HauBERT: A Transformer Model for Aspect-Based Sentiment Analysis of Hausa-Language Movie Reviews †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Transformer Models in NLP
2.2. NLP for Low-Resource Languages
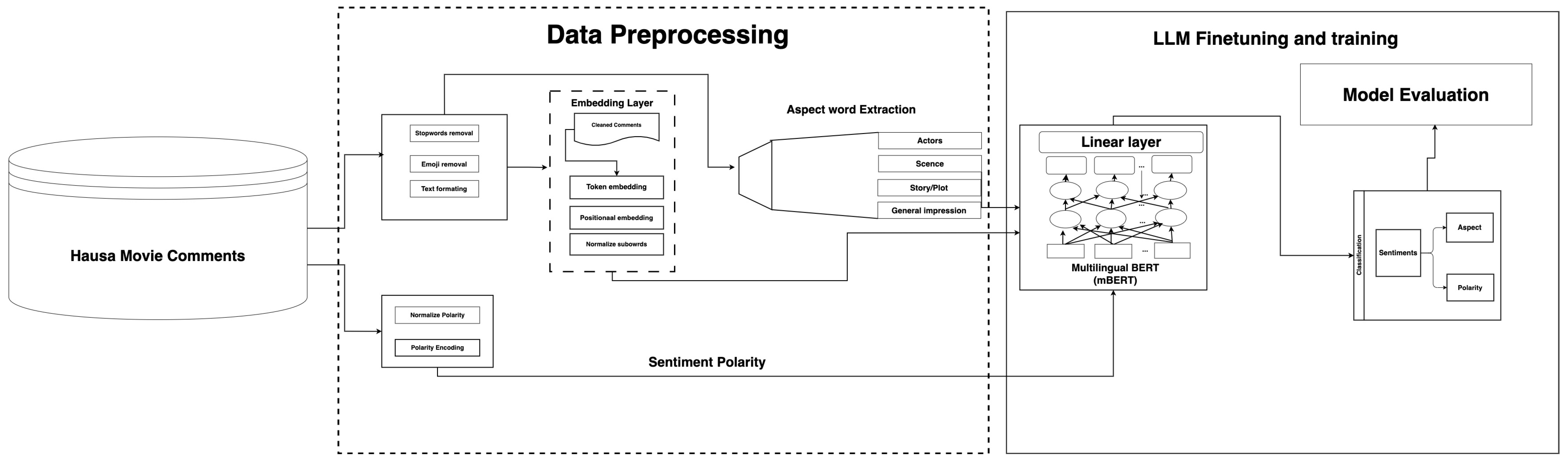
3. Methodology
3.1. Dataset Description
3.2. Dataset Preprocessing and Preparation
Dataset Preparation
3.3. Proposed Model
- Cross-Entropy Loss for Aspect Classification: Computes the loss between the predicted aspect labels and the true labels, encouraging accurate aspect term detection.
- Cross-Entropy Loss for Sentiment Polarity Classification: Calculates the loss for sentiment polarity classification, driving the model to assign correct sentiment polarities to each aspect. The combined loss function is defined as follows:where and are the weights for the aspect and sentiment losses, respectively.
- —The ground truth binary label for the i-th training example, where
- if an aspect is present.
- if an aspect is absent.
- —The predicted probability of the presence of an aspect for the i-th instance.
- N—The total number of training examples.
- —Represents the binary cross-entropy loss, which measures how well the model’s predicted probabilities match the actual labels.
| Algorithm 1 Fine-Tuning mBERT for ABSA in Hausa Language |
Require: Preprocessed dataset with inputs in Hausa; pre-trained mBERT model ; optimizer ; number of epochs E; batch size B; and loss function .
