Abstract
Terahertz (THz) metamaterial absorbers have become a prominent research topic in recent years. In this paper, a hexa-band metamaterial absorber is designed for bio-medical sensing applications. The design can detect changes in the surrounding medium’s refractive index and operates in the refractive index range of 1.3–1.4, with six prominent absorption peaks. The proposed structure comprises a square ring resonator made up of gold with a boss-cross structure at the center, on top of a Gallium Arsenide (GaAs) substrate having a thickness of 8 μm. When the surrounding medium’s refractive index is 1.4, it offers six absorption peaks at 0.537 THz, 2.573 THz, 3.025 THz, 3.146 THz, 3.489 THz, 3.7348 THz, with corresponding peak absorption of 75%, 92.9%, 98.4%, 98.71%, 94.1%, and 99.34%, respectively. The structure has been designed at n = 1.4 instead of n = 1, as several biological specimens, such as blood, breast cells, etc., have refractive index in the range of 1.3–1.4, and it offers 6 bands for n = 1.4. This choice was made because many biomedical applications have a refractive index around 1.4. The design parameters were selected through a parametric analysis, so as to achieve maximum absorption peaks. The design has also been tested with different polarization angles, and it has been discovered that the absorber is polarization-insensitive. This design can inspire future research on the biomedical application of THz absorbers.
1. Introduction
Terahertz metamaterial absorbers (TMAs) specifically cater to applications in the terahertz frequency range. Terahertz radiation lies between microwave and infrared radiation and has unique properties that make it useful for biomedical sensing, spectroscopy, and security screening. The absorption peaks of TMAs can be tailored by modifying the material properties or adjusting the micro-structures, allowing precise control over the absorption spectrum. The versatility and tunability of the TMAs make them an essential tool in advancing terahertz-based technologies