AI-Enhanced Embedded IoT System for Real-Time Industrial Sensor Calibration †
Abstract
1. Introduction
- The development of a low-cost embedded IoT platform integrating temperature and pressure sensors with an ESP32 for real-time calibration.
- The deployment of a lightweight MLP neural network directly on the microcontroller without cloud dependency.
- Experimental validation demonstrating efficiency above 95% with low RMSE and bounded uncertainty across tested ranges.
- Demonstration of a scalable and portable solution applicable to Industry 4.0 environments.
2. Methodology
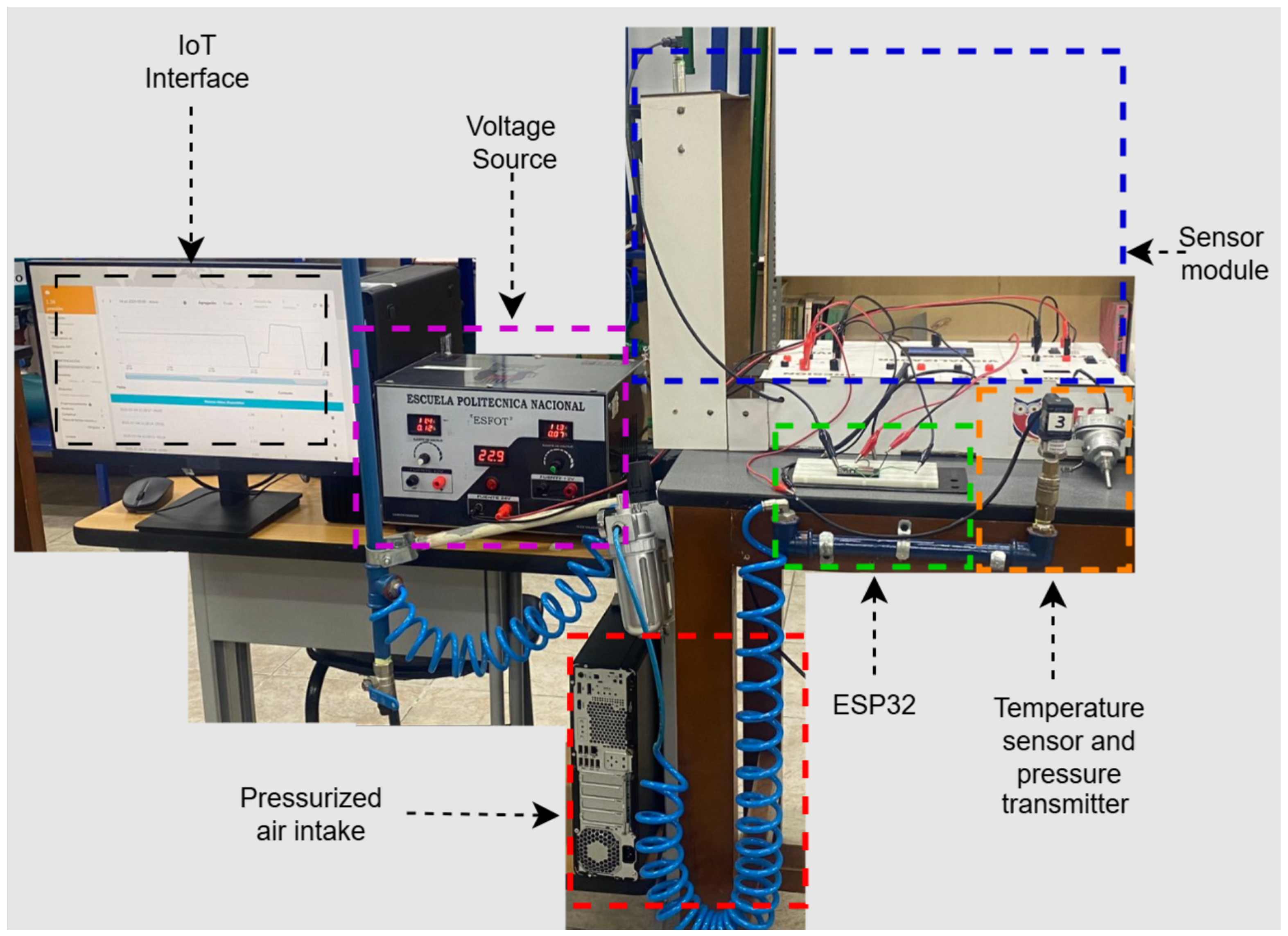
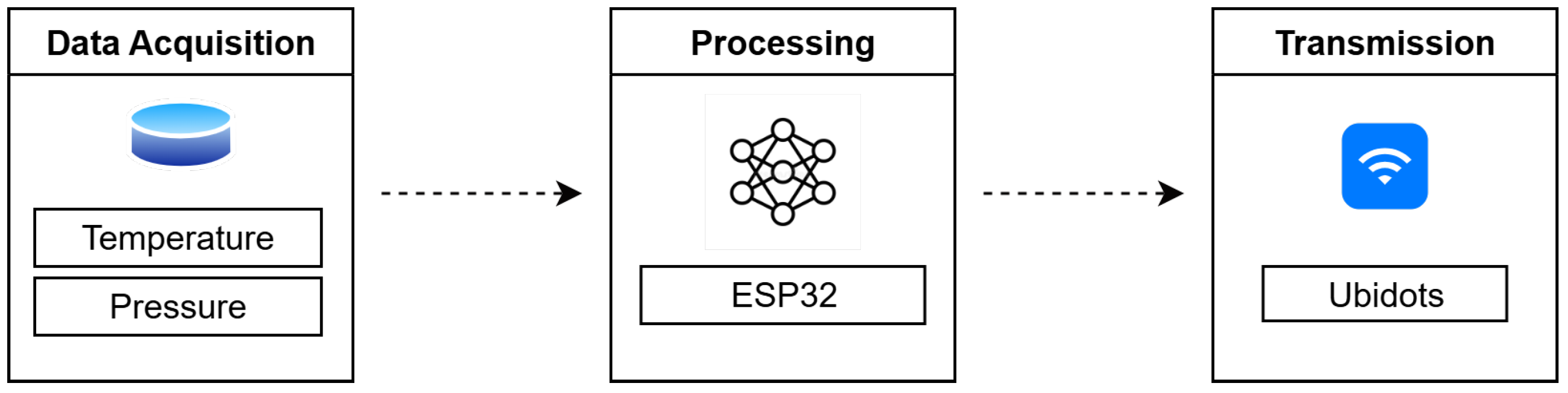
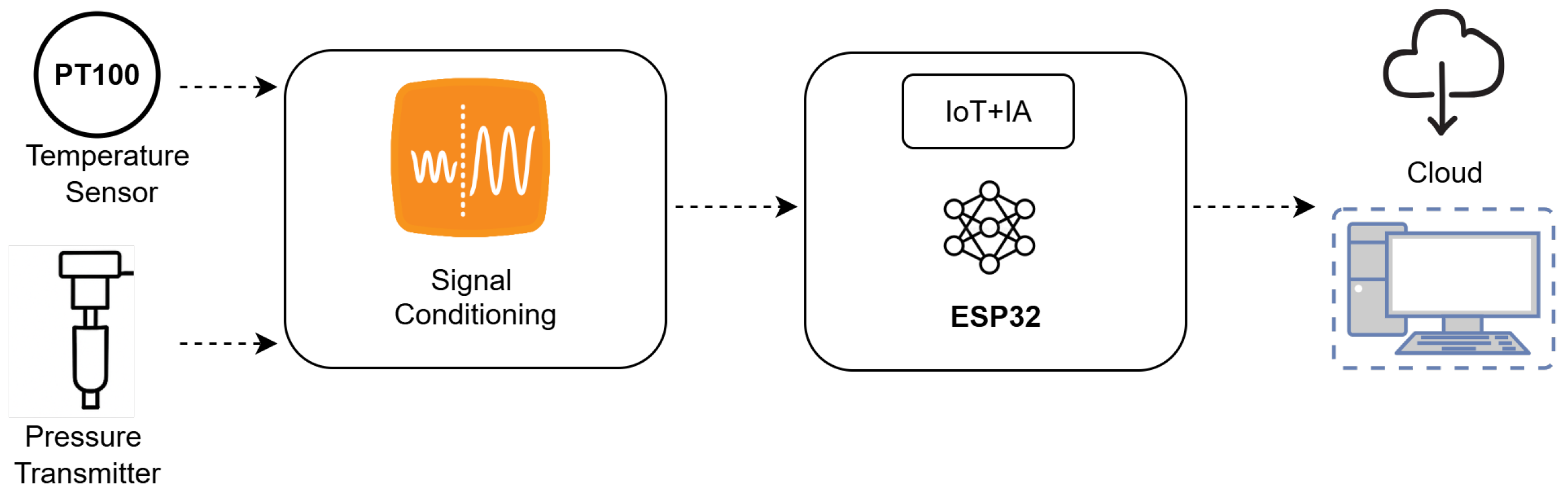
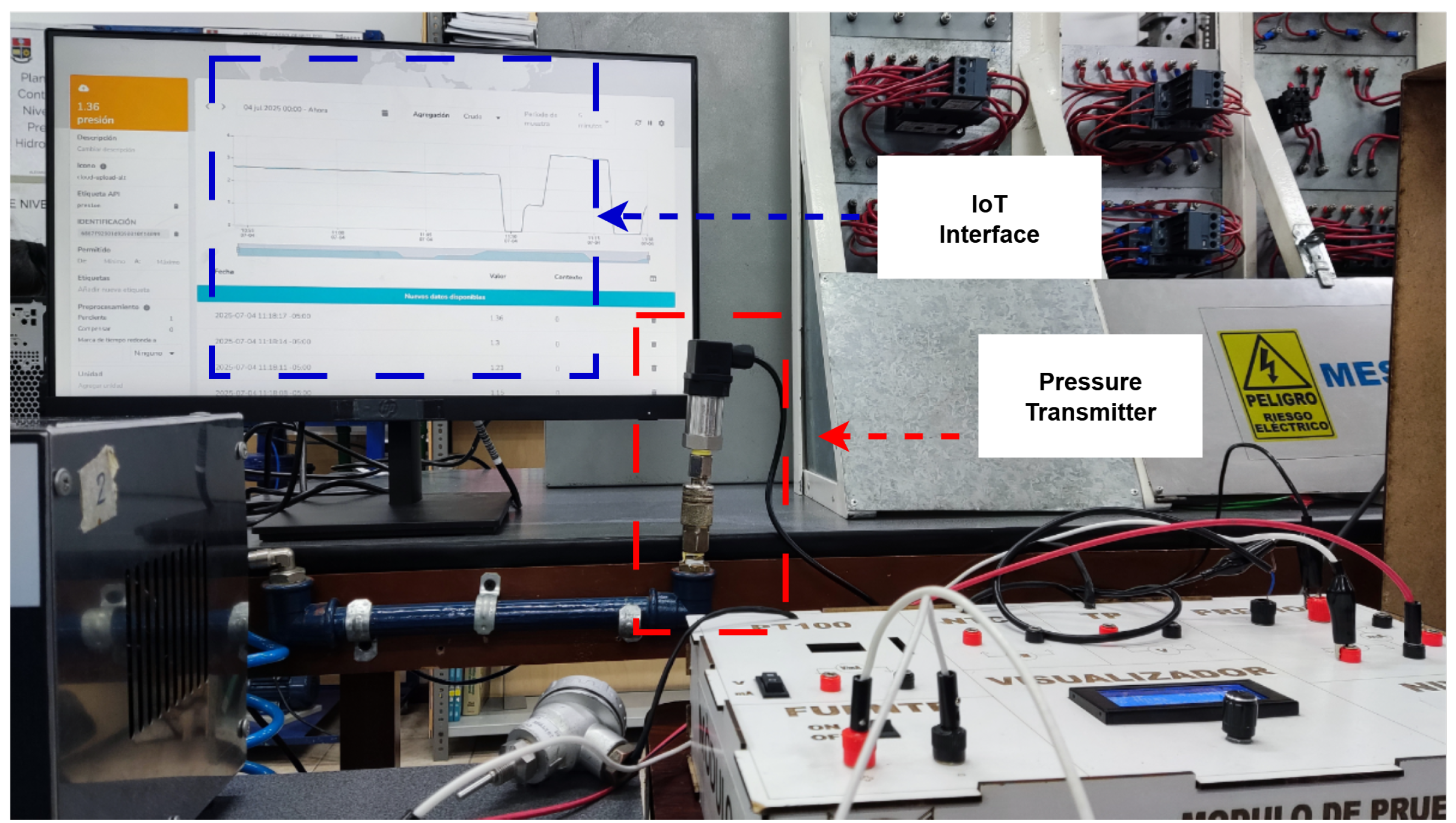
2.1. System Architecture
2.2. Neural Network Integration
2.3. On-Device Inference and Real-Time Operation
3. Implementation and Results
3.1. Experimental Configuration and Test Conditions
3.2. Temperature Calibration Performance
3.3. Pressure Calibration Performance
3.4. Discussion and System Robustness
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fraden, J. Handbook of Modern Sensors: Physics, Designs, and Applications, 5th ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, H. Investigate Calibration Methods for Pressure Transmitters. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2020, 1646, 012084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadezhdin, I.; Goryunov, A. Differential Pressure Transmitter with Unified Electronics Unit. IEEE Sens. J. 2020, 20, 10460–10468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almassri, A.; Hasan, W.; Ahmad, S.; Shafie, S.; Wada, C.; Horio, K. Self-Calibration Algorithm for a Pressure Sensor with a Real-Time Approach Based on an Artificial Neural Network. Sensors 2018, 18, 2561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zhao, C.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H. Machine-Learning-Based Calibration of Temperature Sensors. Sensors 2023, 23, 7347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, D.; Li, Y.; Jin, M.; Guo, Y.; Meng, F.; Liu, Q. Data-Driven Calibration of Tri-Axial Magnetic Sensors. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2025, 36, 035102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samal, L.; Bute, P. Wireless Network for Industrial Application Using ESP32 as Gateway. In Proceedings of the 2023 14th International Conference on Computing Communication and Networking Technologies (ICCCNT), Delhi, India, 6–8 July 2023; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carducci, C.; Monti, A.; Schraven, M.; Schumacher, M.; Mueller, D. Enabling ESP32-Based IoT Applications in Building Automation Systems. In Proceedings of the 2019 II Workshop on Metrology for Industry 4.0 and IoT (MetroInd4.0&IoT), Naples, Italy, 4–6 June 2019; pp. 306–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzman, A.; Lua, C.; Garcia-Rodriguez, J.; Vidrios-Serrano, C.; Meza-Aguilar, M. Real-Time Embedded Control of Vehicle