|
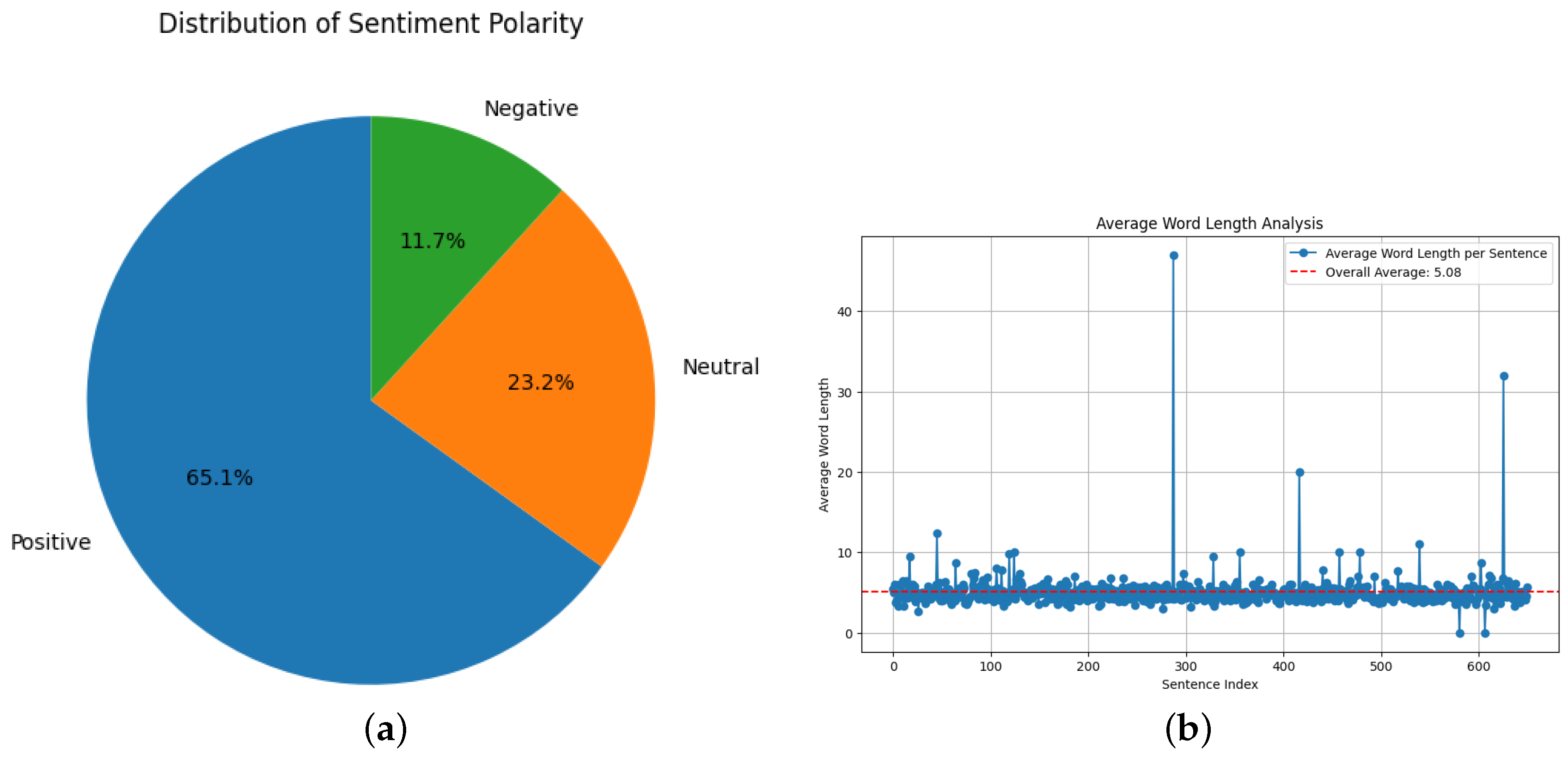
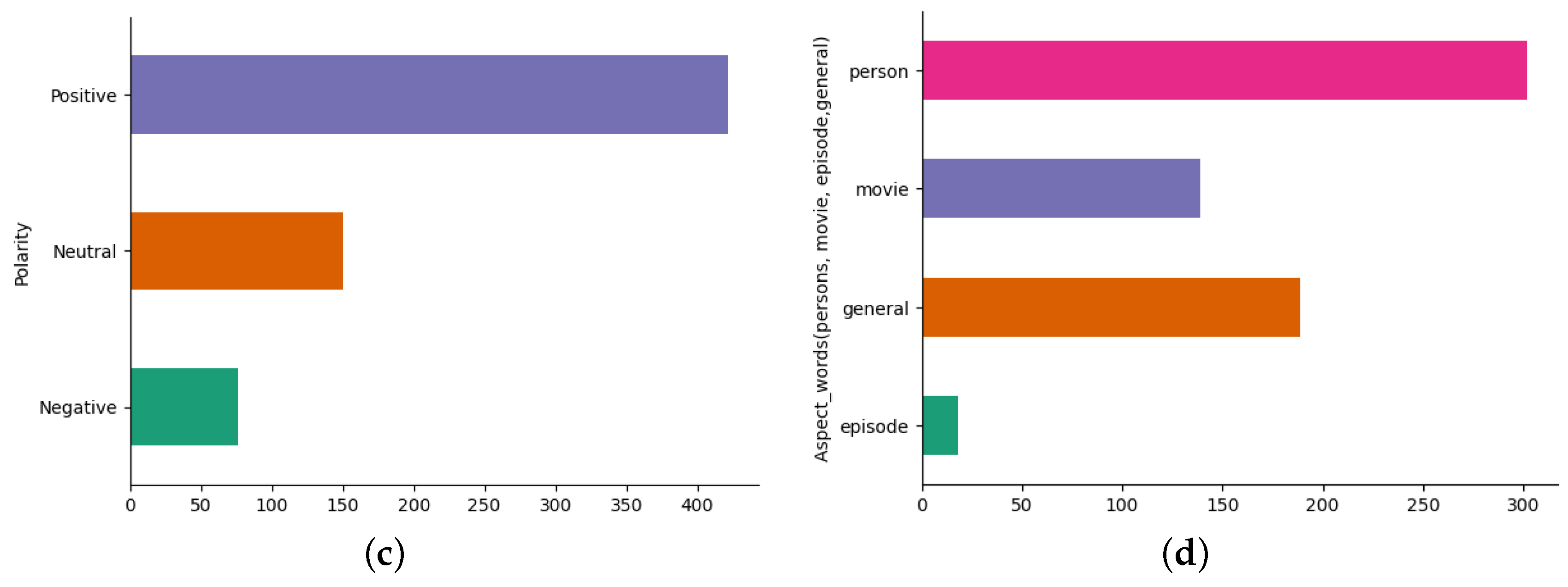
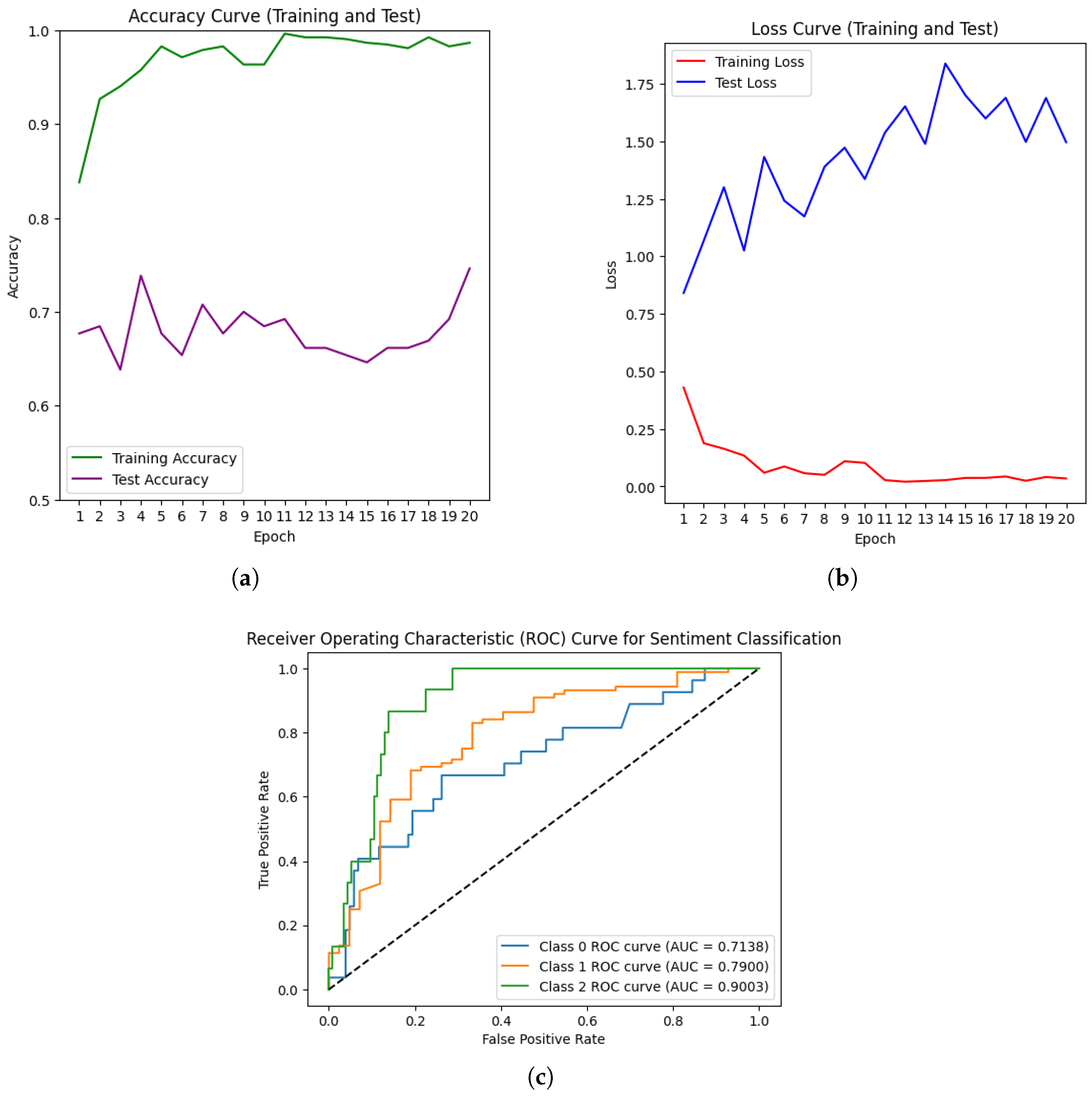
4. Results
4.1. Exploratory Data Analysis
4.2. Experimental Setup and Evaluation Metric
- Aspect Extraction Accuracy: Calculated as the percentage of correctly identified aspect terms.
- Sentiment Polarity Accuracy: Measured as the percentage of correct sentiment predictions for each aspect.
- F1-Score: F1-scores were computed to assess precision and recall for each category in both aspect and sentiment classification tasks.
- True Positive (TP): The model correctly identifies an aspect or assigns the correct sentiment polarity.Example: If the model correctly predicts that “cinematography” is an aspect and assigns it a positive sentiment, this is a TP.
- False Positive (FP): The model incorrectly identifies an aspect or assigns a sentiment when it should not.Example: If the model wrongly predicts “dialogue” as an aspect when it is not annotated as such, this is an FP.
- True Negative (TN): The model correctly ignores a non-aspect term or correctly classifies a sentiment as neutral/absent.Example: If the model does not assign a sentiment label to a word that is not relevant to sentiment analysis, this is a TN.
- False Negative (FN): The model fails to identify an actual aspect or assigns an incorrect sentiment polarity.Example: If the model fails to detect “acting” as an aspect when it is actually present in the dataset, this is an FN.