and applications. Researchers have developed multi-band, broad-band, and tunable TMAs. Tunable TMAs have absorption characteristics that vary with the surrounding medium’s refractive index, which can assist in bio-medical sensing. In 1994, Landy et al. presented the first metamaterial absorber [1]. Subsequently, absorbers with single, dual, triple, quad, penta, and hepta bands [1,2,3,4,5,6,7]. For detection, absorbers having high FoM can be employed [8,9], and [10]. Numerous investigators have suggested multiband absorbers made by fusing several metallic resonators, that is, in [11], the proposal for quad-band absorbers was made by utilizing four distinct resonator sizes; in [12,13], triple and Dipolar resonance was used to build quad-band absorbers. Changes in refractive index can also be sensed by THz metamaterial absorbers [14]. In order to identify biological substances, this work presents a straightforward design for a TMA-based unit cell that is polarisation insensitive and has three concentric square and two concentric cross-shaped resonators placed onto it. It provides an extremely high and tunable absorption spectra, consisting of six prominent absorption peaks, when the surrounding medium’s refractive index is varied between 1.3 and 1.4, aiding in biomedical sensing applications.
2. Methods and Materials
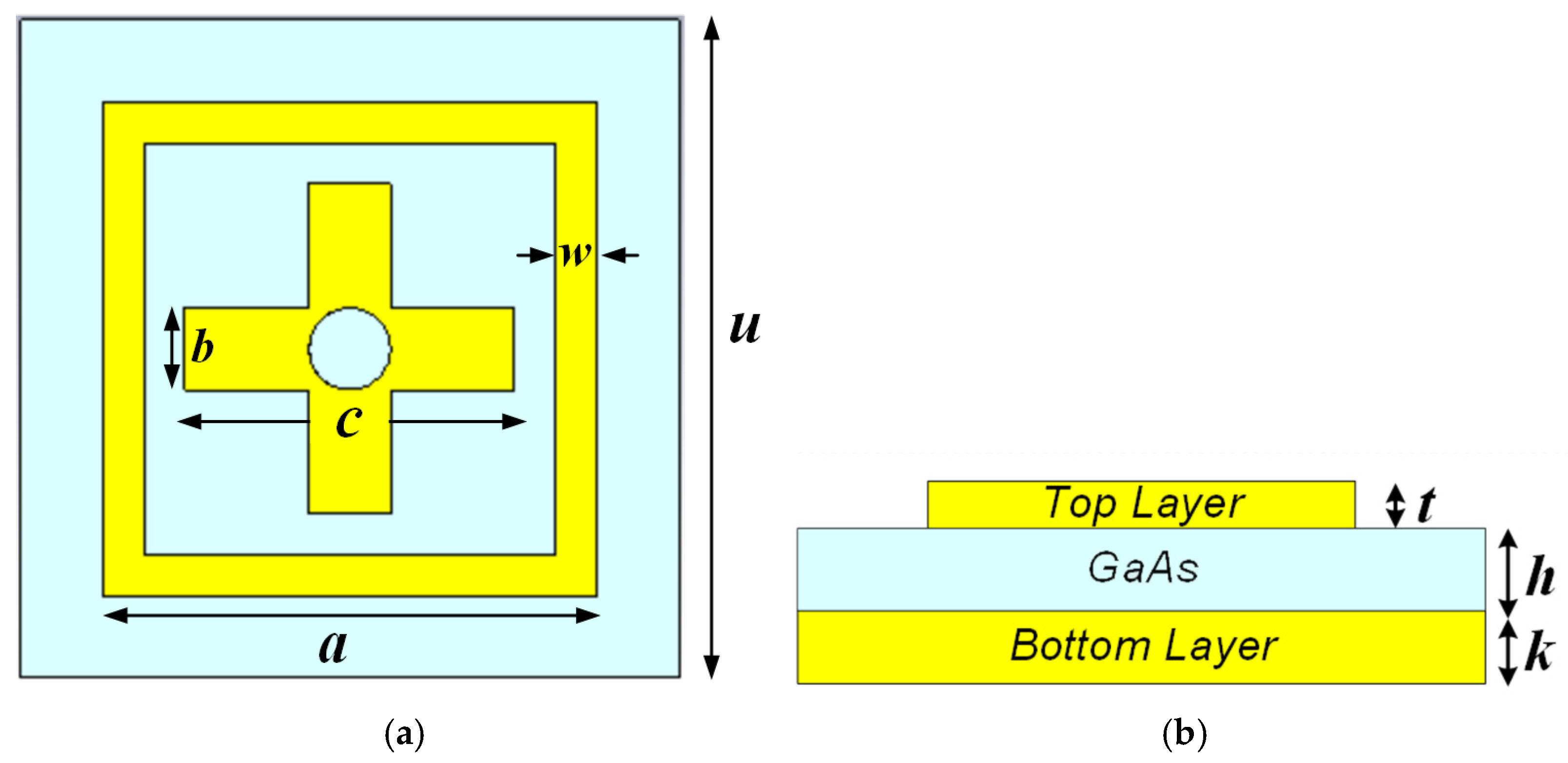
The front aspect of the unit cell design for the suggested terahertz metamaterial absorber is shown in Figure 1. The top and bottom planes of the structure are built of gold because gold has a conductivity of 4.10 × 107 S/m. Due to its broad bandgap and high resistivity, the dielectric spacer built of gallium arsenide (GaAs) has a permittivity of 12.94 and a loss tangent of 0.006. The height of the unit cell is assumed to be h = 8 μm. The upper layer is similarly thick, with 4 μm. The gold-made rear layer’s thickness, k = 7 μm, has been selected to block electromagnetic wave transmission. The unit cell’s length is given by u = 80 μm. The top layer