendicitis patient in Yongzhou, China. Arch. Microbiol. 2024, 206, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, H.; Chen, A.; Wang, Y.; Lu, B.; Wang, Y.; Chen, J.; Huang, Y.; Li, Z.; Fang, Y.; Xiao, T.; et al. Proteus faecis sp. nov., and Proteus cibi sp. nov., two new species isolated from food and clinical samples in China. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2019, 69, 852–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, H.; Wang, Y.; Fang, Y.; Xiao, T.; Huang, Z.; Kan, B.; Wang, D. Proteus columbae sp. nov., isolated from a pigeon in Ma’anshan, China. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2018, 68, 552–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jansson, L.; Akel, Y.; Eriksson, R.; Lavander, M.; Hedman, J. Impact of swab material on microbial surface sampling. J. Microbiol. Methods 2020, 176, 106006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keeratipibul, S.; Laovittayanurak, T.; Pornruangsarp, O.; Chaturongkasumrit, Y.; Takahashi, H.; Techaruvichit, P. Effect of swabbing techniques on the efficiency of bacterial recovery from food contact surfaces. Food Control 2017, 77, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Đurđević-Milošević, D.; Petrović, A.; Ncube, T.; Gagula, G. Surface swab sampling and recovery of Escherichia coli. In Proceedings of the Scientific Conference SANUS 2023, Prijedor, Bosnia and Herzegovina, 23–24 June 2023; pp. 271–279. [Google Scholar]
- Facciolà, A.; Gioffrè, M.E.; Chiera, D.; Ferlazzo, M.; Virgà, A.; Laganà, P. Evaluation of antibiotic resistance in Proteus spp: A growing trend that worries Public Health. Results of 10 Years of Analysis. New Microbiol. 2022, 45, 269–277. [Google Scholar]
- Ghamdi, A.; Zabermawi, N.; Mohamed Aly, M. Biofilm formation of foodborne pathogens and strategies of its prevention and biocontrol: A review. Appl. Food Biotechnol. 2025, 12, 1–8.e4. [Google Scholar]