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abdulrashid, I.; Ahmad, I.S.; Musa, A.; Khalafalla, M. Impact of social media posts’ characteristics on movie performance prior to release: An explainable machine learning approach. Electron. Commer. Res. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuznetsov, I.; Afzal, O.M.; Dercksen, K.; Dycke, N.; Goldberg, A.; Hope, T.; Hovy, D.; Kummerfeld, J.K.; Lauscher, A.; Leyton-Brown, K.; et al. What can natural language processing do for peer review? arXiv 2024, arXiv:2405.06563. [Google Scholar]
- Medhat, W.; Hassan, A.; Korashy, H. Sentiment analysis algorithms and applications: A survey. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2014, 5, 1093–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wankhade, M.; Rao, A.C.S.; Kulkarni, C. A survey on sentiment analysis methods, applications, and challenges. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2022, 55, 5731–5780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, U.; Zandam, A.Y.; Adam, F.M.; Musa, A. A Deep Convolutional Neural Network-based Model for Aspect and Polarity Classification in Hausa Movie Reviews. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2405.19575. [Google Scholar]
- Sultana, N.; Sultana, R.; Rasel, R.I.; Hoque, M.M. Aspect-based sentiment analysis of bangla comments on entertainment domain. In Proceedings of the 2022 25th International Conference on Computer and Information Technology (ICCIT), Cox’s Bazar, Bangladesh, 17–19 December 2022; pp. 953–958. [Google Scholar]
- Baid, P.; Gupta, A.; Chaplot, N. Sentiment analysis of movie reviews using machine learning techniques. Int. J. Comput. Appl. 2017, 179, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuh, R. Hausa Language Variation and Dialects; University of California: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Schouten, K.; Frasincar, F. Survey on aspect-level sentiment analysis. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2015, 28, 813–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanaja, S.; Belwal, M. Aspect-level sentiment analysis on e-commerce data. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Inventive Research in Computing Applications (ICIRCA), Coimbatore, India, 11–12 July 2018; pp. 1275–1279. [Google Scholar]
- Siddiqua, A.; Bindumathi, V.; Raghu, G.; Bhargav, Y. Aspect-based Sentiment Analysis (ABSA) using Machine Learning Algorithms. In Proceedings of the 2024 Third International Conference on Distributed Computing and Electrical Circuits and Electronics (ICDCECE), Ballari, India, 26–27 April 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandal, N.; Tanwar, R.; Pruthi, J. Machine learning based aspect level sentiment analysis for Amazon products. Spat. Inf. Res. 2020, 28, 601–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pontiki, M.; Galanis, D.; Papageorgiou, H.; Androutsopoulos, I.; Manandhar, S.; Al-Smadi, M.; Al-Ayyoub, M.; Zhao, Y.; Qin, B.; De Clercq, O.; et al. Semeval-2016 task 5: Aspect based sentiment analysis. In Proceedings of the International Workshop on Semantic Evaluation, San Diego, CA, USA, 16–17 June 2016; pp. 19–30. [Google Scholar]
- Regi, A.E.; Leelipushpam, G.J. Enhancing Aspect Based Sentiment Analysis Using BERT and Capsule Networks. In Proceedings of the 2024 2nd International Conference on Device Intelligence, Computing and Communication Technologies (DICCT), Dehradun, India, 15–16 March 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharathi, R.; Bhavani, R.; Priya, R. Leveraging Deep Learning Models for Automated Aspect Based Sentiment Analysis and Classification. SSRG Int. J. Electr. Electron. Eng. 2023, 10, 120–130. [Google Scholar]