height is of t = 4 μm, the centered length and breadth of the square is a = 60 μm, the inner cross length of the cross is c = 40 μm and cross breath is b = 10 μm respectively and the out radius of the hollow cylinder is w = 5 μm. The table lists the parameters together with their corresponding magnitudes. The sides of the unit cell have been subjected to recurring boundary conditions. When an electromagnetic wave strikes a structure with a negative z-axis, the magnetic and electric field vectors are once again orthogonal.
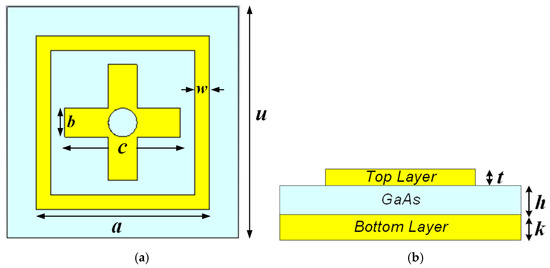
Figure 1.
Proposed structure of metamaterial absorber: (a) top view; (b) side view.
3. Results and Analysis
The numerical simulation and prototype of the structure were created using the CST Microwave Studio. Equation (1) is used to obtain the absorption of the structure:
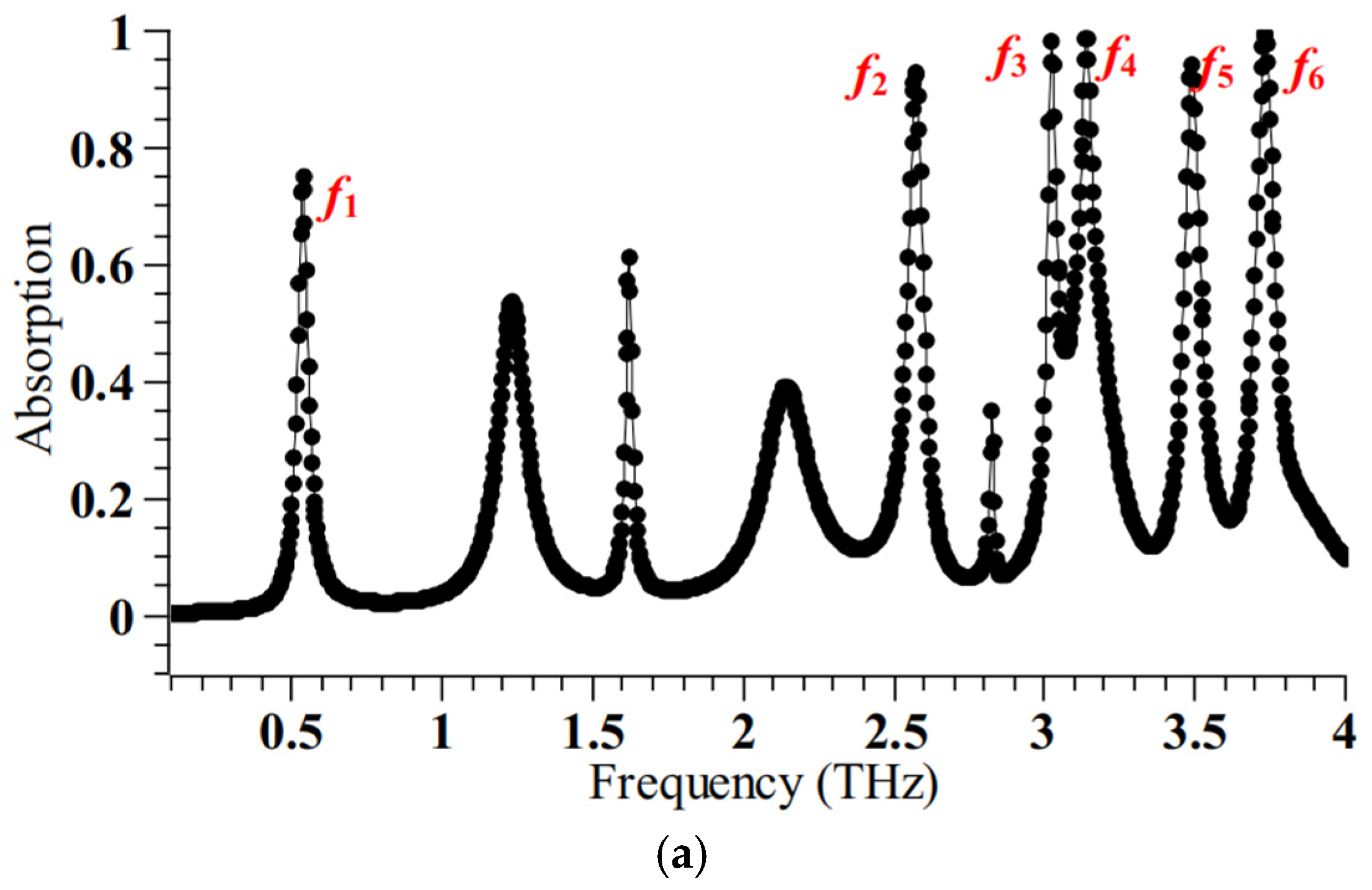
where the absorption, transmission, and reflection coefficients are denoted by A, T, and R, respectively. In order to achieve our primary goal of increasing absorption, we must reduce the transmission and reflection coefficients. The ground metal plate prevents the transmission of electromagnetic waves, hence the transmission coefficient’s magnitude is zero. On the other side, by building the top plane properly, the reflection coefficient may be matched to almost zero. When the surrounding medium’s refractive index (n) is 1.4, the design offers six absorption peaks at 0.537 THz, 2.573 THz, 3.025 THz, 3.142 THz, 3.489 THz, 3.7348 THz, with corresponding peak absorption of 75%, 92.9%, 98.4%, 98.71%, 94.1%, and 99.34%, respectively. The complete absorption spectrum is shown in the Figure 2. Usually, researchers design absorbers considering the refractive index of the surrounding medium to be 1. However, the proposed work considers the refractive index as 1.4. as several biological specimens, such as blood, breast cells, etc., have refractive index in the range of 1.3–1.4.
A = 1 − T − R


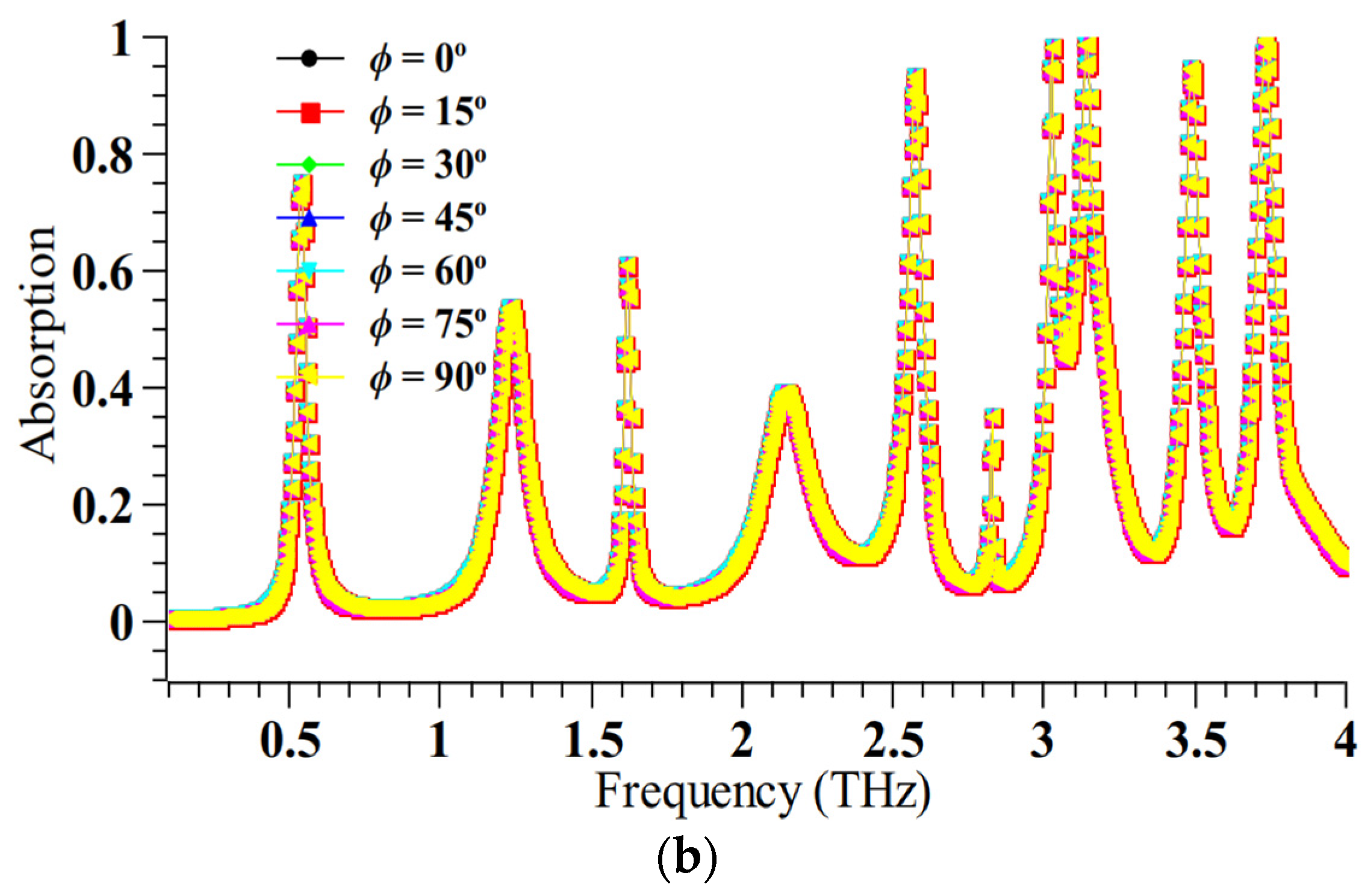
Figure 2.
