Cost-Effective Triboelectric-Assisted Sensory Actuator Designed for Intelligent Robot and Exoskeleton †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
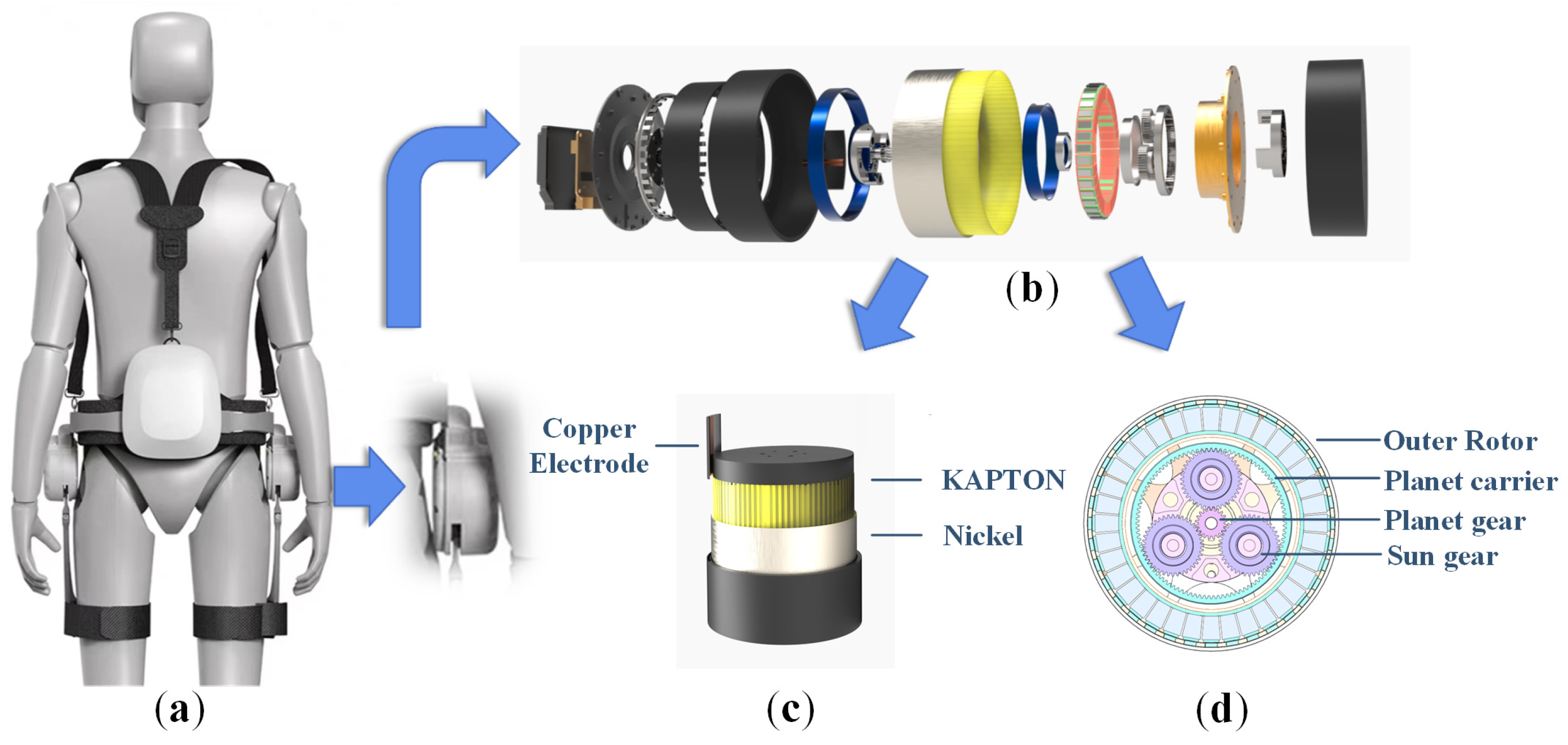
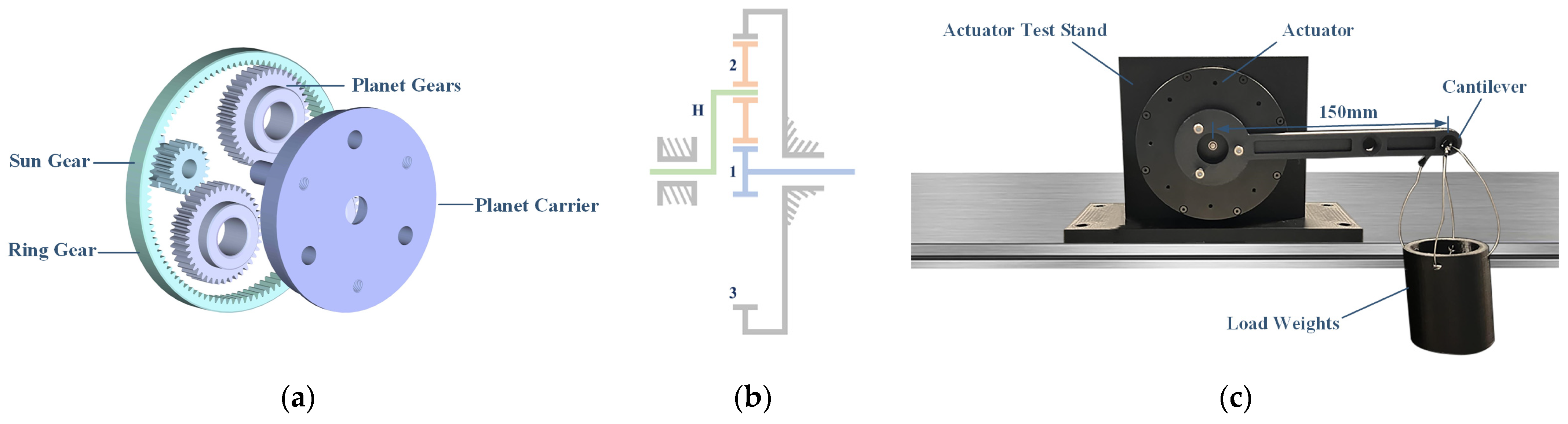