- Vinitha, V.; Bargavi, S.M. A Intensified Approach on Aspect Based Sentiment Analysis Using Pre-Trained Deep Learning Model. In Proceedings of the 2024 International Conference on Recent Advances in Electrical, Electronics, Ubiquitous Communication, and Computational Intelligence (RAEEUCCI), Chennai, India, 17–18 April 2024; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, D.; Gupta, A.; Gupta, V.K.; Gupta, A. Aspect-Based Sentiment Analysis using Machine Learning and Deep Learning Approaches. Int. J. Recent Innov. Trends Comput. Commun. 2023, 11, 118–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Peng, H.; Cambria, E. Targeted aspect-based sentiment analysis via embedding commonsense knowledge into an attentive LSTM. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New Orleans, LA, USA, 2–7 February 2018; Volume 32. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, C.; Huang, L.; Qiu, X. Utilizing BERT for aspect-based sentiment analysis via constructing auxiliary sentence. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1903.09588. [Google Scholar]
- Zvarevashe, K.; Olugbara, O.O. Gender voice recognition using random forest recursive feature elimination with gradient boosting machines. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Advances in Big Data, Computing and Data Communication Systems (icABCD), Durban, South Africa, 6–7 August 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Ramírez-Tinoco, F.J.; Alor-Hernández, G.; Sánchez-Cervantes, J.L.; Salas-Zárate, M.d.P.; Valencia-García, R. Use of sentiment analysis techniques in healthcare domain. In Current Trends in Semantic Web Technologies: Theory and Practice; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 189–212. [Google Scholar]
- Alsaeedi, A.; Khan, M.Z. A study on sentiment analysis techniques of Twitter data. Int. J. Adv. Comput. Sci. Appl. 2019, 10, 361–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, Z.; Yang, E.; Li, D.D.U.; Butler, S.; Ijomah, W.; Li, X.; Zhou, H. Deep convolution network based emotion analysis towards mental health care. Neurocomputing 2020, 388, 212–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, E.; Kang, J.; Choi, D.; Han, J. Understanding customers’ hotel revisiting behaviour: A sentiment analysis of online feedback reviews. Curr. Issues Tour. 2020, 23, 605–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortis, K.; Davis, B. Over a decade of social opinion mining: A systematic review. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2021, 54, 4873–4965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, A.; Chakraborty, P.; Bhatia, M.; Mittal, P. Role of emotion in excessive use of Twitter during COVID-19 imposed lockdown in India. J. Technol. Behav. Sci. 2021, 6, 370–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bashar, M.A.; Nayak, R.; Balasubramaniam, T. Deep learning based topic and sentiment analysis: COVID19 information seeking on social media. Soc. Netw. Anal. Min. 2022, 12, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaturvedi, S.; Mishra, V.; Mishra, N. Sentiment analysis using machine learning for business intelligence. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Power, Control, Signals and Instrumentation Engineering (ICPCSI), Chennai, India, 21–22 September 2017; pp. 2162–2166. [Google Scholar]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, L.; Polosukhin, I. Attention Is All You Need (NIPS 2017). arXiv 2017, arXiv:1706.03762. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Z.; Xu, P.; Liang, D.; Mishra, A.; Xiang, B. TRANS-BLSTM: Transformer with bidirectional LSTM for language understanding. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2003.07000. [Google Scholar]
- Yulianti, E.; Nissa, N.K. ABSA of Indonesian customer reviews using IndoBERT: Single-sentence and sentence-pair classification approaches. Bull. Electr. Eng. Inform. 2024, 13, 3579–3589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Mayhew, S.; Roth, D. Extending multilingual BERT to low-resource languages. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2004.13640. [Google Scholar]
- Devlin, J.; Chang, M.W.; Lee, K.; Toutanova, K. Bert: Pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding. In Proceedings of the 2019 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 2–7 June 2019; Volume 1, p. 2. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Ott, M.; Goyal, N.; Du, J.; Joshi, M.; Chen, D.; Levy, O.; Lewis, M.; Zettlemoyer, L.; Stoyanov, V. RoBERTa: A Robustly Optimized BERT Pretraining Approach. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1907.11692. [Google Scholar]