The absorption spectrum of the metamaterial absorber (a) for polarization angle = 0°; (b) for other polarization angles.
The sensor is found to be entirely polarization-insensitive and the design pattern is symmetrical. Furthermore, to justify the choice of the design parameters a parametric analysis is performed and the results are shown in Figure 3.
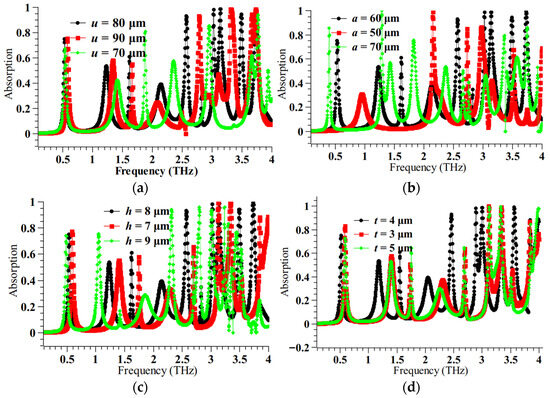
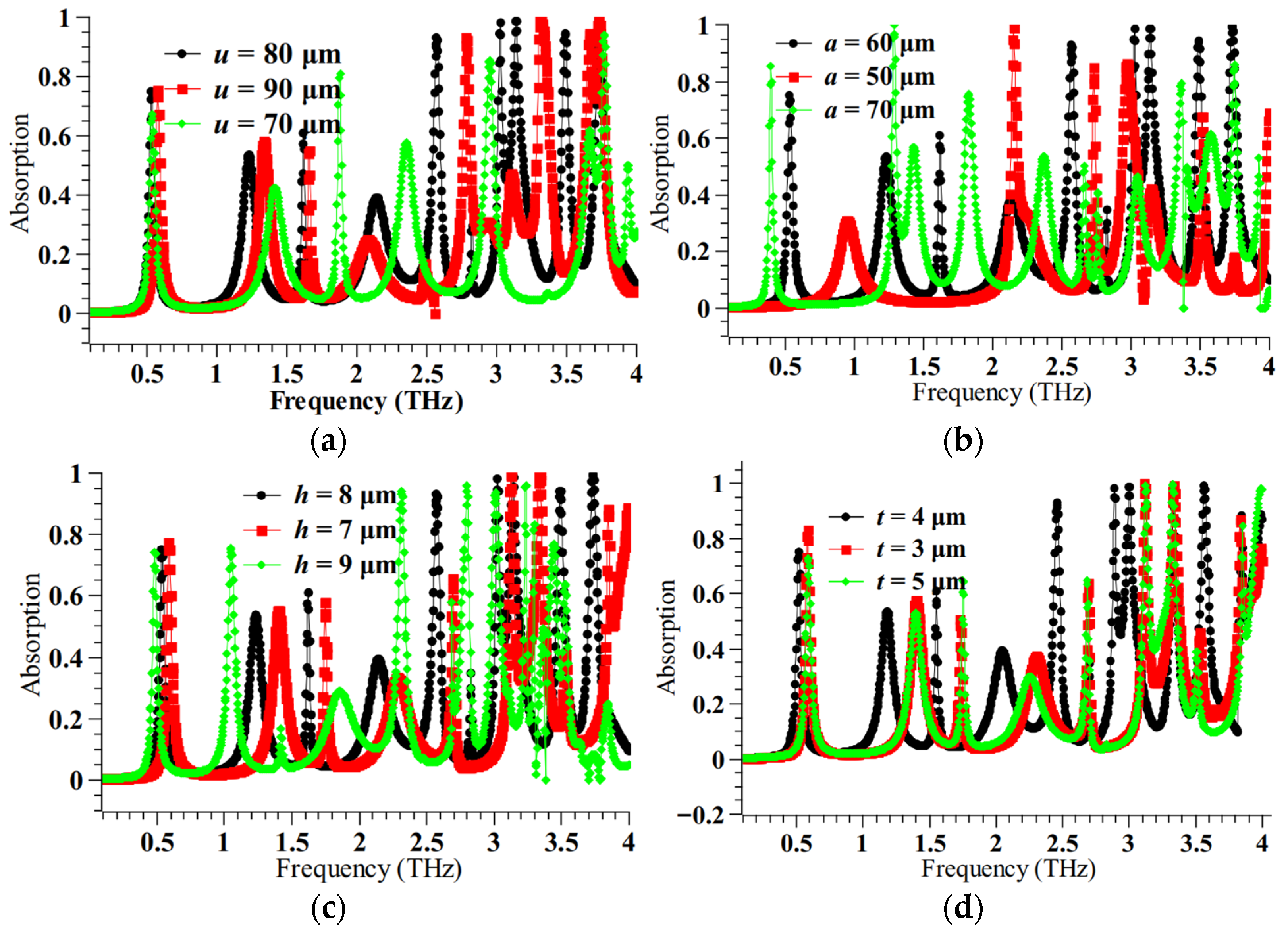
Figure 3.
Parametric analysis for (a) u (b) a (c) h (d) t at n = 1.4.