Dynamics Using ESP32: A Discrete Nonlinear Approach. Electronics 2024, 13, 3967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.; Li, Y.; Nabeed, T.; Rahman, M. Remote Monitoring of Heart Rate and ECG Signal Using ESP32. In Proceedings of the 2021 4th International Conference on Advanced Electronic Materials, Computers and Software Engineering (AEMCSE), Changsha, China, 26–28 March 2021; pp. 604–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, B.; Dixit, K.; Dogra, A.; Nagar, M.; Akram, S.; Kaur, J. Empowering Assets and Vehicles with Cutting-Edge ESP32 Real-Time Tracking System. In Proceedings of the 2024 11th International Conference on Computing for Sustainable Global Development (INDIACom), New Delhi, India, 28 February–1 March 2024; pp. 504–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Baig, M.; Iqbal, M. An Open-Source Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition Architecture for Photovoltaic System Monitoring Using ESP32, Banana Pi M4, and Node-RED. Energies 2024, 17, 2295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaafar, H.; Aminuddin, N. Comparison between NodeMCU ESP8266 and Uno R3 for Software Development Using Ubidots. Malays. J. Bioeng. Technol. 2024, 1, 36–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafar, S.; Miraj, G.; Baloch, R.; Murtaza, D.; Arshad, K. An IoT Based Real-Time Environmental Monitoring System Using Arduino and Cloud Service. Eng. Technol. Appl. Sci. Res. 2018, 8, 3238–3242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linggarjati, J. Design and Prototyping of Temperature Monitoring System for Hydraulic Cylinder in Heavy Equipment Using ESP32 with Data Logging and WiFi Connectivity. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2022, 998, 012042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, V.; Thai, B.; Pham, H.; Nguyen, V.; Nguyen, V. A Proposed Approach to Utilizing ESP32 Microcontroller for Data Acquisition. J. Eng. Technol. Sci. 2024, 56, 474–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annamaa, A. Introducing Thonny, a Python IDE for Learning Programming. In Proceedings of the 15th Koli Calling Conference on Computing Education Research, Koli, Finland, 19–22 November 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Ding, Y.; Hu, S.; Niemier, M.; Cong, J.; Hu, Y.; Shi, Y. Scaling for Edge Inference of Deep Neural Networks. Nat. Electron. 2018, 1, 216–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakr, F.; Bellotti, F.; Berta, R.; De Gloria, A. Machine Learning on Mainstream Microcontrollers. Sensors 2020, 20, 2638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, E.; Zeng, L.; Zhou, Z.; Chen, X. Edge AI: On-Demand Accelerating Deep Neural Network Inference via Edge Computing. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2019, 19, 447–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Dou, Z.; Goel, S.; Klivans, A.; Meka, R. Learning Narrow One-Hidden-Layer ReLU Networks. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2304.10524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raissi, M.; Perdikaris, P.; Karniadakis, G. Machine Learning of Linear Differential Equations Using Gaussian Processes. J. Comput. Phys. 2017, 348, 683–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Shivhare, S. Embedded TinyML for Predictive Maintenance: Vibration Analysis on ESP32 with Real-Time Fault Detection in Industrial Equipment. Int. J. Comput. Model. Appl. 2025, 2, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babiuch, M.; Foltynek, P.; Smutny, P. Using the ESP32 Microcontroller for Data Processing. In Proceedings of the 2019 20th International Carpathian Control Conference (ICCC), Krakow-Wieliczka, Poland, 26–29 May 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinosa-Gavira, M.; Aguera-Perez, A.; Palomares-Salas, J.; Sierra-Fernandez, J.; Remigio-Carmona, P.; De-La-Rosa, J. Characterization and Performance Evaluation of ESP32 for Real-Time Synchronized Sensor Networks. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2024, 237, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dokic, K.; Radisic, B.; Cobovic, M. MicroPython or Arduino C for ESP32—Efficiency for Neural Network Edge Devices. In Intelligent Computing Systems. ISICS 2020; Communications in Computer and Information Science; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dokic, K.; Martinovic, M.; Radisic, B. Neural Networks with ESP32—Are Two Heads Faster than One? In Proceedings of the 2020 6th Conference on Data Science and Machine