- Sanh, V.; Debut, L.; Chaumond, J.; Wolf, T. DistilBERT, a distilled version of BERT: Smaller, faster, cheaper and lighter. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1910.01108. [Google Scholar]
- Conneau, A.; Khandelwal, K.; Goyal, N.; Chaudhary, V.; Wenzek, G.; Guzmán, F.; Grave, E.; Ott, M.; Zettlemoyer, L.; Stoyanov, V. Unsupervised Cross-lingual Representation Learning at Scale. In Proceedings of the 58th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Online, 5–10 July 2020; pp. 8440–8451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emezue, C.C.; Dossou, B.F. MMTAfrica: Multilingual machine translation for African languages. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2204.04306. [Google Scholar]
- Tonja, A.L.; Dossou, B.F.P.; Ojo, J.; Rajab, J.; Thior, F.; Wairagala, E.P.; Aremu, A.; Moiloa, P.; Abbott, J.; Marivate, V.; et al. InkubaLM: A small language model for low-resource African languages. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2408.17024. [Google Scholar]
- Agic, Ž.; Vulic, I. JW300: A Wide-Coverage Parallel Corpus for Low-Resource Languages; Association for Computational Linguistics: Stroudsburg, PA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- da Rocha Junqueira, J.; Lopes, É.; Freitas, L.; Correa, U.B. A Systematic Analysis of Multilingual and Low-Resource Languages Models: A Review on Brazilian Portuguese. In Proceedings of the AMCIS 2024 Proceedings, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 15–17 August 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Nekoto, W.; Marivate, V.; Matsila, T.; Fasubaa, T.; Kolawole, T.; Fagbohungbe, T.; Akinola, S.O.; Muhammad, S.H.; Kabongo, S.; Osei, S.; et al. Participatory research for low-resourced machine translation: A case study in african languages. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2010.02353. [Google Scholar]
- Leong, C.; Shandilya, H.; Dossou, B.F.; Tonja, A.L.; Mathew, J.; Omotayo, A.H.; Yousuf, O.; Akinjobi, Z.; Emezue, C.C.; Muhammad, S.; et al. Adapting to the low-resource double-bind: Investigating low-compute methods on low-resource African languages. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2303.16985. [Google Scholar]
- Adelani, D.I.; Abbott, J.; Neubig, G.; D’souza, D.; Kreutzer, J.; Lignos, C.; Palen-Michel, C.; Buzaaba, H.; Rijhwani, S.; Ruder, S.; et al. MasakhaNER: Named entity recognition for African languages. Trans. Assoc. Comput. Linguist. 2021, 9, 1116–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedderich, M.A. Weak Supervision and Label Noise Handling for Natural Language Processing in Low-Resource Scenarios. Ph.D. Thesis, Saarland University, Saarland, Germany, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oladipo, A.; Ogundepo, O.; Ogueji, K.; Lin, J. An exploration of vocabulary size and transfer effects in multilingual language models for African languages. In Proceedings of the 3rd Workshop on African Natural Language Processing, Virtual Event, 13–16 October 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Alabi, J.O.; Adelani, D.I.; Mosbach, M.; Klakow, D. Adapting pre-trained language models to African languages via multilingual adaptive fine-tuning. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2204.06487. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, G.L.; Mswahili, M.E.; Jeong, Y.S. Sentiment classification in swahili language using multilingual bert. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2104.09006. [Google Scholar]
- Salih Noorain, A.A.; Mohammed Daud, M.D. Semantic Concepts of Hausa Language: An Analytical and Descriptive Study at the Level of Words. Alustath 2023, 62, 386–401. [Google Scholar]
- Abdulmumin, I.; Galadanci, B.S. hauwe: Hausa words embedding for natural language processing. In Proceedings of the 2019 2nd International Conference of the IEEE Nigeria Computer Chapter (NigeriaComputConf), Zaria, Nigeria, 14–17 October 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Denny, P.; Taskova, K.; Wicker, J.; Taskova, K. A Systematic Review of Aspect-based Sentiment Analysis (ABSA): Domains, Methods, and Trends. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2311.10777. [Google Scholar]