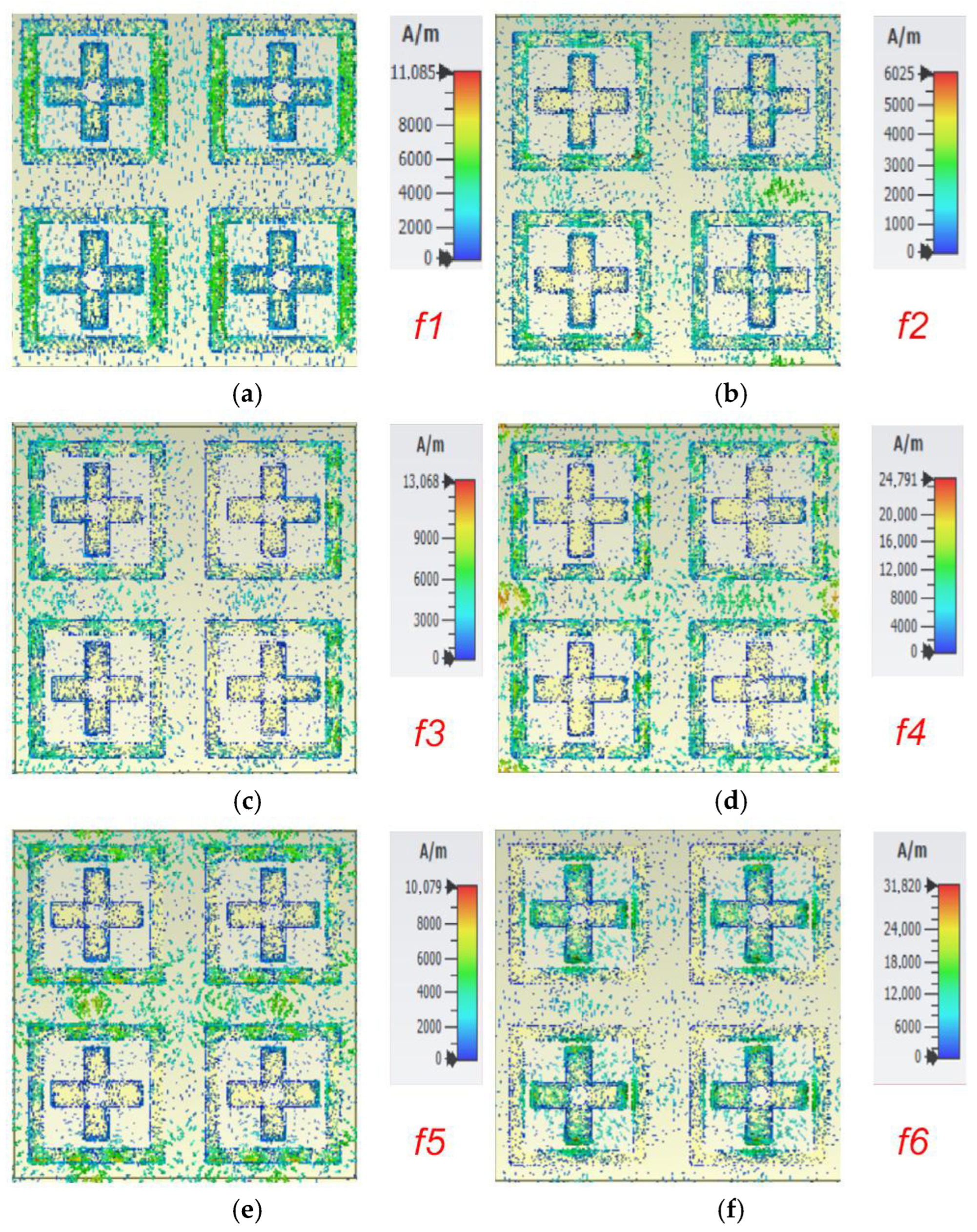
The parametric analysis clearly justifies the choice of design parameters. The best absorption peaks are obtained for u = 80 μm, a = 60 μm, h = 8 μm, and t = 4 μm. For other values, the absorption peaks are either diminished or reduced in number. To further understand the resonance phenomena, the surface current distribution plot is obtained and is shown in Figure 4. Because of the characteristic current distribution, which is a spiral oscillating current, magnetic field resonance is produced, which is responsible for this absorption process.
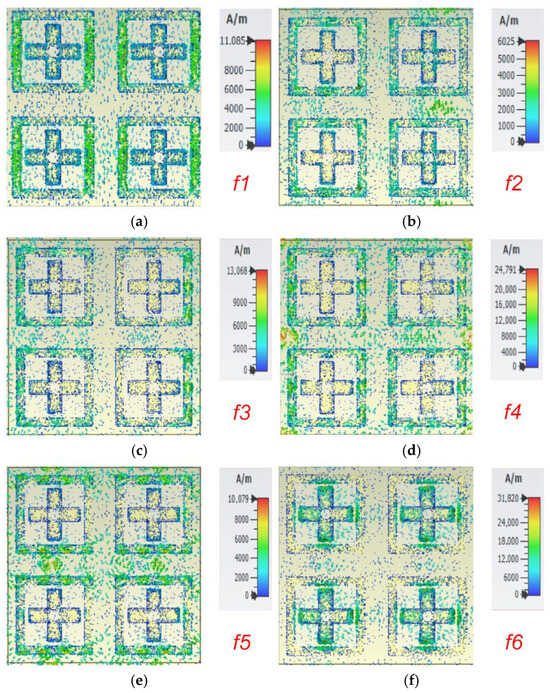
Figure 4.
Distribution of surface current (a) at f1; (b) at f2; (c) at f3; (d) at f4; (e) at f5 (f) at f6.