Learning Applications (CDMA), Riyadh, Saudi Arabia, 4–5 March 2020; pp. 141–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chua, K.H.; Abu, M.A.; Shapiai, M.I.; Haniff, M.F.; Mohamad, R.S.; Abu, A. Analysis of Wind Speed Prediction using Artificial Neural Network and Multiple Linear Regression Model using Tinyml on Esp32. J. Adv. Res. Fluid Mech. Therm. Sci. 2023, 107, 29–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, W.; Zhu, R.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, Z. Design of Adaptive Filter for Weak Signal Acquisition System. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2021, 2026, 012032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez, S.; Bulut, E. WiFi Sensing on the Edge: Signal Processing Techniques and Challenges for Real-World Systems. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2023, 25, 46–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutiara, H.A.K.; Suhendra, T. Field Testing and QoS Analysis of ESP-NOW Communication on ESP32. In Proceedings of the 2024 FORTEI-International Conference on Electrical Engineering (FORTEI-ICEE), Badung, Indonesia, 24–25 October 2024; pp. 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
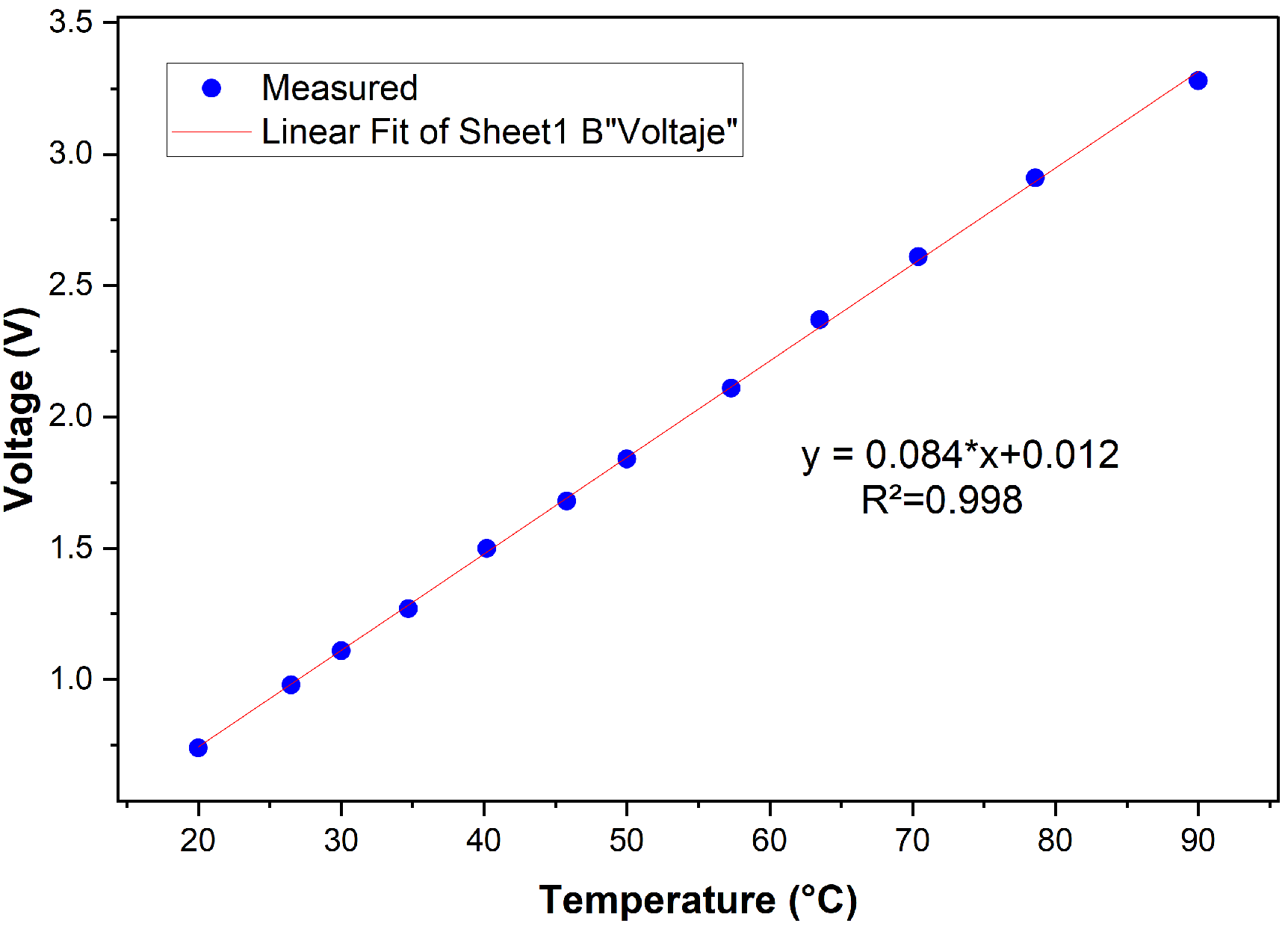
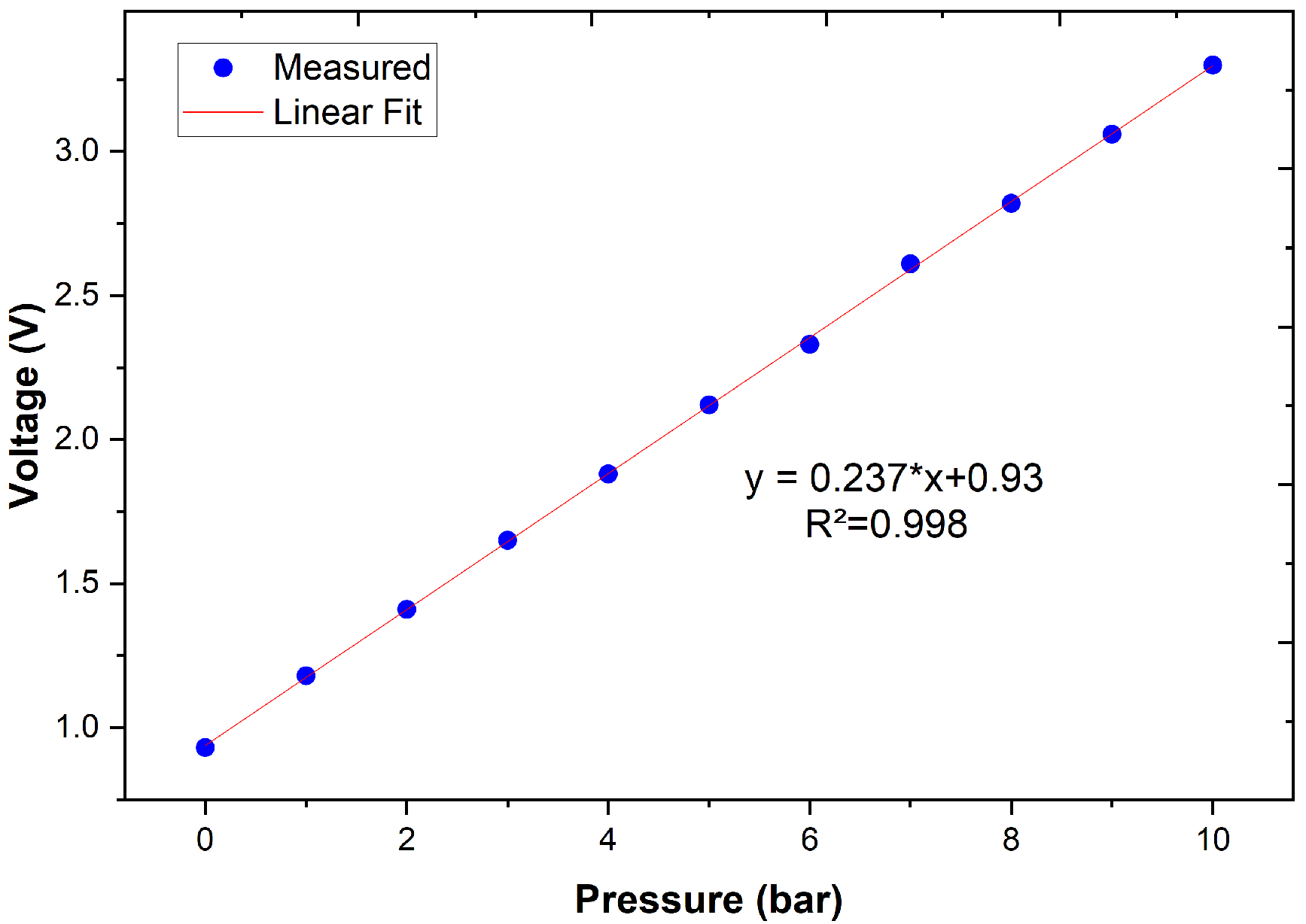
| T (°C) | (V) | (V) | Efficiency (%) | RMSE (V) | Std. Dev. (V) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 90 | 3.28 | 3.30 | 99.3 | 0.0040 | 0.0125 |
| 78.6 | 2.91 | 2.97 | 99.1 | 0.0042 | 0.0132 |