2.1. Designs of Rotational TENG Sensor
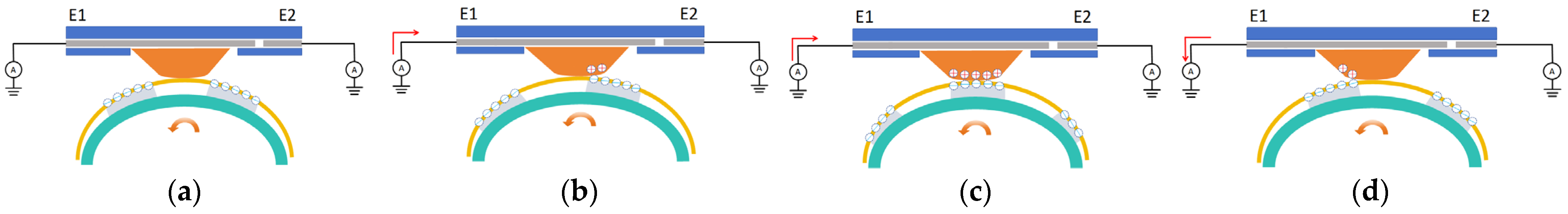
2.2. Working Principle and Sensing Mechanism
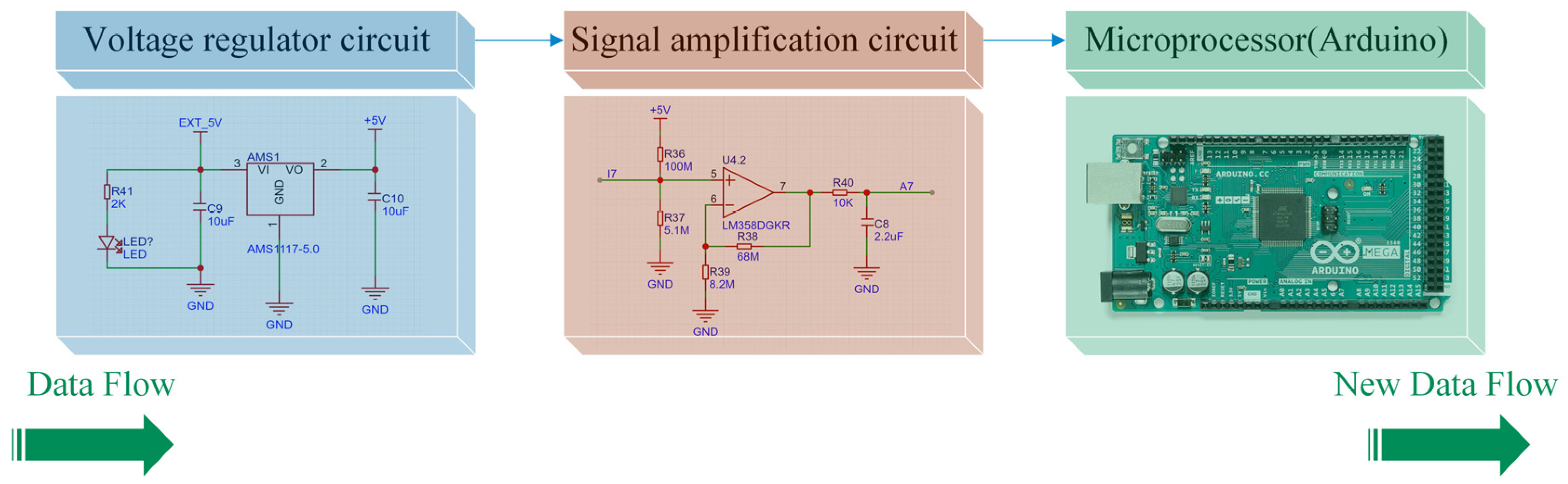
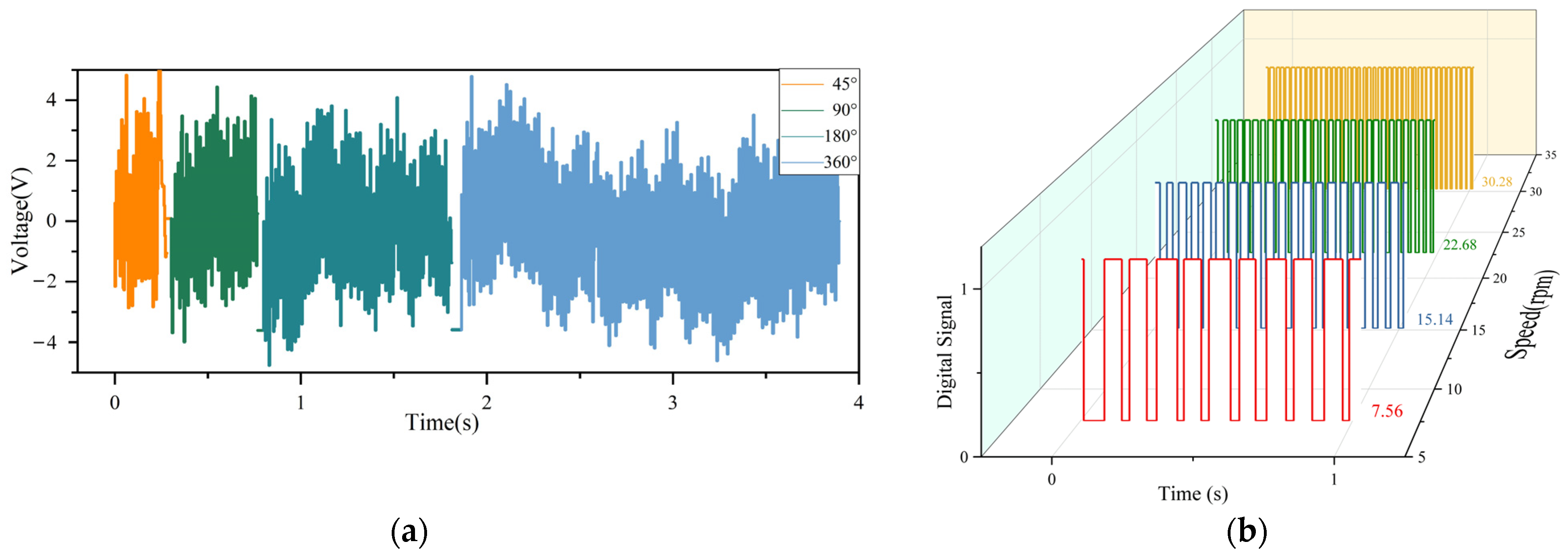
2.3. Signal Processing for Real-Time Manipulation