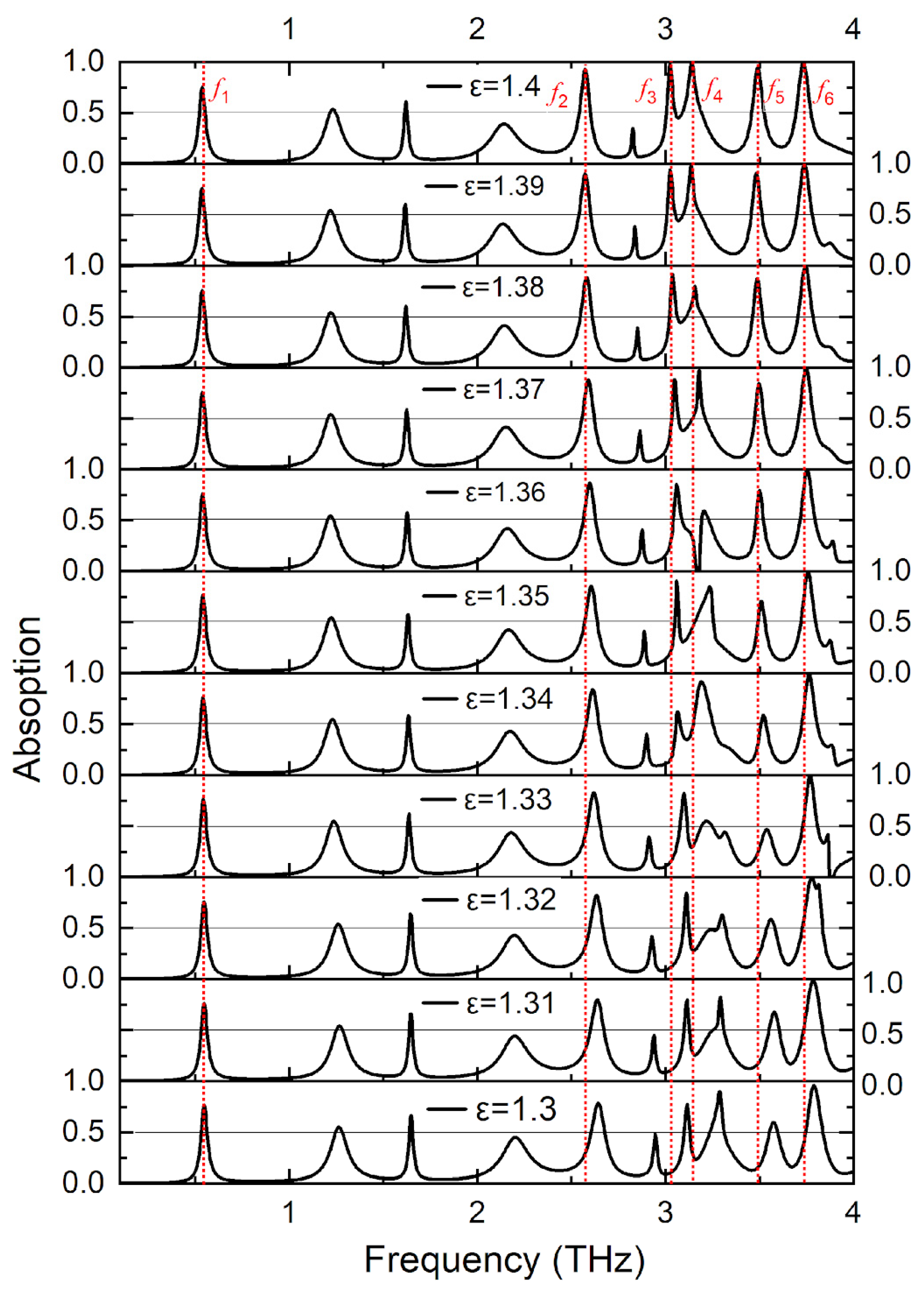
The absorption spectra of the proposed sensor with respect to the changes in the refractive index of the surrounding medium as shown in Figure 5. The peaks of the absorption spectra are also found to vary significantly for a little change in the surrounding medium’s refractive index, demonstrating the effectiveness of the proposed device as a refractive index sensor. The refractive index is varied between n = 1.3 to n = 1.39 with an interval of 0.01 in order to cater to various biomedical sensing applications. This range is chosen because the refractive index of many biological specimens fall in this range. For example, healthy adult blood is around 1.376, while cancerous blood cells have a refractive index of 1.39 [6]. Other cells in our body, such as basal cells, exhibit different refractive indices, which also fall within the range. It can be observed from the figure that the resonance frequency drops when the material’s refractive index increases and vice versa. The plot of resonance frequency vs. refractive indices, from which the value for sensitivity is derived is shown in Figure 4. Also, from these plots the sensitivity (S) of the proposed sensor in different frequency bands is measured. Sensitivity is the measure of the sensor’s ability to sense the changes in the refractive index of the surrounding medium, and is calculated as the shift in resonance frequency per unit change in refractive index, given by Equation (2):

Figure 5.
Spectrum of Absorption for different refractive indexes.