| 50 | 1.84 | 1.88 | 98.9 | 0.0045 | 0.0150 |
| 26.5 | 0.98 | 1.03 | 98.8 | 0.0047 | 0.0180 |
| 20 | 0.74 | 0.75 | 98.6 | 0.0049 | 0.0205 |
| P (bar) | (V) | (V) | Efficiency (%) | RMSE (V) | Std. Dev. (V) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 3.30 | 3.32 | 99.4 | 0.0050 | 0.0110 |
| 7.5 | 2.92 | 2.94 | 99.3 | 0.0048 | 0.0125 |
| 5.0 | 2.50 | 2.51 | 99.2 | 0.0046 | 0.0132 |
| 2.5 | 2.05 | 2.07 | 99.1 | 0.0045 | 0.0145 |
| 0 | 0.93 | 0.94 | 99.0 | 0.0043 | 0.0155 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cuenca-Sánchez, A.; Iza, J.; Proaño, P.; Valenzuela, J. AI-Enhanced Embedded IoT System for Real-Time Industrial Sensor Calibration. Eng. Proc. 2025, 115, 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2025115013
Cuenca-Sánchez A, Iza J, Proaño P, Valenzuela J. AI-Enhanced Embedded IoT System for Real-Time Industrial Sensor Calibration. Engineering Proceedings. 2025; 115(1):13. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2025115013
Chicago/Turabian StyleCuenca-Sánchez, Alan, Jeampier Iza, Pablo Proaño, and Javier Valenzuela. 2025. "AI-Enhanced Embedded IoT System for Real-Time Industrial Sensor Calibration" Engineering Proceedings 115, no. 1: 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2025115013
APA StyleCuenca-Sánchez, A., Iza, J., Proaño, P., & Valenzuela, J. (2025). AI-Enhanced Embedded IoT System for Real-Time Industrial Sensor Calibration. Engineering Proceedings, 115(1), 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2025115013