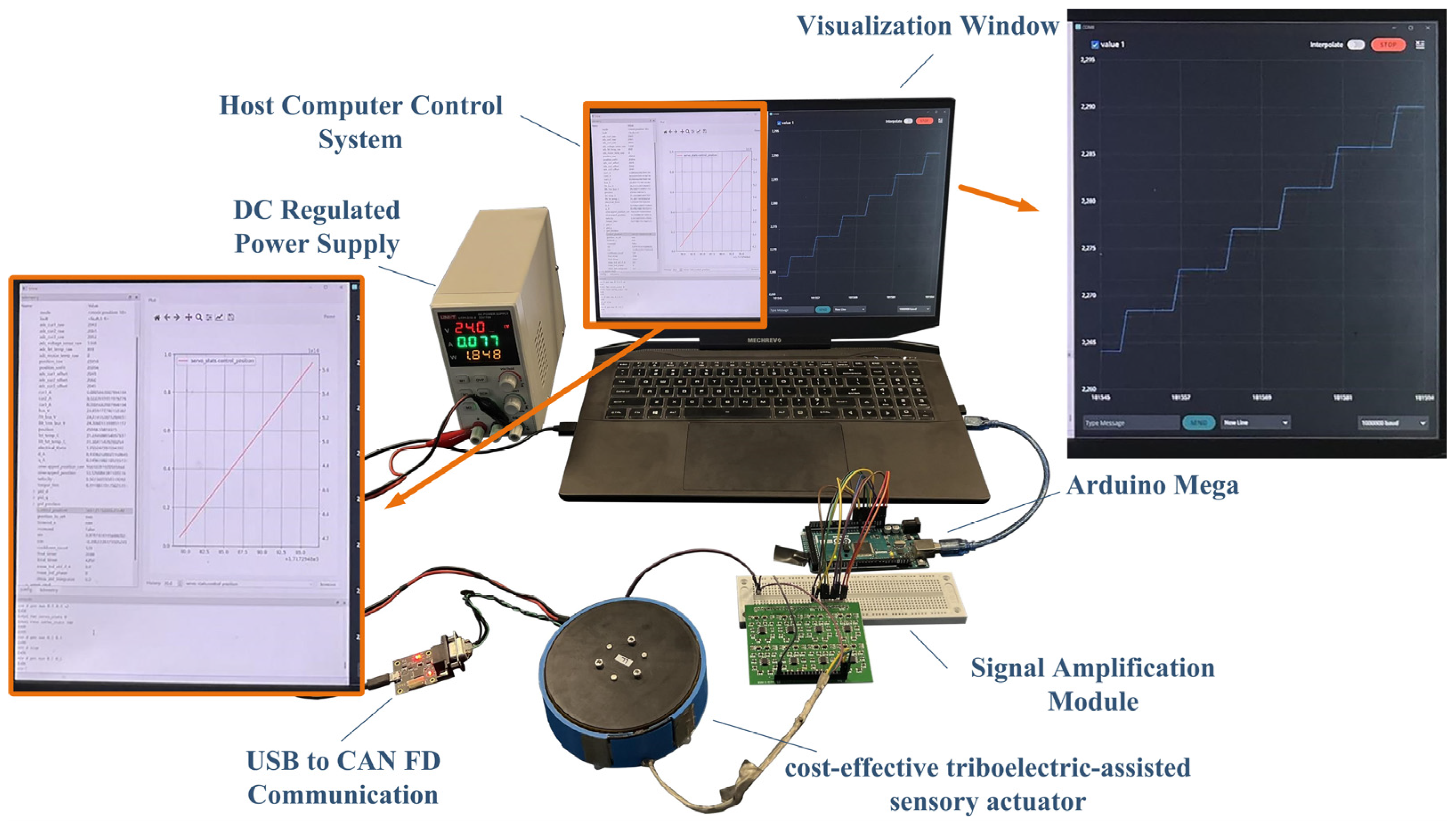
3. Results and Discussion
- When measuring environmental noise to eliminate external influences, if the environmental noise fluctuations are significant, the obtained raw waveform will also fluctuate accordingly, reducing the accuracy of the obtained square wave.
- The micro-slide used to detect the rotation direction may affect the sensor’s measurement accuracy due to the commutation gap that exists during start and commutation.