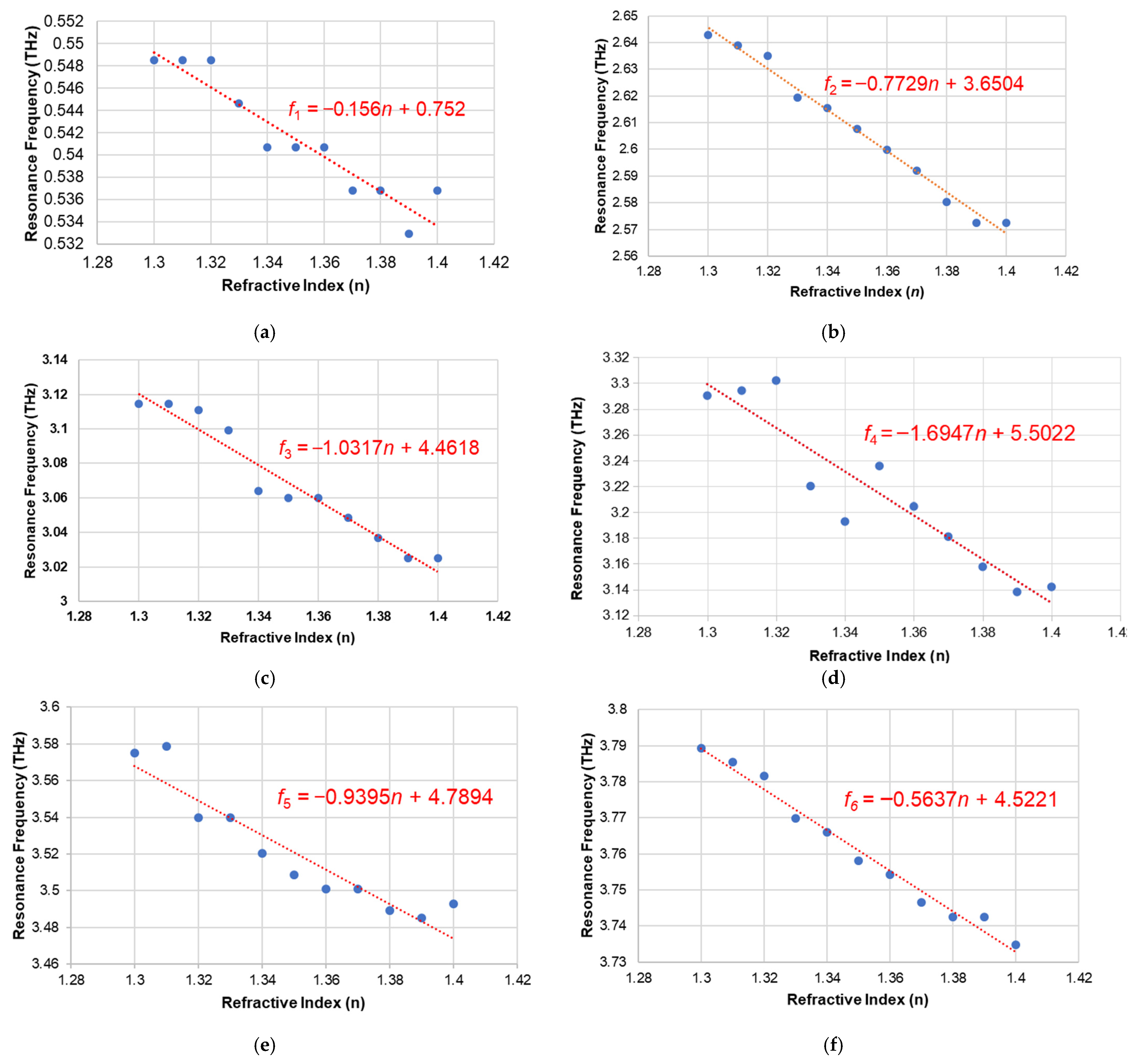
From the results in Figure 6, it has been determined that the suggested biomedical sensor has a peak sensitivity of about 1694.7 GHz/RIU. Furthermore, for any sensing application, the quality factor (Q-factor) of a sensor, which is the resonant frequency ratio to the Full-Width Half Maximum (FWHM), is an extremely important metric. Another important parameter is the figure of merit (FoM), which is the ratio of sensitivity to the FWHM. The Q-factor and FoM are given in Equation (3) and Equation (4), respectively. These metrics for the proposed design are shown in Table 1.
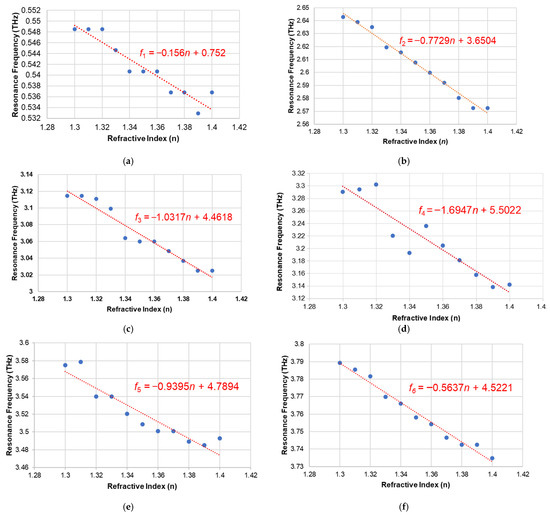
Figure 6.
Plot of the resonance frequency with respect to the refractive index for 6 different frequencies (a) at f1; (b) at f2; (c) at f3; (d) at f4; (e) at f5 (f) at f6.

Table 1.
Six resonance frequencies and their characteristics.
Finally, a comparison is shown with the state-of-the-art in Table 2.

Table 2.
Comparison with the state-of-the-art.