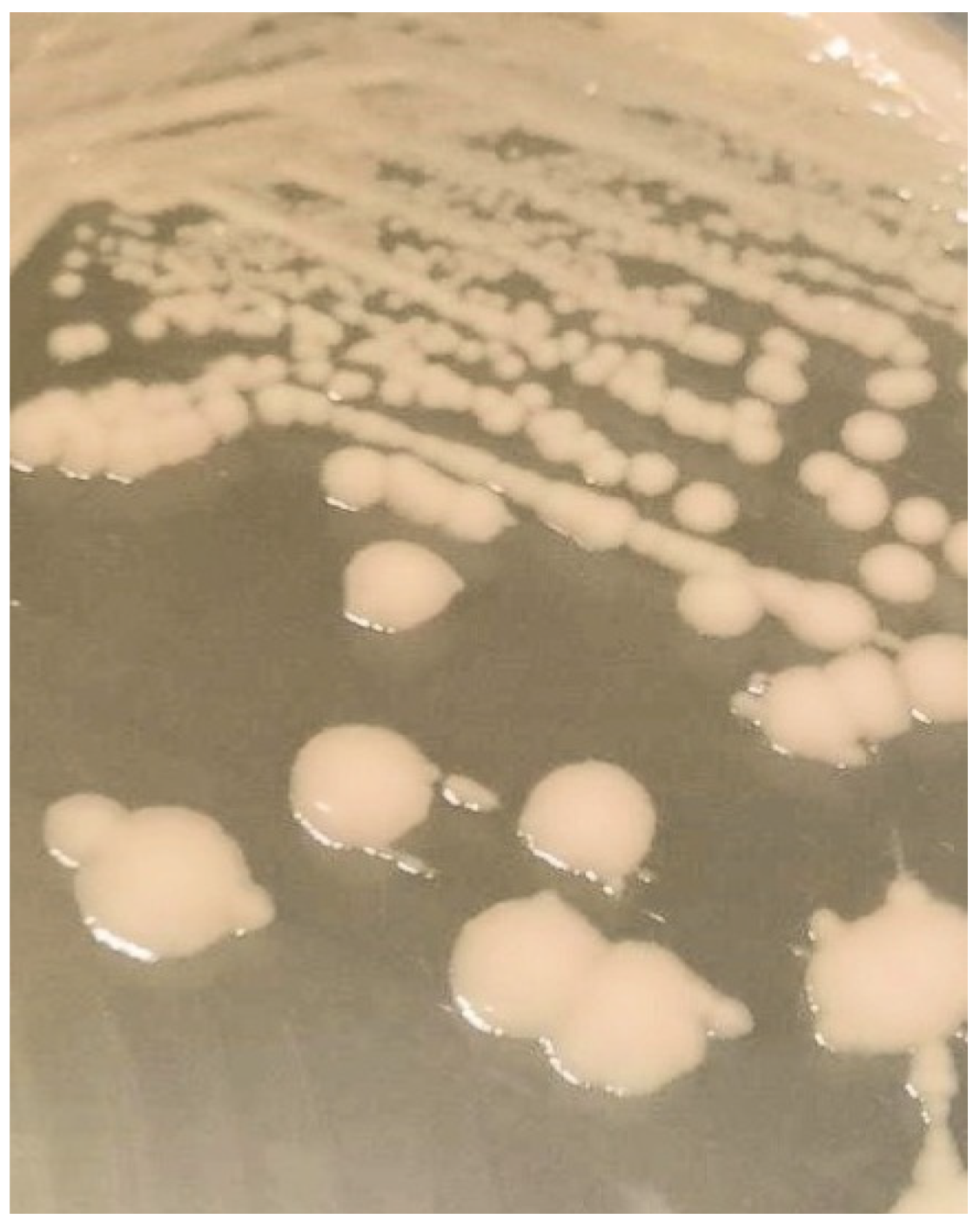
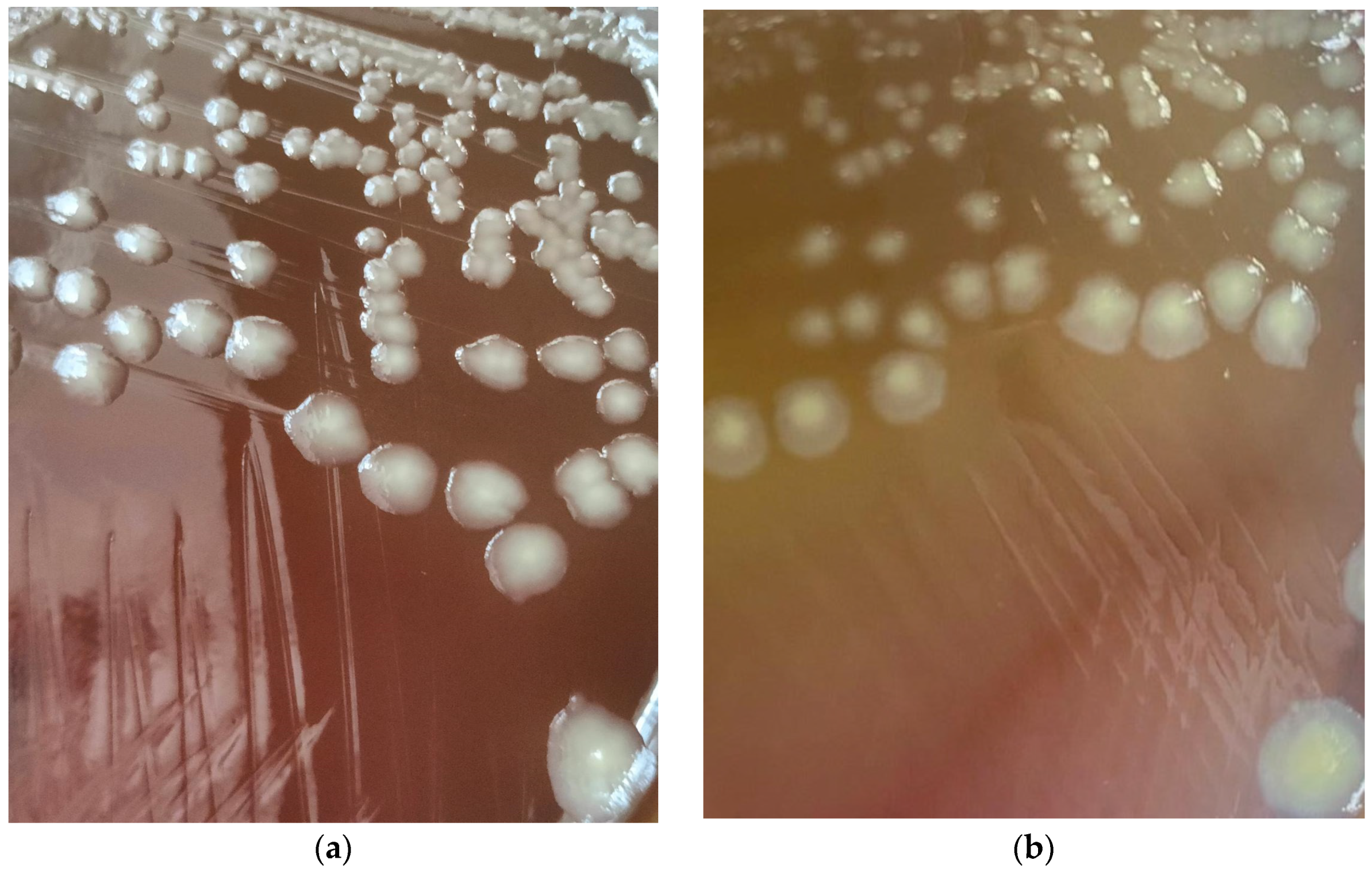
| Level of Surface Artificial Contamination | Estimated Artificial Surface Contamination (CFU/25 cm2) | Estimated Artificial Surface Contamination (CFU/cm2) | Number of Tested Surfaces | Number of Surfaces with Detected Proteus hauseri |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blank control | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| I | 290 | 11.6 | 20 | 6 |
| II | 725 | 29 | 10 | 3 |
| III | 5800 | 232 | 5 | 4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Đurđević-Milošević, D.; Petrović, A.; Elez, J.; Kalaba, V.; Gagula, G. Detection of Proteus spp. in Artificial Surface Samples and Estimation of the LOD of the Qualitative Microbiological Method. Eng. Proc. 2025, 87, 83. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2025087083
Đurđević-Milošević D, Petrović A, Elez J, Kalaba V, Gagula G. Detection of Proteus spp. in Artificial Surface Samples and Estimation of the LOD of the Qualitative Microbiological Method. Engineering Proceedings. 2025; 87(1):83. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2025087083
Chicago/Turabian StyleĐurđević-Milošević, Dragica, Andrijana Petrović, Jasmina Elez, Vesna Kalaba, and Goran Gagula. 2025. "Detection of Proteus spp. in Artificial Surface Samples and Estimation of the LOD of the Qualitative Microbiological Method" Engineering Proceedings 87, no. 1: 83. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2025087083
APA StyleĐurđević-Milošević, D., Petrović, A., Elez, J., Kalaba, V., & Gagula, G. (2025). Detection of Proteus spp. in Artificial Surface Samples and Estimation of the LOD of the Qualitative Microbiological Method. Engineering Proceedings, 87(1), 83. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2025087083