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- El-Atab, N.; Mishra, R.B.; Al-Modaf, F.; Joharji, L.; Alsharif, A.A.; Alamoudi, H.; Diaz, M.; Qaiser, N.; Hussain, M.M. Soft Actuators for Soft Robotic Applications: A Review. Adv. Intell. Syst. 2020, 2, 2000128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, G.-Y.; Zhu, J.; Zhu, L.-M.; Zhu, X. A survey on dielectric elastomer actuators for soft robots. Bioinspiration Biomim. 2017, 12, 011003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanderborght, B.; Albu-Schaeffer, A.; Bicchi, A.; Burdet, E.; Caldwell, D.G.; Carloni, R.; Catalano, M.; Eiberger, O.; Friedl, W.; Ganesh, G.; et al. Variable impedance actuators: A review. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2013, 61, 1601–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, H.-o.; Takanishi, A. Biped walking robots created at Waseda University: WL and WABIAN family. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2007, 365, 49–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pratt, G.A.; Williamson, M.M. Series elastic actuators. In Proceedings of the 1995 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems. Human Robot Interaction and Cooperative Robots, Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 5–9 August 1995; Volume 391, pp. 399–406. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, S.Y.; Huang, T.H.; Yang, X.L.; Jiao, C.H.; Yang, J.F.; Chen, Y.; Yi, J.G.; Su, H. Quasi-Direct Drive Actuation for a Lightweight Hip Exoskeleton With High Backdrivability and High Bandwidth. IEEE-ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2020, 25, 1794–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Yu, L.; Xu, L.; Yan, Z.; Hu, D.; Zhang, S.; Yang, W. Current developments of robotic hip exoskeleton toward sensing, decision, and actuation: A review. Wearable Technol. 2022, 3, e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bajpai, A.; Carrasquillo, C.; Carlson, J.; Park, J.; Iyengar, D.; Herrin, K.; Young, A.J.; Mazumdar, A. Design and Validation of a Versatile High Torque Quasidirect Drive Hip Exoskeleton. IEEE-ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2024, 29, 789–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Chakraborty, B. Design and Realization of an Optical Rotary Sensor. IEEE Sens. J. 2018, 18, 2675–2681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.S.A.; George, B.; Mukhopadhyay, S.C. Technologies and Applications of Angle Sensors: A Review. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 21, 7195–7206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinova, J.; Valenzuela, S.O.; Wunderlich, J.; Back, C.; Jungwirth, T. Spin hall effects. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2015, 87, 1213–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deak, J.; Jin, I. A High-Field Tunneling Magnetoresistive Angle Sensor. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Magnetics Conference (INTERMAG), Singapore, 23–27 April 2018; p. 1. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, X.; Sun, S.; Yan, X.; Yang, P.; Liu, F.; Cao, L. A Novel Circular Position Sensitive Detector for Continuously High-Precision Angle Measurement. In Proceedings of the 2023 24th International Conference on Electronic Packaging Technology (ICEPT), Tianjin, China, 8–11 August 2023; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Nakamoto, H.; Ootaka, H.; Tada, M.; Hirata, I.; Kobayashi, F.; Kojima, F. Stretchable Strain Sensor with Anisotropy and Application for Joint Angle Measurement. IEEE Sens. J. 2016, 16, 3572–3579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manchi, P.; Graham, S.A.; Paranjape, M.V.; Kurakula, A.; Kavarthapu, V.S.; Yu, J.S. Calcium copper titanate incorporated polydimethylsiloxane flexible composite film-based triboelectric nanogenerator for energy harvesting and self-powered sensing applications. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2024, 190, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.; Chae, J.; Cho, S.; Kim, J.W.; Ahmad, A.; Karim, M.R.; La, M.; Park, S.J.; Choi, D. Bidirectional rotating direct-current triboelectric nanogenerator with self-adaptive mechanical switching for harvesting reciprocating motion. Int. J. Extrem. Manuf. 2024, 6, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, L.C.; Zhang, L.F.; Feng, J.G.; Zhang, F.B.; Han, Q.K.; Qin, Z.Y.; Chu, F.L. A hybrid triboelectric-piezoelectric smart squirrel cage with self-sensing and self-powering capabilities. Nano Energy 2024, 124, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Li, Y.; Yang, Y.X.; Wu, Y.B.; Shi, Q.S. Flexible piezoelectric sensor based on polyvinylidene fluoride/polyacrylonitrile/carboxy-terminated multi-walled carbon nanotube composite films for human motion monitoring. Nanotechnology 2024, 35, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.J.; Ding, W.Q.; Liu, J.Q.; Yang, B. Flexible PVDF based piezoelectric nanogenerators. Nano Energy 2020, 78, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masoumi, S.; Shokrani, M.; Aghili, S.; Hossein-Babaei, F. Zinc oxide-based direct thermoelectric gas sensor for the detection of volatile organic compounds in air. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 294, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.; Lee, D.; Park, G.; Park, S.; Khan, S.; Kim, J.; Kim, W. Energy harvesting using thermoelectricity for IoT (Internet of Things) and E-skin sensors. J. Phys. Energy 2019, 1, 042001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Zhu, M.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, Z.; Shi, Q.; Shan, X.; Yeow, R.C.H.; Lee, C. Artificial Intelligence of Things (AIoT) Enabled Virtual Shop Applications Using Self-Powered Sensor Enhanced Soft Robotic Manipulator. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, 2100230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.L.; Sun, Z.D.; Chen, T.; Lee, C.K. Low cost exoskeleton manipulator using bidirectional triboelectric sensors enhanced multiple degree of freedom sensory system. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quigley, M.; Brewer, R.; Soundararaj, S.P.; Pradeep, V.; Le, Q.; Ng, A.Y. Low-cost accelerometers for robotic manipulator perception. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Taipei, Taiwan, 18–22 October 2010; pp. 6168–6174. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; An, J.; Nie, J.; Luo, J.; Shao, J.; Jiang, T.; Chen, B.; Tang, W.; Wang, Z.L. A Self-Powered Angle Sensor at Nanoradian-Resolution for Robotic Arms and Personalized Medicare. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 2001466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.; Gopal, K.; Goswami, Y.; Kundu, M.; Varshney, P. Terahertz field generation from laser interaction with spherical nano-particles: Effect of external magnetic field. Opt. Quantum Electron. 2024, 56, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seok, S.; Wang, A.; Otten, D.; Kim, S. Actuator design for high force proprioceptive control in fast legged locomotion. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Algarve, Portugal, 7–12 October 2012; pp. 1970–1975. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.; Kang, T.; Song, D.; Yi, S.-J. Design and Control of a Open-Source, Low Cost, 3D Printed Dynamic Quadruped Robot. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 3762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, I.S. Design and Kinematic Analysis of a 3D-Printed 3DOF Robotic Manipulandum. In Towards Autonomous Robotic Systems; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 227–239. [Google Scholar]
| Item | Unit Price (CNY) | Required Quantity | Cost (CNY) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3D printing PLA filament * | 62/kg | 60.24 g | 3.735 |
| Double-sided adhesive tape | 4/m | 323.42 mm | 1.294 |
| PET layer | 1.50/sheet | 0.33 sheet | 0.500 |
| Silver conductive paste | 1000/100 g | 0.02 g | 0.200 |
| Kapton film | 23/33 m | 330 mm | 0.230 |
| Copper sheet | 9.50/233 mm | 30 mm | 1.223 |
| Double-sided conductive adhesive | 25/50 m | 30 mm | 0.015 |
| Nickel foil | 26/20 m | 345 mm | 0.449 |
| Insulated copper wire | 3.41/40 pieces | 2 p | 0.171 |
| Signal conditioning circuit | 75 | 1 | 75 |
| Arduino Mega 2560 | 230 | 1 | 230 |
| Total | 312.817 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, H.; Chu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zhu, G.; Li, X.; Zhu, M.; Chen, T. Cost-Effective Triboelectric-Assisted Sensory Actuator Designed for Intelligent Robot and Exoskeleton. Eng. Proc. 2024, 78, 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2024078011
Liu H, Chu Y, Zhao Y, Zhu G, Li X, Zhu M, Chen T. Cost-Effective Triboelectric-Assisted Sensory Actuator Designed for Intelligent Robot and Exoskeleton. Engineering Proceedings. 2024; 78(1):11. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2024078011
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Haowen, Yusong Chu, Yudong Zhao, Guanyu Zhu, Xuan Li, Minglu Zhu, and Tao Chen. 2024. "Cost-Effective Triboelectric-Assisted Sensory Actuator Designed for Intelligent Robot and Exoskeleton" Engineering Proceedings 78, no. 1: 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2024078011
APA StyleLiu, H., Chu, Y., Zhao, Y., Zhu, G., Li, X., Zhu, M., & Chen, T. (2024). Cost-Effective Triboelectric-Assisted Sensory Actuator Designed for Intelligent Robot and Exoskeleton. Engineering Proceedings, 78(1), 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2024078011