4. Conclusions
This investigation and analysis of the design of a unique metamaterial absorber, which may be utilized to identify biological samples, particularly cancer cells, in the terahertz range, are presented in this publication. The suggested absorber is extremely sensitive to changes in the surrounding medium’s refractive index and has been designed to operate with six absorption peaks in the refracive index range of 1.3–1.4. Many biological samples have their refractive index in this range, and thus it may function as a superb biomedical sensor. The sensor has a peak absorption of 99.34%, a peak sensitivity of 1694.7 GHz/RIU, a peak FoM of 22.045 and a paeak Q-factor of 78.9.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.K.M. (Santosh Kumar Mishra) and B.A.; methodology, S.K.M. (Santosh Kumar Mishra); software, S.K.M. (Santosh Kumar Mishra); validation, U.N., S.B. and B.A.; formal analysis, B.A.; investigation, O.A., S.K.M. (Sunil Kumar Mishra) and A.V.J.; resources, A.S.; data curation, U.N.; writing—original draft preparation, S.K.M. (Santosh Kumar Mishra), U.N. and S.B.; writing—review and editing, B.A., A.S. and C.R.; visualization, S.K.M. (Sunil Kumar Mishra), and A.V.J.; supervision, B.A.; project administration, A.S.; funding acquisition, C.R. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author(s).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Landy, N.I.; Sajuyigbe, S.; Mock, J.J.; Smith, D.R.; Padilla, W.J. Perfect metamaterial absorber. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2008, 100, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, P.; Garg, S.; Singh, A.K.; Bansal, S.; Prakash, K.; Gupta, N.; Sharma, N.; Kumar, S.; Sardana, N. Dual Band Graphene Based Metamaterial Absorber for Terahertz Applications. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 13th Nanotechnology Materials and Devices Conference (NMDC), Portland, OR, USA, 14–17 October 2018; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, X.; Lu, C.; Rong, C.; Liu, M. Wide-angle perfect metamaterial absorbers based on cave-rings and the complementary patterns. Opt. Mater. Express 2018, 8, 2520–2531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, P.; Prakash, K.; Khanal, G.M.; Sardana, N.; Kumar, S.; Gupta, N.; Singh, A.K. Quad-band polarization sensitive terahertz metamaterial absorber using Gemini-shaped structure. Results Opt. 2022, 8, 100254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Cen, C.; Liang, C.; Yi, Z.; Chen, X.; Tang, Y.; Yi, T.; Yi, Y.; Luo, W.; Xiao, S. Five-Band Terahertz Perfect Absorber Based on Metal Layer–Coupled Dielectric Metamaterial. Plasmonics 2019, 14, 1621–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shruti; Pahadsingh, S.; Appasani, B. Hexagonal Tiled Terahertz Metamaterial Absorber for Cancer Detection Incorporating Machine Learning. IEEE Sensors J. 2024, 24, 16093–16101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, P.; Prakash, K.; Sardana, N.; Kumar, S.; Gupta, N.; Singh, A.K. Design of an ultra-thin hepta-band metamaterial absorber for sensing applications. Opt. Quantum Electron. 2022, 54, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senesac, L.; Thundat, T.G. Nanosensors for trace explosive detection. Mater. Today 2008, 11, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritar, T.; Tuominen, J.; Ludvigsen, H.; Petersen, J.C.; Sørensen, T.; Hansen, T.P.; Simonsen, H.R. Gas sensing using air-guiding photonic bandgap fibers. Opt. Express 2004, 12, 4080–4087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, S.P.; Lan, S.; Kang, L.; Cui, Y.; Cai, W. Nonlinear Imaging and Spectroscopy of Chiral Metamaterials. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 6157–6162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.-D.; Liu, M.-H.; Hu, X.-W.; Kong, L.-H.; Cheng, L.-L.; Chen, Z.-Q. Multi-band microwave metamaterial absorber based on coplanar Jerusalem crosses. Chin. Phys. B 2014, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.X.; Zhai, X.; Wang, G.Z.; Huang, W.Q.; Wang, L.L. Design of a Four-Band and Polarization-Insensitive Terahertz Metamaterial Absorber. IEEE Photon. J. 2014, 7, 4600108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Cui, T.J.; Zhao, J.; Ma, H.F.; Jiang, W.X.; Li, H. Polarization-independent wide-angle triple-band metamaterial absorber. Opt. Express 2011, 19, 9401–9407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cong, L.; Singh, R. Sensing with THz metamaterial absorbers. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1408.3711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.; Ghosh, I.; Fahad, M.B.; Mishra, S.K.; Yadav, R.; Appasani, B. Ultra Thin Highly Sensitive Metamaterial Absorber Based Refractive Index Sensor for Detecting Adulterants in Alcohol. Prog. Electromagn. Res. M 2024, 126, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Z.; Shang, L.; Yang, J.; Chen, L.; Guo, J.; Liu, Q.; Danso, S.A.; Li, G. Terahertz Sensor with Resonance Enhancement Based on Square Split-Ring Resonators. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 59211–59221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saadeldin, A.S.; Hameed, M.F.O.; Elkaramany, E.M.A.; Obayya, S.S.A. Highly Sensitive Terahertz Metamaterial Sensor. IEEE Sensors J. 2019, 19, 7993–7999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Q.; Dong, G.-X.; Wang, B.-X.; Huang, W.-Q. High-Q Fano Resonance in Terahertz Frequency Based on an Asymmetric Metamaterial Resonator. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, S.; Dutta, P.; Jha, A.V.; Appasani, B.; Khan, M.S. A Biomedical Sensor for Detection of Cancer Cells Based on Terahertz Metamaterial Absorber. IEEE Sensors Lett. 2022, 6, 6002004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du John, H.V.; Ajay, T.; Reddy, G.M.K.; Ganesh, M.N.S.; Hembram, A.; Pandey, B.K.; Pandey, D. Design and Simulation of SRR-Based Tungsten Metamaterial Absorber for Biomedical Sensing Applications. Plasmonics 2023, 18, 1903–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shruti; Appasani, B.; Pahadsingh, S. An All-Metal Terahertz Metamaterial Absorber Using Concentric Octagonal Rings for Refractive Index Sensing. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 2025, 53, 2109–2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).