- Chouikhi, H.; Chniter, H.; Jarray, F. Arabic sentiment analysis using BERT model. In Proceedings of the Advances in Computational Collective Intelligence: 13th International Conference (ICCCI 2021), Kallithea, Greece, 29 September–1 October 2021; Proceedings 13. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 621–632. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, Q.T.; Nguyen, T.L.; Luong, N.H.; Ngo, Q.H. Fine-tuning BERT for sentiment analysis of Vietnamese reviews. In Proceedings of the 2020 7th NAFOSTED Conference on Information and Computer Science (NICS), Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam, 26–27 November 2020; pp. 302–307. [Google Scholar]
- Hoang, M.; Bihorac, O.A.; Rouces, J. Aspect-based sentiment analysis using bert. In Proceedings of the 22nd Nordic Conference on Computational Linguistics, Turku, Finland, 30 September–2 October 2019; pp. 187–196. [Google Scholar]
- Prottasha, N.J.; Sami, A.A.; Kowsher, M.; Murad, S.A.; Bairagi, A.K.; Masud, M.; Baz, M. Transfer learning for sentiment analysis using BERT based supervised fine-tuning. Sensors 2022, 22, 4157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Regatte, Y.R.; Gangula, R.R.R.; Mamidi, R. Dataset Creation and Evaluation of Aspect Based Sentiment Analysis in Telugu, a Low Resource Language. In Proceedings of the Twelfth Language Resources and Evaluation Conference, Marseille, France, 11–16 May 2020; pp. 5017–5024. [Google Scholar]
- Chifu, A.G.; Fournier, S. Linguistic features for sentence difficulty prediction in ABSA. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2402.03163. [Google Scholar]

| Original Hausa Sentence | Tokenized input_ids | Attention Mask |
|---|---|---|
| Fim din yana da kyau. | [101, 4035, 2176, 3693, 2099, 102, 0, 0] | [1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0] |
| Labari bai da ma’ana. | [101, 6784, 2190, 3693, 102, 0, 0, 0] | [1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0] |
| Yan wasan sun yi kokari. | [101, 3157, 2078, 2176, 2099, 102, 0, 0] | [1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0] |
| Sauti yana da matsala. | [101, 4321, 2176, 3693, 102, 0, 0] | [1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0] |
| Hoton fim din yana da kyau. | [101, 7894, 4035, 2176, 3693, 2099, 102, 0] | [1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0] |
| Model | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | F1-Score | AUC-Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HuaBERT Aspect Extraction | 0.96 | 0.93 | 0.93 | 0.91 | 0.94 |
| HauBERT Sentiment model | 0.9281 | 0.9479 | 0.9281 | 0.9082 | 0.9002 |
| Model | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | F1-Score | AUC-Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HauBERT | 0.92 | 0.94 | 0.92 | 0.90 | 0.90 |
| SVM | 0.64 | 0.60 | 0.64 | 0.52 | 0.66 |
| Random Forest | 0.64 | 0.60 | 0.64 | 0.52 | 0.66 |
| Naive Bayes | 0.70 | 0.71 | 0.70 | 0.67 | 0.76 |
| CNN | 0.91 | 0.83 | 0.78 | 0.88 | 0.90 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Musa, A.; Adam, F.M.; Ibrahim, U.; Zandam, A.Y. HauBERT: A Transformer Model for Aspect-Based Sentiment Analysis of Hausa-Language Movie Reviews. Eng. Proc. 2025, 87, 43. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2025087043
Musa A, Adam FM, Ibrahim U, Zandam AY. HauBERT: A Transformer Model for Aspect-Based Sentiment Analysis of Hausa-Language Movie Reviews. Engineering Proceedings. 2025; 87(1):43. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2025087043
Chicago/Turabian StyleMusa, Aminu, Fatima Muhammad Adam, Umar Ibrahim, and Abubakar Yakubu Zandam. 2025. "HauBERT: A Transformer Model for Aspect-Based Sentiment Analysis of Hausa-Language Movie Reviews" Engineering Proceedings 87, no. 1: 43. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2025087043
APA StyleMusa, A., Adam, F. M., Ibrahim, U., & Zandam, A. Y. (2025). HauBERT: A Transformer Model for Aspect-Based Sentiment Analysis of Hausa-Language Movie Reviews. Engineering Proceedings, 87(1), 43. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2025087043








